Why is colposcopy prescribed?
Colposcopy is a procedure for examining the epithelium of the vagina and cervix, which is performed using a colposcope. This is an optical device with a powerful light source, which is a type of endoscope and allows you to magnify the image up to 40 times.
Colposcopy is considered a procedure:
- painless;
- safe;
- having a minimum number of contraindications;
- informative.
Many specialists, along with examination using gynecological speculum and bimanual examination, consider it part of a preventive examination.
She helps:
- assess the condition of the mucous membrane;
- determine the size and shape of the cervix;
- detect in time the onset of pathological processes in the early stages that are asymptomatic.
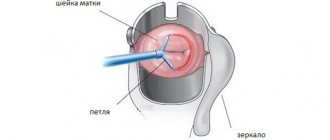
Examination with mirrors is performed for patients who are sexually active. A special instrument in the form of 2 flaps-grooves, equipped with a sliding mechanism, is inserted into the vagina.
During a bimanual examination, the right hand is inserted into the vagina, and the left hand presses on the abdomen. This allows you to palpate the internal genital organs: ovaries, fallopian tubes. These studies can identify pathology, but will not provide accurate information about it.
Also, colposcopy, as a diagnostic procedure, can be prescribed under circumstances indicating a possible pathology.
Namely, when:
- unfavorable results of a previously performed cytological analysis indicating possible malignant neoplasms;
- bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- cervical erosion detected during a gynecological examination;
- suspected changes in the cervical epithelium: polyps, leukoplakia (appearance of keratinized plaques);
- the presence of growths in the anus and on the external genitalia (candylomas);
- complaints of pain during sexual intercourse and bleeding after it;
- the presence of unusual discharge, accompanied by a feeling of itching and burning;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
Colposcopy can be used for:
- clarification of the location of the biopsy (tissue collection for analysis);
- determining the optimal method of therapy;
- monitoring the progress of conservative treatment;
- checking the results of surgical intervention.
The procedure is required to be performed in preparation for IVF.
https://youtu.be/hlAXv9IIdGM
What is colposcopy
Colposcopy is an examination of the vagina and the inner walls of the cervix using special equipment - a colposcope. It consists of optical and lighting systems that allow you to increase the visibility of the organs being tested by 10-40 times.
Colposcopy in gynecology can reveal the most microscopic pathological abnormalities that are invisible to the normal eye.
At this stage of development of medical equipment, an improved analogue was created - a video colposcope. It is equipped with a digital camera, the image is immediately broadcast on the monitor screen.
All finished results are saved in a file; they can subsequently be reviewed by specialists in order to observe the dynamics of treatment or the progression of pathology.
Colposcopy in gynecology helps to detect the development of cervical cancer in the early stages. But based on these results, a final diagnosis is not made; additional tests are required. The procedure reveals the changed areas of the uterine lining and the site for a biopsy.
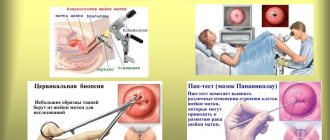
A biopsy is a research method in which a small piece of tissue is removed or cells are collected.
In addition to the presence of superficial changes on the cervix, colposcopy shows:
- Erosion of different shapes and sizes;
- The presence of benign formations in the vagina or cervix;
- Microscopic damage to muscle tissue, as well as hemorrhage.
Doctors recommend undergoing the procedure every two years to avoid complications in the reproductive system. Colposcopy should be performed for women of any age, from teenagers to older women.
There are additional indications for this procedure:
- Girls during pregnancy planning. This is necessary to avoid problems with bearing the unborn child;
- Pregnant women. Usually carried out during the registration period (up to 12 weeks). The second procedure is done at a later date (usually before the 30th week), as an examination before childbirth. It's all about a woman's immune system; during pregnancy it decreases significantly. And various pathologies of changes in the cervix are a consequence of reduced immunity, so during pregnancy they can progress and develop. After childbirth, you should definitely undergo an additional examination of the cervix. Quite often, after childbirth, such pathologies disappear on their own.
- Women over 40 years of age should undergo colposcopy more often - once a year. Starting at this age, a woman’s hormonal balance changes, which increases the possibility of the appearance of neoplasms.
