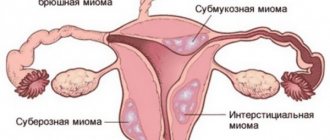
Main classification
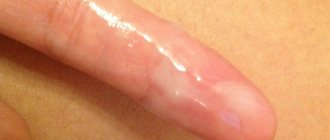
The mucous, light lubricant released from a woman’s vagina is called leucorrhoea. This phenomenon can have many causes, including natural physiological processes or pathological phenomena from the reproductive system.
Regarding the origin that caused the pathological release of secretion, several types of leucorrhoea are distinguished:
- Vaginal - appear during the healing phase of various diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Tubal - appear as a result of inflammation of the cervix or fallopian tubes. A distinctive feature of these discharges is their yellowish tint and liquid consistency;
- Cervical - appear due to dysfunction of the cervix. The main causes are cancer, gonorrhea, chlamydia.
- Uterine - arise due to the presence of inflammatory processes or neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the uterus. In this case, the secretion is watery, purulent, and in the later stages of the disease becomes brown.
If the presence of spotting clots of an uncharacteristic color causes discomfort or unpleasant sensations, you should seek medical help to exclude severe pathologies.
What does white discharge mean during pregnancy?
Conception makes significant changes to a woman's hormonal background. This is also reflected in the nature of intravaginal discharge, which becomes more abundant in the first trimester and has a milky white color.
To protect the membranes from possible infections, the woman’s body creates a special barrier in the cervix, consisting of a thick layer of vaginal secretion.
- Often the process of formation of the so-called “plug” is accompanied by an increase in the volume of whitish discharge, which in its consistency resembles sour cream.
Pregnant women in the first trimester are often concerned that the discharge of leucorrhoea after a short time becomes yellow in color. However, this is a variant of the norm.
Under the influence of high levels of progesterone in a pregnant woman’s body, white discharge can turn yellow due to contact with air. If the expectant mother takes Duphaston or Utrozhestan, the released cervical mucus may turn pale orange after two to three hours of exposure to air.
Whitish, watery discharge can be a warning sign for a long time, especially if it is quite abundant. One of the most important reasons is a violation of the integrity of the placenta or, in other words, leakage of amniotic fluid.
Pharmacies sell special tests that will help a woman distinguish normal intravaginal secretions from amniotic fluid, but it is better to immediately consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Causes
There are over 10 reasons for the appearance of white thick discharge in women - mainly infectious and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system. Pathologies can occur both acutely and chronically - symptoms in the form of vaginal secretion occur in both cases. Occasionally, white vaginal discharge is a consequence of problems with the endocrine or nervous system.
Dysbacteriosis
Violation of the intestinal microflora in 100% of cases leads to the appearance of light, thick secretion. The reason for the development of the condition is the presence of colitis, an unbalanced diet (abuse of hard-to-digest foods), previous poisoning or infectious processes of the digestive tract. In addition to white thick secretion, a woman experiences bloating, pain when palpating the abdominal cavity, and decreased appetite. When visiting a gynecologist, it is important to inform him about the presence of dysbacteriosis or digestive problems.
Thrush
A common female disease, the essence of which is the entry of fungal microflora into the vagina, and its active reproduction within the urinary system. Vaginal candidiasis occurs when:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules
- Long-term antibiotic therapy
- Unprotected intimacy with a partner who does not comply with hygiene procedures fully or is infected with a fungus
- Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- Recently performed diagnostic and treatment procedures using non-sterile instruments
The symptoms of vaginal candidiasis are specific: a woman experiences thick or cheesy vaginal discharge, itching, and swelling of the vaginal tissue. Additionally, problems arise with urination: the process is accompanied by pain, and the urine emits a fishy or acidic smell.
Multiple erosions form on the mucous membrane of the labia - they look like elongated thin wounds that are painful but do not bleed. The defect is detected during examination on a gynecological chair. If left untreated for a long time, thrush takes on a protracted form and is difficult to eliminate.
