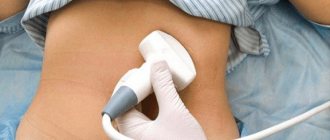
A person’s complaints of severe pain in the left hypochondrium often indicate inflammation of the pancreas. The examination of the patient begins with an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. A diagnostic method based on measuring the intensity of reflection of sound waves from the surface of organ tissues makes it possible to identify the smallest deviations in the functioning of the digestive system.
When assessing an echogram and morphological parameters of tissues, it is difficult for a doctor to make a mistake. The images that the sonographer creates during the examination are different in color. Light colors indicate the presence of seals in the organ, dark and black colors indicate liquid formations. A healthy pancreas, due to its homogeneous watery structure, is displayed in dark colors. The opposite picture indicates pathological changes and organ disease.
If you have been diagnosed with increased echogenicity of the pancreas, then carefully study the information below.
What is echogenicity
With ultrasound, the doctor uses ultrasound for diagnosis. This means that the rays emitted by a special sensor penetrate the body tissues and are reflected back.
The reflected ultrasound is captured by the same sensor, although it is slightly modified. These changes are displayed on the computer monitor, which processes the readings using a special built-in program.
Echogenicity refers to the ability of body tissue to reflect ultrasound radiation. All organs of the body are different, and due to certain changes they exhibit a heterogeneous structure . If the structure of the organ being examined is homogeneous, then ultrasound passes through the tissue freely and is not reflected, so there will be no echogenicity indicator.
But in organs with a dense structure (and the pancreas is one of them) the waves will be reflected. By how the echogenicity changes, the doctor judges the presence of pathological changes. The examined organ tissue may be partially replaced by fatty tissue, and all these changes will be visible on the monitor as objects with different echogenicity.
The conclusion “isoechoicity of the pancreas” is normal, i.e. the structure is homogeneous. Often there may be mixed echogenicity, and then the tissue is heterogeneous.
If the parenchyma is changed, then this may be a temporary phenomenon. Diffuse changes in the parenchyma are caused by the following factors:
- poor diet;
- changes in a person's appetite;
- season of the year;
- chair and many others.
Norms of echogenicity of the pancreas
It should be remembered that altered echogenicity is not a sign of disease, but a characteristic of the organ. And if certain parameters do not correspond to the norm, this indicates that a painful process is occurring in the body.
So, normally, during ultrasound diagnostics, the echogenicity indicator is homogeneous. There is no hyperplasia, foreign objects, areas of fibrosis or necrosis. A high echogenicity indicator indicates that pathological processes are occurring in the gland.
What you need to know about increased echogenicity
Increased echogenicity in the pancreas indicates pathologies such as chronic pancreatitis and tumors. Local hyperechogenicity indicates that the gland may contain stones, salt accumulation or tumors.
All such patients are referred for additional diagnostic examination.
Causes of hyperechogenicity
Increased echogenicity occurs for the following reasons:
- unbalanced diet;
- unfavorable heredity;
- stress;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- pathologies of other gastrointestinal organs;
- incorrect medication use.
Prevention
To prevent another exacerbation and increased echogenicity, the following preventive measures should be observed:
- completely eliminate smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- eat right and on time;
- eat at least 4 times a day, small portions;
- minimize the consumption of canned, fatty, spicy and smoked foods;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- play sports, preferably swimming.
What does hyperechogenicity indicate?
A diffuse increase in echogenicity indicates a tumor or pancreatitis. With tumors, the following symptoms attract attention:
- digestive disorders;
- bowel dysfunction (most often diarrhea);
- flatulence;
- loss of weight and sometimes appetite;
- general weakness.
With pancreatitis, enzymes do not digest food, as is normal, but the parenchyma. Toxins are released that enter the bloodstream, poisoning the liver, kidneys, and brain. Acute pancreatitis is considered the most dangerous.
The pathology is characterized by sharp pain in the hypochondrium, nausea, and vomiting. Blue spots sometimes appear on the stomach.
Acute pancreatitis is dangerous with the risk of death, so the patient needs urgent surgical intervention. The following signs are visible on ultrasound:
- increase in organ size;
- unclear contours and structure;
- dilation of the ducts;
- accumulation of fluid around the organ;
- lack of echogenicity in some areas (this indicates tissue death).
Diffuse changes are also observed with lipomatosis. Lipomatosis is a condition where organ tissue is replaced. This happens, for example, if the patient has diabetes. The size of the organ in diabetes remains unchanged, and echogenicity changes slightly.
Are the figures definitive?
No, moderate or even high levels of change are not permanent. The echogenicity of the organ in question can change under a variety of conditions. Often a pathological indicator appears due to poor nutrition. It’s worth correcting it, and the next study will show the norm.
That is why doctors do not focus on the results of only one ultrasound, but prescribe additional ones for the patient. A person with a history of pancreatic pathology should be constantly monitored by a therapist.
Symptoms
Exacerbation of the pancreas
- flatulence and bloating;
- stool disorder;
- loss of appetite and weight;
- low blood pressure;
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- pain in the upper abdomen, under the ribs;
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- increase in body temperature.
If the echogenicity of the pancreas in an infant is increased, then the likelihood of abnormalities in the development of the organ is high.
