Causes of fluid accumulation
Sometimes fluid behind the uterus appears due to an ectopic pregnancy; in this case, an ultrasound does not detect a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. However, the patient's pregnancy test will show a positive result.
Also, fluid in the cavity behind the uterus is diagnosed on ultrasound due to endometriosis. The disease is characterized by the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus. Endometrial cells bleed during menstruation, which causes blood to appear in the abdominal cavity.
In addition, fluid behind the uterus is detected on ultrasound with purulent salpingitis, endometritis, rupture of the ovary or its cyst. A large volume of fluid indicates more serious diseases, such as malignant ovarian tumors and a number of other pathologies (heart or kidney failure, cirrhosis of the liver), as well as heavy internal bleeding due to injuries in the abdominal area.
Fluid behind the uterus during ovulation
When the dominant follicle ruptures, its contents enter the retroperitoneal space. In this case, the specialist may detect some fluid around the uterus on the ultrasound image. Soon after ovulation it will resolve without treatment or health consequences.
Fluid behind the uterus with inflammation
Sometimes inflammatory processes cause the appearance of exudative fluid in the abdominal cavity and behind the uterus; ultrasound can reliably diagnose it. As a rule, this occurs due to rupture of the pyosalpinx, an accumulation of pus in the lumen of the fallopian tubes. If an ultrasound showed fluid in the uterus, inflammation of the genitourinary organs is possible.
The inflammatory process is accompanied by fever and pain in the lower abdomen. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist may prescribe medication (antibiotics) or recommend surgery.
https://youtu.be/4teq1nZBbXs
Fluid in the uterine cavity
Fluid can be found not only in the uterine cavity, but also in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and in the posterior fornix. As a rule, its formation is provoked by various problems with bearing a fetus, or rather, abortions, curettage and miscarriages. However, doctors also name other reasons:
- Sexual relations with many men.
- Injury to the tissue of the uterus or cervical canal (for example, after an abortion or surgery).
- Alcohol, nicotine.
Girls with hormonal imbalances, following various diets not approved by a doctor, and leading a sedentary lifestyle are also at risk.
Fluid also forms after endometriosis, inflammatory processes (adnexitis, salpingitis), and ectopic pregnancy.
Only timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid serious consequences.
The composition of the fluid formed in the uterus can be different:
- Serozometer - if there is serous fluid in the organ.
- Lochiometra - postpartum discharge has accumulated.
- Pyometra - due to an infectious-inflammatory process, fluid containing pus accumulates.
- Hematometra - the cavity is filled with blood.
Let's look at each situation in more detail.
Amniotic fluid
When pregnancy occurs, the uterus and its cavity increase significantly in size. The weight of the organ increases from 40–60 g to 2–2.5 kg by the end of pregnancy, the longitudinal size from 4–5 cm reaches 40 cm by the time of delivery. The cavity, being a receptacle for the fruit, is filled with the amniotic sac. On the eve of birth, it contains about 3500 g of fetus and up to 1500 ml of amniotic fluid.
The first fluid in the uterine cavity appears already in the second week of pregnancy. It is delimited from the walls of the organ by two layers of the fetal bladder - the chorion and amnion, and is called amniotic fluid. It consists of water with proteins and salts dissolved in it, and is of enormous importance for a developing baby:
- Maintains temperature.
- The first time is a nutrient medium.
- Absorbs shocks (suddenly mom suddenly stood up or ran).
- Silences external noise.
- During childbirth, it helps open the cervix.
The course of pregnancy can be complicated by deviations from the normal amount of amniotic fluid. Polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios can be detected by various signs, including ultrasound. The reasons for these deviations are varied, one of them is the presence of infection in the body of the expectant mother - the so-called chorioamnionitis.
The amniotic fluid may break before the due date. This situation requires immediate hospitalization of the pregnant woman in the maternity hospital, where, after an ultrasound, the issue of pregnancy management tactics is decided.
Lochiometra
This complication occurs in some girls after childbirth. The normal postpartum period is characterized by a contraction of the postpartum uterus to normal size, which is accompanied by specific discharge from the genital tract. These secretions are called lochia. From bloody in the first 3 days after birth they turn into bloody, then into light yellow serous.
