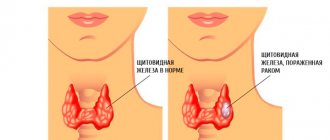
Nodular goiter of the thyroid gland implies the presence of neoplasms (nodules) of various nature and morphology in the thickness of the organ. Now almost every second adult suffers from this disease, and statistics indicate a higher frequency of its prevalence among women. A certain relationship has also been identified between goiter and neoplasms in the female genital organs. These diseases are often combined with each other. During an objective medical examination, a nodule is detected only if its size exceeds 1 cm. Otherwise, pathology can only be detected by ultrasound. When several nodes are identified during examination, we are talking about a multinodular goiter.
The advisability of early detection of the disease is dictated by several factors: the need to exclude malignant neoplasms and prevent hormonal disorders, aesthetic defects and compression of surrounding organs due to a possible increase in the size of the node.
At CELT you can consult an endocrinologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,200
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
What is a nodular goiter of the thyroid gland?
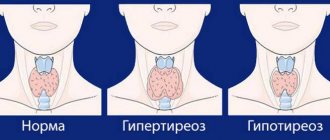
Nodular goiter is commonly called enlargement (hypertrophy) of the thyroid gland. Growing in the lower part of the neck, it really becomes like a bird's crop overflowing with grains. In Russia, thyroid hypertrophy is found in more than a million people, and in women 6 times more often than in men.
A particularly dangerous period for the thyroid gland begins after 50 years, when, due to age-related changes, the functioning of the endocrine glands deteriorates. And if a person also lives in an area where there is not enough iodine in the soil, water and, accordingly, food, the thyroid gland has an even more difficult time.
Such areas are called endemic for iodine deficiency, and enlargement of the thyroid gland due to insufficient intake of iodine into the body is called endemic goiter. The thyroid gland can also enlarge for other reasons: for example, due to autoimmune or oncological pathology, but this is no more than 5-10% of all cases.
In 90-95% of citizens with hypertrophy of the thyroid gland, endemic nodular goiter is diagnosed. The Saratov region, where the author of the letter lives, also belongs to iodine-deficient areas.
And if in general iodine deficiency conditions are observed in every third Russian, then in the Saratov region - in every second. By the way, Moscow and the Moscow region have recently also been added to the list of endemic regions.
The fact that most of the country is in a zone of natural iodine deficiency was recorded back in the 20-30s of the last century, when they began to compensate for its deficiency at the state level by introducing a program to eliminate iodine deficiency diseases.
This work was so successful that in 1970, goiter dispensaries in the USSR were liquidated as unnecessary. But the years that followed the collapse of the USSR forced us to remember this again and return to the problem of endemic goiter.
Endemic goiter
Important : Endemic goiter is diagnosed more often than others all over the world. As a rule, the reason for its development is associated with iodine deficiency.
But there are other reasons. Hyperthyroidism is an increased production of thyroid hormones.
Hypothyroidism is associated with:
- with genetic disorders of the functioning of endocrine gland hormones (for example, cretinism);
- eating goitrogenic foods (for example, cassava);
- side effects associated with the use of certain medications. Symptoms of hypothyroidism:
- hair loss;
- pale and dry skin;
- brittle nails;
- thinning eyebrows;
- cardiopalmus;
- excessive sweating;
- loss of appetite;
- increased blood pressure;
- increase in body weight.
With thyroid diseases, speech slows down, memory deteriorates, drowsiness occurs, and in women, the menstrual cycle fails.
Not all of these symptoms may appear (usually 2 - 3), but they manifest themselves most clearly.
Hyperthyroidism is characterized by:
- toxic goiter of diffuse type;
- active inflammatory processes;
- thyroid oncology.
What are the dangers of iodine deficiency for the body?
Lack of iodine in foods leads to the development of nodular goiter.
Iodine is part of the thyroid hormones that regulate basic processes in the body. They stimulate tissue respiration, regulate all types of metabolism and the activity of every organ, including the brain.
