In the structure of gynecological diseases, polyps of the cervical canal (hereinafter referred to as polyps of the cervical canal) occupy one of the leading places (according to various sources, from 20 to 25%). Therefore, it is important for women to receive comprehensive and reliable information about this disease (types, causes, whether it needs to be removed, how to treat, etc.). The disease is often asymptomatic and is detected only during examination or ultrasound. The main method of treatment is surgical; therapeutic drugs are used to eliminate the provoking factor or cure a concomitant disease. The polyp often recurs, so preventing the recurrence of the pathology is very important. Just like regular visits to the gynecologist and monitoring the condition of your own body.
What it is
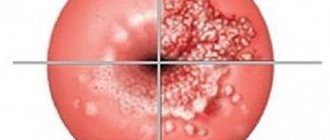
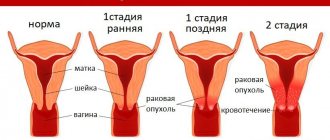
A cervical polyp is a benign neoplasm that develops as a result of excessive growth of the epithelium lining the cervical canal of the cervix. In gynecology, this is a common phenomenon, and patients with this diagnosis can be of any age. The disease is detected in young girls, in women during pregnancy, in older patients (before, after and during menopause).
A benign tumor rarely degenerates into oncology, which makes the further prognosis favorable. The neoplasm can be different:
- on a thin leg;
- with a wide base;
- single;
- multiple (polyposis);
- small (from a few millimeters);
- large (several centimeters);
- different in shape, color and consistency.
It can develop as an independent disease or occur as a concomitant with other diseases, both gynecological (for example, infectious diseases) and systemic (more often with pathologies of the endocrine system). The disease can be successfully treated, but can recur. It is often asymptomatic and does not appear for several years, and then is detected during examination, ultrasound, or during pregnancy.
Preventive routine examinations and contacting a specialized specialist at the first signs of malaise, menstrual irregularities or other problems usually accompanying gynecological diseases help in timely detection.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of cervical polyps, you must:
- avoid stressful situations and depressive episodes;
- undergo annual preventive examinations with a gynecologist;
- eliminate bad habits;
- monitor glucose levels in diabetic etiology of polyposis;
- promptly identify and treat infectious diseases of the genital organs and other diseases of the reproductive system in the form of erosions, pseudo-erosions, etc.;
- avoid casual sexual contacts;
- use barrier contraception;
- Take oral contraceptives only as prescribed by your gynecologist.
Classification
When classifying, the main feature is histological, i.e. the type of tissue from which the tumor was formed is examined. The types of cervical canal polyps are determined after removal and histological examination, but an experienced gynecologist can also preliminarily determine which type of tumor is based on its appearance. Let's learn more about the main types.
Fibrous
A fibrous polyp consists almost entirely of dense fibrous stroma; there are almost no glandular cells in the structure. It is detected more often during examination, since it does not cause severe symptoms and does not cause injury. Usually occurs in older women. It can degenerate into oncology.
Glandular
The glandular polyp is characterized as elastic and soft, which is due to the chaotically located glands. This leads to a quantitative increase in secretions. Most often occurs in young patients. Almost no degeneration into a malignant form has been recorded.
Read more in: endometrial glandular polyp
Glandular fibrous
The glandular-fibrous polyp has a mixed structure. Usually it grows up to 2.5 cm and gives a pronounced clinical picture, which facilitates the detection of pathology. The main risk is considered to be degeneration into an adenomatous polyp.
Adenomatous
Adenomatous polyp is characterized as a precancerous stage of tumor development. Prone to chaotic growth, the structure is heterogeneous, contains different types of tissue, and is densely penetrated by blood vessels with thick walls. Most often detected in postmenopausal patients, physiological changes in hormonal levels can provoke further development of the pathology.
Decidual
Decidual polyp is placed in a special category, since it develops in an existing connective tissue tumor during pregnancy. It is characterized as a decidual reaction of the polyp stroma. Changes in a woman’s body during pregnancy (in particular, the mucous membrane of the cervix) can lead to the formation of false polyps. They are an independent neoplasm and develop directly from decidual structures.
