Scientific verification
The vestibule of the vagina expands only slightly after childbirth. In 1996, doctors in the United States began making special measurements called the “Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System,” which were supposed to clearly indicate medical success in the fight against prolapse after childbirth.
For the first time, the length of the vagina in women was measured fully, before and after. Doctors used the system to study the genitals of several hundred patients and found that after natural childbirth there was a slight dilation of the vaginal opening. Most likely, the responsibility for this phenomenon lies not so much in the direct process of delivery, but in muscle weakness or the consequences of injury in this area.
Pregnancy and childbirth with prolapse
Throughout the entire period of bearing a child, the risk of infection of the genital tract is increased. In addition, partial prolapse of the walls affects the ability to conceive. If pregnancy occurs, it may end in premature birth or miscarriage due to weakness of the ligamentous apparatus.
Experts recommend that pregnant women do Kegel exercises. They not only strengthen the tissues of the genital organs, but also stimulate easier labor. To reduce the load on the vagina, a rubber pessary is installed. A woman must wear a bandage for all 9 months.
When the vaginal walls prolapse, the process of delivery changes. The likelihood of injury to the muscular structures of the pelvis increases. The risk of developing ligamentous insufficiency increases.
Often, to prevent vaginal prolapse, a perineal incision is made, which is most often improperly sutured.
If an episiotomy is not performed when the muscle tissue is weakened, then during childbirth not only the vaginal walls, but also the entire organ may fall out.
Often, childbirth serves as a provoking factor in the development of severe uterine prolapse due to a decrease in muscle and ligamentous tone, failure to maintain proper nutrition and the occurrence of constipation, lifting heavy objects in the early postpartum period.
To avoid the above problems, it is necessary to eliminate the physiological disorder before planning pregnancy. The initial stage allows you to bear a fetus without surgical treatment, but with strengthening of the muscles of the intimate area and abdominal muscles.
Size Variations
What vaginal length is considered normal? It is impossible to give a definite answer to this question, since the female vagina is a very elastic organ. On the one hand, it is small enough to hold a sanitary tampon in place during the menstrual cycle. But at the same time, the vagina can stretch so much that no small newborn baby passes through it. This occurs due to the structural features of the tissue: the walls of the vagina are in many ways similar to the walls of the stomach. They shrink and fold when the body does not need a lot of volume, and stretch when necessary.
How long is the vagina in centimeters? For each woman, this parameter will be different, because the body of any person is initially individual. In addition, even in the same woman, the vagina periodically changes size. It all depends on what exactly needs to be let in or out.
Kegel exercises: work without mistakes
Dr. Tarney states that any of his patients can demonstrate how to contract and release the biceps. But when most girls report that they regularly perform Kegel exercises, the doctor makes sure that one half is doing intimate gymnastics incorrectly, and the other simply cannot maintain normal coordination between the brain and muscles.
To record the location of the muscles involved in the world-famous exercises, you should either place a finger in the vagina and squeeze its walls, or consciously stop the flow during urination. After identifying the muscles, you should practice contracting them for periods of five to ten seconds, alternating contractions with minutes of complete relaxation. If you are concerned about the length of your vagina and are unable to withstand such a long period of muscle tension, start with shorter periods and gradually increase the load. The exercise should be repeated 10-20 times in a row, three times a day. During gymnastics, you need to monitor your breathing and try not to use the muscles of your legs, abdomen or pelvis in any way.
Some women experience nerve tissue injury during childbirth and are unable to feel their pelvic floor muscles. Others simply do gymnastics incorrectly. Interestingly, in the United States of America there are special specialists - therapists who professionally help patients perform Kegel exercises correctly.
What affects vaginal size?
The width and depth of the vagina can change in certain situations. This organ is capable of expanding to accommodate a tampon, finger or penis.
During arousal, the blood supply to the vagina increases. This causes an increase in the length of the vagina and a slight rise in the end of the cervix. This reaction allows the vagina to adapt to the size of the penis, finger or sexual toy.
However, even though the vagina can expand during sexual arousal, a large penis or bulky sex toy can make a woman feel uncomfortable.
Vaginal size and penis length
The average size of an erect penis is 33% larger than the average size of a vagina. While the size of both the penis and vagina can vary, the two organs usually adapt quickly to each other.
In 2020, the results of a study were published that showed that the average length of an erect penis is 13.12 centimeters. Some women experience discomfort if their sexual partner has a penis that is larger than average.
Compatibility of genital organs by size
Mutual sexual satisfaction is the key to a long-lasting relationship filled with love and colorful memories. Latent disappointment in intimacy in one or both partners will sooner or later become a source of mutual resentment and lead to separation. Sometimes lovers blame each other for what happens to their intimate lives, but in fact the problem lies in the anatomical discrepancy of the genital organs.
Types of sexual incompatibility
There are three types of sexual incompatibility:
- psychological;
- physiological;
- psychophysiological.
Mental sexual incompatibility is extremely rare. In this case, partners are not satisfied with intimate relationships due to the fact that they do not like the appearance of their lover, his manners, character, or something else.
Important!
Mental incompatibility is observed mainly in people who enter into arranged marriages. In this case, they will have to get used to each other for a long time in order to learn to enjoy sex.
Physiological incompatibility is more common and is based on a discrepancy in the size of the genital organs. At the same time, partners are faced with the impossibility of giving each other pleasure. Such relationships are doomed to failure in 88% of cases. If there is a strong emotional connection between a man and a woman, which, although it suffers from dissatisfaction in sex, cannot be broken, then they are recommended to find ways to compensate for each other’s physiological deficiencies.
