Causes
Among the possible reasons for the appearance of this type of neoplasm are:
- heredity (found in blood relatives in every generation);
- injury or several consecutive injuries;
- untimely treatment of inflammatory processes (trendovaginitis, bursitis);
- heavy constant load on the joints;
- excess secretion of synovial fluid.
Among the “owners” of benign neoplasms of this type, women under 30 years of age are more common. Doctors believe that this may be due to hormonal changes (pregnancy, childbirth).
For the normal course of childbirth, a woman’s body produces somatotropin (it weakens the ligaments, which makes it easier for the child to pass through the birth canal), but with dysmetabolism, the hormone continues to influence the body without direct need. Thus, due to excessive elasticity of the ligaments, protrusions of the walls of the serous bursa appear.
The occurrence of a synovial cyst or ganglion is also facilitated by constant stress - sports, work - without proper fixation of the joints with an elastic bandage.
Reasons for education
Hygroma refers to benign cystic lumps that form near a joint. The seal is filled with serous fluid and has a dense shell. Examining pathology using a microscopic method, specialists are not surprised when they find mucus that forms jelly-like areas.
The cyst grows slowly, but when exposed to provoking factors, rapid growth of the hygroma is possible. It is diagnosed at any age, but more often young people become patients. The location of the pathology may be:
- The area of the wrist joint.
- Diagnosed in the ankle area.
- It is less common on the knee or elbow joint.
- Observed in the armpit.
- Formed in the area of the upper and lower extremities.
Regardless of the location, the pathology may not show symptoms for a long period of time, which leads to complications during treatment.
Experts recommend promptly seeking a consultation so that the patient receives complete information on the diagnosis of hygroma, learns what it is and how to get rid of the pathological process.
Professionals in this field have identified factors that contribute to the development of the disease. Among them the most common:
- heredity;
- joint injuries;
- sprain;
- low or high intrauterine activity;
- physical activity of the joints.
Heredity is in first place among the causes of the formation of a pathological process. According to statistics, women are more prone to cystic formations than men.
Frequent patients are young women after the birth of a baby. Children and older people rarely complain of symptoms of the pathology.
Hygroma symptoms
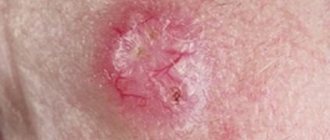
Hygroma on the hand
In the photo there is a hygroma on the leg
type of tumor at the time of removal.
The manifestation of the disease depends on the causes of the tumor and its size:
- slight discomfort with some types of movements, aching pain (tumor size up to 5 mm (see photo above));
- change in skin color - slight constant redness;
- pain when pressing on the tumor, wearing shoes (if the tumor is on the foot);
- difficulty performing motor functions of the joint due to a mechanical sensation of interference or pain;
- neuralgic pain due to pinching of nerves and blood flow;
- decreased skin sensitivity;
- inability to fully bend and straighten the knee joint, severe pain, the appearance of “goosebumps” during forced flexion;
- temperature rise to 37.5 C, constant pain (with tumor trauma, suppuration)
- paralysis of the arm (with axillary tumor localization).
Where does hygroma appear?
- on the wrist joint;
- on the knee joint;
- on the ankle joint (on the anterior lateral surface);
- on the hands and fingers;
- on the back of the feet.
It is much less common to observe hygromas on the elbow joint and in the area of the costal joints on the chest.
The symptoms of hygroma are either very weak or absent altogether. Patient complaints may only be associated with minor pain. A cystic formation causes pain only when its rapid growth begins to compress the surrounding tissues and nerve endings.
If we talk about the danger of this kind of education, then it is, in principle, absent. Not being essentially a tumor, it will not develop into a malignant formation. Sometimes, as a result of mechanical action, a hygroma can rupture, pouring its contents into the tissues surrounding it. But there is no danger in this either, since the hygroma fluid is completely sterile. The occurrence of a defect in the skin of a hygroma when it ruptures is dangerous, as it will become a gateway for infections that can lead to purulent complications.
Tumor types
Depending on the location, several types of hygromas can be distinguished:
1. Wrist, back.
It occurs most often due to the broad ligament that holds the synovial sheaths of the extensor muscles (the pressure on the vaginal walls is constantly strong + thinning of the walls due to constant work). It is possible that the growth of the tumor will lead to compression of the radial artery (resulting in acute pain in the thumb), compression of one or more nerves (decreased sensitivity of the fingers, skin on the wrist and back of the hand).
2. Wrist, palmar part.
In the synovial sheath of the thumb, the tumors are very dense and mobile.
Preparation
Before removing a hygroma, the surgeon must conduct an examination:
- Palpation . Simply by palpating the tumor, the doctor can collect a lot of important data: size and condition, the presence of additional chambers, signs of inflammation, and so on.
- Ultrasound hygromas . Ultrasound examination is one of the most important points in preparation for surgery to remove hygroma. With its help, you can accurately determine its size, shape, structure, and most importantly, its location relative to surrounding tissues, tendons, nerves, and blood vessels.
