- September 19, 2019
- Gynecology
- Svetlana Pavlova
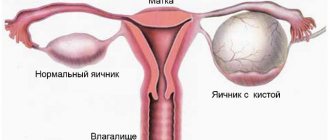
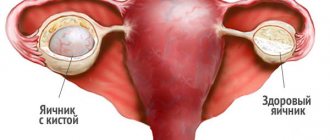
A benign growth on a stalk, inside of which there is a secret that accumulates in the ovarian tissues, is called a cyst. Its size varies from one to twenty centimeters. Is there a cure for ovarian cysts? This is the first question the doctor is asked after a tumor is diagnosed. Depending on the type, both conservative and surgical therapy are used. In most cases, cysts are treatable and do not cause complications.
Causes of the disease, consequences
The main factors for the appearance of a neoplasm are:
- hormonal disbalance;
- stagnation of fluid in the pelvis;
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- various infections;
- endocrinological diseases;
- defects in the development of reproductive organs;
- early onset of menstruation;
- abortions;
- poor nutrition;
- regular stress;
- bad habits;
- negative influence of the social environment.
A cyst occurs on one or both ovaries, in the latter case it becomes a cause of infertility. In addition, the following complications of the disease are possible:
- Twisting of the leg - the cause of sepsis is tissue necrosis. The capsule may suddenly burst and its contents spill into the peritoneum, leading to peritonitis. In these cases, the following clinical picture is observed: vomiting, sharp pain, i.e. symptoms of an acute abdomen.
- The large size of the tumor disrupts the blood flow, as it compresses the blood vessels. Pressure on the intestines and bladder makes it difficult to function. Signs appear only after the size of the cyst increases to seven to eight centimeters in diameter. The woman begins to experience nagging pain in the area of the ovaries, an enlarged abdomen and its asymmetry.
Is there a cure for ovarian cysts? Certainly. Conservative or surgical, determined by the nature of development and degree of danger, which depend on its type.
What it is?
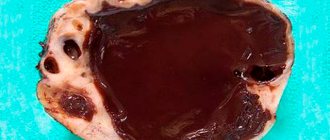
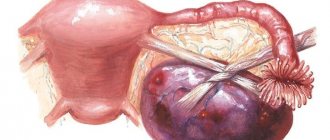
A multilocular (multilocular) ovarian cyst is a benign formation that looks like a vesicle on ultrasound.
The interior of the cavity is divided by thin partitions into several chambers.
There may be two chambers (in this case the cyst is called two-chamber) or more.
Their interior is usually filled with fluid, mucus or, in case of complications, blood and pus.
A multi-chamber cyst can either initially, during the period of its occurrence, have several septa, or acquire them during the process of growth, degenerating from an ordinary single-chamber cyst.
This type of formation occurs quite often in patients, and is not a rare pathology, and under favorable conditions, the doctor will usually suggest its removal in the near future.
Characteristic differences
The tumor is characterized by the presence of dense walls of connective tissue, which are not present in a regular single-chamber cyst. These walls divide the tumor into sections, each of which can be filled with different contents.
A multi-chamber cyst is significantly larger in size than a regular one, is prone to growth, is characterized by severe symptoms and, unlike ordinary neoplasms, is practically not treated with conservative methods. That is, sooner or later the tumor will have to be removed.
How dangerous is she?
A multilocular cyst is considered more dangerous. Due to the presence of several chambers filled with different fluids, during the growth period it is more likely to damage the walls and release fluid into the abdominal cavity, which will inevitably lead to acute sepsis.
Reference. Large tumors can burst even with intense physical activity, extreme fatigue or sex.
Also, large tumors are more prone to pedicle torsion, which causes a loss of nutrition to the tumor and tissue death, leading to acute poisoning of the body with decomposition products. Multilocular cysts are much more likely than small ordinary cysts to degenerate into malignant tumors.
Classification of neoplasms
Cysts are classified according to various characteristics.
In count:
- single;
- multiple.
By localization:
- one-sided;
- double sided
With the flow:
- complicated;
- uncomplicated.
By origin:
- Corpus luteum - its occurrence is associated with the reverse development of the corpus luteum after ovulation. The reason for the formation is hormonal imbalance. There is no need to treat it; it disappears on its own.
- Follicular - formed at the site of a follicle that has not ruptured. The provoking factor is hormonal imbalance. Is there a cure for ovarian cysts? In most cases, it resolves on its own.
- Parovarian - formed from appendages and reaches large sizes.
- Endometrioid - develops from endometrial particles. The capsule is filled with old blood.
- Organic - does not disappear on its own.
- Mucinous - multi-chambered, has a bumpy surface. There is thick mucus inside the cyst. In some cases, its diameter reaches thirty-five centimeters.
- Dermoid - the internal filling is represented by mucus, fatty deposits, bones, hair.