Sometimes, 5–9 days after birth, there is a cessation of lochia secretion, while the uterus does not shrink, but increases in size. The postpartum woman complains of pain in the lower abdomen, soon the temperature rises, and tachycardia appears. This is a lochiometer.
The reasons for its occurrence are that there is an obstacle to the normal outflow of lochia due to the closure of the cervical canal, which means they accumulate in the uterine cavity, stretching it. The canal can be closed by fragments of membranes and blood clots. During a vaginal examination, the diagnosis does not cause difficulties; ultrasound is performed for clarification.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment must be started immediately. Appointed:
- Antispasmodics to relieve cervical spasms.
- Reducing means.
- Antibiotics to prevent metroendometritis.
- During examination, a digital expansion of the cervical canal is performed.
If the measures taken are not enough to empty the cavity of lochia, the doctor performs curettage of the uterus.
Hematometer
This situation is observed in the postoperative period, usually in the first day after an abortion or diagnostic curettage. The reasons are similar to the lochiometer - early closure of the cervical canal with continued bleeding from the wound surface.
Symptoms:
- During the examination, a spherically swollen uterus is discovered, enlarged in size and painful.
- The cervical canal is closed.
When the hematometra is emptied by curettage or aspiration, a large number of blood clots are released. It is possible to perform the intervention under hysteroscopy control.
Bimanual examination and ultrasound help in diagnosis.
Hematometra can occur due to abnormalities in the development of the organ. In this case, menstrual blood gradually accumulates in the closed uterine horn, causing pain in the lower abdomen.
Decoding the result
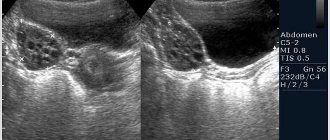
Determining the exact volume of fluid behind the uterus using ultrasound data can be difficult due to the two-dimensional nature of the image. In addition, the fluid spreads between the organs, which also makes it difficult to determine its exact volume. In modern medicine, it is customary to distinguish the height of the formation, correlating the volume of liquid with it. With a height of up to 10 mm, the volume of liquid is considered insignificant, from 10 to 50 mm - moderate. At a height of more than 50 mm, the volume of fluid behind the uterus, diagnosed by ultrasound, is considered significant.
Monitoring of a pregnant woman is carried out from the first days when she registered at the clinic. It is possible that after an ultrasound examination, the doctor sees fluid in the retrouterine space, although this should not be the case. Is this dangerous for the fetus and the expectant mother? By the way, this trouble can also manifest itself in those who are not expecting the birth of a child. Let's try to find the answer to this question.
The retrouterine space, which doctors call Douglas space, in its normal state is a closed cavity located behind the uterus and limited by the peritoneum. Free fluid usually accumulates in the lowest recess of this cavity when viewed relative to the abdominal cavity.
It is necessary to monitor your own health even in cases where there are no obvious reasons for concern. Regular visits to the gynecologist are mandatory; ignoring visits to him is unforgivable frivolity for women at any age.
The female condition can be considered normal in cases where the retrouterine space does not contain fluid. But there are times when a little liquid may be present there without threatening women’s health. The cyclical processes occurring in the body of every woman are “to blame.”
- Reflux of blood into the peritoneal cavity during the menstrual cycle. This is absolutely not dangerous - during menstruation, the endometrium, along with the secreted menstrual blood, “moves” to the abdominal area.
- Ovulation, in which the follicle capsule ruptures and the free egg, ready for fertilization, comes out. The small amount of fluid released during this process will disappear without treatment after a few days; it is absorbed.
- Even girls can have fluid in the space behind the uterus. This may be a consequence of premature puberty. But the final diagnosis will be made by the doctor after the necessary examination has been carried out.
The doctor, most often, does not make an immediate diagnosis, leaving some time to monitor the situation. If the fluid has resolved, then this is a sign of the normal completion of the ovulation process.
If the above cases, in which fluid appeared in the retrouterine space, do not require special treatment, since they do not pose a danger, then a completely different attitude should be taken towards the causes caused by diseases. In itself, the presence of fluid is not a disease, but an important symptom of an illness, sometimes very serious.
- Inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity.
- The presence of polyps on the uterus.
- Diseases of organs that are located near the uterus - ovaries, bladder, fallopian tubes. These are pelvioperitonitis, liver diseases, heart or kidney failure. Organs affected by the disease can secrete an exudative substance and, in some diseases, the doctor will find free fluid in the space behind the uterus. With pelvioperitonitis, peritoneal fluid enters the retrouterine space, the amount of which can be very significant.