In all cases of development of vaginal candidiasis, therapy must begin with diet and temporary cessation of sexual activity. The pathogenic microflora that causes thrush lives in a humid and warm environment, and glycogen serves as a favorable condition for its reproduction. During treatment, a woman should avoid eating sweets (including fruit), carbonated drinks, and coffee.
Endometritis, adnexitis
Inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus and appendages (ovaries, fallopian tubes) occurs due to:
- Hypothermia
- Intimacy with a partner suffering from various urogenital infections
- Previous curettage of the uterine cavity (termination of pregnancy)
- Hereditary predisposition
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules
- Movement of pathogenic microflora from foci located near the uterus and appendages
Among the primary symptoms are the appearance of thick leucorrhoea, a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen, and an increase in body temperature. Vaginal discharge has a purulent or putrid odor. Endometritis can provoke adnexitis, and vice versa.
This is due to the close location of the organs of the female reproductive system. When inflammation becomes chronic, the severity of symptoms decreases somewhat, but the condition is complemented by weakened libido and disruption of the menstrual cycle. Endometritis and adnexitis can lead to problems with conception, provoke cancer, and reduce the body's immune abilities.
Colpitis
Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa causes the penetration of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. This occurs when personal hygiene rules are not followed, allergies to latex, pads or underwear; due to food intolerance. Also, irritation of the vaginal mucosa is facilitated by frequent douching with high concentration solutions, intimacy with a partner who does not take care of personal hygiene. Somewhat less commonly, colpitis is the result of helminthic infestation.
Regardless of the type of pathogenic microflora, a woman experiences:
- Increased body temperature
- Redness of the mucous membranes of the vagina
- Itching and swelling of vaginal tissues
- The appearance of white thick vaginal discharge
- Decreased libido due to pain and general deterioration in health
- Pain and irritation during urination
- Difficulty getting into a comfortable body position
Colpitis can be easily eliminated using an integrated approach. If inflammation is not eliminated in the acute phase of its development, it takes a protracted form. In this case, with every unprotected intimacy, the woman will experience acute pain in the vagina. After infection with fungi, the patient’s sexual partner is highly likely to develop balanoposthitis, an inflammation of the head of the penis.
Gardnerellosis
Vaginosis occurs as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier of bacterial microflora. A woman may not know about the presence of the disease for a long time - for a certain period the infectious process is asymptomatic.
Signs of pathology resemble the clinical manifestations of many gynecological and urological diseases - thrush, inflammation of the ovaries or urethra. Thick leucorrhoea occurs along with other symptoms; it has an unpleasant fishy or putrid odor, entering the bladder and contributing to its inflammation. Gardnerellosis is a leading cause of female infertility.
Taking antibiotics
Long-term antibacterial therapy always negatively affects the state of intestinal and vaginal microflora. Together with the source of inflammation, pathogens partially destroy the natural environment of the digestive tract.
Manifestations of this condition:
- Repeated diarrhea
- Nausea, vomiting
- Loud bowel movements
- Bloating, accumulation of intestinal gases
- Decreased appetite
- Bitter taste in mouth
- The appearance of a gray or white coating on the tongue
- Abdominal pain that worsens on examination
Lastly, after the listed symptoms, a woman experiences a copious amount of thick white vaginal discharge. In most cases, the condition is associated with a separately occurring thrush, although the actual cause of the development of the condition is a violation of the intestinal microflora. To avoid intense damage to it, along with antibiotics, a woman should take Linex, Bifidumbacterin or Nystatin. This will allow you to maintain digestion at a normal level and undergo antibacterial therapy without complications.
Taking birth control medications
Uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives leads to the development of problems with the activity of the reproductive system. The condition of the ovaries is disrupted, which causes the appearance of multiple symptoms, including the discharge of a white thick consistency from the vagina.
Additional symptoms of hormonal imbalance:
- Neurological disorders (headaches, dizziness, weakness, increased fatigue)
- Weakening libido
- Failure of the menstrual cycle, increased volume of blood released
Due to uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives, a woman may develop hormone-dependent tumors of the reproductive system. A gynecologist-endocrinologist deals with the correction of a woman’s health. Treatment begins with the abolition of all hormonal contraceptives.
