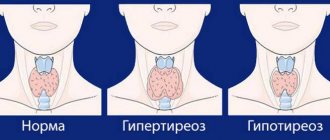
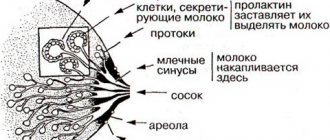
The thyroid gland is one of the organs of the endocrine system. It is located in the area of the cartilage of the same name under the larynx. It synthesizes a number of important iodine-containing hormones (T3 and T4), as well as calcitonin, which regulates calcium metabolism in the body. It has mainly 3 lobes:
- right,
- left,
- isthmus.
This organ should not be underestimated, as it performs a number of vital functions. These include:
- maintaining and regulating basal metabolism. All metabolic reactions within the body are controlled,
- ensuring stable temperature,
- preventing bone fragility by inhibiting osteoporosis,
- participation in the process of growth and development of the organism and the central nervous system.
There are cases when thyroid pathology develops. It can manifest itself as a whole range of different symptoms. To accurately verify the diagnosis and determine the further method of treatment, it is necessary to take blood tests for specific hormones.
Diagnostic methods
Women over 35 years of age are recommended to have their thyroid gland examined once a year.
Modern devices make it possible to detect deviations from the norm in the functioning of the thyroid gland in the early stages using the following methods: 1 Ultrasound. The most accessible diagnostic method, it can be used repeatedly for patients of any age. No preliminary preparation is needed. Only people with a highly developed gag reflex, in order to avoid the urge when the sensor is pressed on the throat, should carry out the procedure on an empty stomach. The patient lies with his head thrown back, and a gel is applied to his throat to facilitate the complete passage of ultrasound. Ultrasound can detect hypothyroidism, nodular and diffuse toxic goiter, cysts, benign and malignant tumors. 2CT (computed tomography). It is used to clarify the diagnosis, assess the structure of the gland and search for pathological nodes. It is used infrequently because the thyroid gland is hypersensitive to even the smallest dose of radiation. For better visualization and a more complete picture, CT scans use a contrast agent. 3MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). No contrast agents are used and there is no radiation exposure. MRI can provide a three-dimensional image but does not differentiate between benign and malignant lesions. In terms of the amount of data provided, it is equal to ultrasound. 4Scintigraphy. It is mandatory to prescribe it if we are talking about a complete examination of the thyroid gland. The method identifies neoplasms and determines their nature. It is based on the fact that the gland consumes more iodine than other organs, so a month before the scan you stop taking medications containing it. At the clinic, the patient drinks an iodine isotope on an empty stomach, and a day later comes for a study, which lasts about 30 minutes. 5Biopsy. Prescribed for patients with nodular neoplasms to determine whether they are benign or not. 50% of women aged 50-55 years and almost 100% of 70-year-olds have nodes. 5-6% of nodes are malignant. Therefore, you should not consider a biopsy prescribed by a doctor as a sign of an upcoming operation.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Wrinkles around the eyes are afraid of this like fire!
>>
To carry out tests and examinations, you should contact a clinic with a good reputation, experienced specialists, since any error can lead to further incorrect actions and treatment.
Disorders of the thyroid gland cause various signs of illness throughout the body. This is a metabolic disorder of the body, a disorder of the nervous system, the skin loses its elasticity, in some cases hair loss and brittle nails occur. In order to identify the causes and eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to examine the thyroid gland.
Rules for taking the analysis
In order for the results of the laboratory test to be as accurate and correct as possible, it is important to follow the rules:
- blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach;
- 24 hours before blood sampling, you must stop smoking, drinking alcohol and significant physical activity;
- hormonal drugs are canceled a month before the study;
- 72 hours before the test you must stop taking iodine-containing drugs.
The patient should come to the laboratory 20-30 minutes earlier than the appointed time and sit quietly in the lobby. Only after such a short rest does the laboratory technician begin the procedure of drawing blood from the ulnar vein for analysis.
To test for thyroid hormones, blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach.
X-ray examination
X-rays as a method of examining thyroid pathologies are used in cases where ultrasound did not provide enough data to make a diagnosis. This is due to the fact that X-rays tend to accumulate in organs and tissues.
An X-ray of the thyroid gland determines the exact location of the organ in cases where it is covered by a large goiter. In such a situation, only an x-ray can reveal the true size of the thyroid gland and determine whether there are pathological neoplasms in it.
The study shows the parameters of the goiter located behind the sternum and provides accurate data on how much it puts pressure on important organs located in the thyroid gland (trachea, esophagus). Another argument in favor of this method is that x-rays make it possible to determine the structure of thyroid nodules and cysts coated with calcium salt. (Ultrasound beams cannot penetrate such a coating).
A referral for an x-ray examination of the thyroid gland is issued by one of the following specialists:
- therapist;
- surgeon;
- endocrinologist;
- oncologist.
Such diagnostics are carried out in municipal medical institutions or in one of the private clinics. The choice depends on the patient's capabilities and preferences.
There is no need to prepare for an x-ray examination of the thyroid gland; it is carried out at any convenient time of the day. The only contraindication for this method is pregnancy. Children of preschool and primary school age are not given x-rays of the organ.
The thyroid gland is examined using a special device. Before the procedure, the patient undresses, removing all things and jewelry from the upper body. Long hair must be tied behind the back, or better yet, pinned up. The patient is helped to sit on the couch; the groin area in women and men is covered with special protective elements made of lead. The tube of the device is directed at the patient and irradiation of the thyroid area begins. The laboratory assistant is in another room. The entire manipulation takes from 5 to 10 minutes. Immediately after the thyroid examination, you can return home or to work.
Based on the images obtained, the specialist makes a conclusion about the size and location of the thyroid gland, the condition of the organ tissues, the nature and condition of the seals, interaction with other organs and lymph nodes. If an x-ray is not performed for the first time, the results are compared with previous ones to determine the dynamics of the disease. With a transcript of the thyroid examination, the patient is sent to the attending physician to prescribe treatment.
Why is the hypothalamus attracted?
More often, endocrinologists require an analysis of the hormones T3, T4, TSH, but if everything is clear with the first ones, then TSH belongs to the hypothalamic-pituitary system, and at first glance, it’s far-fetched, but this is not so. The thing is that it is TSH that is responsible for the production of T3 and T4, under feedback control (the more triiodothyronine and thyroxine, the lower the TSH level).
However, like any other system in the body, the production of T3 and T4 can fail, so it is important to know whether an increase or decrease in the level of T3 and T4 is associated with the functioning of the hypothalamus or not.
What if you just take a TSH test?
Logically, if the hypothalamic-pituitary system fails, then assessing the TSH level will be sufficient. But alas, this is not the case, since in addition to the hypothalamus, the thyroid gland uses an independent system to control the level of thyroxine and triiodothyronine release, so the TSH level may not change in some types of pathologies.
What does a comprehensive study involve?
A comprehensive examination of the thyroid gland allows you to assess its functional activity, as well as get an idea of the state of its structure.
In fact, anyone who notices the manifestation of suspicious symptoms, the explanation for which is difficult to find, should undergo an examination. This will allow you to identify the disease at an early stage, which means starting treatment in a timely manner. Or make sure that health problems are not related to a disorder of the endocrine organ.
Examination using special equipment, instruments, and palpation:
The very first study begins with palpation, which is carried out by an endocrinologist. The doctor palpates the thyroid gland and lymph nodes. Even with a simple examination, the doctor can detect tumors and verify size deviations, if any. This inspection is carried out in two stages. First, the doctor conducts a superficial diagnosis, the next stage is a deep diagnosis. The doctor examines the neck, determining the size of the thyroid gland, the pulsation of the organ, determines the condition of the “butterfly”’s body, painful sensations, and the characteristics of its condition. Ultrasound - an ultrasound examination helps determine the structure, as well as the density of the organ, detect formations, compactions, nodes, and blood supply to the organ. This type of examination is reliable, proven, and can be used to identify many pathologies, but not all. Ultrasound helps determine the correct treatment of an organ for cancer or diagnose thyrotoxicosis. A puncture biopsy is performed if the doctor, during an ultrasound examination, reveals lumps or nodular neoplasms. During a biopsy, material is taken directly from the node for study. By comprehensively studying the material taken, the quality of the nodes and neoplasms is determined: benign or cancerous tumors. Typically, test data confirm the presence of cancerous lesions only in 7% of cases. MRI, that is, magnetic resonance imaging, is used as an additional diagnostic method. It makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional, and, if necessary, layer-by-layer image of the studied area of the thyroid gland. Thanks to MRI, you can accurately obtain the parameters of formations, their contours, understand whether there is a capsule, and see whether tissue germination has begun. It allows you to examine the organ in detail, identify subtle changes, determine the presence of metastases, and recognize enlarged nodes. Scintigraphy is a diagnosis of the thyroid gland using radioisotopes, which helps to determine and evaluate its functional activity, identify foci of the disease, and find changes in the tortuous patterns of blood vessels. This type of diagnosis is considered harmless, but has contraindications that limit its use.