- After a recent artificial termination of pregnancy - abortion, the possibility of the presence of fluid in the retrouterine space cannot be ruled out.
- Ectopic pregnancy. The fluid in this case is blood, which may be caused by deformation or damage to the fallopian tube. It is on it that the fertilized egg that has not reached the uterus is most often attached.
- Malignant neoplasms in the abdominal cavity or pelvic area. Thus, an ovarian tumor is accompanied by ascites, when fluid accumulates in the peritoneal cavity. To exclude the formation of neoplasms, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be required. Only with their help can you “see” and diagnose a tumor.
- Anoplexia is ovarian rupture.
- Endometrioid cysts on the ovaries. Cavity formation of a pathological nature on the surface of the ovaries. This is menstrual blood contained in a membrane of endometrial cells. Due to microperforation of the cyst, blood leaks out. The presence of a cyst is accompanied by a number of additional symptoms: abdominal pain, sometimes very acute, menstrual irregularities, heavy menstruation.
- Purulent salpingitis. Purulent fluid may appear as a result of rupture of the pyosalpinx. Additional symptoms include fever, painful abdomen, and leukocytosis. There is a high probability of developing diffuse peritonitis and, as a consequence, immediate surgical intervention.
To accurately diagnose the disease that caused fluid to appear in the retrouterine space, a mandatory cytological examination of the fluid is required. You also need to be aware of additional symptoms. They are usually present if the fluid is caused by a medical condition.
Although indirect, there are factors that can increase the likelihood of fluid appearing behind the uterus.
Summary
There is no particular cause for concern if fluid is detected in the retrouterine space. But you should not neglect consultation with the doctor who is monitoring the pregnancy - it is better to be safe. Good luck
All women are advised to visit a gynecologist regularly. Often representatives of the fair sex neglect this instruction and go to see a doctor only after any complaints appear. But we should not forget that many ailments, including those in the intimate area, may not manifest themselves for a long time.
This is how the fluid behaves in the retrouterine space. In itself, this phenomenon is asymptomatic and is diagnosed unexpectedly for a woman. It does not always indicate pathology, but it is not an absolute norm either.
In gynecology, there are cases when fluid is formed during the process of ovulation. This is considered a possible variant of the norm. The follicles contain a small amount of fluid, and if it ruptures, it can accumulate behind the uterus. The woman does not feel any discomfort due to this, and the liquid resolves on its own after a few days.
But in other cases, fluid accumulation is a deviation from the norm. This condition can be attributed to symptoms of various diseases. For example, this can happen with inflammation of the pelvic organs. Fluid can accumulate after a miscarriage or abortion, or ovarian rupture. An ovarian or uterine cyst may rupture and leak contents. Any surgical intervention on internal organs can cause fluid formation.
Serious illnesses, as a rule, manifest themselves with a number of symptoms, but sometimes you can find out about the illness only after an examination. Even a small amount of fluid formed behind the uterus can be seen and recognized by an ultrasound diagnostic specialist. Ultrasound examination, in some cases, will help to understand the cause of this phenomenon, indicating the affected, painful organ.
If pathological phenomena are suspected, the doctor will definitely prescribe additional tests and puncture. For example, the presence of blood in the fluid indicates an ectopic pregnancy. And this requires immediate doctor intervention. A fairly common cause of fluid accumulation is a female disease such as endometriosis in chronic and acute forms. The overgrown endometrial tissue bleeds, and this content can fill the empty space behind the uterus.
Other reasons that led to the accumulation of fluid in the retrouterine space may be:
- uterine polyps;
- salpingitis and oophoritis;
- neoplasms in the pelvis;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- bleeding in the abdominal cavity.
Some illnesses can cause large amounts of fluid to accumulate in the abdominal cavity. Ascites, as this phenomenon is called, is most often not associated with gynecological diseases. It is provoked by cirrhosis of the liver, neoplasms of internal organs, heart disease, and poor nutrition with a small amount of protein. The main symptom of this condition will be an increase in the volume of the abdomen, its bulging.
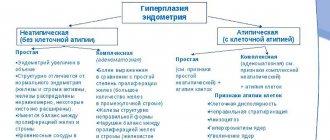
Serozometra - what is it?
