Syphilis is a rather serious disease that affects the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs of a person. Syphilis is a classic disease that is sexually transmitted. The cause of syphilis is unprotected sexual intercourse with a casual or unreliable partner.
The symptoms of syphilis can be quite varied. The manifestation of the disease will depend on the period or stage. Previously, the infection was considered an incurable disease, but now syphilis can be treated with effective antibiotics.
Syphilis
Syphilis
– a venereal disease that has a long, wave-like course and affects all organs.
Syphilis
(Lues) in terms of the extent of damage to the body is classified as a systemic disease, and in terms of the main route of transmission it is considered a sexually transmitted disease.
The disease can affect the entire body: mucous membranes, skin, central nervous, musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, and digestive systems. Syphilis is characterized by the appearance of mucous syphilitic rashes on the skin. The rash is painless, occurs without fever and does not itch.
As the disease develops, the internal organs and systems of a person may be affected. All this leads to irreversible consequences and the person may die. As a rule, treatment of syphilis is carried out by a venereologist. Treatment is based on rational and systemic antibiotic therapy.
Syphilis ranks first in terms of infectious diseases (including STIs), in terms of incidence, degree of harm to health, contagiousness, and difficulty of treatment and diagnosis.
The causative agent of syphilis in the environment can live in moisture for up to several hours. Syphilis is killed by high temperature, drying and disinfectants. The infection can remain viable for several days when frozen.
https://youtu.be/X7nqDNhqB9w
Diagnostics
Photo: netdna-cdn.com
Diagnosis of the disease begins with collecting complaints and the patient’s life history. After identifying characteristic complaints and an objective examination, the doctor establishes a circle of contact persons who could be exposed to infection.
To confirm syphilis, the following laboratory diagnostic methods are used:
- Bacterioscopic examination - allows you to visualize pale treponema, which upon microscopic examination has the appearance of a thin spiral with 8 - 12 uniform curls. In a dark field of view, the mobility of microorganisms is observed, which distinguishes treponemes from many types of bacteria. The material used is discharge from erosive and ulcerative elements in the area of the external genitalia or oral cavity, and punctures from regional lymph nodes. In secondary syphilis, material from various lesions of the skin and mucous membranes is used. For bacterioscopic examination of congenital syphilis, amniotic fluid is used as research material. If the result is negative, a repeat microscopic examination is performed to detect the syphilis pathogen in the material. If detection of Treponema pallidum becomes difficult for any reason, a serological blood test is used to confirm the diagnosis;
- Serological blood tests. These studies are used not only to diagnose the disease, but also to assess the quality of treatment. Since the antigenic composition of treponema pallidum is quite complex, there are many different antibodies in the blood serum of a person suffering from syphilis. In this regard, there are a large number of laboratory serological tests that can determine the presence of syphilis. In turn, they are divided into two groups:
- non-treponemal tests - used for selection. They do not require large expenses, so they allow you to examine a large number of people. However, they have some disadvantages: they have low sensitivity for primary, tertiary and late latent syphilis, and there is also a high probability of obtaining false-positive results;
- treponemal tests are confirmatory. Significantly higher in cost than non-treponemal tests, therefore they are not used for selection. There are many different types of treponemal tests, but in most cases the RV (Wassermann reaction) is used;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a highly accurate diagnostic method that allows you to identify the causative agent of an infectious disease through the study of genetic material. It has a high degree of sensitivity and specificity and can be used at the stage of the incubation period, when there are still no clinical symptoms of the disease;
- Immunoblotting is a method for identifying antigens or antibodies.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of the appropriate clinical picture, detection of the causative agent of the disease using bacterioscopic examination and the results of serological tests.
Periods of syphilis
Syphilis can occur over a long period of time and in waves, alternating with periods of latent and active manifestations of the disease. The existing stages of syphilis differ in a set of different forms of skin rashes (syphilides) and erosions. They appear in response to the introduction of pale spirochetes into the body.
