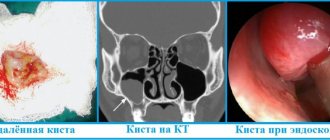
The endocervix is the mucous membrane that lines the cervix. Cysts can form on this membrane along the cervical canal.
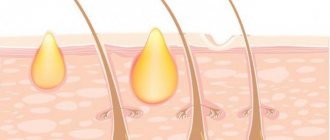
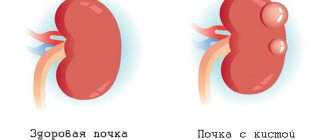
Endocervical cysts look like cyst-like dilated glands. Single endocervix cysts may occur, or small endocervix cysts may be observed throughout the cervical canal. The presence of cysts can be determined by ultrasound examination. According to statistics, endocervical cysts are observed in almost every woman 35-40 years old who has previously given birth. However, recently, cases of cysts occurring in young women who have previously nulliparous have become more frequent.
Forms of endocervical hyperplasia
Hyperplasia in the mucous membrane can differ in its structure and its manifestations are usually divided into the following forms:
- glandular, in which thickenings are formed in the mucous membrane of the endocervix, usually of an uneven focal nature. The glands in this case are different in shape and covered with endocervical epithelium. This pathology is most often found in patients with menstrual irregularities and changes in the cervix that occur as a result of inflammatory diseases;
- glandular-cystic, with dilated cystic glands covered with flattened epithelium;
- microglandular form, characterized by the proliferation of small polyps with closely located small glands. Lined with epithelium with mucous secretion. A similar option is possible in young patients with an irregular menstrual cycle;
- a cystic form of hyperplasia of the cervical canal with an increased number of glands lined with squamous epithelium. This condition is facilitated by a violation of the venous blood supply in the cervical canal;
- microglandular form of an atypical nature, with a large number of small structures of the glandular type. Often in the precancerous stage.
Classification
The classification of nabothian vesicles is of great clinical importance; they are distinguished by two characteristics: number and size.
By quantity they distinguish:
- single endocervix cysts - formed closer to the entrance to the cervical canal, larger in size, more often giving symptoms and leading to complications;
- multiple endocervix cysts are small in size, can be located along the entire cervical canal and remain unnoticed for a long time.
Read more Table of growth of hCG in urine
Based on size, three groups of formations are distinguished:
- small, the size of which does not exceed 3 mm;
- medium - 4-10 mm in size;
- large – more than 10 mm.
Small cysts are more often formed after birth trauma and during the treatment of erosion, when the healing process is underway. They can be located along the entire canal with excessive function of the mucous glands of a hormonal nature.
Endocervix examination
Most often, women do not experience significant symptoms of cervical endocervical hyperplasia. Only some of them feel slight mucous discharge or scanty blood-streaked discharge that occurs between menstruation and during sexual intercourse. When visiting a medical facility if there is a suspicion of pathologies developing in the cervix, an examination is carried out using an ultrasound device. There are various diagnostic methods that allow you to carefully examine the lining of the cervix and detect changes that have occurred in it. The most effective of them are:
- Manual inspection method. As a result of examination on a gynecological chair, a conclusion is made about the possible expansion of the passage of the cervical canal. During an internal visual examination, endocervical hyperplasia is characterized by thickened folding of the mucosa, especially noticeable if it stands out in the lumen of the canal in the form of polyps. The endocervix during this period has an enhanced vascular pattern and its membrane secretes significantly more mucus. Examination of the cervix using mirrors, colposcopy or cytological techniques does not allow obtaining an accurate picture of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. To confirm internal pathology, the most reliable information can be obtained from a histological examination of scrapings of the mucous membrane of the cervix.
- Ultrasound examination of the endocervix . When examining the female genital organs using ultrasound for other complaints, special attention is paid to the examination of the endocervix. To conduct an examination of young girls who have no experience of sexual activity, an ultrasound examination is carried out without internal penetration into the vagina, but with the help of a special sensor placed on the abdominal wall.
- Endocervical biopsy method , in which scrapings of the endocervix are examined in the laboratory under a microscope.
Causes
The following factors contribute to the development of endocervical cysts:
- Infection with infectious bacteria - Trichomonas, gonococci or papillomas.
- The formation of an erosive process in the cervix.
- Development of the inflammatory process as a complication of cystitis, colpitis, salpingitis.
- Ignoring endocervititis: in this case, blockage of the nabothian glands is caused by swelling of the local epithelium.
- Hormonal imbalance, which precedes a violation of the concentration of mucous secretions.
- Poorly installed intrauterine device.
- Fat metabolism disorder.
- Violation by the surgeon of the operating technique or processing of instruments during cauterization of erosion.
Often, cystic endocervicosis develops as a postpartum complication, which is caused by a violation of the integrity of the cervical canal due to the formation of ruptures. Another common reason is multiple surgical terminations of pregnancy.
Treatment methods for endocervical hyperplasia
Treatment of cervical endocervical hyperplasia is carried out with curettage of the inner lining of the cervix. This operation is performed under hysteroscopic control so as not to ignore possible manifestations of focal hyperplasia formed in the corners of the uterus. The complexity and extent of the intervention largely depends on the individual physical condition of the patient, her age and the possibility of the desired pregnancy, as well as the severity of the developing pathology and diseases occurring during a given period.
