Cervical cancer occurs against the background of a persistent viral infection (HPV 16,18, 31 and some other types) in the genital tract. The pathogen leads to abnormal tissue growth and the formation of clones of uncontrollably dividing cells. There are squamous cell and glandular cervical cancer (adenocarcinoma). The first signs of the disease often appear only at stages 3 and 4 (contact bleeding, heavy periods, pain).
To confirm cervical cancer, it is necessary to take a biopsy; to detect a tumor, an oncocytology smear (Papanicolaou test) and a blood test are used. Treatment may be surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
What is cervical cancer
Cervical cancer (CC, cervical cancer) is a malignant tumor that is located in the area of the cervical canal. There are two fundamentally different types of cervical cancer - adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The role of HPV, especially types 16, 18, 31, has been proven in the development of this type of tumor.
In recent years, CC has a leading position among other malignant tumors in women. It is more often found after forty years, extremely rarely in teenagers. Cases of cervical cancer have also been described in girls aged 12-13 years, including those without sexual experience.
Thyroid cancer
PSA is a protein that the prostate gland is responsible for producing. Its main function is to reduce the density of the ejaculate, which has a positive effect on sperm activity. The PSA level in the blood is a tumor marker for prostate cancer, the most common cancer among older men.
Tumor markers are substances that tumor cells can produce. For each type of cancer, a tumor marker is a specific type of protein; its concentration is measured in urine or blood.
Based on the level of the tumor marker, the stage of development of the pathological process can be determined. Thus, the higher the concentration of prostate-specific antigen in a man’s blood, the greater the likelihood of diagnosing a late stage of cancer.
When a malignant tumor forms in the prostate, the amount of antigen produced increases. Its concentration increases in direct proportion as the tumor grows. Therefore, when this indicator goes beyond the normal range, the doctor assumes the formation of a cancerous tumor in the patient’s prostate.
Levels of PSA growth in the blood:
- Above 4, but below 10 ng/ml – suspected formation in the prostate gland. With the help of additional studies, the doctor determines the malignancy of the cells - whether it is an adenoma or carcinoma;
- PSA in the range of 10-20 ng/ml - greater than 50% chance of prostate cancer;
- The antigen concentration is above 40 ng/ml - the doctor assumes the presence of metastases in other tissues and organs.
This malignant tumor occupies a leading place among female neoplasms. Such disappointing statistics are to some extent due to the low qualifications of doctors who perform unprofessional examinations of the mammary glands.
- Palpation of the gland allows you to identify lumps and swellings in the thickness of the organ and suspect a tumor process.
- Breast radiography (mammography) is one of the most important methods for detecting non-palpable tumors. For greater information, artificial contrast is used: pneumocystography (removal of fluid from the tumor and introduction of air into it) - allows to identify parietal formations;
- ductography - the method is based on the introduction of a contrast agent into the milk ducts; visualizes the structure and contours of the ducts, and abnormal formations in them.
Due to the increase in radiation and exposure of people over the past 30 years, the incidence of thyroid cancer has increased 1.5 times. Basic methods for diagnosing thyroid cancer:
- Doppler ultrasound of the thyroid gland is a fairly informative method, non-invasive and does not carry radiation exposure.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used to diagnose the spread of the tumor process beyond the thyroid gland and identify metastases to neighboring organs.
- Positron emission tomography is a three-dimensional technique, the use of which is based on the property of a radioisotope to accumulate in the tissues of the thyroid gland.
- Radioisotope scintigraphy is a method also based on the ability of radionuclides (more precisely, iodine) to accumulate in gland tissues, but unlike tomography, it indicates the difference in the accumulation of radioactive iodine in healthy and tumor tissue. Cancer infiltrate can take the form of a “cold” (not absorbing iodine) and “hot” (absorbing iodine in excess) focus.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy - allows for a biopsy and subsequent cytological examination of cancer cells, identifies special genetic markers hTERT, EMC1, TMPRSS4 of thyroid cancer.
- Determination of galectin-3 protein, which belongs to the class of lectins. This peptide takes part in the growth and development of tumor vessels, its metastasis and suppression of the immune system (including apoptosis). The diagnostic accuracy of this marker for malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland is 92-95%.
