It is important to diagnose the disease at an early stage.
Chlamydia is a common and extremely dangerous infection. It can occur in people of different ages and genders, but most often affects the young population.
This is not surprising, since the main route of transmission of the disease is considered to be sexual. Pathology has an extremely negative impact on the health of the fair sex.
First of all, this is due to the fact that the symptoms of chlamydia in women are often mild or mimic other problems of the genitourinary system. How to diagnose this dangerous disease at the earliest stages of its development? Read our detailed review and don't forget to watch the video in this article.
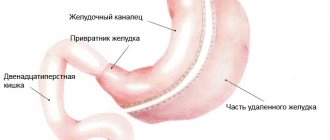
Chlamydia in women
Chlamydia in women
Chlamydia manifests itself in different ways in women. It all depends on the stage of the disease. Most often, the diagnosis of this disease occurs at the moment when the disease is in full swing. But in approximately every third case, it does not make itself known at all. This course of the disease is even more dangerous, since it is difficult to suspect that something is going wrong in the body. Without realizing about health problems, a woman can infect her partner or even conceive a child.
In the case of an existing pregnancy, this state of affairs is no less serious. Lack of timely treatment can lead to irreparable consequences.
The incubation period of chlamydia in women lasts from two weeks to a month. If the infection is sexually transmitted, then after two weeks the first signs are likely to appear.
There are several stages in the development of the disease:
- First stage. Chlamydia enters the vagina, into a comfortable habitat.
- Second phase. At this time, the intracellular stage of development occurs, at which the pathogenic microorganism begins to actively reproduce, and after a couple of days the cell in which it was located dies.
- Third stage. The very period when active growth of microorganisms occurs. They spread quickly and invade new cells.
Diagnostics
The disease is diagnosed by a gynecologist or venereologist after conducting a survey, visual examination and laboratory tests. To detect chlamydia, material taken from the vagina and cervix, urine or blood is used. Then the following tests are carried out:
- Microscopic. The probability of detecting chlamydia in this way does not exceed 15%. However, this method allows you to detect the inflammatory process and suspect the presence of chlamydia.
- Cultural. To do this, the taken material is placed in a special nutrient medium, where microorganisms multiply quickly. This analysis makes it possible not only to determine the type of microorganism, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics. The analysis is repeated 2–3 weeks after the end of antibiotic therapy. If this period is shortened, a false negative result may be obtained.
- Polymerase chain reaction. It is one of the most accurate tests to detect chlamydia. During the process, the DNA of parasitic bacteria is detected in the materials taken for research. Repeated analysis is carried out after 3–4 weeks. If the period is shortened, there is a possibility of getting a false positive result.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. With this test, chlamydia antigens are detected in the patient's blood, which are produced as the body fights pathogenic microorganisms.
Differential diagnosis
The symptoms of the disease are not very pronounced and are practically no different from those symptoms that appear in other sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Even an experienced doctor can find it difficult to distinguish chlamydia from mycoplasmosis, since the symptoms of the disease are similar. Clear formulation is very important, because the treatment of these diseases is different, and incorrectly selected drugs can cause chronicity of the process or the appearance of microorganisms that are insensitive to certain antibiotics.
In differential diagnosis, it is not the external signs of the disease that are taken into account, but the results of laboratory tests.
Routes of infection
The course of the disease in the future largely depends on how exactly the pathogenic microorganism entered the person. There are four main routes of infection:
- Sexual path. Most often, infection occurs this way. The penetration of chlamydia becomes possible as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse. Infection can occur as a result of any type of intercourse: oral, anal and vaginal. With this route, the vaginal mucosa is primarily affected. From there, chlamydia easily spreads to the fallopian tubes, covering the entire surface. If treatment is not started in time, the infection will spread to the urinary tract. It is likely that cystitis will develop.
- Vertical path. This is how a newborn baby becomes infected. If a woman had chlamydia during pregnancy, a fairly large amount of pathogenic flora has accumulated in her vagina. During childbirth, the baby, passing through the birth canal, becomes infected from the sick mother. As a result, he may develop chlamydial conjunctivitis and lung damage. There is an opinion that even while in the womb, a child can already become infected with this infection. But the reliability of this hypothesis has not yet been proven.
- Contact and household path. No one can one hundred percent prove infection with chlamydia in this way, but no one can refute the existence of such a route either. There is an opinion that this infection can be “picked” from the clothes of a random person you meet on the street, on public transport, or simply in a crowd. If you dry yourself with a towel after a sick person, the risk of infection is quite real, since the bacterium can live on cotton fabric for two days. But only if the ambient temperature was +18 degrees. Deviations in temperature conditions of even a degree or two are fraught with the death of the pathogenic microorganism.
- Airborne method. This is a fairly rare route, but this is how chlamydia becomes infected from a patient with chlamydial pneumonia.
Treatment during pregnancy
If you develop this disease during pregnancy, it simply needs to be cured as quickly as possible due to the high risk of infecting the unborn baby.
Because the disease is asymptomatic, chlamydia infection is often diagnosed during pregnancy. When infected with chlamydia, already during pregnancy, symptoms manifest themselves in mucopurulent cervicitis or endometritis.
The process of pregnancy itself with an ongoing disease - chlamydia - can occur with a number of complications, for example, ectopic pregnancy, termination of pregnancy, especially in the early stages of pregnancy, polyhydramnios and late toxicosis.
Treatment for such infections is very important, but after treatment you should not forget about preventive measures.
These measures are:
- refusal of unprotected sexual intercourse, especially with different partners;
- planned visits to the gynecologist;
- annual diagnosis for chlamydia infection;
- use only personal hygiene products;
- increased attention to personal hygiene;
- and don’t forget to pay attention to new symptoms.
Remember that this infection is transmitted from another person, from your partner, who also needs to be checked for the presence of this infection so as not to become infected again.
Chlamydia in women causes
Why is it possible for a woman to become infected with chlamydia?
- The main reason is promiscuity, unprotected sex (this is the most common cause of infection not only among women, but also among men);
- An IUD installed in the uterus, which prevents unwanted pregnancy, can also cause this unpleasant disease;
- The cause of infection can be abortion and other gynecological operations;
- Due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, the possibility of infection also exists.