Scintigraphy allows:
identify the exact location; obtain an accurate assessment of activities; identify inflammatory foci and understand the nature of their changes; if a malignant tumor is detected, then using this method it is possible to determine the size, as well as the exact location of metastases. Laryngoscopy is performed before surgery to excise cancer. The procedure is needed to understand whether there are any disturbances in the movement of the vocal cords that may appear due to the tumor. This process makes it possible to reduce the likelihood of vocal cord complications after surgery. A blood test for the amount of hormones is carried out to study the results of the activity of the gland. The laboratory method gives a visual picture of the level of hormones: T3 - triiodothyronine, T4 - thyroxine, TSH - thyrotropin. Some forms require antibody levels. Therefore, tests are prescribed to determine the presence of antibodies to AT-TG thyroglobulin and AT-TPO thyroid peroxidase.
Calcitonin – promotes the movement of phosphorus and calcium. Indicates the presence of malignant tumors. They call it a tumor marker.
Thyroglobulin is a protein involved in the production of thyroxine.
Thyroid peroxidase promotes the formation of active iodine and the synthesis of hormones.
A blood test is performed on newborns to identify congenital pathologies.
Children at an early age who exhibit deviations from established norms of physical and mental development.
In order for the tests to show a reliable result, blood must be donated, following certain rules recommended by the attending doctor.
Normal thyroid hormone levels in women (table)
Almost 90% of thyroid secretion is T4. This hormone is mainly composed of protein and iodine. It is a depot of iodine required for the construction of the active hormone T3. It is he who influences the functioning of the entire organism.
There is an inverse relationship between the hormones T4 and TSH. If there is a decrease in some, then the concentration of others increases. Initially, there is a decrease in the T4 hormone. If a woman is carrying a child, the amount of thyroid hormones approaches the maximum permissible limit. Due to the physiological processes occurring in the body during this period of time, an increase in thyroxine is observed. This in turn entails a decrease in TSH levels.
Each hormone has its own normal value. You can determine its level for the substance you are looking for by reading the table below.
| Hormone name | Normal value |
| T3 free | 2,63 – 5,68 |
| T3 general | 1,08 – 3,14 |
| T4 free | 9 – 21,0 |
| T4 general | 4,910 – 12,2 |
| Thyroglobulin | thyroidectomy <1–2 normal <50 iodine deficiency <70 |
| TSH | 0,4 – 4,8 |
| (AT-TG) antibodies | <100 |
| (AT-TPO) antibodies | >100 – positive result 30 – 100 – borderline value |
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor. It is carried out by qualified specialists who have experience. Not so long ago, only palpation and visual inspection were carried out. However, in obese people it is very difficult to carry out a visual diagnosis even for an experienced doctor; during examination it is not always possible to identify pathology by simple palpation. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by conducting a comprehensive examination of the functioning of the endocrine organ.
To determine the initial stage of the disease in people with different body weights, make an accurate diagnosis, and select effective treatment, modern diagnostic methods are used to determine:
The size of the thyroid gland, as well as its lobes. Physical state of the shell. The location of the smallest nodules and neoplasms, their parameters, what is their internal structure. What state are the cells in? Accurate analysis of internal circulation. Find out the level of hormonal composition in the blood.
Why getting tested on time is important
One test tube - many answers
The thyroid gland is one of the most important hormone-producing organs; it affects almost all organs and systems, affects the development of the fetus and child, so any deviation from the norm can lead to dire consequences.
A timely test for hormones T3, T4, TSH is a guarantee of timely treatment for many diseases.
Scintigraphy radioisotope examination of the thyroid gland
Classic x-ray examination of the thyroid gland in most cases provides only an approximate description of its condition due to the organ’s great similarity with surrounding tissues. For detailed visualization, an isotope study is carried out, the difference from the usual one is the introduction of isotopes of radioactive elements. By analyzing the radiation visible on the screen of a special device after a certain time, you can get a complete picture of all the parameters of the thyroid gland and nearby tissues and organs.
The introduction of radioactive elements leaves a trace in the body, so it is prescribed as a final method
diagnostics in extreme cases:
- suspected thyroid cancer or possible metastases after tumor removal;
- with non-standard location of the thyroid gland.
The essence of the method is that a scanner of a special device (gamma device) reads isotope radiation from the follicles of the organ that have accumulated the introduced element. It is on the basis of the radiation intensity that the specialist makes a conclusion.
The scintigraphy procedure requires the patient to prepare:
- X-rays can be taken 3 months before or after the thyroid examination.
- For 2 weeks (preferably a month), eliminate medications containing iodine, iron and bromine. If possible, avoid seafood and other dishes containing these elements.
- The examination is done on an empty stomach, so abstinence from food must be at least 8 hours.
The examination uses isotopes of iodine or technetium. Technetium is eliminated from the body faster and is used when examining children and nursing mothers.
The procedure takes several hours (if technetium is used) or about a day (if iodine is administered).
After injecting technetium isotopes into a vein, the patient should drink at least one liter of clean water. An hour later he is placed on a couch near a device that captures radiation. Radiation diagnostics is carried out for several minutes, during which a gamma machine examines the neck area from above and on the sides. The results are recorded in the computer, printed and pinned to a conclusion. An hour and a half after the procedure, the patient is monitored for the level of radiation emitted, and he can go home.
After introducing iodine isotopes into the patient’s body, he can return to his normal life. Examination with a gamma apparatus is carried out every other day. The only restriction is the prohibition of eating food for 3-4 hours after the administration of iodine.
Diagnosis of thyroid diseases using scintigraphy is done by the color of the resulting images. Thus, areas of the thyroid gland that intensively absorb iodine (goiter or benign formation) are colored red; areas that weakly absorb iodine are colored blue (possibly the presence of cancer cells).
The disadvantage of this method of examining the thyroid gland is the lack of 100% reliability of the result and the failure to detect small malignant tumors.
The presence of a malignant tumor can only be confirmed by puncture (biopsy) of the thyroid gland. To do this, a part of the tumor is pumped out with a thin needle and examined in the laboratory.
How is the diagnosis made?
Even with all the information, it is very difficult to make a diagnosis on your own without medical education. You can study for yourself which hormonal indicators are associated with which diseases, but you should not rely on such information.
Although, sometimes this can help avoid the “doctor” trying to “cure” the “disease”. So such information, perhaps, will not be superfluous.
So:
- Hyperthyroidism - T3 and T4 are elevated, TSH AT-TG is low, AT-TPO is normal. With this disease, the thyroid gland begins to produce completely different types of hormones, to which, in turn, the pituitary gland begins to respond. Against this background, the TSH concentration drops.
- Primary hypothyroidism – T3 and T4 are reduced, AT-TG and TSH are increased, AT-TPO is normal. In this case, the pituitary gland reduces its activity, which causes an increase in TSH and a decrease in the concentration of other hormones.
- Secondary hypothyroidism - AT-TG and AT-TPO are normal, and T3, T4, TSH are reduced. Disturbances occur in all functions of the endocrine system, and the pituitary gland becomes less active. Against this background, the hormones T3 and T4 cannot be produced and developed normally.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis - AT-TG and TA-TPO are increased, but other hormones can either remain normal or decrease/increase. The immune system produces antibodies, but the thyroid gland at this time begins to become active or “fall asleep,” which is why the concentration of hormones begins to change.
Ways to test your thyroid gland
The very first, not very effective way, is to independently examine the front of the neck while standing in front of a mirror. Manual inspection is called palpation. This method is negative in that if the thyroid gland and its size are not properly checked, there is a chance of pressing on a nerve trunk or blood vessel. There is a possibility of causing serious complications, including loss of consciousness. Do not apply too much pressure or probe the gland. With a light touch with your palm and fingers, you will already feel whether it is enlarged or not. When you touch the throat, discomfort occurs, possibly even pain.
Sometimes people, not having encountered this problem, do not know where to check the thyroid gland and which doctor to turn to for help. The first visit can be made to your therapist, who can competently check by palpation and determine the change in the size of the gland. A specialist endocrinologist examines the thyroid gland, makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment. The gland is not large in size, located just below the thyroid cartilage, located in the front of the neck. Its structure is made up of two lobes (similar to the wings of a butterfly), they are located on either side of the trachea and are connected by an isthmus. There is also a central, pyramidal lobe.
The weight of the thyroid gland is small, the location sometimes changes with age. In normal condition it cannot be felt. Depending on the degree indicators (0-5), they determine how enlarged the organ is. Diagnosis of the thyroid gland includes a complex of examinations necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. At the first appointment, the doctor, using palpation, can determine the degree to which the gland is located during a given period. Identify the presence of nodes and the appearance of a goiter. The next stage is taking tests, which should show the normal level of hormones produced by the thyroid gland or whether an imbalance has occurred. It is necessary to strictly follow the rules for taking blood tests, established so that the result is as accurate as possible.