- Relapse of thyroid cancer is characterized by a decrease in the level of thyroglobulin and an increase in the concentration of tumor markers EGFR, HBME-1
Mechanism of development and causes of cervical cancer
The provoking factors and reasons for the development of cervical cancer are as follows:
- earlier onset of sexual activity, a large number of partners and ignoring condoms as a means of protection;
- passion for smoking;
- positive results for HPV when tested using PCR.
For cervical cancer, one of the few malignant tumors, a direct relationship has been proven between the development of cancer and infection with the papilloma virus. Therefore, to prevent cervical cancer, there are vaccines against certain strains of HPV to prevent viral infection and the development of cancer in the future. According to statistics, women who have had more than 10 sexual partners are three times more likely to suffer from persistent HPV infection.
After HPV enters the mucous membranes of the genital organs, the virus begins to actively multiply. This is a kind of signal for the immune system to actively fight against the pathogen. If the immunity is sufficient, the body completely eliminates the virus, and it is not subsequently detected in the woman during examination. If the body’s defenses are reduced, the virus continues to remain on the mucous membranes all the time, changing the structure of cells and their life cycle.
HPV affects the genotype of cells, inhibiting those areas that are responsible for controlling the growth and destruction of atypical cells. As a result, new clones of cells appear that divide uncontrollably and therefore grow rapidly. These are cancerous tumors. Thus, the papilloma virus disrupts the natural antitumor defense of the cell.
As the number of abnormal cells increases, the cancer progresses. In the initial stages, women have practically no symptoms of the disease; pathology can only be detected during examination.
Many scientists are inclined to believe that herpes simplex viruses and cytomegalovirus are also important in the etiology of cervical cancer.
We recommend reading about the features of the course of cervical ectopia of the cervix with chronic cervicitis. From the article you will learn about the causes of ectopia, symptoms of cervicitis, cervical ectopia of the cervix, diagnosis and treatment. And here is more information about when and how a cervical biopsy is performed.
Contraindications
Despite the effectiveness of oncocytological research, it may not always be used.
First of all, the procedure is postponed if there is certain discharge. It is not recommended to do the analysis in case of acute inflammation, in the presence of itching and during the menstrual cycle. This is explained by the fact that in such conditions it will not be possible to conduct a qualitative assessment of cellular structures, since the presence of erythrocytes and leukocytes in the collected biological material will hide atypical cells from the detection area.
Types of tumors
Cancer (carcinoma) forms from the upper part of the epithelium of the cervix. Adenocarcinoma is much more common and has a more favorable prognosis. The form of malignancy can be determined only after histological examination, for example, after a biopsy or after surgical removal of an organ. Tumor variant influences the prognosis and treatment of cancer.
Squamous cell keratinizing
This form is characterized by the detection of signs of cell keratinization. They look like "cancer pearls". This type of cervical cancer often develops against the background of tissue leukoplakia. Depending on the degree of cell differentiation, cervical cancer is distinguished:
| Highly differentiated | the most favorable option, the structure of the cells is similar to normal cervical tissues |
| Moderately differentiated | average between the two types |
| Poorly differentiated | the most malignant variant, the cells differ sharply in structure from normal ones, such cancer quickly metastasizes |
Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix without keratinization
Cells of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix without keratinization have a high ability to divide. When examining such tissues using a microscope, keratin “pearls” are not detected. Based on the degree of differentiation, low-, moderate-, and highly differentiated cancers are also distinguished.
Poorly differentiated cancer
This is a type of squamous cell carcinoma. Characterized by the following:
- progresses rapidly;
- more often gives metastases;
- symptoms appear late;
- does not respond well to chemotherapy.
Glandular (adenocarcinoma)
Much less common than squamous cell carcinoma. It is formed from glandular cells and is similar in structure to endometrial cancer. Clinically, it does not have any manifestations for a long time, so it is often detected late. Depending on the histological structure, the following options are distinguished:
- mucinous,
- glandular-papillary,
- endometrioid,
- clear cell,
- serous,
- mesonephric,
- mixed.
