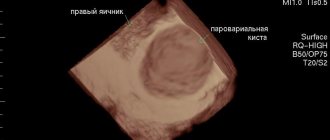
Paraovarian ovarian cyst is a cavitary single-chamber tumor-like neoplasm that forms from the ovarian appendage. Such a cyst is located in the space limited by the layers of the uterine ligaments, between the fallopian tube and the ovary. A paraovarian cyst arises from the tubules of a rudimentary paraovarian formation (periovarian appendage) when embryogenesis is disrupted. Pathology is most often detected during reproductive age (from 20 to 45 years), less often - in puberty (up to 15 years). In Russia, paraovarian ovarian cysts are detected by gynecologists in 9-17% of all ovarian formations.
The oncology center of the Yusupov Hospital diagnoses, treats and rehabilitates patients with ovarian cysts, including paraovarian cysts. The clinic provides conservative and surgical treatment 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. After treatment, patients can undergo a rehabilitation course according to a special program developed by specialists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Types of paraovarian cysts
The paraovarian ovarian cyst is inactive, has slow growth and can remain small in size for a long time. The sizes of paraovarian cysts are:
- Small (up to 3 cm) - such formations do not have legs;
- Large (more than 4 cm) - can form a stalk consisting of an ovarian ligament or fallopian tube. The presence of a leg in a cyst can lead to various complications - torsion, which is accompanied by severe pain.
- Giant (up to 30 cm) - reaching such sizes, the formation leads to disruption of the functioning of neighboring organs and tissues.
There are the following types of paraovarian ovarian cysts:
- Paraovarian cyst on the right - most often occurs in women of childbearing age, but can also form in teenage girls. A paraovarian cyst of the right ovary usually forms between the ovary and the uterus. Often such cysts are pedunculated;
- Paraovarian cyst on the left - most often forms on the left ovary, but can also be diagnosed on the right. The formations reach impressive sizes, but they rupture extremely rarely. May also have a leg;
- Paraovarian serous cyst - has the appearance of a mobile, elastic cyst with a stalk. The cyst has a thin-walled shell, inside of which there is serous fluid;
- Paraovarian cyst during pregnancy – it is characterized by small size, does not affect the development of pregnancy and is not hereditary. Typically, such a cyst does not form a pedicle, but if it does, then if it is twisted, urgent surgical intervention is indicated.
Traditional methods of therapy
Traditional methods should be used with caution, and the effectiveness of such therapy is questioned. Here are some recipes:
- Herbal tincture . You need to take 30 g of aloe, St. John's wort, yarrow and wormwood. Add 500 ml of vodka or alcohol, 500 g of honey, 2 liters of boiled water. Place the mixture in a thermos and leave for 24 hours. Take 10 g orally before each meal.
- Tampon product . You should take a glass of sunflower oil and heat it to a boil. Add 20-30 g of beeswax to it and wait until it completely dissolves. Then add boiled yolk to the mixture. The mixture is cooled, then heated again, and so on several times (two or three). After this, tampons are formed and, if necessary, applied to a gauze base. It should be placed in the vagina once or twice a day.
We recommend reading about ovarian wasting syndrome. From the article you will learn about the causes and symptoms of premature ovarian failure, its diagnosis and treatment. And here is more information about why the stomach on the right hurts during menstruation.
Paraovarian cyst occurs in 3-5% of women. It never acquires signs of malignancy. However, when it reaches a large size, during inflammation or other acute conditions, it becomes necessary to remove it. In other cases, you should simply observe the formation regularly with a doctor.
https://youtu.be/XkNm8thZYvU
Causes of development of paraovarian cyst
There are many theories about the development of paraovarian ovarian cysts. Among them, the most common reasons are:
- Inflammation of the internal genital organs (ovary or uterine appendages);
- Diseases of the endocrine system (hyperthyroidism and others);
- Early puberty;
- Termination of pregnancy (abortion);
- Sexually transmitted diseases;
- Use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Pregnancy;
- Disturbances in the development of the periovarian appendage in embryogenesis;
- Pathological maturation of follicles in the ovaries;
- Excessive exposure to the sun or solarium;
- Overheating in saunas, baths, hot baths;
- Constant stress;
- Bad ecology;
- Taking certain medications.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear only if the volume of the cyst exceeds 5-6 cm. Until this time, there are no clinical manifestations, or they are only slightly expressed. The main signs indicating the presence of pathology:
- increase in abdominal size. This sign is more noticeable in women of thin build, when the cyst reaches 10 cm or more;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen, bursting, pulling, stabbing or aching pain, most often on the affected side. The pain syndrome can intensify with any physical activity;
- frequent urge to urinate (accompanied by pain) and defecate. In some cases, a growing cyst can cause severe constipation;
- change in the nature of menstruation: an increase, or vice versa – a decrease in the amount of blood.