Infection can occur against the background of reduced immunity; this can occur during long-term treatment with antibiotics. Stressful conditions also do not improve immunity. Banal hypothermia leads to a disruption of the immune system and an increase in its susceptibility to various types of infections, including chlamydia. Another common reason for decreased immunity is insufficient vitamin content in the body.
Treatment of chronic chlamydia
The diagnosis of “chronic chlamydia” is made if the duration of the disease exceeds 2 months. This form of the disease is often sluggish, with alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions. Symptoms may be mild or completely absent. But being a virus carrier, a person can infect other people with chlamydia. Chronic chlamydia poses a particular threat during pregnancy. The presence of the virus in the body of the expectant mother increases the risk of miscarriages, premature birth, and the development of intrauterine defects in the fetus.
Treatment of chronic chlamydia in women is carried out in stages and consists of several courses. The duration of the course may be longer than in the treatment of the acute form of the disease. Thus, the antibiotic Rondomycin is taken for 10 days instead of a week, Lomefloxacin for up to 11-12 days. It is also practiced to take several drugs, using antibiotics from the group of macrolides, fluoroquinolines or tetracyclines at the same time. In such cases, the dosage is calculated individually.
In addition, in the chronic form of chlamydia, restorative therapy is very important. It includes taking immunomodulators, adaptogens, vitamin-mineral complexes and physical procedures.
Chlamydia in women. Symptoms
By and large, symptoms of the disease may be completely absent, which is exactly what happens in about a third of cases. But if we talk about sensations, then the very first sign that something is going wrong in the body is a burning sensation, discomfort in the vaginal area.
If the infection has penetrated not only the vagina, but also the urinary tract, then pain is noted when going to the toilet, and cloudiness of the urine is also observed. How long does it take for chlamydia to appear in women? In about two weeks.
A little later, the following signs of chlamydia appear in women after infection. The amount of vaginal discharge increases and it becomes yellowish in color. An unpleasant odor should also be a clue that something is wrong. As the infection progresses, a low-grade fever may appear.
In the later period of the disease, when the pathogenic flora grows more and more, the uterus and its appendages are damaged. At this time, patients often complain of nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. The pain makes itself felt during menstruation, significantly intensifying. Increased physical activity does not go away without leaving a trace, causing severe pain in the abdomen.
If the disease continues over a significant period of time, disruption of the endocrine function of the ovaries may occur. Menstruation may change, become too heavy and painful, or, conversely, disappear.
Drugs for treatment and regimens for their administration
Expert opinion
Lyuvanova Arina Viktorovna, specializes in female venereal diseases
Competent therapy for chlamydia in women involves the use of antimicrobial medications that affect certain types of bacteria, local antiseptics, symptomatic medications and agents that strengthen natural defenses.
As with other bacterial infections, antimicrobial agents are used for chlamydia. Their choice is limited to antibiotics that suppress intracellular microorganisms. These are macrolide, tetracycline drugs, penicillin-based drugs, fluoroquinolones. The standard course of antibiotic therapy is 7-14 days.
Antibiotics
For the treatment of acute uncomplicated forms of the disease, use:
- Azithromycin. The drug is taken once a day in a descending dosage - the first day 1 g, 2.3 days 0.5 g, 4-7 days 0.25 g. At the initial stage of development of the disease, 1 tablet per day is prescribed, while the total the dose for the entire course should not exceed 1 g. If a woman has severe symptoms, the treatment regimen is changed: on the first day, take 1 g of the drug, on days 2 and 3 - 0.5 g each, then reduce the amount by half. The total dose does not exceed 3 g.
- Doxycycline . The dosage regimen is as follows: on the first day, 1 g once, then for 7-14 days, 0.1 g every 12 hours.
- Rondomycin. The first dose is 0.6 g of the drug (4 capsules), then for 7 days, every 8 hours, 0.3 g (2 capsules).
- Syphlox. Dosage regimen: first time 0.5 g of the drug, then for 10 days 0.25 g 2 times a day.
- Clarithromycin. The daily dosage is 0.5 g, the drug is taken for 7 days, 2 times a day.
- Josamycin. The daily dosage is 1 g. Take a course of 7 days, every 12 hours for 0.5 g (take 1-1.5 hours before meals)
- Lomefloxacin. Take 1 time per day, 0.4-0.8 g for 7 days.
- Spiramycin. The maximum amount of the drug per day is 9 million IU. This dosage is divided into 3 doses. Duration 7-10 days.
Penicillin-based drugs, for example Ampicillin, are used to treat chlamydia somewhat less frequently than drugs from other groups. It is used for systemic infection of the body with the causative agent of chlamydia, when not only the genitourinary system is affected, but also other internal organs. The drug is administered intramuscularly in an amount of 200-500 MG at equal intervals. The duration of treatment is 5-7 days.
Tetracycline drugs have a pronounced antimicrobial effect. Often the patient is prescribed Tetracycline in the form of an ointment intended for local treatment. The systemic agent in this group is Doxycycline. The drug must be taken 1 tablet with meals for 7-14 days.
Fluoroquinolones are drugs obtained synthetically (by fluoridation). They have bactericidal properties and destroy enzymes necessary for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora. Drugs in this group, such as Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Lomefloxacin, have a long-term therapeutic effect, so they need to be taken only 1-2 times a day (depending on the stage of development of the pathology). The duration of therapy is prescribed individually.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics can negatively affect your health and cause digestive problems and other dangerous consequences.
Local antiseptic drugs
Most often, Chlorhexidine solution is used to treat chlamydia in women. The product allows you to disinfect affected tissues, relieve inflammation, and prevent the spread of infection. The drug is used to prepare microenemas, as well as local baths. It is recommended to repeat the procedure 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment is an additional measure to speed up the patient’s recovery. Laser irradiation, magnetic therapy, and ultrasound treatment are widely used. These methods relieve inflammation and pain and have a healing and antimicrobial effect. Electrophoresis with the addition of a drug is also often used. This method allows the active components to penetrate deep into the tissue.
