Uterine hyperplasia is a disease of its inner layer, accompanied by an increase in the number of cells of the mucous membrane. In this case, it thickens significantly compared to the norm. The main method of treating a diagnosis of uterine hyperplasia is curettage of its cavity. The cause of the pathology is a hormonal imbalance with a predominance of high levels of estrogen over progesterone. In medical circles, it is correct to say hyperplasia of the endometrial layer. This clarifies the localization of the process.
Risks of getting sick during menopause
Everyone has heard the saying: “hormones are crazy,” and during menopause they really begin to malfunction in our body. The normal functioning of the hormonal sphere keeps all systems of a woman’s body in order, not only monitoring health, but also our emotions and ability to enjoy.
And when a hormone such as estrogen begins to accumulate excessively in a woman’s body, with a decrease in progesterone, this can result in such a dangerous disease as endometrial hyperplasia during menopause. At risk are women with long, heavy periods before menopause, those with fibroids, inflammation of the endometrium, or formations in the breast area.
From the field of anatomy
The uterus is a muscular sac intended for bearing a child, connected to the ovaries, in which eggs grow before being released into this female organ. The inside of the uterus is lined with a mucous substance called the endometrium. The endometrium is intended to become the first cradle for emerging life, to protect and nourish the fetus.
The basal layer of the mucosa is thicker and denser and is the basis for the functional layer. In the functional section there are glands that secrete a mucous substance that prevents the insides of the female organ from sticking together. Connecting these two layers is a mesh-like layer of cells called stroma. Starting from adolescence, the following processes occur monthly in the inner layer of the uterine mucosa:
- Its thickness after the end of menstruation is only 1 mm.
- Before ovulation begins, estrogens act on the mucous membrane, causing it to thicken and its cells to grow in size, reaching 0.4 - 0.5 cm.
- When ovulation occurs, an egg ready for reproduction is released from the ovary into the uterus and meets sperm during sexual intercourse; in its place, a temporary corpus luteum grows, releasing progesterone into the uterus, causing the endometrium to further increase in thickness and begin to produce a special substance. Moving wave-like cilia, growing on ciliated cells, on the inner smooth surface of the functional layer, move the egg to the place where it will attach and grow. The endometrium grows up to 0.8 cm thick.
- In the case of failed fertilization, the functional section begins to thin out, die, and its detachment occurs, causing bleeding, with which it is ejected from the uterus. This is menstruation.
- The basal layer begins to grow internally with the help of stroma, until the next menstruation.
Carrying out the procedure
Curettage is usually performed in the last days of the cycle before the onset of menstruation. During this period, the cervix is most elastic and easier to dilate.
Preparation
Before the procedure, a woman must undergo a general blood and urine test for the presence of inflammatory processes. A blood clotting test is performed. Tests are taken for syphilis, HIV and hepatitis.
Before the procedure, a microscopic analysis of a smear from the vagina and cervix is performed to determine the composition of the microflora.
3 days before cleaning, the patient must stop using vaginal medications, and also stop douching and abstain from sexual intercourse. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Management of pregnancy after IVF, features and recommendations
How is the operation performed?
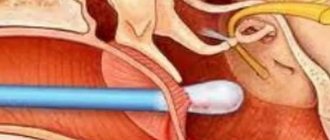
Curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out exclusively in a hospital, under conditions of maximum sterility. Pain relief is carried out by using a mask with nitrogen dioxide or intravenous administration of novocaine. Sometimes general anesthesia is used.
During the procedure, the uterus is expanded with special devices, and its internal size is measured. The upper mucous membrane of the organ is scraped out using a curette. If diagnostics are necessary, the material is sent for histological examination.
When performing an abortion or cleansing after a miscarriage, frozen pregnancy, or childbirth, the aspiration method is used. The contents of the uterine cavity are removed using a vacuum. In the same way, blood is removed from it in case of dysfunctional uterine bleeding or stagnation inside the uterus. This method is more gentle than curettage, since there is no risk of damage to the cervix or uterine wall.
During hysteroscopic curettage, a tube with a video camera is inserted into the uterus to examine the surface. After removing the top layer of the endometrium, make sure that the mucous membrane is completely removed.
