The essence of pathology
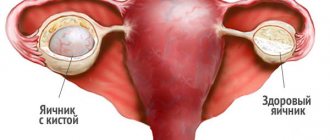
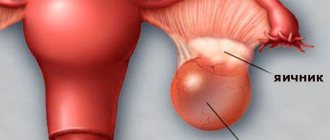
An ovarian dermoid cyst is a neoplasm of an organ with contents inside the capsule formed from germ cells (particles of skin, hair), which, due to disturbances in intrauterine tissue differentiation, are stored in the ovaries.
This tumor is also called dermoid or mature cystic teratoma. Diagnosed in 20% of all cases.
It begins its formation in childhood, but manifests itself already during the period of hormonal changes (puberty). It is characterized by slow growth and can reach 12-16 cm.
Usually localized on one ovary, rarely on both at once. It degenerates into a cancerous tumor in 1-3% of cases. It has a pedicle along which blood vessels pass, so there is a high risk of torsion. According to ICD-10, the disease has code D27 .
Ovarian dermoid cyst: causes, symptoms, treatment, reviews
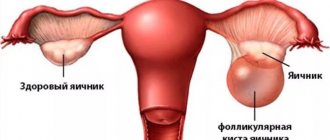
An ovarian dermoid cyst is a pathological growth formed from fragments of germinal tissue. A characteristic feature of a tumor is its specific content. Inside the formation, hair, teeth, nails, the beginnings of adipose and bone tissue, and the secretion of the sebaceous glands are found. In the literature, this type of disorder is called mature ovarian teratoma or dermoid.
The neoplasm occurs when the developmental processes of the embryo are disrupted: a layer of cells of one of the germ layers ends up in places where it should not normally be.
The reason why dermoid restructuring of the appendages occurs has not yet been clarified.
However, increased cell growth is observed at the time of hormonal changes in the female body: puberty, pregnancy and lactation, menopause, taking hormonal medications.
Ovarian dermoid cyst: ICD code 10
According to the international classification of diseases, dermoid neoplasms are classified as non-inflammatory growths on the appendages and are coded N83.2.
Mature cystic teratoma of the ovary, in its composition, is mainly represented by developed tissues of the body, and has a more favorable prognosis.
An immature dermoid tumor with a predominance of undifferentiated structures needs to exclude malignant degeneration.
Symptoms of ovarian dermoid cyst
It is almost impossible to detect a small embryonic tumor. Dermoid transformation of the adnexa is considered the most asymptomatic type of benign adnexal tumors. At an early stage, it is possible to make a diagnosis only with the help of auxiliary research methods during a random medical examination.
Important! Usually a dermoid cyst is detected in the right ovary, which is the first to develop in utero and has a more massive blood supply.
The occurrence of complaints during dermoid transformation is associated with the growth of formation, the gradual replacement of healthy ovarian tissue and compression of blood vessels. When the tumor reaches a large size (7-10 cm), the following symptoms of the tumor are noted:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloating, bloating, feeling of heaviness;
- an increase in waist size, a bulge may appear on the affected side;
- disturbances in the processes of urination and defecation.
Dermoid tumor can be complicated by suppuration and torsion of the pedicle. Capsule rupture rarely occurs due to sufficient film thickness. With the development of such complications, the patient’s condition sharply worsens and a clinical picture of an acute abdomen is observed. Women need surgery.
Photo of ovarian dermoid cyst
Dermoid tumor or teratoma literally translates as a terrible formation. This is due to the specific, extremely unpleasant contents of the tumor.
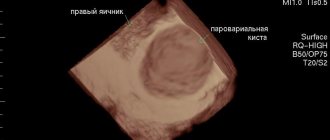
Ovarian dermoid cyst ultrasound photo:
How often does an ovarian dermoid cyst become inflamed?
If an increase in body temperature, chills, weakness, or increased pain on the affected sides occurs, you should think about suppuration of the formation. Dermoid tumors rarely become inflamed. Usually, the complication occurs in patients with chronic diseases of the reproductive systems, if the doctor’s instructions are not followed and an infection occurs.
How quickly does an ovarian dermoid cyst grow?
It is believed that ovarian teratodermoid cysts grow extremely slowly. It usually takes several years for unpleasant symptoms to appear.
However, due to the possibility of developing complications in the form of torsion of the leg, suppuration of the dermoid, it is recommended to remove it as soon as possible.
There is always a risk of malignancy of a dermoid formation - the degeneration of benign growth cells into a malignant one.
Important! A dermoid cyst grows slowly, but the tumor does not regress and constantly increases in size.
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications to dermoid laparoscopy. If necessary, intervention may be delayed. Laparoscopy of an ovarian dermoid cyst is postponed during pregnancy, in the case of a small formation that does not have a negative effect on the fetus and does not cause unpleasant symptoms. In other cases, you should not wait for the process to worsen; the dermoid tumor is removed.
Treatment
Dermoid tumor is treated exclusively by surgery. No medications affect the rate of development of the formation. Due to the likelihood of malignant degeneration and the development of complications, it is recommended to remove even a small ovarian dermoid cyst. When teratomas are detected, it is preferable to perform laparoscopic excision of the lesion.