Disorders caused by iodine deficiency are among the most common non-communicable diseases. If there is little iodine, the thyroid gland increases its size and weight, thus trying to increase the number of cells responsible for the production of hormones.
In such cases, an analysis of the hormonal profile shows that the gland reduces the production of thyroid hormones, while the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) synthesized by the pituitary gland, which stimulates its internal secretion, even increases compared to the norm. But it makes no sense to stimulate the gland: no iodine - no hormones!
That is why it is so important to additionally feed the thyroid gland with the element it needs. It is advisable to ensure that the menu contains a sufficient amount of iodine-rich foods. At least for the prevention of nodular goiter.
According to the standards of the World Health Organization, children under one year old should receive 50 mcg of iodine daily, from one year to 2 years - 70 mcg, from 2 to 6 years - 90 mcg, from 7 to 12 years - 120 mcg, adolescents and adults - 150 mcg, pregnant and lactating women - 200 mcg.
Just keep in mind: although iodine is resistant to cold, it quickly evaporates when heated. During heat treatment, meat and fish lose up to 50% of iodine, and vegetables and milk - 30%. Therefore, it is better to cook vegetables whole, lowering them in boiling water, and steam meat and fish under a lid.
It is useless to put iodized salt in food being prepared: potassium iodide decomposes in a hot environment. It is necessary to add salt to already cooled food!
To prevent the development of nodular goiter, it is recommended to eat 100-150 g of seaweed salad - kelp daily: it has a unique! the ability to accumulate iodine contained in sea water in an organic form that is most assimilated by the body.
It’s not for nothing that as far back as 2000 BC, the Chinese treated goiter with seaweed.
Causes
The reasons why nodes develop are not fully known. For example, the occurrence of toxic adenomas may be associated with a mutation of a certain gene. For example, inherited mutations can be found in thyroid cancer. The etiology of this disease is not fully understood, and often it can be considered as an age-related transformation.
In addition, iodine deficiency in the body can cause this disease. In regions where there is a deficiency of this substance, advanced cases of the disease are observed, which lead to complications. In addition, radiation and poor environmental conditions cannot be ignored.
You can highlight such points as a lack of microelements, as well as taking medications, stress, smoking and the presence of viruses.
Menu for the thyroid gland
Foods rich in iodine
On meat days, the body receives only half of the required daily iodine intake (about 80 mcg), and on fish days it also exceeds the norm (222 mcg). By alternating them, you will provide the thyroid gland with this important element.
| Products | Iodine content (mcg) |
Breakfast
| 100 g bread | 8,5 |
| 20 g butter | 0,9 |
| 100 g cheese | 4,0 |
| Egg | 20,0 |
| Total | About 30 mcg |
Lunch
| Apple | 4,0 |
Dinner
| meat | fish | |
| 200 g meat | 6,0 | |
| 200 g sea bass | 148,0 | |
| 200 g potatoes | 7,2 | 7,2 |
| 200 g salad | 10,5 | 10,5 |
| 100 g cottage cheese | 3,4 | 3,4 |
| Total | 27,1 | 169,1 |
Afternoon snack
| 10 g (1 teaspoon) tea leaves or coffee powder - instant, ground | 0,8 |
| 100 g pie with fish filling | 11,6 |
| Total | 12,4 |
Dinner
| 100 g (half a glass) milk | 3,7 |
| 100 g bread | 8,5 |
| 20 g butter | 0,9 |
| 100 g meat | 3,9 |
| Total | 16,1 |
Classification
Depending on the localization and prevalence of the process, several clinical forms of the disease have been identified. There are different types of nodular goiter according to the degree of toxicity and stages of progression.
Types - diffuse, colloidal, toxic, non-toxic
Nodes can be single - solitary. This is most often the case with thyroid adenoma. It accounts for approximately 60-75% of all single nodular formations. This is a conditionally benign tumor, which is formed by cells that produce hormones and can turn into cancer. A malignant tumor can also be presented from the very beginning as a dense node in the gland tissue.