Consequences of chlamydia in women
A disease such as chlamydia cannot go away without consequences, and often very serious ones.
- Endometritis, salpingitis, salpingoophoritis. These diseases occur as a result of damage to the mucous membranes in the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. All of them are being treated, but there is no guarantee that the disease passed without serious consequences. There may well be scars left in the tubes, which in the future can prevent the desired pregnancy.
- As a result of the same scars in the fallopian tubes, there is a high probability of ectopic pregnancy.
- Infertility and the development of malignant tumors. Such a consequence is likely only as a result of too advanced chlamydia, which was not diagnosed for a long time and was not treated in any way.
- After suffering from chlamydia, even in the case of successful conception, there is no complete guarantee of a positive pregnancy outcome. The likelihood of premature birth increases several times.
Developing complications of untreated chlamydia
As a rule, with the latent course of chlamydia, women develop symptoms and severe consequences of further spread of the infection and damage to other organs by chlamydia.
You can prevent complications of any genitourinary infections by regularly visiting a gynecologist and taking swabs from the genital tract for flora.
Identified diseases in the early stages are successfully treated in a fairly quick time; in case of protracted processes, treatment for complications that arise is quite long.
Among the most common symptoms of complications of chlamydia in women are:
- inflammatory phenomena of the vaginal segments of the cervix;
- damage to the bladder, one of the characteristic signs of which is the release of urine with blood impurities;
- the introduction of chlamydial infection into the urethra, which leads to an increased urge to urinate, pain during emptying of the bladder and the release of purulent contents;
- endometritis (acute pain occurs in the lower abdomen, bleeding from the vagina or discharge of copious mucous contents is possible);
- damage to the Bartholin gland occurs (symptoms of bartholinitis in acute chlamydia manifest themselves in the form of an increase in the size of the excretory duct of the gland, the formation of an abscess is possible, accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees, pain while walking and during bowel movements);
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes, ovaries (severe processes lead to the closure of the lumen of the fallopian tubes and, as a consequence, to infertility);
- urethral stricture with long-term chronic course;
- pelvic inflammation and pelvioperitonitis (with chlamydia, symptoms include chills, acute pain and bloating, the muscles of the abdominal wall are tense);
- chronic pain syndrome develops in the pelvic region (lasts at least half a year);
- chlamydial infection of the eyeballs (hyperemia, burning and itching sensations, swelling of the eyelids appear, when pressing on the lower eyelid, purulent discharge appears;
- damage to the anal area by an infectious pathogen (symptoms from the anus);
- inflammatory processes in the joints.
The progression of the infectious disease is accompanied by fever, headaches, and an increase in the size of the inguinal lymph nodes.
During the chronic period, a woman’s immunity is weakened.
This increases the risk of infection with other, more dangerous, incurable diseases, for example HIV infection, hepatitis.
How to identify chlamydia in women?
How to identify chlamydia in women?
In order to make a conclusion about the presence of infection, it is necessary to conduct a series of tests. Only a comprehensive examination can give a complete picture of a woman’s health status.
Microscopic analysis. First of all, a smear is taken from the woman, but not only from the vagina. Samples of the mucous membrane from the cervix and urethra will also be required. In some cases, smears are taken from the rectum.
The samples taken are prepared in a special way and examined through a microscope.
The result of this study cannot be the ultimate truth, and if nothing was revealed in this way, this does not mean that the woman is absolutely healthy. The fact is that a conclusion can be made based on samples taken from one site. While the infection can safely develop on another.
The adequacy of the result also depends on the laboratory technician conducting the research and the correctness of the sample collection:
- PCR diagnostics. A fairly accurate method, it shows a positive result in the presence of infection and a negative result in its absence. In this case, not a smear is taken for analysis, but a scraping, which makes it possible to examine not only the mucous membrane, but also the cells. In most laboratories, such analysis is carried out in an automated way. This allows for better diagnostics. Error due to human factor is reduced to zero.
- Bacteriological cultures. Mucosal samples are taken from the vagina, urethra, cervix and uterus itself. Subsequently, a flora culture is carried out, which shows whether there are pathogenic microorganisms in the body and in what quantity. In this way, you can immediately find out the sensitivity of bacteria to certain antibiotics.
- Blood analysis. Using this analysis, it is impossible to find the pathogen itself, but it is very possible to identify the amount of antibodies that the body secretes during a particular disease.
Diseases caused by untreated chlamydia
All the diseases listed below are inflammatory in nature, and what is subject to this inflammation is indicated in parentheses. If you wish, you can find photos of the affected organs on the Internet.
- Chlamydia colpitis (vaginal mucosa).
- Cervicitis (cervical canal).
- Endometritis (mucous layer of the uterus).
- Salpingitis (fallopian tubes).
- Salpingophritis (uterine appendages).
- Chlamydial urethritis (urethra).
- Cystitis (bladder).
- Bartholinitis (Bartholin glands).
- Paraurethritis (paraurethral glands).
- Vulvitis (mucous membrane of the external genitalia).
What does chlamydia primarily affect?
Chlamydia, the symptoms and treatment of which are individual (there are no universal signs and medications suitable for everyone), is an insidious and even dangerous disease. First of all, chlamydia reaches the cervix and it is the cervix that first suffers from their negative effects. They invade epithelial cells and begin to multiply inside the cells. Afterwards, pathogens leave the destroyed cells.
In general, infection begins in the lower part of the so-called urogenital tract, which in addition to the cervix consists of the bladder, vagina, urethra and external genitalia, but the cervix is the most vulnerable of them and suffers from chlamydia first. And every adult simply must know how chlamydia manifests itself in order to be able to promptly prevent the possible consequences of the attack of these semi-viruses - semi-bacteria. While they are multiplying, a woman may not feel their presence in her body, but when the incubation period ends, an unpleasant odor from the vagina and purulent discharge appear, which clearly indicate that this is chlamydia, although this diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted only after laboratory tests. During the destruction of epithelial cells, cytokines are released that increase blood supply to areas infested with chlamydia. As a result, the permeability of the capillary walls increases, which causes the appearance of a focus of inflammation. It is from here that the causative agent of the disease enters the lymph nodes and is spread throughout the body by lymph. Thus, chlamydia enters almost all organs and systems, but they especially “love” the mucous membranes, urethra, eyes and joints.
