Predisposing factors and how dangerous the pathology is
Placental polyps in the uterus arise for various reasons; their formation begins before the return of menstruation.
Common reasons that contribute to the formation of polyps:
- An additional lobule of placenta that was not discovered during pregnancy and labor. During the birth of the baby's place, a piece (1-2 cm in size) may come off, and it lingers inside the uterus for some time. Its presence does not allow the myometrium to contract normally and causes bleeding.
- Particles of normal placenta may appear in the uterine cavity if it was tightly attached. This sometimes occurs after a difficult birth (after a caesarean section, in most cases a control curettage is performed).
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Chronic genital infections.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Injury to the genital organs during difficult childbirth.
Pathology is not an independent disease after childbirth; it is considered a secondary complication.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
Treatment of placental polyp is possible only with surgery. After surgical removal of the polyp, a long period of drug therapy follows to restore the body. For several months, a woman should regularly visit a gynecologist, which allows her to monitor the condition of the female genital organs and take timely measures if a pathological process is detected.
Surgical removal of placental neoplasm
Depending on the individual characteristics of each clinical case, the doctor chooses one or another method of surgical removal of the tumor. It could be:
- Surgical therapeutic hysteroscopy. This type of operation is performed using a special probe equipped with a video camera and LEDs. Instruments are inserted into the uterine cavity to remove the polyp.
- Removing the tumor using a forceps. This type of operation is used when the patient has contraindications to polyp removal by hysteroscopy. Also, an indication for removing a polyp using a forceps is its protrusion into the cervix.
- Laser surgery. When using this type of surgery, the body of the polyp is removed by exposing it to a laser beam.
The removed tumor is sent for histology to exclude possible associated complications.
A mandatory step in removing a chorionic polyp is separate curettage of the uterine cavity after surgery.
Prevention of chorionic anomaly
Measures to prevent the development of chorionic pathological tumors in the female genital organs include:
- Pregnancy planning under the supervision of a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
- Agreeing with your doctor on hormonal medications for contraception.
- The expectant mother must register with the antenatal clinic as soon as she finds out about pregnancy.
- Undergoing periodic medical examinations by a gynecologist.
- Conducting obstetrics, caesarean sections and the postpartum period by highly qualified specialists.
- Refusal of non-traditional technologies for childbirth.
Symptoms and differential diagnosis
The main sign of pathology is bleeding after childbirth.
The intensity of the discharge varies, but if it lasts more than 4-5 weeks, you should consult a doctor.
Other symptoms also occur:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pale skin;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- fast fatiguability.
It is quite difficult to detect a placental polyp after childbirth, the symptoms of which are characteristic of other postpartum complications. When carrying out differential diagnosis, the following are carried out:
- assessment of the patient’s complaints (onset of bleeding, intensity);
- collecting anamnesis (how the birth went, previous pregnancies: abortions, miscarriages);
- chairside examination (condition of the cervix after childbirth).
Additional studies are used for diagnosis:
- Ultrasound with a vaginal sensor (detects the formation, its size and location);
- hysteroscopy - a special camera is used to examine the lining of the uterus (you can see not only the polyp, but also the condition of the endometrium);
- Dopplerography - for diagnosing blood vessels (given the intensive blood supply to the placenta, using this method it is possible to detect a formation if it is not possible to use other methods).
Diagnostics
To diagnose a polyp, you need to consult a gynecologist and also prescribe:
- Examination on a gynecological chair, where the doctor examines the cervix.
- Ultrasound examination, which looks for the presence of inflammatory processes and the presence of polyps that are not visible during examination on the gynecological chair.
- Colposcopy. A clearer examination using a special colposcope device, which is inserted through the cervical canal of the uterus.
- Hysteroscopy. The most accurate diagnosis. It is performed using a special video camera, thanks to which the doctor has the opportunity to see the full picture.
Popular articles:
|
Treatment tactics
Treatment includes several areas:
- elimination of bleeding and treatment of anemia;
- removal of pathological formations;
- preventing infection.
