Many people snore in their sleep. But snoring is not as harmless as it seems.
Often when snoring, apnea is observed - the cessation of breathing during sleep.
This can be a physiological process, for example in newborns, or a pathological process.
Impaired breathing is dangerous as it can cause a stroke or heart attack. To treat sleep apnea, you need to find out the cause.
Causes of sleep apnea
During apnea, breathing occurs for 10 seconds or more. In rare cases, the delay time can reach 3 minutes, which in turn has a bad effect on health. In advanced cases, breathing can stop up to 300-500 times per night . At the same time, during the entire sleep, a person does not breathe for a total of 2, or even 3-4 hours.
Sleep apnea is preceded by loud snoring when a person sleeps lying on his back.
The cause of apnea is associated with relaxation of the muscles of the pharynx. Due to weak muscles in the throat, negative pressure is created, and the walls of the airways simply stick together. As a result, air first enters the lungs in limited quantities, thereby leading to snoring, and then does not enter the respiratory tract at all.
The brain reacts to apnea by waking up, but a person with apnea does not remember the awakenings themselves. Such a shake-up is necessary because it “reminds” the body that oxygen is not reaching the lungs. By the way, if the brain did not give wake-up signals, every apnea would end in a fatal outcome .
In addition to relaxation of the pharyngeal muscles, apnea can be caused by:
- excess weight;
- brain diseases;
- atrophy of body muscles;
- abnormal structure of the nasal septum;
- incorrect head position during sleep.
Causes
The main cause of apnea is a violation of the motor function of the muscles and tissues of the larynx. Relaxation of this part of the body leads to interruptions in the supply of oxygen to the lungs, causing the person to begin to choke and wake up.
In most cases, anoe is a congenital pathology that is inherited from parents.
In addition to genetics, there are a number of body characteristics and bad habits that lead to the development and aggravation of the condition:
- Floor. Men are affected twice as often as women.
- Age-related changes. People over 50 years of age are at risk. This is due to weakening of muscles, especially if a person leads a sedentary lifestyle.
- Anatomical features: an enlarged tongue, narrow airways, excessive folds in the mucous membrane, enlarged tonsils and a sunken lower jaw block the normal supply of oxygen.
- Alcoholism and smoking are bad habits that are abused by every third person with apnea.
- Diabetes mellitus increases the risk by 2–3 times.
- Polyps and adenoids.
- Nasal fractures and nasal congestion.
- Taking sleeping pills.
- Hormonal changes in women - pregnancy, menopause.
Excess weight is the most common cause, especially if a person has an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck, chin and abdomen. Accumulations of fat put pressure on the muscles in these areas, preventing the diaphragm and larynx from working properly. Excess weight tends to be deposited in these places specifically in men, so they suffer from apnea more often.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Causes of night sweats: excessive sweating during sleep
Damage to peripheral nerves and hypofunction of the thyroid gland also lead to decreased muscle tone.
Sleep apnea in adults: symptoms
Before we talk about treating apnea at home, we will describe the main symptoms of the disease.
- Snoring . If your partner says that you snore at night, you are clearly at high risk for sleep apnea.
- Sleepiness during the day . Due to lack of oxygen and frequent awakenings, the brain does not rest fully. Therefore, a person with sleep apnea constantly feels tired and overwhelming drowsiness.
- Changes in skin color on the face . Disturbed breathing during sleep gives the skin a bluish tint. The reason for this again lies in oxygen deficiency.
- Nightmares . Deterioration of brain function provokes the appearance of nightmares.
- Dry mouth in the morning . Intermittent breathing dries out the oral mucosa. Because of this, a person with sleep apnea experiences extreme thirst after waking up.
- High blood pressure . During sleep apnea, the level of adrenaline, a stress hormone, increases in the blood, which increases blood pressure.
- Constant headaches . Improper breathing during sleep leads to spasms of the blood vessels in the head, which leads to frequent headaches.
If you find at least one of the listed symptoms, you should visit a doctor.
Causes and pathogenesis
There are two direct causes of apnea syndrome: disruption of neuroregulatory processes in the body and blockage of the upper respiratory tract. Accordingly, there are two main forms of the disease - central and obstructive. There is also apnea of mixed origin, when both influences are present. These forms differ significantly from each other in etiology and mechanism of development.
Central apnea develops when the muscles of the respiratory apparatus are disrupted due to dysregulatory processes. The brain, as the main organ of the central nervous system, regulates all processes occurring in the body. When it stops sending signals to the respiratory muscles, they stop contracting and expanding the lungs.
A similar mechanism is implemented in various diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. These include:
- Head injuries with compression of the brain stem,
- Alzheimer's disease,
- Pick's syndrome
- Encephalitis,
- Parkinson's disease,
- Acute insufficiency of cerebral blood supply,
- Epilepsy.
In more rare cases, the regulation of the breathing process is disrupted due to severe acid-base imbalance, anemia, and sepsis. In children, the causes of the disorder are birth injuries, cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, premature birth, and intrauterine infection of the fetus. In addition to the pathological one, there is also physiological sleep apnea of central origin. It occurs in absolutely healthy people and is characterized by a fairly mild course, rare episodes and the absence of characteristic clinical manifestations.
Apnea syndrome often has a slightly different origin. The obstructive form develops when there is a mechanical obstruction to the flow of air in the pharynx.
In people suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea is one of the many symptoms. For all others, the disease develops in the presence of predisposing factors, which include:
- Stress,
- Obesity,
- Endocrinopathies,
- Narrowness of the nasal passages,
- Hypertrophied sky
- Adenoiditis,
- Deviation of the nasal septum,
- Colds,
- Laryngomalacia,
- Myodystrophy and myasthenia,
- Micrognathia,
- Allergic swelling of the nasopharynx,
- Elderly age,
- Tobacco smoking,
- Chronic inflammation in the nose,
- Anomalies in the structure of the facial skeleton or its structural features,
- Male gender,
- Long-term use of sedatives,
- Alcohol abuse
- Menopause and hormonal changes in the body,
- Hereditary predisposition.
Pathogenetic links of the syndrome:
- Dysregulatory changes or obstruction of the respiratory tract,
- Lack of oxygen in the blood and excess carbon dioxide,
- Change in pH to the acidic side,
- Awakening,
- Hypertonicity of the respiratory muscles,
- Restoration of airway patency,
- Deep breath and strong snoring,
- Restoration of acid-base balance,
- The onset of the deep sleep phase.