What can distort the result
The data obtained during an oncocytological study may not always be correct. Several factors may influence this.
First of all, distortion is possible against the background of a radical change in hormonal levels in patients at a young age. Unreliability of the analysis is possible if the collection of biological material was carried out during the menstrual cycle.
An equally important role is played by the correct implementation of all preparatory instructions. If the necessary hygiene procedures are not followed, the sample may become contaminated with suppositories, gels, ointments or sperm used.
The first signs of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is insidious because the first signs may be symptoms of an already advanced tumor, including the following:
- pathological discharge from the genital tract, especially with an unpleasant rotten odor;
- bleeding of unspecified nature;
- the appearance of blood (usually a scanty smudge) after sexual intercourse, this is the so-called contact discharge;
- pain of different localization in the abdomen;
- disturbance of the outflow of urine (retention), the appearance of blood in it.
What diseases will it show?
Thanks to oncocytological analysis, the following pathological processes can be identified:
- dysplasia;
- presence of malignant cells;
- inflammation;
- bacterial, fungal, viral lesions.
In addition, this study allows us to determine what reaction the body gives during therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating diseases and infectious lesions, as well as during hormonal treatment or taking other medications.
How quickly it develops
Cancer develops over many years—at least five to seven. It is believed that the disease goes through all stages - dysplasia, precancer, and only then cancer appears.
There is a pattern - the earlier a malignant tumor is detected, the greater the likelihood of a complete cure. If CC is detected at the stage of carcinoma in situ and radical treatment is carried out, in 95% of cases recovery is observed, the woman is even removed from the dispensary register.
What are the indicators for blood cancer?
When studying the results of a general blood test, an increase in the number of immature leukocytes will indicate that acute leukemia is developing in the body.
Other blood cells may be in short supply. Anemia is noted.
If the analysis reveals the presence of granulocytes or granular leukocytes in increased numbers, then we can talk about developing chronic leukemia.
Anemia and a decrease in the number of other types of cells may also occur.
Biochemical analysis helps determine whether the pathological process has caused tumor formations in other organs. With blood cancer, a pathological disorder can occur with any type of blood cell, this is clarified through research.
An elevated level of the tumor marker B-2-MG may indicate the presence of multiple myeloma, lymphoma, or lymphocytic leukemia .
The initial stage of cervical cancer and its manifestations
Early stage CC refers to carcinoma in situ (or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) and the first stage of the disease. Main symptoms:
- the appearance of traces of blood from the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort, pain in the abdomen;
- the appearance of scarlet red discharge during physical overexertion.
In the early stages, tumor cells are usually located on the surface of the cervix and do not penetrate deep into the tissue. Therefore, the prognosis is favorable. Treatment at the initial stage is always radical and in most cases leads to a complete cure of the disease with a 98% five-year survival rate.
It is not always possible to notice visually cervical cancer in the initial stages. If tumor cells are hidden inside the cervical canal, it is not always possible to detect them even with colposcopy and taking smears for pathological cells. The size of the affected area in the initial stages of CC is about 1 cm.
Preparation
To obtain the most reliable results, it is necessary to be well prepared for the oncocytological procedure.
Preparing for the analysis involves following certain recommendations given by the attending physician.
First of all, you need to remember that you can donate biomaterial at any time except the days of menstruation. The best period is considered to be the time immediately after the cessation of menstrual flow or immediately before its appearance.
On this topic
- Other diagnostic methods
BRAF mutation
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- October 17, 2020
Two days before the scheduled date for oncocytology, it is necessary to exclude sexual contact, refuse to use tampons, various ointments and gels, and suppositories intended for vaginal administration.
Douching and bathing are not recommended.
It is recommended to refuse any procedures performed in a gynecological chair.
Three hours before the procedure, you should not go to the toilet, which may negatively affect the results of the study.
Subsequent stages
The second stage of CC is established if cancer cells form a tumor of about 5 cm, penetrate the body of the uterus, vaginal tissue, but do not affect neighboring organs and lymph nodes. Such a tumor can be noticed during examination.
