Inflammation again!
Unfortunately, the first signs of trouble in the pelvic floor often escape the attention of not only the women themselves, but also the gynecologists who observe them. Most doctors consider a slightly open entrance to the vagina and slight sagging of its walls to be normal. They are much more interested in treating various inflammations, restoring the vaginal microflora, etc. However, the fight against infections in such patients almost always turns out to be ineffective, because inflammation occurs precisely due to the fact that the open genital opening does not fulfill its protective role. And the woman visits the gynecologist again and again, regularly and unsuccessfully struggling with itching, burning, and pathological discharge.
Meanwhile, if preventive surgical correction of the pelvic floor is carried out in time, then in the future it is possible not only to avoid uterine prolapse, but also to preserve the vaginal flora. This means reducing the risk of inflammatory diseases of the genitals and cervix, improving the quality of sexual life, and also coping with chronic constipation, gas and urinary incontinence common to this disease.
https://youtu.be/mQu_3qsjVs8
Symptoms and signs
Signs of uterine prolapse are individual: in some women the process develops over years and rarely makes itself felt (in the form of small deviations in well-being), in other cases the symptoms are pronounced when the disease develops dynamically.
Initially, women feel pain in the lower abdomen or discomfort in this area. The pain radiates to the lower back and sacrum. These symptoms do not alarm patients, as they associate them with the upcoming menstruation.
If the uterus is significantly lowered, the pain will be bothersome after lifting weights or physical activity. In the future, sex will fade away: it does not bring pleasure and causes severe pain.
Causes of uterine prolapse in women - infographics
The patient may notice white or bloody vaginal discharge. She begins to worry about the feeling of a foreign body inside. A woman is able to feel the cervix or the cervix itself (if it has prolapsed) in the area of the genital slit with her own hands.
When the genital organ prolapses, severe and prolonged bleeding is observed during menstruation, and disruptions in the menstrual cycle are observed. The patient's medical history may include a diagnosis of infertility.
Prolapse of the anterior wall of the vagina leads to a cystocele (protrusion of the bladder into the vagina).
Pathology leads to:
- Problems with urination.
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Stagnation of urine and the proliferation of pathogenic organisms that infect the upper and lower urinary tract.
- Ureteral stenosis.
- Hydronephrosis;
- Urinary incontinence when coughing or laughing too hard.
When the posterior wall of the vagina prolapses, a rectocele or prolapse of the rectum is recorded. This causes regular constipation and problems with gas and stool control. Colitis appears against the background of rectocele.
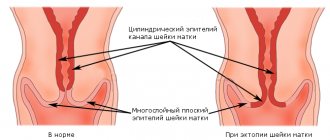
There are frequent cases of ulcers forming on the mucous membranes of the uterus and vagina. The mucous membrane of the organ walls constantly shrinks, cracks and is injured. This leads to infection and bleeding.
Young mothers are in danger
Among the “culprits” of prolapse, doctors name a chronic increase in intra-abdominal pressure that occurs when lifting heavy objects, sneezing and coughing; age-related degradation of collagen fibers of connective tissue; decrease in estrogen levels during menopause; impaired microcirculation in the pelvic area, as well as traumatic childbirth.
Most often, pelvic organ prolapse occurs as a result of injuries (ruptures or cuts of the pelvic floor muscles) in women who have given birth naturally. In cases where only deep layers are damaged, these injuries can go undetected for a long time. The easiest way for a young mother to find out whether everything is okay with her pelvic floor anatomy and whether the muscles were damaged during childbirth is to see a doctor. If no changes are detected, then most likely there will be no problems in the future.
Patient reviews
Despite the fact that at the moment the only radical way to combat uterine prolapse is surgery, not all doctors decide to perform it. Diagnosis often takes many months. Many patients are faced with a situation where, even with complete prolapse of the uterus (the last stage of the disease), the gynecologist insists on conservative treatment, recommends exercises in the pool and gymnastics that strengthen the pelvic muscles.
In their reviews, patients note that conservative therapy is most often ineffective, and in the end they still have to resort to surgery. In addition, many women face a problem in the first months after childbirth, when it is not possible to do long-term exercise and be away for a long time.