- MRI . This diagnostic method is one of the most complex and accurate, but its availability is still quite low. Therefore, it is prescribed only in difficult cases, when it is necessary to have accurate information about the location of the cyst in advance.
- Puncture . In some cases, the doctor takes a sample of the contents of the cyst in advance, more often this is done after removal. This is necessary to conduct a cytological analysis, which will completely eliminate the risk of the oncological nature of the tumor.
Read also: Hygroma causes
In addition, general preparation is required, which is prescribed before any operation: blood and urine tests, as well as tests for HIV, hepatitis B and C, and syphilis.
Diagnostics
To make the correct diagnosis and select the type of treatment for a neoplasm of this nature, you should contact surgeons or orthopedists.
To find out the nature of the formation, X-ray diagnostics, ultrasound, MRI, and sometimes puncture are prescribed.
Research is carried out in order to exclude the possibility of other diseases with similar symptoms, to study the structure of the tumor, the cause of its occurrence and how to treat depending on the location of the formation.
X-ray makes it possible to assess the density of the formation:
- equal to bone density - this means we are talking about osteoma (benign bone tumor), osteosarcoma (malignant tumor);
- the walls of the tumor are calcified - hematoma;
- the walls are smooth, and inside there is a dense substance - an abscess (in the presence of pain, high temperature), tuberculosis;
- homogeneous cavity - it is possible that this is a neoplasm - a lipoma;
- the presence under the formation of an additional cavity with a sequester + reaction of the periosteum - osteomyelitis.
MRI shows everything that an x-ray does, but additionally makes it possible to evaluate the connections of the tumor with bones, blood vessels, and joints. Allows you to more accurately determine the density of fluid in the tumor.
Diagnosis of hygroma
To confirm the final diagnosis and differentiate the disease from other ailments, in particular lipoma, atheroma, rheumatoid arthritis, a comprehensive examination is prescribed, which involves the use of the following methods:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) - hygroma is visualized as a cystic formation, you can see not only its localization, but also structural features and blood supply;
- X-ray examination - provides data on the location of the lesion, changes in neighboring organs;
- hygroma puncture - used as a diagnostic and therapeutic method. It consists of taking intracavitary hygromic fluid to study its composition;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to obtain information about the structure and internal contents of the tumor.
Treatment of hygroma
In modern medicine, it is accepted to treat hygroma only surgically. Radical measures help prevent relapses and avoid inflammatory processes in the joints.
Previously, it was also believed that hygroma could be cured with some folk remedies and physiotherapy techniques.
Drug treatment
This type of treatment is appropriate for inflammatory processes in the tissues near the hygroma, but only if the inflammation is not purulent (without throbbing pain, temperature above 38 C, a sharp deterioration in joint mobility, severe changes in the skin over the tumor).
For purulent inflammation, the mandatory treatment method is surgery, and only after that the doctor prescribes certain medications to completely destroy the infection.
If the inflammation is not purulent (body temperature is up to 37.5 C, there are no skin changes, movements are not constrained, the pain is not severe, but constant, covering the hygroma itself and a small area of tissue near it), then drug treatment of the hygroma is acceptable (it will relieve inflammation, but the tumor itself will not disappear!).
All calculations of drug dosage should be carried out by a doctor, taking into account concomitant diseases and the patient’s age (for children, calculations are carried out based on body weight).
- Tablets: 1 tablet of Clemastine in the morning and evening (course – 7-10 days).
- Powders: 1 sachet of Nimesil in the morning and evening (course duration – week-10 days).
- Ointments: applied in a thin layer 2-3 times a day for no more than 7 days ( Diclofenac, Gistan, Diprosalik ).
Physiotherapy for hygroma will also help relieve inflammation and protect the joint from complications (UHF, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, salt and soda baths).
Surgical methods of treatment
Excision of the tumor is the most effective method, since relapses after surgery occur in 20 out of 100 cases.
Since hygroma is a benign tumor, it is not necessary to remove it. The only exceptions are those cases when there is compression of blood vessels or nerves, joint mobility is severely limited, and there is concomitant purulent inflammation.
In most cases, the operation is performed under local anesthesia and takes about half an hour. Exceptions include multiple hygromas and purulent inflammations. They use general anesthesia. The surgical opening is small, and with minimally invasive access methods, almost invisible.
After the operation, the wound is treated with antiseptic solutions, drained, covered with a tight bandage and the limb is immobilized (plaster splints). If the wound heals well, the stitches do not come apart, and inflammation does not occur, then by the end of the week the stitches can be removed.
Hygroma, diagnosis and treatment
Any swelling is cause for concern. This also applies to hygroma. Despite the fact that it does not pose a danger to the body, it is necessary to differentiate it from other neoplasms. Therefore, a comprehensive diagnosis must be carried out, which includes X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans of both the hygroma itself and nearby tissues.
The most accurate diagnosis is provided by histology of the liquid contents of the formation. To do this, a puncture is taken, and the hormonal drug diprosan is injected orally. In case of infection, antibiotics are used.