In the absence of pronounced symptoms, hyperechogenicity may be caused by dietary errors. With proper adjustments and exclusion of certain foods from the diet, the next study will show the norm.
If the patient has an acute form of pancreatitis, then the level of blood pressure in the pancreatic ducts is higher than normal, the structure is heterogeneous. As a result, the organ is severely injured, and enzymes aimed at helping food digest better can enter nearby tissues. As a result, active digestion of tissues will begin, intoxication of the entire body.
A high level of echogenicity can be determined by the following symptoms:
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- blood pressure drops below normal;
- heart rate increases;
- Severe pain is felt in the hypochondrium on the left side.
If pancreatitis has already become chronic, the organ swells greatly, its size increases, its contours are blurred, and hemorrhages form.
Enzymes necessary for digesting food are produced in small quantities, as a result of which appetite disappears, problems with bowel movements are observed, and there is a feeling that the stomach is full even in the absence of food in it.
What changes occur in the pancreas
As already noted, various types of abnormalities on ultrasound indicate that pathological processes are occurring in the gland. With diffuse changes, the organ may increase or decrease.
Tissues can become denser, their structure becomes heterogeneous. Often the contours of the pancreas become unclear. Decoding the diagnostic results describes in detail all such phenomena.
This is what happens in the gland in the presence of certain pathologies:
- In acute pancreatitis, the pressure in the duct increases. The organ tissues are destroyed and the body is poisoned. Such processes signal themselves with terrible pain.
- In the first stages of chronic pancreatitis, the gland is swollen. Then it decreases and becomes sclerotized.
- With fibrosis, some areas of the organ are replaced by connective tissue.
- Replacement of organ areas with adipose tissue is an irreversible process. With a massive process, the pancreatic parenchyma is compressed.
- In pancreatitis or diabetes, ultrasound shows various signs of changes in the parenchyma, hyperechoic areas are noted in it.
- Structural changes affect the parenchyma, since it consists of many glands.
- The formation of cysts and tumors is possible.
- Reactive changes indicate that the patient has problems with the liver and gall bladder.
- Finally, due to cell death, ultrasound shows fatty degeneration.
It is possible that mild changes may occur that do not affect the functionality of the gland.
Stages and degrees
Pancreatitis comes in two forms: acute and chronic. Their main difference lies in various pathological processes. The chronic form appears after the acute stage and is accompanied by a constant inflammatory process, which ultimately leads to malfunctions of the organ.
Chronic pancreatitis also occurs:
- primary - inflammation develops directly in the gland itself;
- secondary - manifests itself against the background of other ailments affecting the organs of the digestive system.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas occurs with pancreatitis
| toxic | manifests itself against the background of alcohol abuse, smoking, and exposure to certain medications |
| autoimmune | is rare and affects not only the pancreas, but also other internal organs, and this happens due to increased immune function |
| hereditary | appears due to mutation of certain genes |
Chronic pancreatitis is also divided into several clinical groups:
- obstructive;
- calcifying;
- parenchymal;
- pseudomutorous.
Each of these types has its own separate symptoms and time course of the pathology.
According to the nature of the course, the chronic form has 3 stages: mild, moderate, severe. In the mild stage of exacerbation, exacerbations are observed no more than 2 times a year, and this happens due to malnutrition. The average one worsens up to 4 times a year and is accompanied by severe pain. Severe is characterized by long periods of exacerbation.
Malignant tumors of the pancreas come in 4 stages. As it grows, more and more organ tissue is affected and metastases spread.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jBl-afQdqx0
Lipomatosis is classified according to the extent of inflammation:
- first - pathological cells affected about 30% of the organ;
- second - 60% of the gland;
- third – more than 60%.
Also, lipomatosis can be of two forms: focal and diffuse.
Pancreatic fibrosis can have several stages:
- local - this is when the connective tissue has replaced only a small area of the organ;
- diffuse - almost all glandular tissue loses its glandular structure, being replaced by coarse connective tissue.
At any stage of a particular illness, it is important to consult a doctor and select preventive or therapeutic measures to prevent the rapid development of the disease and complications.
Classification of hyperechoic inclusions
The following types of hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas are distinguished:
- Pseudocysts (these are liquid formations that appear due to acute pancreatitis). The outline of the fabric becomes unclear.
- Calcifications, or calcified objects. Appear if a person has suffered a chronic disease of the organ in question (most often pancreatitis).
- Fatty objects replace normal areas. This occurs if a person eats too much fatty food.
- Fibrosis, in which normal areas of tissue are replaced by scars. It is diagnosed after pancreatic necrosis.
- Stones can accumulate in the ducts of the organ.
- Fibrocystic degeneration is usually the result of chronic inflammation of the gland.
- Metastases to the pancreas.
If the diagnosis shows questionable results, the patient is sent for additional tests. This is the only way to make an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of pathology
There are many factors that can cause increased echogenicity of the pancreas. Their list includes a whole range of reasons: from a common cold to a malignant tumor.
Such violations are often temporary. Thus, diffuse echogenicity can be provoked by the following circumstances:
- Seasonal changes;
- Climate change;
- Elderly age;
- Binge eating;
- Prolonged fasting;
- Post-inflammatory period (after suffering an infectious or viral disease);
- Carrying out diagnostic tests on an empty stomach.