Related article: decidual polyp
Kinds
Polyps can be single or multiple. The outer part of the polyp consists of epithelial cells, the same as the cells of the mucous layer of the uterine cervix. Types of epithelium covering the polyp:
- Cylindrical
- Multi-layer and flat
By type, a uterine polyp can be:
- Fibrous;
- Glandular polyp;
- glandular fibrous polyp;
- atypical or adenomatous endometrial polyp.
| View | Description |
| Fibrous | Formed from the connective endometrial layer. It is more often diagnosed in premenopausal or menopausal women. The risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor is high. |
| Glandular fibrous | They are formed from the glandular and connective endometrial layer. Their size can be above average (from 2 cm). After therapy, patients are prescribed a course of hormonal medications and constant medical supervision to prevent relapses. |
| Glandular | One of the simplest types of education. Formed from the mucous membrane of the uterus. They are usually small and more common in young women who have not given birth. The likelihood of degeneration and reappearance after treatment or other complications is minimal. |
| Atypical | Large neoplasms with a homogeneous structure. The risk of degeneration into a malignant form is highest. Therefore, they need to be removed as quickly as possible. And the patient may be prescribed chemotherapy to prevent the development of cancer cells in the cervix or uterine cavity. |
Causes
The only reason for the appearance of a polyp inside the cervical canal has not yet been established. There are several factors that can trigger its development. These include:
- Mechanical damage, including microtrauma. There are many causes of damage to epithelial tissue. Various medical procedures, intrauterine devices (intrauterine devices), complicated births that took place using instruments (for example, obstetric forceps) or ruptures during labor lead to damage to the integrity of the tissue. In response, the body starts the regeneration process and excessive cell growth occurs.
- Various gynecological diseases. Structural - erosion, leukoplakia, etc. or inflammatory - vaginitis, endometritis and other diseases. Dysbiotic processes (long-term disturbances in the structure of normal microflora, changes in pH) can also provoke the development of a polyp.
- Genital infections and infectious inflammation of the external genital organs: often penetrate through the ascending path into the cervical canal, which provokes the development of a tumor.
- Ovarian dysfunction, accompanied by an excess of estrogen and other diseases (fibroids, endometriosis, ovarian polyposis).
- Physiological changes (puberty, pregnancy, menopause);
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity).
- Unexplained etiology: this group includes cases when the development of pathology cannot be explained by the presence of provoking factors. Risk groups include overwork and stress, although there is insufficient evidence of their impact.
As you can see, there are enough reasons for development, but their presence does not indicate the obligatory occurrence of the disease.
Causes of fibromatous polyps of the cervix
The main reason for the appearance of polyps on the cervix is associated with hormonal imbalance in the female body. But there are a number of other factors that can trigger the disease:
- Adnexitis, endometritis and other genitourinary pathologies.
- Endocervicitis.
- Erosion or fibroids of the uterus.
- Various malfunctions in the functioning of the ovaries.
- Venereal diseases.
- Thyroid dysfunction, disruption of the endocrine system.
- Decreased immunity level.
- Too active sex life, constant change of sexual partners, intimate relationships in adolescence.
- Frequent stress, nervous tension, depression.
- Surgical termination of pregnancy.
The inflammatory process in the uterus quite often develops after various surgical interventions on the reproductive organs, curettage.
The cervix can be affected as a result of traumatic effects - therapeutic or diagnostic curettage, surgical termination of pregnancy. As a result, the normal process of tissue regeneration is disrupted, which leads to pathological tissue proliferation and the formation of benign neoplasms.
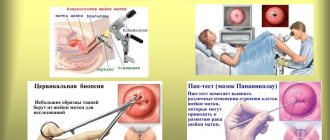
Diagnostics
Examination methods for suspected polyps or their visual detection during a gynecological examination are aimed at determining the type of neoplasm, its shape, structure and location. Diagnostics is carried out in the following ways:
- Ultrasound;
- colposcopy or cervicoscopy (the polyp is visualized). These methods make it possible to identify even very small tumors, study their structure, surface, and the presence of changes in the tissue (for example, necrosis);
- histology of the polyp after sampling (biopsy and fractional curettage of the walls of the cervix).
These tests are mandatory before the removal procedure; additional smears are taken to identify concomitant infectious and sexually transmitted diseases.
Before eliminating a polyp, it is necessary to obtain a clear understanding of its structure. Determining the type of neoplasm, as well as its qualitative characteristics (benign or malignant) is a mandatory step. Differential diagnosis helps in accurately determining the type of tumor. Its removal does not take place without an initial examination of the polyp tissue.
The results shown by histology allow the doctor to choose the correct tactics for managing the patient. And choose the treatment method that will be most effective in each specific case. What to do and which surgical method to choose is determined based on the results of differential diagnosis.
A mandatory comprehensive examination is very important; it allows not only to diagnose a polyp with maximum accuracy, but also to identify concomitant diseases. This is important, since any gynecological problems could cause its development and provoke a relapse in the future.
