Autoimmune thyroiditis of the thyroid gland is an inflammatory disease that is caused by hereditary or extraneous factors, including poor diet and unfavorable living environment. Occurs in 3–5% of the population, in a pronounced form – in approximately 1% of patients. More often in women than in men, 5–6 times, especially after the age of 60 years. Thyroiditis is diagnosed in every third case among endocrine pathologies.
Causes of development of autoimmune thyroiditis
The main factor in the occurrence of this disease is a violation of the immune system, which begins to perceive the cells of the thyroid gland as foreign and produce antibodies against them. Autoimmune thyroiditis appears as a familial disease. Patients and their blood relatives have antibodies to enzymes (thyroid peroxidase) and thyroglobulin, which are involved in the formation of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
In addition, in the families of patients there are other pathologies of an autoimmune nature - type 1 diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis, pernicious anemia, vitiligo. The mere presence of antibodies does not guarantee the development of an active process. Therefore, even with a genetic predisposition, exposure to a provoking factor is necessary. The role of the following reasons has been proven:
- chronic infections of the nasopharynx, especially tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries;
- acute viral infections, especially hepatitis;
- intestinal infectious diseases, yersiniosis (transmitted from livestock, dogs, rodents);
- pollution of soil, air and water with chlorine, fluorine, nitrates (stimulate the activity of T and B lymphocytes responsible for cellular immunity and the formation of antibodies);
- radiation and solar exposure;
- stressful situations;
- long-term, and especially uncontrolled use of iodine-containing drugs or hormones;
- treatment of blood diseases with interferon drugs;
- injuries and operations on the thyroid gland.
Recent studies of the significance of these factors have proven that an important, and perhaps the main one, is the consumption of iodine in quantities exceeding the physiological norm. This applies to food products (red food dyes, preservatives, iodine additives in flour, salt), but more often to medicines and dietary supplements.
It should be noted that self-treatment or prevention of iodine deficiency with iodine or Lugol's solution is extremely dangerous. Similar conditions can also occur when the dose of multivitamins is exceeded or when Cordarone is used for a long time.
Autoimmune thyroiditis can occur after childbirth. Its development is associated with the activation of the body's defenses after a period of oppression during pregnancy. If the patient does not have a hereditary predisposition, then it may spontaneously stop. There is also a painless (“mute, silent”) version of the disease that is not associated with pregnancy or any other known cause.
We recommend reading the article about the symptoms and treatment of hypothyroidism. From it you will learn about the causes and symptoms of hypothyroidism in men and women, as well as about the diagnosis, treatment of the disease and prevention. And here is more information about the treatment of hypothyroidism with folk remedies.
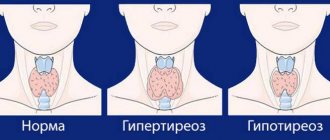
Autoimmune hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a consequence of insufficient synthesis of thyroid hormones. Characteristic of the atrophic form of AIT and the final phase of the hypertrophic form.
Symptoms:
- fast fatiguability;
- absent-mindedness, forgetfulness;
- sudden mood swings, frequent depression;
- poor condition of nails, skin and hair;
- unstable heart function;
- high cholesterol;
- swelling;
- overweight with low appetite;
- menstruation disorders in women and impotence in men.
Patient with typical symptoms of hypothyroidism: facial swelling, excess weight
All these symptoms may appear gradually. The advanced stage of hypothyroidism is more difficult to treat, so you need to undergo medical examination regularly. To diagnose it, you need to donate blood to check the level of thyroid hormones, do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and an ECG.
Most often, treatment of hypothyroidism against the background of autoimmune thyroiditis is lifelong: drugs are initially prescribed that restore hormonal levels, after which their dosage is changed and treatment continues as maintenance therapy.
Important: advanced hypothyroidism is dangerous due to disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, which can lead to stroke.
Classification of Hashimoto's goiter
Depending on the severity of symptoms and changes in the thyroid gland, the disease can have several clinical forms.
Latent
Antibodies are detected in the blood, but there are no signs of changes in the functioning of the thyroid gland. Erased symptoms of a slight increase or decrease in hormone production are possible. During examination, there may be a slight increase in the size of the organ; no seals are detected.
Hypertrophic
With the development of a goiter, there may be a uniform proliferation of tissues - a diffuse increase, or nodes may form against its background (diffuse-nodular form). Sometimes a node is found in unchanged tissue (nodular goiter). In the initial stage, there is excessive synthesis of hormones (hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis), but in most patients the function does not change (euthyroidism) or decreases (hypothyroidism).
As autoimmune inflammation progresses, the thyroid tissue is attacked by antibodies and killer lymphocytes, which leads to its destruction. During this period, the patients' condition worsens, and the production of hormones decreases, a hypothyroid state develops with a decrease in metabolic processes in the body.
Atrophic
The most severe form, since the function of the organ is significantly reduced due to massive destruction of thyroid cells. Its size decreases, and hypothyroidism becomes persistent. It is more common in elderly patients and with radiation exposure at a young age.