If there are several nodes, then a multinodular goiter or a conglomerate goiter develops when several are combined into one large one. If a cyst or nodules occur against the background of diffuse (widespread) changes, the diffuse nodular form of the disease is diagnosed.
Nodular colloid goiter with varying degrees of tissue proliferation appears as an age-related change or with iodine deficiency. In these diseases, follicle cells intensively produce a colloidal substance consisting of thyroglobulin (a precursor of thyroid hormones).
Toxic and non-toxic nodular goiter reflect the functional activity of the thyroid gland. When it functions normally (euthyroidism), there are no symptoms of the disease or a slight increase in the size of the organ appears. The toxic form is the most severe. Tissue proliferation is accompanied by increased synthesis of hormones (thyrotoxicosis). The most typical signs:
- tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, hypertension;
- increased excitability of the nervous system, irritability, fussiness, insomnia;
- protrusion and shine of the eyeballs;
- sweating;
- progressive loss of body weight.
Typical signs of thyrotoxicosis
Degrees
According to Nikolaev’s classification, the following degrees of nodular goiter are distinguished:
- zero – the thyroid gland is not visible, cannot be felt;
- the first is not visible, but upon palpation it can be detected;
- the second is noticeable when swallowing;
- third – the outlines of the neck are enlarged;
- fourth – goiter changes the shape of the neck (configuration deformation);
- fifth – compression of the goiter occurs on organs located next to the thyroid gland.
According to the WHO classification, the zero degree is the same, and with the first, the size of the lobe or both is greater than the terminal phalanx of the patient’s first finger. The goiter is palpable but not visible. All cases of visual enlargement of the thyroid gland are classified as second degree.
Products contraindicated for thyroid nodule
Soy and cruciferous vegetables (radishes, cabbage, turnips, radishes) are contraindicated for the thyroid gland, so you should not eat them more than twice a week. These products are also called goitrogenic - promoting the formation of goiter, since their excess disrupts the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
It is advisable not to buy imported meat and sausage. When fattening livestock, Western farmers use thyreostatics - drugs that suppress the inclusion of iodine in thyroid hormones.
As a result, fluid is retained in the animals' bodies: weight gain increases, but instead of meat, cows gain water - they do not grow, but swell. After sitting for some time on such steaks, you can easily develop a nodular goiter of the thyroid gland.
Diagnostics
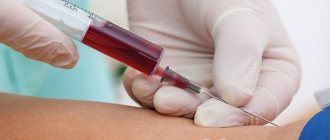
If you suspect a nodular goiter, it is necessary to undergo certain tests. The most accessible and inexpensive diagnostic method is ultrasound. The study allows you to identify even the smallest nodes and determine their size.
To exclude a malignant process, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy is performed: a needle is used to remove material from the node. In the case of a colloidal node, when examining a selected punctate, the colloidal substance and thyrocytes are determined.
In autoimmune thyroiditis, colloidal substance is not detected in the selected punctate, but lymphoid cells are found in large quantities. In case of nodular toxic goiter, a large number of proliferating thyrocytes are detected in the punctate.
To determine the functional activity of the thyroid gland, the level of the following indicators in the blood is examined:
- Triiodothyronine, thyroxine;
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone;
- Antibodies to thyroglobulin;
- Thyroid calcitonin.
The data obtained will allow us to determine hypofunction or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. Detection of high levels of thyrocalcitonin may indicate medullary cancer of the gland.
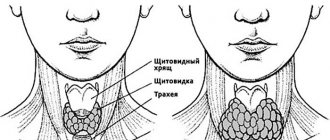
The size of the thyroid gland matters. Symptoms of nodular goiter
Normally, the mass of the thyroid gland is small - 25-30 g. However, it cannot be seen through the skin or palpated on the neck. This size is called zero. When there is a lack of iodine in the body or under the influence of other unfavorable factors, the thyroid gland enlarges. This is a goiter (in Latin - “struma”).
Examination technique: Stand in front of a mirror, tilt your head back slightly and examine the lower half of your neck. Swallow several times, and then use your fingertips to easily, without pressure, palpate the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland and the isthmus between them.