There are 4 stages of the disease:
- Incubation period;
- Primary syphilis;
- Secondary syphilis;
- Tertiary syphilis.
Incubation period of syphilis . This stage of the disease begins from the moment of infection and can last about 3-4 weeks. Spirochetes begin to spread through the blood and lymph nodes throughout the human body. While multiplying, they do not show any clinical symptoms. The patient does not even suspect that he is already contagious. If you start treatment for syphilis from the incubation period, the stage of the disease can last up to several months. This occurs due to the fact that medications are taken that inhibit the further development of the disease.
Primary syphilis can last 5-8 weeks. This stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of primary syphiloma or chancre and subsequent enlargement of nearby lymph nodes.
Secondary syphilis . This stage of development can last from 2 to 5 years. With secondary syphilis, internal organs, systems and tissues of the body are affected. Generalized rashes appear on the skin, mucous membranes, as well as baldness. Secondary syphilis occurs in waves, activating or eliminating symptoms. There are secondary fresh, secondary recurrent and latent syphilis.
Latent (latent) syphilis does not have skin manifestations of the disease, signs of specific damage to internal organs and the nervous system, and is determined only by laboratory tests (positive serological reactions).
Tertiary syphilis is very rare and occurs when there is no treatment. It may take years for tertiary syphilis to appear. During this period of the disease, the patient’s systems and organs are irreversibly damaged. The central nervous system is severely affected. This is a difficult period of syphilis, which can lead to disability and even death.
It is detected by the appearance of tubercles and nodes (gummas) on the skin and mucous membranes, which, when disintegrating, disfigure the patient. They are divided into syphilis of the nervous system - neurosyphilis and visceral syphilis, in which internal organs are damaged (brain and spinal cord, heart, lungs, stomach, liver, kidneys).
Why treatment for syphilis may not be effective
The reasons for the ineffectiveness of treatment worry a significant number of patients diagnosed with primary syphilis, and who could not get rid of their disease, despite all efforts.
There are several important factors.
Firstly, unfortunately, not all patients carefully follow medical recommendations.
Often the patient, having only waited for the symptoms to disappear, already considers himself cured.
And he abandons therapy without completing the entire prescribed course.
As a result, treponema pallidum remains in the body, continuing to gradually undermine it.
Gradually worsening the patient's condition until the symptoms again force him to seek help with a more advanced form of the disease.
Secondly, the treatment may be chosen incorrectly.
This happens if the dose of the drug was calculated incorrectly or the drug was selected inadequately.
That is, a medication was used to which the bacteria is resistant.
Or treatment was simply started incorrectly due to the fact that the diagnosis was initially incorrect.
To ensure the correctness of the chosen therapeutic tactics, it is recommended to constantly monitor the therapy.
And upon completion, take tests that will confirm recovery or, on the contrary, refute it.
Symptoms of syphilis
The symptoms of syphilis are very diverse and it is quite difficult to understand them right away. As the disease progresses, the manifestations of syphilis can change fundamentally. This may be a painful ulcer, which from the first stage subsequently progresses to a severe mental disorder (advanced form). In different patients, the same symptom (sign) may differ depending on the level of immunity, gender or place of occurrence. Treatment of syphilis will also depend on the stage of the disease and its development.
The course of syphilis and certain symptoms may depend on the stage of development of the disease. Additionally, symptoms can vary greatly between women and men.
The first sign of syphilis is the formation of a hard chancre on the glans penis in men and the labia in women. The chancre has a dense formation, a brown-red bottom and smooth edges.
The primary symptoms of syphilis are quite characteristic and, if you consult a specialist in time, you can avoid serious troubles and cure this disease in a timely manner.
As a rule, internal symptoms of syphilis and skin manifestations .
The main symptoms of syphilis:
– Appearance of chancre. This is a smooth, painless ulcer;
– Headaches, pain in joints and muscles, malaise;
- Heat;
– Enlarged lymph nodes;
– Inflammation of the nail (felon). Does not heal for several weeks
– Increased content of leukocytes;
– Decrease in hemoglobin;
– Indurative edema;
– Difficulty swallowing, swollen and red tonsils (amygdalitis).