Stages II A and II B are distinguished. In the first case, cervical cancer spreads to the cervix and body of the uterus, vaginal tissue. In stage II B, the tumor grows deeper, but does not affect nearby organs.
Classification of cervical cancer according to TNM and FIGO
Symptoms in the second stage are more striking than in the early stages of the disease. Contact bleeding appears more often and more distinctly; bleeding during menstruation and constant pain are typical. However, in some cases the disease is asymptomatic.
The third stage of cervical cancer is established if the tumor reaches the lower third of the vagina (stage III A), grows into the wall of the uterus, but does not affect neighboring organs. In this case, the ureters may be compressed (stage III B), resulting in a clinic of impaired urine outflow.
Classification of cervical cancer according to TNM and FIGO
At the last stage of cancer, metastases are detected in neighboring organs (bladder, rectum - IV A) and located far from the original focus (IV B) - lungs, mammary glands, liver. When it grows into the ureters, the outflow of urine is disrupted, into the bladder - traces of blood in the urine, into the rectum - symptoms of hemorrhoids and anal fissure, constipation.
The fourth stage of cancer is characterized by a clear clinical picture:
- very heavy periods, which can even cause a woman to be hospitalized;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- extremely unpleasant odor from the vagina, reminiscent of rotting meat;
- symptoms of damage to other organs - constipation, cystitis, impaired renal function, liver function, etc.
Watch this video about the stages of cervical cancer:
The first signs to start worrying about.
Frequent headaches, chronic fatigue, fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss, frequent bacterial and viral diseases - many people attribute such symptoms to various factors, thereby allowing the tumor to grow, and when obvious symptoms appear, such as damage to the organ itself and nearby tissues, then not all treatment methods become effective.
Suspicion of cancer (general symptoms):
- Sudden weight loss;
- Frequent unexplained pain in the same place;
- Shortness of breath, cough, hoarseness;
- Bleeding;
- Skin changes, appearance of age spots or new moles on the skin;
- Changes in bladder activity;
- Changes in the functioning of the digestive tract;
- Unusual discharge from the breast and genitals;
- The appearance of swelling with hyperemia, compactions, various neoplasms on areas of the skin of the body and head;
At risk are:
- Women over 35 years of age who have not given birth or breastfed;
- People who smoke;
- Obesity, overweight;
- Alcohol addicts;
- Those exposed to radiation, poisoning with carcinogens;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Those suffering from immunodeficiency.
It is necessary to take a general and biochemical blood test at least once a year, as it contains a lot of necessary information. Thanks to these useful data, malignant neoplasms can be diagnosed in a timely manner.
Cervical cancer test
The following tests can be used to detect cervical cancer:
- Pap test or oncocytology smear for cancer cells;
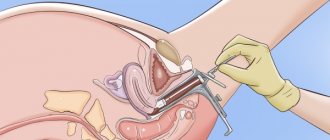
- cervical biopsy or scraping from the cervix;
- colposcopic examination;
- blood tests - they can only suggest the presence of a tumor.
Is it possible to detect cancer using tests?
The most reliable test for detecting cancer is a biopsy. In this case, the altered area of tissue is excised, sent to a histology laboratory and examined under high magnification. This way you can determine the type of cancer, the degree of tissue damage, and even the approximate stage.
All other tests provide only approximate data and cannot completely exclude or confirm the presence of cervical cancer.
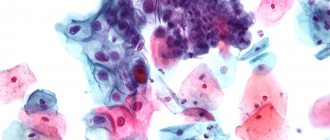
Smear
Can be used to detect precancerous diseases, as well as tumors at different stages. There are two options for smears:
- For oncocytology . They have less information content, but are cheap and easy to use, therefore they are widespread and used in all government medical institutions in Russia and neighboring countries. Using a special cytobrush (sometimes other devices are used), tissue is collected from the surface of the cervix and cervical canal.
Next, the material is sent to the laboratory, where the resulting cells are examined. Atypical, dysplastic, cancerous, and also inflammatory elements can be detected.