After the procedure, ice is placed on the lower abdomen. The patient remains in the hospital for several hours so that doctors can be completely sure that there is no risk of bleeding.
After operation
Immediately after the anesthesia wears off, the woman may feel quite severe abdominal pain for 2-4 hours. Then, for another 10 days, feelings of mild nagging pain persist. The discharge of blood in the first hours is strong and contains blood clots. Then they become spotting and may appear for another 7-10 days after surgery. If they stop too quickly, and at the same time the woman’s temperature rises, this indicates the occurrence of blood stagnation (hematometra) and an inflammatory process. Treatment is carried out with oxytocin, which increases uterine contractility.
To eliminate pain, painkillers and antispasmodics (no-spa) are prescribed to help speed up the removal of residual blood. Antibiotics are taken for several days to prevent inflammation in the uterus.
2 weeks after cleaning, a control ultrasound examination is performed to ensure that the procedure was successful. If the study shows that the endometrium has not been completely removed, cleaning must be repeated. The result of a histological examination of the cells of the removed material is ready in about 10 days, after which the doctor will be able to make a conclusion about the need for further treatment.
After cleaning, your period will begin in 4-5 weeks. The frequency of their onset is restored after approximately 3 months.
Warning:
You should consult a doctor immediately if blood in the discharge does not disappear after 10 days, and the abdominal pain intensifies. The appearance of elevated temperature a few days after curettage should alert you. It is imperative to visit a doctor if menstruation after cleansing the uterus becomes too heavy or very scanty, and their pain also increases.
After the operation, until its consequences completely disappear, it is necessary to avoid douching, inserting tampons into the vagina, and medications not prescribed by the doctor. You should not put a hot heating pad on your stomach, visit a sauna, take a bath, or stay in a hot room or in the sun for a long time.
Aspirin and other anticoagulants should not be taken for 2 weeks after cleansing. Sexual relations can be resumed 3-4 weeks after curettage, when the pain and risk of infection disappear.
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
When the estrogen level is high and progesterone is low and cannot cope with female hormones, the mucous membrane begins to grow uncontrollably. The functional layer of the mucosa grows inside the basal layer and does not come off during menstruation. With endometrial hyperplasia, it is necessary to perform curettage, because both hormonal and endocrine processes are disrupted, and this makes pregnancy impossible.
Typically, this process occurs during premenopause, although hormonal disruptions also occur during childbearing years.
This disease often reveals itself late, goes asymptomatic, intensifies, subsides, and reminds itself again. Endometrial hyperplasia in menopause is often first detected in a prolonged form.
Types of hyperplasia and curettage
Statistics say that this disease is found in every fifth gynecological patient. Recently, an increasing number of representatives of the fairer sex are becoming ill with it. Complications from this disease, including cancer, have also increased.
Let's look at the types of hyperplasia:
- glandular hyperplasia is a non-malignant form, in which glandular cells multiply and accumulate in groups, and not throughout the mucosa. The shape of the glands changes, they increase in size, but continue to perform their functions; curettage is not always carried out, depending on the condition of the organ;
- the glandular-cystic form is a consequence of an imbalance of sex hormones, which can be a consequence of mastopathy, thyroid disease, diabetes, which occur in premenopausal women. The disease is similar to the previous one, but in addition to the growing cells of the glands, cells grow inside their openings and do not allow the secretion to come out. Something like bubbles with mucus inside grow. In addition to the uterus, such cysts can also appear in the ovaries. Cleaning is required;
- cystic type of adenomyosis : similar in manifestations to the previous form, but unlike it, the glands grow greatly with a normal inner layer of these glands. The appearance of tumors at the site of foci of cell proliferation is a common consequence of cystic hyperplasia. Scraping is mandatory;
- hyperplasia in focal form - changes occur in the connecting part, benign polyps grow in it, damage occurs in places, focally, most often in the upper part of the female organ. Endometrial hyperplasia in postmenopause in this form more often ends in cancer than at a young age. Curettage is necessary;
- atypical hyperplasia differs from others by the appearance in the hypertrophied endometrium of atypical cells, which the immune system cannot influence, and the components of the functional layer begin to mutate. Both the inner and basal layers change. In half of the cases the disease turns into cancer, and it is necessary not just curettage, but removal of the female organ;
- The rarest type of hyperplasia is basal , characterized by thickening of the basal layer of the mucosa.