Features of the progression of syphilis
The question often arises among patients about when and how the primary form of the disease turns into secondary syphilis.
Doctors note that the transition usually takes up to several weeks.
In this case, the patient first consults a doctor when the symptoms of the secondary period have already manifested themselves with all their might.
Such symptoms primarily include a rash all over the body and feverish reactions.
This is forced to visit a doctor to find out the causes of the unpleasant phenomena.
If treatment is not done in a timely manner, the disease will move from secondary to tertiary.
In this case, it will no longer be possible to avoid involvement in the pathological process not only of the genital organs, but also of other systems, and especially the nervous system.
If a person with tertiary syphilis is not given medical care, the outcome of the disease is highly likely to be fatal.
Doctors note that it is easier to prevent the disease from developing to the tertiary form than to treat it later.
Symptoms of primary syphilis
The first symptoms of the disease may appear at the place where the treponema has entered the patient’s body. A painless form of ulcer with fairly dense edges appears - a chancre. In most cases it appears on the genitals. The main route of transmission of the disease is through sexual intercourse.
- The chancre does not increase in size, has scanty serous contents or is covered with a film or crust; a dense, painless infiltrate is felt at its base. Hard chancre does not respond to local antiseptic therapy.
- Enlarged lymph nodes (regional lymphadenitis, scleradenitis or lymphangitis);
- Indurative edema, which appears predominantly in the genital area (due to the fact that this is where infection enters the body) and represents a slight increase in the form of a bulge with discolored skin, also painless, lasting from 1 week to 1 month during primary syphilis .
- The formation of a hard chancre, which is an almost painless deep dense ulcer, looks like a pit with a smooth rounded bottom, without bleeding and a tendency to increase in diameter. Chancre can also be present on the body in the form of atypical forms - multiple chancre, chancre amygdalitis (appears on one of the tonsils in the oropharynx, reminiscent of signs of a sore throat), chancre felon (appears on 1-3 fingers of the right hand);
- General malaise, weakness;
- Dizziness;
7. Increased body temperature.
Incubation period
On average, 20 days pass from the first entry of the pathogen into the body until clinical signs of syphilis appear. However, in medicine there have been cases of shortening the incubation period to several days and lengthening it to 5-6 weeks. The first is typical for infection from several sources simultaneously or with the development of a mixed infection (the combined action of several pathogens). A long course often develops while taking broad-spectrum antibiotics for the treatment of another disease.
At this stage of syphilis, Treponema palidum is introduced into the body and reproduces through division (every 28-32 hours the number of microbial bodies increases exponentially). There are no clinical, morphological and serological manifestations of the disease yet: the analysis of the incubation period and the possible route of entry of the infection into the body is carried out after the appearance of its first signs.
This stage of the disease ends with the appearance of primary damage (affect) - chancre, which indicates the development of the clinic of primary syphilis.
Secondary syphilis: symptoms
The process of secondary syphilis begins approximately 2-4 months after the first signs appear. Lasts up to 5 years. At this stage, all human systems and organs can be affected. These are the nervous system, joints, organs of vision, digestion, and blood circulation.
The clinical symptom of secondary syphilis is a rash on the mucous membranes and skin that spreads everywhere. The rash may be accompanied by fever, headache, and body aches. All of these symptoms may resemble a common cold.
Attention! If you do not treat syphilis at this stage, then over time the rash disappears and syphilis flows into a latent stage, which can last up to 4 years. After a certain period of time, the disease relapses.
The main symptoms of secondary syphilis:
– The appearance of a generalized rash on the skin and mucous membranes (syphilitic rash);
– Hair falls out in places on the head, even to the point of baldness;
– Enlarged lymph nodes, cold to the touch, without adhesions, painless or slightly painful (lymphadenitis);
– Increased body temperature to 37-37.5 °C;
- Cough;
- Runny nose;
– Redness of the eyes (conjunctivitis).