Psychophysiological incompatibility is a complex of problems, but it is even less common than psychological incompatibility. In this case, other irritating factors are added to the disproportion of the genital organs, for example, domestic quarrels, inability to make concessions, etc. This leads to the fact that one of the partners does not enjoy sex and becomes emotionally depressed.
Physiological incompatibility and its features
For the first time, Ludwig Levin Jacobson, a Danish anatomist and physiologist, spoke about the optimal combination of genital organs. He compiled a compatibility table.
Very big
| Compatibility | Penis size | Vagina size |
| Fully compatible | Big | |
| Big | Average | |
| Average | Small | |
| Very big | Very big | |
| Compatible in certain poses | Big | Big |
| Average | Average | |
| Small | Small | |
| Average | Very big | |
| Moderately compatible (one of the partners does not get maximum pleasure) | Small | Average |
| Very small | Small | |
| Average | Very big | |
| Incompatible | Small | Large and medium |
| Very small | Large, medium and small |
Muscle tone
What really matters is the size of the vaginal vestibule, or vaginal opening. Most often, gynecologist patients complain about problems that appear after natural childbirth.
According to Tarney, visitors primarily describe changes in sexual function and notice that the vagina feels as if it has become too wide. As a result of this “expansion,” women experience sexual pleasure of less intensity. In fact, recent childbirth changes the sexual experience in many ways, so the feeling of a “wide vagina” almost never has anything to do with the diameter of the vaginal opening.
Problems
According to Dr. Christopher Tarney, the main problem for patients remains the feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse. It is caused by insufficient length of the female vagina or excessive tension in the walls. In some cases, discomfort occurs due to prolapse - prolapse of the uterus, bladder or other organ into the vagina. This often happens after the birth of a child.
However, Tarney believes prolapse is the only real problem. The length of the vagina, in his opinion, in no way affects sexual satisfaction, including because there are very significant variations in the norm.
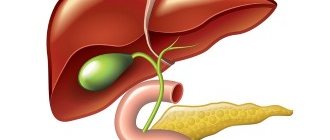
The structure of a woman's vagina
The walls of the vagina are 3–4 mm thick and consist of three layers:
- Internal. This is the mucous membrane of the vagina. It is lined with stratified squamous epithelium, which forms numerous transverse folds in the vagina (they are very clearly visible in the figure). These folds, if necessary, allow the vagina to change its size.
- Average. This is the smooth muscle layer of the vagina. Muscle bundles are oriented predominantly longitudinally, but bundles of a circular direction are also present. In its upper part, the muscles of the vagina pass into the muscles of the uterus. In the lower part of the vagina they become stronger, gradually intertwining with the muscles of the perineum.
- Outdoor. The so-called adventitial layer in the structure of women. This layer consists of loose connective tissue with elements of muscle and elastic fibers.
The walls of the vagina are divided into anterior and posterior, which are connected to one another. The upper end of the vaginal wall covers part of the cervix, highlighting the vaginal part and forming the so-called vaginal vault around this area.
The lower end of the vaginal wall opens into the vestibule. In virgins, this opening is closed by the hymen.
| Name of service | Price |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, K, M, N, diagnostic and treatment, outpatient | 1,800 rub. |
| Removal of condylomas on the mucous membrane / for one zone 0.1 cm * 0.1 cm or (1 mm x 1 mm.), for 1 field. | 1,000 rub. |
| Primary appointment with obstetrician-gynecologist I.A. Vybornova | 2,900 rub. |
| Summarizing the examination results and drawing up an individual treatment program, level 1 of complexity | 1,500 rub. |
| Insertion of an intrauterine device | 3,500 rub. |
| Colposcopy / extended | 2,000 rub. |
| View the entire price list | |
Typically pale pink in color, the vaginal walls become brighter and darker during pregnancy. In addition, the vaginal walls are at body temperature and feel soft to the touch.
Having great elasticity, the vagina expands during sexual intercourse. Also, during childbirth, it can increase to 10-12 cm in diameter to allow the fetus to emerge. This feature is provided by the middle, smooth muscle layer. In turn, the outer layer, consisting of connective tissue, connects the vagina with neighboring organs that are not related to the woman’s genital organs - with the bladder and rectum, which, respectively, are located in front and behind the vagina.
Statistics
Nevertheless, many are interested in the average length of the vagina (well, there must be an average statistical indicator?). For such information, it is worth turning to the study of Masters and Johnson, conducted back in the 1960s. Two scientists described in detail the physical characteristics of hundreds of women who had never been pregnant and found that in the absence of stimulation, the length of the vagina in girls is a minimum of 6.9 cm, a maximum of 8.2 cm. With stimulation, the organ lengthens to around 10. 8 cm and 12 cm respectively. The last indicator is the actual maximum length of the vagina within the normal range. Regardless of the numerical characteristics, it should be borne in mind that the area presumably responsible for the female orgasm is located in the first (outer) third of the vagina.
Pathologies affecting the anterior vaginal wall
An isolated course of diseases affecting only the anterior wall of the vagina is mainly observed in girls and elderly women. Inflammation of local tissues is caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the vagina. Infection of the anterior vaginal wall causes intense pain and burning.
For the development of the inflammatory process, the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms is not enough. They are activated against the background of a decrease in local or general immunity.
Inflammation in older women is caused by the gradual decline of ovarian function, as a result of which the concentration of hormones decreases. Age-related changes in the body lead to thinning of the mucous membrane and disruption of the vaginal microflora. As a result, favorable conditions are created for pathogenic microorganisms.