- Functional is one of the most common forms. The main reason for its formation is associated with a malfunction of the ovaries. Dissolves on its own.
- Papillary - represents growths in the form of papillae.
- Hemorrhagic - formed as a result of hemorrhage of a follicular or corpus luteum cyst.
- Serous - a tumor filled with transparent contents, its size can be up to thirty centimeters. It most often affects women over the age of forty-five.
Types of education
Multilocular ovarian cysts come in several types, differing in symptoms, risk of development and localization:
- paraovarian nodes - always develop during the period of intrauterine development, are not a true ovarian cyst, since they are outside its tissues, and pose a danger only in the form of large multi-chamber formations;
- follicular nodes - develop if normal functioning in the ovaries fails;
- serous and mucinous cystadenoma are benign neoplasms characterized by the basic signs of a multi-chamber cyst - the presence of septa inside the bladder filled with liquid contents.
Reference. The most dangerous serous type of neoplasm. It requires surgical intervention and treatment of concomitant inflammatory processes in the body.
Drug and other treatment
How to treat an ovarian cyst without surgery? At the initial stage, when the tumor does not exceed one centimeter in diameter, and the patient’s condition is satisfactory, the doctor chooses a wait-and-see approach or recommends taking medications if the detected cyst occurs due to a hormonal imbalance.
Doctors opt for the following medications, the course of which lasts from two to six months:
- Hormonal - “Duphaston”, “Zhanin”, “Terzhinan”, “Novinet”.
- Vitamins – “Ascorbic acid”, groups A and B.
- NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen.
- Sedatives – “Novopassit”.
In addition, during this period, women are prohibited from excessive exercise, smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages, taking hot baths, visiting the sauna, and also cannot sunbathe. Such precautions will protect against cyst rupture. Additionally, the doctor may advise following a diet, acupuncture, drinking mineral water, and gentle physical exercise under the supervision of an experienced instructor.
How to determine whether you can get rid of an ovarian cyst without surgery
First of all, if you notice unpleasant symptoms, such as bloating, squeezing pain in the abdominal area, a feeling of swelling in the pelvic area, you should consult a women's doctor. He will conduct an examination and refer you for examination, since only with the help of ultrasound can the exact location, size, shape and filling of the capsule be determined.
After analyzing the information received, the doctor decides on the patient’s management tactics (observation, conservative therapy or surgery).
Symptoms of a multilocular cyst in the ovary
The symptoms of a multilocular tumor do not differ from those of a single-chamber tumor in the ovary. Among the main signs are the following:
- Pain in the lower abdomen of a periodic or constant nature. Localization can be on both the right and left sides. In addition, pain can radiate to the lumbosacral region.
- If the tumor has grown to a large size, then pressure is created on the peritoneum. This results in shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
- The abdomen may increase in size.
- A feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse that was not previously felt.
- Any physical activity provokes the appearance of pain.
- The menstrual cycle is disrupted, usually in the form of a delay in menstruation for varying periods, in rare cases – periodic spotting.
Important. If the pain increases sharply, and previously unnoticed symptoms appear, then seek the help of a gynecologist, since this can threaten not only the health, but also the life of the fair sex.
In addition, you need to pay attention to the formation of such signs:
- The temperature has increased, but there are no other symptoms of colds.
- The presence of lethargy, dizziness and loss of consciousness. This may be evidence that a cyst has burst or intra-abdominal bleeding has appeared.
- The number of hairs in the chin area, nasolabial fold, etc. has increased.
- The weight dropped sharply, although the diet and physical activity did not change.
- Formation of a lump in the lower abdomen.
Conservative method of treatment: features
Doctors assure that it is possible to cure an ovarian cyst without surgery in the following cases if the capsule:
- does not exceed five centimeters in size;
- refers to functional;
- identified less than two months ago;
- has no signs of malignant growth;
All tumor markers must be within acceptable values.
With the conservative method, the doctor may recommend:
- “Utrozhestan”, “Duphaston” - in case of a deficiency or excess of a certain hormonal substance in a woman’s body.
- “Diane”, “Janine”, “Regulon” - suppress hormones that are synthesized in the ovaries and affect the growth of cystic formation.
- “Indomethacin”, “Longidaza” - to relieve inflammatory processes.
- “Lincomycin”, “Vancomycin” - if the cause of the neoplasm is a pathogenic microflora.
- “Wobenzym”, “Timalin” - to increase the body’s resistance to diseases and infections.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Many women leave positive reviews on the Internet about the treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery. When using drug therapy for neoplasms, the following advantages are noted:
- cycle restoration;
- improving the condition of hair and dermis.
The disadvantages include a long course of treatment and side effects from taking hormonal drugs.
Diagnostics
In order to diagnose a two-chamber cyst of the right ovary, doctors send the woman for a series of studies. The doctor can determine enlarged ovaries and painful areas of the abdomen during a gynecological examination.