What about the norms?
As mentioned earlier, standards may differ depending on the laboratory, most often the difference is insignificant, so it is worth giving approximate criteria for reference values that directly depend on age.
| Name | Age | Pregnancy in weeks | |||||||
| Under 4 months | 4 - 12 months | 17 years | 7 – 12 years | 12 – 20 years | Over 20 years old | Under 13 | 13 — 28 | 28 — 42 | |
| Total triiodothyronine (nmol/l) | 1,23 — 4,22 | 1,32-4,07 | 1,42-3,80 | 1,43-3,55 | 1,40-3,34 | 1,2 — 3,1 | |||
| Free triiodothyronine (pmol/l) | 3,1-6,8 | ||||||||
| Total thyroxine (nmol/l) | 69,60 — 219 | 73,0 — 206 | 76,60 — 189 | 77,10 — 178 | 76,10 — 170 | 66 — 181 | |||
| Free thyroxine (pmol/l) | 11,50 — 28,3 | 11,90 — 25,6 | 12,30 — 22,8 | 12,50 — 21,5 | 12,60 — 21,0 | 10,80 — 22,0 | 12,1-19,6 | 9,6-17 | 8,4-15,6 |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (μIU/ml) | 0,7 — 11 | 0,7 — 8,35 | 0,7 — 6 | 0,6 — 4,8 | 0,50 — 4,3 | 0,30 — 4,2 | |||
Important! If the patient has received an analysis for TSH and T4 hormones, the norm of which differs from the values in the table, but coincides with the reference values indicated on the laboratory form, then the latter are considered priority. The same applies to other thyroid-stimulating hormones.
Level up
If T3 and T4 begin, for a number of reasons, to be released more intensely than is necessary for a normally functioning body, a pathological condition called thyrotoxicosis is observed and manifests itself even at the initial stage with the following symptoms:
- tremor;
- sweating;
- nervousness;
- feeling of heat;
- irritability.
Irritability may indicate higher than normal thyroid hormone levels
With further progression of the disease, arrhythmias and heart failure begin to develop. With timely diagnosis and treatment, in most cases, medications are sufficient to relieve this condition.
In severe and advanced cases, it is impossible to do without surgery with possible subsequent therapy with radioactive iodine isotopes.
Downgrade
The opposite situation, when there is not enough thyroid hormone, is called hypothyroidism. Its manifestations are in many ways the opposite of the previous pathological condition.
Hypothyroidism is characterized by:
- Lethargy.
- Weakness.
- Chilliness.
- Swelling.
- Depression.
- Drowsiness.
- Weakening of potency.
- Decline in performance.
- Menstrual disorder.
- Reduced likelihood of conception.
Chilliness may indicate decreased production of thyroid hormones
This state can be compared to winter, when everything in nature falls asleep. In this condition, not only basic tests are done for thyroid hormones, but also for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase.
What is a thyroid biopsy?
It is important to accurately identify changes occurring at an early stage. Because there is also a diagnosis - thyroid cancer
Diagnosis at an early stage allows you to successfully overcome the disease. A biopsy is not a painful or complicated procedure. It is performed on an outpatient basis. Using a long, thin needle, the specialist takes the contents (puncture) from the gland node. And passes it on to the laboratory for testing. The pain when inserting a needle is equivalent to the pain from a regular injection. After the procedure, you should lie down for half an hour. If you strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, there will be no complications or problems.
To prevent diseases associated with problems in the thyroid gland, you need to monitor your health and lifestyle, avoid stressful situations, replenish missing iodine reserves and be sure to periodically show your neck to an endocrinologist. The doctor will choose the most relevant way to check the thyroid gland. Malfunctions in the iron may be due to an excess of iodine, so self-prophylaxis and self-medication are fraught with undesirable consequences. You should periodically check the condition of the thyroid gland, which will allow you to avoid serious health problems.
Sometimes, at the first symptoms and at the very first stage of gland enlargement, the doctor prescribes iodine therapy. Often the primary problems affecting the malfunction of this organ are associated with poor nutrition and lack of iodine in the body. Many people do not consume seafood containing iodine in the required amount. But this is the most important component, which is fuel for the proper functioning of the entire body, especially for the thyroid gland.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=BfBrmhYbXQM
What are the hormones responsible for and need to be tested?
So, what are thyroid-stimulating substances produced by the thyroid gland responsible for:
- growth and development of the fetus (formation of the central nervous system, cardiovascular, respiratory and other systems);
- increased intestinal contractility;
- increased myocardial oxygen demand;
- increase in the number of heart contractions;
- increase in cardiac conduction impulses;
- maintaining normal levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide;
- ensuring normal functioning of the respiratory center;
- influence the destruction of bone tissue and bone formation;
- increase the synthesis of structural proteins in muscles.
Thus, an increase or decrease in synthesis, in a word, a deviation from the norm, will cause problems in almost all body systems. But why is it often not enough to know the meaning of T3 and T4, and doctors prescribe more and more tests.
We must not forget why we breathe
Hormone TSH
Although this hormone is not produced directly in the thyroid gland, it is produced exclusively for it. This is a pituitary hormone that is synthesized when there is a decrease in the thyroid hormones T4 and T3.
Together with the bloodstream, it enters the thyroid gland at special receptors and affects them.
When interacting with receptors, the following occurs:
- The thyroid gland begins to actively synthesize the hormones T3 and T4.
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland by stimulating the growth of tissues of this organ.
Determining an acceptable TSH hormone level is the first and most important indicator of thyroid health.
A healthy person needs to check their TSH level once every five years.
T4 hormone
This is the most primary hormone of the thyroid group. It accounts for 90% of all hormones synthesized in the thyroid gland.
Thyroxine consists of four iodine atoms, which is why its name contains the number 4. Sometimes you can see in the direction for analysis - free T4 or T3. This is a more refined analysis.
T3 hormone
This hormone is the most important in thyroid hormones. Only 10% of the T3 hormone is synthesized in the thyroid gland. The remaining 90% is formed by removing one iodine atom from the T4 hormone. In this connection, the T4 hormone turns into a much more energy-intensive and active T3.
Triiodothyronine reflects all the main functions of the thyroid gland. T4 and T3 - are synthesized in the body to control and manage energy metabolism. Contractions of the heart muscle, the work of the sweat glands, the process of digesting food and its movement through the gastrointestinal tract are processes that require energy. It is these active processes that T3 and T4 control.
Sometimes you can also see different ATs in the analysis. This is an antibody test that is prescribed to a patient if autoimmune pathologies are suspected.
Calcitonin
This hormone is produced in the C cells of the thyroid gland, located next to the follicles. The origin of these cells is neuroendocrine; they are formed in the pancreas in the fetal period.
In terms of number, the C-cells that secrete calcitonin are much inferior to the B and C-cells that enter the thyroid follicles. Based on information in various medical literature, calcitonin is considered a substance that blocks the work of parathyroid hormone, but the effect of calcitonin is several times weaker than parathyroid hormone. In addition, calcitonin is a tumor marker for thyroid cancer.
Calcitonin levels change in the following cases:
- osteoporosis;
- anemia;
- thyroid cancer;
- prostate, breast or respiratory cancer.
AT to TPO
An antibody test in the blood is used as an additional marker to determine if the thyroid gland is malfunctioning. These antibodies are produced against thyroid peroxidase. This enzyme is involved in the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
AT to TG
This type of antibody is produced by the lymph nodes.
It is present in a blood test only in patients with the following diseases:
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- diffuse toxic goiter.
Also, special attention to the increased content of these antibodies is paid to patients diagnosed with papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. This is a significant tumor marker for this disease.
AT to rTSH
These antibodies are produced in the body of a patient with diffuse toxic goiter. and are prescribed only if this disease is suspected. The level of antibodies in a blood test determines the possibility of drug treatment or indications for surgery.
The day before the test, you need to avoid physical activity.
Indirect diagnostic methods
As is known, the function of one or another organ is assessed using indirect and specific tests.
Up until the 70s. XX century both here and abroad, in the vast majority of cases, indirect methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics were used, which, although they were not reliably objective, often supported the previously made diagnosis when a particular disease was suspected.
Indirect methods for determining thyroid disease are based on the study of the physiological functions of the body, which are influenced by thyroid hormones.
The indicators obtained using these methods are not specific for the pathology of this endocrine organ, since similar changes can occur in diseases of other organs.
These methods include the study of basal metabolism, fat (mainly determining the level of cholesterol in the blood) and protein metabolism, the state of the neuromuscular (reflexometry) and cardiovascular (electrocardiography) systems.