First stage of syphilis
Stage 1 of syphilis begins from the moment treponema pallidum reaches a certain concentration in the blood, sufficient for the manifestation of the first symptoms. The primary symptom is the appearance of erosion at the site of infection.
If the infection occurs through sexual contact, the neoplasm appears in the genital area, rectum or mouth, depending on the type of sex during which the infection occurred. In case of domestic infection, the localization of erosion can be any area of the skin.
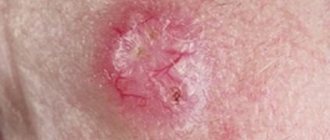
Erosion is chancre or primary syphilide. It has the appearance of a round ulcer with regular outlines, with a diameter of 4-10 mm; in rare cases, a giant chancre up to 15 mm in diameter is observed.
Syphiloma develops gradually from a red spot to a dense ulcer at the base. The dense part of the chancre resembles cartilage tissue to the touch, the surface of the chancre is smooth, covered with a transparent film, which is the highest concentration of bacteria.
Primary syphiloma does not cause discomfort (pain, itching) and, if located in hidden areas, can go unnoticed.
The photo shows chancre of the first stage of the disease.
Chancre goes away on its own, in the first stage of the disease, without the use of therapy.
Classic or typical chancre is the most common, but in rare cases it may have an atypical form:
- Chancre felon is localized on the phalanx of the finger and looks like swollen, inflamed skin with an internal ulcerative part with purulent contents. The panaritium has irregular outlines and a bluish tint. Unlike the typical painless chancre, it causes pain of a shooting nature. This type of chancre is most often found among doctors, as they become infected through the skin of their hands.
- Indurative edema , the main location is the genitals, in women – the labia, in men – the foreskin. An atypical chancre looks like a swollen, enlarged area. When palpated, it has a characteristic solid consistency. Color - from red to bluish. Despite the active inflammatory process in the area of inductive edema, the patient's condition remains stable, without hyperthermia and pain.
- Chancre amygdalitis is an atypical chancre with a localization in the oral cavity - throat, tonsils, chancre is very similar to a regular sore throat. A distinctive feature of amygdalitis from ordinary sore throat is unilateral inflammation (either the left side or the right).
Stage 1 syphilis is also manifested by inflammation of the lymph nodes - regional lymphadenitis, which appears within 10-14 days after the appearance of primary syphiloma. There is a saying in medicine that “lymphadenitis is a faithful companion of chancre,” since inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs only in the area where primary syphilide is localized.
For example, syphiloma in the genital area is accompanied by inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes, chancre of the oral cavity leads to enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, and chancre of the finger leads to enlargement of the ulnar lymph nodes.
No matter in which area the inflammation occurs, there are characteristic features of the lymph nodes during the period of inflammation:
- size - from bean to flattering nut;
- dense to the touch;
- elastic and movable;
- there is no adhesion to surrounding tissues;
- do not cause pain, even when pressed;
- do not change the structure of the skin in the area of inflammation.
Enlarged lymph node during primary stage disease.
Important. When hard chancre is localized on the cervix or in the rectum, the inflammation of the lymph nodes will go unnoticed, as it will occur in the pelvic area.
At the end of the first period, all symptoms and primary chancre disappear, but treponema pallidum reaches its maximum concentration in the blood and increasingly affects the body. The end of primary syphilis in 95% of patients is asymptomatic and only 5% of those infected may experience attacks of headache, general malaise and a hyperthermic reaction.
Diagnosis of primary syphilis
Syphilis in the early stages is very difficult to diagnose and causes difficulty, even for experienced specialists, since the disease with its main symptom - primary syphiloma - is very similar to a number of other infectious and non-infectious diseases. And since at the beginning of the primary stage, laboratory tests may not provide accurate confirmation of the disease, differential diagnosis of syphilis with other diseases is carried out.