Ultrasound examination is the most informative diagnostic method today. Additional equipment (Doppler meter and vaginal sensor) makes it possible to obtain more accurate results. Using ultrasound examination, observation of a two-chamber tumor lasts at least two months.
Important! Gynecologists do not begin treatment of a complicated two-chamber cyst without puncture of the posterior vaginal vault. This procedure is performed to detect blood or fluid in the peritoneal area.
Magnetic resonance imaging in some cases gives more accurate results than ultrasound. This method allows you to determine the condition of the ovaries with a two-chamber cyst, which is difficult to diagnose.
In order to determine the type of formation, the woman undergoes a computed tomography scan. In order to exclude the possibility of the presence of cancer cells in the formation, the doctor refers the patient to have tumor markers tested. If the gynecologist suspects inflammation of the ovary or hemorrhage of the formation, the woman undergoes a general blood and urine test.
The patient must take a test for the level of human chorionic gonadotropin and a pregnancy test. These tests can detect a pregnancy that is occurring outside the uterus. If the doctor suspects that a two-chamber cyst could rupture or twist around its pedicle, he performs a laparoscopic diagnosis.
We recommend you find out: Hypoechoic formation in the ovary, what is it?
Follicular cyst
Among all types of cysts, it is considered the most harmless and occurs most often. If after ovulation the egg does not come out of the burst follicle, then it is modified and converted into a capsule. Often, such a cyst resolves on its own after several menstrual cycles. Is follicular ovarian cyst treated with drugs? They are recommended if it does not disappear naturally. In this case, the doctor recommends hormonal agents that restore the functions of the affected ovary, as well as vitamin therapy. If the neoplasm is small, then the woman is under the supervision of a medical professional. In this case, ultrasound is performed at a certain frequency, recommended by the doctor, in order to analyze the rate of growth of the cyst.
Treatment of endometrioid cyst
The neoplasm occurs as a result of the growth of the endometrium into the ovary. Healing endometrioid ovarian cysts without surgery is possible at the very beginning of the disease. The attending doctor selects hormonal therapy. Most often, the drug of choice is “Janine”.
Thanks to the successful combination of active substances, namely dienogest and ethinyl estradiol, the medication promotes the reverse development of the cyst. Analgesics and NSAIDs are indicated to relieve pain. In addition, if necessary, medications are prescribed to enhance immunity, including vitamins. If there is no effect after three months, there is a high risk of the capsule rupturing and increasing in size. It can develop into a tumor and spread to the bladder and intestines. In this case, only surgery will help.
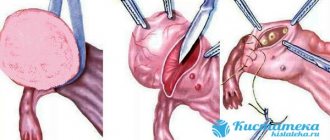
Sometimes, to get rid of an ovarian cyst without surgery, a puncture is performed under local anesthesia and its contents are pumped out. Next, the secret is sent for research. However, in some cases, surgery cannot be avoided. These include: the appearance of signs of dilated veins, pain in the abdomen, difficulties with urination and defecation, as well as a rapid increase in size or twisting of the cyst stalk, or if a danger of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm is detected.
What complications can there be?
Multi-chamber cystic pathology of the ovary gives complications much more often compared to single-chamber cysts, which occur in the form of the following consequences:
- Capsule rupture is possible when lifting weights or making a sharp turn. There is severe pain syndrome, accompanied by traumatic shock and peritonitis.
- Ovarian apoplexy - there is a violation of the integrity of the organ with hemorrhage into its cavity. The acute condition is accompanied by loss of consciousness and a drop in blood pressure below 100/60 mmHg. Art., thread-like pulse. Subsequently, suppuration and the formation of an abscess are possible when an infection occurs. When it breaks into the pelvis, severe peritonitis and sepsis develop.
- Torsion of the cyst stalk - this condition leads to tissue necrosis with the subsequent development of clinical symptoms.
- Malignancy of a cystic formation - late diagnosis of cystadenoma or lack of treatment often leads to the development of a malignant neoplasm with a further unfavorable prognosis.
All complications of a multilocular ovarian cyst are acute conditions that require immediate help. Regular preventive examinations with ultrasound monitoring of the pelvic organs will allow timely detection of the presence of a benign cyst and its high-quality treatment.
List of sources:
- Beloglazova S. E. Modern tactics of managing patients with benign tumors and tumor-like formations of the ovaries. Moscow, 1999.
- Kuznetsova E. P., Serebrennikova K. G. Modern methods for diagnosing tumor formations and benign ovarian tumors / Fundamental Research, 2010. – No. 11.
All information is provided for informational purposes. Do not self-medicate. At the first sign of disease, consult a doctor.