Symptoms
The signs that allow you to identify a polyp are very weak. In addition, they are also characteristic of other gynecological pathologies. Often the disease is generally asymptomatic. And even an examination may not reveal particularly small, deep-lying tumors. The main symptoms are:
- Changes in the menstrual cycle: spotting in the middle of the cycle, before or immediately after the end of menstruation;
- Discharge (mucoid or yellowish);
- Bleeding during contact: gynecological examination, sexual intercourse, use of a tampon;
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse, nagging pain for no reason in the lower abdomen.
If you suspect a polypous formation, you must first consult a doctor who, after examination, will prescribe additional tests and conduct a full examination of the patient. This is the only way to accurately diagnose this disease and choose an adequate treatment method.
Should I delete it?
Is removal surgery necessary? Modern medicine gives a clear answer to this question. The peculiarity of this benign tumor is its structure. Therefore, it is possible to reduce its size only by relieving inflammatory processes in the polyp itself. But at the same time, it does not dissolve and does not disappear anywhere.
Therefore, the question of whether it is necessary to use surgical methods (this is often asked by patients) is not appropriate; there are no other ways to cope with this disease.
It is necessary to remove any pathological focus that can degenerate into oncology. And such a risk, albeit small, exists, especially in older patients. All information about successful conservative treatment of this disease has not been confirmed. Most likely, the recorded facts of complete cure indicate the absence of differential diagnosis. This result is possible when pseudopolyps are detected.
Removal of a polyp of the cervical canal
There are different ways to remove a polyp in the cervical canal area. Modern surgery offers various surgical techniques. A prerequisite (regardless of the chosen tactics) is histological examination.
If necessary, scraping of tissues adjacent to the pathological focus is carried out. This is done if there are inflammatory or necrotic processes in the polyp itself, or if a malignant tumor is suspected and there is a risk of damage to neighboring tissues and organs.
The price of such an operation depends on the chosen method, the extent of the pathology, and the characteristics of the course of the disease. Typically, clinics set a gradation of prices in accordance with the surgical procedure.
Preparing for surgery
There is no special preparation for such an operation; it is usually performed in a hospital setting. After passing all the necessary tests, the patient goes to the clinic. If there are no complications, then all preparation consists of choosing the surgical technique and type of anesthesia. A prerequisite is that the operation is performed on an empty stomach. If you plan to use anesthesia, do an enema the day before (it is recommended to do it in any case to completely empty your bowels). Before the intervention, hair is removed from the external genitalia.
If there are complications in the form of infectious diseases or inflammatory processes, the operation may be postponed. Then, therapeutic drugs are initially used to eliminate complications, and only then surgical intervention is used. During pregnancy, a delay is also used if the polyp does not threaten its normal course.
Methods
In surgery, removal operations are performed using different methods. The choice of tactics is determined after examination and study of the main parameters of the tumor (presence of a stalk or wide base, shape, size, etc.). Often a woman can be offered one of the methods to choose from. Each removal method is actively used in modern medicine, all of them are tested and safe.
Let's look at how a polyp is removed (classical methods, modern methods using special equipment):
- Clamp polypectomy is a classic and proven method. It is usually chosen if the leg is long. The technique is to simply unscrew using a clamp. If there are no complications, curettage and anesthesia are not required (the procedure is painless), then the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis. Curettage after surgery is performed with a special instrument - a curette with an attachment (with a loop or in the form of a spatula).
- Removal of a polyp with a laser is recommended for small tumors (only single tumors in a mild form). Fast healing with this minimally invasive surgery will be an advantage. The recovery period takes only a few days. Laser removal is a fairly accurate method; at the time of its implementation, the doctor can change the intensity of the effect.
- Radio wave removal involves the use of a loop electrode or laser knife, followed by cauterization of the bottom using a special electrode for coagulation. The method is safe, it is used even during pregnancy, there are practically no postoperative risks. Removal using the radio wave method avoids damage to nearby tissues, bleeding and scarring after surgery.
- Hysteroscopy involves the use of a special optical device - a hyteroscope. The advantage will be the ability to assess the condition of the mucosa visually, detect even small endometrial polyps, and identify signs of cell degeneration.
- Cauterization (diathermocoagulation) is carried out using an electric knife with electric current. Often chosen when removing a tumor with a wide stalk. The technique has long been tested, accessible and widespread. But it is not prescribed to pregnant women and nulliparous women. Disadvantages include pain, prolonged healing and postoperative scar formation.
- Cryodestruction (usually with liquid nitrogen) has its advantages and disadvantages. Advantages include painlessness, no bleeding and no scarring. The last factor makes it possible to choose it for nulliparous patients. Disadvantages: prolonged healing and the impossibility of subsequent histological examination.