Treatment of chlamydia in women
If the diagnosis is confirmed and the reality is that the woman really has chlamydia, treatment should begin. How to treat chlamydia in a woman? It is worth considering the fact that treatment should be carried out not only on the partner, but also on her partner, otherwise the risk of recurrence of the infection remains.
Chlamydia is treated with antibiotics; the disease cannot be overcome in any other way. Mainly antibiotics from three groups: tetracyclines, macrolides and fluoroquinolones. Unlike men, treatment for women is not limited only to tablets and ointments for external use. In the case of women, it is also necessary to use suppositories, tampons and douches. Only in this case will recovery come faster and the consequences will be minimal.
In each specific case, the selection of drugs and regimens for their use occurs individually. Only a doctor can prescribe medications based on the research conducted. Under no circumstances should you choose your own medications. This can lead to negative reactions and unnecessary risks.
Treatment regimen for chlamydia in women
If treatment is carried out at an early stage, then only topical medications can be used. At this stage, vaginal suppositories, tampons, and herbal douching are prescribed. To speed up recovery, you must take a vitamin complex. Often at this time, plant-based adaptogens are prescribed to strengthen the body.
The early stage of the disease is the first two months. Treatment is carried out at home; this condition does not require hospitalization. But taking antibiotics is also necessary. Without them, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogenic microorganism. It is true that treatment at later stages will result in a less protracted course of antibacterial drugs.
Among the antibiotics, Doxycycline and Oxytetracycline are very effective in the fight against chlamydia - both drugs belong to the tetracycline group. Medicines such as Erythromycin, both in tablets and in the form of ointment, and Azithromycin are often prescribed. These drugs are from the macrolide group. Medicines such as Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin and other representatives from the group of fluoroquinolones are extremely rarely prescribed for the treatment of chlamydia at an early stage. They are prescribed only if drugs from the two previous groups are powerless.
Doxycycline
Oxytetracycline
Erythromycin
Azithromycin
Levofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin
Azithromycin is very effective in the fight against “fresh” infection. A single dose is sufficient to completely cure the disease.
Do not forget that antibiotics, even in small quantities, upset the balance of intestinal microflora. Therefore, after an antibacterial course, a course of probiotics is required.
If treatment is not started in time, the disease enters the chronic stage. Therapy at this stage becomes much more complicated and requires more time and effort.
Treatment at this stage is carried out in several stages. The first step is to prepare the body, which allows for more effective treatment in the future.
Most often, a course of intramuscular injections is carried out as preparation. A weekly course of Neovir or Cycloferon has an antimycotic and antiviral effect. In addition to injections, a course of tablets is prescribed, for example, Rovamycin. This antibiotic belongs to the group of macrolides and, according to its characteristics, combines perfectly with Neovir, complementing it.
Neovir
Cycloferon
Rovomycin
To make it easier for the body to tolerate such a number of antibacterial drugs, Diflucan is prescribed at the end of each week of treatment. The complex also needs to be supplemented with multivitamins; Suprastin is perfect for the role of such in the treatment of chlamydia; any other analogues may well be suitable.
Diflucan
Suprastin
After completing the first stage, intensive work on the rehabilitation of the body begins. The medications and dosage regimens are completely changing.
At this stage, first of all, it is necessary to restore the vaginal microflora. Therefore, at this stage there is no way to do without vaginal suppositories. Lactobacterin, based on live lactobacilli, is capable of completely restoring damaged mucous membranes and normalizing processes within a course. These suppositories help restore the body's immunity.
To help the immune system recover and prevent relapses, a course of injections is given in tandem with Lactobacterin to help the body effectively fight viruses and infections. Cycloferon, Reaferon or Interlock are perfect for the role of such fighters. It is acceptable to prescribe drugs such as Wobenzym and Phlogenzyme. The last two drugs are often combined with the main drugs, helping to avoid pathologies and complications.
During this period, taking Clindamycin is very effective; it has proven itself in the fight against chlamydial infections, helping even if the virus has settled in the respiratory tract and bone tissue. If the infection is quite severe, at first you need to prescribe the drug in the form of injections, since in this form antibiotics work faster and more effectively. On the tenth day of treatment at most, you must switch to the tablet form of this drug.
Lactobacterin
Reaferon
Wobenzym
Phlogenzyme
Clindamycin
Treatment of pregnant women
Treatment of pregnant women
If a woman infected with chlamydia is pregnant, treatment follows a completely different pattern. Drugs are prescribed so that their use does not have a negative effect on the fetus.
Since high-quality treatment cannot be achieved without antibiotics, and most antibacterial drugs are contraindicated for pregnant women, pregnant women are prescribed antibiotics with a molecular weight greater than the placenta can pass through.
If the disease is at an early stage, then one course is enough for a complete cure. If the disease is already advanced and requires treatment in several stages, then there must be a break between courses of antibiotics. The courses themselves should not be longer than two weeks. During the pause, you need to allow the body to restore the microflora and strengthen the immune system.
In order for the body to feel less interference from antibiotics, immunomodulatory drugs, vitamins and enzymes must be introduced into complex therapy. In some cases, the course does not require constant use of antibiotics; single doses of antibiotics are sufficient.
During pregnancy, drugs such as Amoxicillin, Ofloxacin and Viferon are well suited for treatment of chlamydia. These medications can not only actively fight infections, including chlamydia, but also help restore immunity.
Amoxicillin
Ofloxacin
Viferon
If there are contraindications to these drugs or intolerance to tetracyclines, there are analogues of these drugs among the group of macrolides. So, Erythromycin may well act as a drug. It is taken for two weeks, sometimes 10 days of treatment is enough. Josamycin and Vilprafen are also quite suitable. They are taken for 10 days.
Erythromycin ointment
Vilprafen
How to treat chlamydia?