Sometimes gyrgoma can resolve on its own.
To speed up the process, you should use:
- ointments containing diclofenac, voltaren, indomethacin;
— physiotherapeutic procedures such as ozokerite, electrophoresis, magnet, etc.;
- compresses and lotions made from infusions and decoctions of herbs, recommended by traditional medicine.
Hygroma can be destroyed with strong compression. The low effectiveness of this method, like all those described above, lies in the fact that it preserves the integrity of the capsule. It may fill with serous fluid again, and everything returns to normal. Mechanical compression is also dangerous due to fragmentation of the capsule upon rupture, which can result in the formation of small hygromas.
From all that has been said, the only correct conclusion follows: for effective treatment of hygroma, surgical intervention should be used, using surgical removal of the entire capsule using the enucleation method. Increasingly, not a mechanical incision, but a laser beam is used to remove the formation. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and the wound formed after the procedure is covered with a sterile dressing with an aseptic preparation.
It is useful, together with this bandage, to immobilize the joint affected by the hyrgoma, using plaster or an orthosis in the form of a bandage, corset, or special shoes.
Immobilization of the damaged joint should last from 3 to 4 weeks. Throughout the entire period, it is necessary to continue treatment with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents; when the wound is completely healed, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated.
Prevention
It will not be possible to avoid the appearance of hygroma 100%, but you can minimize some of the causes of its occurrence:
- the load on all joints should be uniform;
- if inflammatory processes occur in any joint, it should be treated immediately, preferably by a doctor;
- observe safety rules when performing work duties or playing amateur sports (avoiding injury);
- To prevent hygroma from appearing on the feet, you should wear comfortable shoes, and if you have flat feet, orthopedic insoles.
Removal of hygroma: what after the operation?
After surgery, your surgeon will apply stitches and a bandage to keep the area clean, reduce the risk of infection, and protect it from accidental bruising. As a rule, the incision does not hurt, but if you experience any discomfort, you can use painkillers. Sometimes your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help prevent infection in the wound. If the hygroma was on the hand or wrist, you may have to wear a support bandage for several days to avoid accidentally hitting your hand and to avoid swelling and discomfort. Move your fingers regularly to maintain joint mobility.
There will probably be hematomas (bruises) after the operation, but they will go away quickly. Temporary loss of mobility, swelling and pain in the joint may occur. If pain or loss of mobility persists for a long time, physical therapy may be needed. The timing of your return to work largely depends on the nature of your work. If you do manual labor, you may have to wait a few weeks. Typically, you can return to work 2-6 weeks after surgery.
Even after surgical treatment of hygroma, the risk of relapse remains: according to statistics, the probability that the cyst will grow again is from 10% to 40%. The chances of a successful cure when the hygroma is removed again are high, but each subsequent operation increases the risk of complications, for example, damage to nearby nerves.
Forecast
The outcome of the treatment of hygroma is clearly positive. It should be remembered that making a diagnosis of “hygroma, synovial cyst, ganglion” is possible only after all the necessary diagnostic procedures have been carried out.
Diagnostics is so important because tumors of the same appearance can hide different diagnoses, including malignant neoplasms.
Relapses after surgical removal of the tumor are 15-20%, after treatment with traditional methods (especially crushing the tumor) - more than 90% of cases.
Indications for hygroma removal
If a neoplasm is detected, it is important to consult a doctor. Only he can make the correct diagnosis. First you need a consultation:
The ganglion is not dangerous from the point of view of transformation into a malignant tumor, but it can reach significant sizes and put pressure on nearby tendons, joints, nerves and blood vessels. If there are no obvious indications for removal, it is enough to periodically observe the tumor with the attending physician or use conservative treatment methods (massage, electrophoresis, mud therapy, UV radiation, paraffin baths and applications). Unfortunately, these methods are not effective enough; relapse occurs in 80–90% of cases.
Surgical treatment of hygroma is recommended in the presence of various symptoms:
The growth and proliferation of hygroma become arguments for eliminating this formation.
- active growth;
- large diameter;
- long-term absence of regression;
- pain;
- restriction of movements;
- discomfort (paresthesia, hyperemia, hyperesthesia, numbness);
- joint inflammation;
- compression of nerves and blood vessels;
- purulent inflammatory process;
- recurrent illness;
- probability of rupture;
- injury;
- cosmetic defect.
For certain diseases and conditions of the body, removal of the ganglion is strictly prohibited:
- oncology;
- immunodeficiency;
- endocrine pathologies;
- decompensation of chronic anomalies;
- inflammatory and herpetic skin formations;
- acute infectious, viral or respiratory diseases;
- blood clotting disorder;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- menstruation.
Return to contents
Postoperative complications
These include:
- wound infection;
- scar formation on the connective tissue of the joint;
- re-formation of the tumor. After a competently performed operation and compliance with all doctor’s instructions, recurrence of hygroma occurs extremely rarely in approximately 5% of cases.