Most women undergo a paid operation, since often in a regular consultation there are difficulties with issuing a referral, making a diagnosis, and determining the stage of the disease. Surgical intervention proceeds, as a rule, without complications. Most patients are satisfied with the result, although some do not tolerate the recovery period well. Women write that surgery has improved their sex lives and overall well-being.
To have surgery or not is a woman’s personal choice. However, many patients report a significant improvement in quality of life, while the risk of negative consequences and complications is minimal. Experience shows that conservative treatment in most cases is useless, and only surgery for uterine prolapse helps solve the problem.
Artistic suturing
There are conservative methods for treating prolapse: exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles; hormone replacement therapy, which replenishes the deficiency of female sex hormones estrogen; vaginal pessary (a special ring is inserted into the vagina for a long time, which supports the uterus in the correct position). None of these methods treat prolapse itself, but only help cope with the symptoms. Gynecologists rightly believe that the problem of pelvic floor muscle failure can only be solved surgically.
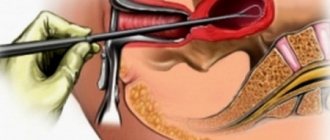
The operation to prevent uterine prolapse is quite simple. A triangular flap of the vaginal mucosa is excised through the vaginal opening, and then the pelvic floor muscles, which have lost their normal location, are exposed. After this, they are captured using a ligature (binding threads) and pulled towards each other, returning to the desired position. After this, the vaginal mucosa and perineal skin are restored.
The relatively short surgical procedure does not require general anesthesia. As a rule, everything is managed with gentle spinal anesthesia, which blocks the innervation below the belt.
The postoperative period lasts from 7 to 10 days.
Classification
Such a concept as a prolapsed uterus goes in tandem with the term “prolapsed vagina”, therefore both pathological conditions are mentioned in the classification:
- 1st degree - the cervix is localized in the middle of the vagina or higher.
- 2nd degree - the vaginal walls and neck of the genital organ are shifted to the vestibule of the vagina.
- 3rd degree - the uterus is in the vagina, and its cervix and vaginal walls are outside it.
- 4th degree – the uterus is located outside the vagina (uterine prolapse).
The benefits are obvious
In addition to the prevention of pelvic organ prolapse, the benefit of such an operation is that as a result the genital fissure is closed, a reliable barrier is created for infections, and tissues manage to avoid pathological changes caused by frequent inflammation.
If perineolevatoplasty is performed at a time when the muscles have not yet lost their ability to contract, the effectiveness of the intervention increases many times compared to performing this operation at a later age. Early surgery allows you to maintain the correct position of the pelvic organs for many years. The operation does not interfere with bearing children in the future. If it is performed during the first years after childbirth, it is equated to an operation to restore a damaged perineum, which is performed in the maternity hospital (perineorrhaphy). Consequently, she does not exclude subsequent vaginal births. If the operation is delayed for many years, not only its effectiveness will decrease, but also the woman’s likelihood of subsequently giving birth naturally.
Perineolevatoplasty is one of the most effective operations aimed at treating genital prolapse.
Indications for surgery
Prolapse of the uterus and vagina is a pathology that inevitably progresses over the years. Conservative methods can only slow down its course, but not stop it. So in the manual on gynecology authored by V.I. Duda notes: “The clinical picture [of this disease] is characterized by a protracted course and steady progression of the process.”
The type of surgery for uterine prolapse largely depends on the woman’s desire and ability to become a mother. The presence of other diseases in the anamnesis and the patient’s plans for sexual activity in the future also have an impact.
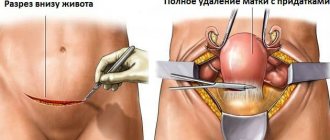
For patients planning childbearing, organ-preserving surgeries are used, which include vaginal plastic surgery and strengthening of the pelvic muscles (levators). For women over 45 years of age, removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) is indicated, which is naturally associated with loss of reproductive function. Some doctors prefer surgery to suturing the ligaments that secure the uterus. A necessary condition for such intervention is the absence of atrophic processes in the genitals.
