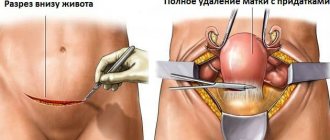
If a woman is definitively diagnosed with uterine fibroids, abdominal surgery may be the only possible method of eliminating this pathological condition. During the procedure, a conservative method may be used, which allows completely preserving reproductive functions, as well as a radical option, which involves complete removal of the uterus. Regardless of the chosen option, abdominal surgery is an intervention in the location of the abdominal cavity using incisions. The surgical intervention requires general anesthesia and observation of the patient in a hospital during rehabilitation.
How is abdominal surgery performed?
Performing abdominal surgery is possible only if there is a certain type of indication and as a last resort; in other situations, doctors tend to use more gentle methods in the form of FUS ablation, embolization and the like.
If the patient’s condition and the nature of the pathology do not allow the problems to be eliminated by conservative measures, the only option is abdominal surgery. This situation also has its positive aspects; it reliably gets rid of myomatous nodes, and removes all pathological tissue, thereby minimizing the possibility of relapses. The success of the operation depends on the preparatory period, during which possible deviations in the state of health are identified through tests and consultations with various specialists.
The operation is performed using incisions in the abdomen, especially necessary to eliminate necrotic processes in the nodes or in case of torsion of the fibroid stalk. Since these conditions are threatening and cannot be delayed, it is with the help of a cavity incision that it is possible to fully assess their severity and take the necessary measures to eliminate it. The operation itself takes place in accordance with certain periods, strictly transforming one into another, as follows:
Anesthesia
To ensure the painlessness of the procedures, general anesthesia is performed using special drugs. To determine the drug used, the patient meets with an anesthesiologist before the operation, who selects the drug for anesthesia based on the individual characteristics of the body. In case of contraindications to general anesthesia or at the choice of the anesthesiologist, a spinal type of anesthesia with a locally targeted effect can be performed.
Performing access
This action is the beginning of the operation, for which an external incision is made in the lower parts of the peritoneum. Its size usually does not exceed 20 centimeters, which is determined by the size of the tumor being removed.
Operation
The next stage consists of direct removal, when the surgeon cuts off the affected organ, while simultaneously taking measures against possible uterine bleeding. If the entire uterus is removed, the tubes are also removed along with it, trying to preserve the ovaries if possible. After removal and visual examination, which makes it possible to verify the correctness of the operation, the stump at the site of removal is sutured with obligatory observance of the tightness of the abdominal region.
Layer-by-layer suturing
Suturing an incision after abdominal surgery involves suturing the tissues in layers, since the peritoneum on the inside has a significant thickness, and the tissues that form it consist of many layers, each of which is sutured.
What determines the choice of method?
Since laparoscopic surgery is a low-traumatic procedure, in many cases it is preferable to abdominal surgery (laparotomy). But such access is not realized for every pathology.
The main indications for elective laparoscopy include:
- diagnostics;
- gynecological manipulations for infertility, ectopic pregnancy, severe secondary dysmenorrhea;
- removal of cysts or fibroids;
- appendix removal;
- operations on organs of the hepatobiliary system.
Laparoscopic diagnosis for emergency indications is carried out in cases of suspected ovarian apoplexy or cyst rupture, tubal/ectopic pregnancy, necrosis of the myomatous node, as well as severe pain in the abdominal region of unknown etiology.
If there are conditions and opportunities for carrying out the intervention in a low-traumatic way, it is more preferable. Although even experts will not clearly answer the question of which is better - laparoscopy or abdominal surgery, since these methods cannot and should not compete with each other.
It is better to entrust the choice of the optimal method of surgery to your doctor - only he can evaluate all the possible advantages and risks of a particular method. It is not worth insisting on laparoscopy - very often it is not able to replace a full-fledged abdominal intervention.
Indications
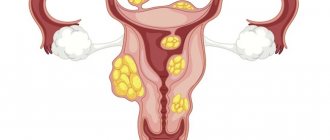
When planning surgery to remove fibroids, many highly individual factors must be taken into account. Thus, abdominal surgery is performed in the following conditions of the body:
- myomatous formation, accompanied by heavy bleeding;
- menstruation with heavy blood loss lasting longer than expected;
- development of anemia;
- as a result of compression of internal organs located near the uterus with disruption of their basic functions;
- large size of fibroid nodes;
- constant feeling of pain;
- formation of a fibroid node in the cervical part of the uterus;
- the presence of cysts, endometriosis, displacement of the organ with its threat of prolapse;
- infertility caused by large fibroid nodes;
- threat of malignant degeneration.
Many of the conditions on the list are so serious that they require immediate surgery.