The obstructive form of apnea has its own developmental characteristics. When a person sleeps, his throat muscles completely relax. For some, they sag inward and collapse, which leads to blockage of the airways and the formation of a mechanical blockage of their lumen. The obstruction interferes with breathing and interferes with airflow. The air stream, vibrating, creates a sound that is perceived as snoring. If the relaxed walls of the pharynx sag very much, they completely block the lumen of the airways for some time, breathing stops. Nerve impulses and muscle contractility are completely preserved. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood increases, which irritates the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata. The respiratory center receives a large amount of information about the gas composition of the blood and the state of the respiratory system as a whole. It sends signals to the muscles and increases its tone.
In persons with obstructive apnea syndrome, similar processes are repeated several times during sleep. Over time, this leads to a persistent increase in blood pressure, the development of coronary insufficiency and acute cerebrovascular accident.
There is a mixed form of apnea, combining features of both of the above forms. It is believed that it develops in individuals with a hereditary predisposition. Among the causes of the pathology, the most common are: congenital heart defects, severe infectious diseases, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, impaired thermoregulation in newborns. Patients experience asynchronous and rapid movement of the chest.
Video: lecture on obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, etiology and pathogenesis
Sleep apnea in children
We should also talk about sleep apnea in children. The causes of the disease in childhood are usually similar to those observed in adults. Stopping breathing in children at night is associated with enlarged tonsils, weak swallowing muscles and neurological pathologies. Apnea is especially common in premature infants and children with cerebral palsy.
The disease can be detected in a child by the following symptoms:
- cough during sleep;
- daytime sleepiness;
- wheezing when breathing;
- sweating;
- bluish skin tone.
What is it like in children and adults
Sleep apnea syndrome is a breathing disorder that occurs when it periodically stops during sleep.
Patients also experience snoring, frequent waking up, and interruptions in heart function.
Approximately 5% of people suffer from this disease, with a higher percentage among men. In women, the syndrome develops during menopause.
There is physiological apnea , when breathing stops for a few seconds no more than 2-3 times per hour. This condition does not threaten health and is normal.
Pathological respiratory arrest is considered when periods of apnea last more than 10 seconds and are repeated up to 100 times per hour. In total, the patient spends up to 3 hours per night without breathing.
This is dangerous because not enough oxygen reaches the brain and hypoxia develops.
In medicine, there are three types of disease:
- Central form. Develops due to problems in the central nervous system or respiratory center.
- Obstructive . It is provoked by diseases of the upper respiratory tract, in which the passage of air becomes difficult. For example, a deviated nasal septum, adenoids.
- Mixed . Combines signs of central and obstructive forms.
Among the causes of pathology are:
- Head injuries.
- Diseases of the central nervous system (Alzheimer's syndrome, parkinsonism).
- Pulmonary hypoventilation syndrome.
- Congenital structural features of the respiratory tract.
- ENT pathologies.
- Obesity.
- Endocrine disorders.
The clinical picture of the disease is represented by the following symptoms:
- Prolonged heavy snoring.
- Frequent waking up.
- Excessive movements during sleep.
- Feeling groggy in the morning.
- Fatigue.
- Decreased cognitive functions: attention, memory, perception.
50% of patients are diagnosed with concomitant diseases: hypertension, ischemia, asthma, tachycardia.
Read about the causes of apnea in children and adolescents here.
Apnea: diagnosis of the disease
Close people living with the patient will help in diagnosing apnea. One of them will have to observe the frequency of breath holdings during sleep. If it turns out that the number of breathing stops is more than 15 per night, it is worth taking measures to treat apnea at home or with a medical specialist.
In addition to the number of apnea attacks, you need to calculate BMI - body mass index . It is calculated using the formula “body weight in kg divided by height in meters to the square power.” The resulting value should be less than 30. If it is more, it’s time to lose weight, since in this case the risk of developing apnea increases.
For example, let’s calculate the normal BMI for a person 180 cm tall and weighing 100 kg. We calculate : 100/1.8*1.8 = 30.8. In this case, BMI is higher than normal, which means there is a high probability of developing apnea.
Blood pressure is more than 140 over 90 mmHg. Art. increases the risk of apnea. Moreover, the risk of developing the disease increases if pressure is combined with excess weight.
Polysomnography can help you determine the presence of apnea . The procedure consists of a dream with sensors connected to the body that record physiological indicators. This diagnostic method determines the frequency and duration of breathing stops during sleep. In addition, polysomnography shows the level of brain and respiratory activity.
The diagnosis will be made by the computer
Diagnosing apnea is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. The patient's stories about his life, about the problems of early life, if he knows, turn out to be one-sided. People who could observe the patient during sleep and witness apnea are invited to participate in the diagnosis. Often conversations and notes alone are not enough, then special studies are carried out in the laboratory:
- Polysomnography, the purpose of which is a comprehensive study of various systems and functions of the body. All sorts of different devices (ECG, EEG, video recording, etc.), constantly transmitting data to the computer, monitor the activity of the central nervous system and muscular system, eye movements, oxygen content in the blood, the frequency and nature of respiratory movements and heart contractions. The specialist, having processed the information and counted how many times during the experiment the patient’s breathing stopped, draws a conclusion about the severity of his condition;
- Sleep latency test, which determines periods of latent sleepiness and the time it takes the patient to fall asleep (the person is asked to arrange a “quiet hour” in broad daylight, when he is usually awake).
Sleep apnea: treatment at home
Treatment of apnea at home involves the following factors.
- Sleep in the correct position . To prevent sleep apnea, it is better to sleep on your side. However, it is difficult to lie down while sleeping without turning onto your back. To avoid sleeping on your back, tie or tape a small ball to prevent you from turning onto your back. In addition to the position of the torso, the correct position of the head, which should be slightly raised, is also important. And for this you need to choose the right pillow.
- Avoidance of sleeping pills and muscle relaxants . Drugs in these groups relax the muscles of the respiratory tract. This means that taking them will only worsen sleep apnea. We also note that these drugs can be dangerous for patients with apnea. When using them, the brain may not signal the body to wake up during apnea, but this can lead to a complete stop of breathing.
- Losing weight . If you are overweight, then to treat apnea you should lose a few kilograms. Calorie counting, proper nutrition and exercise will help you with this.
- Use of CPAP therapy . To do this, use a special device consisting of a control unit and a humidifier in the form of a sleep mask. Thanks to the device, positive pressure is created in the throat, which prevents breathing from stopping during sleep. Note that CPAP therapy is the most effective way to treat apnea at home.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol . Cigarette smoke and alcohol relax the muscles of the pharynx and disrupt the breathing process.
- Humidifying the air in the room . Maintaining proper humidity in the bedroom reduces the incidence of sleep apnea. Humidity is regulated by a special device, which can be purchased at a fairly modest price.
- Using special anti-snoring mouthguards that fix the jaw in the correct position.
Types of apnea
Night apnea is divided into groups and types based on its course, severity, and risk of complications.