Vaginal suturing surgery is recommended for women who no longer plan to be sexually active (mainly the elderly). It is the most effective and minimally invasive. Contraindications include the presence of general diseases and the absence of suspicion of oncological processes in the uterus.
When the prolapse affects neighboring organs (intestines, bladder), during the operation their position and the muscles holding them are corrected. Sometimes it is necessary to combine a vaginal approach with a laparoscopic one to achieve the maximum effect from surgical intervention.
In case of prolapse of the cervical stump after radical surgery, the use of a mesh prosthesis is recommended. It will act as ligaments and allow the organ to be fixed in the required position.
Omission with omission
There are hundreds of more or less effective surgical methods - from simple and accessible to very complex, high-tech. They are selected for each specific case, taking into account the degree of prolapse, concomitant pathologies, and the patient’s age. Here are just a few of them:
► colporrhaphy : suturing the anterior, posterior or both walls of the vagina;
► Neugebauer-Lefort operation : suturing the anterior and posterior walls of the vagina together, leaving only two lateral canals - used only for elderly patients who are no longer sexually active;
► operations with rigid fixation of the uterus and or vaginal vault to the pelvic walls - pubic bones, sacral bone, sacrospinous ligament;
► shortening the uterine ligaments in various ways, etc.
Unfortunately, many of these technologies have a very high relapse rate.
One of the most modern methods of surgical correction, which gives relatively good results, is the creation of new artificial fascia (shells in which muscles are located, like in cases) in place of stretched or damaged tissue. For this purpose, various bioinert synthetic meshes are used, which are not hemmed, but are freely laid in the desired place. After some time, this mesh grows with connective tissue and plays the role of reinforcement that strengthens the pelvic floor. This technology is a real opportunity to quickly eliminate prolapse, however, this method, like other methods of late correction, is not immune from relapses, complications and is not able to fully restore the functions of the pelvic floor.
Video: prolapse and prolapse of the uterus, methods of surgical treatment
No woman is immune from uterine prolapse. This pathology affects well-being and significantly reduces the quality of life. In the initial stages, the problem is eliminated using conservative methods. If organs are severely displaced, surgical intervention is indicated. Reviews after surgery for uterine prolapse are positive. This is the best way to treat the disease and help eliminate the problem.
Is uterine prolapse a disease?
The uterus in the abdominal cavity is supported by the muscular apparatus and ligament system, but over time, these ligaments and muscles weaken for various reasons, which leads to the displacement of the uterus downward under the influence of elementary gravity. As a result of this process, in the absence of appropriate treatment, the reproductive organ descends towards the vaginal canal until it falls out completely.
This disease is called uterine prolapse and, unfortunately, can only be treated surgically. Of course, there are special devices that can keep the uterus in its place, as well as exercises that strengthen the muscles, but if the prolapse process has begun, it can only be stopped through surgery; all other control measures will only bring temporary relief.
Prevalence
According to modern foreign studies, the risk of prolapse requiring surgical treatment is 11%. This means that at least one in 10 women will have surgery for this condition in their lifetime. In women after surgery, in more than a third of cases, recurrence of genital prolapse occurs.
The older a woman is, the higher her likelihood of having this disease. These conditions account for up to a third of all gynecological pathologies. Unfortunately, in Russia, after the onset of menopause, many patients do not turn to a gynecologist for many years, trying to cope with the problem on their own, although every second of them has this pathology.
Surgical treatment of the disease is one of the most common gynecological operations. Thus, in the USA, more than 100 thousand patients are operated on annually, spending 3% of the entire healthcare budget on this.
Providing for surgery
In the initial stages of uterine prolapse, conservative treatment gives good results. If the pathology goes beyond the second degree, it is better to resort to surgical intervention. When choosing a treatment method for uterine prolapse, the doctor takes into account:
- age of the patient - as a rule, surgery for prolapse is more often prescribed for young women;
- the desire to realize childbearing function - if pregnancy is planned, it is better to have surgery and cure the prolapse in advance;
- concomitant pathologies - for fibroids, endometriosis, ovarian tumors, a complex surgical method is recommended;
- degree of pathology - surgery is prescribed for stages 3 and 4 of prolapse.