Taking into account the duration of the disease and the characteristics of its development, appropriate treatment is prescribed; it must be comprehensive. There is no specific treatment regimen, which is why an individual approach is required for each patient. This is due to the characteristics of the body, age, specific indicators, etc.
The main treatment is with antibiotics
What drugs can be used for treatment? Complex therapy is carried out by taking medications, namely, antibiotics, vitamins, immunomodulators, etc. In addition, physical therapy may be performed.
The video in this article explains in more detail how the treatment works.
Treatment with antibiotics
The following antibiotics can be prescribed to treat chlamydia:
- Azithromycin - the drug has a negative effect on microorganisms in the affected area. The medicine spreads quickly, and all thanks to its high concentration, after which the bacteria simply cannot function further. The first day you should take 500 mg of the drug, the next 4 days 250 mg. If you have an individual intolerance to the components included in the composition, you should not take it. Side effects may appear in the form of diarrhea, nausea, stomach pain, etc.
- Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic that has an antibacterial effect. The drug disrupts the production of protein in chlamydia. In addition, it has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. The drug should be taken twice a day, 100 mg, the course of treatment is about 10 days. Contraindications: pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Ampicillin - contains penicillin, it can kill several pathogens at once, as well as other bacteria. You should drink 250 mg of the drug 4 times a day, preferably before meals. More detailed instructions for use are issued by the attending physician, who also determines the duration of the course of treatment.
Each drug is effective in its own way, but there are also contraindications that should also not be forgotten.
Treatment medications are prescribed by a gynecologist or specialized specialists
Treatment with immunomodulators
To treat chlamydial infection, not only antibiotics are prescribed, but also immunomodulators.
The most effective are the following:
- Polyoxidonium is a drug that can improve human immunity. The toxic effect of other drugs is reduced. The medicine is taken by injection twice a day.
- Timalin – increases the functioning of the immune system at the cellular level, improves the condition of the circulatory system.
- 5-20 mg is administered intramuscularly every day. The duration of therapy is 10 days.
When treating chlamydia, such drugs must be taken without fail, since antibiotics have a strong effect on the condition of the body.
Multivitamin complexes
The following vitamins are most often prescribed:
- Aevit - contains vitamins A and E. Blood circulation improves, the protective functions of the body increase. The appointment begins after consultation with the attending physician. Do not take in case of vascular insufficiency or thrombosis.
- Vitrum – supports the body in case of vitamin deficiency, and also reduces the negative effects of antibiotics. The course of treatment and dosage is determined by the doctor. Hives, itching, etc. may occur.
Even though vitamins are beneficial, there are many contraindications for taking them that should be taken into account. The photo below is an example of what vitamins look like.
Vitamins for treatment
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment of urogenital chlamydia have gained particular popularity. They help relieve symptoms of the disease and increase the body's resistance.
Commonly used methods:
- magnetic therapy – eliminates inflammatory processes, relieves swelling, has an analgesic effect;
- Ultrasound irradiation – immunity is increased, tissue regeneration is accelerated, the inflammatory process is relieved;
- electrophoresis - improves metabolic processes, dilates blood vessels, has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
This treatment is not suitable for all patients; the appropriateness of it is determined by the doctor.
Magnetic therapy is carried out
Local remedies for treatment
What to do if for some reason you can’t take your pills? For complex therapy, suppositories and tampons are often prescribed. They can replace harmful medications for pregnant women or while breastfeeding.
Effective means:
- Vitaferon is a suppository whose main component is interferon. It fights infection, improves immunity, and has an antibacterial effect. Two suppositories should be administered per day, the duration of treatment is 10 days.
- Hexicon is the active ingredient in chlorhexidine suppositories. Within 10 days, 2 suppositories should be administered. The negative effect is that the skin becomes dry.
- Clean Point - contains herbal supplements, they quickly relieve inflammation and accelerate regeneration processes.
- Propolis-based tampons are a folk remedy with an anti-inflammatory effect and have a healing and antiseptic effect.
Candles for treatment
Side effects may occur from suppositories, but this is not common.
Medicines to improve microflora and digestion
Such drugs allow you to restore the digestive organs after taking antibiotics and other strong drugs.
These include the following:
- Pancreatitis or Mezim. These are enzyme medications that, by breaking down food to the molecular level, improve the functioning of the digestive system.
- Hepatoprotectors – improve liver function, remove all toxins and harmful substances. They include here Esliver Forte or Essentiale Forte.
- Probiotics are yeast and beneficial microbes aimed at improving the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Hilak Forte and Loktabacterin are included here.
- Bacteriophages are an analogue of antibiotics, but they do not have such negative effects.
In order to prevent pain from chlamydia in women and to prevent serious complications from developing, you should listen to all the recommendations of your doctor. It is important to seek help in a timely manner; this is the only way to reduce the treatment time.
Prevention
Prevention of chlamydia
In the case of chlamydia, as well as other sexually transmitted infections that are primarily sexually transmitted, everything is simple.
To minimize the likelihood of infection, you should not have promiscuous sex or engage in casual relationships. Always use a mechanical means of protection - condoms. It is worth remembering that the latter does not provide a 100% guarantee, so you should regularly visit the gynecologist’s office, taking tests for the presence of all kinds of viruses.
How can you become infected with chlamydia?
Most often, people become infected with chlamydia through sexual contact, because it is not without reason that this disease is classified as an STI (sexually transmitted infection). In addition, medicine knows cases of infection by airborne droplets and even household ones, which happens extremely rarely. The infection can pass from mother to fetus, because during labor, the child is attacked by myriads of chlamydia, which literally “lurk” in the birth canal. Dangerous microorganisms penetrate the lungs or eyes of a newborn, as a result of which the respiratory system is affected and the baby suffers from conjunctivitis.
Treatment of chronic disease
It is believed that it is more difficult to cure chlamydia if the infection has become chronic. However, provided that a competent treatment regimen is drawn up, recovery can be achieved even at an advanced stage of the disease. To do this, the following principles are taken into account:
- The sensitivity of bacteria to a specific drug for chlamydia lasts two weeks. After this, the bacteria are covered with a shell that protects them from the effects of the drug. Therefore, eliminating the pathogen requires periodic changes of medications.