Differences between extended colposcopy
Colposcopy can be performed using a simple or advanced protocol. With a simple colposcopy, the examination is performed without the use of drugs.
A simple procedure allows you to:
- assess the general condition of the genital organs;
- set their size, color and shape
- analyze the features of the vascular pattern and endometrium;
- examine the junction zone - the area where the squamous epithelium of the vagina passes into the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal.
To obtain more accurate results, an extended colposcopy is performed. Its main difference is the use of pigments that color healthy and diseased tissues differently and substances that cause vasoconstriction.
For example, the following can be used for this purpose:
- 3% vinegar solution. Under its influence, blood vessels in healthy areas narrow, but in those affected by the disease they remain the same;
- Lugol's solution. It colors healthy tissues dark brown, while the affected areas remain unpainted.
Also, as part of an extended colposcopy, the cervix can be examined:
| Type of inspection | Description |
| Using yellow and green filters | They allow you to assess the condition of blood vessels |
| Fluorescence colposcopy | After staining with fluorochrome, the examination is carried out under UV rays: in the later stages of cancer, the tissues are not able to fluoresce and are clearly visible against the background of healthy areas. |
| Colpomicroscopy | A method that involves magnifying an image by 300 times or more and allows you to identify microscopic pathological areas invisible to the naked eye. |
| Videocolposcopy and photocolposcopy | Innovative methods of carrying out the procedure, in which the image is displayed on the screen and recorded, which provides ample opportunities for subsequent analysis and assessment of the disease over time |
Types of colposcopy
There are several types of colposcopy:
- Simple or survey - includes examination of the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix and cervical canal without the use of any additional magnifying objects. This diagnostic method allows you to assess the general condition of the tissues, the presence of ruptures, erosions, scars and neoplasms in the mucous membrane.
- With a magnification of 300 times - in contrast to survey colposcopy, a magnification of up to 300 times allows you to study in detail the structure of the cells and tissues that line the vulva, cervix and cervix.
- Extended – indicated for mandatory use in women over 35 years of age and in patients at risk (who have a high risk of developing cervical cancer). During the study, the cervix is treated with a 3% acetic acid solution, which makes it possible to identify elements of tumor tissue even at the initial stage of its formation. After this, the cervical tissues are treated with Lugol’s solution with glycerin - healthy areas of the epithelium are evenly stained, and areas with pathology are not stained, which makes them clearly distinguishable during examination.
- With the use of color filters - when the mucous membrane is stained with a green filter, the vascular network of the epithelium and any changes in it become clearly visible to the doctor.
- Chromocolposcopy - this study uses various dyes. Healthy tissue areas are painted evenly, while modified and damaged areas are not tinted.
Indications for extended colposcopy
Extended colposcopy is a procedure that is required for:
- confirmation and detailing of the diagnosis;
- determining the site for taking a biopsy sample (biopsy sample);
- choosing the optimal treatment method, which depends on the type of disease and the degree of tissue damage;
- the need for surgical intervention - to clarify the boundaries of the affected area. This makes it possible to exclude excision of healthy tissue and prevent a situation where some of the affected cells remained unaffected and eventually relapsed into the disease.
Results of cervical colposcopy
The results are usually immediately formed by the doctor (or all observations and conclusions are spoken out loud for the nurse to record the data) in the protocol of the procedure, the document is drawn up, supplemented with photo or video materials and entered into your outpatient record. One copy of the examination remains in the clinic’s database, the second is necessarily handed over to the patient.
According to the examination and based on the results obtained, the doctor makes a conclusion about the general condition of the woman’s cervix. He also decides on the need for further manipulations, procedures or additional studies, and if a pathology is detected, treatment is prescribed for the patient.
Contraindications
Extended colposcopy is not performed:
- in the presence of an acute inflammatory process affecting the cervix, since inflammation is accompanied by copious discharge that hides the surface of the endometrium;
- during menstruation: hormonal changes characteristic of this period can cause changes in the appearance of the vagina and cervix. Blood and mucus will complicate research and will not allow iodine to evenly stain the mucous membrane, which can lead to false conclusions;
- in the first weeks after abortion, childbirth or surgical treatment of uterine diseases;
- with allergies and hypersensitivity to iodine-based preparations or acetic acid. The procedure is possible using their analogs that do not cause an allergic reaction.