- Papanicolaou (PAP test) . Modern interpretation of smears for oncocytology. The main difference is that after tissue collection, the material is introduced into a special liquid medium, which makes it possible to identify the human papillomavirus. Samples of the material are stored for some time in the laboratory, which allows some research to be carried out, if necessary, without the woman’s additional visit to the gynecologist.
Rules for donating blood
Blood tests can only suggest some types of cervical tumors. To do this, you need to donate blood for tumor markers - CA-125, CEA, ROMA index, HE-4. Exceeding the indicators should be the reason for a detailed examination in order to detect the tumor focus.
A routine blood test changes only in the later stages of cancer - characterized by an increase in ESR, a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells.
Prices for diagnostic tests for oncology
What analysis will show oncology? To diagnose this disease, the usual general blood test is also used. After all, by its nature, a tumor is an actively developing tissue that consumes large quantities of substances that are necessary for the life of the patient’s body. It also releases toxic metabolic products. This leads to changes in blood tests for oncology.
In particular, ESR increases, the number of lymphocytes decreases and the number of neutrophils increases. All this is accompanied by general symptoms:
- Increased fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Lack of appetite.
- Sudden loss of body weight.
In particular, the described symptoms often indicate lymphogranulomatosis, histiocytosis and neuroblastoma.
With the development of a malignant tumor, the hematopoietic system often suffers, causing the hemoglobin level to decrease. The toxic effects of tumor cell metabolic products damage the membranes of red blood cells. Therefore, in a blood test for oncology, their pathological varieties - echinocytes - can be detected. Bone marrow cancer has a high number of immature blood cells.
Carrying out a blood test for oncology is no different from the usual. The biomaterial is taken on an empty stomach (at least 4 hours must pass since the last snack). The blood is collected into a test tube. Analysis results are provided in 1-2 days.
But it should be noted that a general blood test for oncology will not be specific. It is unprofessional to make a diagnosis of cancer based on its results. For example, ESR increases with any inflammation in the body. Anemia also occurs with poor nutrition and lack of iron in the body.
The results of a general blood test for oncology will include the following indicators:
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). If it is higher than normal, this indicates the presence of inflammation in the body. If the acceleration is 30% higher than normal, there is reason to suspect cancer.
- Both a decrease and an increase in the number of leukocytes. In oncology, both of these phenomena are observed. If the level of white blood cells is reduced, this indicates that the systems responsible for their production are in a pathological state. This is observed in bone marrow cancer. If the level of leukocytes is exceeded, this may also indicate a malignant tumor. Since the body actively produces antibodies here to fight foreign cells.
- Decreased hemoglobin levels. This can be considered a sign of oncology in a blood test if the platelet level has also decreased. A low degree of blood clotting, among other things, indicates leukemia.
- Increased number of immature blood cells. As we have already noted, this is observed in pathologies of the bone marrow, where they are produced.
- Many granular and immature leukocytes were found.
- A large amount of lymph in the blood and, accordingly, lymphocytes.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what diseases cause night sweats in women
What analysis will show oncology? As for the urine test, in this case it will not be specific. But any deviations from the norm here indicate the need for additional diagnostics.
It is important to pay attention to the following:
- Blood in urine. Among other things, it may indicate cancer of the urinary tract or bladder. But it is also a symptom of urolithiasis and glomerulonephritis.
- Ketone bodies. Their content in urine indicates active catabolism (that is, tissue breakdown) in the body. But this may indicate not only tumor processes, but also diabetes. And also talk about following a strict diet.
Cervical cancer treatment
Treatment of cervical cancer can be surgical (the tumor is removed), as well as conservative - chemotherapy, radiation treatment. Conservative methods are used in advanced stages, when it is impossible to remove the tumor.
What to do in the early stages
Detection of cervical cancer in the early stages is the key to a complete cure for the disease. Depending on the depth of tissue damage, conization of the cervix (for intraepithelial neoplasia), high amputation (removal of part of the cervix, but preservation of the uterus), resection of the body and cervix complex (the issue of appendages is discussed individually) is performed.
Removal of part of the cervix while preserving the uterus
There is no need for chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
If the patient is pregnant
Detection of cervical cancer during pregnancy may be an indication for early delivery or termination (in the early stages). Only with carcinoma in situ and suspected stage 1 cancer can it be allowed to carry the baby to 35-37 weeks - until the moment when the fetus is practically formed and ready for life outside the womb.