Fluid can accumulate not only behind the uterus, but also in the reproductive organ itself. This condition in gynecology is called serozometra. It has more serious causes and always speaks of a pathological process. Mucus, blood, and pus may accumulate. A disorder associated with poor discharge of postpartum discharge (lochia) is called lochometra.
Very often, serozometra is a consequence of sudden hormonal changes in the body, for example, during the premenopausal period. The volume of fluid may be insignificant, diagnosed only during ultrasound. And it can reach very impressive volumes, with the uterus enlarging so much that it can be felt in the lower abdomen. Serozometra is characterized by certain symptoms; they occur in combination or only a few occur individually.
The first thing a woman may notice is a nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen, which can appear regardless of the menstrual cycle. A common symptom is profuse, thin, grayish discharge. A woman may notice difficulty or frequent urination, a slight increase in body temperature to 37–38 degrees, and pain during intercourse.
Treatment for serozometra begins with cleansing the uterine cavity and removing fluid from it. A histological examination is carried out to refute or confirm the development of cancer. If the serosometer is of bacterial origin, then a course of antibiotics is necessary. The final stage is aimed at consolidating the result and improving the body’s protective functions.
If, as a result of an ultrasound examination, fluid was detected in the pelvic area, then this is a reason to visit a gynecologist. If additional examination indicates the pathological nature of the condition, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Since fluid accumulation behind the uterus is not classified as a separate disease, treatment is prescribed based on the cause. For example, if endometriosis is confirmed in the early stages, conservative methods are possible, including hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed - removal of overgrown areas of the endometrium using laparoscopy. If the reason is not related to gynecology, the doctor will refer the woman to another specialist who can prescribe her the necessary treatment.
After getting rid of the disease, you should reconsider your attitude towards health. Once every six months it is necessary to undergo ultrasound diagnostics and visit the doctor of the profile who performed the treatment. Do not forget about regular visits to the gynecologist, at least once a year.
This is a kind of preventive measure that will save your health, help to promptly identify fluid in the retrouterine space and quickly get rid of it.
Popular articles
- The success of a particular plastic surgery largely depends on how...
Lasers in cosmetology are used quite widely for hair removal, so...
Regular visits to the gynecologist are not a whim of the doctors themselves. All representatives of the fair sex should visit a doctor several times a year. Often women neglect this instruction and come for examination only when any signs appear. However, one should not lose sight of the fact that some pathologies in the reproductive organs may not appear for a long time. This is how the fluid behind the uterus behaves, the detection of which most often comes as a surprise to the woman.
Liquid formations: natural process or pathology?
The presence of free water in the Douglas space is not a disease, but may be a symptom of pathology. Fluid behind the reproductive organ or in the paraovarian areas accumulates in the middle of the menstrual cycle, after the onset of the ovulation process. This is a normal phenomenon and does not require specific treatment. It means the release of the egg from the follicle and the possible occurrence of pregnancy.
Quite often, free fluid behind the uterus is a sign of pathology of a woman’s internal organs. It is extremely difficult to determine the exact volume of such a formation on ultrasound, because it spreads between the reproductive organs. Doctors have developed certain criteria to assess the condition of the fluid in the retrouterine space (the length of the vertical level of the formation is measured):
- accumulation of water up to 10 mm is considered insignificant;
- from 10 mm to 50 mm - moderate stage;
- more than 50 mm - significant.
The volume of water behind the uterus is compared with the woman’s menstrual cycle. If the doctor has suspicions about the cause of the presence of a large amount of water behind the uterus, he may order additional instrumental tests.
Ovulation process as one of the reasons
Ovulation is a natural process in which water accumulates in the pouch of Douglas. It does not cause serious problems, since a small amount of liquid is formed. The ovulation process occurs as follows:
- follicles are formed first;
- one of the vesicles outstrips the growth of the others, and the formation of an egg occurs in it;
- liquid formation reaches up to 20-25 mm in diameter;
- then the follicle ruptures so that the egg leaves the membrane and begins to move towards the reproductive organ.
In a healthy woman, the ovulation process occurs monthly. When a cell is released from the follicle and travels to the uterus, this is ovulation. There is fluid in the follicle, but it is very small. If the bubble ruptures, water can enter the abdominal cavity. On an ultrasound, the doctor will see a small amount of it, which is normal. The liquid resolves after a few days and does not cause any discomfort to the woman. In addition to ovulation, the formation of water in the retrouterine space can occur for such natural reasons as early puberty, menstruation.