Colposcopy will not cause harm, but will be useless if the patient before the procedure:
- had sexual intercourse;
- used contraceptives;
- performed douching;
- took some medications.
For virgins, the procedure is possible if the location of the virgin pleura allows the insertion of speculum into the vagina. If research is absolutely necessary, the virgin pleura is first removed.
When is the best time to do a colposcopy?
- The best time to perform colposcopy of the cervix is days 5-7 of a woman’s monthly cycle.
- On the eve of the examination, you should not use vaginal suppositories, lubricants, or douche.
- You should abstain from sexual intercourse two days before the procedure.
- After topical drug treatment, a woman should wait at least 7 days before having a colposcopy.
Colposcopy should not be done during menstruation!
What pathologies are visible during examination?
Extended colposcopy is a procedure that allows you to detect cervical cancer or precancerous changes in the epithelium in the early stages, as well as determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
The procedure allows you to diagnose the following pathologies:
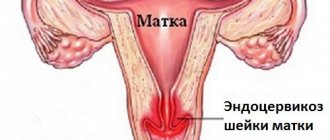
- cervical endometriosis;
- cervical erosion;
- polyps or condylomas on the internal genital organs;
- papillomavirus;
- inflammation of the cervical canal (endocervicitis);
- pseudo-erosion of the cervix (ectopia);
- endometrial hyperplasia - proliferation of the uterine mucosa;
- uterine fibroids.
Results of the procedure
All results, including deviations from the norm that colposcopy will show, are described verbally by the doctor in his conclusion. He also attaches a schematic representation of the identified pathological foci in the form of an imaginary watch dial, the condition of the cervix recorded on colpophotography and video recording.
When interpreting the results, the following signs are taken into account:
| Criterion to be assessed | Condition is normal | Deviations (differences from the norm) |
| Cervical size | Not changed | Hypertrophy - enlargement of the cervix, atrophy - reduction |
| Form | Conical | Incorrect |
| Visualization of the transformation zone | Located inside the cervical canal | Enlarged, with large nabothian cysts |
| Transition zone between stratified squamous and columnar epithelium | Clear | Vague |
| Vessels | Without features | Atypical |
| Retention cysts | No | Eat |
| Glands | Not rendered | Identified, closed or open |
| Areas of keratosis | No | Eat |
| Mosaic (vascular anomaly) | No | Delicate or rough mosaic. |
| Puncture (pinpoint capillaries that appear through the epidermis) | Tender | Rough |
| Borders of abnormal epithelium | Not visible | Detectable, clear or fuzzy |
| Ectopic epithelium | No | Eat |
| Mucosal atrophy | No | Yes (the epithelium is unevenly stained with Lugol's solution) |
| Acetoble epidermis (turns white after treatment with acetic acid) | No | Eat |
| Iodine-negative areas (poor staining) | No | Eat |
| Areas of endometriosis (a disease in which endometrial cells appear in unusual locations) | No | Eat |
What diseases can be detected
Colposcopy and cytological examination of the cervix can diagnose many diseases, including:
- congenital and acquired ectopia of the epithelium;
- true cervical erosion;
- endometriosis;
- condylomas;
- polyps of the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- eroded ectropion;
- cervicitis;
- leukoplakia (dysplasia) of the cervix;
- cancer (carcinoma) of the cervix.
On what day of the cycle is it better to do it?
Colposcopy can be done on any day except menstruation days.
The most favorable period is considered to be from the 5th to the 7th day from the beginning of menstruation. It is best for biopsy and scraping to identify abnormal cells.
Is there a need to do colposcopy during pregnancy?
The main reason why a doctor may suggest that a pregnant woman undergo this type of examination is a suspicion of cervical erosion. Under the influence of hormones that support pregnancy, erosion can progress rapidly and make natural childbirth impossible.
Both simple and extended colposcopy are safe procedures that do not affect the condition of the expectant mother and fetus, the course of pregnancy and childbirth. The only exception is the threat of termination of pregnancy, since inserting speculum into the vagina can trigger the onset of labor. Otherwise, there are no prohibitions on conducting research.
A limitation is placed on biopsy, which is usually combined with colposcopy. This is explained by the fact that such manipulations increase the risk of early miscarriage or premature birth in the 3rd trimester. The sample is taken only for serious medical reasons, for example, if cancer is suspected.