What is laparoscopy
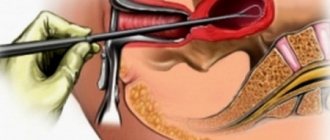
One of the breakthroughs in medicine was a new method of performing operations - laparoscopy. Its essence is that ordinary cuts with a scalpel are replaced with several punctures in certain places. Most often, this type of surgery is used in the abdominal and pelvic area. The main diagnostic tool is a laparoscope, consisting of lenses and a tube. A lighting cable is attached to the tube. During the operation, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide, which acts as an air cushion for the internal organs. Removal or correction of damaged organs is carried out with special surgical instruments - manipulators.
Preparation for abdominal surgery
The preparatory period for the upcoming operation performed by the abdominal method consists of the following points:
- Laboratory tests are examined, foci of infection and the presence of inflammation are identified;
- consult with a therapist;
- ECG, ultrasound, in some cases, if indicated, MRI;
- gynecological examination to check for the possibility of erosion, and if it is detected, taking a smear for a biopsy.
If the myomatous formation is large, three months before surgery, treatment with hormones is carried out to help shrink the tumor and facilitate its removal.
Scope of operational actions
The patient’s condition after the operation and the duration of recovery depend on the volume of actions performed and the degree of pathological changes in the reproductive system at the time of the operation. If abdominal surgery uses conservative methods, then both the intervention itself and the rehabilitation period will require less effort and a short rehabilitation period.
In the case where the operation was carried out in a radical way, much more time may be spent on restoring the physical and psychological state, as well as on the operation itself with the removal of fibroid nodes along with the uterus.
The duration of the entire operation performed by the cavity method takes from 40 minutes to 2 hours.
Why doesn't everyone recommend laparoscopic surgery?
Of course, after these positive qualities, few will doubt which operation is better: abdominal or laparoscopy for the patient. But when comparing, complications that are acceptable in medical practice cannot be excluded when laparoscopic surgery is performed. So, as with conventional manipulations, there is a risk of damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs. With major bleeding, the surgeon has no view, and stopping the bleeding becomes more difficult. A bloated stomach creates some discomfort, but cannot harm a person, with the exception of painful sprains. Over time, the phenomenon passes through intercellular metabolism.
If we are talking about whether abdominal surgery or laparoscopy is better when removing the uterus, then we need to consider all the options, consequences, and risks for the patient.
https://youtu.be/gW_furAjHVI
Source: proskopiyu.ru
Myomectomy
Conservative myomectomy is a surgical intervention that removes fibroids while preserving the integrity of the uterus and its reproductive capabilities, and even menstrual function is preserved. An important advantage of this method of surgery is its low invasiveness and short recovery period after it.
The disadvantages include the possibility of relapse even several years after the operation, as well as the risk of damage to nearby organs from working with the instrument.
But are such operations always possible?
“Laparoscopy is a modern surgical method that allows you to gain access to the abdominal cavity using small puncture holes,” says Philip Levshin, an obstetrician-gynecologist at a network of reproductive and genetics centers. — Since such an operation does not involve layer-by-layer opening of the abdominal wall, the invasiveness of the intervention is significantly reduced, the rehabilitation period is shortened, and the risk of complications is reduced.
Initially, laparoscopy was used only for diagnostic purposes, but then it became a full-fledged medical and surgical technique that makes it possible to perform complex operations.
Moreover, some interventions simply cannot be performed using laparotomy (an incision in the abdominal wall).
Article on the topic
If the fibroid grows. Is it possible to save the uterus?
Complications
A feature of abdominal surgery is the risk of postoperative complications, and they can manifest themselves during the procedure, not to mention the rehabilitation period, during which the possibility of their development increases even more.
It can be:
- uterine bleeding;
- mechanical injuries to organs adjacent to the uterus;
- development of peritonitis and sepsis;
- purulent inflammation of the postoperative scar.
Compliance with all requirements reduces the risk of complications, however, their likelihood cannot be completely excluded.
Recovery in the postoperative period
The recovery period as a result of surgery to remove fibroids usually takes about one month; in the case of serious conditions that require long-term abdominal surgery, recovery of the body can last up to two months or more.
For rapid healing of surgical incisions, it is recommended to completely abstain from sexual relations, strictly follow the recommended diet, and prevent the occurrence of intestinal disorders and constipation. It is necessary to exclude physical overexertion and provide the body with a sufficient amount of food with a high protein content. There is no need to give up light exercise; dancing, gymnastics, swimming, walking every day, but without excessive fanaticism, are suitable.
It is better to consult a gynecologist about the intricacies of the rehabilitation period; by correctly following his advice, you will be able to ensure a quick recovery with no complications.