Formation of hemorrhage in the pouch of Douglas
The fluid behind the uterus may be bloody. This kind of education is not the norm. The occurrence of bloody discharge in the pouch of Douglas means the presence of a pathology that can lead to the formation of apoplexy. Causes of hemorrhage:
- vessel rupture;
- the presence of a follicle cyst;
- ovarian cyst or stroma.
After the integrity of the ovarian tissue is broken, water is released into the abdominal cavity. The formation of bloody fluid in the retrouterine space causes pain, weakness, and dizziness. In this case, the woman experiences discharge of a characteristic color - red or dark brown.
Liquid in the space of Douglas may turn into clots. The main reasons for this phenomenon are:
- permanent injuries;
- hard sex;
- lifting weights;
- hyperemia;
- inflammatory process;
- dilated vessels.
Such pathologies cannot be allowed to occur. If a girl knows about the presence of diseases in the female part, then she should visit a gynecologist and be treated to prevent apoplexy and subsequent penetration of fluid into the retrouterine space.
Examination required if there is a suspicion of an inflammation process
Liquid in this space can accumulate against the background of natural processes, which should not frighten a woman:
- In girls and young women during early puberty, excess fluid may be observed in the cavity. The gynecologist will check the problem and diagnose the norm.
- Menstruation. During menstruation, bloody discharge can be thrown into the pouch of Douglas. In this case there is also no reason to worry. During menstruation, the endometrium, together with secretions, enters the abdominal cavity.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cosamomglavnom
Currently, although relevant clinical studies are being conducted, there is no accurate way to determine the safe amount of fluid accumulating in the pouch of Douglas. There are suggestions that it should not exceed 20 ml.
A schematic diagram of the pouch of Douglas in women is shown in the photo below.
The space itself has a rather small volume, but the amount of fluid accumulated in it depends on the constitutional characteristics of the female body and the parameters of the small pelvis.
If fluid accumulates in the pouch of Douglas, and the clinical picture is supplemented by abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, and dizziness, the gynecologist may recommend the following diagnostic techniques and tests:
- A standard laboratory test of blood samples, including determination of the leukocyte formula.
- Laboratory testing of urine samples.
- Determination of pain upon palpation of certain areas of the pelvis.
- Additional pelvic ultrasound.
- Diagnostic puncture of the fluid followed by its bacteriological examination.
In cases where the results of bacteriological examination of the punctured fluid are negative, the pouch of Douglas does not contain pus or blood. The liquid will be clean and transparent.
Receiving blood that does not contain clots indicates that there is bleeding inside the peritoneum, caused by an ectopic pregnancy, rupture of a cyst or spleen.
When, according to the results of a bacteriological examination, pus is detected in the extracted fluid, the specialist concludes that an inflammatory process is occurring in the female body. That is, only additional examination and tests provide grounds for concern.
We looked at the reasons why fluid accumulates in the pouch of Douglas in women.
Other conditions for the formation of pathology
The formation of water in the Douglas space is often the cause of some pathological process occurring in the internal reproductive organs of a woman. Doctors identify many diseases that can lead to fluid accumulation. These include the following pathologies:
- inflammatory process in the surface layer of the endometrium (endometritis);
- inflammation in the kidneys, liver, heart failure lead to the formation of ascites, as a result of which free fluid flows into the pelvic organs;
- benign formations characterized by limited growth of the endometrium in the form of a tubercle on a thin stalk;
- an infectious disease accompanied by unilateral or bilateral inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis);
- adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes);
- oophoritis.
The formation of fluid in the pouch of Douglas may indicate the presence of an ectopic pregnancy, in which a pregnancy test will show a positive result. In addition, this phenomenon causes endometriosis, the appearance of endometrioid cysts on the ovaries, and a condition after an abortion. If you find an accumulation of fluid behind the uterus on an ultrasound, you should not panic. A competent doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment, consult the patient and give recommendations on tactics for the woman’s further actions.
The pouch of Douglas, or retrouterine space, is an anatomical space located in the posterior part of the woman's pelvis. It is located between the posterior wall of the uterus, the cervix, the posterior vaginal fornix and the anterior wall of the rectum. In physiological terms, the pouch of Douglas is said to be free, meaning it does not contain fluid or tissue.