Table No. 1. Differential diagnosis of syphilis and other diseases at the first stage of the disease:
| Photo | Symptom |
Genital herpes | The rash with genital herpes is similar to small multiple blisters of small size, but unlike syphilis, there is severe itching and burning. Herpes is not accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes. |
Trichomonas erosions (gonorrheal erosions) | Unlike syphilitic erosions, they have an irregular shape and a yellow coating on the surface, and also cause pain. |
Scabies ecthyma | It differs from chancre in the pairwise arrangement of papules and itching. The rashes have no compaction at the base and the disease is not accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes. |
Balanoposthitis | Rash on the penis. They differ from syphilitic rashes in their irregular shape, the combination of rash elements into one whole and the absence of compaction at the base. The disease is accompanied by symptoms of the inflammatory process (hyperthermia, weakness). |
Lichen planus | The location of the rash is on the body of the penis, which is rare with a syphilitic infection. The difference between papules and syphilitic ones is the absence of ulcerative lesions and the depressed part of the papule in the center, there is no lymphadenitis. |
Cervical erosion | Localized at the inlet of the uterus. Erosion of irregular shape with unclear outlines. It has a long chronic course, in contrast to the rapidly passing primary syphilide. |
Cervical cancer | It has a chronic course with the presence of tuberous erosion, which bleeds and has a developed edge. |
Angina | Similar in appearance to atypical chancroid amygdalitis. In both diseases, the temperature may be elevated and symptoms of an acute inflammatory process may be observed. A distinctive feature - chancre amygdalitis is characterized by unilateral damage and inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes. |
Stomatitis | Rashes with stomatitis are accompanied by painful sensations. |
Basic methods of laboratory testing of syphilis in the primary period:
- microscopic examination of discharge from chancre;
- analysis of punctate from lymph nodes (using puncture);
- serological diagnosis using RIF, RIBT, RPR study;
- PCR diagnostics.
Treatment of primary syphilis
Treatment of primary syphilis is carried out with antibacterial drugs from the penicillin group. They are most active against treponema pallidum, but have a significant disadvantage - frequent allergic reactions in patients and the need for frequent administration (quickly eliminated from the body) to maintain the required therapeutic concentration. In case of penicillin intolerance, alternative drugs from other groups are selected.
Table No. 2. Basic treatment regimens with penicillin drugs and alternative drugs from other groups:
| A drug | Reception features |
Retarpen | Retarpen is the drug of choice for the treatment of syphilis. 2.4 million units are prescribed once every seven days. Duration of treatment is two weeks. |
Bicillin 5 | 1.5 million units twice a week. Duration of treatment is 2.5 weeks. |
Benzylpenicillin | 1.2 million units, once a day. The course of therapy is 10 days. |
Ceftriaxone | Replacement of the penicillin group for allergic reactions. Daily dose 0.5 g, course duration up to 10 days |
Azithromycin | Replacement of penicillin in case of intolerance. Daily dose 0.5 g, course duration up to 10 days. |
Doxycycline | An alternative to the penicillin group. Daily dose 0.2 g in two doses. The duration of therapy is at least 15 days. |
Important. 95% of cases of infection occur through sexual contact. In this case, the type of sex (anal, vaginal, oral) does not matter.
Tertiary syphilis
If syphilis is not treated in a timely manner, then several years after infection, symptoms of tertiary syphilis appear. Major disturbances in human systems and organs appear. The person's general appearance is disfigured and he may become disabled. In some cases, death occurs.
Today, fortunately, infection at the third stage of development is rare. However, you should not wait for the development of the tertiary stage of the disease and, at the first symptoms, immediately go to the doctor so that he can prescribe a course of treatment for syphilis.
Symptoms of tertiary syphilis:
– Damage to the skin and mucous membranes;
– Formation of gummas, which are initially soft tissue tumors, and then degenerate into fibrous scars;
– Vascular damage – syphilitic aortitis, syphilitic endarteritis;
– Brain damage – progressive paralysis;
– Damage to the musculoskeletal system;
– Damage to the nervous system – neurosyphilis.