Good afternoon. I was diagnosed with a paraovarian cyst on my right ovary with a diameter of 10 mm. Half a year ago. I recently had an ultrasound done, she has grown and now her size is 17 mm. The doctor advised it to be removed by laparoscopy. I am 23 years old, I have never been pregnant, the cyst itself does not bother me. Tell me, is the operation really necessary and will they save my ovary? (Irina, 23 years old)
Hello Irina. The fact that your cyst has grown by almost 1 cm in six months is, of course, not very good. It is this type of cyst, alas, that never resolves, and therefore you can only get rid of it in one way - surgery. Don’t be afraid of the operation, with such a size of the tumor it will go quickly, and of course they will leave the ovary for you. Decide to remove it, and you will save yourself from this problem for life.
Symptoms of a paraovarian cyst
Symptoms of a paraovarian ovarian cyst depend on its type and size. Small cysts are usually asymptomatic. Large cysts have the following symptoms:
- Bursting, pulling and aching pain in the side, lower abdomen or lower back;
- Severe pain on the right or left, depending on the location of the cyst;
- The presence of a round formation on palpation;
- Discomfortable sensations not associated with ovulation or menstruation;
- Increased pain during physical activity;
- Frequent and painful urination, abnormal stool;
- In case of complications - symptoms of acute abdomen;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Abdominal enlargement not associated with pregnancy;
- Changes in blood volume during menstruation (decrease or increase);
- Pathological discharge during menstruation.
Therapeutic approach
After receiving the results of the diagnostic examination, a decision is made on the choice of method for removing the cystic formation. It is worth immediately noting that treatment without surgery is not provided in this case.
If the tumor is small in size, then wait-and-see tactics are used. In this case, the patient should be constantly under the supervision of a gynecologist to assess changes in the course of the pathological process.
For large paraovarian cysts, surgical intervention is always prescribed. Any operation is planned and requires preliminary preparation. To do this, the woman must be admitted to the hospital several days before the procedure to undergo a full examination.
A prerequisite is to pass:
- electrocardiography;
- fluorography.
It is also necessary to undergo urine and blood tests.
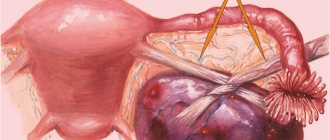
Two techniques are used to remove a cystic tumor.
Laparoscopy
This operation is used when the size of the cyst is no more than three centimeters. The procedure is minimally invasive. To carry it out, special equipment is used. Removal of the cyst is carried out as carefully as possible so as not to injure the ovarian tissue.
The laparoscopic method involves several small incisions through which all manipulations are performed. After the intervention, there are practically no traces left on the body.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The duration of the rehabilitation period is no more than five days.
Laparotomy
Prescribed for cystic formations larger than 3 centimeters. To reach the cystic growth, an incision is made along the line on the abdomen. The operation is traumatic. The possibility of damage to healthy tissue cannot be ruled out.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
The recovery period occurs for at least 10 days. Everything will depend on the patient’s condition.
The choice of surgical intervention is carried out individually for each case. In this case, it is important to take into account such indicators as size, localization and degree of the pathological process.
After surgical treatment, antibiotic treatment is always carried out.
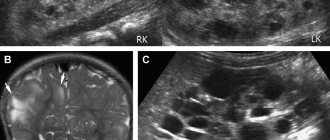
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms appear that may indicate the presence of a paraovarian ovarian cyst, as well as when planning pregnancy, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
When you first contact the Yusupov Hospital, highly qualified doctors will conduct an examination on a gynecological chair to detect a pathological formation. To confirm the diagnosis, additional instrumental and non-instrumental research methods are used, which have European quality certificates:
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (transvaginal - through the vagina and transrectal - through the rectum);
- Echoscopy;
- Laparoscopy.
Left-sided paraovarian cyst during pregnancy
Every expectant mother, when a tumor is discovered, immediately begins to worry about the health of the baby and is interested in the negative impact of the cyst on pregnancy. Doctors are confident that this diagnosis does not affect the fetus or the woman’s health. However, if the tumor was detected before pregnancy, it must be removed immediately. After surgery, the body needs at least a year to recover from stress and recover. If a cyst is detected during pregnancy, no medications are prescribed, since this type of formation can only be treated with surgery or alternative means.