Surgical treatment of hygroma is a simple operation that can be performed even on an outpatient basis. Only after it has been carried out can we talk about successful getting rid of the tumor on the joint. Competent actions of the surgeon and compliance with the recommendations of doctors are a guarantee of complete recovery.
Peculiarities
- Removal surgery for small hygromas is often performed as part of outpatient treatment or in a day hospital. In the case of large formations, complicated by rupture of the walls, suppuration, it is better to perform the operation in a hospital, where the doctor will be able to monitor any changes in the patient’s condition and the behavior of the hernia itself. It is for these reasons that hospitalization may be required.
- Pain relief during standard surgery is carried out using local anesthesia. General anesthesia is provided for rare complex cases when the surgeon expects that removing the pseudotumor and cleaning the wound bed will take longer than usual or that opening the joint is necessary.
- How long does the procedure take? As a rule, the duration of the operation is between 30 and 40 minutes.
- Many patients find that removing a lump in the tendon area is quite simple. However, a certain difficulty arises if a cyst of the wrist joint is removed. Therefore, removal of hygroma on the wrist is performed only by qualified surgeons with real practical experience. This is due to the fact that large vessels, ligaments and nerve bundles are located near the cyst. And in order to prevent relapses of the pathology, it is important to completely excise both the capsule and the isthmus connecting it to the joint capsule, and then properly sutured the damaged tissue.
Hygroma of the hand
Hygroma of the hand is a volumetric formation filled with viscous contents, which is anatomically connected to the sheath of the tendons of the hand or the joint capsule. Regarding the nature of this formation, there are still tough discussions in medical circles about which group it should be classified into: tumors or cysts, since hygroma of the hand has signs of both.
Important to know and remember! Hygroma never degenerates into a malignant tumor. If this happens, it is due to an initially incorrect diagnosis.
The prognosis is favorable. Most often, the formation does not cause any discomfort to the patient, except cosmetic. In some cases, hygroma, reaching large sizes, may be accompanied by limited mobility in the wrist or inflammation.
Causes
To date, the true cause of the development of hygroma of the hand has not yet been established, but there are several theories that try to explain its origin:
- Inflammatory theory. According to it, the formation is a consequence of an inflammatory process in the synovial membrane of the tendon or joint capsule. It appears in a weak spot due to increased pressure of the synovial fluid inside.
- Tumor. This theory is based on the similarities of this cyst with tumors: frequent relapses after surgical removal, a genetic predisposition to the disease, and the presence of pathological cell types in histological examination.
- Dysmetabolic. According to this theory, due to metabolic and endocrine disorders, a large amount of synovial fluid is produced in the body, which leads to high pressure inside the tendon sheaths. Because of this, a protrusion is formed.
There are several factors that increase the risk of developing a tendon cyst:
- a history of inflammatory lesions of the tendons, their sheaths, and joint membranes;
- increased daily load on the hands (people of certain professions, for example, pianists, computer typists, seamstresses, etc.);
- past traumatic injuries to the hands;
- the presence of a tendon cyst in close relatives.
The essence of the disease
As already mentioned, hygroma is an oval or round formation, which inside is filled with a viscous transparent or yellowish secretion. Any tendon cyst is anatomically connected to the tendon sheath or joint capsule.
The shell is made of dense connective tissue, which has signs of a degenerative-dystrophic and metaplastic process. It is the shell that is the cause of all troubles. It contains atypical cells of 2 types:
- fusiform, which ensure the growth of the tendon cyst;
- spherical, which produce the contents of the cyst.
The most favorite location is the hand and the area of the wrist joint. The second place is occupied by the area of the ankle joint. A child often has a hygroma of the popliteal fossa, or Baker's cyst. All other localizations are much less common.
A characteristic feature of this neoplasm is frequent regrowth even after surgical removal. Therefore, it becomes clear that neither conservative therapy, nor folk remedies and various ointments can rid a person of a tendon cyst once and for all.
Signs of hand hygroma
The disease is very easy to suspect, since the formation has a characteristic appearance. This is a small bump on the back or palmar surface of the hand, which rises above the surface of the skin. In some cases, a tendon cyst may not show itself outwardly if it grows not outward, but inward (under the tendon).
Most often, patients complain of a cosmetic defect, very rarely such a formation hurts, or a limitation in the range of motion in the hands develops. When a tendon cyst reaches a large size, it can compress the blood vessels and nerves of the hands, causing corresponding symptoms.
The main clinical signs of hygroma:
- the formation is soft and elastic on palpation;
- hygroma is characterized by low mobility, as it is connected to the tendon sheath;
- the skin over the hygroma is not changed, it is easily displaced (with suppuration, redness of the skin and its hyperthermia occur);
- the cyst has clear contours;
- size varies: from a few mm to 4-5 cm;
- in most cases there is no pain; if the hygroma is located near the nerves, then chronic pain syndrome may occur;
- when the blood vessels are compressed, the pulse in the radial artery disappears, patients complain of cold hands and pallor;
- if the cyst reaches a large size, the function of the wrist joint may be limited.