During pregnancy, tissues become inflamed due to hormonal changes in the body. During this period, the concentration of estrogen decreases, maintaining vaginal acidity within normal limits.
Another common problem found in women of any age is a cyst in the anterior vaginal wall. This neoplasm can be congenital or acquired. The last form of cyst occurs due to damage to the tissues that make up the anterior wall. This happens when:
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- labor activity;
- surgical treatment of the vagina and uterus.
Small cystic neoplasms do not interfere with normal life activities and childbirth. If they begin to grow, surgery is performed to excise the cavity.
Is it possible to reach the uterus with your fingers?
It is unlikely that you will be able to feel the body of the organ itself, since it is located quite deep. Can you touch the cervix with your fingers? It is possible, and some women regularly determine the condition of their own cervix in order to find out whether ovulation has occurred. To carry out the procedure, use the instructions:
- Wash your hands with soap and trim your long nails to avoid scratching the vaginal lining.
- Take a comfortable position. Some women prefer to have their cervix examined in a sitting position.
- Insert your middle finger deep into your vagina until it hits something hard. This is the cervix. It is impossible to move your finger further than that.
If ovulation occurs, the humidity and consistency of the cervix changes. It becomes soft and pliable, due to the increased work of the glands inside the vagina, a large amount of mucus is formed.
The length of the vagina varies depending on the monthly cycle. So, before the onset of menstruation, it shortens, and with the onset of ovulation it becomes longer.
Dimensions
The female reproductive system undergoes a number of changes throughout life in terms of the size and structure of organs. This is due to both the growth of the body, hormonal surges and changes, and special physiological processes, such as menstruation or pregnancy.
The normal length of the vagina is about 8 cm along the front wall, while its length along the back wall can reach 10 cm. When aroused, this distance can increase by several centimeters.
Since the inner surface of the vagina is clearly folded, it can stretch and take on different shapes, widths and lengths. This feature is necessary so that the fetus can pass through the birth canal.
In turn, the length of the cervix is approximately 3-4 cm. Thus, the distance from the entrance to the vagina to the uterine cavity is about 13-14 cm. The diameter of the canal is usually no more than 8-9 mm, increasing to 10-11 mm during pregnancy and during menstruation. The actual length and diameter of the canal, as well as the distance to the uterine cavity, can be determined using an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
Vaginal prolapse
The term vaginal prolapse usually refers to the prolapse and prolapse of the internal genital organs:
- vagina,
- cervix,
- body of the uterus.
These include disturbances in the location of the uterus, the walls of the vagina in the pelvic area, from the displacement of organs to the exit of the vagina or even beyond it.
Such disorders are usually treated surgically. According to world statistics, about 11% of women in different age groups are at risk of surgical correction of prolapse (prolapse or protrusion of the pelvic organs from their natural position).
Risk factors for vaginal and other pelvic organ prolapse
- vaginal delivery;
- violation of the synthesis of sex hormones (improper synthesis or lack of hormone replacement therapy in the perimenopausal period);
- physical exercise;
- “systemic” connective tissue insufficiency: the patient or close relatives (mother, sister) have varicose veins of the lower extremities, hernia, mitral valve prolapse;
- traumatic injury to the pelvic floor as a consequence of improper management of childbirth through the natural birth canal, subsequent incorrect comparison of tissues after perineal ruptures during childbirth.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms of vaginal and uterine prolapse
Most often, prolapse or prolapse of the vaginal walls occurs in people of late reproductive age and the elderly. The main complaints of patients can be divided into two groups: firstly, directly related to prolapse of the vagina and pelvic organs and, secondly, related to the functional characteristics of adjacent organs.
The main symptoms of the first group: sensation of a foreign body in the vagina, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, the presence of a so-called hernial sac in the perineum. The second group includes symptoms of urinary disorders, including acute urinary retention or urinary incontinence that occurs during stress, urge urinary incontinence, and constipation. These are accompanied by frequent complaints of pain and discomfort during sexual activity.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose prolapse of the vagina and other genital organs, a doctor will do the following:
- taking anamnesis;
- gynecological examination. As a rule, a gynecological examination is sufficient to make a diagnosis. On examination, the cervix extends beyond the vaginal ring. A stress test is performed, in which the patient is asked to push for a more reliable assessment of prolapse, and a cough test: checking urine loss during exercise;
- instrumental examination: ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Prevention and treatment
There are measures to prevent the development of prolapse (prolapse) of the vagina and other pelvic organs, for example, Kegel exercises, but these preventive measures are effective if the exercises are started in a timely manner and carried out regularly. There is also outpatient conservative treatment in the form of installation of a vaginal ring to maintain the correct position of the uterus. If preventive measures are ineffective and the woman desires to continue her sexual life, surgical treatment is performed.
Today, there are several approaches to performing the operation: vaginal hysterectomy, laparoscopic supravaginal amputation and robot-assisted surgery.
Vaginal hysterectomy with vaginal wallplasty
- own tissues. In this case, no incisions are made on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, all manipulations are carried out through the vagina, including the removal of the uterus without appendages, then the excess vaginal tissue is cut out and sutured, thus forming the anterior and posterior walls of the vagina;
- the use of a mesh prosthesis installed through the vagina, the so-called anterior prolift (Proliftanterior). In this case, an incision is made in the anterior wall of the vaginal mucosa, retreating 2-3 cm from the urethra, with the help of special conductors, the mesh is passed through the membrane of the obturator foramen and the mesh is removed through incisions on the skin on the right and left in the perineal area at a distance of 3-4 cm from the genital slit. Then the mesh is straightened over the back surface of the bladder and fixed without tension. After which the defect in the anterior vaginal wall is sutured with separate sutures. This operation is possible while preserving the uterus. When pelvic organ prolapse is combined with symptoms of urinary incontinence, it is possible to carry out a combined treatment: installing an anterior lift in combination with a TOT mesh prosthesis (transobturator sling. See urinary incontinence).
