Where is growth hormone produced?
The gland that secretes growth hormone is called the pituitary gland. But only one part of it is responsible for the production of somatotropin - the anterior lobe. The hormone is a peptide because it has a protein structure (a certain sequence of amino acids).
Depending on the time of day, different concentrations of the hormone in the blood are observed. The main amount of somatotropin is synthesized at night during sleep, and during the day its gradual decrease is observed. The effects on the adult body are associated with the peculiarities of its mechanism of action.
The peptide hormone stimulates the production of insulin-like growth factor IGF-1, which is responsible for:
- muscle cell hyperplasia;
- launching fat burning processes;
- formation of a pronounced relief due to the summation of the previous two actions.
An important condition for the period when synthetic analogues of growth hormone are actively used is the preparation of a proper diet.
To do this, first of all, you need to know which products contain the necessary elements to increase the synthesis of somatotropin.
Since its structural material is amino acids, when they are lacking, the formation of the hormone slows down. Therefore, foods rich in animal and vegetable protein are included in the diet:
- lean meat;
- red and white varieties of fish;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- legumes;
- nuts.
Special preparations are also used to increase the concentration of growth hormone. But their incorrect use does more harm than good and leads to deterioration in human health.
What is somatotropic hormone responsible for?
At a young age (up to 20 years), the described chemical compound is released in increased quantities. It is necessary for the normal development of long tubular bones, therefore this substance is also called somatotropic growth hormone. After 20 years, when the musculoskeletal system is almost formed, its production decreases significantly. Somatotropic hormone (GH) produces other effects:
- activates and supports T-cell immunity;
- intensifies sweating;
- increases the elasticity of ligaments;
- slows down the aging process;
- improves calcium absorption in the intestines.
The influence of somatotropic hormone on metabolism
Athletes are paying close attention to GH because of its ability to accelerate the burning of fat reserves and build muscle mass. Somatotropic hormone is produced by cells of the adenohypophysis (somatotrophs), in terms of molecular structure it is similar to prolactin and placental lactogen. For this reason, women should also monitor the concentration of GH. It improves the silhouette, provides support to the ligaments in the mammary gland area, and helps maintain a youthful and toned body.
The effect of somatotropic hormone on metabolic processes:
- enhancing protein synthesis and slowing down their breakdown;
- preventing the deposition of adipose tissue;
- increased blood glucose levels;
- decreased excretion of sodium and potassium from the body.
Instructions for use of Somatotropin
The use of somatotropin preparations must be agreed with a doctor.
After taking tests and determining the level of natural growth hormone, it will be easier to decide how to take the hormone and in what dosages.
Considering that somatotropin indirectly regulates the secretion of certain glands (pancreas and thyroid), constant monitoring of the concentration of their hormones in the blood is mandatory. Since with a genetic predisposition there is a risk of developing diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism.
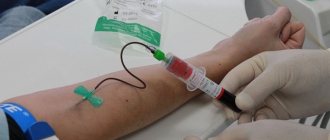
To get good results from using injectable forms of the hormone, you should learn how to inject the drug correctly:
- the injection is carried out only subcutaneously (using your fingers to form a fold of skin into which the solution is injected);
- the injection site should be constantly changed to prevent lipoatrophy;
- the daily dose should be divided into equal parts and injected throughout the day;
- The procedure should be carried out in the morning and evening (in accordance with the natural rhythm of hormone production).
Important! To prevent local adverse reactions (inflammation and abscess), you must follow the following rules:
- carry out all manipulations with clean hands;
- use disinfectant solutions to treat the injection site;
- use sterile water to dissolve the drug (if necessary);
- Only new disposable syringes and a sharp needle are suitable for use.
How to increase the amount of Somatotropin in the body
You can increase the level of growth hormone production in the body without resorting to medications. To do this, just follow a few rules:
- Compliance with the training regime. Regular physical activity activates the release of growth hormone into the blood. When the body adapts or stops exercising, a decrease in its level to the initial values will be observed.
- The duration of sleep should be at least 7-8 hours. Moreover, it must be done at night, since it is at this time that the peak content of growth hormone in the blood is observed.
- Maintain normal body weight. Excessive amount of adipose tissue in the body suppresses the production of somatotropin.
Attention! High levels of insulin (which is often observed in obese people) help suppress the synthesis of growth hormone.
- Stick to proper nutrition, enriching your diet with protein foods and reducing sugar intake.
- To refuse from bad habits.
In adults there is:
- increased bone fragility;
- decrease in the percentage of muscle mass;
- fat deposition, mainly in the abdominal area;
- deterioration of thought processes;
- increased fatigue.