Currently reading: What are the names of pancreatic cells and their functions?
The reasons for the high echogenicity index are often pathological inclusions. Usually, if they are present, the ultrasound report records this: “hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas.” The most serious problem that can be hidden under this formulation is malignant formation. However, one should not rush to conclusions, since local increased echogenicity is also evidence of a number of other pathologies, which we will talk about later.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Before the examination, patient preparation is necessary. It is carried out on an empty stomach, the last meal should be approximately 12 hours before the ultrasound. For a few days, you need to eliminate foods that lead to the formation of gas from your diet.
On the day of the procedure, the patient is prohibited from smoking, drinking alcohol or taking medications..
The examination itself is painless and takes up to 20 minutes. The subject lies on the couch on his back, then turns over onto his right and left sides. A harmless gel is applied to the stomach. If you have a tendency to flatulence, then you need to take several sorbent tablets.
After all procedures are completed, the doctor analyzes the information received and makes a diagnosis. Ultrasound is completely harmless to the patient and can be performed as many times as needed.
How is pathological hyperechogenicity of the pancreas treated?
Treatment of all conditions associated with hyperechogenicity is prescribed only by a doctor.
Therapy depends on the cause of hyperechogenicity:
- In acute pancreatitis, drugs are prescribed that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the gastric mucosa. Agents that can reduce pancreatic enzyme activity are also needed. It must be remembered that therapy for an acute disease is carried out in the surgical department.
- For lipomatosis, a diet low in fat, especially of animal origin, is indicated.
- In the presence of calcifications and areas with fibrosis, along with the prescription of a diet, the issue of surgical intervention is decided.
- With reactive pancreatitis, proper nutrition and therapy for the underlying disease are necessary.
- Exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis are treated in a hospital setting. Intravenous injections and infusions are indicated.
- Treatment of carcinoma is carried out surgically; often the patient may require chemotherapy.
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in reducing pancreatic hyperechogenicity. The patient should give up fried, smoked, and salty foods.
Alcohol and smoking are strictly prohibited. It is also important to limit your consumption of sweets.
It should be remembered that increased hyperechogenicity is not a disease, but a characteristic of the organ. Based on the results of the ultrasound, appropriate treatment is prescribed. It is possible that the patient may require additional instrumental examinations and tests.
Nowadays, you can very often come across an ultrasound report that states that the echogenicity of the pancreas is increased. Some people, having read this about their organ, immediately begin to look for treatment on the Internet, while others, on the contrary, consider it absolutely unimportant. Meanwhile, such an ultrasound symptom may indicate a very serious pathology of the gland. It is not a diagnosis and requires consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Medications
Drug treatment for increased echogenicity is selected depending on the type of pathology. If a malignant neoplasm is detected in the pancreas, the patient undergoes surgery and chemotherapy in a hospital setting.
To stop the development of lipomatosis, it is enough to adjust your diet by adding dietary dishes to it. And in case of exacerbation of pancreatitis, drug treatment is additionally selected in addition to the diet.
To overcome the disease and prevent complications, drugs enriched with enzymes are recommended that help reduce the level of acidity in the stomach and agents that help reduce the fermentation activity of the organ.
The following medications give the best effect:
- Rutacid. This drug, presented in tablet form, helps reduce the level of acidity in the stomach.
Its main component is hydrotalcite. If a patient has problems with the pancreas and liver, then this drug is prescribed to reduce the amount of acid that passes from the stomach to other organs. You need to take the medicine 4 times a day, 2 tablets. It is better to take it after a meal, the interval should be at least 1 hour. The tablets should be chewed well and then washed down with water. The average duration of treatment is 1 month. This drug should not be prescribed to children under 12 years of age, to patients sensitive to the drug, or to those with renal failure. If the dose and course are exceeded, symptoms such as belching, diarrhea, and allergies may occur. Sold freely, average cost 220 rubles.
- Nexium. The drug is presented in tablet form, containing exomeprazole. It is this substance that reduces the level of acid in the stomach, suppressing excessive secretion production. Take 1-2 tablets once a day, the duration depends on the severity of the disease, the standard course is 4 weeks. Before taking the tablet, you can dissolve it in water to make it easier to drink. The drug is not prescribed to children, women during pregnancy and lactation, or those with special sensitivity to the components.
- Aprotinin. This is an injection solution with the active ingredient of the same name, which helps suppress excessive fermentation. Prescribed to patients with acute pancreatitis, when tissue necrosis has already begun. The drug is administered 5 ml per day every hour, on the first day, and then up to 3 times a day, the duration of therapy is 3-5 days. The drug is not recommended for poor blood clotting, acute reactions to components, or the first trimester of pregnancy. Among the adverse events, an allergic reaction is most often observed. Price in Russian pharmacies from 500 rubles.
To relieve pain, you can take No-shpa, Diclofenac, Drotaverine.
Traditional methods
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas can also be treated using traditional medicine.
The following recipes give good results; with their help you can normalize the functions of the organ:
- Tincture of pink radiola. Before each meal, half an hour before, drink 1/2 tsp. The course is at least a month.
