Diagnostics
The doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes the necessary treatment for fibroids after collecting data about what worries the patient, as well as whether there are hereditary factors that could influence the occurrence of the disease. In order to understand that interstitial-subserous uterine fibroids or other types of neoplasm are progressing in the body, you should undergo the following diagnostic measures:
- Get examined by a gynecologist;
- Donate blood;
- Undergo an ultrasound examination;
- Undergo computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These procedures will help you understand how large the fibroid has reached and where exactly it is located.
Why does it happen?
The main cause of fibroids is hormonal changes. This triggers excessive growth of smooth muscle cells in the body. Age-related changes also affect neoplasms, for this reason they are more often found in adulthood and premenopause.
Its appearance is also influenced by ovarian diseases, nervous strain, and chronic infectious diseases. Various surgical procedures can provoke the formation of a tumor. This includes diagnostic curettage, abortions, laparoscopic examination, etc. All this injures the tissues of the uterus.
Attention! Additionally, the causes of the development of the disease can be: genetic predisposition, long-term use of hormonal drugs, problems in the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Symptoms of subserous uterine fibroids
Sometimes the nodes do not cause concern to the woman, and the presence of fibroids is discovered by the gynecologist during a routine examination. Most often this happens when a small intramural or subserous tumor appears. The presence of symptoms occurs due to the number of nodes formed, the size and location of the tumors.
Representatives of the fair sex often experience symptoms such as:
- Very strong and prolonged discharge with clots during menstruation. As a rule, the period of critical days passes painfully;
- Between menstruation, spotting appears;
- Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, pain and heaviness;
- Lower back pain.
Symptoms
Almost all uterine formations with a benign nature of a small size, including intramural-subserous fibroids in the uterus, occur hidden. Pathology is detected by ultrasound. With the rapid growth of nodes, signs appear.
The disease is accompanied by:
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- unpleasant pulling sensations in the stomach, lower back;
- increased urge to urinate;
- frequent constipation, discomfort when visiting the toilet;
- inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- excessive sweating;
- cycle disruptions (menstruation becomes painful and prolonged);
- rapid fatigue;
- edema (due to impaired venous blood flow).
Interstitial tumor, like submucosal tumor, is characterized by heavy menstruation. Subserous fibroids of the uterine body are characterized by pain.
Pathology, if not treated in time, leads to infertility and miscarriage. The tumor can develop into cancer.
Manifestations of fibroids in the uterus depend on location and size. However, the disease often occurs latently, even if the tumor is large or multinodular. Determined by ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Uterine fibroids are characterized by the following symptoms and signs:
- menstrual disorder (menstruation becomes heavy, painful, irregular);
- increased urge to urinate;
- constipation;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen;
- infertility.
The pathology is often characterized by convulsions (due to compression of muscles and nerve endings). More girls face illness.
In addition to the general symptoms, there are specific ones:
- Submucosal fibroids are characterized by uterine bleeding and severe pain.
- Intramural and interstitial fibroids are accompanied by an increase in the duration of menstruation.
- Cervical formations are characterized by dysuric phenomena, difficult defecation, and severe pain.
The development of pathology is divided into 3 degrees:
- The first or the formation of an active growth zone in the muscle layer with acceleration of metabolic processes.
- Second or growth of formation (no signs of differentiation).
- Third or maturation of fibroids.
Prognosis and prevention
Subserous fibroids are tumors in which the risk of transformation of benign cells into malignant ones is extremely low. Therefore, the prognosis for this disease is quite favorable. If the disease is detected in time and the doctor prescribes the correct treatment regimen, the patient will be able to overcome the disease. As a preventative measure, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a gynecologist at least once a year.
Women should adhere to the following preventive rules:
- Proper nutrition, including fruits and vegetables in the diet;
- Moderate physical activity;
- Regular sex life;
- Use of COCs;
- Vitamins that will restore hormonal balance;
- Ultrasound and examination by a gynecologist once a year.
Dangers of the disease
Why is uterine fibroid of the subserous variety dangerous?
- The presence of nodes reduces the contractility of the myometrium, and painful and heavy menstruation begins, leading to the development of iron deficiency anemia.
- Growing nodes can put pressure on the bladder and there will be frequent painful urges or difficulty urinating. When the rectum is compressed, there will be frequent constipation and possible hemorrhoids.
- The development of the disease can lead to infertility.
- Degeneration of the benign nature of the myomatous node into malignant.
The probability of degeneration of subserous leiomyoma into a malignant tumor is 1-2%. But when it comes to human life, all risks should be reduced to zero. To avoid the development of dangerous complications, you need to undergo regular medical examinations.