Correction of pelvic organ prolapse using prolift surgery is performed mainly in elderly, postmenopausal women.
Laparoscopic supravaginal uterine amputation and sacrocervicopexy
This is a two-stage operation for uterine prolapse, consisting of laparoscopic supravaginal amputation of the uterus and sacrocervicopexy - fixation of the cervix with a mesh prosthesis to the sacrum. This operation is performed mainly on women of late reproductive age. 4 incisions are made on the skin, trocars for instruments are installed in the right, left iliac region and above the pubis. With the help of bipolar energy and in a sharp way, the body of the uterus is removed, leaving the cervix, according to indications, in combination with removal or without appendages on both sides. Then it is performed by isolating the periosteum in the sacral area. After removal of the uterine body, a mesh prosthesis is fixed to the cervical stump in front and behind. Then the mesh prosthesis is fixed to the periosteum of the sacrum. After which the prosthesis is closed by the peritoneum. The removed uterus is removed from the abdominal cavity. The pelvic cavity is drained. Then sutures are placed on the anterior abdominal wall.
Robot-assisted surgery
Since 2014, our hospital has been able to perform this type of operation using the Da Vinci robotic surgeon.
5 incisions are made on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, trocars are installed through which operating instruments are inserted, Da Vinci robot manipulators are fixed to the trocars, with the help of which the surgeon located at the console controls the instruments. The stages of the operation are the same as for the laparoscopic approach. Thanks to the 3D image of the robot's camera, a neurosaving effect of the operation is achieved. With the help of more precise movements of the robot's instruments, a 2-fold lower volume of intraoperative blood loss is achieved compared to laparoscopic access. The rehabilitation period when performing surgery with the help of a robot is significantly shorter in duration than during laparoscopy, as a result, the patient returns to normal life faster.
After operation
The very next day after the operation, the patient is allowed to stand up, drainage is removed from the pelvic cavity, and she is allowed to take liquid food and walk. The postoperative period usually takes from 5 to 7 days. Sutures from the anterior abdominal wall are removed on the 7th day. The period of complete rehabilitation takes up to 1 month. Sexual rest is prescribed for 2 months. Limit physical activity to 5 kg for life. 2 months after the operation, the patient is invited for a follow-up examination.
The cost of operations for vaginal and uterine prolapse can be found here .
← Back
How does the vagina change with age?
Studies have not confirmed the difference between vaginal depth in women who have given birth and those who have not given birth.
The size of the vagina does not change over time. This issue was studied by scientists, but the studies did not find a connection between the depth of the organ and the woman’s age.
Gynecological examination. What do you need to know?
But the labia can change their appearance. This happens because over time, the production of estrogen in a woman’s body decreases, and this leads to a decrease in the level of fat and collagen.
The tissue of a woman's external genitalia may change color, become darker or thinner during menopause, when the body experiences critical hormonal changes.
Some women may find that their vagina changes its characteristics after giving birth. During this period of life, the tissues of the organ actually undergo changes in connection with the general preparation of the woman’s body for the birth of a child. However, later the vagina again acquires the size and shape that it had before childbirth.
Scientists found no differences in vaginal length in women who had given birth compared to those who had not yet undergone childbirth.
If a woman thinks her vagina has changed after giving birth, her doctor may recommend Kegel exercises. This type of physical activity involves tensing and relaxing the muscles responsible for controlling urination. Performing exercises helps strengthen the pelvic floor.
Vagina: size matters!
home
>
Health - news
When it comes to the role of size in the intimate sphere, men feel the center of attention.
And completely in vain! It turns out that the size of the vagina matters.
And here some representatives of the stronger half often find themselves at the mercy of ridiculous myths regarding their chosen ones.
Thus, the most common myth is about the alleged dependence of the depth and width of the vagina on sexual activity and the number of partners. This is an extremely ridiculous misconception! Just as a man’s penis is a given to him by nature, so women are born with vaginas that are completely different in depth.
When a woman is not aroused, the length of the vagina averages from 7.5 to 13 cm, and the width is such that 2-3 fingers fit there. In a state of arousal, two-thirds of the vagina can stretch another 5 cm and expand up to 5 cm. This is due to the fact that during arousal, the female genital organs shift in the upper direction.
Sometimes you hear about the “infinite stretchability of the vagina.” Perhaps this is true. During sexual arousal, one third of its upper part narrows due to blood flow, and the vaginal tissues become firm and elastic. Thanks to this, the vagina tightly clasps the inserted penis. Therefore, the thickness of the penis does not have the importance that most men give it. The vagina is so flexible that it can accommodate any size penis. There is even a concept - vaginal accommodation, which means that with a permanent partner, a woman’s vagina adapts to the size of this man’s penis.
Although there is no strict relationship between a woman’s height and the size of the vagina, large sizes are somewhat more common in tall women, and small sizes in short women. However, according to obstetrician-gynecologists, there are women of short stature (less than 150 cm) whose vaginal depth is 11-14 cm,
and, conversely, tall women who had it small. For example, with a height of over 170 cm - 6-8 cm.