Zero magnification
The neck looks perfect, the thyroid gland is not visible or palpable.
First degree (gland weight - 40-50 g)
The mirror still doesn’t reflect anything suspicious, but you can’t fool your fingers - they detect the isthmus of the thyroid gland.
Your actions
Eat foods rich in iodine and avoid stress - stress depletes the thyroid gland. The initial degree of enlargement of the thyroid gland may not be considered a goiter at all, but may be a variant of the physiological norm if the function of the gland is not reduced.
Second degree (50-70 g)
The contours of the gland appear when swallowing, the lateral lobes and the isthmus are palpated.
Your actions
The recommendations are the same as in the previous case, plus consultation with an endocrinologist. You need to visit him at least twice a year, although treatment as such may not be required.
For some women, for unknown reasons, the thyroid gland is enlarged for most of their lives, from adolescence until menopause, and then gradually returns to normal size.
Third degree (80-90 g)
Symptom of a “thick neck” - the gland is not only palpable, but also clearly visible.
Your actions
Get tested! Goiter can be a consequence not only of iodine deficiency, but also of other thyroid diseases. If the problem is still iodine deficiency, it will be served to the starved organ “on a silver platter”, forcing it to penetrate through the skin of the neck in an electromagnetic field by electrophoresis.
In 15 procedures for 15-20 minutes, the thyroid gland will have time to stock up on iodine and shrink in size.
Fourth degree (100-140 g)
Classic goiter - the lower part of the neck in front and on the sides is swollen like a bag.
Your actions
Let's run to the doctor! It is especially alarming if seals (nodes) are felt in the thickness of the thyroid gland. In this case, you should be led by two specialists - an endocrinologist and an oncologist.
Fifth degree (from 150 g and above)
The gland is very large.
Your actions
This, fortunately, is rare, and there is only one recommendation - hurry to see a doctor! The literature describes colossal cases - 50 times compared to the norm! - enlargement of the thyroid gland. Her record weight is impressive - more than 1 kg. Imagine what it's like to carry such a load around your neck!
Symptoms of the disease
Often, provided that the thyroid gland is of normal size and its function is optimal, patients do not report any complaints. Clinical manifestations make themselves felt only if excessive enlargement of the organ leads to compression of the surrounding anatomical structures, as well as in case of dysfunction of the gland itself.
Mechanical compression of nearby organs causes various complaints depending on which organ is affected. Thus, compression of the larynx and trachea leads to breathing problems, foreign body sensation, a constant dry cough and a hoarse voice. Compression of the esophagus makes swallowing difficult. Compression of blood vessels is fraught with the appearance of general cerebral symptoms, as well as difficulty in the outflow of venous blood from the upper parts of the body. Pain may also be observed at the location of the thyroid gland due to the development of an inflammatory process in it or a rapid increase in the size of the pathological focus.
Violation of the functional activity of the organ leads to the appearance of hyper- or hypothyroidism. Hyperfunction is manifested by characteristic symptoms of thyrotoxicosis: prolonged low-grade fever, trembling at the fingertips, increased heart rate, protruding eyeballs, increased irritability, insomnia, pronounced appetite, accompanied by weight loss.
Reduced thyroid function or hypothyroidism is manifested by clinical symptoms opposite to thyrotoxicosis: decreased body temperature, bradycardia, drowsiness, and lack of appetite. Patients are concerned about dry skin, pain in the cardiac region, a decrease in blood pressure, a depressive state develops, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, genital area, patients often become susceptible to diseases of the upper respiratory tract and acute respiratory viral infections.
How to treat nodular goiter of the thyroid gland
Levothyroxine sodium - a drug for the treatment of nodular goiter
On the website we provide you with reference information. Complex treatment of diseases and high-quality diagnostics can only be carried out by experienced doctors. Remember that any medications have side effects and contraindications .
While there is not enough iodine and the hormone thyroxine containing it in the body, many special receptors are produced in the cells that increase the sensitivity of tissues (and especially the heart muscle) to adverse effects.