Diet
Carrying out abdominal surgery affects not only the organs of the reproductive system, but also the anterior abdominal wall, so it is necessary to ensure careful treatment of the organs located there to prevent tissue injury. During the postoperative recovery period, the patient must adhere to a certain diet, including liquid dishes in the menu that prevent constipation, as they contribute to tension in the abdominal muscles during defecation difficulties.
Forecast
If the operation to remove fibroids is successful, then the possibility of a further healthy and fulfilling life for the patient is more than likely. Intimate life does not suffer, since the most sensitive areas for sexual life are located in the vagina. The ovaries continue to function and produce the required amount of necessary hormones. Adhesive processes that form as a result of the operation can overshadow the state of usefulness; however, following the doctor’s advice and using special means during the rehabilitation period, they soon cease to bother you.
Why is hysterectomy dangerous for a woman in the future?
The effects of hysterectomy can take quite a long time to appear.
Unfortunately, more than 70% of women develop post-hysterectomy syndrome after surgery.
Most often, this condition occurs against the background of a reduced level of estrogen in the patient’s body. Most doctors agree that only if you have two ovaries, you can delay the development of menopause as much as possible (by 5-6 years) with a hysterectomy. But at the same time, the younger the patient, the earlier she may experience estrogen deficiency.
https://youtu.be/AdmY5lCPt4g
Low levels of the hormone estrogen are an impetus for the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Thus, for women under 50 years of age who have undergone an extirpation procedure, the risk of developing cardiac pathologies increases significantly.
According to statistics, removing the uterus increases the likelihood of developing thyroid and kidney cancer. It is impossible to predict exactly what consequences await a woman after extirpation. Patients note the manifestation of such signs of menopause as: unstable psycho-emotional state, insomnia, feeling of heat. Already at the age of forty, a woman can experience all the “delights” of postmenopause.
Impaired metabolism, in particular calcium deficiency, is a common cause of osteoporosis. Estrogen deficiency causes vaginal dryness and significantly reduces the quality of sexual life. The woman stops experiencing orgasm, the number of sexual acts decreases significantly. The natural functioning of the urinary system is disrupted.
More than 20% of patients develop urinary incontinence. Failures in the functioning of a woman’s endocrine system lead to obesity (every third patient suffers).
Alas, not every woman understands the dangers of having a hysterectomy, which is why many take their health so lightly. Further consequences of surgical removal of the uterus along with fibroids will persist for many years.
Myoma removal price
It is quite difficult to determine exactly the cost of the operation; all cases are purely individual and depend on many factors. The price primarily varies due to the location of the clinic in a certain region, the status of this medical institution, its availability of modern equipment involved in the operation, the qualifications of the doctor, the cost of medications and materials. The final cost of abdominal surgery to remove fibroid nodes is significantly influenced by the stage of the disease and its nature, as well as the size of the myomatous formation. On average, for this operation in a private clinic you will need to pay from 10 to 70 thousand rubles.
Pregnancy after surgery
Abdominal surgery with the removal of myomatous formations is one of the most traumatic, therefore, with a preserved uterus and the possibility of conception, you can plan a pregnancy no earlier than in a year. Before conception, a woman should check the condition of postoperative sutures in the uterine cavity, due to the fact that due to existing scars, the elasticity of its walls becomes much worse and fetal growth during pregnancy can cause serious complications, including suture dehiscence.
If fibroids are detected in a timely manner and comprehensive therapeutic treatment is carried out, after surgery to remove fibroids, a woman can have no doubt about her abilities regarding the upcoming pregnancy. Abdominal surgery with preservation of reproductive functions allows not only to eliminate the disease itself, but also to enable a woman to become a mother. To prevent a radical method of removing myomatous formations, doctors recommend visiting a gynecologist at least twice a year and undergoing an examination with him in order to timely detect pathological changes.
Sick leave
A sick leave certificate, in the case of abdominal surgery to remove fibroids, is issued with an update every 15 days, and the total duration of sick leave largely depends on the patient’s condition and can last for a year. If the patient’s condition has not improved during this time, she is sent to medical examination to determine whether she can begin work, and if so, then with what duties.
Rehabilitation depending on the type of operation
The recovery of the body and the speedy return of the patient who had uterine fibroids removed is determined by many factors, where the type of surgical intervention plays an important role.
The longest and most difficult postoperative period after removal of uterine fibroids is characteristic of abdominal operations.
After getting rid of the tumor in this way, the patient remains in hospital for 8 to 14 days, and the entire rehabilitation lasts for 1–1.5 months.
When removing fibroids using the laparoscopic method, the patient is observed in the hospital for 3 days to a week, and the recovery process takes no more than a month. Approximately the same indicators accompany rehabilitation during vaginal hysterectomy.