- If the disease has become chronic, you will need to undergo several courses of treatment. They involve the use of various drugs and combination agents.
- It is important to take the prescribed medications completely, without stopping taking them after the symptoms disappear. This will reduce the likelihood of survival of a small number of bacteria, which will require stronger drugs to combat.
- Regardless of the type of medication, it is required to take it in significant quantities. Small doses will significantly reduce its effectiveness.
- Treatment should be prescribed during the period of exacerbation of the infection, since during remission the bacteria are less sensitive to the action of antibiotics.
And for the therapy to bear fruit, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Diagnosis of chlamydia
Chlamydial infection is diagnosed according to the same principles as other infections. To test for chlamydia, discharge from the cervical canal of women and the urethral canal of men is used. Urine sediment can be used for testing. When taking a smear from the cervix, a special brush is used. The procedure takes place from the cervical canal.
Chlamydia is often found with pathogens of other diseases that are sexually transmitted - gonococci, mycoplasmas, trichomonas and ureplasmas due to the same route of transmission.
Molecular biological methods
Chlamydial DNA diagnostics (PCR) is a highly sensitive technique. Its specificity reaches 80 – 100%. greatly simplifies the research.
Culture diagnostic method
and allows the detection of viable bacteria. However, its sensitivity is low and amounts to 40 – 60%. In addition, the technique is quite labor-intensive and time-consuming. But the delivery of material to bacteriological laboratories and its storage have certain limitations.
Direct immunofluorescence method (DIF)
The results of the study depend on the quality of the material obtained and the qualifications of the laboratory personnel. Quick results are a clear advantage of this method.
Bacterioscopic method
To carry out this method, it is necessary to have a scraping of the affected mucosa, since chlamydia multiplies intracellularly, where they are located in the form of reticular bodies.
Serological methods
Serological methods are not recommended for diagnosing chlamydia in the Russian Federation.
If you are young and sexually active, get tested for chlamydia infection once a year or whenever you change sexual partner.
Rice. 13. In scrapings from the conjunctival epithelium, intracellular inclusions of pathogen bodies are visible.
Damage to the visual organ by chlamydial infection
When the infection spreads, one eye is most often affected, but inflammation can occur on both sides.
Symptoms of chlamydial eye damage have an acute or subacute course, sometimes becoming chronic.
Signs of the disease are:
- blepharitis - inflammation of the edge of the eyelids, which is difficult to treat;
- conjunctivitis (swelling of the lower and upper eyelids, redness of the eyeball and pathological discharge);
- in acute processes, there is an increase in the sensitivity of the eyes to bright light, lacrimation, and the release of purulent secretion, which leads to gluing of the eyelids;
- on the side of the affected eye, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the Eustachian tube and eardrum develops, regional lymph nodes enlarge; as a result, noise and pain occur in the ear, and hearing decreases;
- Pathological changes form on the mucosa.
The acute process of eye disease can last from several weeks to 2-3 months.
Symptoms
The incubation period of infection ranges from – 1 week to – 2 months, during which time the infection spreads in the body. In 45% of men and 65% of women, the disease does not give any manifestations during this period and can only be detected through laboratory testing of biomaterials.
With acute chlamydia, men and women experience different symptoms. At the same time, the female body is more susceptible to infection - infection occurs faster and the consequences are more serious.
Preventive actions
An alternative to taking medications to combat parasites that have already entered the body are simple measures to protect the body from such an invasion. They are:
- in the use of protective equipment in sexual activity;
- in refusing unverified partners;
- using only your own personal hygiene products;
- maintaining hygiene when visiting public places;
- in regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- in careful attention to deterioration in health.
If you have already been diagnosed with chlamydia, in addition to using the treatment methods recommended by your doctor, it is important to take care of changing your lifestyle and diet. You should reduce physical activity and devote enough time to rest.
It is also useful to avoid intimacy for a while. A diet for chlamydia involves avoiding coffee drinks, alcohol of any strength, spicy and salty foods, and sweets. Strengthening the immune system will also help reduce cigarette consumption.
What causes the disease?
The reason is microorganisms that make up one of the groups of sexually transmitted diseases:
- This is an intracellular organism that is obligate , that is, it can live in the body by lining up in the internal environment of cells. In its mechanism of life activity it is similar to the action of viral particles. It has a gram-negative wall and contains nucleic acids that represent the genome.
- Chlamydia does not produce its own energy, so vital activity is carried out at the expense of the energy of the host body . Transmission from a sick person occurs through a certain form of life activity—an elementary body. As soon as it penetrates the body of a healthy person, it increases in size and develops vital functions.
- In the process of its life activity, a natural chain of immunological reactions occurs in response to the pathogen.
- This microorganism can die on its own in the environment within a day at normal temperature ; if it is raised to a boiling point, chlamydia is destroyed in about 1 minute.
- They are not resistant to sunlight or disinfectants.
- They enter the host cells due to endotoxins and exotoxins , as well as proteins that carry out adhesion.
Who needs mandatory examination
As mentioned above, contraceptives cannot guarantee complete protection against the disease.
In addition to those people who lead an immoral lifestyle, there are other people who are at risk and require mandatory examination:
- married couples at the stage of family planning;
- other family members suffer from chlamydia;
- women in the first months of pregnancy or after childbirth;
- women who have had an abortion.
Before marriage, it is recommended that both partners undergo examination, thus strengthening relationships and maintaining health.
How to identify chlamydia, how to cure and prevent it? These and many other questions can be answered just above. Remember that the health of each person depends, first of all, on himself. Preventive measures are not complicated, but they are effective.
Treatment
Is there a cure for chlamydia?
Modern medicine answers the question of whether chlamydia can be treated in women completely in the affirmative. For the most favorable outcome of the disease, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear.
In this case, treatment will take less time, and the consequences will be less harmful to women's health, especially reproductive function. To avoid relapse of the disease, simultaneous treatment of both partners is strongly recommended.