Excess growth hormone in childhood leads to gigantism, and in adults - to acromegaly (enlargement of individual parts of the body due to bone growth).
Somatotropic hormone is reduced
A deficiency of this substance is also fraught with problems, but less serious than its excess. Growth hormone deficiency in adults provokes:
- muscle weakness;
- obesity;
- apathy;
- acceleration of aging;
- chronic cardiovascular diseases;
- decreased libido;
- depression;
- muscle wasting;
- atherosclerosis.
Somatotropic low hormone in children (pituitary dwarfism) leads to delays in physical development:
- short stature;
- small facial features;
- reduced feet and hands;
- pale skin;
- thin voice;
- absence of secondary sexual characteristics of libido in adolescence;
- late onset of menstruation;
- undeveloped muscles.
Why is somatotropic hormone reduced?
Pituitary dwarfism can be congenital or acquired. More often, the pathology under consideration is explained by genetics, especially if the growth hormone is low in the child since infancy. Another factor is identical to the situation with excess growth hormone. Fluctuations in its concentration are caused by the growth of tumors in the area of the pituitary gland. Reduced growth hormone in adults is diagnosed for the following reasons:
- previous brain surgery;
- head irradiation;
- severe infectious diseases;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- endocrine imbalance.
How to increase growth hormone?
To properly solve the problem described, it is important to determine what caused it. If the increase in growth hormone occurs due to the presence of a benign tumor in the pituitary gland, surgical removal will be required. In other cases, normalization of the concentration of a chemical substance is carried out using conservative methods. With medication you can quickly and permanently stabilize growth hormone; the drugs that are used for this are:
- Somatropin;
- Biosome;
- Rastan;
- Genotropin;
- Humatrope;
- Norditropin and analogs.
In the treatment of children, other hormones necessary for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and puberty are additionally used:
- estrogens;
- testosterone;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- progesterone;
- thyroid regulators.
Side effects Somatotropin
Since growth hormone is produced in the body, its physiological concentrations do not cause negative effects. But when its content in the body increases due to drug injections, the risk of side effects increases significantly.
Most often, Somatotropin has a peripheral negative effect on the body associated with organs that are most susceptible to the influence of the hormone. In most cases, they are reversible. Therefore, stopping growth hormone medications or reducing the dosage results in the disappearance of all negative symptoms.
List of possible side effects of growth hormone drugs:
- swelling (due to fluid accumulation in tissues);
- increased blood pressure;
- tunnel syndrome, manifested by pain in the limbs and their partial numbness;
- decreased production of thyroid hormones, which can lead to hypothyroidism;
- increase in size (hypertrophy) of internal organs (mainly the heart);
- acromegaly (in rare cases).
Also, due to the effect on blood glucose levels, there is a risk of developing diabetes.
How to determine hormone levels?
To determine how much growth hormone is in the body, you should remember that it is produced in impulses. And therefore you need to know how to take this test in order to get a reliable result.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes such a test if there is certain evidence that the level is different from the norm.
In order to check the functioning of the pituitary gland, specialists use tests for other hormones, and an analysis for growth hormone is done additionally if necessary.
If the doctor still prescribes such an examination, then you should remember several rules:
- X-rays cannot be taken 7 days before the test. Otherwise the data will be incorrect;
- the day before the study, you need to use a strict diet and under no circumstances eat fatty foods;
- 12 hours before the test you should not eat any food at all;
- you must stop smoking at least three hours before blood sampling;
- The analysis is done in the morning on an empty stomach, at this time a person has the lowest level of growth hormone.
Following these simple rules will help you get reliable results.
Somatotropin in sports
Due to the ability of somatotropin to influence the growth of muscle fibers, it began to be used by athletes in various sports.
Some studies indicate a low ability of the hormone to influence strength and endurance. But despite this, growth hormonal drugs are actively used to build muscles and reduce body fat (to achieve pronounced relief).
For these purposes, the medical instructions for use (to compensate for the deficiency of one’s own hormone) are not suitable.
In sports, higher dosages are used, greatly exceeding therapeutic ones. This achieves excessive stimulation of muscle cells, which leads to the desired result.
In addition to the basic rules for using drugs, there are several more points in bodybuilding:
- for a beginner, the dosage should not exceed 4-5 units per day;
- the drug is started in small quantities, gradually increasing the dose to the required values;
- workouts primarily include weight-bearing strength exercises and high-intensity sports;
- The duration of the lesson should be at least 1-1.5 hours with a frequency of 4-5 times a week;
- Diet preparation is possible with the inclusion of specialized sports nutrition.