At the same time, hormonal changes in a pregnant woman’s body can affect the condition of her genital organs, in particular the vaginal mucosa, and lead to distorted results. For this reason, colposcopy should be performed by an experienced gynecologist.
Study protocol
The standard colposcopy protocol fits on A4 format. It indicates the name of the medical institution, the patient’s data, the full name and position of the doctor, and the date of the examination. The results of colposcopy are directly entered into the table with the indicators already entered. The doctor just has to enter the data obtained during the examination into it, that is, compile a transcript. Some items in the document are marked with “+” or “—” signs (based on the principle of detected or not detected).
Also attached to the protocol is a detailed description of the results, that is, a detailed transcript. It is compiled by a gynecologist after receiving the results of additional studies. Based on this document, the final diagnosis is made.
Today, colposcopy has become one of the main examination methods in gynecology. This is due to the fact that it can be used to identify pathological changes in the epithelium of both the vagina and the cervix at the cellular level.
There are two types of colposcopy:
- Simple. The vagina and cervix are examined without using any medications.
- Extended colposcopy is used to clarify the simple use of substances that are used to treat the vagina and cervix. Use Lugol's solution and acetic acid.
This type of research has virtually no contraindications, it is painless, easy to perform and quite informative.
Preparing for the examination
If you have the symptoms described above, it is advisable to perform a colposcopy as quickly as possible on any day. If it is part of a routine preventive examination, it is better to schedule a visit to the gynecologist for the 2nd week of the menstrual cycle. The beginning of the cycle is considered the first day of menstruation.
In preparation for the procedure, you must:
- 2 weeks before the test, stop taking medications or find out in advance from the doctor whether the drug you are taking can affect the result of colposcopy. The greatest risk of obtaining inaccurate data is possible when taking antibiotics, antifungals and hormonal agents;
- refrain from sexual intercourse for 2-3 days: microtraumas of the vagina, possible during sexual intercourse, and residual seminal fluid will complicate diagnosis;
- during the same period of time, do not use lubricants, intimate lubricants and deodorants: all these substances, changing the microflora of the vagina, can distort the results. For the same reason, it is necessary to refrain from douching, baths, washing with soap or special products for caring for the intimate area for the remaining time before the procedure;
- a day before the examination, take a shower and perform epilation of the intimate area.
Immediately before colposcopy, you should empty your bladder and do a cleansing enema, which will facilitate the procedure and relieve physical and moral discomfort. If the procedure is performed in a private clinic, the patient will be provided with everything necessary.
To visit the antenatal clinic you will need to prepare:
- diaper;
- socks;
- medical gloves.
How is it performed and how long does the procedure last?
Colposcopy is a painless but unpleasant procedure. Proper preparation for it and knowledge of what will happen in the next 5-15 minutes will help reduce discomfort.
Extended colposcopy is a procedure that is carried out according to the following steps:
- The doctor conducts a conversation. The patient is asked questions regarding age, the beginning of the last menstruation, the number of pregnancies, births and abortions, information about previous operations on the uterus, and complaints.
- The woman is asked to remove clothing from the lower part of her body if it interferes with the procedure, lie down in a gynecological chair, bend her knees and spread them wide.
- The procedure begins with a routine gynecological examination using speculum, during which the doctor will receive general information about the condition of the genital organs and determine whether there are any obstacles to colposcopy.
- After the examination, the doctor places a colposcope at a distance of approximately 10-15 cm from the vagina and, directing a beam of light to the desired area, examines the vagina and cervix.
How to prepare for colposcopy
Before your colposcopy, your doctor may recommend that you:
Avoid vaginal sex for one or two days before the procedure.
The treatment you have will depend on the extent of your pathology, as well as what treatment the clinic has and the preference of the doctor or nurse. This is also known as large loop deletion of the conversion zone. . Local anesthesia is usually given before any treatment to numb the cervix. Treatment is usually very simple and quick. There is a small risk of bleeding during treatment.
- Cone biopsy.
- Very rarely, removal of the uterus and cervix.
If this is the case, you will need to be hospitalized.
After treatment, you may feel slight discomfort like pain for a period. Painkillers such as paracetamol can help relieve pain. Do not use tampons a day or two before the procedure.