If blood loss is severe, a blood transfusion may be required. To increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, medications containing iron are prescribed.
Formations are removed surgically using several methods:
- scraping;
- using laser;
- using radio wave equipment;
- using electric current.
Curettage of the placental polyp after childbirth or vacuum aspiration is performed under anesthesia.
The biomaterial is subjected to histological examination.
In the period after removal of the polyp, medications are prescribed to prevent the development of a bacterial infection (antibacterial, hormonal drugs).
The use of medications has a negative impact on the possibility of natural feeding: medications pass into breast milk, which can negatively affect the baby’s health. During the period of treatment, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding and express milk to maintain lactation.
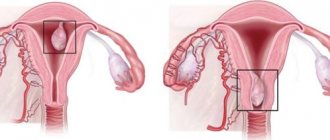
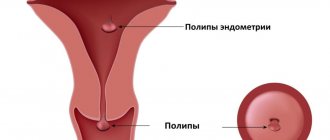
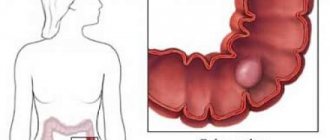
What is a placental polyp after childbirth and during pregnancy?
A placental polyp during pregnancy is a small growth of mucous tissue that grows into the lumens of the cervix, uterus, or beyond these organs.
During pregnancy, a serious disruption of the usual hormonal levels occurs, which is necessary for:
- Laying the necessary organs and systems of the fetus;
- Determining the gender of the unborn child;
- Normal functioning of the whole body.
Under the influence of hormonally determined processes, chorionic tissue (otherwise known as decidua) grows, which penetrates into the lumen of the cervical canal in the form of polyps.
Almost 20% of all pregnant women have benign growths in the cervix or in the organ cavity (endocervical polyposis).
There are two main types of polyps during pregnancy:
- Decidual pseudopolyp;
- True polyp with a tendency to decidualization.
Polyps during pregnancy are difficult to attribute to endometrial disease, since they undergo self-amputation some time after delivery. Often, after control tests and stabilization of hormonal levels, the question of the presence of polyps disappears by itself.
Important! Some polyps not only do not go away, but become a cause of justified concern. Thus, during pregnancy, growths can provoke serious complications, including early delivery or miscarriage.
HCG for placental polyp
The abbreviation hCG stands for human chorionic gonadotropin. The analysis is carried out to reliably determine pregnancy and its normal course. However, the hCG test is known not only in obstetric diagnostic practice, but also in the field of oncology.
Based on the test results in men and non-pregnant women, it can be assumed:
- Development of diabetes mellitus;
- Oncological disease;
- Pathologies of the kidneys, liver, spleen.
Normally, hCG in an adult varies between 0-5 mU/ml. The result of an hCG test for a non-pregnant woman is here. During a woman's pregnancy, these indicators increase, constantly change, and the maximum concentration of the hormone is reached in 7-15 weeks of pregnancy.
Around the end of the second trimester, these indicators decrease. If women are diagnosed with polyps of the uterus or cervical canal, then the analysis may indicate the onset of malignancy of the pathological growth.
Possible complications
The main complications of the pathology are:
- polyp infection;
- sepsis;
- endometriosis;
- degeneration into a malignant neoplasm;
- tissue necrosis;
- uterus removal;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- infertility;
- death due to severe bleeding or sepsis.
The placental formation that occurs during pregnancy does not pose a threat: during labor it comes out along with the placenta.
If any symptoms appear that indicate atypical signs of the early or late postoperative period, you should consult a doctor.
Causes
The formation occurs due to the growth of remnants of placental tissue in the uterine area. The reason for this may be a poorly performed abortion or unprofessional cesarean section, and the pathology may appear after miscarriages or even childbirth.
The most common factors leading to the development of placental polyp are:
- poorly performed emptying of the uterus, inaccurate curettage;
- non-compliance with recommendations during the postpartum period;
- in case of cesarean section, placental tissue may not be completely eliminated;
- during intrauterine fetal death, typical signs may be absent, which leads to the adhesion of unformed placental particles to the uterine cavity;
- when terminating pregnancy in the early stages.