The presence of traces of fluid in the retrouterine space may indicate ovulation, and in this case there is no cause for concern. A larger volume of fluid can be visualized during transvaginal ultrasound. It is always necessary to determine the nature of the detected secretion - bloody fluid, peritoneal fluid (ascites), pus, etc. For this purpose, a diagnostic puncture of the retrouterine space is often performed to obtain material for research and determine the probable cause of fluid accumulation.
The reasons for the presence of fluid in the pouch of Douglas are usually diseases of the genital organs, but not always. If fluid in the retrouterine space appears on certain days of the menstrual cycle, there is no reason to worry.
Sexually mature women and girls regularly - especially immediately after ovulation (just after half of the cycle) - have a small amount of free fluid. However, if the presence of fluid is detected in the first phase of the cycle or at the end of the second, and in large quantities, then pathology of the uterine appendages or abdominal cavity can be suspected.
Deadlines
If fluid is detected in the pouch of Douglas during an ultrasound, it is very important to determine the time when it formed. If this happened after ovulation occurred, then it is probably here for about 2-3 days.
When the presence of fluid is accompanied by symptoms of an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs, we can assume the spread of inflammation and the occurrence of purulent reactions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertise
In such a case, a woman should not ignore the results of an ultrasound examination. It is important to undergo additional examination prescribed by your doctor.
When is fluid puncture required in the pouch of Douglas in women?
Fluid in the retrouterine space causes
The most common causes of fluid behind the uterus are diseases:
- rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- dropsy of the ovary;
- endometriosis;
- rupture of an ectopic pregnancy;
- adnexitis;
- ovarian cancer;
- peritonitis;
- enteritis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- ovarian hyperstimulation (after hormonal stimulation).
Depending on the nature of the fluid behind the uterus:
The presence of bloody fluid behind the uterus may result from:
- bleeding into the abdominal cavity from the pelvic organs,
- rupture of ectopic pregnancy,
- rupture of ovarian cysts,
- presence of foci of peritoneal endometriosis.
A large amount of ascites (peritoneal) fluid may be due to:
- female genital cancer (ovarian, fallopian tube, cervical cancer),
- cirrhosis of the liver,
- circulatory failure.
The presence of purulent fluid may indicate:
- inflammation of the pelvis (for example, appendages);
- or abdominal cavity (eg, peritonitis, inflammatory bowel disease).
Diseases in which there is free fluid in the space of Douglas
Ovarian cyst rupture
An ovarian cyst is an abnormal space inside the ovary, surrounded by a wall. There are several types of ovarian cysts: simple, filled with serous fluid, dermoid cysts and endometrial cysts (chocolate cysts that form during the process of endometriosis). Sometimes a cyst can form at the site of an unruptured follicle during ovulation - this type of cyst is usually absorbed spontaneously. Unfortunately, it can also happen that a cyst in the ovary indicates the presence of cancer. Cysts may sometimes cause no symptoms and are discovered incidentally during a routine abdominal ultrasound. Sometimes, however, their presence can cause various ailments:
- menstrual irregularities,
- irregular bleeding not associated with the monthly cycle,
- abdominal pain,
- pain in the ovarian area where the cyst is located.
It happens that the cyst ruptures, then the woman feels severe pain, and during an abdominal ultrasound they find the presence of fluid in the retrouterine space. Treatment of cysts, if they do not give any symptoms, can only consist of their systematic observation. However, if cysts cause problems or grow larger, they require removal (either laparoscopically or traditionally depending on the type of cyst).
Rupture of an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy
When does ectopic pregnancy occur? An ectopic pregnancy occurs when fertilized eggs implant in a location other than the uterine body. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is estimated to be approximately 1% of all pregnancies. The most common site of ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian tube. In fact, the embryo can implant almost anywhere: in the cervix, ovary or abdominal cavity. The most dangerous for a woman’s health and life is abdominal or cervical pregnancy, but, fortunately, they occur very rarely.
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy? During an ectopic pregnancy, abnormal discharge and bleeding may occur, in addition, there may be abdominal pain and sometimes difficulty defecating. In a situation where an ectopic pregnancy ruptures, acute abdominal pain appears while an ultrasound examination will reveal fluid in the pouch of Douglas. Treatment for ectopic pregnancy is always surgical.