Possible complications
With timely diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis is favorable; treatment is effective if up to 40–50% of thyroid cells are affected. However, these symptoms of thyroiditis affect other organs and systems, so different consequences are possible.
Arrhythmia leads to heart failure and can cause myocardial infarction. Hypothyroidism negatively affects the reproductive system: it causes miscarriages, infertility, in addition, it causes depression, weakens mental and physical abilities.
Stages of the disease
The disease goes through several stages in its development. The patient does not always have all of them. A monophasic course for a long period is possible.
Euthyroid
The thyroid gland is functioning normally. This phase of autoimmune thyroiditis lasts several or decades, and can last a lifetime.
Subclinical
It begins with an exacerbation due to a massive attack of T-lymphocytes. These cells intensively enter the thyroid gland and begin to destroy its tissue. In response, the pituitary gland intensively produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thus stimulates the formation of thyroxine, maintaining its normal level.
Thyrotoxic
When cells are extensively damaged, hormones from them enter the blood. This is accompanied by symptoms of thyrotoxicosis (tachycardia, weight loss, sweating, hand tremors). Along with hormones, parts of the follicles also enter the bloodstream. They act as antigens and provoke the formation of antibodies to their own cells.
Hypothyroid
The reserves of hormones in the thyroid gland are not unlimited, and over time, due to a decrease in the volume of functioning tissue, their formation decreases. When the number of cells capable of synthesizing thyroxine and triiodothyronine decreases to a critical level, hypothyroidism begins to progress. At this stage, autoimmune thyroiditis is most often diagnosed.
The hypothyroid state usually lasts about a year, and then the gland restores its functions, but sometimes it remains persistent and irreversible.
Autoimmune thyroiditis: the thyroid gland benefits from natural helpers
When I began studying naturopathy, I learned that many autoimmune problems are caused by viruses—particularly the Epstein-Barr virus. Many people have it in different forms. Anthony William in the books “Life Changing Foods”, “Looking Inside the Disease”, “Thyroid Healing” gives a protocol for deactivating the Epstein-Barr virus.
The protocol is divided into 3 parts and takes 90 days. I find it quite heavy and give fair warning that I couldn't handle all the nuances. I went through it with breaks and some deviations, but still respecting the basics. I hope that a positive result will still be achieved. It is necessary to take tests. My dosage of the hormone has already been reduced to 50 mg; it is impossible to sharply reduce or completely stop taking it. I would like to note a clear improvement in my well-being; I no longer get tired as quickly or as much as I did before.
The protocol includes the following parts:
A - cleansing the liver, lymphatic system and intestines. Preparation for parts B and C.
B - removal of heavy metals.
C - fight against the virus.
Each stage lasts 30 days.
As an addition to the protocol, Anthony recommends taking certain supplements and including certain foods in your diet. Each of which is important for fighting the virus that damages the thyroid gland.
Nutrition for AIT. These are aloe vera, apples, bananas, coconut, lemons and limes, oranges, tangerines, papaya, mangoes, maple syrup, pears, pomegranates, nuts (walnuts, brazil, almonds, cashews), wild blueberries and other berries, arugula, asparagus, Atlantic seaweed, avocado, basil, cauliflower, celery, cilantro, cruciferous vegetables, cucumbers, dates, fennel, figs, garlic, ginger, hemp seeds, kale, lettuce, onions, parsley, potatoes, radishes, sesame seeds, spinach, sprouts and microgreens, zucchini, sweet potatoes, thyme, tomatoes, turmeric, watercress.
As for vitamins and supplements, these are:
- B12 (methyl with adeno);
- Zinc - zinc (liquid form of zinc sulfate);
- Vitamin C - strengthens the immune system;
- Spirulina - removal of heavy metals;
- Cats claw - cat's claw, has antiviral and antibacterial effects;
- Licorice root - licorice root, antiviral, antibacterial effects, restores the adrenal glands;
- Lemon balm - lemon balm, antiviral, antibacterial effects;
- L-lysine - lysine, antiviral effect, anti-inflammatory effect;
- Chaga mashroom - chaga mushroom, antiviral, stimulates liver function;
- 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, the active form of vitamin B9, supports the functional state of the reproductive and nervous systems, reduces homocysteine levels;
- Barley sprout juice extract is necessary for the removal of heavy metals;
- Monolaurin has an antiviral effect;
- Hydrosol silver has an antiviral effect;
- L-tyrosine to support thyroid function;
- Ashwagandha to stabilize the functional state of the adrenal glands;
- Red seaweed for removing mercury;
- Nettle leaf, adaptogen;
- Vitamin B complex;
- Magnesium to balance thyroid hormones;
- Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, to strengthen the endocrine system;
- Fucus vesicularis, it contains a lot of iodine and mineral components, it removes heavy metals;
- Selenium has an antiviral effect, improves the conversion of thyroid hormones;
- Curcumin supports the functioning of the nervous system;
- Chromium is necessary for the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- Vitamin D3 is important for stabilizing the immune system;
- Ionized copper to remove toxic copper and strengthen the body’s resistance to the virus.