Some tendon cysts grow very slowly, while others grow quickly. It is worth knowing that hygroma never disappears on its own. If this happens, it is due to the presence of a valve between its cavity and the tendon sheath. In this case, the contents of the hygroma flow over and it decreases. But any subsequent load on the hand contributes to the return of the tendon cyst.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing hygroma is not at all difficult. But you need to take into account that very dangerous diseases, for example, malignant tumors, can be hidden under its mask. Therefore, hygroma should be a diagnosis of exclusion.
The diagnostic program includes:
- X-ray examination of the hands;
- conducting an MRI or CT scan;
- Ultrasound of a tendon cyst;
- diagnostic puncture and biopsy of the formation, followed by cytological and histological examination of the samples.
The final diagnosis is established only after all of the above examinations have been carried out and a malignant nature has been excluded.
Treatment of hand hygroma
Hygroma can be treated conservatively and surgically. Therapy is used for cosmetic or medical reasons. In the latter case, the cyst is symptomatic (pain, compression of blood vessels, nerves, limitation of movements in the wrist, infection and suppuration).
It is important to know! Today, conservative therapy is considered inappropriate, since in 80-85% of cases a relapse of the disease develops. The only method that allows you to get rid of hygroma once and for all is considered to be surgery to remove the cyst.
Conservative therapy
It is used when surgery is contraindicated or the patient categorically refuses surgical removal of the cyst. Several techniques are used:
- Hygroma puncture involves evacuating its contents using a puncture with a thin needle. After the secretion is sucked out, antiseptics and antibiotics are introduced into the formation cavity to prevent suppuration. Sometimes several punctures are needed for the tumor to completely disappear. Often after puncture, the formation becomes multi-chambered, which greatly complicates its surgical removal in the future. The method gives relapses in 70-80% of cases, since the hygroma capsule remains in place.
- Sclerosis. At the initial stage, the contents are evacuated with a syringe and a needle, as during a puncture, and then sclerosing substances are injected into the cyst cavity, under the influence of which the hygroma capsule collapses and its cavity is removed. The effectiveness of this treatment is higher than a regular puncture, but the risk of relapse is still high.
- Blockade with glucocorticoids. After the contents of the hygroma are evacuated, the glucocorticoid drug Diprospan is injected into its cavity. It helps eliminate inflammation and fill the cavity with connective tissue.
- Crushing the hygroma. Today this method is not used, as it is considered ineffective, very painful and dangerous for the patient.
- Physiotherapy. It can be used as an independent method, but is most often used as an addition to the main treatment, for example, such procedures are often prescribed during the rehabilitation stage after surgery. It is important to remember that any such procedures are prohibited in case of inflammation of the formation and its traumatic crushing.
Surgery
This is the only effective method of getting rid of hygroma, but even after surgery, relapses occur if the surgeon leaves at least one small piece of atypical tissue.
Indications for surgery:
- external cosmetic defect;
- large and rapidly growing education;
- hygroma infection;
- compression by the formation of blood vessels and nerve fibers;
- limited mobility in the wrist joint due to hygroma.
There are 3 methods for removing hygroma:
- classic excision with a scalpel with wide open access;
- removal using endoscopy and minimally invasive access;
- laser removal of tendon cyst.
Hygroma of the hand is a very common disease, especially among people leading an active lifestyle. It should be remembered that it is much easier to remove a tendon cyst at the initial stage than when it reaches a large size. Hygroma does not go away on its own, so do not hesitate to visit a doctor.
Add a comment
- My spina.ru © 2012—2019. Copying of materials is possible only with a link to this site. ATTENTION! All information on this site is for reference or popular information only. Diagnosis and prescription of medications require knowledge of the medical history and examination by a physician. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor regarding treatment and diagnosis, and not self-medicate. User AgreementAdvertisers
Clinical picture
The difficulty of detecting hygroma at an early stage of development is that the pathology practically does not reveal itself due to its asymptomatic course. Therefore, patients miss the optimal time for its treatment without surgical intervention.
During its development, the neoplasm begins to show the following clinical signs:
- The presence in the area of the joint is a rounded formation that is soft to the touch.
- Pain when pressing on the tumor.
With exacerbation of inflammation, increased pain and redness of the skin at the site of the lesion cannot be ruled out. Joint dysfunction is also possible.
Complications of surgery and relapses
The operation to remove hygroma is not a major surgical procedure, but complications may include:
- Infection in the wound, suppuration.
- Bleeding if an artery is damaged.
- Disruption of innervation in case of nerve damage.
Unfortunately, relapses of hygroma after its surgical removal account for up to 30% of cases. Main causes of relapse:
- Hereditary weakness of connective tissue.
- Insufficiently removed capsule.
- The junction of the hygroma with the joint capsule is not sutured.
- Failure to comply with the restrictive regime in the postoperative period.
- Returning to the previous job that caused the illness.
Complications
Pain and swelling may occur in the weeks following surgery. This is a normal phenomenon that in most cases goes away on its own.