In general, the hormonal background of pregnancy contributes to the progression of tumor diseases, including cervical cancer.
Radiation treatment (radiotherapy)
To destroy a tumor, various types of radiation are used (X-ray, proton, radionuclide and others), which focuses specifically on the tumor. For this purpose, special marks are made on the body, which reduce the likelihood of damage to neighboring structures.
Radiation therapy for cervical cancer is carried out as an independent treatment (in later stages, when there is no point in removing the tumor due to its prevalence), or in combination with surgery and chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy
Operation
Surgery can be performed at different stages and have different purposes. The following options are possible:
- removal of part of the cervix - in the initial stages of cancer and precancer;
- excision of the cervix, body of the uterus and part of the vagina is a standard surgical intervention for cervical cancer.
As a rule, some lymph nodes are removed, especially if they are suspiciously enlarged.
In late stages of cervical cancer, operations are palliative in nature and aimed at improving the woman’s quality of life. For example, if the outflow of urine is disrupted, a way to excrete it is created; if there is obstruction of the rectum, an artificial opening for the discharge of feces can be formed.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs that suppress the growth of tumor cells. The method is used in the following cases:
- if a woman refuses other types of treatment for personal reasons;
- if there are contraindications to surgery;
- in case of tumor recurrence or metastases;
- to reduce the size of the tumor for the purpose of its subsequent removal.
Chemotherapy
Modern approaches to treatment
The goal of modern medicine is to detect cervical cancer in the early stages, when a complete cure for the disease is possible. In this case, you can use the most gentle methods - removing part of the cervix. At the same time, sexual and reproductive function is preserved in full; a woman can become pregnant and bear a fetus.
When cervical cancer is detected in advanced stages, a combination of several types of treatment is used , for example, chemotherapy and subsequent surgery, radiation therapy before or after surgery, etc.
Diet
For prevention and after detection of a tumor, it is important to maintain proper nutrition. The diet must be enriched with foods that contain vitamins A, E, B, C, microelements (especially selenium), omega-3 and omega-6 - polyunsaturated fatty acids. All these are components of the body’s antioxidant system, which fights abnormal cells, preventing them from increasing in number.
The diet should consist of:
- proteins of plant and animal origin;
- healthy fats – fish, eggs, vegetable oils, dairy products;
- complex carbohydrates – fresh fruits and vegetables.
Consequences of treatment
Depends on which method of tumor removal/slowing its growth was chosen:
- surgical removal - if only part of the cervix is excised, the woman does not notice any changes after recovery and can even plan a pregnancy; if the uterus and cervix are removed, then menstruation stops, she will not be able to carry and give birth to a child on her own;
- radiation therapy – the consequence of treatment may be damage to neighboring organs with the development of proctitis and cystitis;
- chemotherapy can have unpleasant complications at the time of administration - nausea, vomiting, bowel dysfunction, fatigue, lethargy, etc.
Observations after treatment
All women with detected cervical cancer are subject to dispensary registration. The dynamics of the disease and the person’s condition in the first five years are monitored. Depending on the stage, observation by an oncologist at your place of residence or in a specialized center is necessary.
After surgical removal of the tumor, observation is indicated for two years with an in-person appointment with a doctor every 6 months.
Surveillance is necessary for early detection of symptoms of cancer progression and timely treatment.
Blood chemistry
What analysis shows the presence of cancer in the body? One of the most accurate and detailed here is biochemical. With its help, you can determine the first symptoms of the presence of cancer cells in the body.
A biochemical blood test for oncology will differ in the following indicators:
- Albumin, total protein. Cancer cells actively consume protein. Therefore, its level in the blood will decrease. At the same time, the patient notes a loss of appetite and weight, since proteins, the main building material for cells, cease to enter the body in the required quantities. If the tumor affects the liver, the person will suffer from protein deficiency even with a normal diet.
- Urea. If this indicator is higher than normal, there is reason to suspect both deterioration of kidney function and active protein breakdown. This is observed during the active growth of the tumor, and during intoxication with metabolic products of cancer cells, and during the active decay of cancer cells during the treatment of the disease.