Symptoms of neurosyphilis
At the end of the second stage, neurosyphilis begins to develop, the main symptoms of which are:
– Damage to blood vessels (vasculitis, intimal hyperplasia, where milliary gummas ultimately form) and the membranes of the brain and spinal cord;
– Development of syphilitic meningitis in chronic form;
– Argyle-Robertson symptom;
– Among other, but rarer symptoms, there are syphilitic neuritis and meningoencephalitis;
– Paresis, paralysis, ataxia;
– The patient practically does not feel support under his feet;
– Dizziness, headaches, insomnia;
– Visual impairment;
– Impairments in mental activity – forgetfulness, inattention, lethargy, etc.
Congenital syphilis: symptoms
It is transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy, and due to the fact that at this time the child is just developing, then after birth, he often experiences the following symptoms:
– Congenital lack of hearing (deafness);
– Parenchymal keratitis;
– Hypoplasia of dental tissue, or so-called. "Hutchinson's teeth."
After the infection is stopped, congenital pathologies usually remain, which worsens the patient’s quality of life.
Third stage of syphilis
The third stage of syphilis, like the secondary one, affects all systems and internal organs, but with pathological and irreversible changes. In 25% of advanced tertiary syphilis, death is observed. This stage of syphilis is manifested by skin lesions, like the first two, but with serious damage.
Skin manifestations of the tertiary stage are called tertiary syphilides, they manifest themselves in the form of:
- Tuberous syphilide. This is a tubercular formation in the lower layers of the epidermis, dense structure and up to 7 mm in diameter. They can be located either in groups or individually. As they mature, they begin to protrude above the surface of the skin and ulcerate, turning into open ulcers. This erosion can take several weeks to heal, forming scar tissue after healing.
- A gummous node that forms in the subcutaneous layer of tissue. The gummous nodule has the size of a nut with a diameter of up to 2 cm, a round regular shape and a dense structure; when it occurs, the skin acquires a purple tint. At the initial stage of development, it is mobile, and when subjected to mechanical action it causes mild pain. In the process of further development, mobility is lost due to fusion with the surrounding soft tissue. At the final stage it turns into an open ulcer with purulent contents. Healing occurs with the formation of a scar.
Syphilitic gumma.
The tertiary stage of syphilis is characterized by pathological damage not only to the skin, but also to all soft, cartilage and bone tissues, as well as internal organs. The defeat occurs when syphilitic gummas form on them.
The most common lesions of gummas occur on:
- Joints – fibrous gumma affects the knee and elbow joints.
- Tongue – gumma of the tongue, enlarges and completely atrophies the tongue, leading to its complete destruction.
- Hard palate - the gumma of the hard palate is localized in the oral cavity. During the growth process, it affects bone tissue, which leads to the union of the oral cavity and nose.
- Soft palate – gumma of the soft palate affects the pharynx and makes breathing difficult.
- Nose – gumma of the nose affects the back of the nose and leads to the destruction of bones, resulting in the collapse of the nose.
- Liver – Liver gumma causes liver failure, leading to death.
- In the stomach – gastric gum disrupts its normal functioning.
Gummas also damage the brain and other organs.
Important. In 90% of patients with tertiary syphilis, the functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted and leads to myocarditis and aortitis, which are complicated by heart failure.
Diagnosis of the tertiary period
Since during the tertiary period the concentration of treponemes in the body decreases significantly, RPR diagnostics give a negative result, therefore the study is carried out using RIF and RIBT studies. They give a positive result in 98% of cases.
Diagnosis at the third stage is aimed at determining the degree of pathology of internal organs, therefore the examination includes:
- Ultrasound of all internal organs;
- x-ray of lungs and bones;
- ECG;
- rhinoscopy;
- gastroscopy;
- liver tests;
- cerebrospinal fluid puncture.