- Iris and wormwood. Take both ingredients in equal quantities, add 500 ml of water, and prepare a decoction. Leave for a couple of hours. Take 1/2 tbsp. before eating.
- Propolis tincture. 1 tbsp. l. tincture pour 2 tbsp. vodka, leave for 2-3 weeks. Take 50 drops once a day, adding them to milk or chamomile decoction.
- Potato juice. 1/2 tbsp. Drink freshly squeezed juice 30 minutes before meals for 2 weeks. Afterwards take a 10-day break and repeat the course.
- Herbal collection. In equal quantities, take dill seeds, St. John's wort, coriander, mint, elecampane root, and dried herbs. Mix, select 1 tbsp. l., pour 250 ml of boiling water, let it brew. Take 1/2 tbsp. 5 times a day.
Other methods
Food must be boiled or steamed. It should only be eaten warm. No smoked meats, fatty, spicy, salty. You should not eat mushrooms or food with spices. Alcohol is strictly prohibited.
The diet should consist of:
- lean meats and fish;
- vegetables, stewed or boiled;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- fruit jelly.
You need to eat 4-5 times a day, in small portions.
The concept of echogenicity
Echogenicity is a term that is used only to describe the ultrasound picture. It refers to the ability of the tissue to which ultrasound is directed (that is, high-frequency sound) to reflect it. The reflected ultrasound is recorded by the same sensor that emits the waves. Based on the difference between these two values, a picture of different shades of gray is constructed, observed on the device’s monitor screen.
Each organ has its own echogenicity index, and it may be homogeneous or not. The following dependence is observed: the denser the organ, the more echogenic it is (displayed as a lighter shade of gray). Liquids do not reflect ultrasound, but transmit it. This is called “echonegativity,” and fluid structures (cysts, hemorrhages) are called anechoic. For the urinary and gall bladder, the cavities of the heart, intestines and stomach, blood vessels, and ventricles of the brain, this “behavior” is the norm.
Thus, we have analyzed what the echogenicity of the pancreas is - this is the ability of this glandular tissue to reflect high-frequency sound emitted by an ultrasound transducer. It is compared with the properties of the liver (they should either be equal, or the pancreas should be a little lighter), and based on the resulting picture, they talk about a change in the echogenicity of the gland. The homogeneity of the organ is also assessed by this indicator.
An increase in the echogenicity of the pancreas is described when there are fewer normal glandular cells in the tissue of the organ (as we remember, fluid reduces echogenicity, and glandular cells are rich in it). Such a change can be observed both locally and diffusely. In addition, some factors may temporarily affect this indicator.
Warning! The description of echogenicity alone is not a diagnosis.
conclusions
From the above, we can conclude that a change in the echogenicity of an organ can indicate many diseases or may even be a temporary phenomenon. An increase or decrease in echogenicity is not a diagnosis, but only an indicator that pathology exists. If there is a suspicion of a particular disease due to impaired echogenicity, specialists prescribe additional types of diagnostics. So, if a tumor is suspected, blood tests are examined and other research methods are used, such as biopsy, computed tomography, etc. After determining the type of tumor, whether it is malignant or benign, the type of therapy is determined and treatment is carried out.
References: https://lekafarm.ru/stati/uzi-podzheludochnoy-zhelezy-pokazaniya-kak-delayut-normy-i-rezultaty.html medclic.ru/uzi/podzheludochnoj/ https://www.fundamental-research. ru/ru/article/view?id=33417 Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
When the echogenicity of the entire gland increases
A diffuse change in the permeability of pancreatic tissue to ultrasound can be a symptom of pathology, but can also be observed normally. This cannot be said about foci with increased echogenicity - this is almost always a pathology.
The echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased in the following pathologies:
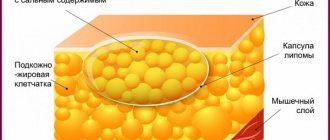
- Glandular lipomatosis, when glandular tissue is replaced by fat cells containing almost no intracellular fluid; however, the size of the pancreas is not increased. This condition is most often asymptomatic. Read more about this disease in the article: How to recognize and treat pancreatic lipomatosis in time
- Swelling of the gland that develops with acute pancreatitis. Accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting.
- Organ tumor. If the ultrasound describes the pancreas with increased echogenicity, then there are necessarily symptoms of the disease: weight loss, pallor, weakness, lack of appetite, frequent bowel movements.
- Pancreatic necrosis, accompanied by the death of organ cells, will also appear on ultrasound as a lighter area. This disease has such signs as severe abdominal pain (up to the development of painful shock), disturbance of the general condition, uncontrollable vomiting, and diarrhea.
- As a result of diabetes mellitus, which is manifested by thirst in the absence of hot conditions, elevated temperature, active work, as well as frequent and abundant (including night) urination.
- Development of connective tissue in the gland (fibrosis) - usually as a result of inflammation or metabolic disorders. In this case, a person may remember cases of unstable stool and abdominal pain. Ultrasound shows not only an increase in echogenicity, but also a decrease in the size of the gland and the tuberosity of its contours.