- Changes in blood glucose levels. An increase in the indicator indicates diabetes mellitus, sarcoma, liver cancer, reproductive system organs and other oncological diseases. The fact is that tumor cells inhibit the production of insulin, causing the body to respond untimely to an increase in blood sugar levels. Therefore, several years before the appearance of obvious symptoms of cancer, the patient may experience signs of diabetes mellitus. In particular, this occurs with cancer of the mammary glands and uterus.
- Bilirubin. Its level will be exceeded in case of any liver damage. Including in oncology.
- AlAT. Its level increases with tumor damage to the liver. But it may also indicate the development of other diseases.
- Increased alkaline phosphatase. It may be a sign of a malignant tumor of bone tissue, as well as metastases in them, damage to the liver, gall bladder by oncological formations.
For this study, blood is donated from a vein. It is advisable to come to the treatment room before breakfast, on an empty stomach. Otherwise, false analysis results may occur. The answer is prepared as standard - in 1-2 days.
Will the tests show oncology? The specificity of this study does not make it conclusive. That is, based on biochemical analysis alone, it is impossible to suspect oncology. But deviations from the norm here are a reason to worry and undergo additional examinations.
Prevention measures
To prevent cervical cancer, the following is important:
- have as few sexual partners as possible;
- use condoms for protection;
- undergo a timely examination by a doctor.
Given that HPV is important in the development of cervical cancer, there is a vaccine against some strains of the virus. It is performed on girls and boys during adolescence before the onset of sexual activity. These are Cervarix and some others.
We recommend reading about what cervical ectropion is. From the article you will learn about the causes of ectropion, symptoms and consequences of the pathology, differences from erosion, and treatment. And here is more information about why cervical erosion occurs.
Cervical cancer is a serious disease. Detection of a tumor in the early stages helps almost everyone to completely recover from the pathology. Treatment is selected taking into account the type of tumor, its size, and the involvement of adjacent structures.
FAQ
When deciphering blood tests, patients often ask questions about how this or that indicator can change with cancer and what this can mean. Let's look at the most common of them.
Can a good blood test be detected in cancer patients?
Yes, it can if the disease is detected in the initial stages or at the compensation stage. In addition, do not forget that there are a huge number of types of blood tests and a situation may arise that there are no changes in the general analysis, and tumor markers were not detected.
However, the situation when a general blood test for cancer does not have any abnormalities does not occur so often
Is it possible to determine the stage of cancer using a blood test?
Oncology is staged based on many criteria, and most of them are purely clinical - the spread of the primary tumor, the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes and nearby organs, and so on. Therefore, if it is possible to draw a parallel with the stage using a blood test, then it is very approximately, and such an analysis should be highly specific, such as genetic tests or determination of tumor markers.
Is there a specific test to detect stomach cancer?
Stomach tumors cannot be detected by analyzing general blood tests. However, today there are innovative molecular tests that make it possible to determine gastric cancer and its antigenic set. This is the detection of PEA-1 tumor markers and the Foundation One genetic test, which completely determines the antigenic profile of a cancer cell. This test will show the cancer itself and determine its aggressiveness.
These tests are not carried out in all clinics in the world and are expensive. At the First Tel Aviv Medical Center, the patient has the opportunity to order all the latest genetic and molecular tests.
Can a blood test detect cancer?
Most often, even general and biochemical blood tests will show changes in indicators in the presence of cancer. However, this does not always happen and these changes may be associated with other reasons - infections, stress, and so on.
Identification of specific tumor markers is a more specific criterion, but they can also be elevated in related pathologies. But innovative genetic tests will always give an answer - what type of tumor led to the changes, whether it is treatable and show the degree of aggressiveness of atypical cells.
However, such tests are not performed in the CIS countries, so the answer to the question is no, there is no general test that determines cancer in the blood.
What tests should I take for blood cancer?