Depending on the reduction in the volume of inhaled air, sleep apnea syndrome can be complete or partial. In the first case, breathing stops completely, there is no air circulation in the bronchopulmonary tract. Compression of the chest quickly increases, and suffocation develops. With partial disruption of breathing during sleep, ventilation of the respiratory system is reduced to 40-50%. This condition is called hypopnea.
Considering the causes of apnea, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- obstructive sleep apnea syndrome ─ occurs against the background of obstruction of the respiratory tract;
- sleep apnea of the central nervous system ─ develops due to disturbances in brain activity;
- mixed form ─ includes mechanisms, signs of obstructive and central syndrome.
The severity of the pathology is determined by the number of episodes of respiratory arrest per unit of time. Mild degree ─ 5-15 apneas/hour, moderate ─ 15-30 apneas/hour, severe ─ 30-50 apneas/hour. An extremely life-threatening condition when the number of stops in chest respiratory movements exceeds 60 episodes per hour.
Development of the central type of disease
Brain damage can also be one of the causes of apnea.
The mechanism of central sleep apnea is based on malfunctions in the part of the brain responsible for respiratory function. The absence of signals in the form of nerve impulses, which are normally sent to the smooth muscles of the bronchi, pectoral muscles, and diaphragm, leads to the cessation of the act of inhalation and exhalation.
Factors that increase the risk of central sleep apnea:
- the use of drugs of narcotic origin that depress the activity of the central nervous system ─ morphine, barbiturates, antipsychotics;
- congenital, acquired brain defects ─ cysts, absence of the cerebral hemispheres in a newborn, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain against the background of dropsy;
- neurological diseases that cause sleep apnea ─ multiple sclerosis, senile dementia (Alzheimer's disease), epilepsy;
- skull injuries, damage to the cervical spine, benign and malignant tumors;
- acute infections ─ meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess;
- somatic diseases that impair blood circulation ─ stroke, atherosclerosis, acute heart failure;
- metabolic disorders, insufficiency of chemical elements ─ hypocapnia (lack of carbon dioxide in the blood), deficiency of K, Mg, glucose, excess Na, proteinuria (high protein content in the urine).
Men over 40 years of age and obese people are predisposed to central sleep apnea.
Obstructive type disease
Normal breathing at night and breathing with apnea \ Photo mayoclinic.org
This is the most common type of pathology. During sleep, adults' airways become blocked. The act of inhalation and exhalation becomes superficial, then stops for a short period of time. The process of restoring breathing is accompanied by snoring, a suffocating attack, and sudden movements of the chest. This is due to the fact that the skeletal muscles and diaphragm begin to work harder.
According to WHO statistics, 12 million people suffer from the disease.
At-risk groups:
- people with obesity of different stages;
- hypertensive patients;
- smokers;
- people with endocrine diseases ─ diabetes, hypothyroidism;
- patients over 45 years of age;
- patients with anatomical features ─ narrow larynx, trachea, wide neck.
Periodic apnea is caused by allergies, infectious inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. In children, obstructive sleep apnea is associated with swelling of the tonsils, proliferation of the adenoids, and swelling of the soft palate. Newborns and infants in the first months of life stop breathing due to abnormal development of the jaw, cleft palate, recessed tongue, atrophy of the laryngeal muscles, and blockage of the respiratory tract.
Mixed or complex type of disease
An attack of mixed type apnea occurs in 75% of cases in patients with a history of heart failure. Brain disorders and obstruction of the bronchopulmonary tract are simultaneously involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. Breathing is blocked at the level of the pharynx.
People with a mixed type of pathology traditionally suffer from snoring. Initially, doctors suspect obstruction and prescribe appropriate treatment, which does not bring a positive result. Only then do they resort to combination therapy that affects processes in the brain.
Some experts classify the mixed type of disease as obstructive.
Treating sleep apnea with a doctor
If treatment for sleep apnea at home is ineffective, consult a sleep specialist . An experienced specialist, after talking with you, will prescribe appropriate therapy that will help avoid complications of this disease.
In some cases, treatment of apnea requires the help of a surgeon. And it is usually associated with plastic surgery of the soft tissues of the pharynx.
As a rule, treatment of apnea by specialists includes:
- Medications . For apnea, medications are usually prescribed to stimulate breathing, such as aminophylline.
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) . Surgery to remove the uvula, tonsils and part of the roof of the mouth makes breathing easier for a patient with apnea.
- Palate plastic surgery . With the help of surgery, part of the palatal tissue is corrected, which also improves air flow through the upper respiratory tract. The operation is performed using cryo- or laser therapy.
- Changing the shape of the nasal septum . Facilitates the passage of air in the nasopharyngeal area.
Treatment
The method of therapy directly depends on what type of apnea is diagnosed. First of all, treatment of apnea should be aimed at eliminating the causes, so therapy for the central nervous system, obesity, diabetes, etc. is needed.
For mild obstructive apnea, which is caused by anatomical features, surgical intervention is prescribed. The attending physician prescribes the method of therapy after a complete diagnosis.
In moderate and severe forms, surgery is ineffective, since mechanical obstruction is not the main danger factor. How to treat? In this case, CPAP, BIPAP and TRIPAP machines are used.
Surgery
Prescribed for enlarged tonsils, curvature of the lower jaw and nose. Includes the following types of operations:
- The use of the Pillar system is the introduction of synthetic plates into the soft palate, which make it stiffer and support it like a frame. Effectively eliminates snoring.
- Adenomectomy - removal of hypertrophied lymphoid tissue. Polyps are removed from the upper part of the nasopharynx under local anesthesia.
- Tracheostomy - opening the trachea and inserting a special tube that provides constant access to air, even when the airways are completely blocked.
- Bariatrics. It is performed for severe obesity and is a surgical reduction in the size of the stomach. The person begins to consume less food and loses weight.
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty is the removal of part of the soft palate.
- Tonsillectomy - removal of hypertrophied tonsils.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Obstructive sleep apnea: what is it?
CPAP
This is one of the best and safest ways, which involves wearing a special mask that covers your nose and mouth before going to bed.
Air is supplied under pressure through a special tube, ensuring a constant supply of oxygen to the body. Modern devices have special settings for humidity and air temperature, which allows you to create the most comfortable conditions for the patient.
An effective treatment for tongue apnea is the placement of rubber mandibular splints on the teeth, which help keep the jaw and tongue in a safe position.
When diagnosing the central form, along with the main treatment, the diuretic Acetazolamide is used, which relieves swelling and improves blood supply to brain cells.
Treatment of apnea with folk remedies
Treatment of apnea at home involves the use of folk remedies. However, these drugs are ineffective in combating the disease. In any case, before starting such therapy, consult your doctor.