Hormone synthesis
Scheme of formation of the main thyroid hormones
The process of producing thyroid hormones consists of five successive stages:
- Absorption of iodides circulating in the blood by the thyroid gland.
- Oxidation of iodides with the formation of free iodine molecules.
- Iodization (saturation with iodine) of tyrosine residues in the composition of thyroglobulin.
- The breakdown of thyroglobulin, the secretion of hormones T3 and T4 into the blood.
- Conversion of T4 to T3 (occurs both in the thyroid gland and in peripheral tissues).
The main place of formation and storage of biological active substances of the thyroid gland are its functional units, called follicles, which consist of special cells - thyrocytes.
Note. In some literature, thyrocytes are called thyroid A-cells, but in fact these two terms mean the same thing.
Thyrocytes synthesize the main hormones - thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Their chemical formulas are almost identical except for the content of iodine atoms. The molecule of the first contains four of them, and the second - three, respectively.
Substances can be present in the blood in two states:
- free form (FT4 and FT3, from free) – biologically active;
- bound form (in combination with specific transport protein globules).
Important conditions for the formation of hormones are the presence of iodine and tyrosine (amino acid). First, thyroglobulin is formed in the follicles, which is a special protein that is collected and stored inside the follicle.
This substance provides a reserve from which ready-made hormones will be quickly produced when needed. After synthesis, they enter the bloodstream, where special thyroxine-binding transport proteins - albumin and globulin - are attached to them.
Thyroglobulin is a glycoprotein, i.e., a two-component compound of protein and carbohydrate molecules. Its molecular weight is approximately 600,000 daltons. This is a fairly large compound, so it is impossible for it to enter the blood in this state, but this can occur in the presence of pathological processes in the organ, for example, with thyroiditis, when the integrity of the follicles is destroyed.
In order for the formation of basic hormones to proceed correctly and in the required quantities, it is important to have pure (“elementary”) iodine in the blood, which is formed by the oxidation of a substance in the form of iodide supplied with food or from the environment. First, one or two iodine atoms can associate with tyrosine, thus producing monoiodotyrosine and iodotyrosine, which are the precursors of functionally active thyroid hormones. Then these molecules combine and form thyroxine (a complex of two diiodotyrosine molecules) or triiodotyrosine (an association of monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine).
Calcitonin is produced by parafollicular cells or C-cells of the thyroid gland. This is an essential element for the exchange and absorption of calcium and phosphorus ions, and is extremely important for the normal functioning of the structural units of bone tissue - osteoblasts.
Note. Calcitonin is significantly different in structure from other thyroid hormones - its molecule is a long chain consisting of 32 amino acids (polypeptide).
Signs and causes of thyroid dysfunction
There are a lot of diseases associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland; they affect approximately 10% of the world's population. Most often they are found in residents of countries with a low level of development, as well as in regions with a predominance of heavy industry, and, consequently, a high level of environmental pollution. However, these are far from exhaustive causes of thyroid diseases. The occurrence of abnormalities in the thyroid gland is influenced by:
- Lack or excess of iodine in the human body. This occurs primarily due to an unbalanced diet and neglect of special vitamin complexes. The absorption of iodine by the body reduces the impact of such factors, the entry into the body of chemical elements (bromine, chlorine) that displace iodine, and the use of certain medications. Lack or excess of iodine negatively affects adults and children. In men and women, some body functions are impaired, and in children, physiological and mental development slows down.
- Heredity. Approximately every fifth case of thyroid disease is determined at the genetic level, and this factor is more common in women than in men.
- Fluctuations in hormonal levels that occur at birth, during puberty in adolescents, during pregnancy and during age-related changes in men and women after 45-50 years.
- Infections and inflammations of internal organs, especially the brain.
- Severe blows or injuries to the neck and head.
- Long-term exposure to radiation when living in a contaminated area, radiation sickness.
- Long-term disruption of psychological comfort due to constant exposure to stressful situations, overwork and heavy physical labor.
The thyroid gland is expecting a miracle
A small organism is able to change the habitual way of a woman’s body
During pregnancy, the synthesis of hormones in a woman’s body may change, or may remain the same as before. If there is any suspicion of thyroid pathology, the doctor must react in time.
A pregnant woman needs to be registered with an endocrinologist only if deviations from the norm have been identified. Read more about hormonal changes during pregnancy in the video in this article.
Pregnancy is a difficult period in terms of restructuring the body. The attentive attitude of doctors towards a pregnant woman guarantees the correct development of the fetus, and control of thyroid-stimulating hormones is actually a prerequisite.
Table: Reference values of thyroid hormones during pregnancy:
| Index | Trimester of pregnancy | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| TSH, µIU/ml | 0,20-3,50 | 0,20-3,50 | 0,20-3,50 |
| T3 total, nanomol/l | 1,30-2,70 | 1,30-2,70 | 1,30-2,70 |
| T3 light, picomol/l | 2,30-6,30 | 2,30-6,30 | 2,30-6,30 |
| T4 total, nanomol/l | 100-209 | 117-236 | 117-236 |
| T4 st., picomole/ | 10,30-24,50 | 8,20-24,70 | 8,20-24,70 |
Hormones
| OBS80 | 10 tests | 3 760 rubles |
| OBS76 | 3 tests | 1 010 rubles |
| OBS75 | 5 tests | 1 740 rubles |
| 64 | 385 rubles | |
| 169 | 810 rubles | |
| 149 | 407 rubles | |
| 168 | 990 rubles | |
| 57 | 440 rubles | |
| 197 | 590 rubles | |
| 199 | 1 280 rubles | |
| 100 | 680 rubles | |
| 99 | 480 rubles | |
| 205 | 460 rubles | |
| 101 | 385 rubles | |
| 65 | 420 rubles | |
| 195 | 900 rubles | |
| CATEPL | 1 980 rubles | |
| 7716BTK | 66 650 rubles |
Radiation methods
As we know, the thyroid gland is a lobular organ that is located in the middle of the neck. It consists of two lobes on each side, which are connected by an isthmus. In many people it is absent or appears as a thin strip of fibrous tissue. Note that the size and volume of the gland can vary depending on gender and age.
Radiation diagnostics of the thyroid gland is a whole complex of actions, which includes radiography and computed tomography. An X-ray image can show the presence or absence of certain tumors, as well as the deposition of calcium salts. As in the previous diagnostic methods, with the help of x-ray examination you can find out about the location and size of the gland. The advantages of this method are that the image is a documentary diagnostic paper and it is static. The disadvantage of this method is that during such an examination the body receives a certain amount of radiation. Despite the fact that it is insignificant, such research is often not worth conducting.
Computed tomography is a modern research method. However, this method is used to study cells. This method is effective if the gland exerts strong pressure on neighboring organs, and also when it is necessary to evaluate the method and need for surgical intervention. In this case, computed tomography can show the exact location of tumors.
MRI is a method that is absolutely safe for the body. This is an expensive procedure, but it does not expose the diseased organ to additional radiation. As a result, the specialist receives a cross-sectional image, on which one can detect the size and location of even small formations, changes in the shape and structure of the gland.
Thyroid gland: extended examination
This profile includes the following tests:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin)
- Free thyroxine (free T4)
- Free triiodothyronine (free T3)
- Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (AT-TPO, microsomal antibodies)
- Antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG)
Screening laboratory assessment of the thyroid gland.
The thyroid gland is one of the most important organs of the human endocrine system. The main function of the thyroid gland is to produce thyroid hormones. They regulate most metabolic processes in the body.
Why is it important to have your thyroid examined?
The thyroid gland affects the entire body as a whole, and even the most insignificant, at first glance, deviations from the norm have an impact on the body’s metabolism, cardiac, nervous and reproductive systems. The earlier a thyroid pathology is detected, the easier it is to treat.
Why is it better to undergo a comprehensive examination?
The thyroid gland synthesizes 2 main hormones: T3 and T4, the formation of which is regulated by TSH (synthesized in the pituitary gland), it is important to see the whole picture. In addition, TG and TPO are involved in the formation of hormones in the thyroid gland, to which, in some forms of pathology, antibodies are formed in the thyroid gland, therefore, to assess the function of the thyroid gland, a comprehensive examination is necessary
The value of laboratory tests increases with simultaneous ultrasound examination (US).
Symptoms of thyroid dysfunction (in children and adults):
- Sudden weight changes;
- Unstable menstrual cycle in women and teenage girls;
- Change in appearance: problems with skin, hair, nails;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular systems;
- Memory deterioration, slow thinking and speech;
- Increased sweating, hand tremors and increased body temperature
- Weakness, irritability, tearfulness;
- Decreased immunity, tendency to colds.
Who should have a thyroid examination?
Everyone without exception: women and men, children.
For the purpose of prevention and if one or more of the above symptoms occur, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination of the thyroid gland: take tests, undergo an ultrasound (hyperlink) and, based on the results of the examination, consult a doctor (hyperlink to our partners).