I deliberately do not write the dosage of the products, since before using them, in any case, you need to consult a specialist.
Why is autoimmune thyroiditis dangerous?
In Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, Hashimoto's thyroiditis affects from 4 to 12% of the population, depending on the region. As the environment becomes polluted, its prevalence increases. The difficulty of early detection of the disease is due to the fact that more than one year or even a decade passes from the moment of autoimmune damage to complications. Signs of the disease are detected when the gland is significantly destroyed, when the patient loses the ability to produce hormones.
In addition to the clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism (weakness, impaired thermoregulation, drowsiness, low blood pressure), its consequence can be infertility. Moreover, it occurs not only in the obvious variant of the disease (manifest), but also in the latent (subclinical) variant.
If, with severe manifestations, patients cannot become pregnant due to ovulation disorders, then subclinical hypothyroidism is accompanied by habitual miscarriages. An excessive reaction of the immune system is often explained by infertility in endometriosis.
If conception does occur, then during pregnancy hypothyroidism has an adverse effect on the expectant mother and child. This manifests itself in the following complications:
- threat of premature birth;
- preeclampsia (high blood pressure, edema, seizures);
- placental abruption;
- slowing of intrauterine development of the fetus;
- bleeding after childbirth;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- anemia.
Placental abruption
The newborn has pathologies of the nervous and skeletal systems and a slow heart rate. The combination of autoimmune thyroiditis and thyroid cancer is not common, but possible.
Treatment of thyroiditis
The patient is observed by an endocrinologist who prescribes non-steroidal or steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve symptoms. Monitors medical history and administers hormone therapy.
Video from Elena Malysheva:
Acute thyroiditis with purulent inflammation is treated in a hospital setting, in the surgical department. Antibacterial and antihistamine drugs are used, as well as means for detoxification and strengthening the immune system. If necessary, surgery, opening and drainage of the abscess are performed.
- Medications for hypothyroidism - thyroid hormones of the thyroid gland (thyroxine, triiodothyronine) are prescribed. Given the chronic nature of the disease, treatment is carried out for a long time. The level of TSH in the blood serum is checked two months after the start of use.
- Glucocorticoid drugs are used when autoimmune thyroiditis is combined with a subacute type of the disease. Prednisolone is usually recommended at a dosage of 40 mg/day with a gradual decrease.
- Surgical methods - thyroidectomy (partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland) is used. The operation is performed when the organ is rapidly enlarged, when the trachea and cervical vessels are compressed, when cancer is detected, and in the absence of positive dynamics from conservative therapy.
- “Folk remedies” is an auxiliary technique against inflammation, to strengthen the body. They do not cancel timely diagnosis and are not able to compensate for drug treatment. Prepare compresses with wormwood infusions, with the addition of essential oils, and make an iodine grid (only after hormonal tests). Consume persimmons, seaweed (dried or frozen), and other foods with a high iodine content in the diet.
Symptoms of pathology in adults and children
Most patients at the subclinical and euthyroid stage of the disease do not realize that they have thyroiditis. At this time, the thyroid gland retains its size, is not painful, and the hormonal balance is not disturbed. Some patients may develop nonspecific signs that do not lead them to see a doctor:
- discomfort in the neck area,
- feeling of a lump in the throat,
- fast fatiguability,
- general weakness,
- flying joint pains.
In the first years of the disease, autoimmune thyroiditis usually manifests itself as hyperthyroidism. It is called hashitoxicosis. More often found in children in the form of:
- tendency to tearfulness, anxiety, agitation;
- increased irritability, aggressiveness;
- accelerated and increased heartbeat;
- increased upper pressure (high systolic and pulse);
- sweating, poor heat tolerance;
- trembling of eyelids, fingers;
- weight loss.
Autoimmune thyroiditis in children
This stage is short-lived and, unlike toxic goiter, does not lead to the appearance of eye symptoms (bulging eyes, increased shine of the eyes, widening of the palpebral fissure). Subsequently, thyroid function weakens by an average of 5% every year. The phase of relatively normal functioning lasts a long time, and only with the development of hypothyroidism can autoimmune thyroiditis be suspected.
In the hypertrophic form, signs of compression of adjacent tissues come to the fore. Patients experience difficulty breathing, swallowing, possible hoarseness, short-term attacks of dizziness or fainting. In cases of severe hypothyroidism, patients note:
- apathy, lethargy, drowsiness;
- constant chilliness;
- memory loss;
- swelling of the face, legs;
- steady increase in body weight;
- hair loss, increased brittleness of nails;
- dry skin;
- decreased blood pressure and slowed heart rate.
Watch the video about autoimmune thyroiditis:
Symptoms at different stages
The disease progresses slowly, gradually showing certain signs.
- Euthyroid stage - immune cells begin to perceive thyrocytes in the thyroid gland as foreign elements and direct antibodies against them. With small losses of hormones, the functions of the organ do not change; sometimes its increase is noticeable.