Minor changes in the size of the vagina throughout life are possible: the depth of the vagina may decrease - but this may be the result of childbirth or artificial termination of pregnancy, as a result of which the uterus “drops”, but definitely has nothing to do with the woman’s sexual activity! Also, in women who are indifferent to sexual activity, and in those who experience difficulties in achieving orgasm (or who do not experience it at all), atrophy of the vaginal muscles is observed: it seems to be lazy, does not want to clasp the shaft of the penis, and is in an eternally relaxed state , and therefore gives the impression that it is very wide.
If you compare the average sizes of the penis and vagina, it turns out that they are perfectly adjusted, they fit each other exactly. Despite this, many men prefer women with narrow,
a small vagina, like that of virgins. But if the partner feels the woman’s vagina as small and tight, regardless of the length of the inserted penis, it means that she is not aroused enough and is not yet ready for intercourse
VAGINA AFTER BIRTH
Vaginal dilatation after childbirth is even more common. This is due to the fact that after childbirth, the vaginal walls relax for a while. This can provoke psychological problems in the family and cooling between spouses.
A man may experience decreased sexual sensitivity due to insufficient girth of the penis due to vaginal enlargement. To restore vaginal tone, women must do special gymnastics. Moreover, it must be done both during pregnancy and after childbirth (already 7-10 days after birth). Once again, we are talking about special Kegel exercises.
The technique of sexual intercourse can help in many ways to overcome these inconveniences.
Unfortunately, exercises and poses that reduce the size of the vagina cannot always solve the problem. What to do? To come to terms with this fact, as one comes to terms with old age, death, and everything inevitable? Of course not!
In this case, the only way to restore the lost harmony of sexual life is intimate plastic surgery.
A vagina that is too wide can also cause delayed ejaculation in a man due to reduced mechanical stimulation during friction.
Intimate plastic surgery for suturing the size of the vagina - posterior colporrhaphy returns the fullness of intimate life at any age.
na-med.ru
Full-width / Middle / Regular Print Version
Changes during pregnancy and after childbirth
What is the distance to the uterine cavity during pregnancy? As labor approaches, the cervical canal begins to shorten and by the end of 38-39 weeks it can reach 1.5-2 cm. At this time, the distance from the entrance to the vagina to the uterus can be 9-10 cm.
In the initial stages of pregnancy, the length of the cervical canal remains within 4-4.5 cm, and the distance to the uterus remains within normal values. Along with this, structural changes occur, which help determine pregnancy in the early stages. During a gynecological examination, your doctor may notice the following signs:
- the neck, namely its outer part, acquires a bluish tint;
- the walls become loose and soft;
- the cervical region drops slightly lower, and starting from the second trimester, the normal position returns again.
Similar changes are characteristic of the vagina during pregnancy. It becomes somewhat longer, however, the distance to the uterus remains almost the same, since there is a simultaneous descent of the cervical canal towards the end of gestation. There is also a softening of the walls and some swelling of the tissues.
What size should a vagina be?
In the ancient world, female genitals were considered something dirty and indecent. Jokes involving female genitalia were considered extremely obscene. But the situation changed dramatically with the development of anatomy. The term “vagina” appeared, an organ connecting the clitoris and female labia with the uterus. And as the vagina was studied, more and more interesting facts about this organ became known. However, the question of what size a woman should have a vagina never ceases to worry.
Type of act
During sexual arousal, the width should be 3 fingers maximum, the length should not be 15 centimeters. Difference from the normal state: during sexual caresses and increased sensitivity, the size can increase up to 5 centimeters, as muscle displacement occurs.
Question: The size of the vagina changes after childbirth, with age or not.
Answer: Unfortunately, the size changes because the muscles of the walls are stretched. It is recommended to stimulate with gels and suppositories once every three years.
This is due to the fact that the muscles wear out and elasticity is lost. In this case, you need to choose good products for yourself: suppositories or gel lubricants.
If you know the length and size of the vagina and you understand that it needs to be narrowed, the following will help:
| 1 | Vagilex | Hot new product ! Suppositories that eliminate muscle strains, age-related and physiological changes. Instant vaginal tightening. Discount until December 31, 2020! | td> |
These products eliminate distension, pelvic organ prolapse, vaginal wrinkles, farts, discoloration and unpleasant odor.