Endometrial hyperplasia in menopause occurs not so much because of the strong increase in estrogen, but because of the duration of the increase in its amount. At the beginning of menopause, when menstrual cycles begin to pass without ovulation, the initial part of the cycle increases in time, and the decrease in progesterone does not allow it to cope with its function.
Endometrial hyperplasia in postmenopause appears relatively rarely, because the functional layer of the mucosa already dries out and does not grow. Many gynecological problems, such as fibroids, endometriosis, breast formations do not cause adenomyosis, but are indicators of increased female hormones, and therefore the risk of hyperplasia.
In case of early menopause, up to 45 years of age, diagnostic and therapeutic curettage is also prescribed in connection with the possible occurrence of this disease. This leads to the conclusion that before the end of menstruation, it is necessary to undergo regular examination by a gynecologist twice a year, and an ultrasound examination once a year. Almost always, to eliminate the pathology, it is necessary to carry out a curettage procedure.
Menstruation after removal of endometrial polyp or endometrial hyperplasia
Diagnostic curettage is often a planned operation, which is prescribed to women of reproductive age (menstruating) at the very end of the cycle, that is, 2-3 days before the start of a new one. During menstruation, it makes no sense to take the endometrium for analysis due to the impossibility of obtaining informative material for histological examination.
The endometrium, the top layer of the uterus, is removed during the procedure. But the ovaries continue to work, which means bleeding will still occur during menstruation, in response to a decrease in progesterone. But usually these discharges are not abundant.
If curettage was performed as an emergency surgical intervention due to a woman’s life-threatening condition, for example, uterine bleeding, then again, menstruation must be expected in the near future. Your period may come after 2 weeks if this minor operation was performed in the middle of the month. For this reason, doctors try to schedule planned operations at the end of the cycle, so that critical days do not occur after postoperative bleeding, but begin before its completion.
Women with untreated endometriosis, uterine fibroids and other gynecological pathologies can experience very heavy and prolonged periods after curettage, which last 10 days or even longer, since in most cases curettage is not a treatment, but a diagnostic procedure. With its help, doctors can exclude or confirm an oncological process.
Less painful and scanty monthly discharge is observed after diagnostic curettage (LDV or RDV) performed to remove a uterine polyp, including the placental one. After all, this benign neoplasm itself is the cause of large blood losses.
How to get your period if it's late
If the delay is less than 2 weeks, doctors advise waiting for the natural onset of your period. But if this does not happen, progesterone may be used. This is a hormonal drug that is injected intramuscularly or taken orally in the form of tablets (Duphaston or Utrozhestan).
The scheme is as follows: for five days, a woman takes 1 tablet of the drug (10 mg of progesterone) 2 times a day. And after the end of treatment, on days 3-7, menstruation begins.
In the future, the doctor may prescribe oral contraceptives (for example, Regulon) to normalize the cycle.
In what case is curettage performed?
If a woman is bleeding, this is the main danger signal, in which case you should not delay going to the doctor. Blood during menopause is an abnormal phenomenon, because the ovaries stop working.
The specialist will refer the patient for an ultrasound examination in order to determine the thickness of the uterine lining and the size of the female organ.
Normally, the endometrium reaches a thickness of 0.5 cm, and in postmenopause - 0.4 - 0.5 cm; if it increases to 0.7 cm, the woman is prescribed a repeat ultrasound after three months, and after six months. When the mucous membrane increases to 0.8 cm in thickness, the patient is sent for curettage, since this symptom is already considered dangerous to health. If the thickness exceeds 1 cm, the inside of the uterus is cleaned in the same way, but the cervix and the female organ itself are scraped out separately, and the removed epithelium is examined to identify pathologies.
The inspection takes place using special mirrors. A biopsy and examination with a hysteroscope are performed, as well as diagnostic cleaning. When menopause occurs, the uterus is normally reduced, the epithelium is modified, dried out, the cervix is narrowed and not elastic.
The structure of the endometrium is also studied, which also changes during menopause. If mucus is found in the uterus, its composition must be examined.