HGH Somatropin preparations
Growth hormone preparations are presented in two groups:
- products registered in Russia for medical use;
- products manufactured exclusively for use in the world of bodybuilding, which have not been registered on the Russian pharmaceutical market.
The second group is most widespread among athletes, since its acquisition does not require a prescription from a doctor. These drugs are manufactured abroad and their supply to the country is illegal. Among them there are their favorites, which are considered the best.
The most positive reviews received:
- HGH Somatropin amino acid 191 10vials x 10iu from GenoPharm;
- Canada Peptides Somatropin 191aa 10 IU.
These drugs are of high quality, so they have virtually no negative feedback.
Somatropin and bodybuilding:
STH is increased
Excess growth hormone in the body can cause more serious consequences. Height increases significantly not only in adolescents, but also in adults. The height of an adult can exceed two meters.
At the same time, there is a significant increase in the limbs - hands, feet, and the shape of the face undergoes serious changes - the nose and lower jaw become larger, the features become coarser. Such changes can be corrected, but in this case, long-term treatment under the supervision of a specialist will be required.
Somatropin and sleep: an obvious relationship
As mentioned above, sleep has a direct effect on the production of growth hormone. If we consider that about 90% of somatropin is released into the blood at night, it becomes obvious that with insomnia or lack of sleep, the hormone is simply not produced. The person looks older, feels weak and sick, and muscle tissue decreases.
How to increase the production of growth hormone through sleep? It’s very simple: set up a routine so that you fall asleep no later than ten o’clock in the evening. This habit will ensure normal hormone production for a person of a given age. Of course, with the help of sleep you cannot achieve off-scale somatropin levels in the blood, but you can establish its regular production.
Causes
Increased growth hormone.
Excessive concentrations of growth hormone cause serious and life-threatening pathologies. If growth hormone is increased in children, gigantism develops. The child’s growth is accelerated and differs significantly from that of his peers. Internal organs similarly increase in size. With age, excess growth hormone leads to acromegaly and accompanying diseases and symptoms: • hardening and thickening of the skin; • excessive hairiness; • heavy sweating; • increased fat content of the epithelium; • excess cholesterol and vascular atherosclerosis; • diabetes; • calcium deficiency in the body; • pathologies of the nervous system; • enlargement of facial features and body parts; • migraine; • decreased visual acuity; • epilepsy; • gynecomastia; • impaired sense of smell; • fluctuations in the menstrual cycle; • sexual dysfunction; • changes in appetite and sleep quality.
STH deficiency.
It manifests itself with many symptoms characteristic of a decrease in the rate of development of the body. They are characteristic primarily of children. • short stature. • fast fatiguability. • increased sweating. • violation of thermogenesis (sometimes cold, sometimes hot). • increased formation of wrinkles and signs of accelerated aging. • reduced tolerance to physical activity (muscle wasting, decreased muscle mass). • tendency to obesity. • fragility of bones (history of fractures). • heart disease (atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular accident). • depression. • sexual dysfunction and decreased sexual desire. • acceleration of aging. • acromegaly. • pituitary tumors; • tumors in other organs that produce somatropin or somatoliberin; • pathologies of receptors sensitive to growth hormone; • chronic renal failure; • alcoholism. Sometimes the hormone can be elevated due to random reasons. The following factors can be identified that increase the formation of growth hormone: • consumption of foods rich in proteins; • long-term fasting (more than 15 - 16 hours); • excessive physical activity; • stress; • use of drugs with amino acids, hormonal contraceptives, antiviral drugs, insulin. In children, the main causes are: • Hereditary dwarfism; • pituitary dwarfism (insufficiency of pituitary gland function); • hypothalamic syndrome; • Injuries; • Infectious disease; • Failure of one of the internal organs; • Inflammatory disease of the large intestine; • Tumors. There are two groups of causes of deficiency of GH secretion in adults: • deficiency of GH secretion since childhood; • post-traumatic secretion deficiency that developed in adulthood. Pseudo-deficiency of growth hormone is also described when its concentration in the blood decreases in the following conditions. • physical activity in a cold room; • condition after childbirth; • obesity; • thyrotoxicosis; • hypercortisolism; • Addison's disease; • heart failure; • critical clinical conditions.
Pituitary adenoma:
- Monoclonal tumor (somatotropinoma).
- Mixed adenoma - in addition to GH, prolactin, TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH can be produced.
- Ectopic tumor from cells of the APUD system, producing GH or somatoliberin:
- tumors with an endocranial location (in the pharyngeal or sphenoidal sinus);
- tumors with extracranial location (in the lungs, mediastinum, gonads, intestines).