As a rule, treatment of apnea with folk remedies includes:
- Eating baked carrots . Bake the carrots in the oven until done. Then, take one carrot before bed.
- Gargling with olive oil . Dilute 1 tbsp. a spoonful of oil in a glass of warm water. Gargle the resulting solution daily to prevent apnea.
- Taking cabbage juice with honey . Using a juicer, extract the juice from fresh cabbage. Afterwards, strain it all through a sieve and add 1 tbsp to the juice. a spoonful of honey. Pour half a glass of boiled water there. Take the finished product 1-2 tablespoons before bed. The duration of treatment for apnea in this way is 1 month.
- Rinsing the nasopharynx with sea salt . Take a small syringe and fill it with water with some sea salt. After this, rinse your nose 3-4 times. Salt water moisturizes the nasopharynx, reducing the risk of apnea.
- Taking a decoction with mint, yarrow and lemon balm . After preparation, the drink is cooled and taken half a glass daily 15 minutes before bedtime.
Treating sleep apnea with surgery
People suffering from severe forms of sleep apnea syndrome are advised to undergo surgery. The feasibility of the surgical operation is determined by the doctor based on observations, tests, and identification of laryngeal obstructions. Surgical treatment is recommended for people if therapy is ineffective. A variety of surgical procedures have been developed for patients with varying levels of obstruction:
- tonsillectomy - removal of tonsils;
- conchotomy - reduction or removal of turbinates;
- polyectomy - removal of polyps;
- plastic surgery of the nasal septum - correction of curvature;
- Pillar palatal implant system – small cylindrical implants support and strengthen the patient’s soft palate;
- uvulopalatopharyngoplasty - removal of tonsils, part of the uvula of the soft palate, excess tissue of the pharynx;
- somnoplasty - plastic surgery of the soft palate;
- myotomy of the genioglossus muscle - dissection of the genioglossus muscle;
- osteotomy of the upper and lower jaw - the middle zone of the face, the lower jaw and palate are moved forward;
- The Riley-Powell-Stanford surgical protocol consists of two stages. On the first, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty is performed, on the second, myotomy of the genioglossus muscle;
- tracheostomy is an operation aimed at anatomical changes in the airways.
- Laryngospasm in children and adults - causes, symptoms, emergency care and treatment
- 10 causes of hypertension in women and men - how to recognize the disease by the first symptoms
- First aid for cardiac arrest
Treatment of snoring and apnea
In addition to apnea, you should also treat snoring. To do this, it is recommended to sing loudly . Singing strengthens your vocal cords and trains your throat muscles, which in turn reduces the likelihood of snoring and sleep apnea.
If you don't feel like singing, read aloud regularly . Voice reading is effective for treating snoring and sleep apnea. In addition, by reading aloud, you not only reduce the risk of sleep apnea, but also gain useful information. As a bonus, reading books or articles out loud trains your memory.
You can get rid of mild apnea with the help of yoga or auto-training . Both are aimed at restoring physiological processes in the body, thanks to which the disease can be cured.
Sleep apnea syndrome: how it happens
During an attack of apnea, breathing stops and the brain stops receiving oxygen. At this time, the brain sends a signal to the body to wake up and restore oxygen supply. A person with apnea usually does not remember such awakenings and continues to sleep.
The number of breathing stops due to apnea can reach more than 200 times per night . And this has a bad effect on overall health.
The pathology often does not make itself felt and is detected if the person sleeping next to him notices periodic pauses in breathing in his bed partner. But if a person with apnea lives alone, then he may not notice the disease for more than 10 years , although he is faced with symptoms of the disease.
Sleep apnea in adults disrupts the functioning of the entire body. After all, not only the brain, but also other organs suffer from a lack of oxygen. Against this background, heart problems and cyanosis - blue discoloration of the skin - may appear.
In advanced cases, the body cannot recover from nighttime respiratory arrests during the daytime. Oxygen metabolism in such people is impaired even during wakefulness.
Along with oxygen deficiency, metabolism deteriorates, which leads to rapid weight gain. All this is accompanied by changes in hormone levels, which in turn increases the risk of endocrine diseases.
Apnea-related diseases
- Arterial hypertension - increased blood pressure more than 140/90 mmHg. Art.
- Obesity.
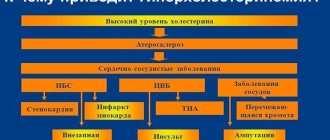
- Atherosclerosis , the precursor of which is high cholesterol.
- Brain pathologies accompanied by deterioration of memory, attention and mental performance.
- Heart failure - blood transport through organs and tissues is disrupted.
- Coronary heart disease and angina , which are characterized by attacks of pain behind the sternum.
- Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm disorder.
- Heart attack and stroke.
- Diabetes.
Diseases associated with sleep apnea in adults increase the risk of sudden death . It is often discovered that a person with one of the above diseases also suffers from sleep apnea.
Exercises to treat apnea
Treating apnea at home also includes special exercises that train the muscles of the pharynx and jaw. Such gymnastics relieves the sufferer from snoring and reduces the frequency of respiratory arrests.
The set of exercises looks like this:
- Move your jaw back and forth while pressing your chin into the area under your lower lip. When performing the exercise, you should feel the resistance created by pressing your hand. To start, do 10-15 of these movements. Then, over time, increase the number of repetitions to 30-40. This exercise trains the jaw muscles, which reduces the frequency of snoring.
- Use your thumb to press on the roof of your mouth for 30-60 seconds. The pressure should be noticeable, but do not press too hard to avoid damaging the oral mucosa. To achieve a therapeutic effect, do 2-3 such approaches. The exercise corrects the muscles of the palate, which also reduces the frequency of breathing pauses during sleep.
- Stick your tongue forward as far as possible. Then pull it towards your nose, chin, and left and right cheeks. Hold your tongue in each position for 5 seconds. Do 20-30 of these movements.
- Move your tongue towards the pharynx and back. The mouth must remain closed. Perform 50-100 of these movements.
- Move your jaw clockwise and then counterclockwise. Make 10 movements in one direction and the same in the other direction.
- Strain your neck and pronounce all the vowels of the Russian alphabet loudly 10 times.
Please note that for maximum effect, exercises should be performed regularly. Moreover, it is advisable to conduct such training 2 times a day: during the day and before bedtime.
Apnea symptoms
In children, symptoms of sleep apnea manifest themselves through attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, as well as urinary problems. But snoring and holding your breath, contrary to popular belief, are not always related to each other. Not every person who snores suffers from breath-holding, and vice versa - not all people with apnea snore. The main symptoms of apnea in adults are as follows:
- irritability;
- memory impairment;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- chronic lack of sleep.