Take an over-the-counter pain reliever before your colposcopy.
The date of colposcopy must be chosen in such a way that the procedure does not occur during menstruation.
Sensations during and after examination with a colposcope
During colposcopy, the following unpleasant sensations are possible:
| Part of the procedure | Description |
| When introducing mirrors | There may be a feeling of pressure and fullness from the fact that the edges of the mirrors rest against the walls of the vagina. If the patient is nervous, tense or not prepared for the procedure, for example, a full bladder, unemptied bowel, then the discomfort is more pronounced. |
| When treated with a solution of vinegar and Lugol | There is a slight burning sensation |
| When taking a biopsy, scraping | There may be a feeling of tingling, stretching, extending to the lower back. |
| After the procedure | Patients report discomfort in the genital area if a biopsy was performed. Spotting and spotting is possible, and sometimes women complain of mild aching pain in the lower abdomen. Normally, all these sensations gradually weaken and disappear after 2-3 days without therapy. |
You should consult a doctor if after the procedure:
- your health has worsened
- the temperature has risen;
- heavy bleeding began;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor appeared, accompanied by itching and burning.
In the absence of these symptoms, after colposcopy you can take a shower, but it is better to refrain from baths on the 1st day.
If a biopsy was not taken, there are no restrictions on having sex, otherwise you must stop doing it in the next 3 days : during this time, the wounds remaining after taking the samples will have time to heal. You can also take any medications, including contraceptives, and lead a normal lifestyle.
Recovery period after the procedure
In most cases, complete restoration of the microflora and general condition of the woman’s mucous membrane occurs after 2-3 weeks, if the colposcopy was extended. With a simple procedure, this period is reduced to several days. During this entire period, it is recommended to observe the following rules:
- Refuse sexual relations.
- Avoid visiting solariums, baths, saunas, and swimming pools.
- Avoid taking hot baths. It is better to limit yourself to a regular shower at this time.
- Reduce physical activity. It is especially not recommended to lift heavy objects.
- Use acetylsalicylic acid and preparations containing it.
- Engage in douching and other procedures that affect the vaginal microflora.
Decoding the results
The patient receives the protocol form 2-3 days after the procedure if she had it done in a private clinic, and a week later if performed in a antenatal clinic.
If the checkboxes are only under the heading “Normal colposcopic results”, and in the “Conclusion” column it is written “Without pathology”, then everything is fine. If there are notes in other sections, there may be problems.
Norm
The protocol must include information about the condition of the vagina and cervix and the nature of the epithelium covering them.
The form may contain the following terms and abbreviations:
| Abbreviation | Decoding |
| MPE | Multilayered squamous epithelium, in other words, the vaginal mucosa. |
| C | The columnar epithelium covering the surface of the cervical canal differs from the MPE in structure, appearance, and functionality. |
| ST | The transformation zone is the place where the columnar and flat epithelium “join”, the area where cell degeneration occurs. |
| OPZH (OZH) | Open ducts of glands located in epithelial tissues. |
| KRZH (ZZH) | Closed glands: if the opening of the gland becomes blocked, then the secretion produced by the gland accumulates in its body, and the gland gradually turns into a cystically dilated or alarming cyst. |
| OCE | The vascular pattern evenly covers its surface. The presence of atypical cells here may indicate pathology. Vascularization is a term that characterizes the process of formation of new vessels. |
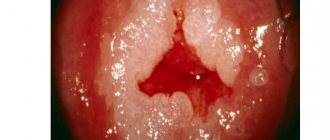
Normally, the length of the cervix is about 30 mm, the shape of its external os can be slit-like (in women who have given birth) or dotted (in women who have not given birth). Healthy squamous epithelium has a smooth surface and a pale pink color; when treated with a vinegar solution, it does not discolor; when stained with Lugol, it acquires a uniform dark brown tint; there are no unpainted areas.
The columnar epithelium should normally be located inside the cervical canal and, in the lens of a colposcope, look like a red surface covered with small tubercles.
The appearance and location of the transformation zone depends on the woman’s age.
There are:
- Type 1 ST – in young girls and pregnant women. The zone is completely located in the cervix and is clearly visible;
- Type 2 ST – in adult women. May partially extend into the cervical canal (barely visible during colposcopy);
- Type 3 ST – in older women (menopause). Not visible during colposcopy.