Inflammation of the appendages
Adnexitis is characterized by the so-called ascending path - vaginal microbes enter the higher organs of the female reproductive system. Until recently, the most common pathogen causing inflammation of the appendages was gonococcus. Currently, due to a significant decrease in the incidence of gonorrhea, the bacterium is no longer the most common organism. The etiological factors of adnexitis also include the following pathogens:
- chlamydia;
- Mycoplasma genitalis and other mycoplasmas;
- coli;
- group B streptococci and other streptococci;
- Gardnerella gardnerella vaginalis.
Chlamydia and gonococci have the greatest share in the formation of infection leading to inflammation of the appendages.
What symptoms does adnexitis cause? First of all, there may be pain in the lower abdomen, usually the pain is bilateral. In addition, dyspareunia (pain during intercourse) may be present, as well as abnormal discharge from the genital tract associated with inflammation of the cervix or vagina. Abnormal bleeding occurs - intermenstrual bleeding or very heavy menstrual bleeding and a fever above 38 C. An ultrasound examination may reveal the presence of fluid behind the uterus. Treatment of inflammation of the appendages consists of the use of antibiotics and symptomatic therapy.
Ovarian cancer
This cancer does not cause any symptoms for a long time, the presence of symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen, abdominal enlargement or vaginal bleeding, unfortunately, indicate the severity of the cancer.
Peritonitis
The presence of purulent fluid in the retrouterine space may indicate the presence of peritonitis and requires clarification of the diagnosis and examination of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract.
Symptoms of stagnation
The serozometer appears as:
- frequent and abundant gray discharge;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen (character – pulling);
- pain syndrome that occurs during intimate intercourse;
- increase in temperature (slight);
- difficulty urinating;
- the appearance of gray discharge after sexual intercourse.
The presence of fluid in the fallopian tubes is not accompanied by specific symptoms. In most cases, the patient learns about the rapidly progressing pathology only after an ultrasound examination. Nonspecific signs of the presence of pathological contents in the fallopian tubes are pain during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of fluid in Douglas space
Symptoms depend on the cause of the fluid accumulation. For example, in the case of a rupture of an ovarian cyst, pain in the abdominal cavity may appear, which periodically becomes sharp and cutting, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. If an ectopic pregnancy ruptures, you may experience spotting and bleeding from the vagina, pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the ovaries, and sometimes a feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
When the appendages become inflamed, sudden cramping pain occurs on both sides of the abdomen, intensifying during sexual intercourse. Sometimes it radiates to the groin area and thighs. Accompanied by weakness, fever or febrile condition.
Symptoms of pathologies of the pouch of Douglas
Signs of diseases appear from the first days of their development, which is the first signal for the mandatory conduct of a more thorough diagnosis of the abdominal organs.
The following symptoms of damage to the pouch of Douglas region are distinguished:
- redness of the lower abdomen, which manifests itself in a change in the color shade of the entire area of the skin surface or its individual sections;
- increased body temperature, which can vary from 37 to 39 degrees Celsius and above (this symptom is characteristic of the presence of purulent-inflammatory processes in the peritoneum);
- sharp or nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which is spasmodic or throbbing in nature;
- purulent and mucous discharge from the vagina in women, which indicates acute inflammation of the anterior part of the pouch of Douglas with the spread of pathology to the internal organs of the reproductive system;
- frequent urination, the appearance of a false urge to go to the toilet, which are often confused with signs of cystitis, but with a more detailed examination, a much more serious health problem is established;
- dull or sharp pain in the anus, which is present both at rest and during physical labor;
- an increase in the size of the lower part of the abdominal cavity in conditions where the rest of the abdomen remains of normal size, and the person himself does not suffer from excess body weight.
The intensity of the symptoms of pathologies directly depends on the severity of the current disease. With a purulent-inflammatory process, the disease always develops dynamically with high body temperature, increased levels of leukocytes, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, and severe pain.
Diagnostic puncture through the posterior vaginal fornix
Retrouterine puncture is a simple invasive technique that is particularly useful for diagnosing intra-abdominal pelvic bleeding and detecting abnormal ectopic pregnancies. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. Puncture of the pouch of Douglas is performed through the vagina using a 20 ml syringe and a needle with a length of min. 20 cm and diameter 1.5 mm. After inserting the speculum, the gynecologist inserts a needle through the posterior vaginal fornix and then aspirates its contents into a syringe.