Frank conversation in the maternity hospital
The doctor was shocked after looking at my ultrasound. I couldn't understand his reaction. He stood and stupidly insisted that this, a priori, could not happen, because he personally wiped the uterine cavity with napkins and there simply COULD NOT be anything foreign left there. Here it should be noted that I gave birth by agreement and chose the doctor myself, so this situation with the polyp completely unsettled me, and the doctor was unpleasant that because of this story a shadow might fall on his reputation. And to understand everything, he took me to a maternity hospital ultrasound.
Symptoms
In the initial stages of development of the pathology, women notice spotting or slight bleeding; other signs are often absent. Further bleeding increases and sometimes causes hospitalization; urgent therapeutic measures will be required.
Less often, patients complain of pain discomfort in the lower abdomen, but this is not always the reason for contacting a specialist, since it is considered normal after childbirth or abortion.
After a few weeks, increased bleeding is not always observed, but the symptoms become more pronounced, the following signs appear:
- General weakness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- The occurrence of shortness of breath even with minor physical exertion.
- Increased number of heartbeats.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
Anemia (anemia) often develops, which requires contacting a specialist, otherwise the disease will progress. Since a woman’s body is weakened, her immune system is weakened, and there is not enough rest due to caring for a newborn, anemia can become dangerous to health and life.
With a sharp decrease in the immune system, infections can occur and inflammatory processes can form, which reveal themselves through a number of signs:
- Increase in temperature.
- Bloody discharge with a bad odor.
- Itching, burning sensation in the genital area.
- Increasing pain in the lower abdomen.
Further, in the absence of the necessary treatment, more serious complications arise, which, in turn, will require long-term therapy or surgery.
Since the clinical picture of a placental polyp resembles many other diseases associated with the reproductive system, it is necessary to carry out a set of diagnostic measures.
Postpartum placental polyps
Placental polyp after childbirth is not an independent disease. Clinicians attribute the pathology to secondary complications of pregnancy or the birth process.
The classic reason, which lies in the name of the polyp, is the attachment of fragments of the placenta to the mucous membranes of the uterus with subsequent formation into polypous structures. In this case, the body of the polyp consists entirely of placental tissue and blood clots.
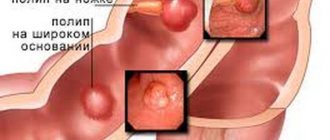
After some time, it is possible to determine the nature of the growth, which is formed on a high thin stalk or a wide base. The second case poses the greatest danger in terms of the development of cancer.
On a note ! Treatment is usually surgical, but in the absence of concern and an unpleasant clinical picture, systematic monitoring of the dynamics of tumor development is possible.
Predisposing factors
Placental polyps form during pregnancy, which was artificially interrupted or completed by natural birth. Fragments of the remaining placenta and fibrin villi give impetus to the formation of polyps.
The main reasons are considered:
- Insufficient volume of manipulations in the early postpartum period;
- Incomplete removal of placenta after cesarean section or natural birth;
- Insufficient curettage during miscarriage or instrumental abortion;
- Incomplete removal of the fertilized egg during medical or “velvet” abortion;
- Intrauterine fetal death.
Note ! The remains of the placenta are attached to the wall of the uterus and are connected to it by vessels, which over time grow into muscle-connective tissue.
Based on the type of connection, polyps are divided into:
- destructive,
- separate parts of the placenta,
- preserved villi.
What are the dangers of pathology?
The main danger lies in the malignant degeneration of the pathological focus.
Other dangers of placental polyp lie in the following manifestations::
- Vascular trauma and hemorrhage;
- Infection and stagnation of mucus;
- Necrotization of tissues due to torsion of the polyp stalk.
Attention ! If the growth is pinched by the cervix or torsion, the woman urgently requires hospitalization due to the risks of miscarriage, as well as the high threat of blood loss.