Deviations
The pathological areas discovered during the examination are marked on the diagram of the cervical canal, for which there is a circle in the upper part of the form. The doctor accompanies his notes with brief comments. Subsequently, when taking tests or during surgical treatment, the drawn up diagram will help to find problem areas.
If there is a pathology, the following terms and abbreviations may appear in the protocol, diagram and conclusion:
| Reduction | Term | Description |
| YNE or YNU | Iodine-negative epithelium | This is a group of atypical cells that did not change their color after staining with iodine. The absence of color indicates a precancerous state of the epithelium: the presence of pathological cells that can give rise to malignant neoplasms. |
| ABE | Acetowhite epithelium | Areas that, when treated with acetic acid solution, became white due to a pathological change in tissue structure (dysplasia). In this case, it is important how quickly the color change occurred and how long it took to restore the color: the faster the discoloration process, the more serious the problem. |
| MP | Puncture and mosaic | Changes in the appearance of the endometrium, indicating problems with blood vessels. After treatment with vinegar, the mosaic looks like small bright polygons on a pale pink background, and the punctuation looks like a vascular pattern. Puncture and mosaic can be light and rough, indicating deep changes in tissues, the risk of developing dysplasia and cancer. In any case, its presence is the basis for further research, in particular, a biopsy. |
| AC | Atypical vessels | These are vessels that do not narrow when treated with a vinegar solution. In the presence of AS, a targeted (point) biopsy is performed to determine the causes of pathological changes. In the presence of AS, the degree of vascular damage is usually indicated: mild, moderate, severe. |
Extended colposcopy with vinegar and Schiller's test
During colposcopy, other pathologies can be identified, which must be mentioned in the study protocol:
- candilomas - growths protruding above the surface (exophytic) or flat (endophytic);
- inflammatory processes, diffuse or local. Areas affected by inflammation look like blurry red spots that acquire a whitish tint after treatment with a vinegar solution;
- atrophy is a thinning of the epithelium, often occurring during postmenopause and resulting from estrogen deficiency. The condition is harmless and treatable. Atrophy is diagnosed by uneven coloring of the epithelium upon contact with iodine;
- endometriosis is a pathological growth of the endometrium of the uterus; during colposcopy, the affected tissue has a bluish tint and bleeds when pressed;
- adenosis - the presence of zones of columnar epithelium in the vagina.
FAQ
Despite the fact that before the procedure the doctor talks in detail about everything that will happen, questions always remain about the examination and diagnosis. Most often, patients are concerned about the following.
Is it painful to have a colposcopy or not?
In general, the procedure is painless, especially when performed by a highly qualified doctor. Mild discomfort or tingling may occur when using solutions, but this is uncommon. Therefore, to the question whether colposcopy is painful or not, the answer is negative. If during the examination you feel severe pain, you must immediately inform your doctor.
How long does the procedure take?
On average it does not take much time. Depending on the individual case, the procedure takes 20–30 minutes.
How to prepare for cervical colposcopy?
A diagnostic test such as colposcopy does not require special preparation. But patients are not recommended to have sexual intercourse several days before the procedure, and the use of vaginal creams and douching are also undesirable.
How often can and should you do a colposcopy of the cervix and which doctor should you contact?
A referral for a diagnostic examination is given by a gynecologist. He also recommends a preventative care plan, which may include a colposcopy. It all depends on your individual situation and medical history (if any).
If there are no serious problems, then the procedure, as a preventive measure, is recommended to be performed once a year.
Are there any consequences after the colposcopy procedure?
Over the next 3-5 days, you may experience a brownish discharge due to the use of iodine or another solution. Therefore, patients are advised to bring panty liners with them to use after the procedure.
In very rare cases, slight spotting and slight discomfort in the lower abdomen may occur. Sometimes the doctor may recommend taking painkillers.
What to do after the procedure?
If nothing particularly bothers you, then there is no need to take any special action. But it is highly desirable during the period while the discharge and/or slight malaise persists:
- abstain from sexual intercourse;
- do not use tampons;
- do not take a bath (shower only) or go to the pool;
- do not douche.
The doctor will tell you more about everything at your appointment.
Is it possible to have a colposcopy during menstruation?
