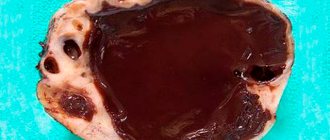
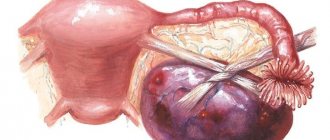
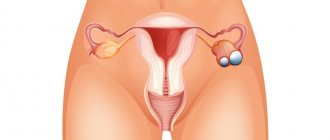
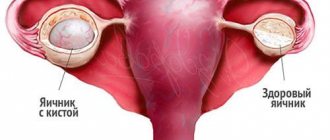
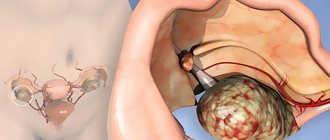
Serous ovarian cystadenoma is a benign neoplasm that forms from epithelial cells on the gonads. Inside the spherical cavity there is a liquid that has a yellowish tint. This pathology is widespread in medical practice, which most often occurs in women during menopause (45-55 years). Every woman should know that serous ovarian formation, if treated inappropriately, can transform into a malignant tumor. Such a process is fraught with severe, irreversible consequences, and in some cases, death.
In this article, we will look in detail at what a serous cyst is, why it occurs, what complications it leads to, and what methods exist to eliminate it.
Causes of formations
The following conditions can cause the development of cysts:
- The presence of sexually transmitted diseases in the body;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Constant, promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Long-term abstinence from sexual pleasures;
- Beginning of menopause;
- Inflammatory processes affecting the functioning of the reproductive organs;
- Recently experienced poorly performed surgical interventions (artificial termination of pregnancy, medical operations, curettage);
- Constant excessively intense physical activity;
- Frequent stress, depression;
- Malnutrition, adherence to various diets that are hazardous to health.
https://youtu.be/LaPrnZDnAec
Causes of ovarian cystadenoma
Ovarian cystadenoma can develop as a result of the following six factors:
Follicular cyst
― forms after ovulation, when the pituitary gland releases a small amount of luteinizing hormone, signaling the follicle to release an egg. If the release does not occur, the follicle cannot rupture and begins to grow, turning into a cyst. This formation is harmless and usually resolves on its own within two menstrual cycles.
Metabolic disorders
- in the premenopausal period, metabolic changes occur (diabetes, obesity), a woman’s hormonal levels are disrupted, an excess of estrogen is observed, and the risk of developing ovarian cystadenoma increases.
Luteal cyst
― is formed during the production of a large amount of estrogen and progesterone by the burst follicle, which prepare the body for conception. Then the follicle becomes a corpus luteum, which is capable of accumulating blood and fluid; if fertilization does not occur, then after a while it disappears on its own. You feel nagging pain in the pelvis and abdomen, and there is a risk of internal bleeding if the cyst ruptures.
Teratoma
- Occurs mainly in women under 30 years of age. Develops from germ cells (primary oocyte).
Endometriosis
is a condition in which the endometrial cells that normally line the inside of the uterus begin to grow outside of it.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- a condition in which many small and harmless cysts develop on the ovaries when the balance of female hormones changes.
Also, the reasons for the formation of cystadenoma can be stress, bleeding during menopause, ectopic pregnancy, abortion, sexual abstinence, surgery, genital infectious diseases (syphilis, chlamydia) and heredity.
Localization
Benign progression of a serous neoplasm usually involves damage to one uterine appendage. Pathology can form both in the area of the right ovary and in the area of the left. The tumor often has a special “leg” that connects the spherical cavity with the fallopian tubes and gonads. If the patient was diagnosed with both a cystadenoma of the left and right ovaries, doctors prescribe a more extensive examination. A similar phenomenon, in 70% of all cases, indicates the progression of cancer.
Causes and symptoms of cystoma
Doctors have not yet established the exact cause of the cystoma, however, there are certain theories associated with the appearance of the tumor.