Vaginas come in different sizes
Women should know that their vaginas are different and come in different sizes, both in length and width. To understand what we are talking about, we offer you photos of the sizes of cups for menstruation.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
VAGINA (vagina; vagina, pussy, yoni); The internal genital organ of a woman, involved in the process of sexual intercourse, is part of the birth canal during childbirth. In an adult woman, it is a muscular-elastic tubular formation (a hollow tube of muscles, a muscular elastic tube) 7-9 (8-12) cm long, 2-3 cm in diameter, lined with mucous membrane, located in the pelvis between the urethra and the urinary tract. bladder in front and rectum in back. The upper end of the vagina covers the cervix, the bottom ends with the opening of the vagina (opens into the genital slit), which in virgins is limited by the hymen. 1 - Bartholin's glands open at the vestibule of the vagina; 2 - perineum; 3 - urogenital diaphragm; 4 - anus (anus); 5 - vagina; 6 - anterior vaginal vault; 7 - cervix; 8 - posterior vaginal fornix; 9 - rectum; 10 - rectal uterine pouch (Douglas space); 11 - serous membrane of the uterus; 12 - uterosacral ligament; 13 - serous membrane (peritoneum); 14 - funnel; 15 - suspensory ligament of the ovary; 16 - fallopian tube; 17 - fringes; 18 - ovary; 19 - uterus; 20 - round ligament; 21 - vesicouterine pouch; 22 - bladder; 23 - pubic fusion (symphysis); 24 - pubis; 25 - urethra (urethra); 26 - clitoral vein; 27 - body of the clitoris; 28 - G-zone; 29 - head of the clitoris; 30 - urethra; 31 - hymen (remains); 32 - labia minora; 33 - labia majora In a calm state, the walls of the vagina are located opposite each other, but it is exceptionally flexible. During intercourse, the vagina expands to accommodate the penis, and during childbirth it expands several times, forming the birth canal through which the baby passes, moving from the uterus to the outside world. Between the walls of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix, a depression is formed - the vault of the vagina, in which the anterior, posterior (deepest) and lateral parts are distinguished. The vagina is surrounded on all sides by peri-vaginal tissue; It is abundantly supplied with blood from the systems of the uterine, internal genital and inferior vesical arteries. Numerous veins form a venous plexus around the vagina, blood from which enters the internal iliac vein system. Lymph from the vagina flows into the inguinal, iliac and sacral lymph nodes. The vagina is innervated by branches of the inferior epigastric plexus, pelvic splanchnic and sacral spinal nerves. The vaginal wall consists of mucous (mucosal), muscular and adventitial (connective tissue) membranes. Mucosa (mucosa) is very thick, it forms several longitudinal and circular folds, which allows it to stretch during childbirth, and is covered with stratified squamous epithelium, in which three main layers are distinguished: basal, intermediate and superficial, or functional. The epithelium undergoes changes due to changes in the secretion of ovarian hormones due to age, phases of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. The greatest thickness of the epithelium is observed in women of childbearing age in the middle of the menstrual cycle; at the same time, the cytoplasm of epithelial cells contains the maximum amount of glycogen. Similar changes occur in newborn girls due to the influence of estrogenic hormones from the mother. The mucous tissue of the vagina changes in response to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle and, above all, to the level of estrogen. Under the influence of estrogen, glycogen is synthesized (a form of carbohydrate storage). Bacteria present in the vagina help convert glycogen into lactic acid, which acidifies the vaginal environment. When treated with antibiotics, these bacteria are suppressed and the acidity of the vaginal environment decreases, resulting in the growth of fungi and bacteria. Vaginal mucosa is lubricated by fluids penetrating the vaginal walls, especially during sexual arousal. The vagina is also lubricated by mucus coming from the uterus. There are no glands in the vaginal mucosa. Before the onset of puberty, girls whose hormone levels have not reached adult levels have thin vaginal walls and are prone to bacterial infections due to glycogen deficiency. During reproductive age, poor hygiene, use of contraceptives, sexual intercourse and wearing tight, non-absorbent underwear can lead to vaginal infections. In menopausal women, due to decreased estrogen levels, vaginal mucosal cells lose glycogen, and the acidity of the vaginal environment decreases, which affects the vaginal tissue, which becomes fragile, easily injured and susceptible to infection. Hormone replacement therapy, which many women undergo during menopause, stops the thinning of the vaginal mucosa and restores acidity in the vagina. The lack of estrogen observed in women during menopause affects the blood supply to the pelvic area and the soft tissues of the vagina, impairs the elasticity of the pelvic structures and can lead to internal displacement of the uterus, bladder, rectum and intestines. The most common symptom of vulvo-vaginal diseases is acute itching, which can be caused either by infection or, in rare cases, by precancerous and cancerous conditions. Any complaints of this kind should undergo a medical examination (see also lubrication; cleanliness and sexual odors; episiotomy). 1 - Funnel of the fallopian tube; 2 - Ovary; 3 - Fallopian tube; 4 - Fundus of the uterus; 5 - Vaginal part of the cervix; 6 - Vagina; 7 - Clitoris; 8 - Cavernous body of the clitoris; 9 - Bulb of the vestibule; 10 - Large gland of the vestibule (Bartholin's gland); 11 - Vaginal vestibule and vaginal fissure; 12 - Vaginal artery; 13 - Internal pudendal artery; 14 - Round ligament of the uterus; 15 - Uterine artery; 16 - Internal iliac artery; 17 - Ovarian artery; 18 - Supporting ligament of the ovary The vestibule of the vagina is surrounded by a cavernous (cavernous) body (bulbus vestibuli; vestibular bulb; vestibular bulb), which fills with blood during sexual arousal; after sexual intercourse (coitus), the enveloping muscle (M. bulbocavernosus) again displaces the blood. In the lower part of the vestibule of the vagina there are the mouths of the Bartholin's glands, which secrete a mucous secretion that lubricates the entrance to the vagina. In the upper third of the vestibule of the vagina there is the mouth of the urethra. The clitoris juts into the vestibule from above. The ability to have an erection is given to it by another cavernous body, which is attached to the pubic bone with two oblong projections and is surrounded by muscles. The cervix projects into the posterior part of the vagina; it forms the vaginal vault (fornix) here. The posterior segment of the fornix is at the height of the pouch of Douglas, which is the outermost part of the abdominal cavity, lined