Testing during menstruation is not recommended because the results may be inaccurate. In this regard, the doctor is often asked the question on what day (first, last) of the cycle during menstruation can a colposcopy be done. The best time for diagnosis is the first days after the end of menstruation. The doctor agrees on this with the patient in advance.
Is it possible to have a colposcopy during pregnancy?
In general, the procedure is safe for the fetus throughout the entire period of pregnancy. And the question of whether such a diagnosis is needed or not is decided by a gynecologist.
. If there are no prerequisites and compelling reasons, the examination is not prescribed. After childbirth, colposcopy can be performed after 1.5 months.
Why is colposcopy prescribed and performed for pregnant women and at what stages (early, late) during pregnancy is it required? Here everything depends on the patient’s medical history (whether she had diseases of the reproductive system), on how the pregnancy proceeds, on the doctor’s decision. If you are afraid, worried and worried, then do not hesitate to ask the doctors of our center in St. Petersburg questions about why colposcopy during pregnancy, whether it is safe for the child, etc.
Initial examination
At the initial consultation, the doctor conducts a simple examination of the patient and collects the necessary information, asking questions about the state of health, complaints, medical history (if any), symptoms, etc.
At the initial appointment, you can also ask any concerning questions: why a colposcopy is being done, which doctor will perform the procedure, what preparation should be done, are there any contraindications, what are the indications for the examination, etc.
Diagnostics
If examination and analysis of the information received does not make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, then the doctor gives an appointment for examination. The doctor also gives a referral for colposcopy of the cervix if the previous transcript showed poor results. If you have previously undergone this examination, then you need to tell your doctor about it and it is advisable to bring its results.
In addition to colcoscopy, the following may be prescribed: smears, ultrasound and additional examinations.
Repeated appointment
At the second visit, a direct examination is carried out and, if necessary, the diagnostic and treatment plan is adjusted if the results of other tests are already known.
Control reception
Depending on each individual case, the doctor may schedule an additional visit after the end of the course of treatment to again perform a colposcopy procedure to check for relapses and to assess the patient’s health condition.
Where can I have a cervical colposcopy in St. Petersburg?
To undergo the procedure, we invite you to visit us at the medical office. We employ highly professional diagnosticians, have modern equipment and take an individual approach to the treatment and monitoring of each patient. In addition to this, we have some of the most affordable prices for cervical colposcopy and other types of diagnostics and treatment in St. Petersburg.
The interpretation of colposcopy of the cervix shows that everything is fine with you and there is nothing to worry about, or there are still problems in gynecology. The timing of the analysis results is individual, depending on the specific situation.
Condition of the vagina after extended colposcopy
After the procedure there should not be any pain, but slight inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, causing discomfort, is possible. As a rule, discomfort disappears without treatment within 24 hours. If a biopsy sample was taken, there may be some slight bleeding, and when stained with iodine, it may turn dark brown.
Colposcopy (simple or extended) as part of a preventive examination is recommended for every woman annually under the age of 35 or once every six months for older ages.
Compared to other diagnostic procedures, colposcopy has a number of advantages: information content, speed, painlessness, safety. It allows you to identify dangerous diseases in time and preserve women's health.
The main diseases that colposcopy can detect
.
Cervical cancer Genital warts Inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis) Precancerous changes in cervical tissue Precancerous changes in vaginal tissue Precancerous changes in vulvar tissue Vaginal cancer Vulvar cancer During colposcopy, the appearance of the mucous membrane is assessed: the color of the tissue, vascular pattern, violations of the integrity of the epithelium, the presence and shape of glands , boundaries of identified formations. The normal mucous membrane of the cervix is pale pink, shiny, with a slightly bluish tint in the second half of the menstrual cycle. Lugol's solution uniformly colors its surface dark brown. For erosion
cervix (a section of the vaginal part of the cervix, devoid of epithelial cover) the surface of the erosion is smooth or fine-grained, red, blood vessels in the form of loops are visible.