These include:
- hormonal imbalance. Since ovulatory proliferation occurs every month, hyperplasia develops over time. Taking coc and frequent pregnancies reduce the likelihood of tumor growth;
- hereditary factors. This parameter is considered fundamental because mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes occur;
- ovarian diseases. We are talking about corpus luteum cysts and PCOS;
- menopause. During this period, hormonal changes occur, which serves as a provocateur for cystadenoma.
As for general symptoms, as a rule, they do not appear if the size of the cyst is less than 3 cm. In this case, the patient is under observation and OK is prescribed to her. If the “dropsy” does not decrease, more serious treatment is prescribed.
Complaints appear if the size of the cystadenoma is 5-7 cm.
The clinical picture here is as follows:
- constipation;
- pain localized in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- difficulty urinating;
- bloating;
- When a tumor is torsion, acute pain may occur, even to the point of fainting.
A serous cystoma in the right ovary compresses the kidneys, as a result, the outflow of urine is disrupted. The cystoma of the left ovary puts pressure on the intestines.
Symptoms
Symptoms that appear during the progression of a serous tumor can have two degrees of severity:
- General;
- Life-threatening.
Most often, in the initial stages of the disease there are no signs, which complicates the process of timely detection and treatment.
Are common
Serous cystomas are characterized by:
- Aching pain that manifests itself in the affected side of the peritoneum, lower back and groin area;
- Increased urge to urinate due to tumor pressure on the bladder;
- Disruptions of the menstrual cycle, excessively scanty or intense bleeding;
- Pain syndromes that appear during sexual intercourse;
- Slight increase in body temperature;
- Frequent nausea and vomiting;
- Increased irritability, sudden changes in mood;
- Problems with the bowel movement;
- Increase in volume of the abdominal cavity.
Dangerous
There are also symptoms, the presence of which indicates a serious complication of the pathology:
- Intense pain, cutting and stabbing in nature;
- “Hard” abdomen syndrome – tension of muscle tissue in the area of the affected ovary;
- Increase in temperature to more than 38.5 degrees;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Short-term or prolonged loss of consciousness;
- Spasms and tremors in the limbs;
- Unreasonable decrease in blood pressure;
- Heavy sweating, feeling of chills;
- A panicked and overexcited state, which is replaced by lethargy and apathy.
As a rule, the signs described above indicate such dangerous conditions leading to inflammatory processes and infection of the hematopoietic system:
- Rupture of the cystic cavity due to an excess of its contents;
- Twisting of the pedicle that connects the gonad and the neoplasm. With such a complication, nutrients stop flowing into the cystadenoma, and it undergoes a necrotic process (death);
- Accumulation of purulent fluid inside a tumor neoplasm, leading to infection of the body.
It must be remembered that the conditions described above can lead to death, so you should contact a medical facility immediately.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
At the first signs of cystadenoma, you should consult a gynecologist. During the examination, the doctor will examine the symptoms and conduct an examination with palpation to preliminary determine the type of formation, its location, size, and mobility. Various types of instrumental studies are also prescribed:
- Ultrasound diagnostics to determine the type of cystadenoma and determine its exact size. Nearby organs are also checked for growths and metastases. It is best to perform an ultrasound a week after the end of your period.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the type of cystadenoma
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed if malignant tumors are suspected and to clarify the diagnosis. Using these methods, you can obtain highly informative layer-by-layer images of any organ.
- Colonoscopy may be necessary if there is suspicion of tissue growth in the intestinal area or the appearance of tumors and metastases there. Diagnostics is carried out using a special tube, at the end of which there is a small video camera.
If the presence of cancer is suspected, women are prescribed a blood test to determine the number of tumor markers CA-125, HE4. Differential diagnosis should be carried out with various types of tumors, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, appendicitis and some other diseases and conditions of the body.
Diagnostics
To identify a cystic neoplasm on the ovary, the following diagnostic measures are performed:
- General survey of the patient;
- Examination of the patient on a gynecological chair;
- Ultrasound of the uterine appendages to determine the size of the cyst;
- Analysis for tumor markers to confirm or refute the benign nature of the tumor;
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the pelvic organs.