Treatment of tertiary syphilis
How to treat stage 3 syphilis depends on the degree of damage to the body. The main direction, as in the first two stages, is to take antibacterial drugs, but according to a certain scheme, additional symptomatic treatment is prescribed, depending on the damaged organs.
The basic treatment regimen for the tertiary stage with antibiotics to combat Treponema pallidum:
- Preparatory treatment of syphilis is taking tetracycline (if intolerant, replace it with erythromycin). The course duration is at least 14 days.
- The course of treatment with penicillin drugs, the duration of treatment depends on the severity of the condition.
- A break in treatment is 14 days.
- Second course of penicillin therapy. The duration depends on the severity of the damage to the body.
- Taking medications based on Bismuth. The duration and dosage are prescribed strictly according to an individual scheme, which depends on the severity of the condition, the individual characteristics of the body and the age category of the patient. The instructions prohibit the use of drugs by patients with impaired liver and kidney function.
- Third course of penicillin drugs.
Additional treatment:
- taking symptomatic medications to treat damaged organs;
- taking immunostimulating drugs to increase the body's resistance;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- therapy for damaged skin
Complications and diagnosis of syphilis
The disease is very dangerous due to its complications. Treatment of syphilis at the tertiary stage is very difficult, since all body systems are affected and the person can die. If this is intrauterine infection with syphilis, then the unborn child will subsequently acquire congenital syphilis, which has symptoms such as: Hutchinson's teeth, deafness, parenchymal keratitis.
Diagnosis of syphilis
Diagnosis of the disease “syphilis” may directly depend on the degree of development of the disease. Diagnosis is based on the tests obtained and the patient’s symptoms.
If this is the first stage of syphilis, then it is necessary to examine the lymph nodes and chancre. At the second stage, the affected areas and mucous membranes can be examined. As a rule, when carrying out diagnostics, research methods such as serological, immunological, bacteriological and other methods are used.
It should be borne in mind that at certain stages of the disease, the results of the tests may be negative. This makes it difficult to conduct a correct analysis.
To confirm the diagnosis, a specific Wasserman reaction is performed, but it often gives false test results. Therefore, to diagnose syphilis, it is necessary to simultaneously use several types of tests - RIF, ELISA, RIBT, RPGA, microscopy method, PCR analysis.
When diagnosing syphilis, you should not self-diagnose, even if severe symptoms are observed. Lumps, rashes, and enlarged lymph nodes may occur with other diseases. In addition, under no circumstances should you treat syphilis yourself. It is imperative to contact a specialist.
Possible complications of syphilis
Primary seronegative or seropositive syphilis can lead to a number of serious complications.
Even if it does not progress, moving into the secondary and then into the tertiary stage.
For example, the course of the disease is often complicated by gonorrheal, chlamydial, and trichomonas infections.
Because of this, therapy is complicated, the symptoms become more blurred.
Also, the disease can lead to the development of balanitis, balanoposthitis in men, and often causes vaginitis in women.
In rare cases, as doctors note, gangrene may develop.
Most often this happens if the primary chancre is complicated by an additional infectious process that can lead to tissue death.
Causes of syphilis
The causative agent of the disease is a bacterial microorganism, Treponemapallidum (treponema pallidum). The bacterium can enter the body through abrasions, microcracks, and wounds. Through the lymph nodes it enters the general bloodstream, affecting the skin, nervous system, internal organs and skeleton.
Once in a person, the infection spreads throughout the body. As a result of infection, very complex immune processes occur. After a person is cured, immunity to the disease is not fully formed and one can become infected with syphilis more than once.
How can syphilis be transmitted?
Methods of transmission of syphilis:
- sexual (95%) after contact with a sick partner;
- It is very rare to get sick with syphilis at home (this is due to the fact that the bacterium dies without the conditions it needs when it dries);
- in utero - this is how children become infected in the womb
- through breast milk from a sick mother to her child;
- during childbirth during the passage of the child through the birth canal;
- through blood used for transfusion.