with peritoneum. Since the uterus is most often tilted forward, during a criminal abortion, the pouch of Douglas can be punctured, which causes life-threatening inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis). As a result of contractions of its own muscle fibers and pelvic floor muscles, the vagina can change shape, diameter and depth. During the period of sexual arousal, the blood supply to the vagina increases, transudation (the release of the liquid part of the blood from the capillaries and venules) into the vaginal lumen increases, and its lengthening occurs. The mucous membrane has the ability to absorb sperm plasma. During pregnancy, due to hypertrophy and hyperplasia of muscle and connective tissue elements, the vagina lengthens and expands. During childbirth it stretches greatly; about a week after birth, its size decreases, but the vaginal lumen remains wider. The vaginal mucosa does not have glands, and the liquid part of its contents is formed as a result of transudate (liquid part) of blood from the surrounding vessels. The vaginal lumen contains 0.5-1.5 ml of liquid, which is a transudate of blood and lymphatic vessels, the secretion of the endometrial glands and the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. Mixed with this liquid are desquamated cells of the upper layers of the vaginal epithelium, mucus from the cervix, a variety of bacterial flora, as well as lactic acid, which promotes self-cleaning of the vagina. Depending on the type of cells, the nature of the bacterial flora and the pH of the vaginal contents in adult women, there are 4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness. (determined by laboratory examination of a vaginal smear). At the first degree of purity, the reaction of the vaginal contents is acidic, it contains many epithelial cells and Dederlein vaginal bacillus (lactic acid bacteria), and there are no leukocytes and pathogenic microbes. Thanks to the activity of bacteria, lactic acid is formed, which creates an acidic environment that is destructive for pathogenic microorganisms and promotes self-cleaning of the vagina. With the second degree of purity, individual leukocytes appear in the vaginal contents, the number of lactic acid bacteria decreases, individual pathogenic microbes are identified, and the reaction of the environment is acidic. The third degree of purity is characterized by the presence in the vaginal smear of a significant number of leukocytes and individual representatives of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora (for example, streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli, sometimes Trichomonas), a small number of Dederlein bacilli, a weakly acidic or slightly alkaline reaction of the vaginal contents. With the fourth degree of purity, the vaginal smear contains no lactic acid fermentation bacteria (Dederlein bacilli), a variety of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora are detected (streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli, sometimes Trichomonas, chlamydia), a large number of leukocytes, and the reaction of the vaginal contents is alkaline. Normally, the vagina has the first or second degree of cleanliness, and its contents have a whitish color and a characteristic odor; the third and fourth degrees of purity indicate the development of inflammatory processes. A healthy woman usually does not feel vaginal discharge. The appearance of copious discharge most often indicates an inflammatory disease (vulvititis, vulvovaginitis). In newborn girls, the reaction of the vaginal contents is sour, Dederlein's rods are found in it. Subsequently, until puberty, the reaction of vaginal contents is alkaline or neutral. It can contain staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli, which plays a certain role in the occurrence of inflammatory processes. By about 13 years of age, the reaction of the vaginal contents shifts to the acidic side, which is due to the formation of lactic acid by the newly appeared Dederlein bacillus. The external appearance and consistency of vaginal discharge depend on hormonal levels and the vaginal environment. This is especially true for the mucous secretions of the cervix. A significant amount of uterine mucus is produced simultaneously with the egg during about half the cycle, its color and structure vary depending on the environment in the vagina for the rest of the time. Special mucus accompanies the penetration of sperm into the uterus. The lubricant released in the vagina during sexual arousal is also different from other secretions. The vaginal mucosa is surrounded by a muscular layer, especially developed immediately behind the outermost part of the vagina - the entrance to the vagina, limited by the hymen. Muscle tissue contains muscle ligaments that run longitudinally and circumferentially. These muscles are well supplied with blood, and during sexual arousal the vaginal wall swells. The muscles of the pelvic floor connect to the walls of the vagina in the middle (along the length) of the vagina. These muscles are responsible for keeping the vagina erect, tight and hard. Exercising these muscles prevents them from weakening. Many women can consciously contract and relax these and other muscles and thereby contribute to more successful sexual intercourse (Kegel exercises). The size of the entrance depends on the degree of tension of the muscle that locks the entrance to the vagina. In the normal state, the edges of the entrance touch; when the muscle relaxes, as well as during sexual arousal, the entrance may gape. Branches extend to the vagina from the common uterovaginal plexus (plexus uterovaginalis), the lower anterior sections of which are called the vaginal plexus. The uterine and vaginal plexuses are connections of a large number of nodes and nerve branches of varying sizes and shapes, forming a relatively dense network. Surrounding the vagina, the nerve branches pass to its walls, forming a dense network, in the loops of which smaller nodules lie. The vaginal part of the common uterovaginal plexus is connected with the plexus of the bladder and rectum, and also through the uterine plexus with the plexuses of the ovaries and the nerves surrounding the fallopian tubes. Vaginal examination is part of a gynecological examination and includes internal vaginal (digital) examination, rectovaginal examination, and examination using vaginal speculum. Examination of the vagina in children and virgins using special small vaginal speculums with a lighting system or an optical device (vaginoscope) is called vaginoscopy. To examine the vaginal mucosa, a colposcope can be used (an optical binocular system mounted on a tripod, with interchangeable eyepieces that magnify the image by 4-40 times, and an illuminator). For vaginal malformations, rectal-abdominal wall, X-ray (vaginography) and ultrasound examination are used. A cytological examination of a vaginal smear (determining the cellular composition and the ratio between