Anesthesia is used according to indications. Some of the described methods involve completely painless removal (this is confirmed by numerous reviews from patients). In difficult cases, along with resection of the polyp, amputation of the cervix is performed. Typically, this volume of surgical intervention is used for frequently recurrent disease and for the degeneration of cells into atypical ones (oncology).
Resection means any of the described methods; the choice of resection tactics is determined by the doctor. In some cases, an ablation is performed - removal of the uterine mucosa (but the uterus itself is not affected by such an operation); in others, more extensive intervention is required. For example, with frequent relapses in postmenopausal women, removal of the uterus may be recommended.
Does it hurt to remove
An important question that patients often ask concerns the pain of surgery. When removed, the polyp itself is usually not sensitive. The volume of surgical intervention is important (the procedure of curettage and removal by some methods is painful). The patient’s sensations depend on the chosen method, the use of anesthesia and the individual pain threshold.
Dates
How long it takes to remove a polyp directly depends on the chosen method. Only one operation is performed on an outpatient basis - classic polypectomy using a clamp. Other options require hospitalization. If there are no complications, then all postoperative symptoms usually go away quickly. The operation itself takes less than an hour.
Discharge after surgery
After the procedure, blood is usually released for several days. The duration of bleeding depends on the method. The consequences of minimally invasive surgical interventions usually end within two days. After removal followed by curettage, bleeding may last longer. Sometimes there is a discharge of the ichor type or yellow color.
Related article: discharge after polyp removal
If the method did not involve the formation of a postoperative crust, then there should be no other separations from the genital tract. When the scab is separated, the ichor is usually released on the 4th – 5th day.
Price
The price for removing a tumor depends on several factors:
- cost of initial examination and diagnostic procedures;
- volume of pathology (with or without curettage):
- the cost of removal by a certain method, for example, laser (considered the most expensive method) or conventional surgical instruments (usually the cheapest option).
How much the operation costs is usually determined by each clinic. The price can vary from 2,000 to 12,000 thousand rubles. What matters is the status of the medical institution (prestigious ones usually have higher prices), the upcoming volume of intervention, the method, the use of anesthesia, the duration of subsequent hospitalization, etc.
Reviews
Marina, 22 years old
I had the operation quite recently. Everything went quickly and painlessly. Now my periods have returned, my cycle has returned to normal, everything is fine.
Elena, 53 years old
After the doctor diagnosed me with multiple polyps, I wanted to refuse surgery. But he convinced me of its necessity. We settled on cauterization. Six months passed and a follow-up examination was done. There is no relapse, all indicators are normal.
Olga, 24 years old
The polyp was discovered only in the 5th month of pregnancy, when bleeding began, and my gynecologist diagnosed a threat of miscarriage. Before this, at 3 months there was also increased uterine tone, probably due to a polyp. They removed it literally in 10 minutes, they just “unscrewed” it. It’s not painful, it’s not scary, now all that’s left is to get the histology results.
Do I need to remove polyps in the cervix?
The management tactics for patients diagnosed with a uterine polyp (endometrial polyp) and a cervical polyp (cervical canal polyp) are different. If, in case of a polyp in the uterine cavity, surgical removal of the polyp is required - hysteroresectoscopy - and separate diagnostic curettage to assess the condition of the surrounding tissues to exclude atypia, then in the case of a cervical polyp, options are possible. This is primarily due to the very low percentage of malignancy.
Removal of polyps in the cervix (cervical canal) is necessary when:
- bloody discharge;
- inability to get pregnant;
- scanty or heavy periods;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- in postmenopause.
Depending on the patient’s age, size and location of the polyp in the cervix, the doctor may prescribe a simple polypectomy, polypectomy with separate diagnostic curettage, conservative treatment or observation. The last 2 tactics are applicable within the framework of the modern interpretation of the formation of cervical polyps. They rather have a scientific concept. Standards of medical care in the Russian Federation suggest the following type of manipulation when diagnosing a cervical polyp: - hysteroscopy with RDV for certain indications or - various methods for removing a polyp in the cervix without entering the cavity. The method of polyp removal depends on the location in the cervix and its size.
Possible methods for removing polyps in the cervix:
- the radio wave method using the Surgitron apparatus is applicable for small polyp sizes;
- unscrewing the polyp stalk and cauterizing the growth site. Used for large polyps;
- laser vaporization of a polyp is effective for small polyps, because the beam itself coagulates the vessels, reducing bleeding. It has limitations for histological examination of the polyp due to severe tissue changes when exposed to a laser beam;
- hysteroresectoscopy with separate diagnostic curettage is prescribed for postmenopausal women with bleeding symptoms, as well as for the growth of a polyp from the uterine cavity.