All types of metabolism are disrupted, and early atherosclerosis begins, leading to strokes and heart attacks. All this requires hormonal correction - thyroxine replacement therapy, which is prescribed by an endocrinologist.
It is carried out with the help of levothyroxine sodium (it is available under different trade names L-thyrox, L-thyroxine, thyro-4, euthyrox ) and triiodothyronine (liothyronine, trionine).
The drugs are similar in their effect and indications for use: the only difference is that triiodothyronine acts faster and is metabolized, that is, destroyed in the body. The dose of drugs is selected strictly individually. There are combination drugs consisting of these two drugs: thyrocomb and thyrotom .
In the early stages of endemic nodular goiter and for its prevention, iodine preparations are used, for example, potassium iodide and sodium iodide . In more advanced stages, iodine is prescribed together with thyroxine in the form of a combination drug iodotirox .
When thyroid function decreases, the formation of a number of vitamins is disrupted. No matter how much you eat carrots and apricots, rich in carotene, from which vitamin A is synthesized in the body, it will not bring any benefit - because the synthesis process does not work.
Without this important vitamin, the skin and nails suffer, hair falls out, vision becomes blurred, in short, a clinical picture is created that is typical of decreased thyroid function. Vitamin A preparations will bring improvement, but its predecessor, beta-carotene, will be useless.
Massage for nodular goiter of the thyroid gland
Do not try to activate the thyroid gland through massage. Do not knead the skin covering it and the front surface of the neck. Large vessels supplying the brain pass through here, and reflexogenic zones are located that turn off the heart and breathing.
In addition, mechanical effects on the thyroid gland sometimes provoke tumor growth and enhance hormonal disorders. Another thing is a neck massage from the back. It relieves symptoms of stress, including excessive tension in the neck muscles, which compress blood vessels and disrupt the blood supply to the gland.
Muscle spasm contributes to the development of osteochondrosis, which affects the roots of the cervical nerves serving the thyroid gland. Foot massage will also improve its function. They are reflexively connected with the internal organs, and the thyroid gland has a place of honor at the base of the big toe on the plantar side.
Sit on the sofa with your knees bent, lubricate them with cream (to make your hands glide better) and carefully knead this area, first on the right, then on the left. Start with light rubbing movements, gradually increasing the pressure. By doing a massage for 5 minutes a day, you will feel an improvement by the end of the second week.
Complications
What happens if the goiter is simply not treated? Well, just think, it’s a big gland, it’s just ugly, so cover it with a scarf and that’s it. Is it so? Of course no. An enlarged gland affects the entire body, and not only because it does not secrete hormones correctly. A person develops:
- compression of the trachea - severe shortness of breath occurs, breathing becomes difficult, a person may even suffocate in his sleep.
- the esophagus is compressed, the nerves around it atrophy, digestion is disrupted
- the so-called “goitrous heart” is formed - its function increases, blood vessels dilate, and a heart attack may occur
- hemorrhages in the gland tissue
- inflammation of the gland
- ultimately - malignant degeneration of the gland.
So it is still necessary to treat it.
Treatment of nodular goiter of the thyroid gland with folk remedies
Traditional medicine knows many ways to combat nodular goiter, but they are not suitable as independent therapy: use them as a supplement to the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Lemon with honey
Lemon and honey treat the thyroid gland
Wash 2-3 lemons, grate them on a fine grater along with the peel. Mix 1 cup of the resulting mass with an equal amount of honey. Take 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day in between meals until the “medicine” runs out. Store in the refrigerator.
Prognosis and prevention
It is quite difficult to predict the further outcome of the disease, since everything depends on certain cases. However, if measures to eliminate the disease are taken in a timely manner, then only the most positive results can be achieved and the best can be obtained.
As for prevention, there are no specific measures, but it is worth taking into account certain factors that should be paid special attention to.
It is necessary to follow a special diet and also get enough vitamins from food so that you can feel better. A competent approach to getting rid of this disease, as well as timely preventive measures, will eliminate the main symptoms and get the best.
conclusions
Thus, although this disease is serious, with timely treatment and compliance with all the requirements of a specialist, optimal results can be achieved. However, there are certain ways to prevent this disease.