After the operation, hormonal medications are prescribed to restore the functions of the endocervix.
After completing a course of drug treatment, it is necessary to periodically visit a gynecologist to prevent possible relapses. During this period, the patient needs to undergo an ultrasound examination every six months to exclude the possible development of oncological formations of the cervix and its mucous membrane.
There is another method used to treat pathologies of the endocervix membrane - using laser cauterization. This method is used to cauterize focal lesions to remove the pathology. This method allows you to preserve not only the functions of the endocervix, but also the patient’s ability to subsequent motherhood. Radical methods using surgery and complete removal of the uterus along with the cervix are used only as a last resort, when the pathological process leaves no chance of recovery and to save the woman’s life.
What is an exocervix smear? Analysis transcript
This mucous layer is located on the vaginal area of the cervix, that is, it is in contact with the microflora of the vagina. Normally, the upper layer of the exocervix is squamous stratified epithelium.
To detect pathologies, the doctor prescribes an exocervix smear to the patient. An inflammatory cytogram may show the presence of columnar epithelial cells, which is an abnormal situation.
There should be a clear boundary between the cylindrical and flat epithelium, located at the site of the external pharynx. If columnar epithelium covers the exocervix, then this will not be the norm. This condition is called cervical ectopia. To avoid complications from this pathology, you need to be treated.
Sometimes this phenomenon is considered an exceptional norm, in particular this applies to the age of girls from birth to puberty. That is, at the time of puberty, clear boundaries between the cylindrical and squamous epithelium should form.
Preventive measures
An important condition for preventive measures for endocervical hyperplasia comes down to early diagnosis of the disease. This is one of the main measures to prevent the occurrence of malignant cells. Women going through menopause are at greatest risk of developing into malignant neoplasms. The following points should also be included in the prevention of endocervical hyperplasia:
- refusal of physiotherapeutic procedures;
- immune system support;
- avoid abortion;
- regular sex life;
- competent use of contraceptives;
- reduce the intake of hormonal drugs;
- maintain normal body weight, especially during menopause;
- allocate time for recreational physical education;
- Do not get carried away with using tampons during menstruation, use them in cases of extreme necessity, as they can injure the vagina.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis of endocervical hyperplasia depends on the causes of the pathological process that has arisen, as well as on the severity of its course. The greatest likelihood of a favorable outcome will be obtained in case of timely diagnosis of the disease and proper treatment. It must be remembered that neglect of one's health and untreated hyperplasia can not only lead to infertility, but also cause more serious diseases, for example, oncology. As a rule, it is better to prevent most diseases or treat them at an early stage than to struggle with the severity of its manifestations for a long time.
Treatment of Nabothian cyst of the cervical canal with medications
This therapy is possible only in the following cases:
- A single, small formation was diagnosed.
- The disease is not accompanied by any symptoms.
- The results of tests for infections and inflammatory processes are negative.
Basically, treatment with one or another drug cannot get rid of such a disease as Nabothian cysts of the endocervix. The main purpose of taking medications is to eliminate the cause of the appearance of cystic formations and prevent further development of the disease.
Therapy aimed at suppressing the development of nabothian cysts is based on the reasons for their appearance and consists of:
- Taking hormone-containing drugs for the corresponding disorder.
- Taking antibacterial drugs when detecting hidden infections.
- Taking antibiotics in the presence of inflammatory processes.
In addition, treatment with medications should be accompanied by maintaining the general health of the patient and taking immunomodulators and vitamins.
Functions of the endocervix
The main role of the process of childbirth in the female body is assigned to the uterus. A new life begins to develop in it and comes out of it into the light. This transition occurs through the cervix, inside which there is a canal called the cervical canal. The endocervix is the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the cervical canal. The lining of the endocervix consists of pores capable of secreting a certain amount of cervical mucus, the nature of which directly depends on the phase of the ongoing menstrual cycle and hormonal levels.
In addition to participating in the process of fetal advancement, during labor, the cervix is also assigned some other functions. The structural features of the canal in the internal structure of the cervix make it possible to carry out the protective function of the endocervix, carried out using a biological barrier. The formation of a mucous plug in the endocervix, containing substances with bactericidal properties, protects the uterus from the penetration of pathogens of infectious diseases. The cervix, using an internal canal, connects the uterus to the vagina, which allows for the monthly removal of secretions and sloughed endometrial mucosa from the body of the uterus at the end of the menstrual cycle. In such a situation, the excretory function of the endocervix is performed.
The endocervix can be subject to various pathological changes occurring in the cervical canal. The most common case is the occurrence of neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the endocervix in the form of cysts or polyps. These tumor processes are easily detected by ultrasound examination. Depending on the degree of development and pathological condition, a technique is selected, which can be carried out in a conservative or surgical correction way.
What is cervicitis and how to treat it?
If cervicitis is not treated, the result will be erosion and polyps, changes in the structure of the cervix - its skin becomes thinner or thicker, which complicates conception.
Advanced infection can spread to other organs (ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder). It is cervicitis that causes female infertility, miscarriages and premature birth. There is a risk of dangerous complications such as bartholinitis, perihepatitis and cervical cancer. Also, prolonged ignoring of symptoms can provoke the disease to become chronic.