The hyperechoic pancreas can also be a temporary phenomenon, manifested by:
- as a result of reactive inflammation in many infectious diseases: influenza, pneumonia, meningococcal infection. This requires treatment of the underlying disease;
- when changing the type of food consumed;
- after a lifestyle change;
- at certain times of the year (usually spring and autumn);
- after a recent heavy meal.
In such temporary conditions, the echogenicity of the pancreas is moderately increased, in contrast to pathologies, when significant hyperechogenicity is noted.
Local increase in echogenicity
What are hyperechoic inclusions in the pancreas? It can be:
- pseudocysts - liquid formations that develop as a result of acute pancreatitis; with this disease, the contour of the pancreas becomes uneven, jagged, hyperechoic;
- calcification of tissue areas - calcifications; they are also formed as a result of inflammation (usually chronic);
- areas of adipose tissue; they replace normal gland cells in case of obesity and excessive consumption of fatty foods;
- fibrous areas - where areas of normal cells have been replaced by scar tissue; usually this occurs as a result of pancreatic necrosis;
- stones in the gland ducts;
- fibrocystic degeneration of the gland is either an independent disease or an outcome of chronic pancreatitis;
- metastatic tumors.
Treatment of pathological hyperechogenicity
Treatment of conditions where the echogenicity of the pancreas is increased is prescribed only by a gastroenterologist, who must find the cause of this ultrasound symptom:
- if the cause is acute pancreatitis, therapy is carried out with drugs that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and inhibit the enzymatic activity of the pancreas;
- if hyperechogenicity is caused by lipomatosis, a diet with a reduced amount of animal fats in the diet is prescribed;
- if the etiological factor is calcifications, fibrosis or stones in the ducts, a diet is prescribed, and the need for surgical treatment is decided;
- reactive pancreatitis requires treatment of the underlying disease and diet.
Advice! Not a single specialist proceeds from the assumption that it is necessary to treat the tests, and not the person. Increased echogenicity of the pancreas is an ultrasound symptom, not a diagnosis. It requires further examination, and therapy is prescribed only on the basis of subsequent data.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas is the conclusion of an ultrasound examination. Some people immediately look for treatment methods on the global network, while others are indifferent to this diagnosis. How should you react if you have been diagnosed with increased echogenicity of the pancreas? In this situation, you need to consult a gastroenterologist for advice.
When to see a doctor
Any even minor symptoms should force a person to seek advice from a specialist. Often tumors in the early stages, like many diseases, are asymptomatic.
The following symptoms should make you think about your health:
- tachycardia;
- discomfort in the hypochondrium on the left side;
- a feeling of nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting;
- low pressure;
- difficulties with bowel movements;
- decreased appetite;
- feeling that the stomach is full, but not a single piece of food has entered it.
If you have at least 1-2 symptoms, you should definitely visit a therapist. He will prescribe an examination and visit to a gastroenterologist.
What does the term “echogenicity” mean?
This concept is used only to describe ultrasound examination.
This refers to the ability of body tissue to reflect high frequency waves. This indicator is recorded by the same device that emits the waves. Based on the differences between these two indicators, we can say that the echogenicity of the gland is increased or decreased. This is displayed on the device screen. Each person has his own indicator, moreover, it can be both homogeneous and heterogeneous. Doctors noticed the following pattern: the denser the organ, the higher the level of echogenicity. Therefore, one should not be surprised by such a diagnosis, and the notes in the ultrasound doctor’s report indicate that the pancreas has increased echogenicity and a heterogeneous structure. Any liquid is not able to reflect ultrasonic waves; it transmits them.
Now you know what echogenicity of the pancreas is. This indicator indicates how much the tissue can reflect high-frequency waves that come from the ultrasound of the drug. Next, this value is compared with liver indicators; the values should be equal. Depending on the difference in indicators, they speak of increased density of the pancreas or the opposite situation.
The echogenicity of the pancreas is increased, let’s take a closer look at what it is? This indicates that there are not enough cells in the organ. After all, liquid significantly reduces the level of echogenicity, and there is quite a lot of it in glandular cells. There are both local and diffuse changes in the pancreas, with increased echogenicity. In addition, other factors may also influence increased echogenicity.
Diagnostic methods
The only way to detect a hypoechoic area is to resort to ultrasound diagnostics. In this case, the examination is carried out with a special device that emits ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is a painless and completely safe procedure
In contact with internal organs, ultrasonic waves are reflected and returned. Thanks to this, everything that happens is displayed on the monitor. Subsequently, the doctor deciphers the results obtained.
Ultrasound is harmless regardless of the patient's age. The method can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The method does not require special preparation. An exception is abdominal ultrasound examination. In this case, sometimes you need to fill your bladder or follow a diet.
This is useful: how harmful is ultrasound.
Before performing an ultrasound, an acoustic gel is applied to the area being examined. The product promotes better glide. Does not interfere with visualization and does not cause an allergic reaction.
After diagnosis, you need to remove the remaining gel. This can be done using dry wipes. The doctor will decipher the indicators and confirm or deny the likelihood of the presence of hypoechoic tissue.
From this video you can learn more about benign formations in the mammary gland:
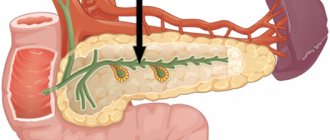
Pancreas
It plays the role of an endocrine channel. With any disease, no organ can replace its role. The pancreas is responsible for the production of enzymes involved in digestion. It also produces hormones important for the functioning of the body.