Exercises for proper breathing during apnea
You can get rid of apnea and snoring with proper thoracic and abdominal breathing . Before you begin, sit or lie down in a comfortable position. Afterwards, inhale deeply through your nose, while sticking out your stomach. Exhale slowly and draw your stomach back. Take 7 such breaths.
The next stage is chest breathing, in which it is no longer the stomach that should be “inflated,” but the chest. While in the same comfortable position, take a deep breath through your nose. As you inhale, expand your chest by filling your lungs with air, while trying not to protrude your stomach. Exhale and repeat inhalation 6 more times.
Another exercise for training proper breathing is gymnastics of the larynx muscles . To perform it, lie on the bed and put a pillow under your head. Then, press your chin to your chest and exhale forcefully through your nose. When performed correctly, breathing should be noisy. The exercise is performed for no more than 5 minutes.
Healthy lifestyle against disease
This advice is one of the most common for all patients, and not just patients with sleep apnea. As soon as a person is diagnosed with this syndrome, he will have to change his usual routine. This is one element of how to treat sleep apnea.
Sleep disturbances of this kind and a person’s lifestyle are seriously connected and influence each other. For some patients being treated for sleep apnea, simply losing weight is enough. Excess weight puts pressure on all human internal organs, and the respiratory system is no exception. As soon as the interference disappears, the apnea goes away.
Treating sleep apnea with weight loss is a common technique. 77% of all people suffering from excess weight acquired various sleep disorders along with it. And 70% of people suffering from nocturnal respiratory arrest are, in addition to the syndrome, overweight. Experts have noticed that as soon as a person loses excess weight, his quality of sleep improves. The opposite effect was also observed: as soon as the patient began treatment for sleep apnea, his weight decreased.
Back in 2009, workers at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, led by Professor Martin Neovius, began to think about what apnea is and how to treat it with maximum efficiency. Studies have shown that after just 9 weeks of severe calorie restriction (up to 500 calories per day), overweight men lost weight and experienced a reduction in the frequency of sleep apnea attacks to 21 per hour.
The final part of the study clearly states that even a year after such a strict diet, and even if the subjects regained most of the weight lost during the experiment, the quality of their sleep remained at the same, improved level.
Apnea is often a result of being overweight. Treating apnea with weight loss is a very effective technique
Even if the treatment of sleep apnea syndrome was carried out using a diet with less stringent restrictions on the number of calories (ranging from 1200 to 1500 per day), positive dynamics were still observed. Scientists have already conducted such a study in Pennsylvania. The size of the group of subjects is 250 people. Compared to the control group, the condition of the subjects improved three times.
When treating sleep apnea, the patient should pay attention to how he spends his time before bed. Dinner should be eaten no later than 4 hours before a person gets ready to go to bed. A heavy, hearty dinner is prohibited 2 hours before bedtime. If you want to eat, it’s better to grab something light, like a glass of kefir with cookies or an apple.
Before going to bed, it is forbidden to take alcoholic drinks and sedatives, as they weaken the tone of the pharyngeal muscles and ultimately make it difficult for a sleeping person to breathe. Reduced tone causes the wall of the airway lumen to collapse, and the person simply stops breathing.
The best sleep is on your side. When a person lies on his back, the risk of the tongue retracting during snoring and blocking the airway increases. This is another common cause of sleep apnea.
A person involuntarily turns on his back during sleep. To prevent this from happening, you can use a little trick. At the level of the back, sew a small pocket to the clothes you wear to bed. closing with a button. There you need to get a tennis ball. As soon as the sleeper begins to turn onto his back, the ball will begin to cause discomfort.
As a result, the sleeper awakens and again assumes the correct position. True, for those who very actively toss and turn in their sleep, such a trick may not be suitable - sleep will be disturbed too often.
True, such torment is justified - you will have to endure at least a month so that the body gets used to sleeping on its side and the person stops rolling over onto his back.
The correct selection of pillows also affects the frequency of attacks. If it is too high, the head will be placed in the wrong position on the pillow and the airways will eventually be compressed. This will eventually lead to stopping breathing and waking up again. It is better to replace the pillow with a flat or orthopedic one. The best option is to replace the bed with a new one, with a slightly raised headboard, then you won’t have to choose a pillow to suit you.
Complications of apnea
If sleep apnea is left untreated, the disease can lead to dangerous complications. Among them are:
- Cardiovascular diseases - heart attack, stroke, coronary heart disease, hypertension, heart rhythm disturbances, etc.
- Diabetes . With apnea, the production of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels, is disrupted.
- Impotence . Holding your breath during sleep reduces testosterone concentrations in men. As a result, this reduces libido and prevents the appearance of an erection.
To avoid complications, apnea should be treated promptly. Moreover, treatment should not be limited only to traditional methods. In most cases, it is extremely important to consult a doctor who will select the right therapy program for you.
Sweet dreams to you!
Video on how to treat apnea at home:
Which doctor should I contact?
A person cannot independently determine his apnea . Relatives can tell you about frequent stoppages of breathing.
At home, the Rovinsky method is used. During sleep, the relative should measure with a stopwatch how long the pause without breathing lasts and count the number of such periods per night.
Patients are recommended to undergo examination by a cardiologist, neurologist and ENT specialist.
To determine the cause, the following research methods are used:
- Laryngoscopy and pharyngoscopy. Detect deviated septum, sinusitis, rhinitis, polyps, etc.
- ECG . Helps confirm or exclude diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Electroencephalogram of the brain . Detects changes in the form of tumors, foci of excitation, consequences of injury and other pathologies.
Polysomnography helps to clearly reconstruct the picture of the disease.
It measures the electrical potential of the brain, air flow, the volume of oxygen passing through the lungs, and the degree of tension in the chest and abdominal wall.
The main signs that are a danger signal
Experts divide all symptoms of sleep apnea in adults into two categories: those that occur during the day and at night. Daytime signs are:
- deterioration in concentration, difficulty concentrating on any activities or things;
- apathy, lethargy and drowsiness;
- dry mouth, often thirsty;
- headaches, migraine;
- decreased sexual desire, no desire for intimacy;
- soreness in the heart area;
- frequent changes in blood pressure;
- development of impotence;
- emotional disorders manifested by sudden changes in mood;
Nighttime symptoms include the following:
- various sleep disorders;
- the appearance of rhonchopathy or snoring;
- sudden awakenings at night due to inability to breathe;
- the appearance of realistic, often scary dreams;
- development of enuresis - urinary incontinence at night;
- the occurrence of causeless and sudden attacks of panic fear;
- the appearance of insomnia;
- grinding of teeth and increased salivation;
- hyperhidrosis – excessive sweating during sleep.