The following clinical signs appear: diffuse or local thickening of the thyroid gland, identification of nodular formations. Patients notice a sensation of a “lump” in the throat, problems with breathing and swallowing, and moderate pain in this area, especially when trying to turn their head.
- Subclinical stage - symptoms worsen, additional thyroid-stimulating hormones are activated, and the thyrotoxic phase begins.
- Thyrotoxicosis - the following signs are noticeable: dysbacteriosis, indigestion, rapid heartbeat, cessation of menstruation, fatigue, irritability.
- Hypothyroidism - antibodies continue to destroy thyroid cells, then the person feels depressed. Movement slows down and appetite worsens. The skin becomes pale and swollen, thickens (does not come together with a pinch). Hair falls out faster, joint problems are possible.
In acute thyroiditis, patients experience:
- Arrhythmia, headache, hyperemia.
- Congestion of blood vessels in the neck.
- Increased body temperature.
- Chills, fever, feeling of weakness.
- Profuse sweating.
- Tremor, trembling of fingers.
Hormone analysis and other diagnostic methods
Autoimmune thyroiditis is difficult to identify before the onset of hypothyroidism. To make a diagnosis, take into account:
- manifestations of the disease;
- data from laboratory and instrumental research methods;
- the presence of similar pathologies in blood relatives.
When examining the patient, they find:
- general blood test – increased lymphocytes;
- blood immunology – antibodies to thyroglobulin, thyroid peroxidase, thyroxine, triioditronine;
- blood hormones - when TSH increases, hypothyroidism is detected. If thyroxine is normal, then it is subclinical, and if it decreases, it is obvious;
- Ultrasound – dimensions are reduced or increased depending on the shape, echogenicity is reduced;
- a biopsy is indicated when a node is detected to exclude its degeneration into a malignant tumor.
In order to confirm chronic autoimmune Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the simultaneous presence of the most important signs is necessary: antibodies to thyroid peroxidase exceeding 34 IU/l, hypoechogenicity on ultrasound and symptoms of hypothyroidism. None of these criteria alone provides grounds for a definitive diagnosis.
Causes of AIT
Although the causes of the disease are unknown, features of the disease have been identified.
The disorder is 7 times more common in females than in males, especially in pregnant women.
The risk of developing AIT may be higher if you have a family history of people with autoimmune diseases, including:
- Flayani's disease (diffuse toxic goiter) causing thyrotoxicosis;
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- skin tuberculosis with ulcers and nodules (lupus);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- vitiligo (a type of skin disease);
- chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex.
Treatment of acute and chronic forms
There is no specific therapy for the disease that would prevent its further progression. Despite understanding the causes and mechanisms of development of autoimmune thyroiditis, its treatment is limited to compensation for disturbances in the formation of hormones.
Thyrostatics (Mercazolil, Espa-carb) are not used for hashitoxicosis, since hyperthyroidism is associated with the destruction of the thyroid gland, and not with increased synthesis of thyroxine. For palpitations, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, hand tremors and sweating, the beta blocker Anaprilin is indicated.
If hypothyroidism develops, replacement therapy with levothyroxine (L-thyroxine, Euthyrox) is prescribed under the control of the content of pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood.
Taking into account the examination data, hormone intake can be started already at the subclinical stage and during the period of euthyroidism in a minimal dose. This therapy inhibits the formation of TSH and the progression of autoimmune destruction. To reduce the antibody titer, selenium (Cephasel) is added to the treatment for three months.
Glucocorticoids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) are used for exacerbation of inflammation, which most often occurs against the background of viral or bacterial infections in the autumn-winter period. For mild inflammatory processes, non-steroidal drugs (Voltaren, Indomethacin) are used. If the goiter reaches a large size, patients undergo surgery to remove the gland.
Treatment
No specific treatment for AIT of the thyroid gland has been developed, because no way has been found to prevent the development of autoimmune processes.
Therefore, treatment is symptomatic. If the symptoms of the disease are completely eliminated with the help of maintenance therapy (or without it), you can live with this diagnosis for the rest of your life.
Due to low immunity, it is necessary to take some precautions: avoid contact with infectious patients, ventilate rooms more often, try to refrain from stress, spend less time in the sun, and, if possible, not undergo X-ray examinations.
Surgical removal of the affected half of the thyroid gland
The stage of euthyroidism is not treated, because it does not interfere with the functioning of the body and does not disrupt its functions.
In case of hyperthyroidism against the background of autoimmune thyroiditis, drugs are prescribed to treat tachycardia, sedatives, and drugs that suppress hormone secretion.
For hypothyroidism, patients are prescribed a synthetic analogue of thyroxine or triiodothyronine. In the absence of antibodies, iodine is additionally prescribed. Treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis with drugs such as Endorm is necessary to restore the functions of the gland and relieve inflammatory processes.
Fact: surgical treatment is prescribed quite rarely; the most extreme measure is complete removal of the affected gland.