Scheme and course of treatment
Treatment of chlamydia in women, after confirmation of the diagnosis, consists of antibacterial and restorative therapy. Physiotherapy and local treatment are also possible.
How to treat chlamydia? Since the causative agent of the infection is chlamydial bacteria, antibacterial drugs are prescribed during treatment: macrolides, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines. We will tell you more about the drugs below.
How to treat chlamydia? In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is prescribed, which includes electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ionophoresis, etc. Using local treatment, vaginal and rectal suppositories, baths, tampons and enemas are prescribed.
Since self-medication is unacceptable here, only a doctor should select the medicine. If a woman is diagnosed with an infection, her partner should also be tested for chlamydia. And if necessary, a man with chlamydia should also undergo a course of treatment.
Antibiotics for chlamydia
Antimicrobial drugs are the main means in the complex treatment of chlamydia. The chronic form of this infection requires the use of not one, but several similar drugs at once; most often, a combination of 2 drugs of this pharmacological group is used. The dermatovenerologist adjusts the dosage and duration of treatment depending on the patient’s body’s response to the antibiotic, the form of the disease, and the dynamics of the disease.
When choosing the most effective drug, the doctor is guided by laboratory test data regarding the sensitivity of a particular pathogen to certain antibiotics. A combination of laboratory culture methods with a type of study such as an antibiogram will help determine this indicator more accurately.
| Name of the drug | Treatment regimen for chlamydia |
| Doxycycline (Dorix, Vibramycin, Vibra-Tabs) | 2 times a day 100 mg after meals for uncomplicated chlamydia for 10-14 days, for chronic and complicated chlamydia - more than 14 days |
| Erythromycin (Erythran, Eracin) | 4 times a day 500 mg an hour before meals, the duration of the course of treatment is the same as for Doxycycline |
| Sumamed (Azithromycin, Zithromax) | 250 mg once a day for a course of 11 days, the full course is 3 g, the first dose is 500 mg, for complicated forms 2 weeks |
| Lomefloxacin (Levaquin) | 600 mg once a day after meals for 10-14 days, in complicated forms for more than 14 days |
| Ofloxacin (Floxin, Zanotsin, Tarivid, Ofloxin) | 2 times a day after meals, 300 mg for 10 days, for complicated forms 14 days |
| Rovamycin | 3 times a day, 3 million IU 2 hours after meals for 10 days, with a complicated form 14 days |
| Vilprafen | 2 times a day, 500 mg after meals for 10-12 days, for complicated forms 14 days |
| Pefloxacin (Abactal) | 2 times a day, 400 mg with meals for 10 days, for complicated forms 14 days |
| Ciprofloxacin (Tsifran, Tsiprobay, Tsiprinol, Tsiprolet) | 2 times a day, 500 mg for a week |
| Levofloxacin (Nolicin, Norbactin, Urobacid) | 2 times a day, 400 mg for 10 days |
What happens during chlamydia?
Microorganisms invade a cell, multiply, and are transmitted to other cells, forming a colony. When cells are destroyed, parasites invade new cells. The entire development cycle of chlamydia lasts up to 72 hours.
The life cycle of chlamydia occurs in two stages (outside the cell and inside the cell). Up to 1000 new infected cells are formed at a time. The infection has several periods of active reproduction (up to 6-7 outbreaks), due to which the incubation period of chlamydia lasts approximately 21 days. The human immune system recognizes parasites and produces antibodies to chlamydia, which makes it possible to detect chlamydia in the blood.
Given this life cycle of chlamydia, the disease can be asymptomatic. First of all, microorganisms attach to the urethra, fallopian tubes, conjunctiva of the eyes, endometrium, causing various diseases of these organs.
Popular article: Cure eye chlamydia - save vision
The first symptoms may appear some time after infection. In rare cases (especially in children), symptoms may appear in the first weeks after infection.
Treatment regimens
Currently, the following antibiotic regimens are considered the most effective:
- Continuous treatment, which is carried out for seven or more life cycles of pathogenic microorganisms (12 days).
- Pulse therapy, which involves taking drugs in three courses over seven days with breaks a week. This approach is used if the patient is diagnosed with chronic chlamydia.
Sometimes doctors prescribe treatment with one antibacterial drug, but more often they prescribe two drugs belonging to different groups.
The monotherapy approach is less effective, and in 50% of cases, symptoms of chlamydia reappear after some time. Combined treatment is also prescribed when several types of pathogenic pathogens are detected at once. To improve performance, many patients are recommended to drink immunity boosters. Doctors sometimes prescribe such drugs before starting antibiotic therapy. It is advisable to immunostimulate the body and select the type of medication after receiving the results of the immunogram. For chlamydial infection, interferogen drugs (cycloferon) and interferons (viferon) are used.
To restore vaginal microflora and treat intestinal dysbiosis, patients are prescribed medication with probiotics. Acylact (vaginal suppository) and gynoflor in tablet form have a good effect. For the prevention and treatment of intestinal microflora disorders, it is recommended to drink bifidum, bifiform, lactobacterin.
Often, after using antibiotics, women develop candidiasis. To prevent the appearance of its symptoms, the antifungal drug nystatin may be prescribed.
Since many drugs intended for the treatment of chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections increase the load on the liver, to maintain its functions, hepatoprotectors Essentiale Forte and Karsil are added to the drug regimen.
Forms of chlamydia
According to etiology, this disease is divided into:
- Anthroponotic
- Anthropozoonotic
Depending on the type of flow and time of appearance:
- Fresh defeat. On average, no more than two months pass from the moment of infection. It is characterized by damage to the lower parts of the urogenital tract (cervical canal, vagina, urethra).
- Chronic . It manifests itself as asymptomatic carriage or stages of remission and unexpressed exacerbations with the addition of sluggish inflammation of the pelvic organs. With this manifestation, infection usually occurs at least 2 months ago, in some cases it is several years.
By topographic distribution:
- Local chlamydia , characterized by urethritis, cervicitis, colpotomy, bartholinitis, etc.
- Rising . The spread of chlamydia beyond the lower parts of the genitourinary tract is a clinical picture of endometritis, salpingitis, adnexitis, pelvioperitonitis, peritonitis.