Therefore, a disease such as increased echogenicity of the pancreas should be treated immediately when the first symptoms appear. Other diseases of this organ should not be ignored. One of the most dangerous diseases is pancreatitis, in which there is a release of enzymes in large quantities. They break down organ tissue and, when they enter blood cells, can cause very serious consequences for the entire body.
What does increased echogenicity of the pancreas mean?
Reduced echogenicity of the pancreas, in contrast to increased echogenicity, is not always a pathology. Diffuse changes in echogenicity do not always indicate the presence of a disease. What does increased echogenicity of the pancreas mean?
- The echodensity of the pancreas is increased in the case of pancreatic lipomatosis. In this case, the pancreatic tissue is replaced by cells made of fat. They contain virtually no liquid. It is worth considering that lipomatosis of the gland has no symptoms.
- The echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased in the case of edema of the organ; this disease develops in acute pancreatitis. Symptoms of this disease are vomiting and diarrhea.
- Possible diseases include pancreatic tumor.
- The echogenicity of the pancreas is significantly increased, possibly due to diabetes mellitus.
Changes in echogenicity may be temporary due to the following reasons.
- A sharp change in lifestyle.
- Eating dense foods before an ultrasound scan.
- In spring or autumn, echogenicity may increase.
- In case of infectious diseases, such as influenza or pneumonia. In order to reduce echogenicity, treatment for a viral disease should be undertaken.
In case of temporary changes, a moderate increase in echogenicity is observed. In the case of hyperechogenicity, the cause can only be the presence of some pathology.
Acute pancreatitis on ultrasound
Acute pancreatitis is a severe complication of gallstone disease or a consequence of toxic effects, such as alcohol.
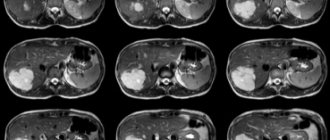
Mild pancreatitis is not visible on ultrasound (CT is a more sensitive method). Severe pancreatitis is easily detected by ultrasound. When an unusually clear and contrasting pancreas stands out from the surrounding tissue, edema of the parenchyma and surrounding fatty tissue can be assumed. If a thin layer of free fluid is visible around the pancreas, along the stomach, at the hilum of the liver and spleen, pancreatitis can be confidently diagnosed.
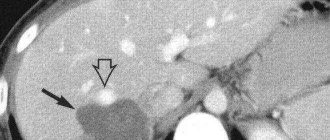
| Photo. Acute pancreatitis on ultrasound: A - Swelling of the pancreatic parenchyma (p), the contour of the pancreas is unusually clear, a small accumulation of fluid along the border (arrows). B, C - Accumulation of fluid along the contour of the body of the pancreas, a thin rim of fluid along the splenic vein (arrows), the parenchyma is heterogeneous, the surrounding tissue is hyperechoic - swelling and inflammation, the common bile duct is dilated (B). In this case, gallstone disease must be excluded. |
Almost all pancreatic tumors are hypoechoic compared to the normal pancreas. It is impossible to distinguish between focal pancreatitis and pancreatic tumor using ultrasound alone. A tumor and pancreatitis can be combined.
| Photo. Acute pancreatitis on ultrasound: The pancreas is unusually contrasted against the background of hyperechoic surrounding tissues, a thin strip of fluid along the contour (A), a hypoechoic focus in the tail (B), fluid in the hilum of the spleen (C). A hypoechoic tail can be mistaken for a tumor. |
In severe cases of pancreatitis, pancreatic fluid digests surrounding tissue, forming pseudocysts. Such cysts can be single or multiple. They may increase in size and rupture.
On ultrasound, pseudocysts are defined as oval or round hypoechoic formations with clear contours. In the early phases of cyst formation, it is a semi-liquid formation and has a complex echostructure with internal reflections and unclear contours. Later, due to autolytic processes and sedimentation of a suspension from blood and pus, clear signs of liquid contents appear and a false capsule with smooth walls is formed. Infection of pseudocysts often occurs, then internal echo structures or thin delicate septa can be detected. When a cyst is detected, it is important to trace the connection of the cyst with the duct, as this is important for determining treatment tactics. When a pseudocyst is more than 10 cm in size, difficulties arise in determining its source.
| Photo. A - Large pseudocyst between the head of the pancreas and the liver after pancreatitis. B, C - Severe necrotizing pancreatitis longitudinal (B) and transverse (C) sections: extensive necrosis, melting of the surrounding fat in the tail area, accumulation of fluid around the gland. |
Treatment of the disease
Not everyone knows what increased echogenicity of the pancreas is and what to do in this case. It is necessary to consult a medical specialist. He will prescribe additional studies that will help determine the exact cause of the increased level of echogenicity. Once the cause is known, the doctor draws up a course of treatment. If the cause is lipomatosis, then there is no need for treatment.
In the same situation, when you are diagnosed with acute pancreatitis, this may mean hospitalization. After all, this disease is characterized by severe pain in the abdominal area. Symptoms such as nausea or diarrhea are also common. Quite often, mixed echogenicity of the pancreas is diagnosed, which indicates that the tissue of the organ is heterogeneous.