Iatrogenic factors. Genetically determined endocrinopathies:
- MEN-1 syndrome (multiple endocrine neoplasia) - primary hyperparathyroidism, islet cell tumors, adenohypophysis tumors. Carcinoid tumors of the digestive tract, multiple facial angiofibromas, collagenomas, subcutaneous and visceral lipomatosis, melanomas, leiomyomas of the esophagus, lungs, rectum, uterus;
- McCune-Albright syndrome - osteofibrous dysplasia, local dermopathy (appearance of café-au-lait spots on the skin), pituitary tumor;
- Carney complex - mixed (GH-prolactin-secreting) tumors, cardiac myxoma, patchy skin pigmentation, nodular adrenal dysplasia, schwannomas, etc.;
- isolated familial acromegaly - registered when 2 or more cases of acromegaly (gigantism) are detected in a family in the absence of signs of MEN 1 or Carney complex. It is distinguished by the early onset of the disease, more frequent development in men and rapid growth of adenomas.
A peptide hormone secreted by adenohypophysis cells. The main function is to stimulate the growth and development of the body. Has an anabolic effect, enhancing protein synthesis; participates in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, being an insulin antagonist, etc.
Most of the effects of GH are mediated by the participation of insulin-like growth factors, mainly IGF-1, synthesized in the liver and to a lesser extent in target organs. The hypothalamic releasing factor somatoliberin has a stimulating effect on the production of growth hormone, and the hypothalamic hormone somatostatin suppresses the production of growth hormone.
- Diffuse or nodular enlargement of the thyroid gland associated with excess GH and increased renal clearance of iodine. Secondary hypothyroidism may develop;
- Secondary hypogonadism due to a lack of gonadotropin production or concomitant hyperprolactinemia: women - menstrual irregularities such as oligo- and amenorrhea, galactorrhea, infertility; men - gynecomastia, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction;
- Development of insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinemia, direct lipolytic effect of growth hormone, impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus;
- Pathology of phosphorus-calcium metabolism - hypercalciuria (nephrolithiasis), increased levels of inorganic phosphorus in the blood serum.
The loss of calcium in the urine is compensated by the acceleration of its absorption through the gastrointestinal tract due to increased PTH production. Acromegaly can be combined with hyperparathyroidism and parathyroid adenomas.
- Disproportional enlargement of the hands and feet (pasty hands and feet), thickening of the fingers (cigar fingers);
- Pain and decreased mobility in the joints due to the development of secondary osteoarthropathy (bone growth, joint deformation);
- Spinal deformation of the kyphoscoliosis type with the formation of osteophytes and the development of radicular pain;
- Osteoporosis and osteopenia;
- Muscle weakness. Primary hypertrophy of muscle tissue is gradually replaced by proximal myopathy; patients are concerned about muscle weakness and decreased tolerance to physical activity.
- Splanchnomegaly (increase in the mass of all internal organs). As the disease progresses, functionally active connective tissue is replaced with the development of multi-organ sclerotic changes and organ failure;
- Changes in the cardiovascular system:
- angiopathy associated with sclerotic changes;
- cardiosclerosis;
- acromegalic cardiomyopathy - concentric hypertrophy is replaced by dilated cardiomyodystrophy with the development of progressive heart failure;
- rhythm and conduction disturbances, valvular disorders due to ventricular hypertrophy;
- arterial hypertension caused by sodium and water retention, decreased production of atrial natriuretic peptide, insulin resistance, increased vascular tone;
- Changes in the respiratory system:
- macroglossia. Often the development of obstructive sleep apnea, as a consequence, chronic hypoxia. Thickening of the vocal cords and the appearance of a characteristic low, rough voice;
- pneumosclerosis;
- emphysema;
- development of pulmonary heart failure;
- Loss of pain and tactile sensitivity of the fingers of the extremities, the appearance of paresthesia due to compression of the median nerve in the deformed carpal canal, as well as segmental demyelination of peripheral nerves;
- Headache;
- Narrowing of visual fields, swelling and atrophy of the optic discs;
- Anosmia;
- Diencephalic epilepsy;
- Hydrocephalus;
- Hypopituitarism;
- Hypothalamic disorders - fever, eating disorders, changes in sleep/wake patterns;
- Diabetes insipidus;
- Damage to the III-VI pair of cranial nerves with the development of ptosis, diplopia, pupillary dysfunction, ophthalmoplegia, facial analgesia, pain along the trigeminal nerve, and hearing loss.