Surgery for uterine prolapse is prescribed if the pathology worsens the patient’s quality of life.
Typically, women complain of pain in the uterus, lack of intimate life, fears and complexes. In the later stages, when the function of the excretory system is impaired, they experience urinary and fecal incontinence, which promotes association. Surgical treatment helps correct these problems and eliminate prolapse.
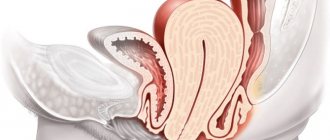
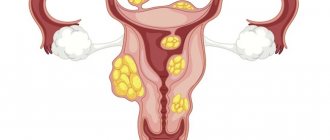
What is prolapse of the reproductive organ?
As gynecology says, uterine prolapse or prolapse is a pathological prolapse of the uterine cavity, as well as the cervix, which has unpleasant consequences for the patient.
Not only elderly and elderly women suffer from the disease, but also young girls. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in women whose age ranges from 30-45 years.
However, the definition of prolapse means prolapse of not only the uterine cavity, but also the intestines and bladder. For a certain number of reasons, the pelvic floor, or rather its layers, are no longer able to contain the internal organs.
Moreover, when visiting a doctor, the gynecologist notices that the genital organ and its neck are located much lower than their natural presentation, and sometimes even fall out into the vaginal cavity. Of course, in this case, the woman requires urgent treatment, otherwise this pathology will cause a large number of complications for the patient’s health.
What causes partial or complete uterine prolapse? The uterine fundus may begin to descend for a number of reasons, which are important to pay special attention to when making a diagnosis.
These include:
- diseases related to metabolism;
- damage to the pelvic floor that occurs as a result of trauma;
- disruption of the female body’s production of steroid hormones;
- systemic underdevelopment of the base of the connective tissue (for example, the development of a hernia in a woman, varicose veins, joint dysplasia, and so on);
- labor activity;
- patient's age;
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent and prolonged constipation;
- excessive obesity.
Uterine prolapse is known to cause serious complications for women's health. Therefore, it is recommended to begin treatment of the disease immediately after detecting its signs, otherwise the consequences of uterine prolapse will be disastrous.
How is the operation performed?
If wearing a bandage, following physical therapy and taking certain types of medications do not help get rid of the pathology, the doctor decides to perform an operation to return the uterus to a normal and natural state.
It is important to note that surgery for prolapse of the reproductive organ has certain pros and cons. However, if a woman’s condition is critical, the doctor, without hesitation, decides to perform surgery.
Currently, all types of operations are divided into certain groups:
- operations that can strengthen the pelvic muscles (as a rule, this is a two-stage operation called colpoperineolovatoroplasty);
- an operation performed on the uterine ligaments (it involves suturing and shortening the ligaments of the uterus, which are located on its anterior wall);
- strong fixation of the uterine cavity to the walls or pelvic floor;
- strengthening the uterine ligaments that secure this reproductive organ;
- if the subsidence is severe, which has a negative impact on health, endoprostheses are used to secure the organ in the correct position;
- narrowing of the vaginal cavity, through which the uterus cannot descend;
- removal of the uterus, which only the attending physician has the right to prescribe.
The operation is most often performed through the vaginal cavity, or using laparoscopy.
When a woman feels heaviness in the pubic area and pain in the vagina, in most cases gynecologists diagnose prolapse of the genital organ - prolapse.
This pathology may be insignificant, and then you can get by with conservative methods of eliminating the problem - gymnastics, hormonal drugs, wearing a bandage, etc.
But in some cases, such therapeutic tactics are not successful, and then surgical intervention is necessary.
Treatment of prolapse is necessary, because without it, the reproductive organ can completely fall out of the genital slit. In addition, the pathology can become complicated, and the consequences can be very serious.
About the features of the recovery period
After surgery for uterine prolapse, the patient requires medical supervision. Hospitalization lasts from 2-3 days to 2 weeks and depends on the speed of tissue recovery, the woman’s age, and the result of the operation.
It is not recommended to stand up on the first day after surgical treatment, as tension in the perineal muscles can lead to sutures coming apart.