Nutrition
Products containing iodine.
Increase. Treatment of nodular goiter of the thyroid gland with folk remedies can alleviate the patient’s condition, but in combination with prescribed doctor’s instructions. It is dangerous to treat thyroid diseases yourself only with folk remedies. Treatment of any disease must be combined with a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition.
If you have iodine deficiency (in many cases this is the cause of goiter), you need to eat: foods containing iodine, seafood, iodized salt, eggs, seaweed, kiwi, rye bread. It is also important that the body is cleansed of toxins and therefore you need to eat foods: porridge, grain bread, beans, beets, pumpkin, beets, apples, freshly squeezed juices and fruits, and drink a lot of water. Be sure to get tested for iodine deficiency.
Our doctors:
Mikhailova Elena Vladimirovna
Endocrinologist, diabetologist, candidate of medical sciences
44 years of experience
Make an appointment
Slovesnova Tatyana Alekseevna
Endocrinologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 46 years
Classification of toxic goiter by severity
The classification of diffuse goiter is established by the relevant documents of the World Health Association, according to which there are three degrees in increments of one, starting from 0 (the mildest form) and ending with 2 (the most severe form). Diffusely toxic goiter of the thyroid gland of grade “0” is not palpable at all and is not visualized during external examination. The next, first degree, is characterized by an externally imperceptible increase in the size of the thyroid gland, but at the same time it can already be felt very well during palpation. The latest, degree 2, is not only determined by palpation, but is also perfectly diagnosed by visual inspection.
There is another division of diffuse toxic goiter according to severity, proposed by a famous Russian endocrinologist, suggesting a greater division of the disease into degrees, according to which 5 types of tumor are distinguished according to the severity of development.
- Grade 0, similar to the WHO gradation, is characterized by the complete absence of external signs of toxic goiter, which is also not detectable by palpation;
- Grade 1 is characterized by the ability to palpate an enlarged gland, but there are still no external signs of enlargement;
- 2nd degree is characterized by the manifestation of an enlarged organ during swallowing movements;
- at grade 3, a syndrome called “thick neck” is noted due to an increase in the visual size of the neck due to significant proliferation of the soft tissues of the thyroid gland;
- 4th degree – goiter becomes obvious;
- Grade 5 involves a significant enlargement of the gland, which puts pressure on nearby organs.
The division into degrees is not in a cause-and-effect relationship with the specific characteristics of the goiter and is adopted only to characterize the size of the enlargement of the gland and determines the characteristic features of the growth of the organ. Diagnosing toxic goiter of the 1st degree will make it clear to an experienced endocrinologist when reading the medical history that the patient has a formation that cannot be determined visually, but it is possible to palpate it. The second degree in the form of a diagnosis will indicate a noticeable change in the size of the gland, which can manifest itself when swallowing.
The appearance of a grade 3 history is a reason to contact a specialist, since this leads to the formation of a cosmetic defect in the form of a thickened neck, which for any person, and women in particular, is an unpleasant factor that cannot be veiled with clothing, despite the absence of obvious concerns from the enlarged organ. However, we must not forget about treatment.
Most people who are diagnosed with diffuse toxic goiter skip the moment of contacting a specialist
The reasons for this are not the negligence of patients or their persistent reluctance to go to the hospital, but the absence of obvious symptoms of the disease. During the development of toxic goiter, an increase in hormone production occurs, which is not accompanied by pain or other obvious symptoms. It is possible to detect the disease at an early stage only with the help of ultrasound or palpation of the corresponding area of the neck.
In addition, diffuse goiter of a toxic nature can be divided into degrees when there is thyrotoxicosis. In this case, there are also 3 degrees of severity:
- mild or the first, in which the appearance of a goiter is accompanied by increased nervous excitability and decreased activity. Also, in mild cases, slight weight loss occurs and tachycardia may occur. This is affected by thyrotoxicosis;
- in the second or moderate severity, heart rhythm disturbances become more noticeable, the pulse increases significantly, weight is lost several times faster and a state of chronic fatigue may occur;
- the third or severe degree, considered the most severe form of the disease, leads not only to constant irritability, but also to a complete loss of strength and activity. Serious problems appear in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, liver function is disrupted, and the psyche suffers.