Types of apnea: obstructive absence of breathing
More often, doctors are faced with obstructive lack of breathing. In this case, the lumen of the respiratory tract critically narrows, the muscles of the pharynx relax, and the air flow is interrupted. Oxygen levels drop and the person is forced to wake up to regain breathing. However, these awakenings are so short-lived that they are not remembered the next morning. On average, a person suffering from this type of apnea experiences such attacks of respiratory arrest 5-30 times per hour. Naturally, we are not talking about any full-fledged sleep or rest. Obstructive sleep apnea, the treatment of which must begin when the first symptoms of the disease are detected, can lead to a number of problems with health and well-being.
What it is
Sleep apnea syndrome is a disorder accompanied by episodes of awakening due to disruption of the respiratory organs. A person can wake up up to 60 times during the night. This does not allow you to get a full night's sleep. Sleep disturbance affects well-being and performance. With a long course of the disease, nervous disorders develop. Sleep becomes superficial and short-lived.
Involuntary cessation of breathing during sleep is provoked by a number of external and internal factors. Most often, the problem lies in the structure of the nasal passages. Otolaryngological abnormalities can be acquired or congenital. Brief interruptions in respiratory function may occur due to obstruction of the breathing tube.
The main danger of breathing pauses is oxygen starvation. When there is a lack of oxygen, brain cells develop life-threatening diseases. According to statistics, men are most prone to sleep apnea. In women, this problem occurs during menopause.
Attacks of shortness of breath lasting less than 10 seconds, repeated no more than 5-6 times per night, are considered the normal limit.
Surgical intervention
In many cases, the treatment of respiratory disorders caused by improper structure of the nasopharynx or sagging soft tissues is performed through surgery. Whether surgery is needed or not is decided only by the attending physician after analyzing all the patient’s test results and studying the structure of the oropharynx. Surgery is a last resort; it is resorted to in cases where medication methods have not brought a positive result. The most commonly performed types of surgery are:
- tonsillectomy - this treatment involves the removal of the tonsils, which caused the inflammatory process;
- conchotomy - removal or reduction of nasal concha;
- polyectomy is the removal of polyps located in the nasal cavity;
- alignment of the nasal septum;
- installation of implants in the soft palate, which are necessary to strengthen and support soft, sagging tissues that have lost their elasticity and tone;
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty is the removal of excess tissue from the oropharynx, uvula and tonsils;
- somnoplasty is an operation on the soft palate;
- myotomy is an operation on the genioglossus muscle;
- osteotomy is an operation on the lower and upper jaw;
- tracheostomy is the elimination of anatomical abnormalities localized in the trachea and nasopharynx.
Sleep apnea therapy
When treating, a somnologist takes into account the stage of severity of the disease, existing complications, the general condition of the patient, as well as his age.
- There are two main ways to solve the problem of OSA in the world:
- 1.Surgical – surgical intervention on the nasopharynx
- 2.Non-surgical
- Non-surgical is divided into:
- The use of oral applicators - the basic principle of operation is that the device slightly moves the lower part of the jaw forward and keeps the airways open. The applicator is effective only for mild apnea and treats snoring. There are contraindications!
- CPAP therapy - positive pressure treatment
- Weight loss program
Illustration of the mouth applicator effect
Traditional methods of treatment
Alternative medicine offers many options for getting rid of apnea. Simple and affordable recipes can be an excellent aid to the traditional treatment of the disease.
- To moisturize the mucous membranes of the throat and nose before going to bed, rinse your nose with salt water, pour it into your palm, suck it in with your nose and immediately blow your nose. To prepare the mixture, dissolve a teaspoon of sea salt in a glass of warm water.
- Cabbage juice has also long been used in the treatment of sleep apnea. Add a teaspoon of honey to a glass of freshly squeezed juice. The drink should be consumed within a month before bedtime.
- Healing sea buckthorn oil will help improve nasal breathing. It is enough to instill 5 drops of oil into each nostril for several weeks before going to bed. This method helps relieve inflammation from the tissues of the nasopharynx, has a healing effect, and restores blood circulation.
- Carrots have proven to be effective in treating snoring. You need to eat one baked root vegetable three times a day before meals.
- Yoga can also be used as a treatment for sleep apnea. Simple exercises performed 30 times in the morning and before bed will help you forget about attacks of the disease. Move your tongue forward while lowering it towards your chin. Hold your tongue in this position for two seconds. Press your chin with your hand and move your jaw back and forth, applying some force.
- The easiest and most enjoyable way to treat mild to moderate apnea is singing. Simply chant daily for half an hour to strengthen your throat muscles. This method is really effective.
This treatment of sleep apnea with folk remedies will help cope with the problem, provided that all doctor’s recommendations and subsequent preventive measures are followed.
Treatment with drugs
Medicines are used only to treat central apnea, which has a different mechanism of action compared to obstructive apnea. Medicines used include acetazolamide or zolpidem and triazolam. However, their use is associated with certain health risks, so their prescription and use are controlled by a doctor.
To treat the obstructive type of apnea, breathing training is one of the effective methods. It is necessary to increase respiratory activity, keep the muscles of the upper respiratory tract toned, set a threshold for micro-awakenings and suppress REM sleep.
At this point in time, doctors have not scientifically proven the effectiveness of all medications used.
Sleep Apnea Surgery
For severe forms of sleep apnea, surgical intervention is recommended to get rid of the problem once and for all. The following methods are used:
- tracheostomy;
- UPFP;
- implantation;
- laser.
Tracheostomy is the most difficult option, which is prescribed only in the case of particularly dangerous pathologies that pose a threat to life.
During surgery, a hole is made in the neck into which a tube is inserted. The method is not the best: after such an intervention, patients experience numerous psychological and physical inconveniences. During UPPP (uvulopalatopharyngoplasty), the airway is widened by removing excess tissue from the throat. Most often this concerns the tonsils, too long “tongue” or adenoids. The same procedure is carried out using a laser beam. The main disadvantage of the procedure is that the pathology may reoccur and sleep apnea will return.
No doctor can guarantee that the syndrome will not return after surgery. If this happens, you will have to choose other treatment methods or switch to sleeping using a CPAP machine.
Diagnostics
The first step is to diagnose respiratory pathology by family and friends. However, in order to fully verify their words, a special diagnostic procedure may be prescribed - polysomnography. It is carried out in a medical facility, in a sleep laboratory. The patient falls asleep, and during this time, for 7-8 hours, special sensors connected to the body record information and transmit it to the screen. The device determines the level of oxygen in the blood, the number of inhalations and exhalations, the duration of breathing pauses, an indicator of brain activity, heart condition, and eye activity during sleep.
Based on the data obtained, the specialist makes a diagnosis and determines the severity of the pathology. After this, the doctor often prescribes a suitable treatment method.