Bed rest is prescribed for 1-3 days. During this time, it is important to adhere to the recommended diet to avoid constipation and additional stress on the pelvic floor muscles.
The patient is prescribed medications:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics to prevent complications;
- painkillers and antipyretics for symptomatic relief;
- anti-adhesion drugs - help prevent prolapsed organs from sticking together;
- suppositories and gels based on estrogen to stimulate regeneration.
With vaginal access, it is not recommended to sit for 1 month, have sexual intercourse for 2 months, and swim in public waters and baths for 2-3 months.
Wearing a bandage
The support device is recommended to be worn by patients with weak abdominal muscles, as well as those who have given birth repeatedly. If the uterus was removed during prolapse, the use of a bandage will be a mandatory measure in the recovery period.
The device reliably fixes the pelvic organs (bladder, intestines, appendages - if they are preserved) and allows them to assume a normal anatomical position without relying on the cavity of the reproductive organ.
And intimate life physical activity
Physical activity after surgery is contraindicated for all women. Depending on the technique and the result obtained, the period of restrictions varies from 1 to 6 months. Intimacy should be avoided for 3-4 weeks if abdominal access was chosen. If there are stitches in the vagina, the period of abstinence increases to 1-2 months. Bloody discharge from the genital tract can last 1-3 weeks.
Exercises, special exercises
Sports after surgery are prohibited for several months. It is better to check with your doctor individually for the exact dates, as they may differ for each patient. After completing the recovery period, it is recommended to do daily Kegel exercises. Training the pelvic floor muscles will be a good prevention of relapse.
Yoga, bodyflex and Pilates have a positive effect on the condition of muscles. When selecting a training regimen, it is necessary to inform the instructor about the treatment performed in order to exclude gymnastics that could be harmful.
Diet, diet
In the first days after treatment, a woman needs a light, high-calorie and easily digestible diet. It will help eliminate bloating and constipation. It may take from 1-2 days to several weeks to restore digestive function. Until the excretory system starts working like a clock, you will have to stick to your diet.
In the future, it is recommended to consume foods with a large amount of fiber and coarse fiber. They promote proper digestion and daily cleansing of the intestines. Drinking regime is of no small importance. To prevent pyelonephritis and cystitis, you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of water. It is necessary to organize your diet and diet so that you receive a sufficient amount of vitamins, microelements, and amino acids every day. They ensure proper muscle function. Vitamins B, C, E, iron, coenzyme and polyunsaturated fatty acids are especially important for women after prolapse.
Alcoholic drinks must be excluded from the diet. You can indulge in a glass of good dry red wine with dinner. You should not lean on sauces and marinades, smoked foods, fatty foods and canned food.
Thermal procedures and personal hygiene
During the first two months after surgery for uterine prolapse, swimming in a public body of water is not recommended. If the access during the operation was transvaginal, the time of this restriction can be extended to 6 months. Much depends on the speed of restoration of perineal tissue. It is recommended to avoid thermal procedures, as they negatively affect the functioning of the vascular system and can cause complications.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to maintain personal hygiene. Existing seams must be treated with antiseptics prescribed by the doctor. You should wash yourself at least 2 times a day with herbal decoctions or special gels for intimate hygiene without fragrances or dyes. You should stop using panty liners. During discharge, you can use cotton hypoallergenic intimate hygiene products. The use of tampons is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
After completing the recovery period, you must be regularly examined by a gynecologist.
Women of reproductive age should visit a doctor at least 2 times a year, even if there are no complaints. Menopausal patients visit the gynecologist after surgery at least 4 times a year. Recurrence of uterine prolapse should not be ruled out if during the operation the cavity of the reproductive organ was not completely removed.
Price
The problem of pelvic organ prolapse has become increasingly common in recent years. For this reason, the question of what the cost of surgery for uterine prolapse remains relevant. The pricing policy for each private medical institution is set individually. It depends on the qualifications of specialists, available equipment and reputation. The average cost of treatment in a private clinic can reach up to 100 thousand rubles. In a public medical institution, hysterectomy is performed free of charge if indicated.
When installing a prosthesis, the patient will have to pay from 20 to 30 thousand rubles for the device.