Paraovarian ovarian cyst: treatment in Moscow
Unlike functional ovarian cysts, paraovarian cysts do not go away on their own. If the process is asymptomatic and the cyst is small in size, then the patient can be under dynamic observation by the attending physician. However, the most commonly used surgical treatment method is enucleation of the cyst, due to the fact that paraovarian cysts are diagnosed in patients of reproductive age and are often complicated. Before planning a pregnancy or undergoing IVF (in vitro fertilization), removal of the cyst is also recommended.
In the oncology department of the Yusupov Hospital, surgical treatment of paraovarian cysts is performed laparoscopically, or less commonly, laparotomy. Surgeons with extensive experience use gentle methods, as a result of which they manage to preserve the ovary and fallopian tube. If necessary, targeted puncture of the paraovarian cyst is used with aspiration of the serous contents and the simultaneous injection of alcohol into it, which promotes closure of the cavity.
Possible complications and consequences
Paraovarian cysts themselves do not pose a danger due to the fact that they do not have the ability to become malignant. The main thing is to diagnose them in time and conduct dynamic monitoring. They do not prevent pregnancy, but if they are large, they can compress the fallopian tubes, resulting in the possibility of blocking their patency. During pregnancy, they do not have any effect on the fetus.
Large cysts can be complicated by torsion of the pedicle, suppuration or rupture:
- Twisting can occur with a sudden change in body position or heavy physical activity. Torsion contributes to the appearance of sharp, cramping pain in the lower abdomen (a stronger feeling of pain occurs on the affected side). They are not controlled by painkillers, so emergency hospitalization and removal of the formation are indicated.
- Suppuration occurs as a result of bacteria entering the cyst. It festeres, and all signs of inflammation appear: pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, nausea, fever. In this case, urgent removal of the cyst is indicated.
- Cyst rupture carries the same threat as peritonitis. With strong tension in the abdominal muscles, heavy physical activity, or sharp turns, the membrane may rupture, causing the liquid contents of the formation to enter the abdominal cavity and cause an inflammatory reaction. Accompanied by sharp dagger pains throughout the abdomen, radiating to the groin and lower back. In this case, under no circumstances should you hesitate; you need to call an ambulance for further hospitalization. An emergency laparotomy is performed with removal of the cyst and lavage of the abdominal cavity.
As a rule, doctors try to preserve a woman’s reproductive organs as much as possible. But in some cases this becomes impossible, and then the ovary and fallopian tube must be removed along with the cyst. Since the second ovary remains intact and is functioning properly, pregnancy is possible.
A paraovarian ovarian cyst cannot recur after removal.
Paraovarian ovarian cyst: treatment without surgery
A paraovarian ovarian cyst is the only type of formation that does not become malignant, but still significantly worsens a woman’s quality of life. Therefore, the interest of patients with this diagnosis in how an ovarian mass can be cured without surgery is natural.
In the early stages of cyst development, when there is no need for surgical treatment, you can try treatment with folk remedies. For this use:
- Aloe, yarrow, St. John's wort, wormwood (all herbs 50 g each), ethyl alcohol (0.5 l) and honey (0.5 kg). Plants are poured with 3 liters of boiling water and poured into a thermos overnight. Then the remaining ingredients are added to the broth. Take 1 tbsp orally. l three times a day before meals
- Olive or sunflower oil (200 ml), 30 g beeswax and boiled egg yolk. The olive oil is heated, wax and crumbled yolk are added. Bring to a boil and leave to cool. The procedure is repeated 2 times. The resulting ointment is applied to a tampon, which is kept in the vagina for a long time for 5 - 8 hours.
The use of traditional methods must be agreed upon with the attending physician after examination and diagnosis.
Treatment of paraovarian ovarian cysts is carried out in the best oncology center in Moscow, as well as in the network of partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital. The staff includes experienced doctors and nurses who ensure a comfortable stay in the hospital. You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone.
Author
Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Head of the Oncology Department, oncologist, chemotherapist, Ph.D.
Reasonable restrictions in the presence of a paraovarian cyst
In the presence of a paraovarian cyst, intense physical activity associated with straining and sudden changes in body position is undesirable: rotation, jumping, somersaults, falls, etc.
The possibility of performing physical exercises (types of exercises and intensity of the training process) and other physical activity should be individually agreed with the attending physician.
Sexual activity with a paraovarian cyst is not contraindicated. However, during sexual intercourse, it is advisable to refrain from positions that cause or intensify discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen.
If you have a paraovarian cyst, it is advisable to refrain from thermal procedures, including taking general baths with a water temperature above 38°C.
It is advisable to refrain from sunbathing in natural conditions and solariums.
There are no special features or dietary restrictions for paraovarian cysts.