Based on the diagnostic results obtained, the doctor decides how to treat the disease.
Treatment of ovarian cystadenoma
If a pathological ovarian cystadenoma is detected, surgical intervention is necessary.
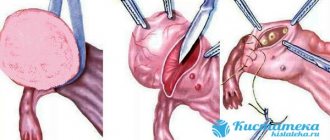
The scope of the operation is determined individually. If the tumor is larger than 3 cm, the ovary is removed completely, but patients who are planning a pregnancy are careful not to injure the gonads. Laparoscopy is considered the safest method of treating ovarian cystadenoma. This surgical intervention is performed through several incisions in the peritoneum, which allow the necessary instruments (forceps, electric scissors) to be delivered into the body cavity. The advantage of this operation is quick recovery, a low percentage of postoperative complications, and the opportunity to have children.
The surgeon's tasks differ somewhat depending on the age of the patient. In young girls, it is important to preserve as much ovarian tissue as possible. If the operation is successful, then the level of sex hormones is normalized, the weight remains normal, and the woman’s reproductive function is not lost.
For older women, the main task of the surgeon is to reduce the risks of complications later. During the operation, all foci of inflammation are removed, minimizing the risk of occurrence and exacerbation of existing diseases.
Auxiliary therapy is traditional methods of treatment, which include the use of tincture of acacia, chamomile, mint, dandelion, green walnuts, burdock juice, blackberries and cranberries. It is also recommended to take a course of vitamin E to avoid ovarian depletion. In the postoperative period, physical activity should be excluded and the recommendations of the gynecologist should be followed.
What is an ovarian cyst and does it need to be removed?
Complications and consequences
A serous ovarian cyst can lead to the following complications:
- Impaired functioning of the ovaries, which leads to infertility;
- Degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one;
- Increased pressure on the intestines or bladder, leading to inflammatory processes and disruption of their functionality;
- Compression of blood vessels localized in the organs of the reproductive system, as a result of this process, expansion of the venous pathways in the abdomen and legs occurs;
- Increased likelihood of spontaneous abortion.
Causes of hydatid
Official medicine identifies several main reasons that can contribute to both the occurrence of pathology and the growth of cystic formation.
The main causes of ovarian hydatid are:
- Pregnancy outside the uterus. Mandatory interruption of fetal development in a non-standard place (for example, in the ovary) with some degree of probability can contribute to frequent periodic inflammation and deterioration of the functioning of the fallopian tubes. The combination of these factors may ultimately cause the formation of a hydatid.
- Miscarriage, abortion. They are one of the main reasons that can contribute to the rapid growth of hydatids and are likely to lead to infertility.
- Operations in the pelvic area. These surgical interventions significantly affect the weakening of the body's immune system, which in turn reduces protective processes in the reproductive system in women.
We recommend you learn: Ascites in benign ovarian tumors
Treatment methods
Unfortunately, treatment of serous cystoma is possible only through its surgical removal. The fact is that the tumor, according to medical practice, practically does not respond to any group of pharmacological drugs. The only thing is that if the tumor is small and does not cause any discomfort in the patient, then the doctor can prescribe expectant therapy and stop the growth of cystadenoma with the help of hormonal agents.
Types of operations
Surgical intervention to excise a benign cavity can be performed in the following ways:
- The laparoscopy method is a frequently used and low-traumatic operation, during which the doctor makes three neat holes in the abdominal cavity (in the area of the affected appendage) and performs the necessary manipulations, controlling the entire process using the built-in optical device in the laparoscope;
- Laparotomy surgery is a cavity intervention in the affected area of the body. This type of surgery is rarely used and can bring a lot of unpleasant complications, and is also famous for its long rehabilitation period and the subsequent formation of scars.