Decoding the research results
It is best to allow an hour for the entire visit. This may include information about your periods, the date of your last period, what contraception you use and your general health. You will be asked to lie in a lounge chair or couch in the same position as during the cervical spine screening. Some clinics may allow you to spread your legs in soft supports called stirrups. An instrument called a speculum will be inserted into the vagina. It is gently opened to reveal the neck of the uterus, at the top of the vagina. The doctor or nurse will then look through the colposcope to get a good view of your cervix. The colposcope itself does not go inside your vagina. It's essentially like a large pair of binoculars on a stand that you can move around. There is also a light that will help you see inside your vagina. This means you have the opportunity to watch too - but only if you want to! A long smear is used to force fluids onto the cervix. These fluids stain any abnormal cells that may be present. Two different liquids are commonly used: weak vinegar and iodine. You can also take a small tissue sample from the cervix. This will be sent to a laboratory for further study. The biopsy is only a pinhead size; however, it can be painful to take. If this is expected, a local anesthetic is usually used to numb the cervix initially. It is sometimes recommended that you be treated at your first colposcopy visit. You are unlikely to bleed a lot. However, you may have some discharge or staining from the iodine used in the examination. It will most likely come out or drain blood if you have had a biopsy or treatment. However, don't worry if you forget the sanitary protection - the clinic will give you a platform.
- Usually the doctor or nurse will start asking you a few questions.
- You will then be asked to remove your clothing from your belt.
- This is with your knees bent and your legs.
After your colposcopy, you can usually return to work or continue with your normal day.
With pseudoerzia (ectopia)
the stratified squamous epithelium of the cervix is replaced by cylindrical epithelium with clear, even contours. Colposcopy shows a cluster of small papillae of a bright red color.
Glandular polyps
have a shiny surface and color from light pink to bluish-purple. Glandular polyps can be single or multiple, their sizes are different. The surface of the polyps can be represented by columnar epithelium; during colposcopy, these polyps can look like ectopia.
You will likely have a small amount of bleeding, especially if you have a tissue sample. This may last three to five days and you should wear a sanitary pad. You should not have sex or use vaginal creams or pessaries until the bleeding stops. Typically you have to wait five days.
What are the risks or complications of colposcopy?
You may notice a dark liquid material on the pad. It is sometimes green or looks like coffee granules. This is normal and is fluid that was pushed against the neck of your uterus during the examination. Some women find it a little uncomfortable. Complications may rarely occur. These may include severe bleeding and infection. If you experience heavy bleeding, smelly vaginal discharge, or severe pain in the lower abdomen, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Endometriosis
cervix (the appearance of tissue similar to the mucous membrane of the uterine body, which undergoes changes during the menstrual cycle) is an irregular ovoid-shaped formation of bluish-purple or pink color, protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane and bleeding when touched. Their sizes often change depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. With extended colposcopy, the color of endometriosis lesions remains almost unchanged.
Once a small tissue sample has been taken, it is sent to the laboratory for further examination under a microscope. The cell abnormality that may be seen is called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Rarely, a biopsy may show changes in your cells that have already turned into cancer.
Remember that the purpose of cervical screening is to prevent cervical cancer. This is by detecting and treating early changes in cells that, if left untreated or uncontrolled for several years, can develop into cancer. The results of your colposcopy and a small sample taken will indicate whether you need any treatment. Sometimes the doctor or nurse may assume you have treatment at your first colposcopy visit. However, they may suggest that they are waiting for the results of your biopsy before you have any treatment.
Leukoplakia
(a thickening of the mucous membrane of the cervix, which, if left untreated, can develop into a tumor) has the appearance of whitish, rough spots or thin films that are easily removed.
Papilloma
– growths of pink color, in individual papillae there are dilated vessels. Application of a 3% acetic acid solution causes vascular contraction and blanching of the mucous membrane.
What diseases can be detected by this study?
This depends on the clinic you visit. Biopsy results may take several weeks. Not everyone who has a colposcopy needs treatment. If the doctor or nurse feels that you have only a mild abnormality, they may suggest that you have a repeat colposcopy in 12 months. Changes in the neck of your uterus may return to normal on their own, and they may simply need monitoring.
What treatment options are available?
The goal of treatment is to destroy or remove all the abnormal cells on the neck of your uterus without affecting too much normal tissue. Most treatment methods can be performed on an outpatient basis, with colposcopy. Treatment may cause slight discomfort, perhaps similar to a period of pain.
Cervical cancer
has the appearance of swollen glassy areas with tuberous protrusions on which blood vessels can be seen. Under the influence of vasoconstrictors (for example, acetic acid), they do not narrow.