Scheme for diagnosis and treatment of cervical polyps:
Colposcopy is an examination of the vaginal part of the cervix using a colposcope (optical instrument). Painless and highly informative procedure.
Polypectomy is a surgical procedure for removing (excising) a polyp using various methods.
RDV (separate diagnostic curettage) (separate diagnostic curettage) is a surgical method for diagnosing and treating various pathologies of the mucous membrane of the uterus and cervix (cervical canal). Read more…
Hysteroscopy is a method of optical visualization of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and the uterine cavity, allowing to diagnose pathological changes in these organs. Read more…
This method of removing cervical polyps is recommended for all women over 27 years of age.
The laser coagulation method allows you to eliminate polyps without significant tissue damage. The method involves precise laser on tissue.
Radio wave is one of the methods for removing polyps using the Surgitron .
Histology is a highly informative diagnostic method for studying tissue cells for atypia.
Speculum examination is a gynecological procedure that allows you to examine the cervix on a chair.
Surgery to remove a cervical polyp at the Medservice clinic
The operation is done in one day. After examination, confirmation of the diagnosis and passing tests, the patient is admitted to the clinic’s operating room, where, under intravenous anesthesia, “Diprivan” is put into medicated sleep. Vital functions are monitored by the clinic’s anesthesiologist. The procedure of polypectomy (hysteroresectoscopy) followed by separate diagnostic curettage lasts no more than 20 minutes. After complete recovery, with recommendations, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy, the patient goes home. The hysteroscopy report is issued on the same day. The material from the polyp and surrounding tissues from the cavity and cervix is sent for histological examination. Based on the histology results, the doctor can prescribe appropriate treatment to exclude relapse.
| SERVICE | Cost, rub. | WHAT IS INCLUDED |
| 1. Initial appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 2 000 | Ultrasound, examination, consultation |
| 2. Tests on the day of surgery | 4 150 | Blood for HIV (600), syphilis (600 rub.), hepatitis B (450 rub.) and C (400 rub.). Coagulogram (1200 rub.) Smear (900 rub.) |
| 3. Anesthesia care | 3 900 | Intravenous anesthesia “Propofol”. Monitoring vital functions during surgery |
| Removal of cervical polyp (surgitron, laser, instrumental, cervical curettage) | 2 950 | Polypectomy |
| Histology of biomaterial from the cervix | 2 000 | Test for atypical cells |
| TOTAL | 15 000 | |
| If separate diagnostic curettage is indicated> | ||
| Surgical removal of cervical polyp by separate diagnostic curettage without / with hysteroscope | to points 1-3: +5 950 /+13 950 | Separate curettage of the cavity and cervix without/with visualization of the procedure |
| Histology of biomaterial from the uterine cavity | 2 000 | Test for atypical cells |
| Histology of biomaterial from the cervix | 2 000 | Test for atypical cells |
| TOTAL without / with hysteroscopy | 20 000/28 000 | |
Recovery period after
After the operation, it will take some time for the body to recover. The main signs of a normal process in the postoperative period will be:
- absence of any discharge;
- cycle normalization;
- reduction in the amount of blood released during menstruation;
- the duration of menstrual bleeding is reduced (reviews from women confirm this).
Recovery usually occurs quite quickly. If the signs of the development of the disease were unpleasant symptoms (they are listed above), then they usually disappear immediately after surgery.
Rehabilitation most often involves a number of restrictions:
- more careful hygiene to eliminate the risk of germs;
- It is not recommended to use tampons during menstruation (the first 2 - 3 months);
- limiting physical activity, lifting heavy objects is especially not recommended;
- It is prohibited to visit baths, saunas, take hot baths, or swim in open water;
- After surgery, sexual contact is excluded for 2 weeks.
Antibiotics in the postoperative period are taken only when indicated on the recommendation of a doctor. Contraceptive methods should be discussed with your gynecologist to avoid pregnancy in the first six months. In case of any deviations from the norm (appearance of pain, discharge of any type, unscheduled menstruation), you should see a doctor immediately. The patient is being seen by a gynecologist because... there is a risk of relapse, especially in the presence of certain concomitant diseases (most often hormonal).
Will drug therapy help?
After identifying a tumor, women are usually interested in possible treatment options. Many people want to try medical methods before the removal procedure. Does it make sense to try therapy or folk remedies? Usually, the disease cannot be cured without surgical removal. An exception would be a pseudopolyp, which can be treated with medication. As well as the decidual form, which after childbirth may disappear on its own.
The article has already mentioned that therapy is indicated before removal surgery only under certain conditions. It is used if:
- a woman has been diagnosed with an infection or sexually transmitted disease;
- in the tumor itself there are inflammatory processes with vivid symptoms, and they need to be reduced before surgery;
- it is necessary to strengthen the immune response (taking vitamins is usually recommended).