Depending on the area of damage to the gonads, the doctor determines the type and purpose of the operation necessary in this case:
- Cystectomy - during the treatment, only the pathological neoplasm is excised, and the appearance and functioning of the uterine appendages are completely preserved;
- Wedge-shaped resection - if this method of excision of a serous cyst is chosen, the doctor removes the area of affected tissue in the shape of a wedge, while preserving healthy areas of the gonads;
- Ovariectomy - a benign or malignant tumor is stopped along with the uterine appendages;
- Adnexotomy - along with the cystadenoma, the affected ovaries, fallopian tubes, and, sometimes, the reproductive organ itself are removed.
The choice of surgical intervention is made exclusively by a qualified doctor, who is based on the diameter of the tumor, its nature, the degree of damage to the gonads and the effect on nearby organs.
Classification
Doctors classify cystadenoma as a group of epithelial tumors. The formation of “dropsy” occurs from the integumentary secretion. Tumors are classified into the following:
- serous;
- mucinous.
In turn, papillary and smooth-walled forms of cystoma are distinguished.
The simplest is considered to be a serous cystoma or cyst of the right or left ovary, and the most complex in structure are called mucinous formations. Neoplasms that grow on the inner walls are considered dangerous.
Gynecologists also distinguish the concept of “borderline tumors”. These include growths with a low degree of metastasis. To a greater extent, this term should be attributed to papillary cystadenoma.
What type of cystadenoma are you diagnosed with?
serousmucinous
In women over 40 years of age, epithelial type formations are diagnosed in most cases. In young patients, tumors are mostly benign.
Smooth-walled serous cystadenoma is characterized by a unilateral lesion. It has the following properties:
- there is a leg;
- the location is fixed above the uterus;
- upon palpation, a slight displacement is felt;
- dense capsule with a thickness of 1 to 4 mm;
- there is one chamber, less often their number reaches three;
- outer and inner surfaces without roughness;
- on ultrasound the contents are transparent and light;
- minimal risk of malignancy;
- main danger: compression of nearby organs and tissues.
Often, serous “dropsy” affecting the left ovary leads to constipation, as the sigmoid colon is compressed. Localization on the right side affects the ureter.
Serous papillary cystadenoma is characterized by the presence of papillary growths on the outer or inner surface of the formation. The clinical picture here is as follows:
- adhesions form in the abdominal cavity;
- bilateral lesion;
- the location is fixed in the thickness of the ligaments;
- presence of a leg.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment of serous ovarian cystadenoma, the prognosis in 95% of all recorded cases is favorable. Late detection of a tumor, inappropriate therapeutic actions or disregard for one’s health, as a rule, result in severe, irreversible consequences (transformation of the tumor into oncology, complete infertility, infection of the circulatory system, etc.), and in some, especially advanced cases, death . That's why medical experts recommend carefully listening to your body's warning signs.
By following some preventive recommendations, you can reduce the likelihood of the formation of a pathological neoplasm and, accordingly, prevent the development of its various consequences:
- Visit the gynecological office twice a year to examine and determine the condition of the internal organs of reproduction;
- Do not neglect the use of contact contraceptives (condoms) in order to prevent unwanted pregnancy;
- Avoid engaging in promiscuous sexual relations;
- When choosing birth control pills, consult your doctor;
- Look after your psychological health, rest more often, spend time with loved ones, change the depressing environment;
- Lead an active lifestyle;
- Get rid of bad habits (drinking alcohol, drugs and smoking tobacco products);
- If you notice the first symptoms of any pathological condition, immediately go for examination to a medical professional.
Types of formations
Depending on the nature of the formation, serous cystadenoma can be:
- Smooth-walled (simple). Simple ovarian cystadenoma mainly affects only one ovary and has a single chamber. But there are also multi-chambered ones with watery yellowish contents. The size of the tumor varies from 4 to 15 cm. Simple serous cystadenoma is most often diagnosed in patients over the age of 50 years. It does not interfere with normal childbearing if it does not exceed 3 cm.