Functional neoplasms
In this case, it is possible to treat ovarian cysts without surgery. The doctor prescribes hormonal medications, which, when taken, resolve small luteal and follicular tumors. Preference is given to progesterone-based drugs, such as Marvelon, Regulon, Janine. They reduce the concentration of estrogen in the blood. To normalize the ratio of hormones, Duphaston is often prescribed for a course of up to three months. The regimen and dose are selected individually based on the results of laboratory tests.
It is important to know that after the age of fifty, functional cysts, which have the ability to resolve on their own, do not form. This is due to the fact that menstruation and related processes occurring in the reproductive organs cease. It is at this age that the risk of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm increases. Cysts in pregnant women usually disappear by the sixteenth week. In the early stages, it is possible to take Duphaston under the supervision of a physician.
Use of the drug "Duphaston" in therapy
Can ovarian cysts be treated with this hormonal drug? Dydrogesterone, which is the active ingredient of the drug, replaces natural progesterone, performing all its functions. When used to treat neoplasms of a follicular nature, it promotes the correct transition of the first phase of the menstrual cycle to the second and does not give the endometrium a chance to grow. If the cyst is endometrioid, then long-term use of Duphaston is indicated, as it prevents the appearance of new capsules.
During its use, in rare cases, unwanted reactions occur - hemolytic anemia, rashes on the dermis, migraine, hypersensitivity of the mammary glands, bleeding. The latter goes away after increasing the dosage. Treatment with this medication is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. If a woman becomes pregnant during Duphaston therapy, she must immediately notify her doctor, who will develop a plan for gradually stopping taking the pills. During pregnancy, the medicine is approved for use until the twelfth week, then the dose is reduced and treatment is stopped.
Gynecologists claim that the effectiveness of this remedy is quite high. The dose and treatment regimen are selected for each patient individually, taking into account the general nature of the pathology, test results and examination data. After taking the medicine, women note that hormonal levels improve and the cycle normalizes. The drug does not contribute to weight gain and body hair growth, and the timbre of the voice does not change.
Prevention
Knowing about the potential causes, you can prevent the occurrence of the disease. It will be difficult to eliminate all factors, but it is partially possible to cope with some issues.
Prevention includes the following activities:
- weight control - excess weight affects hormonal levels;
- maintain an active lifestyle;
- undergo a preventive examination with a gynecologist at least once a year;
- if you have a history of cysts, then you should avoid activities that stimulate blood circulation in the pelvic organs, such as going to the solarium, spending a long time on the beach;
- Do not self-treat with hormonal drugs.
A cyst with a septum is not polycystic, that is, it does not threaten a woman with infertility. But this does not mean that such a neoplasm does not require monitoring and treatment. Any tumor is unpredictable, therefore an appropriate response to it is required - visiting a doctor and following all his instructions.
Treatment of functional cysts with folk remedies
How to cure an ovarian cyst without surgery, using the experience of herbalists? There are many traditional medicine recipes to get rid of this problem. Here are some of them:
- Immerse the core of a small onion in honey, wrap it in gauze and insert it into the vagina at night for ten days.
- Pour one hundred grams of walnut shell partitions into one and a half liters of water and cook for about twenty minutes. For two weeks, take one hundred milliliters daily.
- Pour one hundred grams of acacia flowers into half a liter of a forty percent alcohol solution. Infuse for seven days, take a tablespoon three times a day for a month.
- Grind young burdock leaves and squeeze out the juice. Drink two tablespoons three times a day, course - a month. The finished juice can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than three days.
Symptoms of a mass formation of the left ovary
Most often, the presence of cysts does not cause any symptoms. They can only be seen during an ultrasound examination. However, 10% of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome experience the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- bloody discharge from the vagina between cycles;
- pain in the lower abdomen on the left side;
- pain during sex and after physical activity;
- attacks of sudden acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- irregular menstruation;
- false urge to urinate or defecate;
- palpation of the cyst, enlargement of the abdomen;
- infertility;
- obesity;
- fever;
- constipation;
- tachycardia.
The symptoms of a left ovarian cyst are very similar to manifestations of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, heart or pancreas. It is very important to undergo a full medical examination if any signs of illness appear. Even in the absence of symptoms, for preventive purposes, women need to visit a gynecologist once every six months.
Diet food
Can ovarian cysts be treated without surgery? Of course, a properly formulated diet can help solve this problem, but only on the condition that the neoplasm is insignificant and does not pose a threat to life. Medical professionals recommend a diet aimed at normalizing hormonal levels with the mandatory inclusion of:
- raw or stewed vegetables (eggplant, zucchini, cabbage);
- cottage cheese;
- apples;
- berries;
- fermented milk products;
- lean meats;
- sea fish.
Strictly prohibited:
- tea, coffee, alcohol-containing drinks, as well as with gas;
- fast food;
- cocoa;
- baked goods;
- chocolate;
- sweets;
- spices;
- seasonings;
- fatty and fried foods.