1 740
rubles
+ taking blood from a vein: 160 rub.
1
working day
(the specified period does not include the day of taking the biomaterial)
It is preferable to take blood in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of overnight fasting (you can drink water), or 4 hours after a light meal during the day. On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude increased psycho-emotional and physical stress (sports training), alcohol intake, and smoking an hour before the study. Recent effects on the thyroid gland, including surgery, radiation therapy, drug therapy (including taking thyroid hormones, iodine-containing drugs), may affect the result of a thyroid-stimulating hormone test. The conditions and time of the study in such situations are determined by the attending physician.
How are thyroid hormones synthesized and what are they needed for?
The basis for the creation of these biologically active substances is the amino acid tyrosine. During nutrition, iodine enters the body. For the body to function adequately, it needs to receive approximately 120-135 mcg of this microelement per day. After entering the intestine, it is absorbed by the villi of the epithelium and, with the blood flow, settles in the follicles of the organ. There, the process of incorporation of iodine into the matrix of thyroglobulin (protein, precursor of biologically active substances) occurs.
After this, differentiation of hormones into T3 and T4 occurs, depending on the number of microelement molecules in its composition.
You should also know that the amount of T4 synthesized is 20 times higher than T3. But the effectiveness of the latter is 6-8 times higher than the efficiency of thyroxine. That is why we cannot talk about the greater importance of this or that substance.
The main functions that these substances perform in the human body are the following:
- Activation of the thermoregulation center. Heat production and oxygen absorption increases in all tissues and cells with the exception of the main brain, spleen and testicles. They remain intact. That is why one of the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis or hyperthyroidism remains fever and profuse sweating.
- Stimulation of the formation of steroids by the adrenal cortex. T3 and T4 play an important role in the process of growth and development of the entire body. When they are deficient, mental and physical retardation is often observed.
- Increasing the body's intake of vitamins.
- Activation of nervous and mental activity of the main brain. In areas where the soil contains little iodine, children in schools are regularly given Antistrumin, a drug that contains a 5-day supply of this microelement. This is done to improve their academic performance and normalize the functioning of the central nervous system.
The question of how much of these substances is needed in the human body for its normal functioning has been well studied. There are special tables and generally accepted indicators that indicate the functional activity of the organ. It is enough to submit the material for examination and wait a little.
Ultrasound examination
Radiation diagnostics of the thyroid gland includes several research methods used for certain indications. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed when the shape or size of the gland changes, lumps appear in it or cancer is suspected, as well as for patients registered with an endocrinologist due to changes in the thyroid gland.
No special preparation is needed for the procedure; it can be performed at any time of the day on an empty stomach or after meals.
Children, teenagers and elderly people are prohibited from eating heavy food before the procedure, since the pressure of the sensor on the thyroid gland may trigger the gag reflex. Women can do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland on any day of their cycle, although some experts believe that the result is more accurate in the second third (from 6 to 10 days).
The radiation procedure on the thyroid gland is performed on the patient in a separate room in a state of complete rest. The specialist runs the sensor along the neck in different directions to find out all the details of the clinical condition of the thyroid gland. Studying the image on the device screen allows you to draw conclusions about:
- the size of the thyroid gland and its lobes;
- the state of the boundaries of the thyroid gland and its internal structure;
- location of tumors and nodules, their size and content.
Analysis of the results of thyroid ultrasound is not always enough to determine the diagnosis of diseases. If malignant changes in the thyroid gland are suspected, the location of the thyroid gland is abnormal, or symptoms are vague, additional examinations are prescribed. Subsequent radiological diagnostics include an x-ray of the organ or an isotope study of the thyroid gland.
It was ours, it became someone else's
A separate link in the laboratory diagnosis of the thyroid gland is the analysis of hormones and TPO, the norm of which begins with the number zero. The decoding of the abbreviation sounds like: determination of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase. If translated into accessible language, this is the definition of specific substances that are released when the body considers the thyroid gland foreign.
Such antibodies appear only in autoimmune diseases, so they are prescribed extremely rarely. The upper limit of normal reaches 34 IU/ml; it does not depend on the patient’s age, unlike other values.
Preparing for radioisotope scanning
The method is based on the ability of thyroid cells to accumulate iodine or technetium, which is found in places with the most intense blood flow
Therefore, it is important to exclude the use of drugs that stimulate organ function (levothyroxine, iodine) or inhibit (Mercazolil, Espa-carb, Tyrozol). The first ones are canceled 20 days in advance, and the second ones – 5 days in advance.
The same rule applies to dietary supplements, vitamins, and iodized salt.
Drastic changes in diet are not required, but if the daily diet has not previously included iodine-containing foods (seaweed, midi, shrimp, squid, sea fish), then you should not consume them before diagnosis.
Watch the video about scintigraphy:
If the patient has been prescribed a study with an iodine preparation (excretory urography, angiography), then they are sent for a scan no earlier than 25 days later. Women who are breastfeeding should notify their functional diagnostics doctor about this.
Palpation
The simplest diagnosis of thyroid disease is an examination. An experienced doctor can determine the mobility and size of the gland. He can also determine the presence and location, and even the nature of the goiter. Let us remember that it can be nodular or diffuse.
During the diagnosis, the doctor grabs the neck and gently presses on the area of the gland. For the patient, this procedure is practically painless, but it allows one to establish a diagnosis with an accuracy of up to 60%. In this case, palpation of the lymph nodes is mandatory. So, if they are increased in size against the background of low tooth mobility, then this may indicate the presence of cancerous tumors.
Note that there are 6 levels of gland size. At level zero it is of normal size, but at level five it can reach significant sizes and make breathing very difficult. In this case, the doctor should check whether the gland is compressing the carotid artery.
Reasons why people decide to undergo a comprehensive thyroid examination
The most common cause of thyroid disease is iodine deficiency. A test for iodine deficiency can be done at home. Using a cotton swab soaked in iodine, draw a very small grid on the elbow bend, and after 2 - 3 hours, examine the area. When traces of the mesh are not noticeable, it means there is not enough of it and, vice versa. A small home study of the condition of the neck will not give an accurate idea of whether there is an ailment or whether it has begun to develop. Only a specialist can make such a conclusion.
Pathologies can be different, as well as symptoms of the disease:
If, upon visual inspection in front of a mirror, at least a slight deformation of the neck is noticed.
For example, the lower part of the neck is slightly widened.
The skin of the cervical area, where the thyroid gland is located, is reddish, and swelling has appeared. During swallowing, the Adam's apple is invisible. There is a noticeable asymmetry in the neck. Clear contours of folds appeared in the cervical area. When you feel the neck where the thyroid gland is located, lumps are detected. Sudden weight fluctuations. When a person suddenly loses weight or gains weight, this is evidence that the organ is not coping with its function. Nervous state, decreased performance, accompanied by irritability, emotional imbalance, lethargic, drowsy state. Feeling of a lump in the throat, the voice timbre became lower. The cycle of menstruation is disrupted, it is difficult to conceive a child, and men experience sluggish potency. The hair has become thinner, the nails are peeling, the skin has a fading appearance. Hormonal imbalance caused by childbirth, during adolescence, during pregnancy, in people after 45-50 years. Physical injuries to the neck. Violation of the body's thermoregulation. A prerequisite for going to a consultation with an endocrinologist may be, for example, a long period of ineffective treatment of cardiovascular diseases, or a constant feeling of fatigue.
The patient got ready
Smoking before visiting the hospital is a big mistake
Without a doubt, the doctor is obliged to talk about the basic rules, and the patient must take this into account before going to the laboratory, but if this does not happen, then it is worth clarifying what and how.
- Choosing a laboratory. The simplest thing is to get tested at the very clinic to which the patient is assigned, but, as practice shows, this is not always possible. Patients most often choose the laboratory they trust more or follow the doctor’s instructions, both decisions are rational.
- Bad habits . Smokers will have to put down cigarettes 3 hours before the test. It is better not to drink alcohol the day before for moral and ethical reasons rather than because of data distortion.
- Nutrition. You will also have to refuse food; if you cannot come to the procedure on an empty stomach, then you must abstain from food for at least 2-3 hours. At the same time, drinking pure still water is quite acceptable.
- Overvoltage. During the two days before laboratory diagnostics, it is advisable not to overdo it both physically and emotionally; the advice is relative, but it may affect the results.
- Taking medications . As mentioned earlier, many medications affect the results, so first of all, you need to decide with a specialist which drugs need to be excluded 2 days before the test, and whether this is necessary.
Important! Choosing a laboratory is a responsible undertaking, since each repeat analysis will need to be taken there. This is due to differences in diagnostic methods, so even reference (normal) values may differ.
Taking blood for analysis
Taking blood is a completely harmless and common procedure.