Hormonal agents should be used before and after surgery if it is necessary to reduce the level of estrogen, which is a provoking factor for the development of a number of gynecological diseases.
How does a cervical polyp affect pregnancy?
If a woman manages to become pregnant with cervical polyposis, then the disease will not affect pregnancy in any way. For small tumors, treatment is carried out after childbirth. But if the polyps are multiple and large, the doctor may order removal within the first 13 weeks of the gestational period.
Polyps can prevent pregnancy under the following circumstances:
- Disturbed hormonal levels. In this situation, an increased level of estrogen is determined, under the influence of which the uterine mucosa thickens and grows. Since estrogens are increased, the concentration of progesterone, which is responsible for pregnancy, is reduced. Such disorders lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle and ovulation, making fertilization of the egg much more difficult. Therefore, with cervical polyposis, a woman is recommended to first undergo treatment, and only then plan a pregnancy.
- Large size polyps. Such neoplasms prevent sperm from penetrating the egg. This is another reason to remove polyps before planning a pregnancy.
Folk remedies
Treatment without surgery is impossible. Therefore, doctors recommend not to waste time (to prevent the tumor from developing and to prevent its degeneration into a precancerous or cancerous tumor). The modern level of medicine makes it possible to cope with many diseases using therapeutic methods, but polyp is not one of them.
You should not pay attention to reviews about the treatment of polyps with folk remedies that confirm the effectiveness of this method. Usually we are talking about relieving symptoms; the neoplasm can decrease in size due to the attenuation of pathological processes in the polyps themselves.
But at the same time, the problem remains unresolved and over time all the symptoms will return. Official medicine is categorical on this issue.
If for other gynecological diseases (for example, with a polyp in the uterus) doctors themselves often recommend traditional methods, in this case there is no official confirmation of their effectiveness.
Folk remedies can be used instead of medications for the same purposes (normalize hormonal levels, eliminate infection, etc.). The polyp itself will need to be removed in the future.
The most popular traditional methods of treatment:
- collection of herbs (celandine, cinquefoil, chicory);
- tampons with different compositions. On the first day with a “filling” of onions baked in the oven, on the second - from a mixture of finely chopped fresh onions and laundry soap (in equal proportions) on the third - tampons with honey, cottage cheese and aloe;
- for oral administration, a mixture of yolks, pumpkin seeds and vegetable oil is recommended;
- garlic tampons;
- douching with infusion of celandine.
There are other methods that have proven effective in the fight against polyps, but when localized in the cervical canal, they usually do not bring the desired result. But they can significantly reduce the size of the tumor, remove accompanying symptoms, and improve the general condition of the body. This will certainly make further surgery less traumatic. But before you start using folk remedies, you should consult with a specialized specialist.
Cervical polyp: why does it appear and what to do with it?
A woman is most often warned that there is something wrong with her reproductive system by symptoms such as menstrual irregularities, pain in the lower abdomen, and vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. But a cervical polyp is a disease that can occur without visible external signs. We talked about it, as well as the benefits of regular preventive examinations, with Lana Taimurazovna Andieva, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Clinic Vladikavkaz.
— Lana Taimurazovna, tell us about cervical polyps: what are they?
— A cervical polyp is a benign formation that grows from the wall of the cervical canal. May have a stalk or a wide base. Depending on the morphological characteristics and the predominance of one or another type of tissue, polyps are glandular, fibrous and glandular-fibrous.
— Why do polyps appear on the cervix?
— The causes of the development of polyps can be inflammation, hormonal disorders, trauma to the cervix due to childbirth or surgery, including abortion.
70% of patients with cervical polyps are patients with chronic inflammatory processes of the female genital organs: endometritis, salpingo-oophoritis, cervicitis, colpitis, etc. Cervical polyps, which are formed due to hormonal disorders, accompany cervical fibroids or endometrial hyperplastic processes . The disease occurs in women who have given birth many times, as well as those who have had numerous abortions in history or any operations on the cervix that led to injury to the cervical canal.
Read material on the topic:
Fear has big eyes. Is fibroids really that dangerous?
— What are the symptoms of cervical polyps?
— The disease can be asymptomatic and discovered accidentally during a vaginal examination, ultrasound or colposcopy. The patient may also be brought to us by bloody discharge from the genital tract after sexual intercourse; menstrual irregularities, which are expressed in an increase in the intensity of blood discharge; the appearance of intermenstrual spotting, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, serous or serous-purulent discharge.