- Extragenital chlamydia. Expressed by symptoms of pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, paraproctitis, arthritis, etc.
Prevention of household infection
Personal hygiene rules should be observed
Living with a sick person, but not having a close relationship with him, it is almost impossible to become infected. Possible causes of infection include removing the bathtub and toilet.
In order to generally reduce the risk of household infection to a minimum, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- After contact with sick people, it is recommended to wash your hands with soap and warm water. Children with symptoms of conjunctivitis or bronchitis cannot be excluded from the risk group.
- When visiting a public toilet, it is not recommended to have direct contact with the toilet; use a disposable napkin. According to statistics, 5% of sick people become infected in this way.
- It is not recommended to use public hygiene items - towels, dishes. Also have your own blades and machines.
In order to prevent infection, experts recommend using alcohol-based antiseptics.
Complications and prognosis
There is no need to wait for the complications described below to appear; you should consult a doctor in time so as not to miss the progression of the disease.
Complications in women
- Inflammation of the pelvic organs (infection of the uterine appendages, inflammation of the fallopian tubes).
- Colpitis (replenishment of the vaginal mucosa).
- Cervicitis (replenishment of the cervix), cervical erosion. The disease often increases the risk of cervical cancer.
- Endometritis (replenishment of the endometrium).
- Bartholinitis (inflammation of the large gland of the vestibule). This inflammation leads to the formation of a Bartholin gland cyst and an abscess (opening of the cyst).
- Infertility.
- Habitual miscarriage.
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages
- Long-term intrauterine mortality.
- Conjunctivitis with inclusions (more common in children).
- Extensive damage to the respiratory system, heart, liver and gastrointestinal tract.
- Damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Complications in men
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra.
- Balanoposthitis is a lesion of the glans penis and foreskin.
- Prostatitis is a lesion of the prostate gland.
- Cysts on the prostate gland.
- Atrophy and sclerosis of the prostate gland.
- Decreased function and shrinkage of the prostate gland.
- Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa.
- Arthritis is damage to the joints.
- Orchitis is inflammation of the testicle.
- Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis.
- Vesiculitis is inflammation of the seminal vesicles.
- Extensive damage to the respiratory system, heart, liver, gastrointestinal tract (mainly rectum).
- Peritonitis is inflammation of the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum.
- Deterioration in sperm production.
- Impotence.
- Pyelonephritis – replenishment of the kidneys.
- Narrowing of the urethra.
With timely detection and proper treatment, the prognosis can be quite favorable.
How to determine the existence of an infection?
Making a diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the symptoms that occur with chlamydia are also characteristic of other infections. In order to detect the disease in women, it is necessary to undergo the following tests for chlamydia:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- bacterioscopic analysis of secretions;
- PCR diagnostics;
- culture with antibiotic susceptibility test.
The most effective method in diagnosing the disease is PCR analysis. However, you should pay attention to the fact that test results may be false negative, even if there are obvious symptoms of chlamydia. Possible reasons for this result:
- the discharge was taken or examined unsuccessfully;
- less than 30 days before the test, the patient took antibiotics, used suppositories or douches that affect chlamydia;
- it was not taken into account that before collecting the material it is forbidden to urinate for 1 hour;
- the discharge does not contain the genome of the microorganism; this is possible when inflammation is concentrated in the deep parts of the genitourinary system.
Therefore, it is recommended to combine various tests, and also take them again if the results are questionable. In addition to determining the causative agent of chlamydia using PCR diagnostics, it is also necessary to evaluate the body’s immune response (the presence of antibodies to chlamydia), which is determined by serological methods such as ELISA.
Chlamydia during pregnancy is confirmed by the presence of antibodies to chlamydia in a blood test and the presence of chlamydia in the discharge. In addition, if chlamydia is detected, pregnant women need to be tested for microplasma, ureaplasma, and other infections.
When diagnosing the disease in one of the sexual partners, his other partners should be tested for the presence of chlamydia. This must be done even when they do not have characteristic symptoms of the disease, because the risk of infection in this case is up to 80%.
Types of chlamydia and their effect
Our object can be added to the defined view. In nature, there are several types of chlamydia, each of them is dangerous for humans. Types of chlamydia:
- Pneumonia (chlamydia pneumonia) is transmitted by airborne droplets and leads to inflammation of the respiratory tract.
- Chlamydophilafelis (chlamydia felis) - transmitted by contact with a cat, causes conjunctivitis.
- Chlamydophilaabortus (chlamydia abortus) - transmitted from animals, causes miscarriages.
- Chlamydiapsittaci (chlamydia psitaki) is a type of occupational disease; affects the bronchi and lungs.
- Chlamydiatracomatis (chlamydia trachomatis) is pathogenic only for humans, transmitted mainly through sexual contact. Affects the genitals (urogenital chlamydia). In this case, it is a venereal disease.
Chlamydia Psittaci
Chlamydia infection in any form can affect different organs and systems. But there are certain species that are especially pathogenic for humans: Ch. psittaci, Ch. tracomatis and Ch. pneumonia.
Description of the disease
The causative agent of chlamydia in humans is a microorganism called Chlamydia trachomatis. They are difficult to classify as a bacterium or a virus because they exhibit characteristics of both life forms.
Most of chlamydia's life cycle takes place inside the cell, which it needs to produce enzymes that it cannot produce on its own. This is where bacteria multiply. Therefore, they are classified as intracellular parasites. As soon as the division process is completed, new chlamydia leave the cell, which then dies.
The entire cycle takes 2-3 days. The bacteria then look for a new home, and the process repeats. As the infection spreads, it rises from the lower organs of the genitourinary system to the upper ones.
A feature of chlamydia is resistance to unfavorable conditions. According to research results, bacteria remain viable in room conditions for up to two days. And the incubation period of the disease takes up to two weeks.
Since chlamydia infection leads to serious impairment of reproductive functions, you should undergo examination and begin treatment at the first signs of deterioration in health. Also, women who do not have a regular sexual partner, as well as those planning pregnancy, should make an appointment with a doctor.