Despite the fact that the production of the substances under study is concentrated in the thyroid gland and hypothalamus, hormones bound to proteins or in free form circulate in the bloodstream. It is for this reason that they do not do anything supernatural with the patient, but only collect venous blood.
A certain category of patients cannot leave the house, or even their bed, so for such people blood is drawn at home. Unfortunately, not all laboratories provide home visits, but this is possible. In severe cases, it is necessary to more carefully approach the issue of choosing a laboratory or transporting the patient to the place of blood sampling.
The procedure itself is quite primitive and usually does not take more than 5-10 minutes. The instructions according to which the nurse draws blood have not changed for several years, so you should not be scared when you see a very young specialist; even a medical student can perform such manipulation.
Take it again
If any pathology is detected, the patient will need to undergo a repeat laboratory test during or after the prescribed treatment. There is no point in repeating a blood test for the hormones TSH and T4 more often than once every 2 months.
It will definitely not be possible to see the dynamics earlier than in a week, since during this time the level simply did not have time to change.
And then something went wrong
Finding out the results is not so bad, the main thing is not to panic
Undoubtedly, distorted results do occur in practice, and not all of them can be avoided; patients who sincerely care about their health need to be aware of what can cause deviations from the norm.
- Hemolysis. The blood simply does not reach the laboratory in a reliable form; this happens extremely rarely. It is simply impossible to carry out diagnostics with such blood, so instead of the result you will receive a message that the blood needs to be re-dated.
- Fat level. If the patient’s biochemical analysis showed a pronounced disorder of lipid metabolism, then the examination for AT TPO will have to be postponed.
- Pregnancy. In the 3rd trimester, the TSH level may increase and still remain normal for a particular woman. Regarding T3 and T4, it must be said that they can increase in any trimester of pregnancy.
- Time. As a laboratory, the timing of the collection is also important, levels can vary throughout the day, so it is preferable to give blood for monitoring at the same time during the day.
- Medicines and narcotic drugs. In addition to medications, narcotic substances, including morphine, heroin, methadone and others, affect the results. Regardless of whether the patient uses such substances for medical reasons or without them, the results may be distorted.
Decoding the research results
It is important that only an experienced doctor interpret the results of such a study. You should not try to decipher the analysis of thyroid hormones yourself, since only a qualified specialist - an endocrinologist - can make an accurate diagnosis.
You should not try to decipher the analysis of thyroid hormones yourself, since only a qualified specialist - an endocrinologist - can make an accurate diagnosis.
The results may vary, for example:
- If TSH increases, we can conclude that the patient has a state of hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland performs its functions at an insufficient level. But here the T4 and T3 indicators will also be an important point. With an increase in TSH, but a decrease in T4, we can talk about the presence of obvious hypothyroidism, called manifest. If the T4 level is normal against the background of an increase in TSH, then the form of hypothyroidism is defined as subclinical.
- If the TSH value is normal, but T4 is decreased, the test will need to be retaken in another laboratory, since such results are a clear error in the study in almost 99% of cases.
- If the TSH test results are normal, but there is a reduced T3 value, it is also necessary to retake the test, since such data are also considered a laboratory error.
- The analysis will also need to be retaken if the results show a decrease in T3 concentration against the background of normal TSH and T4 values.
- An error in the study is the result in which, against the background of normal TSH, there is an increase in the values of T3 and T4 or one of them. In this case, the study will also need to be repeated.
- A decrease in TSH in most cases may indicate an excess of gland hormones, that is, the presence of a condition of thyrotoxicosis. The presence of overt thyrotoxicosis is indicated by an increase in the level of T3 or T4 against the background of a decrease in the TSH value. If T4, like T3, are normal against the background of a decrease in TSH, then thyrotoxicosis has a subclinical form, and its degree is determined by the TSH value.
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are special immunoglobulins that destroy the enzyme contained in the cells of the thyroid gland and is responsible for the transition of iodine molecules into the active form necessary for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. They are specific markers of autoimmune damage to the thyroid gland. Normally, their content in the blood ranges from 0 to 34 mU/ml. An increased level of Ab-TPO is observed in the following cases:
- autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's disease);
- thyroid cancer;
- diabetes mellitus and some systemic connective tissue diseases (systemic vasculitis, rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus).
Detection of elevated levels of Ab-TPO in pregnant women indicates a high risk of developing hypothyroidism in the child (congenital or developing immediately after birth).
In some cases, more often in middle-aged and mature women, increased levels of Ab-TPO are observed in people who do not have any diseases.
Thyroxine and triiodothyronine
The main thyroid hormones, as mentioned above, are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Entering the blood, they very quickly bind to proteins and become inactive. After this complex reaches the target organ, it disintegrates and the hormones again become active (free).
When determining total T3 and T4, both their bound and free forms are taken into account. Currently, preference is given to determining the level of free thyroxine and triiodothyronine, since it has a significantly greater diagnostic value.
Normal values for free T4 range from 9 to 19 pmol/l, and for free T3 – 2.62 to 5.69 pmol/l.
Increased levels of triiodothyronine are observed in hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, pregnancy, and liver diseases.
Only an endocrinologist can correctly interpret the results of a laboratory test for thyroid hormones.
The causes of low T3 levels can be hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, and prolonged fasting.
Increased thyroxine levels occur in patients with subacute thyroiditis. Other causes of this condition may be an excess of iodine in the body, pregnancy, and certain types of malignant tumors.
Hypothyroidism and prolonged fasting lead to a decrease in the concentration of T4 in the blood.
Checking the thyroid gland using ultrasound and biopsy
If necessary, the doctor may continue to examine the thyroid gland. The next stage of testing, after receiving the results of blood tests, will be to study the functions and structure of this organ using ultrasound
It is important to have the organ checked in a good, specialized clinic, a qualified specialist in the field of endocrinology. An ultrasound machine allows you to see all the processes taking place in the gland, this is primarily its density, size (reduced, increased), see the presence and size of nodes
If ultrasound studies show that a problem has arisen and undesirable changes are occurring, you should move on. Only a specialist can tell you how to check the thyroid gland and what other method can be used to make a more accurate diagnosis.
Unfortunately, not everyone understands the importance of needle biopsy of the gland. People, even without knowing the essence of the process itself, panic
If the nodes are enlarged, it is necessary to find out what kind of tissue this is due to - benign or substandard. Using this method, you can determine the exact degree of thyroid condition.
When is it necessary to be examined?
It must be understood that such laboratory tests should be carried out to confirm the clinical opinion of the attending physician. However, you can additionally donate blood for preventive tests. There are often situations when the pathological process has already started, but is still proceeding in a latent stage. In this case, you can act proactively and begin to treat the disease at an early stage.
However, the indications for checking the condition of the thyroid gland are the following:
- Hypo- or hyperthyroidism. Determining the amount of organ hormones can accurately indicate the functional activity of the parenchyma and thyrocytes.
- Monitoring the quality of treatment and the effectiveness of therapy. This is especially important for diffuse toxic goiter and hypothyroidism.
- Mental retardation in children's development. They donate blood to verify the possible cause of this pathology. Cretinism is one of many diseases that causes disorders of the central nervous system at an early age.
- Any increase in the size of the thyroid gland (goiter).
- Heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias, tachycardia, extrasystole).
- Baldness.
- Reproductive system disorders with possible infertility.
- Lack of menstruation.
- Impotence or decreased desire for the opposite sex.
In all these situations, it is necessary to donate blood for tests to measure the concentration of organ hormones in the serum.
Normal TSH in children
According to a study that measured TSH levels in children from birth to 18 years of age, thyroid-stimulating hormone levels vary quite a bit depending on the age of the child.
For full-term newborns, the range of normal TSH values is quite large and can be 0.7-16 mIU/L. Gradually, the TSH level begins to decrease and by the year it is approximately 0.4-8.8 mIU/l, from 1 year to 6 years - 0.4-6.5 mIU/l, from 7 to 14 years - 0.4-5 mIU/l. The level of TSH in the blood gradually decreases, approaching adult values, while free thyroxine (free T4) will remain fairly stable during this time.
How to decipher a TSH test - is it normal or not?
As a rule, a TSH test is considered mandatory for patients with disorders in the body associated with the functioning of the thyroid gland. Surgical treatment of this organ in the past is also a direct indication for regular testing. In order to correctly decipher the analysis and determine whether the level of the hormones being determined is normal, or whether there are abnormalities in the blood, the endocrinologist relies on several fundamental points.
Firstly, male and female thyroid-stimulating hormone levels should normally differ from each other. In representatives of the fairer sex, it can significantly exceed the values that reflect thyroid hormones (TSH) in a blood test in men. The norm in women is about 4.2, while in men the figure rarely exceeds 3.5. However, this is not the limit. During pregnancy, thyroid hormones may also increase. TSH (the norm in women allows one to determine the degree of increase in the concentration of substances in the blood) in expectant mothers sometimes reaches 4.7.