Different ways of performing the operation
The procedure is often compared to an abortion, but this is incorrect. Curettage is diagnosis and treatment, and abortion is the destruction of a natural gift. Moreover, such a comparison is possible due to the technical nuances of the operation, the use of instruments and the process technology itself.
Scraping is carried out in 3 ways:
1. Using a curette blindly.
2. Using a hysteroscope (in this case it is called hysteroscopy).
3. Separate curettage using one of these methods.
Curettage for diagnostic and surgical purposes using a curette
Method 1. Blindly
1. Curettes of several numbers are used, mostly small ones.
2. After dilation of the cervix, the curette is carefully inserted to the fundus of the uterus and withdrawn. At the same time, the doctor presses on the mucous membrane (endometrium).
3. The curette is first passed along the anterior wall, then along the posterior, lateral and corners of the uterus.
4. With complete curettage, the curette is carried out over the entire surface of the epithelium.
5. The resulting material (scraping) is removed with a curette into a prepared tray and sent to the laboratory.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 20-30 minutes. Before this operation you should not eat or drink. You will also need to do a cleansing enema the night before. And after the procedure, treatment with medications (hemostatic agents and antibiotics) is prescribed for 3-4 days.
What to do after surgery?
This is how long the recovery period lasts. It can be done at home, but in case of the following symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance:
The essence of scraping
This is a medical procedure that is performed after anesthesia is injected into a vein. A special instrument called a curette is used to scrape the endometrium from inside the uterus, and, naturally, injure the cavity of the female organ. This operation is considered therapeutic and diagnostic, due to the fact that the removed endometrium and polyps, if present, end up on the laboratory table, where they are examined for accurate diagnosis. Therefore, cleaning is often carried out not only with an accurate diagnosis, but also in cases where there is only a suspicion of some kind of illness.
This makes me think: maybe there is no need to do this cleaning? Maybe it’s possible to get by with injections and pills, physiotherapy? But, as we saw above, a disease such as endometrial hyperplasia in menopause, in most cases is treated surgically: either by curettage, or a laser, or a creo-device, and sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire organ.
No matter how experienced the doctor is, injuries during this operation are inevitable; it is good that after menopause there is no question of the risk of infertility. After all, cleansing is also carried out on young women, and it is also present during abortion. So cleaning itself at a younger age can lead to adenomyosis in menopause, and, ironically, you will have to do the same curettage again.
A procedure such as hysteroscopy helps solve this problem. Using the hysteroscope device, the doctor can see the inside of the uterus on the monitor, and diagnostic cleaning is not required, because all the pathologies are obvious.
Also, diagnostic curettage can be replaced with an endometrial biopsy, when a thin tube is inserted inside and sucks up tissue for analysis. And there is no need to do cleaning “just in case.” With hysteroscopy, there are all conditions to carry out a clean scraping of tissue, without leaving part of the mucous membrane inside, and to precisely remove polyps or cysts. So those ladies who live in areas where hospitals are equipped with this new equipment to eliminate female pathologies are terribly lucky.
Indications and contraindications for uterine curettage
Separate curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal is most often indicated for tissue collection for histological analysis, which is why it is called diagnostic. The therapeutic goal of the intervention is to remove the changed tissue and stop bleeding. The reasons for curettage of the uterine cavity are:
- Metrorrhagia - intermenstrual, postmenopausal and dysfunctional bleeding;
- Diagnosed hyperplastic process, polyp formation, tumor pathology of the mucous membrane;
- Incomplete abortion, when fragments of placental tissue or an embryo could remain in the uterus;
- Termination of short-term pregnancy;
- Dissection of adhesions (synechias) in the uterus.
- Postpartum endometritis.
Uterine bleeding, perhaps, remains the most common cause of curettage. In this case, the operation has, first of all, a therapeutic purpose - to stop the bleeding. The resulting endometrium is sent for histological examination, which makes it possible to clarify the cause of the pathology.
curettage for endometrial polyp
Curettage for polyp and endometrial hyperplasia, diagnosed by ultrasound, eliminates the pathological process, and histology clarifies or confirms the existing diagnosis. If possible, polypectomy is performed through hysteroscopy, which is less traumatic but just as effective as curettage.