Lack of vitamins
Hypovitaminosis rarely manifests itself as a disorder of the organs of the female reproductive system. Basically, this concerns the fullness of the menstrual cycle. But in 1% of cases, a lack of vitamins in the body is accompanied by the appearance of white vaginal secretion. Having established the relationship between nutrient deficiency and the appearance of discharge, you need to adjust the diet in favor of foods containing B vitamins.
Stress
The ovaries have a natural synchronization with parts of the brain. Therefore, the impact of irritating factors immediately affects the endocrine system and ovarian activity, leading to hormonal imbalance. The appearance of a copious amount of leucorrhoea indicates an imbalance of estrogen in the blood. To eliminate the symptom, it is enough to normalize the psycho-emotional state. In severe stressful situations, you should visit a psychologist (for consultation) and a neurologist (to obtain medication prescriptions).
Climate change
In a small number of cases, the acclimatization process leads to hormonal imbalances, and the woman experiences problems with ovarian function. Among other symptoms, the patient develops vaginal discharge of a thick, odorless consistency. They do not cause discomfort, but serve as a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacterial microflora. To prevent the development of infection, a woman should carefully and timely perform intimate hygiene measures, avoid stress, and prevent overwork.
Why does discharge appear with a pronounced sour odor?
White mucous discharge is called leucorrhoea. Leucorrhoea is a physiological phenomenon caused by the rejection of spent cells, the secretion of the vaginal glands, effusion of blood vessels, etc. During the period of release of the egg from the follicle, the amount of leucorrhoea increases.
White discharge on panties due to thrush
If a woman is bothered by white, cheesy discharge with a sour milk smell, and there are complaints, then the cause is more likely to be thrush (vaginal candidiasis).
Its symptoms are:
• itching in the vagina; • hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane; • discomfort during sexual contact, after hygiene procedures; • increase in the amount of discharge in the morning.
And, of course, there is a white discharge with a specific smell.
The following are considered predisposing factors to the development of thrush:
• hormonal instability; • moving to another climate zone; • stress; • malfunctions of the immune system; • frequent change of sexual partners; • background pathology (DM, HIV infection, etc.); • STIs; • chronic diseases of the urogenital tract; • taking contraceptives, etc.
Important! It is better not to self-medicate, but to confirm even an obvious diagnosis. White discharge and itching are not always symptoms of thrush; some sexually transmitted infections have similar symptoms.
Diagnosis is also necessary because the causative agents of candidiasis may hide more serious infections, for example, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, which occupy a leading position among the predisposing factors of infertility.
Before going to the doctor, you will feel better by irrigating the vagina with soda, which will reduce itching and relieve tissue inflammation.
It should be noted that symptoms and signs of thrush can also appear in girls who are not sexually active. Candidiasis is not considered a sexually transmitted disease, since fungal microorganisms are part of the vaginal microflora. Under some conditions, beneficial lactobacilli die, and opportunistic pathogens—in this case, Candida albicans, the most common causative agent of thrush—multiply.
After the onset of sexual activity, a girl may develop symptoms of a fungal infection due to the invasion of foreign flora and disruption of the vaginal biocenosis (a set of habitual microorganisms). There is no need to panic or blame your partner; Just submit some trivial smears for microscopy first. If the diagnosis is confirmed, it is quite simple to cure thrush; it is much more difficult to ensure that there are no cases of its recurrence.
To treat vaginal candidiasis, use antifungal antibiotics, suppositories and tablets for local therapy (administered transvaginally), products that support the functioning of the immune system and multivitamins. Treatment of the partner is usually not required; condoms must be used while taking medications.
The girl's white discharge is most likely also caused by a fungal infection. In this case, it is worth contacting a pediatric gynecologist and, perhaps, paying more attention to hygiene procedures. As a rule, after baths with soda and applying antifungal cream to the intimate area, the situation resolves within 5 to 7 days.