Nodal pathologies
Nodes can form in different parts of the gland. They are asymptomatic, so most often they are discovered completely by accident. At the same time, nodular pathologies are very common. To diagnose them, palpation, ultrasound, and laboratory tests are used. Sometimes a needle biopsy is performed, which can give very accurate results.
We reviewed all methods for diagnosing thyroid diseases. From this we can conclude that at the moment there are modern techniques that make it possible to find out about the condition of this organ without surgical intervention. At the same time, ultrasound diagnosis of the thyroid gland remains the most popular research method. In principle, there is nothing wrong with this method, since it provides fairly accurate information. However, treatment depends on the diagnosis of the thyroid gland, so you should approach this issue very carefully and consult the best specialists.
Remember that doctors advise visiting an endocrinologist’s office every year. Moreover, it is recommended to undergo a diagnosis of thyroid diseases and undergo tests, even if there are no special indications for this. Starting from the age of 25, every year it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. Timely tests and diagnosis of the thyroid gland will allow you to avoid a huge number of problems.
People at risk should pay special attention to their health. These are adults and those who have a family history of thyroid disease. Those who live in radiation zones and are susceptible to irradiation of the head and neck should also be careful. Remember that even a detected node may turn out to be colloidal, and then no treatment will be needed. This formation should not be removed, as it is not dangerous to health. But at the same time there may be a serious formation, from which it is possible to successfully recover only at the beginning of the journey.
Initial and subsequent examinations
When making an initial visit to an endocrinologist with the above complaints, after an external examination of the organ and palpation of the gland, the specialist will refer the patient for an ultrasound and a blood test for hormones. Further examination is prescribed in accordance with the results obtained. If the organ is functioning normally, all hormones are within normal limits and no antibodies have been detected, then you should look for the root of the problem elsewhere. It should be noted that the symptoms of thyroid diseases are quite general and characteristic of many diseases. For example, drowsiness, fatigue, and hair and skin problems may be symptoms of the gastrointestinal spectrum. it is not worth insisting on more in-depth examinations - for example, radioisotope scanning of the thyroid gland Ultrasound and hormone tests will show pathologies if they are present in the endocrine system. More often, the opposite situation occurs - there are no symptoms as such, but the pathology is revealed during an examination - this means that the disease is asymptomatic.
If large nodes or diffuse enlargement of the entire organ are detected, further examination is carried out - a biopsy or scan of the thyroid gland with radioactive iodine or technetium is prescribed. Further examination makes it possible to more accurately determine the functionality of various parts of the organ, identify clearly benign nodes, tumor formations, and identify papillary or medullary cancer.
It is important to note that almost all basic types of thyroid examination are safe for the body and can be repeated even several times a month. A number of studies have contraindications: for example, scintigraphy and CT cannot be performed on pregnant and nursing mothers.
Complete and accurate diagnosis of thyroid cancer , as well as other pathologies, nodes, tumors, autoimmune pathologies, gives rise to effective individual therapy and increases the chances of a quick and complete cure.
Other methods
Now let's look at other methods for diagnosing the thyroid gland in more detail. Scintigraphy is often used. This is a method in which radioisotope substances are introduced into the body. They accumulate in the gland, and then appear in pictures after using gamma cameras. Thus, the specialist receives a three-dimensional model of the organ, on which the accumulation of radioisotopes is clearly visible. This diagnostic method is especially useful for cancer tumors. Harmful isotopes are very quickly eliminated from the body through feces and urine.
Tissue biopsy is a well-known cellular diagnostic method that is used when cancer is suspected. Thanks to this method, it is possible to determine the nature of neoplasms with absolute accuracy. The principle of this method is that a sample of thyroid tissue is taken from the patient. Using a special game, the doctor makes several punctures in the neck area and transfers the resulting material to a cytologist. In fact, biopsy and puncture are the same procedure.
Cytological diagnosis of the thyroid gland
Material for cytological examination is obtained by puncture of the thyroid gland. This is a simple and fairly cheap method, which is also painless. This preoperative method allows for morphological verification of a certain process. Cytological examination is often carried out in parallel with histological examination. The goal of the first is to reduce the number of mandatory operations performed on patients without tumors. This method is also often used to prevent malignant lesions. At the same time, it has gained great popularity because there has been an increase in cases where patients are operated on, even if there is no particular need for it. The fact is that with such intervention the risk of various complications increases.
The indication for cytological examination is a tumor. Also, research using this method is prescribed for nodular formations. In principle, for any minor pathologies, it would be correct to conduct such a study of the organ in order to outline a specific treatment plan. This is why surgeons, cytologists and endocrinologists must work together. The essence of their work should be a comprehensive diagnosis based on different levels of research.
Let's look at how the puncture is performed. The patient should take a horizontal position. He is not allowed to talk or swallow. The specialist uses 23-gauge needles to pierce the neck. In this case, local anesthesia can be used. The value of such an analysis increases significantly if the material is immediately assessed by a cytologist. To obtain the most accurate diagnosis and exclude the possibility of malignancy, at least two punctures are performed.
Prevention of thyroid diseases
It would seem easy to prevent the disease - simply eliminate the factors contributing to the development of the disease.
But in reality, it is not always possible to follow this advice. However, it will still be possible to do something.
If you can’t move from a city with an unfavorable environment, rent or buy a dacha in the area - regular walks in fresh, clean air will have a positive effect on the body’s resistance to disease.
It’s even easier to diversify your table with sea fish. Tasty and healthy - cod liver. Eat raw carrots and cabbage. Think about oatmeal more often. There is no need to even remind you about eggs and milk.
Most people are already tired of advice on a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and exercising.
But after reading about the thyroid gland at least in this article, having learned what is behind this disease, you will probably change your mind about the boring recommendations and reconsider your daily regimen.
Avoid stressful situations, be less nervous. If you cannot cope with this yourself, contact a neurologist or psychotherapist.
Learn auto-training that will definitely help you cope with yourself and the situation.
Summer, sun. However, excessive tanning will not please the thyroid gland; it will only harm it.
After consulting with your doctors, do not deny yourself herbal teas and infusions. They have a more gentle effect on our body than medications.
What determines the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood?
In addition, thyroid-stimulating hormone in the body can change its concentration depending on many features caused by biorhythm, age, the presence of other chronic diseases, etc. When compiling an anamnesis, it is extremely important to provide the specialist with detailed information on this issue.
A highly qualified doctor can draw objective conclusions from the test results and predict further developments. He can clearly answer questions about certain indicators in the analysis, whether they are the norm or serve as direct evidence of severe disorders in the body.
Often patients try to decipher the test readings for the thyroid hormone TSH themselves. False conclusions and experiences have never brought benefit to anyone, so it is better for a doctor to interpret the test results.
Periodic TSH testing is the key to timely treatment
In addition, a lot of other problems with the most important systems for the human body can be revealed by this analysis of thyroid hormones. TSH in patients who have undergone surgery or have chronic diseases should be constantly monitored by a specialist. The answers from this analysis clearly reflect the condition of the thyroid gland.
If any serious changes are detected at the initial stage or current dysfunctional processes in the organ are identified and treatment is started early, the patient’s chances of full recovery increase several times. In order to avoid complications and take appropriate measures to prevent deterioration of the patient’s well-being, it is necessary to regularly conduct control TSH testing.
Causes of elevated TSH
In case of deviations from the results, it is necessary to urgently take effective measures. You should find out whether there is a threat to your health if your thyroid hormone (TSH) is elevated. What to do in this case depends on the reason that provoked the increase in its concentration in the blood. The main factors that contribute to this:
- certain forms of thyroiditis;
- post-surgical syndrome in case of complete removal of the thyroid gland or its individual lobe;
- benign or malignant formations of the pituitary gland;
- thyroid oncology;
- cancer processes of the breast, lungs or other organs;
- disruptions in the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- complicated degree of toxicosis during advanced pregnancy;
- absence of the gallbladder due to removal;
- mental and somatic diseases.
Why do you need to prepare specifically for research?
In addition, recent X-rays and ultrasound may distort the results of the examination. Increased levels of TSH (thyroid hormone) can be triggered by stressful situations. Nervousness, anxiety, frustration - all this contributes to the intense release of chemicals in the body.
With a responsible and high-quality approach to the procedure, the result of a blood test for the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone will closely correspond to the real picture of the patient’s health. Thanks to accurate information, it is possible to timely carry out preventive measures to prevent thyroid diseases or begin treatment of an existing progressive pathology. In some patients, such restrictions can cause a lot of indignation, however, in order to obtain reliable data on the condition of the organ, desires and ambitions should be neglected. This is the only way to avoid having to undergo a repeat test.
Why are these tests prescribed?
Analysis of thyroid hormones is relevant in practice:
endocrinologists;
- therapists;
- cardiologists;
- immunologists;
- psychiatrists;
- gynecologists and other specialists.