the number of cells of different layers of the epithelium) makes it possible to judge the hormonal activity of the ovaries. During sexual arousal, transudate begins to sweat from the venous vessels of the vaginal walls and secretion is released by the Bartholin glands and glands of the vestibule of the vagina, as a result of which it becomes moist, which facilitates the insertion of the penis (or even testicles) of a man. If they are insufficiently secreted, insertion of the penis becomes painful. In this case, the use of lubricants is recommended. At the same time, the woman’s external genitalia become more sensitive to tactile stimulation, which causes a specific mental sensation of sexual arousal. The vagina is not a completely sensitive organ, but it does have two particularly sensitive areas: the vaginal opening and the “G” area. The vaginal opening responds to stretching. The most pleasant movements for a woman are the withdrawal of the penis when the upper edge of the head scrapes along the folds of the continuation of the clitoris at the upper part of the entrance to the vagina. If a woman’s vagina is too wide, then you can insert another finger or two in addition to the penis and stretch it. When stretched, a woman feels a special buzz. With the remaining fingers you can caress the perineum and clitoris. Seminal fluid gradually flows out of the vagina after sexual intercourse. A healthy vagina cleans itself as a result of the work of the endocrine glands. A woman needs to keep only her external genitalia clean and wash herself daily. Therapeutic douching is carried out as prescribed by a doctor. In a non-excited state of a woman, the length of the vagina is 7.5-13 (10-12) cm, and the width is such that 2-3 fingers fit there. If a woman is not aroused, the walls of the vagina will touch. When aroused, they become moisturized and stretched: two-thirds of the vagina can stretch another 5 cm and expand to 5 cm, which facilitates the insertion of a penis. This increase in size is due to the fact that when aroused, the female genital organs shift in the upper direction. During sexual intercourse during sexual arousal, when a woman is fully aroused (during the platophase), one third of its upper part narrows due to blood flow, and the vaginal tissues become elastic and elastic, and the inner part (the volume of the vagina near the cervix) expands and increases, thereby creating a reservoir for sperm. The narrowing of the outer third of the vagina helps partners feel each other better, which further increases the level of sexual arousal. Although the vagina in its outer third tightly encircles the inserted penis and therefore the thickness of the penis does not have the importance that most men attach to it, in the further two-thirds of the vagina (especially in multiparous women) the penis can dangle freely. Therefore, it is important to maintain the tone of the vaginal muscles (Kegel exercises). Impaired elasticity of the vagina, its narrowness due to infantilism, injury, and disease can serve as an obstacle to normal sexual life. Insufficient stimulation (both psychological and physical), scarce vaginal discharge (insufficient lubrication of lubrication with gland vagina), due to low estrogen levels, vaginal infections, some diseases or medication, reduce the genital response. If a woman makes sexual intercourse before she is completely excited, and is not ready for sexual intercourse, the penetration (introduction) of a penis into the vagina can be painful, unpleasant, difficult and even impossible. If the intercourse still occurs, then the vagina is irritated, frictions cause pain in the inguinal region, and an orgasm is not achieved. In this case, it is important to extend preliminary caresses and, before the introduction of the penis, use water -based lubrication (or use male discharge at the stage of active sublimation of the seed). In addition to sexual function, the vagina serves as a channel for removing menstrual blood and the secret of the glands of the cervix and the body of the uterus, in childbirth the vagina together with the neck forms the tribal canal and is stretched to sizes that can skip out the child. The accumulation of air in the vagina and the “release” of it during intercourse with an “indecent” sound are quite common. The air can begin to accumulate in the vagina after childbirth. This can also be a sign of a hernia or uterine prolapse. Some experts consider a similar manifestation of a symptom of weakening or premature muscle relaxation. But if there are no physical deviations, you can consider such a sound a sign of a good sexual reaction. Most doctors advise treating this with humor and include, for example, music. The structure of the vagina partly resembles the rectum of a person. There is an Eskimo legend about the unfortunate fate of Nukarpiartekak. He comes to the needle to the girl and finds that, figuratively speaking, he bit more than he can swallow. He still begins to make love with the beauty, but then, to his indescribable horror, he discovers that he is entirely sucking in the vagina. Gradually, part after part, it disappears in it. On the morning of the next day, Nukarpiartecak is no longer there, and now his ownerless Kayak lies on the banks of the river. A beautiful girl comes out of her needle to urinate, and the skeleton of her yesterday’s lover falls out of her body. The female of the elephant vagina is just a spacious pipe almost 50 cm long. It can be expected that this channel can significantly increase with the introduction of the male penis. There is a huge virgin pole across the vagina. The vagina of the female whale is a long elliptical shape of the gutter, which is located directly above the anus, is from 1.8 to 2.4 m in length and, if necessary, can lengthen when the penis is introduced.
Way out
Women who can consciously squeeze and unclench their pelvic floor muscles are able to increase or decrease the size of the vaginal opening. According to Dr. Tarney, increasing the tone of your pelvic floor muscles can help combat the feeling of a “wide vagina.” For these purposes, it is very useful to perform Kegel exercises - among other things, specific gymnastics for the intimate muscles helps to improve the overall quality of sex.
According to a study published in the Australian Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology in 2008, women who regularly performed Kegel exercises reported experiencing more intense sexual satisfaction than those who did nothing. The only problem with such gymnastics is that most women do not understand how to do it correctly.
Sources
- https://www.syl.ru/article/195369/new_kakaya-dlina-vlagalischa-u-devushek-i-jenschin-maksimalnaya-dlina-vlagalischa
- https://medmaniac.ru/glubina-vlagalishha/
- https://vashamatka.ru/info/skolko-santimetrov-do-matki-i-kakova-glubina-vlagalishha.html
- https://ginekola.ru/ginekologiya/matka/rasstoyanie-ot-vlagalishha-do-matki.html
- https://omolodet.ru/kak-uznat-razmer-vlagalishhaj/
[collapse]