The causative agent of the disease
Manifestations of syphilis are caused by the proliferation of Treponema pallidum in the human body. It is a gram-negative spirochete capable of active movement and rapid division. However, Treponema pallidum is not the only dangerous bacterium from the spirochete family: other infectious agents belonging to this taxonomic group also cause Lyme disease, leptospirosis and relapsing fever. Due to their pathological properties, spirochetes easily overcome the natural barriers of the body.
Treponema pallidum itself is a spiral-shaped bacterium. Due to the small size of the pathogen, it is impossible to detect using a light microscope, so dark-field microscopy methods are used to identify the infectious agent. Treponema pallidum is not able to remain viable for long outside the host tissue, so syphilis is most often transmitted through direct contact with another person. In an infected body, the bacterium prefers to multiply in the lymphatic system and gradually spread to other tissues. The patient remains a source of infection throughout all stages of syphilis.
Treatment
Photo: uflebologa.ru
Specific treatment is prescribed after diagnosis. The main drug used to treat syphilis is an antibiotic. As a rule, antibacterial agents of the penicillin series are prescribed, since Treponema pallidum has not yet lost its sensitivity to these drugs. If a person is allergic to penicillins, other antibiotics, for example, tetracyclines, are prescribed.
The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician and depends on the stage of the disease. As you know, the earlier syphilis is diagnosed and treatment is started, the shorter the duration of treatment. That is why it is extremely important to immediately consult a doctor after detecting the first symptoms of the disease.
Persons who have had sexual or close household contact with people who have infectious forms of syphilis are prescribed preventive treatment. It is worth noting that preventive treatment is carried out if no more than 2 months have passed since the moment of contact. Preventive treatment is not used if contact with persons with tertiary, late latent, visceral syphilis and neurosyphilis has been registered. Preventive treatment is prescribed to pregnant women who have or have previously had syphilis, as well as children born to such mothers.
It is important to note that syphilis does not create lasting immunity, that is, after complete recovery, there is a possibility of becoming infected again. In this regard, it is extremely important to follow preventive measures that reduce the risk of syphilis transmission.
Medicines
Photo: diagnosislab.com
The following representatives of the penicillin antibiotics can be used to treat syphilis: bicillin-1, bicillin-3, bicillin-5, sodium salt of penicillin, potassium salt of penicillin, novocaine salt of penicillin.
Antibacterial agents of the penicillin series have a bactericidal effect, which is associated with their ability to disrupt the synthesis of the cell wall of microorganisms. Penicillins are well distributed throughout the body, quickly reaching therapeutic concentrations in almost all tissues and body fluids. There are low concentrations of penicillins in the cerebrospinal fluid, the internal environment of the eye and the secretion of the prostate gland. Representatives of this group of antibacterial agents have low toxicity, but the following side effects may occur when taking them: nausea, vomiting, flatulence, stool upset, headache, dizziness. Before prescribing the drug, the presence of allergies to drugs is clarified, since there is a concept of cross-allergy between all penicillin antibiotics, as well as partially cephalosporins and carbapenems.
Folk remedies
Photo: aktei.ru
Of course, there are no folk remedies that can cure a person of syphilis. However, there are preventive measures that, if followed, will significantly reduce the risk of contracting syphilis. These include:
- presence of a permanent sexual partner who has a health certificate;
- exclusion of casual sexual relations;
- use of barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse. However, it is worth noting that the presence of skin defects that are not covered by a condom does not protect against the possibility of transmitting syphilis;
- Regular screening for syphilis.
If you have had sexual or close household contact with a person with syphilis, you should immediately contact a medical facility. The appropriate specialist will prescribe a range of laboratory tests, based on the results of which, if necessary, prescribe treatment. In addition, it is important to remember that when diagnosing syphilis, you should never have sexual contact with other people in order to prevent them from becoming infected.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.