- Papillary (papillary) or, as doctors sometimes call it, rough-papillary cystadenoma. Cystadenoma papillary or papillary cyst is considered the next stage of the disease, since the papillae appear only several years after the development of the tumor. A borderline papillary cyst is characterized by abundant and frequent papillary formations with fields of extensive dislocation. Papillary cystadenoma can be chambered and develops in both ovaries. With everting papillary cystadenoma, the growths are located outside the capsule. Inverting is characterized by the presence of papillae in the middle of the cyst. With a mixed form, the papillae are located inside and outside.
- Serous papillary cystadenomas develop into a malignant form with a 50% probability. They are single-chamber and multi-chamber. Inside they are filled with a transparent liquid of a brownish or dirty yellow hue. Papillary cystadenoma of the ovary is one of the most dangerous formations, since it tends to grow into nearby organs. As a result of this process, the functioning of the urinary tract and intestines is disrupted, diarrhea and problems with urination occur.
- Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary is very similar in nature to serous cystadenoma, but unlike the latter, it has a mucous substance in the cavity. The tumor is covered with cells similar to the mucus-secreting cells of the uterus. The structure of the tumor is a cavity with chambers and partitions and is easily diagnosed using ultrasound. As a rule, this formation occurs simultaneously on both the right and left ovaries. The tumor can reach large sizes (up to 30 cm), and therefore must be surgically removed.
Smooth walled cystadenoma
Serous cystadenoma
Serous papillary
Serous papillary
Pseudomucinous cyst
Treatment of ovarian hydatid
But how to get rid of tumors when diagnosed with ovarian hydatid? Few people also know that this is a treatment that requires surgical intervention. True, patients are operated on only in cases of hydatid overgrowth. And this is mainly laparoscopy.
The doctor sets the day for the operation and prepares the patient for several days. The patient undergoes all tests and is examined. The anesthesiologist prepares the patient for anesthesia, as it will be general, due to the extensive operation.
If laparoscopy is not suitable, then the operation will be abdominal. Afterwards, the patient remains in the hospital for about seven days. This is taking into account that there will be no complications. Abdominal surgery is more complicated and, accordingly, it takes longer for the body to recover.
There are also many alternative treatments.
Treatment
Ovarian cysts are a common cause of lower abdominal pain and infertility. They come in different origins and structures, but a cyst of any type at a certain stage of its development may require surgical treatment. A modern gentle surgical method is laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, which allows to shorten the length of hospitalization and speed up the patient’s postoperative recovery.
Young nulliparous women undergo wedge resection. Resection is the removal of part of the ovary. The operation is performed to remove the damaged part of the organ. This procedure ranks first among gynecological manipulations.
Indications for ovarian resection
The most common cause is tumors. Cysts often grow on women's ovaries. They appear for various reasons. But some cysts tend to resolve on their own, without treatment. And others need to be deleted. If the tumor has grown very large, the ovary cannot be saved.
Tumors for which surgery is indicated:
- carcinoma;
- endometrioma;
- dermoid cyst;
- cystadenoma;
- polycystic disease
What is hydatid ovary
Many women who have this diagnosis are wondering: ovarian hydatid - what is it? It is important to understand that this is a neoplasm that most often occurs at the base of the ovary. That is, its location is the fallopian tubes.
The danger of this pathology is that the woman may remain infertile. Hydatida blocks the release of the egg from the ovary and prevents it from moving through the tube. And this, in turn, leads to the inability to get pregnant, since the sperm is simply not able to reach the egg and fertilize it.
A hydatid is a cyst (pathological cavity) filled with fluid inside. On ultrasound examination, the neoplasm is detected in the form of a circle or oval with clear outlines. Most often, the disease does not cause any particular concern, but may manifest itself with some symptoms.
Possible consequences
The nature of hydatid is benign, but it should not be ignored. The chances that a neoplasm will transform into a malignant one are almost zero, but similar cases have still been recorded in gynecological practice.
If the disease is neglected, complications may occur in the form of infertility. The thing is that the cyst compresses the soft tissue, thus forming obstacles for the egg to enter the fallopian tubes. In addition, the normal functioning of the ovaries is disrupted, and this affects ovulation.