Curettage is not uncommon after medical abortion and childbirth, when continued bleeding may indicate retention of fragments of placental tissue, an embryo, in the uterine cavity, and the formation of a placental polyp. Postpartum acute inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometritis) is also treated by removing the inflamed tissue and is supplemented by subsequent conservative treatment with antibiotics.
Curettage can be performed as a medical abortion. Thus, curettage of a frozen pregnancy diagnosed at a short term is one of the main methods of removing pathology, widely practiced in most countries of the post-Soviet space. In addition, a pregnancy that is developing favorably is terminated in this way if it is not possible or the deadline for vacuum aspiration is missed.
A woman who decides to have curettage during a normally developing pregnancy is always informed by the doctor about the possible consequences of the procedure, the main one being infertility in the future. There are also certain risks when curettage of a frozen pregnancy, so a competent specialist will try to avoid this operation altogether or suggest a vacuum abortion.
Adhesions (synechias) in the uterine cavity can be eliminated with a curette, but this pathology is increasingly becoming an indication for curettage due to the introduction of hysteroscopic techniques. After instrumental dissection of synechiae, there is a risk of their re-formation and inflammatory complications, so gynecologists try to avoid such radical action.
hysteroscopy
If there are absolute indications for curettage, then it is advisable to supplement it with hysteroscopy, because acting blindly, the doctor cannot rule out that the operation is not radical enough, and a hysteroscope makes it possible to examine the surface of the uterus from the inside and make the treatment as effective as possible.
Diagnostic curettage of the uterus can be performed routinely when, during examination and ultrasound, the gynecologist suspects hyperplasia or tumor growth. The purpose of such an operation is not so much treatment as obtaining fragments of the mucosa for pathohistological analysis, which makes it possible to accurately say what exactly is happening to the endometrium.
In the vast majority of cases, during curettage, the gynecologist sets the task of obtaining not only the endometrium, but also the lining of the cervical canal, which will somehow be passed through by the instrument, so curettage of the cervical canal is usually a stage of one large operation.
The mucous membrane of the cervical canal has a different structure from the endometrium, but polyp formation and tumor growth also occur in it. It happens that it is difficult to determine where exactly the process comes from, but the pathology can also be combined, when one thing happens in the endometrium, and something completely different happens in the cervical canal.
Separate curettage of the cervical canal and the uterine cavity is necessary to obtain tissue from both parts of the organ, and to prevent it from mixing, the gynecologist first takes samples from one part, placing them in a separate container, and then from the other. This approach allows the most accurate assessment of the changes occurring in each area of the uterus through histological analysis of the tissue obtained.
When prescribing curettage, the doctor must take into account the presence of contraindications, which include inflammatory changes in the genital tract, acute general infectious diseases, suspected perforation of the uterine wall, and severe concomitant decompensated diseases. It is worth clarifying, however, that when curettage is performed for health reasons (massive uterine bleeding), in the case of acute endometritis after childbirth or abortion, the doctor may neglect some obstacles, since the benefits of the operation are incommensurate with the possible risks.
Video: separate diagnostic curettage
How is a woman prepared for curettage?
Without preparation, the operation is not performed unless the woman is bleeding and immediate intervention must be performed. Before curettage, the patient is referred to a local therapist and specialists to find out contraindications to the procedure. Tests are also carried out:
- extended blood test;
- hepatitis test;
- AIDS test;
- for sexually transmitted diseases;
- heart electrocardiogram;
- vaginal smear;
- It is imperative to do an ultrasound of the female organ before the operation. Modern devices perfectly show the state of the endometrium, and there is no need to prescribe cleaning in order to make a diagnosis.
When diseases are identified, inflammatory processes and infections are first eliminated.
Preparation for the Russian Far East
Before endometrial RDV, a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist is required. The date of the examination is set taking into account the day of the menstrual cycle - it is important to choose a time a few days before your period. This will make curettage as close as possible to the physiological natural rejection of the functional layer and minimize stress for the body. If the purpose of RDV is also the removal of a polyp, the time may be chosen immediately after the end of menstruation. Thin endometrium will allow you to accurately determine the location of the formation and effectively remove it.