DETAILS: Pressing pain in the heart area causes and dangerous signs
Other manifestations
- A characteristic change in facial features due to enlargement of the brow ridges, cheek bones, lower jaw, hypertrophy of soft tissues (nose, lips, ears);
- Hardening and thickening of the skin, hyperpigmentation, most often in the area of skin folds. Often - hypertrichosis, hirsutism, oily seborrhea, acne vulgaris, acanthosis nigricans (acanthosis nigricans, a type of papillary pigmentary dystrophy of the skin), increased humidity (overproduction of the sebaceous and sweat glands);
- The proliferative and antiapoptotic effects of GH and IGF-1 lead to an increased risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms. Thus, the prevalence of thyroid cancer, breast cancer and colorectal cancer is significantly higher than similar indicators in the general population.
Somatropin for children: indications for use and consequences of use
Growth hormone has been used for decades to treat muscle wasting and dwarfism in children. The hormone has helped tens of thousands of children around the world grow to average human height, while without the use of the drug they could have stopped at 1.35-1.40 m and not grown higher. Regular injections of somatropin helped them reach 1.65-1.70 m, that is, normal average human height. At the same time, bone, cartilage and muscle tissue also showed a normal rate of development, as befits a healthy person.
Alas, not all children responded positively to exogenously supplied somatropin. The minimum values of the own (endogenous) hormone in the blood did not increase. Such low absorption of the hormone occurs in approximately 5% of cases. Tips on how to increase growth hormone in a child without injections will not help in this case either. Such problematic absorption of somatropin is associated with personal intolerance and is quite rare.
Are there any side effects of using injectable somatropin? The fact of increased growth hormone in children with exogenous intake has been studied for decades by scientists from different countries, and today we can say with confidence: there are practically no side effects on the body and there are no far-reaching consequences from using the drug. In this case, the hormone was used both in moderate and increased doses. In some cases, there was a discrepancy between the growth rate of muscles and skeleton, however, this clinical picture can be corrected with the help of sports activities, physiotherapy and massage. A course of somatropin for a child should be carried out under the close supervision of an orthopedist, endocrinologist, and immunologist. Supervision by specialists will help minimize side effects and determine the optimal dosage for each individual case.
GABA Supplementation and Changes in Blood Somatropin Levels
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) acts as a special substance that can become an integral part of some neurotransmitters and help increase their secretion. Regular use of drugs with GABA helps to increase the proportion of endogenous somatropin production by approximately 30%.
GABA can be taken in the form of tablets (“Aminalon”), as part of sports nutrition (for example, almost all amino acid complexes contain GABA) or to enrich your diet. Nuts, avocados, and some types of fish contain high amounts of gamma-aminobutyric acid. GABA drugs also have a positive effect on sleep - this will indirectly help increase the production of growth hormone.
Somatropin and physical activity: how to train to accelerate hormone synthesis
Physical activity promotes the release into the blood of not only growth hormone, but also neurotransmitters responsible for good mood and vigor. That’s why regular exercise, both strength-training and athletics, is so important.
Every adult should devote himself to physical education for an hour at least two or three times a week. Even if you have health problems and contraindications to performing certain exercises, you can practice swimming or gymnastics. Regular, albeit moderate, physical activity will not stop the endogenous production of somatropin.
Recent studies have shown that high-interval physical activity is particularly good at stimulating the release of growth hormone into the blood. It should be noted that if after training a person suffers from insomnia or spends the evening drinking alcoholic beverages, then one cannot count on the production of the hormone. Only a regularly observed healthy lifestyle and an integrated approach will help improve the situation with neurotransmitter and hormone deficiency.
What is somatropin and how does it affect the body?
Peak production of this substance by the anterior pituitary gland occurs between the ages of one and ten years. It is during this period of time that the body grows most intensively: bone tissue, internal organs, muscles, skin, teeth. A colossal amount of energy is required for the growth process to proceed normally.
In some cases, the endocrine system is disrupted and the growth process may stop. In this case, the child may be diagnosed with dwarfism or muscle atrophy, as well as certain skeletal diseases. Adults may also be diagnosed with a disease that requires high doses of the hormone (acromegaly, anterior pituitary adenoma). In this case, injections of somatropin are prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly, the dose is prescribed individually, depending on the patient’s age and the severity of the disease.
Artificially synthesized growth hormone is currently available in two forms:
- recombinant - is the result of genetic engineering, the structural formula of which contains 191 amino acids;
- synthetic somatropin, which contains 192 amino acids.
The most famous somatropin drug on the pharmaceutical market is Jintropin; it can be purchased at any pharmacy with a prescription from a doctor. The cost of the drug is quite high - for a box with 10 ampoules, 10 units of the drug in each, you should pay about seven thousand rubles. This amount of medicine lasts on average for two weeks. It is also possible to increase growth hormone naturally, without resorting to injections, but of course, it is not so effective.