More serious complications rarely develop. May occur:
- Suppuration;
- Heavy bleeding;
- Loss of sensation due to damage to nerve fibers;
- Relapse of the disease;
- Adhesive processes.
The disease can recur if the capsule was not completely excised during the removal process. Sometimes the pathology returns if the mouth of the cyst was poorly sutured.
It is important to follow a gentle regimen after surgery. If you quickly begin to load the joint, there is a high risk of complications. Taking all prescribed medications and not exercising will allow the patient to recover faster.
How to remove hygroma
Until recently, treatment of hygroma was carried out by crushing it, while the entire contents of the cyst were poured into nearby tissues. The serous fluid contained in the cyst cannot cause inflammation, since it is completely sterile. However, this technique is not effective in 90% of cases, because in most cases the cyst grows back. Some time after crushing, the edges of the shell grow together again and fill with liquid.
Modern medicine provides more effective conservative and surgical methods for removing such pathologies. In addition to classical surgical excision, the cyst can be removed endoscopically or using a laser. Treatment can also be carried out through puncture or sclerotherapy, however, these methods cannot guarantee that the hygroma does not recur.
Performing a puncture
When performing a puncture, the formation is punctured, then the accumulated fluid is pumped out of it. This procedure is not a surgical procedure and is considered a conservative method of therapy. After the fluid is pumped out of the hygroma capsule, special medications are injected into the cyst to prevent inflammation and infection.
We recommend reading Angioma (skin, liver, body) - causes, types and treatment
Since after the puncture, pathological hygroma tissue still remains in the affected area, after some time it recurs. To prevent the recurrence of the cyst, it is imperative to remove the abnormal tissue through surgery.
Carrying out arthroscopic surgery
This is a minimally invasive operation that involves only a few punctures. One puncture is needed to insert a camera through which the doctor controls all actions performed. A surgical instrument is inserted through the second hole. After removal of the cyst, the surgical site is treated with an antiseptic and a fixing bandage is applied, with which the patient can go home.
Carrying out a classic operation
Traditional surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia, but if a child needs to have a cyst removed, they may be given general anesthesia. The removal takes about 30 minutes, after which the patient must remain in the hospital for another day under the supervision of doctors.
The operation is performed according to the following algorithm:
- Apply a tourniquet above the affected area;
- Administration of local anesthesia;
- Dissection of soft tissues with a scalpel over the cyst;
- Pumping out serous fluid;
- Removal of the hygroma capsule;
- Treating the wound surface with an antiseptic;
- Stitching.
If the formation is small, a small incision is made, after which almost no traces remain. After removing the tumor, the sutures are removed after 10-14 days. During this period, the patient should keep the limb completely at rest, avoiding any stress on the joint where the operation was performed. Sometimes a synovial cyst occurs in the area of the knee joint; in this case, the operation is performed in the same way, but the rehabilitation period takes longer.
Carrying out laser removal
The laser therapy method has proven itself very well. Treatment of hygroma with a laser is almost no different from traditional surgery, only in the technique of dissecting soft tissues. During laser therapy, the scalpel is replaced with a powerful laser, which not only dissects the skin, but also excises the tumor itself. Before removing pathology with a laser, it is necessary to first perform a puncture and pump out all the liquid from the capsule.
Hygroma is removed as follows:
- using endoscopic needles, two small holes are made in the tumor;
- through the first hole, fluid is pumped out from the cyst capsule;
- a laser is inserted into the second hole, which vaporizes the pathological tissue of the cyst;
- After removal, the wound surface is treated with an antiseptic and sutures are applied.
The procedure takes no more than twenty minutes, and after removal of the tumor, a barely noticeable scar remains. Rehabilitation after laser removal of hygroma takes very little time.
Conservative treatment methods
Many ways to get rid of a tumor have been described. The most common:
An experienced doctor will make a diagnosis during the examination; sometimes an x-ray or ultrasound will be required.
- physiotherapy. Electrophoresis, ultrasound, heating, mud applications help relieve pain and relieve the cause of inflammation;
- drug treatment. It is used in case of inflammation of the contents of the hygroma and surrounding tissues;
- crushing the tumor. Used for small hygromas. Very painful, leads to relapses and complications;
- puncture. The liquid contents are removed with a syringe. The probability of relapse is almost 100%.
It is impossible to get rid of the tumor using the described means; treating hygroma without surgery helps relieve pain and stop inflammation. The cause of the lump remains, and it can only be eliminated through surgery.
Diagnostic features
In the vast majority of situations, diagnosis of the pathology is made without difficulty, based on the characteristic clinical picture, patient complaints, and characteristic features of the development of hygroma. But sometimes, especially when they are deep localized or close to articular structures, a more detailed study of synovial cysts is required. This requires additional instrumental studies: x-ray, ultrasound, tomography. They also resort to biochemical and microscopic examination of the contents of hygromas through puncture of their cavity.
These methods provide enough information to also make a differential diagnosis. This is necessary to exclude many other types of soft, bone or cartilage tissue neoplasms in the patient. For example, lipomas, atheromas, epithelial cysts.