How to treat autoimmune inflammation of the thyroid gland using traditional recipes
Treatment of AIT of the thyroid gland with folk remedies involves the use of plants that contain substances beneficial to the organ, in particular iodine. When choosing a treatment method, it is necessary to take into account the degree of iodine deficiency - medications should compensate for it without leading to excess iodine and subsequent hyperthyroidism.
During treatment, be sure to check with an endocrinologist and donate blood to a laboratory to determine the level of iodine-containing hormones.
Walnuts
Young walnuts contain the most iodine and nutrients. But it is difficult to eat them, so treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis is carried out with decoctions and tinctures. For the decoction, you will need to crush half a glass of nuts along with the peel, pour in a liter of boiling water and leave for 20-30 minutes. Drink the resulting folk remedy after straining twice a day, 3 tbsp. l.
The tincture is prepared with vodka. For a half-liter bottle you will need to take a glass of chopped walnuts. Let the product brew for a month in a glass container, which is placed in a cool and dark place. Wipe the thyroid area with the tincture several times a day.
White Potentilla
Traditional healers recommend using the three-year-old roots of pyatipal in the form of a decoction. For 2 tbsp. chopped roots you will need to take 2 cups of boiling water. Mix the ingredients and let it brew for 20-30 minutes. Take half a glass twice a day before meals. Herbal treatment for thyroiditis lasts a month, with a break between courses of at least a week.
Sea kale
Kelp contains large amounts of iodine, which is deficient in most people diagnosed with thyroiditis.
In addition to eating seaweed as food, you can prepare a tincture from it: mix a teaspoon of kelp, lungwort and capsicum (red), then pour in 1 liter of boiling water. Let it brew for 20-30 minutes, and drink the resulting decoction during the day, dividing it into 5 servings.
It is best to brew kelp in a thermos to consume the infusion warm.
Chinese lemongrass
You can buy the tincture at a pharmacy or prepare it yourself according to a folk recipe. This will require 2 tbsp. l. lemongrass berries and half a glass of medical alcohol. Grind the berries (you can use a blender), add alcohol and leave for 10 days in a dark and cool place. Use glass containers for infusion and storage. For autoimmune thyroiditis, take 20 drops twice a day for a month, then take a break for 2-4 weeks.
Pine buds
A tincture is prepared from pine buds. 2 packs of buds from the pharmacy are crushed, in a blender, and then poured with a liter of vodka. You need to leave for 3 weeks, strain before the first use. The thyroid area is wiped with the tincture several times a day.
Cocklebur herb
This plant contains iodine. To treat thyroiditis, it is better to use cocklebur in the form of homemade oil. To do this, mix 5 tablespoons of chopped herbs with the same amount of vegetable oil, pour the mixture into a glass container and leave to infuse for a month in a dark and cool place. Lubricate the thyroid area before going to bed.
The use of such methods is contraindicated if autoimmune thyroiditis has led to benign or malignant formations in the gland
Celery
A smoothie made from celery, lemon and sea buckthorn is useful for autoimmune thyroiditis, as it provides the thyroid gland with the necessary antioxidants and normalizes its functions. To prepare according to the folk recipe, you need to mix the juice from 350 g of celery stalks with freshly squeezed lemon, and then add a glass of crushed sea buckthorn. It is better to process all ingredients in a blender.
Drink a glass twice a day before meals for a month. The break between courses of treatment for thyroiditis is at least a week. It is worth giving preference to these plants when preparing a diet.
Celandine
After surgical interventions, unsightly scars remain on the skin in the area where the thyroid gland is located. If desired, you can cure them or make them less noticeable using folk remedies. One of them is celandine - a suitable raw material for homemade medicinal oil. To prepare it, you need to take 2 tbsp. l. dry celandine grass and fill it with the same amount of olive or linseed oil. Leave for a month in a dark and cool place, strain before use.
Rub the resulting oil into the thyroid area before going to bed. Also, in case of thyroiditis, celandine accelerates the healing of cystic neoplasms and prevents their appearance.
Propolis
This bee product is used to make ointments for the thyroid gland. 100 g of propolis should be poured with 30 ml of ethyl alcohol, placed in a water bath and stirred constantly until dissolved evenly. Then cool and mix with Boric ointment (100 g). Apply the resulting medicine to the neck in the thyroid area in two layers (the second after the first has dried). Then wrap it in a handkerchief or scarf. Wash off in the morning. Use once per day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Before using propolis for its intended purpose, check for an allergic reaction by applying a little ointment to your wrist.
Milk thistle
Methods to “accelerate” metabolism during hypothyroidism are often dangerous and have a large number of side effects. Milk thistle meal stands out against their background. Treatment of thyroiditis according to a folk recipe with this ingredient accelerates metabolic processes by normalizing the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, cleansing the liver of toxins, and increasing the filtration functions of the organ.
Milk thistle meal for thyroiditis should be taken a teaspoon three times a day half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is a month, after which you need to take a break for 2-3 weeks and, if desired, begin treatment for thyroiditis again.