You should not try to treat acute pancreatitis at home, as intravenous medications are required. For this disease, treatment must be comprehensive.
Malignant tumors affect the exocrine region of the gland. This is typical for older people. Much more often this disease occurs in males. The main symptoms are rapid weight loss and severe abdominal pain. Treatment is carried out using a surgical method in combination with chemotherapy.
Another type of tumor is cystadenocarcinoma, which is quite rare. Its symptoms are pain in the upper abdomen. In this case, the prognosis for the course of the disease is most favorable. It is worth remembering that regardless of the reason for the increase in echogenicity, these deviations should not be ignored. The sooner the examination is completed, the sooner treatment will begin.
A person’s complaints of severe pain in the left hypochondrium often indicate inflammation of the pancreas. The examination of the patient begins with an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. A diagnostic method based on measuring the intensity of reflection of sound waves from the surface of organ tissues makes it possible to identify the smallest deviations in the functioning of the digestive system.
When assessing an echogram and morphological parameters of tissues, it is difficult for a doctor to make a mistake. The images that the sonographer creates during the examination are different in color. Light colors indicate the presence of seals in the organ, dark and black colors indicate liquid formations. A healthy pancreas, due to its homogeneous watery structure, is displayed in dark colors. The opposite picture indicates pathological changes and organ disease.
If you have been diagnosed with increased echogenicity of the pancreas, then carefully study the information below.
What is echogenicity
Echogenicity is a sign system used by uzologists, which allows one to establish the correspondence of the anatomy of organs to the level of reflection and absorption of high-frequency waves. Liquid tissue of the pancreas is characterized by an average echogenicity. The echo density of the liver parenchyma is used as a standard sample.
Echogenicity scale for assessing study results
Using ultrasound, you can not only determine the degree to which internal organs perceive high-frequency waves, but also obtain information about other equally important parameters. During the examination of the gland, the following parameters are carefully studied:
When determining the volume of the pancreas, the length of the head, body and tail is calculated. Ideally, they should not exceed 30, 24 and 25 mm, respectively. An increase in the latter indicates local or general inflammation in the organ. Abnormally large sizes are a typical sign of pancreatitis. Causes of increased size can also be: abdominal trauma, cystic fibrosis, biliary dyskinesia, hepatitis, infectious diseases. Local changes are associated with malignant tumors and cysts.
In appearance, the digestive gland resembles a comma and has an oblong shape. Sometimes there is a thickening in the head area. Ring-shaped, additional, split forms are deviations from the norm. Improper development of the organs of the digestive system is associated with disturbances in the processes of embryogenesis.
Healthy pancreas. The dark longitudinal stripe is the hypoechoic shadow of the duct.
As for the external contours, they must be clearly defined in the longitudinal and cross sections. Blurring of any part of the gland may indicate the development of an inflammatory process. Blurred outlines and swelling also cause diseases of the organs adjacent to the pancreas (stomach and duodenal ulcers). Uneven borders are created by tumors, cysts, and stones. The contours of malignant formations are lumpy and blurry.
The structure of the digestive gland should be homogeneous and fine-grained. Having discovered single fatty inclusions or numerous calcifications and pseudocysts in the organ, the doctor has every reason to suspect fibrolipomatosis and chronic pancreatitis in the patient.
Insufficient preparation of the person himself can lead to errors in research results. Three days before the procedure, the patient must adhere to a diet that eliminates the possibility of increased gas formation. For prevention, patients are recommended to take adsorbents. On the day of the procedure, it is advisable to empty your bowels and limit your food intake.
What does increased echogenicity mean?
An unusual increase in the recoil force of the waves indicates compaction of the parenchyma and a reduction in the amount of fluid in it. Diffuse hyperechogenicity, the causes of which are external factors, is not considered a pathology. Most often it manifests itself in the hot season, after eating hot and rich food, and during colds.
Echogenicity increases markedly with inflammation. Causes for concern may be: tumors, metastases, calcium deposits and stones, cysts, fibrosis. Such inclusions are the consequences of ignoring the early symptoms of pancreatitis.
A number of parameters indicate acute pancreatitis:
- General increase in organ size.
- Presence of large echogenic areas.
- Heterogeneity of structure.
- Exceeding the width of the gland duct.
- Blurred boundaries.
A more severe form of the disease involves changes in the density and contours of neighboring organs. Possible formation of pseudocysts.
When diagnosing chronic pancreatitis, the following picture is observed:
- Echogenicity increases slightly.
- The width of the duct increases by more than 2 mm.
- The size of the gland itself increases.
- Unclear outline.
- Heterogeneous structure.
- There is fluid in the omental bursa behind the stomach.
The disease may be accompanied by the formation of stones. In the picture they appear as spots with an echogenic trace. The progressive disease is easy to notice due to the significant discrepancy in the ratio of the size of the gland to the Wirsung duct. The latter is greatly swollen in width.
Parameters such as increased echogenicity and blurred contours suggest that healthy cells in the organ have replaced fat cells, which occurs with lipomatosis. Hyperechogenicity along with a decrease in the pancreas indicate the development of fibrosis. The growth of connective tissue and its replacement of normal cells is accompanied by the appearance of scars.