Progress of the operation
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia. General anesthesia is chosen only in particularly difficult cases when a long operation is expected. As a rule, surgical intervention lasts no more than 30 minutes. Small hygromas can be removed on an outpatient basis or in a one-day hospital setting.
Operation stages:
A rubber tourniquet is applied to the limb.
- Infiltration of anesthetic at the incision site and along the edges of the tumor.
- A small skin incision is made over the tumor.
- Educational puncture to extract fluid. Sometimes surgeons excise the hygroma along with its contents.
- Careful isolation of hygroma from surrounding tissues to the very base. Isolating only the upper, most accessible part of the hygroma is not enough. A significant part of its shell remains deep in the tissue, and after 2-3 months after the operation, fluid begins to accumulate in the hygroma again. Therefore, it is necessary to isolate the entire shell of the hygroma to the junction of its base with the joint
- Excision of protrusion.
- Suturing the synovial bursa at the excision site.
- Suturing the wound.
- Applying a tight bandage and fixing the joint with an orthosis or plaster splint.
Painkillers are prescribed according to indications. Daily dressing changes are carried out. If inflammation threatens, antibiotics are prescribed.
The sutures are removed on the 7th day, the fixing bandage is removed after 2 weeks.
How is the operation performed?
Removal of hygroma is the most effective method of treating this type of cyst. There are other methods, such as puncture and physiotherapy, but only radical removal allows you to get rid of it, practically eliminating the risk of relapse.
And although this operation, like any other intervention, is associated with certain risks, they are compensated by the opportunity to get rid of hygroma once and for all. And competent preparation for removal and rehabilitation after it can reduce risks.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated for large hygromas, having several chambers, affecting vessels and nerves, or severe pain.
- Arthroscopic treatment - a manipulator probe resembling a tube is inserted through a small puncture, through which the formation is peeled off and removed from the joint and tendons. The advantages of this technique are that this operation is less traumatic and does not leave visible cosmetic defects.
- Classic method with ligation of the mouth. An incision is made above the hygroma, the wound is expanded, the upper part of the tumor is clamped, and the rest of the tumor is cut off from below with jaws, separating it from the surrounding tissue. Next, the mouth of the ganglion is sutured to avoid relapse. The edges of the wound are compared and sutured in layers.
- The laser removal method is similar to the classical method, the only difference is that instead of a scalpel and scissors, a laser beam is used, which eliminates blood loss and reduces tissue trauma, and there is no cosmetic defect.
Signs of the disease
It is difficult to identify the disease in the initial stages of formation due to the lack of pronounced symptoms. A small lump appears on the arm or leg. At the initial stage, hygroma does not hurt and does not cause discomfort to the patient. To prescribe adequate treatment, it is necessary to accurately establish the diagnosis in order to exclude possible dangerous formations.
Hygroma is distinguished by the following symptoms:
- the formation has clear, precise boundaries from nearby tissues;
- the seal is formed in the form of a ball.
The knot can be a single variant or appear in multiples on one joint. The tumor can grow slowly or become large in a short period of time (2-3 hours), affecting the functionality of the affected limb. As the seal grows, it puts pressure on the nerve endings, causing pain.
Before choosing a removal method, the patient is assigned to diagnose the body - laboratory and instrumental. The doctor needs to distinguish the disease from a malignant neoplasm.
Contraindications for surgery
The following factors are contraindications to surgical removal of a synovial cyst:
- presence of acute infections;
- diseases of bones and joints;
- chronic blood diseases;
- heat;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- pregnancy period.
You should not choose a treatment method for hygroma on your own; it is better to undergo a full examination and consult with a specialist. If inflammation is present, it is recommended to first undergo conservative treatment with antibiotics. Before performing surgical removal of a tumor, surgeons must make sure that there are no contraindications and minimize the risks of any complications.
Causes and mechanism of formation
As with many other diseases, the exact causes of hygroma have not been established. But there are assumptions about the following factors that can be considered predisposing with a very high degree of probability:
- hereditary predisposition, which is confirmed by repetitions of cases of ganglion formation in relatives;
- a single, but quite serious injury to a joint or tendon, after which an atypical proliferation of connective tissue begins with the development of a benign tumor;
- chronic trauma, characteristic of certain types of professional or sports activities (for example, if a person constantly makes movements in the wrist joint during the day, then the possibility of developing a hygroma of the carpal localization increases significantly).
The contents of the ganglion may consist of red blood cells and fibrin strands
All these factors are “trigger”, that is, it is because of their influence that the growth of connective tissue begins at a speed much higher than the need for physiological regeneration. In addition, as a result of the influence of predisposing factors, the cells of the connective tissue of the tendon sheaths or joint capsules are divided into two types. Some of them begin to divide uncontrollably and intensively, ensuring the appearance and growth of hygroma (when examined microscopically, they have the shape of a “spindle”). Others, spherical in shape, become producers of liquid, which gradually fills the resulting space.