Causes of the disease
The cause of the development of such a phenomenon as toxic goiter is a genetic defect of unknown origin that affects the production of antibodies by the human immune system. Occurring disturbances in the process of regulatory function lead to an increase in the synthesis of antibodies, the target of which is the thyroid gland. During the development of a toxic goiter of a diffuse nature, the body begins to perceive thyroid cells as a foreign body, and the immune system begins to actively fight the “stranger,” thereby leading to the proliferation of soft tissues and increased cell division. Thyrotoxicosis in this case increases.
Antibodies to the TSH receptor, which are produced by the immune system during the inhibition of foreign gland cells, can have a stimulating effect on them, which leads to rapid tissue proliferation. In this case, the antibodies act as substitute receptors for the hormone TSH, since the brain area that receives signals from the hormone mistakes the action of the antibodies for the activity usual for thyroid cells.
Diffuse goiter is the only autoimmune disease, during which the tissue of the affected organ grows. Since the disease is genetic in nature, the presence of goiter is not uncommon in childhood. When selecting a statistical array of cases of the disease, a clear family predisposition can be traced, while the presence of diffuse goiter in one of the parents is not a mandatory cause of a similar disease in the child, although the risk increases several times.
Symptoms
If at the very beginning of its development the disease does not have obvious symptoms, then as it progresses, signs appear that may indicate the presence of a diffuse neoplasm and thyrotoxicosis. For the most part, they are similar to the symptoms of other thyroid diseases. Manifestations of the disease include:
- a state of permanent fatigue, causeless irritability and nervousness appears;
- normal heart rhythm is disrupted;
- against the background of increased appetite, weight loss occurs, which is accompanied by bouts of diarrhea;
- diastolic blood pressure decreases;
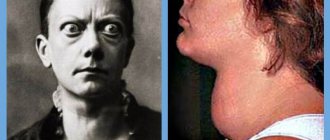
- with grade 2 goiter, there is a significant dilation of the blood vessels, which leads to darkening of the skin, especially in the folds, hives, and itching;
- hair loss;
- tremor of the limbs;
- the appearance of a painful shine in the eyes, which can be externally characterized as a feeling of fear, anger or surprise.
An enlarged thyroid gland returns to normal before our eyes! At night... Read more »
How do you know that everything is fine with your thyroid gland? Read more "
Do you have a sick thyroid gland? Endocrinologist's advice - to protect yourself, take... Read more »
“Goiter” and thyroid nodules will disappear if you brew and drink every day... Read more »
As the disease progresses, bulging eyes syndrome appears, and the gaze will appear scared, angry or surprised in the absence of such emotions in reality
Diagnostic measures
When diagnosing an existing goiter, including thyrotoxicosis, to determine its characteristics, such as type and severity, there are a number of special laboratory methods and instrumental studies.
First of all, a blood and urine test is taken from the patient. A general blood test determines the content of the two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland, T4 and T3 (thyroxine and triiodothyronine). The level of TSH or thyroid-stimulating hormone is also determined. In the case of an increase in the level of the main hormones synthesized by the gland, we are talking about hypothyroidism, which is a concomitant disease with diffuse type neoplasms.
In addition, an important step is to determine TSH in the blood serum, which will allow us to draw a conclusion about the sufficiency or insufficiency of iodine intake. With iodine deficiency, an increased content of this hormone is observed.
After undergoing laboratory tests, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, which makes it possible to determine diffuse goiter. Also, with the help of ultrasound, it is possible to identify follicular nodes, if present, which can develop in parallel with a simple goiter.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the presence of toxic goiter
Instrumental studies include radioisotope scanning, which makes it possible to most accurately determine the shape of the existing goiter and trace the dynamics of its increase in size. T also determine thyrotoxicosis. In addition, the doctor may decide to perform a fine-needle biopsy to verify that the tumor is benign, since histological analysis of the puncture allows one to accurately determine the type of tumor present.