Important! Another complication is torsion of the ovarian pedicle, leading to severe pain, necrosis and fever. In this case, emergency surgery is indicated.
If the tumor has reached a large size, then its rupture is possible. The woman begins to feel intense and unbearable pain. Sometimes life-threatening internal bleeding develops.
In most cases, women do not even notice single formations, since there are no pronounced symptoms. However, if the tumor begins to grow, it causes discomfort. Then it is better to go to the doctor immediately.
Useful video on the topic:
Treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery
Therapeutic tactics, as an alternative to surgery, include conservative treatment with the use of medications. This method is suitable only for treatment provided that the serous cyst in the left ovary has the appearance, size, location and condition characteristic of the initial stage of the disease. The woman’s age will also influence the choice of drug treatment, and accompanying treatment methods (acupuncture, physiotherapy, mud therapy, folk remedies) are discussed individually.
Medical care for solving the problem of benign formation may include a wait-and-see approach. Some cases when the presence of pathology is diagnosed do not require urgent or complex intervention - only observation by a doctor for a certain period of time. Often this approach is successful in the treatment of a functional tumor, and since with small sizes of the pathological formation it is not always possible to accurately determine its type, the observation method is justified.
Articles on the topic
- Pain due to ovarian cysts in women: what to do
- Causes, signs and how to treat endometrioid ovarian cyst
- Ovarian hyperplasia - signs and diagnosis, manifestation, types, methods of therapy and prevention
Waiting tactics
In medical practice, this method is used at an early stage, when it is difficult to make a correct diagnosis. On ultrasound examination, the serous cyst of the left ovary appears as a black spot with clearly visible boundaries, which coincides with the signs of a functional neoplasm, which resolves itself over time. The use of watchful waiting, which can last from a month to three, helps to avoid unnecessary treatment and surgery. If the cystic formation does not go away, then this is a sure sign of cystadenoma.
Drug therapy
A serous cyst is fluid in the ovary that is hidden in a dense capsule, often with a single chamber. If the cystadenoma has affected one organ, and its size ranges from 4 to 10 cm, then a drug treatment method is used. Timely therapy helps prevent the appearance of papillary (papillary) cysts, when examination reveals overgrown formations. Both ovaries are covered with cystic tumors that have a stalk, and the next stage of development of a serous cyst is dangerous: it degenerates into a malignant tumor.
A conservative medical method at an early stage of pathology is aimed at resolving a benign formation, therefore anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Taking vitamin complexes and hormone therapy helps slow down the growth of serous cysts. The latter is a combination of estrogens and gestagens, which simultaneously helps normalize the menstrual cycle. In case of bleeding, hemostatic drugs are prescribed, and in case of complications or rupture, surgery cannot be avoided.
Surgical methods
The indication for removal of a cystadenoma by surgery will be the size, examination data, the patient’s age and the stage of the tumor. A serous type cyst poses a threat to life not only by the possibility of developing into a malignant tumor, but also by growing into the abdominal cavity. A less traumatic surgical method, laparoscopy, is often suitable for removing cystadenomas. Just a few small incisions promote rapid recovery of the body, reduce the risk of complications and prevent the formation of adhesions.
If there is a need for a traditional surgical operation, then the doctor will have to decide on one of the existing methods:
- wedge resection (excision of cystic tissues with maximum preservation of healthy ones);
- cystectomy (helps preserve organ function when the capsule is removed);
- oophorectomy (removal of the cyst along with the ovary);
- adnexectomy (removal of the ovaries, uterine appendages).
Reasons for appearance
Hydatida is a congenital disease.
A newborn girl is already born with such an education.
Possible reasons for the formation of hydatids in the embryo:
- If during pregnancy the mother took medications with a known harmful composition or poorly studied components,
- The mother's work or life in harmful conditions,
- X-ray examinations during pregnancy.
The influence of these factors is important mainly from 8 to 20 weeks of pregnancy.