Dimensions for surgery
Before raising the question of surgical removal of subserous uterine fibroids, the doctor first determines the size of the tumor. For this purpose, an ultrasound scan is performed. Surgery may be required in the following situations:
- If the total volume of the tumor looks like six to seven weeks of pregnancy, and the size of the node is 20 mm. If the tumor grows rapidly, surgery is required;
- If the fibroid has reached medium size and resembles pregnancy at eight weeks and the node reaches a size of no more than 40 mm;
- Large fibroids, which consist of one or more nodes, size is 60 mm. In this case, urgent surgery is required;
- For submucosal fibroids, surgery is required if the node reaches 50 mm; for larger sizes, other options for treating the disease must be considered.
Clinical picture
Since the tumor grows in the abdominal cavity, no noticeable symptoms are observed. Obvious signs appear when subserous fibroids become large. The grown tumor begins to affect nearby tissues and organs.
Suspicion of fibroids should be caused by symptoms such as:
- constant constipation;
- problems with urination;
- hypertension;
- dizziness;
- discomfort in the abdomen and lower back;
- the appearance of pain above the pubis.
Symptoms are especially pronounced when standing for a long time or during heavy physical activity. If the pain is similar to contractions, this indicates an exacerbation of the disease. It is worth noting that when the tumor fuses with the abdominal wall, the patient begins to suffer from constant aching pain.
Treatment
The doctor prescribes individual treatment for subserous uterine fibroids based on the examination results and the size of the fibroid nodes. Large tumors are removed surgically. If the myomatous nodes are small, then sometimes you can limit yourself to conservative therapy, embolization of the uterine arteries, or carry out regular monitoring of the tumor and make sure that it does not increase in size. This procedure is performed approximately four times a year in order to monitor the growth of fibroids.
Conservative treatment
This type of conservative therapy requires the following medications:
- Combined oral contraceptives, which include progesterone estrogen;
- Antiestrogens, they are prescribed to patients over 45 years of age;
- Antigonadotropins and gonadoliberins;
- Gestagens.
Patients must undergo treatment for three months. In parallel with this, the patient is required to follow a certain diet. At the end of treatment, the woman should be observed by her doctor.
FUS ablation
It is a type of therapy in which tumors are destroyed remotely using focused ultrasound under the control of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. Ultrasonic evaporation of tumor tissue occurs. The main advantage of this procedure is that sound waves do not harm the tissues of the human body. Removal of fibroids is thus well tolerated by patients. This type of therapy is the safest in the process of removing formations.
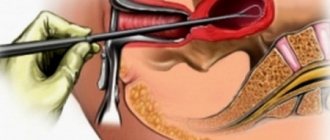
Myomectomy
This process involves a procedure in which the nodes that have formed in the uterus are surgically removed. In this case, the body of the organ is sutured. If a woman wants to preserve reproductive function, then she should choose this technique. This method also allows you to keep your menstrual cycle unchanged.
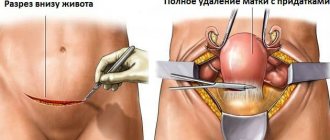
In some cases, a hysterectomy is required. The procedure involves removing the uterus. It is usually carried out when the subserous fibroid reaches too large a size and there is a threat to life. Also, its use is necessary when it is impossible to eliminate the disease by other means.
Abdominal surgery to remove uterine fibroids
Before the procedure, it is important to follow all established recommendations of the specialist. According to many doctors, abdominal surgery is becoming the only way to effectively treat fibroids. After surgical treatment, you need to be observed by a doctor for a month.
Abdominal surgery is indicated in the following cases:
- The neoplasm is of medium size, and one node is larger than the others;
- The tumor becomes larger;
- Due to fibroids, heavy uterine bleeding occurs;
- Infertility due to tumor growth;
- Necrosis of the muscle node.
Folk remedies
Treatment of fibroids with folk remedies is suitable for women with small fibroid nodes. This method is best used exclusively in combination with the main treatment. Before you start taking decoctions, tinctures and other remedies, you should consult your doctor.
Effective recipes:
- Herbs that stop bleeding. If the discharge during menstruation is very strong, then decoctions of burdock, nettle, barberry, and shepherd's purse help well. They help reduce the amount of blood.
- Potato juice. Helps get rid of inflammation, spasms, pain. It strengthens the immune system and improves metabolism.
- Flax seeds. Effectively fights the disease. The seeds balance the balance of hormones contained in the female body.
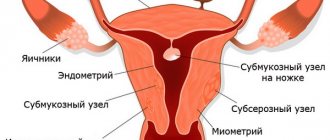
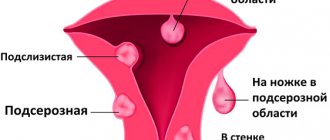
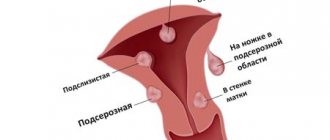
Classification
Submucosal nodes:
- Type 0 is a pedunculated submucosal fibroid located in the uterine cavity.