Pears and apples
The seeds of these fruits contain a large amount of antioxidants, as well as iodine and selenium, which are useful for inflammation of the thyroid gland. However, including them in the diet for thyroiditis is contraindicated, since pears and apples contain large amounts of sugar. Therefore, the best solution would be to cook compote from still green fruits and drink a glass of it 3 times a day. You can also consume a serving of seeds from one apple or pear twice a day.
Juices from carrots, beets, cabbage
Freshly squeezed juices contain antioxidants. They accelerate the removal of toxic substances formed when the thyroid gland does not function properly. Antioxidants also slow down the process of breakdown of gland cells during thyroiditis.
You should start drinking carrot, beet and cabbage juices in small quantities - 2-3 tablespoons per day. Gradually increase your juice consumption to 2 glasses per day, dividing this volume into 3-4 doses.
For folk treatment of thyroiditis, only fresh homemade juices are suitable. Store-bought products or homemade juice, squeezed more than an hour ago, no longer have the required concentration of nutrients, since they quickly oxidize.
How to diagnose
How to treat AIT?
In order to diagnose autoimmune hypothyroidism, it is necessary to undergo the following set of measures:
- Examination by an endocrinologist. During this time, the specialist will be able to identify whether there are deviations from the normal size of the thyroid gland. The doctor will find out from the woman what symptoms bothered her. Based on the information received and the results of the examination, he will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis of whether autoimmune thyroiditis preceded hypothyroidism.
- Examination of the thyroid gland using ultrasound, MRI, as well as radioisotope diagnostics. As a result of the studies, changes in the size and structure of the thyroid gland will be identified.
- Donating blood for hormone tests: TSH, free T3 and T4. In addition, an antibody test and a general biochemical blood test are performed.
Such a comprehensive examination will allow the doctor to obtain the maximum amount of information to diagnose CAIT resulting in hypothyroidism.
A blood test will allow the doctor to identify the disease at a subclinical stage of development. This is when there are no obvious symptoms yet, but the disease is already developing in the body. Subclinical hypothyroidism is characterized by normal T3 and T4 levels with elevated TSH levels. By starting treatment at this stage, a woman will be able to stop the destruction of the thyroid gland.
Basic rules of treatment
Specific treatment for the thyroid gland in AIT has not been developed. So far, endocrinologists do not have effective methods to relieve autoimmune inflammation.
Principles of therapy for hypothyroidism against the background of AIT:
- Replenishment of T3 and T4 deficiency. To normalize hormonal levels, thyroid hormone substitutes with levothyroxine are prescribed - Eutyrox, L-Thyrox euro. Medicines stimulate metabolism, which reduces the risk of complications from the gastrointestinal tract, hematopoietic and cardiovascular systems.
- Relieving inflammation in the gland. To reduce the severity of autoimmune reactions in thyrocytes, glucocorticosteroids are used - Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Betaspan. The drugs are recommended only for the combined course of autoimmune and subacute thyroiditis.
- Decrease in the number of antibodies to gland cells. To reduce the content of autoantibody titers in the blood, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are taken - Methindol retard, Bioran, Diklak.
In the hypothyroid phase of AIT, the thyroid gland is greatly reduced in volume. A lack of iodine-containing hormones leads to weakened immunity, which increases the risk of infectious diseases. To improve the body's resistance to bacteria and viruses, immunostimulants are used - Immunal, Liasten, Imumod, as well as folk remedies.
Diagnosis of the disease
An experienced endocrinologist will immediately recognize a patient with autoimmune thyroiditis, because external signs speak for themselves. But clinical studies are still needed here:
- Blood test for the amount of thyroid hormones. In addition, it is necessary to diagnose the activity of the pituitary gland, which synthesizes thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). This is the main thyroid hormone, completely controlling its activity. Decreased or elevated values lead to a positive diagnosis.
- Testing blood serum for the presence of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (AT-TPO) and thyroglobulin (AT-TG).
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland - allows you to determine the size of the organ, its structure and consistency, as well as the presence of tumors and nodes.
- Thyroid scintigraphy is a method that determines its functional activity. A special apparatus examines whether the gland is capable of capturing iodine from the bloodstream, because thyroid hormones are then synthesized from it. A sufficient supply of iodine to the gland guarantees its stable functioning.
- Fine-needle biopsy is performed after all of the above measures, if their results indicate the presence of a disease, and even more so if nodular formations are detected. During the biopsy procedure, the doctor uses a special needle to remove a small part of the thyroid tissue for histological examination. Using this method, you can find out the nature of the tumor and exclude malignant neoplasms.
Diagnostics
General clinical methods are easy to use, do not require material costs on the part of the state or the patient himself, are informative in the case of a typical course of the disease, and are also time-tested and proven by many generations of doctors.
Inspection
An enlarged and swollen thyroid gland looks like a neoplasm on the front surface of the neck; as a rule, the skin over the gland becomes slightly pink, inflammation is accompanied by itching. Regional lymph nodes (in the neck) are enlarged and painful, the veins of the neck are swollen and enlarged, the face is swollen and pink.