Prevention of apnea syndrome
To prevent the development of pathology, it is first necessary to promptly treat disorders of the ENT organs and lungs. In addition, to prevent sleep apnea from occurring in older adults, they need to lead as healthy a lifestyle as possible. It is mandatory not only to give up bad habits, but also to play sports, which can improve the condition of the respiratory tract and cardiovascular system.
In addition, the use of tranquilizers and sleeping pills should be avoided. To prevent the development of such a pathology, it is necessary to take care of the best possible conditions for sleep. It is necessary to eliminate sources of noise and light in advance. Don't read books or watch TV. Taking relaxing baths with decoctions of medicinal plants, a course of massage and meditation can have a positive effect.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Sleep apnea has different causes. The pathology is usually diagnosed in people who snore and are obese. The anatomical features of the respiratory organs, in particular the nose, larynx and pharynx, also play an important role. This phenomenon occurs especially often in people with narrowed airways.
Also at risk are hypertensive patients, smokers and alcohol drinkers.
The reasons for the development of pathology include:
- Anomalies in the development of the upper respiratory tract;
- Adenoids, tonsil hypertrophy;
- Neoplasm in the pharynx (both benign and malignant);
- Swelling and inflammation in the tissues of the neck;
- Kyphoscoliosis and acromegaly;
- Use of tranquilizers and alcohol;
- Age over fifty years;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Brain injuries, Alzheimer's syndrome.
In most cases, sleep apnea occurs in adult men, less often in women. Based on the results of numerous studies, it was found that every fourth inhabitant of the planet may suffer from pathology. However, in most people the disease remains unrecognized. In our country, people diagnosed with sleep apnea undergo surgery for snoring, but this method is ineffective and even dangerous to health.
Classification of the syndrome
With the advent of modern methods for studying the behavior of the body during sleep, this pathological condition has been studied in some detail. There are several classifications that describe this disease. Based on the mechanisms of development, obstructive sleep apnea is distinguished, as well as cerebral and mixed forms. Each option has its own characteristics.
- Obstructive apnea occurs due to occlusion or collapse of the upper pathways. Respiratory regulation by the central nervous system is preserved, as is the activity of the respiratory muscles. Obstructive apnea is classified as a separate syndrome complex, which includes a number of respiratory dysfunctions that appear during sleep. There are at least 4 states of this type. The most common syndrome is hypoventilation. It is characterized by a steady decrease in pulmonary ventilation and blood oxygen saturation. The second most common is pathological snoring syndrome. There are no objective reasons for the appearance of this disorder, but during sleep the upper respiratory tract is greatly reduced, which leads to a decrease not only in the level of lung ventilation, but also in blood oxygen saturation.
- Central apnea is diagnosed when there are disturbances in the areas of the central nervous system responsible for regulating nerve impulses to the respiratory system. This variant of the disease is rare.
- Another type of this pathology is represented by obesity-hypoventilation syndrome. With this option, gas exchange disturbances caused by excess body weight are observed. With this variant of the course of the disease, there is a persistent decrease in blood oxygen saturation with daytime and nighttime attacks of hypoxia.
- The syndrome of combined obstruction of the respiratory tract, manifested by attacks of apnea at night, develops due to obstruction of the upper airways, usually at the level of the pharynx and in the lower bronchi.
- Mixed sleep apnea syndrome usually includes elements of central and obstructive forms. This variant of pathology is quite rare. An increased risk of such a disorder is present in children with congenital developmental pathologies.
There is also a classification that takes into account the degree of manifestations of sleep apnea syndrome. This parameter is very important to monitor, since such indicators determine how dangerous this condition is for a person. There are 4 main degrees of severity of this pathological condition.
- If no more than 5 episodes per hour occur during sleep, a borderline state may be diagnosed.
- When the number of attacks is from 5 to 15 per hour, this is a mild degree of sleep apnea. In the future, the situation may worsen.
- If 15 to 30 episodes occur per hour, the average severity of this disorder is diagnosed. This option requires the use of a CPAP machine to treat apnea.
- When the number of episodes exceeds 30 attacks per hour, a severe degree of this pathological condition can be diagnosed. In this case, targeted therapy is required, including the use of hardware breathing support.
Forms, their symptoms and signs
Sleep apnea is divided into several forms (obstructive and central, other types), each of which has its own characteristics.
Some symptoms are common to all types of pathology - the presence of short-term stops in breathing at night and deterioration in the body's performance during the day.
The patient may not experience disruptions in respiratory function . The attack is more noticeable to people around you (for example, a sudden cessation of snoring).
When breathing stops, a reflex awakening occurs, so when sleep is interrupted, a person experiences a feeling of fear and anxiety. Sudden awakening is always accompanied by a deep breath.
General symptoms:
- excessive sleepiness during the daytime;
- deterioration of concentration and memory;
- sleep disturbance due to frequent waking up;
- tendency to rapid heart rate;
- sudden mood swings and irritability;
- frequent urge to urinate at night;
- decreased performance;
- bruxism (teeth grinding during sleep);
- regular increase in blood pressure;
- impotence or decreased libido;
- sudden increase in body weight;
- excessive sweating during sleep.
Central
The central type of syndrome occurs due to a temporary cessation of oxygen supply to the lungs due to lack of respiratory effort. The pathological process is associated with disruption of certain areas of the brain.
Among all forms of the disease, this type of apnea is considered the most dangerous. The brain stops sending signals to muscle tissue.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the consequences of the disease can cause death.
Main symptoms:
- snore;
- daytime sleepiness;
- sleep disorders;
- the patient remembers the attacks.
Obstructive nocturnal
The obstructive type of syndrome is a consequence of temporary obstruction of the upper respiratory tract.
The progression of pathology is influenced by the tone of the laryngeal muscles and the internal size of the respiratory tract.
The syndrome manifests itself in the form of frequent awakenings at night, regular headaches during the daytime and general weakness of the body.
Main symptoms:
- snore;
- excessive irritability;
- morning headaches;
- the patient does not remember the attacks.
Mixed
The mixed form of the disease includes the causes and symptoms of other types.
Characteristic symptoms of the syndrome are a tendency to increase blood pressure and disturbances in heart rate. The consequence of the pathology is hypoxemia.
No snoring in your sleep
Snoring is one of the main symptoms of the syndrome . In rare cases, pathology appears without this sign.
The syndrome can be suspected by the presence of additional symptoms - daytime sleepiness, headaches, decreased performance, difficulty concentrating, etc.
It is extremely difficult to independently diagnose apnea without snoring. The problem is identified through a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Sudden
Sudden apnea syndrome is a pathological condition characteristic of newborns and infants.
The cause of an attack can be internal and external factors (small particles entering the respiratory tract).