Hysteroscopy
— What diagnostics may be required to confirm the diagnosis?
- Hysteroscopy helps to fully describe the formation, see where it comes from, its size. Ultrasound and colposcopy can detect a cervical polyp, but they may not notice it if the polyp does not protrude into the vagina, but remains in the canal. And examination with a hysteroscope gives us the opportunity to examine the cervical canal from the inside.
Read more about gynecological ultrasound in our article
— Is it necessary to remove a polyp on the cervix? Is it possible to get rid of this formation without surgery?
“It definitely needs to be removed.” It is impossible to cure a cervical polyp with conservative therapy, without surgery. Removal of a polyp in the cervix is a surgical procedure, after which a histological examination of the removed material is required.
— What methods exist for removing cervical polyps?
— The most optimal, I think, is the radio wave method. In our clinic we have a Fotek device, which can perfectly remove polyps of the cervical canal. It has many advantages. Among them are the accuracy of the section, the thinness of the incision, minimal trauma to the tissue in the surgical area, a significant reduction in pain during operations, as well as a smoother course of the postoperative period. Plus, the procedure is almost bloodless, since coagulation (“sealing”) of the vessels is carried out at the same time.
There is also a method when this operation is performed under the control of a hysteroresectoscope, and a method when the cervical canal is curetted to remove polyps. But with the Fotek device, in my opinion, this can be done much better - both in terms of rehabilitation and the operation itself.
— Is anesthesia used when removing a cervical polyp?
— If separate diagnostic curettage is performed, or the polyp is removed in a hospital setting, then a short-term anesthesia is given. But, as a rule, it is enough to locally anesthetize the neck, and the operation will be easy. It will not cause any discomfort to the patient.
— Why is a polyp on the cervix dangerous? What will happen if it is not treated?
— A polyp on the cervix does not often become malignant. Maximum up to 10% of cases. However, if such a risk exists, the polyp must be removed and subjected to histological examination.
— Is it possible to prevent the disease?
- Here we will return again to the reasons that cause the development of cervical polyps. It is necessary to visit a gynecologist in a timely manner, monitor the cleanliness of the vagina, be sure to get tested for sexually transmitted infections, treat inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in a timely manner, and pay attention to hormonal abnormalities. During surgical interventions, perform manipulations in the cervical canal as carefully as possible, without injuring the cervix. But the last point no longer depends on the patient, but only on the doctor.
You can make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
The editors recommend:
Myths and truth about cervical erosion Endometriosis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What does a pelvic MRI show in women? Precancer: to be afraid or not to pay attention?
For reference:
Andieva Lana Taimurazovna
Graduate of the North Ossetian State Medical Academy in 1999.
In 2002 she completed her residency. She specialized in colposcopy at the Rostov Oncology Research Institute, and in radio wave surgery at the Center for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology in Krasnodar.
Currently, he is an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Clinic Vladikavkaz.
Receives at the address: st. Barbashova, 64a.
What is the danger
If you do not seek qualified medical help, self-medicate, or ignore dangerous symptoms, complications may occur. The most harmless of them are the further development of the pathological process and polyposis.
Complications without removal are as follows:
- anemia due to regular bleeding;
- degeneration of cells into atypical ones (oncology);
- blockage of the cervical canal by an overgrown tumor and the development of hematometra (accumulation of menstrual blood in the uterus with subsequent inflammation, sepsis and death);
- risk of uterine bleeding;
- necrotic processes in the tumor itself;
- during pregnancy – threat of miscarriage or miscarriage.
These are the consequences if the growth is not removed in a timely manner. Hysteroscopy and histological examination will help in differential diagnosis. If it turns out that an outwardly similar neoplasm is actually a pseudopolyp, sarcoma, or submucous uterine fibroid, then the treatment tactics may be changed. For example, it is strictly prohibited to remove pseudopolyps. Their cellular structure is completely different, and attempting surgery will result in bleeding.
Making an erroneous diagnosis is practically impossible with the modern level of medicine. Therefore, if the gynecologist talks about the need for surgery, you should agree. This will help avoid various serious complications.
Folk remedies in the treatment of cervical polyps
Folk remedies for cervical polyposis are not particularly effective, and in no way affect either the cause of the disease or the areas of altered tissue. In addition, this disease is fraught with the development of cancer, so you should not take risks and decide on such therapy.
The danger of self-medication using alternative medicine methods also lies in the fact that most prescriptions involve intravaginal insertion of tampons, or douching with medicinal solutions or decoctions. Such rash actions can lead to serious complications.
If you have cervical polyposis, nothing should be done without first consulting a gynecological oncologist. In some cases, oral use of decoctions or infusions of medicinal plants is allowed, but strictly according to the regimen developed by the doctor. For this, the patient may need additional consultation with a herbalist.