This fact is very important for understanding the mechanism of development of ganglion relapses. If during surgery at least a very small part of the spindle-shaped or spherical cells remains not removed, then, continuing to divide and produce a liquid component, they soon form a new synovial cyst, which is a relapse.
This modern view of the mechanism of the appearance of neoplasms and their relapses is fundamentally different from the previous view. Previously, it was believed that the walls of the hygroma were simply protrusions of joint capsules, tendon sheaths or periarticular bursae, and their contents were an arbitrary combination of intercellular and synovial fluids. This theory could in no way explain either the continued growth of cystic formations or the appearance of relapses after seemingly radical removal of the tumor.
It is the amazing ability of even a very small number of ganglion cells to give rise to a new cyst that can answer the question of whether hygroma is dangerous and how dangerous it is. On the one hand, not a single case of malignancy of synovial cysts has yet been reported in clinical practice. But, taking into account the constant deterioration in the quality of nutrition, increased drug load and the negative influence of environmental factors, this fact cannot be considered constant and immutable.
A single but severe injury can lead to the formation of a synovial cyst
On the other hand, joint hygroma, for example, constantly increasing in size, has the most negative effect on all articular structures, which significantly reduces their functionality. If we take into account the possibility of its repeated relapses, then we can say this: “Yes, indeed, some localizations and types of hygromas may still pose some danger to the patient’s health, but in no case to life.”
Where can a hygroma form?
A benign neoplasm is usually localized on the part of the joint where it extends. However, sometimes it also appears in the flexion zone. This mainly applies to hygroma of the hip joint and knee.
A hernia most often forms on the following parts of the body:
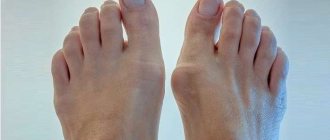
- On the hand. The most common location of thickenings. There is hygroma of the wrist joint of the hand, as well as the elbow. Usually occurs in professional athletes whose activities involve active movements of the arms. Hygroma on the hand sometimes appears in small children who crawl a lot, leaning on their palms. The tumor causes a lot of discomfort, especially during active movements. Partial loss of legal capacity occurs;
Most often it occurs in the hand area.
- on the foot. Hygroma of the ankle or knee usually occurs in people who spend a lot of time standing or walking a lot. The main places of localization are in the foot, ankle, knee, and hip joint. The development of compaction provokes pain, especially when it comes into contact with shoes;
- cervical hygroma. A hernia of this type develops mainly in the embryonic period and is detected in newborns. Cystic formation is associated with impaired development of the lymphatic system, as well as with infections suffered by a woman during pregnancy. The thickening may resolve spontaneously. If it remains, it is removed surgically, since it threatens developmental defects. In some cases, doctors may recommend induced termination of pregnancy. If a neoplasm occurs in an adult, it is often multiple. 2 – 3 or more cysts are detected;
Cystic formation is associated with impaired development of the lymphatic system.
- tumor in the clavicle and mediastinum. It often increases greatly in size and begins to put pressure on the internal organs of digestion and breathing. Requires mandatory treatment, as it provokes impaired swallowing function and difficulty breathing. In most cases, hernias of this type are detected in young children in the first years of life. Sometimes combined with a cervical tumor;
- on the head, a neoplasm develops as a result of traumatic brain injury. Subdural hygroma provokes the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and causes numerous neurological disorders.
Rehabilitation
Doctors advise taking all precautions during the postoperative period. After surgical excision of the tumor, a sterile bandage is applied to the suture, secured with an elastic bandage. The dressing is changed daily, observing hygienic measures, treating the operated area with an antiseptic solution - brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide. Patients are prescribed ointments to speed up wound healing. To prevent the development of the inflammatory process, antibiotics are prescribed.
The limb is securely fixed using a splint. This measure is necessary to prevent complications and relapses of hygroma. The duration of immobilization is at least 10 days. During the rehabilitation period, physical activity is limited, because the musculoskeletal system is weakened.
During the recovery period after hygroma removal, physical inactivity is avoided. To restore joint mobility, a set of physical therapy exercises is performed.
Experts also recommend physiotherapeutic procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- warming up;
- ultrasound treatment;
- ozone therapy;
- paraffin treatment;
- balneological procedures.
The essence of the
Removal of hygroma localized in the hand area is the surgical elimination of the swelling itself and the root cause of its appearance. The joint and tissues adjacent to it are restored, the mobility of the structures returns, and the pain syndrome disappears. As a result, the patient’s quality of life improves; he can wear comfortable clothes and not feel embarrassed about his appearance.
Types of surgery
Hygroma can form in the area of any joint. There are several types of surgical interventions in surgery:
- removal of hygroma of the hand, palm;
- finger;
- ankle joint;
- feet.
Removing hygroma through a needle
The principle of therapy is the same, so there are usually no difficulties. The patient can independently choose the type of treatment: surgical or laser removal. But I must follow medical recommendations and take a responsible approach to preparation.
Material on the topic: Arthroscopy of the ankle joint