Respiratory arrest is indicated by sudden cessation of crying , cyanosis of the skin, rapid heartbeat and decreased muscle tone.
Idiopathic hypoventilation
It is difficult to determine the cause of this form of the disease. Snoring with pauses in breathing occurs in healthy people.
The danger of idiopathic hypoventilation is the high risk of death.
Among the factors that provoke the syndrome, experts highlight congenital underdevelopment of the respiratory center.
A special feature of the disease is the absence of more symptoms of apnea (except for snoring and attacks of respiratory arrest).
Possible complications
This disease should not be ignored, as the consequences can be very unfavorable. The presence of sleep apnea syndrome has an extremely negative impact on a person’s quality of life, as he constantly feels overwhelmed. Due to a decrease in the ability to concentrate, the risk of injury at work, at home and when driving a car increases significantly. With severe snoring, a person begins to disturb others, which often leads to conflicts and the appearance of complexes.
The development of sleep apnea contributes to the appearance of various heart pathologies at an early age. Having this type of night breathing disorder increases the likelihood of a heart attack in relatively young men and women. In addition, a decrease in tissue oxygen saturation creates the preconditions for the development of atherosclerosis. Among other things, apnea often creates the preconditions for damage to cerebral blood vessels. This increases the risk of stroke at a young age.
It is worth noting that this pathology can cause a complete stop of breathing and then the heart. This disorder is called sudden death syndrome. The patient may not have any gross pathologies, but the signals that are sent to the brain about a decrease in blood oxygen saturation are insufficient to wake up. Among other things, sleep apnea syndrome significantly worsens the prognosis of many chronic diseases. This sleep disorder is especially dangerous for patients suffering from bronchial asthma, bronchitis and COPD.
How dangerous is apnea?
Hypoxia is the main danger facing sleep apnea. A decrease in oxygen levels to a minimum level causes a person to become quiet, the skin turns blue, and a signal is sent to the brain that it is necessary to wake up. Upon awakening, a person inhales oxygen, thereby restoring impaired breathing. This state of affairs cannot be called normal. A person chronically does not get enough sleep, unable to get into much-needed deep sleep. This leads to constant stress and disruption of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. In this regard, the level of injuries at work and at home is increasing.
Often, in patients with sleep apnea syndrome, the level of morning pressure increases, the heart rhythm is disturbed, which leads to the development of ischemia, stroke, and atherosclerosis. Against the background of apnea, the condition of patients suffering from chronic diseases, for example, lung pathologies, worsens. As a significant side effect, one can also note the suffering of loved ones who are forced to not get enough sleep next to a person who regularly snores.
Drug therapy for apnea
Sleep apnea cannot be treated with medications alone: individual medications are used as part of complex therapy.
One of the most common mistakes is that patients often self-prescribe sleeping pills or sedatives. This only aggravates the situation - tranquilizers promote maximum muscle relaxation, which increases the frequency of attacks. Intranasal corticosteroids are used with caution, and they are not suitable for every patient: the drugs can cause additional sagging of the soft tissues blocking the respiratory passage. Along with other therapeutic methods, Modafinil or Provigil are prescribed, drugs that are effective against narcolepsy.
Which specialist should I contact?
Many people are interested in which doctor to go to if a person has respiratory problems? If a man or woman systematically stops breathing at night, and this problem is accompanied by snoring, then the first thing you need to do is consult a therapist. It is this doctor who must diagnose, interview and examine the patient; in some cases, the therapist determines the reason why the pathology appeared. In addition, this doctor may recommend making any lifestyle or dietary adjustments, and may also prescribe medications to get rid of the problem.
If there are diseases of the nasopharynx, manifested in acute or chronic form, if the patient has pain in the throat area, then he needs to see an otolaryngologist or ENT specialist. This doctor will examine the patient and prescribe either special procedures or effective medications, and in some cases, surgery.
When a patient has disturbances in the structure of the upper or lower jaw, and they provoke respiratory obstruction, it is necessary to consult a dentist. It is this doctor who will analyze the situation,, if necessary, perform jaw surgery, and make an intraoral applicator.
In some cases, a somnologist listens to the patient’s complaints and suggests how to treat sleep apnea in an adult. Consultation with a somnologist is necessary if insomnia and other sleep disorders are present.
Necessary diagnostics for sleep apnea
If you have problems with sleep and suspect apnea, you should contact a general practitioner, who can subsequently redirect the patient to a neurologist or somnologist. The specialist needs to be told about the general psychological state, bad habits, and chronic diseases. During the physical examination, the size of the neck and tonsils is assessed.
Most likely, the patient will be prescribed the following tests:
- general blood analysis;
- blood for sugar;
- assessment of glycated hemoglobin;
- biochemical analysis;
- thyroid hormones;
- blood lipid spectrum;
- urine test - general and albumin.
The main diagnostic method for apnea is polysomnography - a procedure in which body functions are recorded after deep sleep has occurred. It is recommended that people who are at risk undergo the procedure periodically. You will have to visit a special sleep center.
Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- slipvideoendoscopy;
- respiratory monitoring during sleep;
- pulse oximetry;
- ECG.
CPAP THERAPY
This is a compressor with a tube and a mask; it supplies air to the respiratory tract while you sleep. CPAP therapy is a method in which a machine constantly maintains the required pressure in the airways. The CPAP machine is an effective treatment in a short time.
- Advantages
- Painless
- Effectively
- No side effects
- Just
Disadvantages
The only disadvantage or inconvenience is the mask on the face while sleeping. But the positive result of treatment of moderate and undoubtedly severe apnea, close to 100%, eliminates this drawback.
Main symptoms of sleep apnea
One of the obvious signs of sleep apnea is constant sudden awakenings, which the patient himself is often unable to explain. If you enter a risk group, you should immediately consult a doctor for additional diagnostics. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it will be to get rid of it.
The symptoms that occur with sleep apnea resemble neurological diseases. These include:
- constant daytime sleepiness;
- chronic fatigue;
- memory impairment;
- decreased attention;
- irritability;
- constant depression;
- impaired potency or libido;
- morning cephalalgia (headache).
In children, the symptoms are somewhat different, but also resemble neurological pathologies. This disease provokes hyperactivity, urinary incontinence, headache in the morning, and constant drowsiness. Underweight and stunted growth are also possible.
Mouth devices
If respiratory arrest during sleep is caused by the retraction of the tongue and the blocking of the airways with its help, as well as other structural features of the lower jaw of a particular patient, apnea attacks can be prevented by using devices for the mouth.
As a rule, these are mouthpieces, mouthguards and clamps that prevent the tongue from falling back, pushing the jaw forward. In this position, the tongue simply cannot fall into the airways. But such devices only help if the patient has a mild form of the disease.