If there are complaints from the patient about various ailments, additional tests and studies may be prescribed, which most often include reading an electrocardiogram, since an increase in diffuse goiter leads to changes in heart rhythm and tachycardia. How to treat diffusely toxic goiter?
Epidemiological picture of morbidity
Multinodular euthyroid goiter is the appearance of nodular formations in the parenchyma of the gland, which increase in size over time.
There are two main causes of the disease: sporadic and endemic.
The first type is determined by the presence of individual causes for each sick person, and the second type depends on the epidemiological picture in the region, which is associated with a lack of iodine in food and water.
Fact!
When the marginal picture of the incidence of multinodular goiter exceeds the 5% threshold, doctors begin to talk about an endemic factor in the occurrence of pathology.
Forecast
Euthyroid goiter has a fairly favorable prognosis, regardless of whether it is diffuse or nodular. The mortality rate is extremely low, since the only cause of death can be asphyxia due to compression of the trachea, but this happens extremely rarely and at a time when the patient is aware of his pathology and is under the supervision of a doctor. The quality of life during and after the disease does not change significantly.
Conservative treatment makes it possible to normalize the volume of the thyroid gland in diffuse goiter in almost 100% of cases. Some patients develop nodules that require additional monitoring. Persons over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo an annual preventive examination by an endocrinologist, an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland and a blood test to determine the level of TSH.
Surgical treatment of nodular goiter eliminates the risk of relapse or malignant degeneration of the node, so the prognosis is also favorable. Increased autonomous activity of the node can lead to the development of hyperthyroidism, therefore intact nodes require constant monitoring and timely prescription of medication or surgical treatment.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
The correct functioning of this gland is extremely important for the body, because otherwise it is subject to intense destruction. Forming in the third week of intrauterine development, after birth this organ, which resembles a horseshoe in its shape, serves as a kind of talisman of beauty, optimism and procreation for women and men. Any pathology is a reason to pay attention to the condition of the thyroid gland, especially if nodules and goiter form.
It is not easy for a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis, because the primary signs are almost invisible. But it seems possible to diagnose euthyroidism of the thyroid gland, like thyroiditis, based on a number of symptoms:
- fatigue, drowsiness, which causes a constant feeling of tiredness;
- enlarged thyroid gland:
- discomfort in the neck area, resembling a lump in the throat;
- sudden weight loss;
- arrhythmia, rapid heartbeat.
Diagnosis of euthyroidism is complicated by the fact that this condition practically does not manifest itself in any way. Therefore, people consult a doctor only after the thyroid gland has significantly increased in size. However, there are still signs of pathology, you just need to pay attention to them in time.
- increased irritability;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- feeling tired and overwhelmed;
- hoarse voice;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- causeless weight loss.
Treatment of colloid nodule
In most cases, if there are small nodes that do not cause problems for a person, treatment is not carried out. Patients are only required to follow a diet that consists of iodine-rich foods and regular examinations by an endocrinologist to monitor the dynamics of the disease. It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination twice a year to accurately determine whether the tumor is progressing in its growth or, conversely, decreasing in size.
In cases where the growth of the colloid node occurs at a rapid pace and the size of the formation leads to compression of adjacent organs, a decision is made on a surgical operation performed under general or local anesthesia. The operation itself is quite simple and short in time. Its duration is no more than an hour. Upon completion of the operation, a cosmetic suture is applied to the incision site, which has the ability to quickly dissolve without leaving visible marks. The surgical method of treating colloid nodes does not require long-term hospitalization, does not lead to complications and only requires observation for a certain time by the attending physician.
Another way to eliminate colloidal tumors is modern minimally invasive techniques, including laser thermotherapy and ethanol sclerotherapy. These methods avoid surgical procedures and are no less effective. In any case, the decision to choose a treatment method falls on the shoulders of the doctor observing the patient.