Ultrasound alone is not enough to accurately diagnose a patient. The patient is sent for auxiliary procedures: magnetic resonance or computed tomography, laparoscopy or biopsy.
A lighter image of the pancreas indicates increased echogenicity
Types of hypoechoic formations
Detection of a hypoechoic structure of the pancreas during an ultrasound examination may indicate the development of an acute form of pancreatic damage to this organ. Moreover, the acute form of pancreatitis is accompanied by a loss of clarity of the contours of the gland, which prevents a full examination of the parenchymal organ. Over time, as this pathology progresses, the contour lines of the gland become more and more blurred, until it is completely impossible to visualize them.
In some cases, it is possible to identify individual hypoechoic areas against the background of multiple hyperechogenicity. Such processes can occur when, after intense fibrolipomatous processes in the gland, destructive disorders with an inflammatory nature begin to develop.
The progressive stage of acute pancreatitis contributes to a significant increase in the size of the parenchymal organ, and also acts as an acute factor that reduces echogenicity.
In some cases, echogenicity may be reduced to such an extent that the pancreas is almost impossible to distinguish from the splenic and portal veins.
Zones of hypoechoic formations are also detected during the development of hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Hemorrhagic pancreatitis can not only reduce the level of echogenicity of the organ under study, but also increase it to a significant size and cause an edematous state of the soft tissues adjacent to this organ.
A decrease in the level of pancreatic density can be either diffuse or focal. With a diffuse decrease in the ability to reflect ultrasound, edema occurs when the level of fluid content in the gland increases. This mainly happens with the development of acute pancreatitis, or the manifestation of a severe allergic reaction with existing hypervolemia, that is, an increased level of water content in the body.
The formation of focal hypoechogenicity may be preceded by the following pathological changes:
- cystic lesion of the parenchyma;
- development of a pancreatic cyst;
- the appearance of a tumor-like neoplasm;
- an increase in the diameter of the ducts of the gland being studied.
It is important to remember that the focal type of the gland’s ability to reflect ultrasound can be not only reduced, but also increased, depending on what type of tumor-like neoplasm occurs.
Heterogeneity of structure
In a healthy person, pancreatic tissue is homogeneous, fine-grained, and homogeneous. The echostructure suspiciously increases in subacute and chronic pancreatitis, cysts and tumors.
Acute interstitial pancreatitis is often diagnosed in people who abuse alcoholic beverages and high-fat foods. On palpation they feel sharp pain. Unpleasant symptoms are associated with swelling of the gland. A person complains of cramps in the upper abdomen may contact a doctor.
The heterogeneity of the structure is indicated by arrows (white and dark areas).
Severe pain in the left or right hypochondrium occurs with chronic pancreatitis. During periods of exacerbation of the disease, the patient experiences an increase in temperature, abnormal blood pressure, changes in the color of the skin and sclera (jaundice). The patient is worried about constant nausea, vomiting, and lack of appetite. In addition to poor nutrition, the following diseases can affect the development of pancreatitis:
- Cholecystolithiasis.
- Ulcer penetration.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Parasites (worms).
- Typhoid and typhus.
- Alcohol abuse.
There are many lovers of alcoholic beverages among men, so the likelihood of chronic pancreatitis in the stronger half of humanity is much higher than in women.
Heterogeneity of structure in children
Changes in the homogeneity of the structure of the pancreas often occur in childhood. They manifest themselves as disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Disturbances occur due to spasms of the gland ducts and increased enzyme activity. The obstructed outflow of the latter causes swelling of the pancreas in the child.
This form of the disease occurs even in children 1 year of age. Parents who do not follow the schedule for introducing complementary foods (early inclusion of meat and fish dishes in the menu) can be blamed for this.
Features in children
Indications for ultrasound of the pancreas in children:
- abdominal pain;
- profuse loose stools, vomiting;
- fast weight loss;
- suspected anomaly of pancreas development;
- suspicion of cysts, stones, necrosis or fibrosis of the gland;
- diabetes.
Nausea is an indication for ultrasound of the pancreas in children.
Carrying out an examination of a small child is difficult, and ultrasound results may be distorted, but data such as echo density, the presence of edema, and heterogeneous structure of the organ necessary for a quick diagnosis can be obtained.
Why deviations are dangerous
Negligence towards pancreatitis can increase the risk of new foci of inflammation. The combination of diseases affects the overall health of a person. A critical manifestation of complications is disability.
If treatment of the disease is not started at its early stage, pancreatic enzymes enter the blood and create conditions for infection of other organs. Several diseases find a corresponding response:
- Liver and kidney failure.
- Bleeding in the stomach and intestines, erosions, ulcers.
- DIC syndrome (blood clotting disorder).
- Purulent-necrotic parapancreatitis.
- Mechanical jaundice.
- Liver hepatosis.
- Cholangitis, cholecystitis.
- Abdominal abscess.
Necrosis of the gland parenchyma develops tumors and cysts. Malignant tumors often appear in older men. Unusual thinness, loss of appetite, abdominal pain are the main symptoms of the disease. Only adequate timely therapy can reduce the chances of such complications occurring.