View of the neck of a person suffering from thyroiditis
Palpation
Examination of the gland by palpating it. In children, the surface is smooth, the edges are clear, in adults - on the contrary - a heterogeneous consistency, a bumpy surface.
Collection of family history data
- Burdened by the autoimmune status of the thyroid gland (corresponding diseases of the patient and his relatives).
- The presence of other endocrinological (diabetes mellitus, decreased activity of the adrenal cortex), autoimmune (rheumatoid arthritis, B12-deficiency anemia) diseases.
- X-ray exposure to the head, neck, upper chest or exposure to radioactive iodine in these areas of the body in the past.
Instrumental and laboratory diagnostics are an excellent addition to the main examination of a diseased organ, but almost always financially significant for the sponsor of its implementation.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Different types of ultrasound allow you to carefully and thoroughly evaluate the parameters of the thyroid gland: volume (see What should be the volume of the thyroid gland), location, clarity of contours, density, homogeneity of the tissue itself, as well as blood flow in local vessels.
It is important to know! Echogenicity is the ability of tissue to reflect the flow of ultrasonic waves (high-frequency sound) that is directed at it.
Small areas of thyroid tissue with reduced echogenicity or uniform hypoechogenicity of the entire organ are determined.
Laboratory diagnostics
- Complete blood count: an increase in the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) indicates the presence of inflammation.
- Immune panel tests: increased titers (concentrations) of antithyroid antibodies (ATA) or autoantibodies in the blood serum.
- Study of hormone levels: an increase in TSH, which is inversely proportional to the increase in triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4).
This is interesting! Thanks to modern laboratory research, a fact has become known: 50% of relatives of people suffering from AIT also have circulating antibodies to the thyroid gland in their blood serum.
Needle biopsy
This research method is an intravital sampling of material by puncture and is an alternative way for further research of the thyroid gland. Rarely used due to possible organ trauma. Such a biopsy is indicated if there is no information content according to the ultrasound picture and if the titer of autoantibodies to the thyroid gland is low.
Definition of thyroiditis
thyroiditis photo
The least common of all types of thyroiditis in clinical practice is acute thyroiditis, which can be purulent or non-purulent. As a rule, purulent thyroiditis develops against the background of a chronic or acute infection, such as pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc. The causative agent of this type of disease is usually pyogenic streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus, which are introduced from neighboring organs by contact, hematogenous, and also lymphogenic methods.
As for non-purulent thyroiditis, it can develop after treatment of diffuse toxic goiter with iodine or after a closed injury in the area of the thyroid gland.
Women aged 30-35 years often experience subacute thyroiditis, which develops after various viral infections. With repeated viral infections or with overcooling of the body, de Quervain's thyroiditis (the second name for this disease) is prone to relapse.
Video: Autoimmune thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis (another name is chronic autoimmune thyroiditis) is especially dangerous, since in this case autoimmune damage to the thyroid gland occurs. In this case, antibodies are formed to such components of the thyroid gland as thyreoglobulin and the microsomal fraction. As a rule, Hashimoto's chronic thyroiditis acts as a “second disease”, accompanying other thyroid diseases. In clinical practice, such thyroiditis is observed in patients suffering from endemic goiter, Graves' disease, gland cancer and adenoma.
And Riedel's thyroiditis (fibrous chronic thyroiditis of the thyroid gland) still has an unknown etiology. The spread and progression of this type of thyroiditis throughout the entire gland leads to the development of hypothyroidism. Fortunately, in clinical practice this disease is extremely rare.
Much more common in people is autoimmune thyroiditis, which is an inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland of autoimmune etiology, belonging to a heterogeneous group. In the case of this type of thyroiditis, destruction of follicular cells and follicles of the thyroid gland occurs.
Diet
Although a diet for autoimmune thyroiditis may improve thyroid function, dietary changes are unlikely to replace the need for prescription medications.
Antioxidant-rich foods (fruits and vegetables)
Blueberries, tomatoes, bell peppers and other foods rich in antioxidants can improve overall health and benefit the thyroid gland. Eating foods high in B vitamins, found in whole grains, may also help.
Selenium
Small amounts of selenium are needed for enzymes that make thyroid hormones work properly. Nuts and seeds rich in magnesium and selenium, especially Brazil nuts and sunflower seeds, can promote a healthier thyroid.
What you shouldn't eat
Dietary supplements of iron and calcium, and consumption of foods high in fiber may reduce the effectiveness of some medications.
Avoid eating soy products, broccoli, cauliflower and cabbage as these foods can suppress thyroid function, especially when eaten raw.
Causes
Autoimmune thyroiditis is most often caused by a hereditary predisposition. But for its development some factors are necessary:
- the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- exposure to radioactive radiation;
- improper use of hormonal drugs;
- numerous viral infections;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- taking too much iodine;
- selenium deficiency;
- severe psycho-emotional stress;
- unfavorable environmental situation.