For hemoblastoses, the most effective will be a general blood test with a formula of cellular elements and a detailed biochemical analysis with the identification of tumor markers NSE and CEA-5
Deciphering a blood test for bone marrow cancer
In this situation, the general analysis will include immature cells and progenitor cells that are not normally found in the blood. During a tumor process in the bone marrow, they do not have time to develop to mature forms, enter the bloodstream and cease to perform their function
Blood tests for uterine, lung, breast, brain and prostate cancer
As already mentioned, the specific location of the tumor cannot be determined by general blood tests. But most cancers have a corresponding marker in the blood, which increases as the tumor develops.
| Localization | Tumor marker |
| Mammary cancer | CA-15-3 CA-50 |
| Lungs' cancer | REA NCE SCCA |
| Prostate cancer | PSA |
| Uterine cancer | TPS |
| Brain cancer | NSE |
In addition, high-tech laboratories around the world conduct genetic molecular tests for the antigenic profile of cancer cells - Oncotype DX, Foundation One, Mammaprint, which detects breast cancer and others. In developed countries, these tests have long become the gold standard in oncology and doctors do not get by with just general blood tests and detection of tumor markers. These tests have significantly increased the effectiveness of cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Useful video
Watch this video about the treatment of cervical cancer:
Similar articles
- Tumor in the vagina: symptoms, inside, on the walls...
If a tumor is detected in the vagina, do not immediately panic, since they can be benign and malignant. By location they are inside on the walls, at the entrance, on the stump, near the vagina. There are no symptoms for small sizes. Treatment involves removal. Read more - Relationship between endometrial and cervical cancer and pathology
Some associate endometriosis and cancer as a single pathology. However, this is not true, although the diseases have many similarities. Can endometriosis develop into cancer? No, but both diseases can be detected in one woman. Read more
- Periods after cancer
Menstruation often occurs during cancer, and it can also become the first symptom of the onset of cancer. Menstruation varies depending on the woman’s age, as well as the location of the tumor. Read more
- Cervical fibroids: submucous, subserous...
Depending on the type, cervical fibroids can be submucous or subserous. The permissible size at which surgery can be avoided is a maximum of 6 cm. Symptoms up to 3 cm are imperceptible, pregnancy is almost impossible. Traditional methods can only be used in combination with hormonal treatment. Sometimes a hysterectomy is recommended. Read more
Laboratory diagnostics
Malignant cells during their development consume a large amount of useful substances, taking “building material” from vital systems and poisoning them with the products of their existence.
This action causes certain changes in the patient’s well-being:
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- loss of appetite;
- sudden weight loss.
If you lose weight suddenly, get a medical examination
Such symptoms should alert a person and encourage him to get examined.
The following conditions may be grounds for testing:
- the appearance of severe, unremitting pain in a certain organ that does not respond to antispasmodics and analgesics;
- development of prolonged inflammation, exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- unreasonable temperature rises;
- development of immunodeficiency;
- changes in taste sensations and dysfunction of olfactory receptors.
A mandatory indication for a general blood test is a preventive examination once a year. For biochemical studies and tests for proteins produced by cells of various tumors - predisposition to cancer at the genetic level.
The results of laboratory tests are not always decisive for making a diagnosis. Often they need to be confirmed using instrumental diagnostics:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT scan.
- Mammography.
- Scintigraphy.
- Ultrasound.
- Biopsy.
- Pathomorphological examination.
- Dermatoscopy.
As you can see, many tests can detect signs of cancer. But not all of them are equally specific. In many cases, additional diagnostics are required.
With the development of tumor cells, an increased amount of useful substances is required, which are taken up by cancer cells and poisoned by the products of their vital activity. This process causes certain changes in the patient’s well-being - general weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite and weight. If severe, unabating pain in a certain organ begins to bother you, which is not relieved by painkillers, inflammation develops, chronic diseases worsen, the temperature rises for no reason - this should serve as a reason to get tested, check and find out whether there are cancerous foci in the body.
https://youtu.be/11gxRkmxHMg
A mandatory indication for a general analysis is an annual preventive health check. To donate blood for biochemical analysis and for tests on the level of proteins that are synthesized by tumor cells, the indication is a predisposition to cancer at the genetic level, and if you have crossed the 40-year age threshold.