The presence of a small paraovarian cyst (up to 2.5 cm in diameter) is not a contraindication for sanatorium treatment in Pyatigorsk.
A paraovarian cyst is not a contraindication for travel by underground (metro), land (car, train and other rail transport), river, sea and air transport. Horseback riding is not recommended.
A paraovarian cyst is not a contraindication to the insertion of an IUD (intrauterine device, “spiral”).
At the Women's Health Resort Clinic, you can conduct an ultrasound examination using an expert-class device with 3D/4D, elastography, power Doppler and color Doppler mapping modes in order to identify a paraovarian cyst.
The remote high-density LED monitor of the ultrasound machine allows the doctor to comment on the “live” image, and the Patient to actively participate in the discussion of what she saw.
The ability to record ultrasound data on a disk and/or flash card (USB drive) allows you to save objective information for doctors and an electronic medical history. Cost of the study
The cost of a pelvic ultrasound is 1,550 rubles.
The resort clinic for women's health operates both for paid services and in the voluntary health insurance system.
Each doctor at the Clinic has long-term experience, several specializations and is able to comprehensively assess the situation.
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Cherenkov V. G. Clinical oncology. — 3rd ed. - M.: Medical book, 2010. - 434 p. — ISBN 978-5-91894-002-0.
- Shirokorad V.I., Makhson A.N., Yadykov O.A. The state of oncourological care in Moscow // Oncourology. - 2013. - No. 4. - P. 10-13.
- Volosyanko M.I. Traditional and natural methods of preventing and treating cancer, Aquarium, 1994
- John Niederhuber, James Armitage, James Doroshow, Michael Kastan, Joel Tepper Abeloff's Clinical Oncology - 5th Edition, eMEDICAL BOOKS, 2013
Diagnosis of the disease
Before symptoms appear, the cyst is often diagnosed completely by accident, during a routine examination. If the size of the formation exceeds 5 cm, there is a high probability that the doctor will “see” the cyst during a gynecological examination in the chair. In addition to ultrasound examination and MRI, for an accurate diagnosis, the doctor can prescribe a diagnostic laparoscopy to the patient: under general anesthesia, special tubes are inserted into the abdominal cavity to determine the exact size and location of the cyst, as well as take a biopsy to differentiate the tumor.
In addition, the woman is prescribed hormone tests to assess the state of her hormonal levels.
The essence of pathology
A paraovarian cyst is a tumor-like formation that forms from the epididymis.
The cyst is localized in the space between the broad ligaments of the uterus along with the fallopian tube and ovary. It is a formation that has a cavity inside itself and originates when embryogenesis is disrupted from the periovarian appendage (rudiment).
Most often, a paraovarian cyst appears in women aged 20 to 40 years, and extremely rarely - at puberty.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
Paraovarian cysts are not that uncommon these days. Most often found during reproductive age. They are not dangerous because they do not undergo malignancy. But they can increase sharply in size if hormonal imbalances occur. Typically, women are advised to undergo dynamic monitoring by a doctor.
Prognosis for treatment of dangerous formation
Based on the fact that during surgery all elements of the paraovarian cyst are removed, the prognosis is quite favorable. Even if this neoplasm was discovered at one stage of the patient’s pregnancy. In this situation, the doctor constantly monitors the condition of the cyst and eliminates it only after the birth of the child. As for conception itself, it is quite likely, however, there is a risk of torsion of the cyst stalk, which can occur with an enlarged uterus. Therefore, a woman is recommended to plan a pregnancy only a month after removal of the cyst. Nevertheless, with timely diagnosis and treatment, it is possible not only to avoid complications, but also the very occurrence of a paraovarian cyst.
Is it possible to cure the disease with folk remedies?
As mentioned earlier, even the most modern drugs are not able to remove the tumor, let alone treatment at home. However, medicinal herbs can, at least slightly, slow down the growth of tumors and even out hormonal levels. However, before turning to healing plants for help, you should consult an experienced specialist. According to herbalists, the most suitable recipes for this pathology are:
- ointment made from sunflower and linseed oils, with the addition of egg yolk and beeswax;
- alcohol tincture with wormwood, St. John's wort and yarrow;
- decoction of yarrow and rosehip.
Hello, Doctor. I do not know what to do. Just yesterday, during an ultrasound, the doctor discovered a cyst in me, its diameter is 6 cm. How can it be dangerous? (Elena, 34 years old)
Hello, Elena. In your case, the pathology can lead to dangerous complications, such as: suppuration, rupture of the capsule with the release of contents into the abdominal cavity, or torsion of its legs (if there is one). All 3 complications are very dangerous. I advise you to quickly consult a gynecologist for advice. Cysts of this size can only be treated surgically.