Is it possible to have sex
The following factors should be considered when answering this question:
- after the endocervical polyps have been removed, the minimum break in intimate life should be 2 weeks;
- Polyps of the endocervical canal of the cervix are usually removed after the end of menstruation, and no later than after 10 days. Consequently, by the time postoperative rehabilitation is completed, the woman may begin her next period (especially if the cycle is unstable). Therefore, the break in intimate life will be increased until it ends completely;
- If complications arise (spotting, bleeding, discharge), you should visit a gynecologist before resuming intimate life.
Technique for polypectomy of the uterus, cervix and cervical canal
Before starting any treatment, diagnostic procedures are prescribed: general clinical laboratory tests (blood, urine, feces to assess the woman’s somatic condition). Next, a hysteroscopic examination is performed to perform a tissue biopsy to determine the nature of the polypous growths.
The manipulation is carried out 10 days before the active phase of the menstrual cycle or immediately after the end of menstruation. This period is most favorable for complete visualization of the condition of the mucous membranes.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, so additional testing is carried out for allergic reactions to sedatives. In rare cases, polypectomy is performed under local anesthesia.
The preparatory period includes following a gentle diet and antibacterial treatment of inflammatory processes if present. An important assessment in carrying out safe removal is the degree of cleanliness of the vagina.
After laying the women on the couch and anesthetizing them, a number of the following manipulations are carried out::
- Expansion of the cervical canal;
- Insertion of a probe with a video camera and lighting into the uterine cavity;
- Detection and resection of polypous lesions;
- Coagulation of blood vessels in the wound surface.
The total duration of the manipulation does not exceed 30 minutes. The resulting samples of removed polyps are sent for histological examination. Histology allows you to assess the degree of potential cancer risks for a woman.
Even with timely diagnosis and removal of growths, they are prone to relapse, so not only the wounds are cauterized, but also the pathologically altered endometrium is scraped out. Curettage alone is not effective against polyps, so the procedure is combined simultaneously with hysteroscopy. Curettage is also performed under general anesthesia.
Polypectomy of growths of different localization does not differ in execution techniques. Thus, for polyps of the cervical canal, cervix and uterine cavity, general curettage and combined removal methods can be used.
When polyps are removed from the uterine cavity, an additional expansion of the cervical canal occurs. There are no other fundamental differences in the removal technique.
Laser uterine polypectomy
Laser polypectomy is a progressive, but more controversial method of treating polyps of the internal genital organs.
- On the one hand, laser is a bloodless removal method that helps prevent the formation of adhesions and scarring.
- On the other hand, laser cauterization provokes strong smoke, which makes it difficult to visualize what is happening and does not allow an adequate assessment of the condition of the wound surface.
It is the lack of control over what is happening during the manipulation that determines the degree of various postoperative complications.
The disadvantages of laser removal are the high cost of the procedure. Not every clinic can afford the placement of modern equipment with multiple optional characteristics.
Possibility of relapse
Treatment is necessarily surgical. After this, the woman is considered completely cured, but remains at risk and should be under constant medical supervision.
This means that relapse is possible.
The patient is given an individual schedule of visits, but an unscheduled appointment is also possible if any alarming symptoms reappear. Reviews and statistics indicate that recurrent polyps of the cervical canal are not a common occurrence.
Recurrent polyp is usually associated with provoking factors. That is, if the disease was initially caused by a hormonal imbalance, then without its stabilization the risk of relapse increases. This applies to any reason. Women during menopause are at risk; they have the most frequent recurrences.
Symptoms and signs
With a polyp of the cervical canal, the symptoms appear as follows:
- Bleeding. They occur during physical activity and sexual intercourse when the tumor grows in the vagina. Discharge from a polyp of the cervical canal indicates damage to the growth. Minor bleeding may occur a few days before or after your period. The appearance of bloody discharge in elderly women may indicate malignant degeneration of tumors.
- Mucous or purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor. Evidence of infection.
- Pain. With cervical polyps, the symptom appears when the tumor reaches a large size. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the lumbar region and lower abdomen. During sexual intercourse, the pain intensifies, which is a sign of injury to the growth.
- Menstrual irregularities. The presence of benign neoplasms in the cervical canal contributes to an increase in the duration of menstruation. This is due to an increase in estrogen levels, which contributes to the thickening of the endometrium. Frequent heavy bleeding leads to the development of anemia.
- Infertility. The inability to conceive is associated both with hormonal imbalance and the presence of a mechanical obstacle that prevents sperm from penetrating into the uterus.