In preparation for the Russian Far East, you will need to take tests:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- coagulogram (determination of clotting characteristics);
- ECG;
- blood tests for infectious diseases (HIV, hepatitis B, C and syphilis);
- flora smears;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- biochemical blood test (determining the functioning of the liver, kidneys, and glucose levels);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
At the first consultation, the specialist will tell you what you need to take with you from personal belongings and hygiene items, and will also advise you on how long you need to abstain from food and drink before and after the operation.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia in menopause
- diagnostic curettage is performed;
- after analyzing the material from the uterus, the gynecologist selects a set of hormones necessary for the stagnation of hyperplasia, and during the treatment process observes changes in the mucous membrane and the state of hormonal balance;
- abnormalities found in the uterus are scraped out using a laser in some areas of cell proliferation;
- in surgery, a combination of hormonal and surgical forms of influence is carried out; hormones reduce the thickening of the epithelium, and during surgery, a smaller area needs to be cleaned;
- if the disease relapses, the organ is removed, after which a course of hormones is administered again.
After scraping
If a woman has undergone this operation, she should not forget about the problem and undergo an examination by a gynecologist, and if prescribed, an ultrasound examination four times a year from the date of the procedure. Curettage has some health consequences: within three to ten days there may be bleeding, and this fact should not frighten the patient. This removes the remaining endometrial particles. After six months, the doctor must do a diagnostic cleansing to make sure that the disease has not returned, and prescribe the woman medications that the doctor considers necessary during this period.
You need to know that in case of severe bleeding, taking hemostatic drugs will not solve the problem, but will only delay it, and you will have to go for curettage. But you can lose precious time, exhaust your body from blood loss, and also get cancer, which, in most cases, ends in death.
In conclusion, we want to warn you that at an appointment with a gynecologist, you can ask him a question about whether curettage is really necessary, whether it is possible to get by with a biopsy or taking medications in your case. This is your health and your life, and surgical intervention is definitely necessary only in case of severe bleeding or recurrence of the disease. Be healthy!
Interesting video on this topic:
About
After the procedure
A successfully performed diagnostic intervention does not guarantee the absence of complications, since successful rehabilitation depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body.
In the first hours after surgery, the patient may feel severe pain. These manifestations do not last longer than 2-4 hours, turning into mild nagging pain that persists for 7-10 days.
Do I need to use antibiotics, can I take painkillers, what kind?
To prevent the development of inflammatory processes, antibiotics are prescribed to each patient after curettage. In addition, women with a low pain threshold should take painkillers to relieve acute pain.
For these purposes, antispasmodics (No-spa or Drotaverine), analgesics (Indomethacin, Ibuprofen), and antidepressants are used.
How long does the discharge last?
Patients are often interested in how much bleeding there is and whether there may be other discharge after cleaning the uterus. The average duration of bloody spotting is 3-9 days.
In gynecological practice, there are cases when it is not necessary to talk about how much blood is flowing, because after cleaning the uterus, the patient experienced a cervical spasm, and a hematometra (large blood clot) formed inside the organ.
This condition is usually accompanied by severe pain, fever and requires immediate medical attention. The diagnosis can be clarified using an ultrasound that detects the spasm. When the uterus does not contract, Oxytocin is most often used, which stimulates its contractility, as well as antispasmodics and analgesics.
When will the monthly cycle be restored?
Normally, the first menstruation after curettage occurs within 4-6 weeks. During this period, the uterine mucosa is regenerated, the endometrium is restored, and therefore menstrual function is restored.
If contraception is abandoned at the end of this period, a woman is able to become pregnant even before the cycle is restored. When planning a pregnancy, it is better to carry out the conception procedure after 3 full menstrual cycles.
If the first menstrual flow after diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is abundant or, conversely, too scanty, accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, you need to contact your doctor.
In this case, the menstrual cycle takes much longer to recover, and its inherent cyclicity is often disrupted. The same complications result from the formation of synechiae (adhesions) that interfere with menstrual function.
When can you have sex?
It is better to postpone restoration of intimate relationships after this procedure for 2 weeks. The restriction is associated with an increased risk of pathogenic microorganisms entering the uterus, leading to the development of an inflammatory process.
After curettage, the cavity of this organ represents an extensive wound surface, extremely susceptible to infection.
It is quite possible that even after this period, sexual intercourse may be accompanied by pain or discomfort. These unpleasant phenomena usually last a short time and pass quickly.
Share this post
▲ error: Who's here?