Sometimes the puncture is performed under ultrasound guidance to avoid the risk of puncturing large pelvic vessels. After the needle is removed, the contents of the syringe are carefully inspected. The obtained material can also be submitted for cytological or bacteriological examination. Detection of clot fragments or bloody fluid may indicate bleeding into the abdominal cavity due to a disturbed ectopic pregnancy. This condition, with the presence of clinical, laboratory and ultrasound symptoms, is an indication for surgery to remove a disrupted ectopic pregnancy, most often using the laparoscopic method.
The lack of content obtained during puncture of the retrouterine recess does not exclude bleeding into the peritoneal cavity or the existence of an ectopic pregnancy, especially when symptoms indicate irritation of the peritoneum. Bleeding may be minimal or there may be post-inflammatory adhesions that prevent collection of material for examination. The presence of bloody fluid may also indicate endometriosis. The bloody contents of the Douglas cavity can become infected (superinfection), worsening the condition of the patient suffering from endometriosis. Treatment includes aspiration of hemolyzed blood from the pouch of Douglas and laparoscopic removal of endometriosis.
Health care
Before starting to treat fluid in the uterus, the doctor must perform a puncture. The sample is taken using laparoscopy. The dynamics of growth in the amount of accumulated fluid can be monitored by ultrasound.
Treatment for dangerous accumulations in the fallopian tubes should be immediate. Otherwise, the pipe may rupture. Peritonitis forms, the progression of which in most cases leads to the death of the patient.
Because the presence of fluid may indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm, a thorough examination is vital.
It is important to pay attention to strengthening the immune system. To do this, the patient must undergo a course of treatment with immunocorrectors.
Operation
When diagnosing pathological accumulations in the fallopian tubes, treatment can only be surgical. The operation involves removing scar tissue. It is difficult to say how favorable the prognosis is. This depends not only on the degree of obstruction, but also on the age of the patient. The younger she is, the more favorable the result.
If the patient plans to have children in the future, then the operation is performed using endovideosurgical equipment. If pregnancy is not planned, the doctor decides to eliminate the fallopian tube.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of pathology using this method involves complete relief of the infectious process. The patient is assigned to undergo:
- Magnetophoresis.
- Electromagnetophoresis.
- Laser phoresis.
Taking homeopathic medicines and vitamin therapy also helps to get rid of dangerous symptoms.
Traditional medicine methods
Treatment of pathology involves strengthening the immune system. This is greatly facilitated by herbal medicine and the use of juices squeezed from fresh vegetables and fruits. Freshly squeezed juices saturate the female body with the vitamins it urgently needs. Thus, healthy and nutritious juice from sea buckthorn berries, beets and celery is considered an excellent remedy.
Treatment with a bath based on mustard powder is considered no less effective. To prepare a healing bath, you need to dissolve the powder, cool slightly and take for 20 minutes. The course of treatment is no more than two weeks. “Bath therapy” is not recommended during and before menstruation, as well as after surgery (gynecological).
It is impossible to treat the disease without using decoctions from:
- calendula;
- boron uterus;
- chamomile;
- sage
Cytological examination of fluid
Detection of an increased amount of peritoneal fluid may be sufficient reason to maintain oncological activity. Ascites fluid collected during puncture of the retrouterine cavity should be sent for cytological examination to confirm or exclude a tumor. Detection of the presence of cancer cells in abdominal fluid provides valuable information to the physician, as it may indicate the appearance of a primary malignancy of the female genital organs.
In women who have previously had cancer and have undergone surgery, this symptom may indicate that the cancer has returned. Typically, the presence of tumor cells in the peritoneal fluid is associated with a greater spread of gynecological cancer, which is an unfavorable prognostic factor in these patients. It should be noted that cytological examination of fluid from the peritoneal cavity is only an auxiliary method in identifying malignant tumors of the ovary, fallopian tube, and cervix.
Cytological examination of the liquid sediment can also reveal an increased number of inflammatory cells, which appear in various inflammations of the pelvic organs. Finally, increased amounts of peritoneal fluid result from other diseases, such as liver cirrhosis or circulatory failure.