The function of the thyroid gland affects the functioning of the cardiovascular, nervous, digestive, hematopoietic, and reproductive systems.
Thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism can mimic the clinical picture of other diseases. For example, “masks” of low thyroid function are depression, obesity, chronic constipation, iron deficiency anemia, dementia, infertility, menstrual irregularities, hearing loss, tunnel syndromes and other conditions.
Thyrotoxicosis must be excluded if tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, arterial hypertension, insomnia, panic attacks and some other pathologies are detected.
Indications for thyroid hormone testing:
- presence of signs of thyrotoxicosis (tachycardia, extrasystole, weight loss, nervousness, tremor, etc.);
- the presence of signs of hypothyroidism (bradycardia, weight gain, dry skin, slow speech, memory loss, etc.);
- diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland upon palpation and according to ultrasound data;
- nodular formations of thyroid tissue according to examination and additional studies;
- infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- miscarriage;
- a sharp change in weight against the background of a normal diet and physical activity;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- dyslipidemia (increased total cholesterol and atherogenic index);
- anemia;
- impotence and decreased libido;
- galactorrhea;
- delayed mental and physical development of the child;
- control of conservative treatment for thyroid diseases;
- control in the postoperative period (subtotal resection, lobe resection, extirpation of the thyroid gland) and after radioisotope treatment.
In addition, a test for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is included in neonatal screening, that is, it is mandatory for all newborns in Russia. This study allows you to timely identify congenital hypothyroidism and begin the necessary treatment.
Thyroid hormones are normal
The enemy got scared, ran away, everything comes into balance, including the function of the thyroid gland. Usually the level of its hormones in the blood is constant, but not always.
We already understand about stress, but not only does it cause fluctuations in thyroid hormones, but also illnesses.
Symptoms that should prompt you to go to an endocrinologist:
- Unexplained sudden weight loss
- Hair is brittle and comes out in clumps
- Severely dry skin with cracks appearing
- Unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant
Already these few signs require consultation.
Norm TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
TSH can be measured in mIU/L (milli international units per liter), mIU/L (same as mIU/L, only instead of international units, Unit of Action, AU), µIU/ml (micro international units per milliliter) , mU/L (milliunits per liter). Conversion factor: µIU/ml = mIU/l = honey/l = mU/L.
Norm and deviations from the norm of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in adults according to the American Thyroid Association (ATA) (mIU/l)
According to a 2013 study, the reference range for TSH increases with age, while free T4 decreases. At the age of 60 to 79 years, the normal TSH level is 0.4-5.8 mIU/l, from 80 years and older - 0.4-6.7 mIU/l. Using age-appropriate TSH norms, especially in people over 70 years of age, helps avoid misdiagnosis of subclinical hypothyroidism and unnecessary treatment.
A normal TSH level indicates normal functioning of the thyroid gland, but cannot exclude the presence of inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland (for this purpose, TPO-AT tests and ultrasound of the thyroid gland are performed).
When interpreting the TSH test, it is necessary to rely on the reference interval of the laboratory where the test was taken.
How to check your thyroid at home
If you suspect a disease, it is advisable to go to the hospital to see an endocrinologist and undergo a gland examination. But few people want to spend time on a medical examination without knowing for sure whether there are problems. The best option is to check your thyroid gland at home using simple tests.
Inspection, palpation and determination of organ size
Examining the thyroid gland yourself is quite simple. The procedure will help determine whether the size and structure of the gland are normal. To do this, you need to take water into your mouth in front of a large mirror, take a sip and look carefully at your neck. Normally, there should be no bulges on one side, redness, or bumps. The Adam's apple should move smoothly, without sudden jumps. You can also feel the thyroid gland: it should be moderately dense, mobile, painless.
There should be no asymmetrical bumps. If they are palpable, then these are nodes that can be either benign or malignant. The presence of nodules in the thyroid gland is a reason to urgently go to the hospital.
A regular iodine solution will help determine iodine deficiency. They need to draw a mesh on their wrist. If the pattern disappears completely within a couple of hours, it means there is not enough iodine.
The second version of the test: draw 3 stripes on the inner surface of the shoulder overnight - 1 mm, 3 mm, 1 cm thick. If in the morning there are 2 stripes left (the thin one will disappear), then everything is fine. If the thick line just doesn't go away, it's a cause for concern, but nothing serious. And if all the lines disappear, you need to urgently see an endocrinologist.
Eyebrows can tell you a lot about the state of your thyroid gland. If everything is not in order with the thyroid gland, they thin out and shorten at the outer edge. You can measure their length using a pen. It should be placed vertically against the outer corner of the eye. If the tip of the eyebrow extends beyond the handle, then everything is fine. If not, the organ cannot cope with its functions.
Specific symptoms
To check your thyroid yourself without doctors, you should also look for signs of disease. In a person with a diseased thyroid gland, the lower part of the neck is swollen, there may be redness and itching of the skin in the center, the voice becomes hoarse, intellectual performance and concentration deteriorate. An increase in nearby lymph nodes indicates a malignant or inflammatory process in the organ.
Signs of iodine deficiency:
- dryness of the epidermis and mucous membranes;
- weight gain;
- constant diarrhea or constipation;
- arrhythmia;
- menstrual irregularities;
- low blood pressure;
- impotence.
With thyrotoxicosis, the eyes bulge, a decrease in body weight occurs, regardless of appetite, hair falls out, and a “surprised mask” forms on the face.
With hypothyroidism, the body temperature is always slightly lower than normal, and with hyperthyroidism it is higher.
Norms
In the absence of pathology, the volume of the “thyroid gland” in adult men is up to 25 cm³, and in women – within 18 cm³.
This endocrine organ tends to increase slightly in size during puberty, as well as during pregnancy and postmenopause.
Diseases and pathological conditions in which a specialist is obliged to refer the patient for additional examination of a given endocrine organ:
- unmotivated mood swings;
- hair and eyebrow loss;
- constantly cold extremities;
- increased fatigue;
- high prolactin content;
- weight gain and obesity;
- hyperthyroidism;
- hypothyroidism;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- nodular goiter
- infertility;
- heavy periods;
- constipation;
- memory impairment.
Plisov Vladimir, medical observer
11 total today
( 61 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)
Urine analysis according to Sulkovich: norms and interpretation in children
Rheumatic tests (markers of autoimmune diseases)
Related Posts
Causes of decrease and increase in thyrotropin
Could an increase or increase in TSH levels be the cause of the presence of any other diseases besides hypo- and hyperthyroidism? The answer will be unequivocal - of course. Malfunctions of the thyroid gland are the most common diseases indicated by a poor thyroid-stimulating hormone result. However, an increase in TSH is the first sign of no less serious pathologies:
- Malignant tumors in the brain;
- Malfunctions of the central nervous system;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis;
- Thyroid hormone resistance syndrome;
- A serious pathology in late pregnancy is gestosis.
In some cases, test results with elevated TSH levels in the blood plasma indicate non-compliance with recommendations before donating blood. It is possible that the patient unknowingly took medications or became very nervous on the eve of the test. As for women, there are often cases when the test is taken in the early stages of pregnancy, which the woman simply did not know about at that time, and the norms for this period are completely different. Therefore, before taking a blood test, it is so important to visit an endocrinologist, and the final result should also be assessed exclusively by a specialist.
Thyrotropin in some cases may decrease, this happens due to the following reasons:
- Presence of mental illness;
- Systematic stress, depression;
- Malfunction of the pituitary gland;
- Uncontrolled use of medications;
- Sheehan syndrome;
- Neoplasms on the thyroid gland;
- Graves' syndrome;
- Diffuse goiter.
A decrease in thyroid-stimulating hormone often occurs due to an incorrectly prescribed dosage of hormone replacement therapy. This phenomenon is called drug-induced hyperthyroidism, and is treated by a gradual reduction and further selection of the dosage of L-thyroxine. A decrease in TSH value often occurs with an overdose of drugs that contain thyroid hormones.
With anorexia, closed brain injuries, and thyroid cancer, TSH levels in the blood plasma drop to critical levels.
Lab tests
For a complete examination of the thyroid gland, blood tests that show excess or deficiency of hormones are also very important. Depending on the results, drug therapy is prescribed. There are no special preparation requirements. Blood can be donated for hormones at any time of the day, for women - regardless of the day of the cycle. If you are treating thyroid disease with thyroxine, it is enough to stop taking medications on the day of the test. There is no need to stop taking iodine-containing medications. If a calcitonin test is prescribed, you need to quit smoking within 3 days (nicotine reduces the levels). Elderly people undergoing drug treatment for other diseases should consult an endocrinologist about interrupting medications - some medications affect the level of thyroid hormones.
For primary diagnosis, the most frequently prescribed tests are the levels of TSH, FT3 (free), FT4 (free), as well as ATTPO - antibodies that indicate the development of autoimmune pathologies.