Possible complications
In all cases of inflammatory and infectious processes of the organs of the urogenital tract, there is a risk of the disease progressing to the chronic stage. This aggravates the patient’s well-being and creates difficulties in finding the optimal type of treatment. For protracted diseases, the therapeutic course takes twice as long.
Complications of diseases that lead to the development of a large amount of thick discharge:
- Infertility. Consequences of chronic adnexitis. Due to inflammation, the fallopian tubes are stuck together with pathological secretions. Therefore, sperm cannot fertilize the egg, and conception does not occur.
- Adhesive disease. Characteristic adhesions occur in areas of prolonged inflammation in the organs of the genitourinary or digestive system.
- Ectopic pregnancy. It can be tubal, ovarian or even abdominal. Serves as a consequence of prolonged inflammation in the urogenital tract.
- Intestinal obstruction. Develops due to the formation of adhesions in the digestive or urogenital tract.
Inflammation of the internal uterine layer leads to its thinning and weakening, so in pregnant women the implanted fertilized egg may be rejected. As a result, the woman experiences a miscarriage. This can happen both in early pregnancy and immediately before childbirth. Also, against the background of diseases that cause thick leucorrhoea, uterine bleeding, hormonal imbalance, the formation of fibroids or cystic cavities may occur.
Additional signs
White discharge is not a single symptom of the disease. They are often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- 1Itching in the intimate area of varying intensity. Sometimes it appears before copious discharge. With candidiasis and trichomoniasis, itching is observed more often than with bacterial vaginosis and mycoplasmosis.
- 2Swelling and redness are signs of an inflammatory reaction.
- 3 Increased bleeding. In inflamed mucous membranes, vessels are easily damaged, slight bleeding appears after sexual intercourse, gynecological examination, and so on.
- 4The smell may also change. Normal female discharge is odorless, less often slightly sour. With candidiasis, the sour smell becomes more pronounced and pungent. Gardnerellosis is accompanied by an unpleasant fishy odor. A sharp, heavy odor is observed with purulent inflammation (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis).
The appearance of white vaginal discharge may be accompanied by dyspareunia - painful sensations during sexual intercourse. They are also observed during examination. Pelvic pain occurs when the upper floor organs (the mucous membrane of the uterus, appendages) are involved in the inflammatory process.
Dysuric disorders mean involvement of the urethra and bladder (urethritis and cystitis).
A change in the nature of discharge due to a delay in menstruation may be the first sign of pregnancy.
Lubrication during the development of candidiasis
Candidiasis or thrush is a common infectious disease. Its causative agent is the pathogenic fungus Candida. The disease progresses when the bacterial microflora is disrupted, or when transmitted from a sick partner to a healthy one during sexual contact.
Characteristic differences in lubricant for candidiasis:
- abundant
- strong sour aroma
- curdled consistency
- the shade is white, but, subject to the addition of other infections, may change
- accompanied by pain when urinating, burning, itching in the area of the internal and external genitalia
This disease is contagious and can become chronic, so it requires immediate treatment.
Leucorrhoea in infectious diseases
Vaginal discharge is a common symptom of several sexually transmitted diseases in women, most of which are sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Vaginal discharge due to trichomoniasis
Vaginitis with trichomoniasis is manifested by abundant foamy leucorrhoea, often with an unpleasant odor . Long-term (chronic) vaginitis is accompanied by thick white or yellow leucorrhoea. As a rule, discharge from urogenital trichomoniasis is combined with unbearable itching in the area of the external genitalia. The diagnosis of urogenital trichomoniasis is never made on the basis of symptoms alone; to make a diagnosis of trichomoniasis, the following studies must be performed:
Examination under a microscope of a native (unstained) vaginal smear Examination under a microscope of a vaginal smear stained with special dyes Cultural method of research - growing colonies of microorganisms obtained from the vagina on special nutrient media with subsequent study of the resulting cultures. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a research method based on the study of the genetic material of Trichomonas vaginalis.