- Type 1 - the node protrudes into the uterine cavity by more than half.
- Type 2 - the node protrudes into the uterine cavity by less than half.
Other types:
- Type 3 is an intramural fibroid that does not protrude into the uterine cavity, but is adjacent to its mucous membrane.
- Type 4 is an intramural fibroid, which is located deep in the muscles.
- Type 5 is an intramural subserosal node that protrudes less than half of the way out on the surface of the uterus.
- Type 6 is an intramural subserosal node that protrudes more than half of the surface of the uterus.
- Type 7 is a pedunculated subserosal node that is entirely above the surface of the uterus.
- Type 8 - fibroids that have a specific localization (for example, in the cervix).
- Hybrid nodes that affect both the mucous membrane of the uterus and its outer surface. They are designated by two numbers.
Depending on the number of nodes, there are three types of fibroids:
- Single - 1-2 nodes, which can have different sizes.
- Multiple. More than 3 nodes are detected. Treatment usually helps reduce symptoms, but it is often not possible to remove all fibroids, and some may grow large over time.
- Mixed. There are many fibroids, but at least one of them is large and dominant. For example, multiple fibroids with a large subserous node may be diagnosed. It can be removed, but another node may grow strongly in the future. Multiple and mixed fibroids pose a particularly big problem in women of reproductive age before menopause, since sex hormones promote the growth of nodes.
Formations are distinguished by size, structure, and location. There are these types of nodular formations.
Table - Types of fibroids
| Groups | Varieties |
| By degree of maturity |
|
| By number of nodes |
|
| To size |
|
| By localization |
|
A hormone-dependent neoplasm of a benign nature, which consists of muscle and connective tissue, as well as blood vessels, is called fibromyoma (more connective fibers) or myoma (muscle). No woman is immune from the occurrence of pathology, but women of childbearing age are more susceptible to tumor formation. It is diagnosed in girls over 30 years of age.
Often, fibroids occur hidden. The first signs occur when nodes rapidly grow and compression of neighboring organs occurs.
The origin of the formation occurs in the wall or in the uterine cavity. It is often detected on the neck.
If the formation is not localized in the body of the reproductive organ, it does not interfere with successful conception. Large nodes negatively affect the course of pregnancy. They provoke disruption of the normal position of the fetus, premature birth, and miscarriage. The most dangerous location of nodular fibroids is considered to be on the cervix, since childbirth is often complicated by severe bleeding.
| Group | Varieties |
| By tissue composition |
|
| By location |
|
| In count |
|
| According to the activity of metabolic processes |
|
Cases of fibroids developing during pregnancy are not uncommon. The formation is detected in young girls, often by ultrasound. Observation is indicated for women who have been diagnosed with pathology. Small knots do not harm the baby. Large fibroids in the body of the uterus negatively affect the course of pregnancy and can lead to miscarriage and early birth.
Often in women with the disease, the baby has a breech or transverse presentation. They do not give birth on their own; they undergo a caesarean section.
During breastfeeding, fibroids, if they are not multiple nodes, may completely disappear or significantly decrease in size.
Postoperative period
After the operation has been performed, patients remain in the hospital for some time to avoid complications. Every woman's body reacts differently to surgery.
During the recovery period, you may experience:
- Heat;
- Weakness;
- Swelling of the limbs.
To recover faster, you need to adhere to a balanced diet (it is very important to include proteins in your diet). You should also spend more time outdoors and limit yourself from physical activity. It is highly recommended not to sunbathe and visit SPA salons, beaches and saunas. Sexual rest should last for 2-3 months. In addition to the rules described above, to avoid relapses, the doctor prescribes hormonal medications.
Reasons for development
As noted, the development of a tumor can be influenced by the following factors:
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- hereditary predisposition;
- damage to the uterine myometrium.
Symptoms of subserous pathology are focused on painful sensations of a pulling, aching nature. The area of their localization is the upper abdomen, with irradiation to the back.
The pain may intensify after physical fatigue, stiffness of the pelvic muscles, or against the background of colds.
Subserous uterine fibroids and pregnancy
During pregnancy, subserous myomatous nodes are quite common. In this situation, it is necessary to follow all existing doctor’s recommendations. Any self-medication, in this case, is extremely contraindicated. Danger arises when multiple fibroids appear, the size of which exceeds 5 cm. This can provoke deformation of the fetus. During pregnancy and childbirth, the following problems sometimes arise with fibroids:
- Difficulties arise in feeding the nodes, which can provoke a miscarriage;
- Sometimes late toxicosis appears, which has a bad effect on the child’s health;
- The interaction between mother and fetus is disrupted.
Doctors will do everything possible to save the baby's life. With subserous fibroids, the expectant mother has every chance of bearing and giving birth to a healthy child.