Diagnosis of thyroiditis
When diagnosing autoimmune thyroiditis, a specialist first of all pays attention to studying the medical history, as well as the characteristic clinical picture. The diagnosis of “autoimmune thyroiditis” is easily confirmed by detecting a high level of antibodies acting against thyroid proteins in a blood test.
Laboratory tests in the blood also show an increase in the number of lymphocytes with a general decrease in the number of leukocytes . When a patient is at the stage of hyperthyroidism, there is an increase in the level of thyroid hormones in the blood. the pituitary thyrotropin increases . In the process of establishing a diagnosis, attention is also paid to the presence of changes in the immunogram. The specialist also prescribes an ultrasound examination, which can detect an enlargement of the thyroid gland, and in the case of nodular thyroiditis, its unevenness. a biopsy is prescribed , in which cells characteristic of the disease autoimmune lymphomatous thyroiditis are isolated.
It is important to differentiate subacute thyroiditis from acute pharyngitis , purulent thyroiditis , infected neck cyst , thyrotoxicosis , thyroid cancer , hemorrhage into the nodular goiter , autoimmune thyroiditis and local lymphadenitis .
Other forms of thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis is a viral type of thyroid disease that is accompanied by the destruction of thyroid cells. As a rule, subacute thyroiditis appears approximately two weeks after a person has had an acute respiratory viral infection. This could be the flu , mumps , measles and other ailments. It is also generally accepted that the cause of subacute thyroiditis can be the causative agent of cat scratch disease.
Typically, subacute thyroiditis presents with a number of common symptoms. A person may have a headache, feel a general malaise, weakness, muscle aches, and weakness. The temperature may rise and chills may appear. Against the background of all these symptoms, the patient’s performance significantly decreases. However, all these symptoms are nonspecific, therefore, they can be observed with any infectious disease.
With subacute thyroiditis, some local symptoms also appear that are directly related to damage to the thyroid gland. Inflammation of the gland, stretching and swelling of the capsules occurs. The patient complains of intense pain in the gland area, which becomes even stronger during palpation. Often, even the lightest touch to the skin in the area of the gland brings a person very unpleasant sensations. Sometimes the pain radiates upward, spreading to the ear, lower jaw, and sometimes to the back of the head. During the examination, the specialist usually notes the high sensitivity of the thyroid gland and the presence of mild signs of hyperthyroidism.
Quite often today, asymptomatic thyroiditis , which is called so because the patient has no symptoms of the inflammatory process of the thyroid gland.
To this day, the exact reasons that lead to the manifestation of asymptomatic thyroiditis in a person have not been established. But thanks to research, it has been established that a certain autoimmune factor plays a leading role in the manifestation of the disease. In addition, according to statistics, this disease is very often observed in women in the postpartum period.
This disease is characterized by a slight enlargement of the thyroid gland. There is no pain, but there is a spontaneously passing phase of hyperthyroidism, which can last for several weeks or months. Often after this, the patient experiences transient hypothyroidism, in which the euthyroid status is later restored.
The signs of asymptomatic thyroiditis are very similar to the signs of autoimmune thyroiditis. The only exception in this case is the fact that, as a rule, the gland is restored, and therapy with thyroid hormone lasts relatively short time - a few weeks. However, frequent relapses of the disease are possible.
The body's response to illness
Since the thyroid gland affects all organs and systems in the body, symptoms can manifest themselves from different sides. For good organ performance, sufficient iodine content is necessary. However, if the body feels a lack of it for quite a long time, this can lead to a decrease in the rate of growth and cell division, which causes negative changes in the gland, as well as nodular formations.
Nodular goiter with symptoms of AIT subclinical hypothyroidism can form due to many reasons, such as:
- iodine deficiency;
- pollution and toxins;
- viral infections;
- constant stress;
- smoking;
- prolonged period of taking medications;
- genetics.
Next, questions about how to treat autoimmune thyroiditis, nodular goiter and hypothyroidism will be discussed. But first, let's look at methods of dealing with nodular formations.
By periodically visiting an endocrinologist, you can monitor the condition and health of the thyroid gland. Thanks to this, it will be possible to recognize any manifestations of disorders and begin immediate treatment. Treatment methods include the following:
- correct use of radioactive iodine;
- using medications that stop thyroid production;
- surgical intervention.
Forecast
The disease progresses quite slowly. Within fifteen years, on average, the patient feels sufficient performance and body condition. Under the influence of risk factors, relapses can develop, which are easily stopped by a course of medications.
Exacerbation of thyroiditis can be accompanied by both hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. Moreover, most often hypothyroidism as a consequence of thyroiditis in the acute phase occurs in the postpartum period in women. In other patients, thyrotoxicosis often predominates.
Hormone treatment is not always lifelong. Such a prognosis is possible only with congenital pathologies of the thyroid gland. In other cases, promptly started courses of replacement therapy with synthetic hormones are enough to reduce the dose of hormones over time and stop taking them altogether.