Vaginal discharge due to bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is the most common condition that causes foul-smelling discharge. The cause of the development of bacterial vaginosis is the excessive growth of bacteria on the vaginal mucosa, which are normally present inside in small quantities (synonymous with vaginal dysbiosis). Such bacteria include: Gardenerella vaginalis, Bacteroides, Peptococci, etc. Women with bacterial vaginosis develop white discharge with an unpleasant “fishy” odor (fishy smell). As with trichomoniasis, the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis cannot be made based on symptoms alone. Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis is based on the following research methods:
pH-metry. Normally, the vagina has an acidic environment, while with bacterial vaginosis the environment becomes alkaline. Examination under a microscope of unstained vaginal smears Examination under a microscope of vaginal smears stained with special dyes When a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis is made, the attending physician prescribes treatment.
Vaginal discharge due to vaginal candidiasis (thrush)
Urogenital candidiasis (thrush) is an inflammatory disease of the genital organs in women and men, caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Women with candidiasis (thrush) develop a thick white vaginal discharge (specific curdled discharge) with a sour or bready odor. Other symptoms of urogenital candidiasis in women are discomfort and itching in the genital area, often accompanied by cramps and pain when urinating. Diagnosis of thrush is carried out on the basis of the following studies:
Examination under a microscope of native (unstained) vaginal smears Examination under a microscope of stained vaginal smears Mycological examination - identifying the type of fungus that causes thrush.
Self-medication of the above infectious diseases of the genital area is not recommended. Often the cause of leucorrhoea can be several infections at once , for example a combination of bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis. In such cases, treatment should be carried out according to special schemes and determined only by the attending physician based on the test results obtained.
Lubrication during the development of gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis is one of the variants of bacterial vaginosis. Malaise manifests itself against the background of an imbalance of microflora in the female genital organs. There are many causes of this disease, the most common of which are:
- promiscuity
- unbalanced diet
- venereal and chronic diseases
- taking antibiotics or birth control
- incorrect douching technique
- hormonal disorders
- weakened immune system
- stress, fatigue
Leucorrhoea with gardnerellosis has a pasty or uniform texture, a grayish-white color and a pronounced “fishy” aroma. The problem is accompanied by itching and burning, unpleasant painful sensations during urination or sexual intercourse.
Nonspecific vaginitis and cervicitis
Vaginitis and cervicitis caused by bacteria, representatives of normal microflora, are called nonspecific. The most common causes of inflammation are mycoplasmas M. hominis, ureaplasma, staphylococci, streptococci, enterobacteria (including E. coli), and Klebsiella.
In addition to copious liquid or thick white discharge with or without a pungent odor, a woman may experience discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse. Itching and burning in the vagina are rare. The spread of infection from the vagina into the urethra during sexual intercourse often causes urethritis and cystitis.
What is considered normal?
Normally, a secretion comes out of the vagina of a healthy woman - transparent or whitish in color. Its quantity and consistency change during the menstrual cycle, but the smell remains faint and sour.
Normal stages of secretion appearance:
- at the beginning of the cycle - scant
- in the middle of the cycle - a slight increase in density and quantity
- period of ovulation, before the onset of menstruation - the appearance of copious creamy sputum
Also, a certain amount of lubricant is released during or after sexual intercourse.
Clots on the eve of menstruation
Before the onset of menstruation, the mucous secretion has a uniform, creamy texture. The shade of sputum can vary from light beige to white.
Leucorrhoea during ovulation
Ovulation is the rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature egg. This phenomenon is accompanied by the release of viscous elastic mucus, similar to egg white. The color of the secretion can be colorless, with a white or yellow tint. In some cases, bloody streaks are observed.
Mucus during pregnancy
In early pregnancy and during the formation of a mucus plug, abundant light beige or white clots may be observed in the cervical canal. Such a secretion is considered a variant of the norm, provided that it is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations or discomfort. Otherwise, you should consult your doctor.
Signs of normal, healthy vaginal discharge:
- They are liquid, transparent (mucus, jelly-like)
- The amount of discharge is insignificant
- No noticeable odor
- They do not irritate the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs and are not accompanied by any symptoms of the disease (itching, temperature, pain, discomfort in the genital area).
The amount of normal vaginal discharge and its consistency may vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the woman's condition. Vaginal secretions increase at certain times of the menstrual cycle (around the middle of the cycle, at the time of ovulation), during breastfeeding, or during sexual arousal. An increase in vaginal discharge in healthy women may occur due to stress, changes in climate conditions, or the use of certain medications (for example, hormonal contraceptives).
An increase in the amount of vaginal discharge (more abundant and thin) is observed during pregnancy and gradually increases towards the end of pregnancy. The intensification of vaginal discharge in pregnant women is explained by an increase in the concentration of sex hormones during this period.
An increase in secretion, an abnormal odor or change in consistency, or pain, itching, or burning that accompanies vaginal discharge may be signs of infection or other more serious conditions.
Leucorrhoea - excessive or unusual in nature (smell, color, consistency, quantity) discharge (profuse milky-white, yellow-green, bloody, liquid or thick, odorless, etc.), causing itching, burning and a constant feeling of wetness .
Pathological vaginal discharge - leucorrhoea - can be very diverse in color (red-bloody, brown, gray, black, whitish, greenish, yellowish, pink), consistency (jelly-like, curdled, foamy) with or without odor. Leucorrhoea may be accompanied by other symptoms (itching, irritation, pain) or may be the only symptom of the disease.
Unlike leucorrhoea, physiological vaginal discharge is light and light. Usually they do not cause irritation to the skin and mucous membrane of the genital organs; their number increases slightly before menstruation, during pregnancy and the postpartum period, and in girls - during puberty. The total amount of secretion that accumulates in the vagina during the day does not normally exceed 1 ml and is not felt.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is pathological lubrication, a woman should see a gynecologist, who will conduct an appropriate examination and, if necessary, prescribe tests.
Diagnostics include:
- examination on a chair
- colposcopy if erosion or dysplasia is suspected
- flora smear
- bacterial sowing
- PCR smear analysis
- transvaginal ultrasound
If problems are observed in a pregnant woman, this should be reported to the obstetrician-gynecologist during a routine examination.
Treatment
Treatment for leucorrhoea is prescribed by a gynecologist after identifying the root cause. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, because incorrectly selected drugs will only aggravate the patient’s condition.
Therapeutic measures are aimed at:
- elimination of the cause depending on the pathogen: antibacterial or antiviral drugs, surgery, etc.
- restoration of normal microflora balance
- improving immunity (if necessary)
- restoration of affected tissues, improvement of blood circulation and microcirculation: physiotherapy, swimming, physical therapy.
After treatment, the patient must follow preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of the disease occurring in the future.
Prevention
To avoid the development of conditions that lead to the appearance of thick white discharge, a woman should:
- Avoid unsupervised use of any medications. Even if a specific drug was prescribed by a doctor, exceeding the prescribed dosage is contraindicated
- Undergo seasonal vitamin therapy (spring, autumn)
- Perform hygiene procedures in a timely and thorough manner
- Balance your diet
- Limit yourself from stressful events
- Strengthen immunity by normalizing the quality of nutrition, improving working and rest conditions
- Avoid casual sex
- If possible, do not use vaginal tampons - use pads
- Don't get too cold
- If you do not want to get pregnant, choose the optimal type of contraception together with your gynecologist.
It is equally important to avoid staying near sources of toxic effects and not to use the intrauterine device for longer than the prescribed period.
Video: What discharge should women be wary of?
- How to treat pimples on lip
- Urine with blood in women
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin in women
- Itching under the mammary glands in women
- Bone pain on big toe
- Hair is falling out a lot - what to do?
- Red spots on the face are flaky and itchy
- Pain in the hand
- Chills without fever
- Leg cramps
- Pain in the coccyx or in the coccyx area
- What to do if your throat hurts, it hurts to swallow, but you don’t have a fever?