Important! The volume of intervention depends on the size of the cyst, the advanced state of the condition, and the occurrence of complications. In severe cases, the ovary may have to be removed.
Reviews about treatment without surgery for ovarian dermoid cysts
Dobrovolskaya Svetlana Mikhailovna, 32 years old, Tula A year ago, a large dermoid cyst was found in the left ovary. Doctors advised to remove the formation, but I did not agree. For some time I tried to use folk remedies, but there was no result. Due to the deterioration of the condition, I had to agree to laparoscopy.
After the operation, she recovered quite quickly. Tikhonova Daria Olegovna, 34 years old, Perm After IVF in the second trimester, a formation measuring 3.5 cm was found on the right appendages. It turned out to be a dermoid cyst. There were no complaints, the pregnancy was desired and proceeded normally. During gestation, the teratoma was not touched, the size of the tumor was simply controlled.
After childbirth, doctors insist on removing the formation.
Reviews about laparoscopy for ovarian dermoid cyst
Meleshko Katerina Vasilievna, 29 years old, Kerch Two years ago I was diagnosed with a dermoid tumor of the right ovary. The doctor advised to remove the formation. On the doctor’s recommendation, I chose gentle laparoscopy and am planning to have another child.
A wedge-shaped resection was performed on the appendages, and the cyst did not return. She recovered quickly, leaving two barely noticeable scars. I'm happy with the result! Tamara Mikhailovna Mayorova, 28 years old, Stavropol. Instead of the desired pregnancy, an ultrasound showed a 2 cm cyst in the right ovary, presumably dermoid.
However, there were doubts that the formation could turn out to be a follicular cyst and resolve on its own. The gynecologist clearly advised me to remove the tumor, not to wait, because I really want to give birth. To be sure, we decided to do an x-ray; a dermoid tumor was confirmed.
After a short preparation, laparoscopy was performed. Histology showed a mature teratoma. Now I'm waiting for a refill.
Forecast
Although the ovarian dermoid cyst is characterized by extremely slow growth, it requires surgical treatment to eliminate undesirable consequences.
If the teratoma is removed in a timely manner before complications develop, the prognosis for women's reproductive health is favorable. At an early stage, it is possible to completely excise the pathological node with minimal damage to the surrounding ovarian tissue.
Without surgery, there is a risk of inflammation, suppuration, rupture and malignant degeneration.
In this case, the prognosis is unfavorable: the looming threat to life at the time of the operation does not make the issue of preserving the opportunity to conceive a child a priority.
Source: https://ginekola.ru/ginekologiya/yaichniki/dermoidnaya-kista-yaichnika-prichiny-vozniknoveniya.html
Mechanism of formation and reasons for development
Germ layers (layers) appear during the division of the embryo in the womb . There are three types:
- external (ectodermal),
- middle (mesodermal),
- internal (endodermal).
Then the layers shift, and various tissues, structures and organs are formed from them. Sometimes a chromosomal malfunction occurs, which results in a disruption in the division of layers, and cells from one leaf are split off and attached to another.
As the organism develops, cells foreign to a given sheet remain in the tissues that formed this layer. In particular, particles of skin, hair, and cartilage remained in the ovarian tissues, forming a dermoid .
The growth and development of cysts can be triggered by hormonal changes in the body during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. Abdominal trauma can also be a provoking factor. Thus, hormonal changes and injuries are the impetus for development, and chromosomal disruption is the cause of the tumor .
Treatment
In this case, treatment is only surgical; conservative methods are not effective. Puncture is used only in the most extreme cases, when the operation is not possible for medical reasons.
Most often this concerns older people. In this case, the contents of the tumor are aspirated, followed by rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
As for the traditional removal of a neck cyst, such an operation is performed under anesthesia; excision can be carried out either through the mouth or externally, depending on clinical indicators. To prevent relapse, excision is performed together with the capsule.
Removing lateral tumors is more difficult, since the tumor is localized near blood vessels and nerve endings.
If the patient has already been admitted with a purulent process and formation, then the tumor will be opened and drained, followed by removal of the fistulas. All fistulas, even thin and inconspicuous ones, must be excised, as they can cause a relapse.
To clarify their location, the surgeon may first inject a staining agent (methylene blue, brilliant green).
After the operation, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy. You should also carry out regular dressings with mandatory treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic substances.
Symptoms of neoplasm
At the initial stage, the dermoid does not manifest itself in any way. The tumor does not cause hormonal disruptions and does not disrupt the menstrual cycle, so it can be diagnosed by chance during a preventive ultrasound. As the tumor grows, the patient may experience the following symptoms :
- Pulling pain in the lower abdomen.
- Distension, pressure inside the abdominal cavity.
- Thin women experience an increase in abdominal circumference.
- Frequent urination.
- Intestinal dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea).
- When inflammation occurs, the temperature rises.
- In case of torsion, there are general signs of intoxication: nausea, vomiting, fever, severe pain.
Read our article about what to do in case of torsion of an ovarian cyst.
Prevention and prognosis
Mature teratomas have a favorable prognosis. Due to the presence of a stalk of the tumor, it is recommended to remove it even if it does not cause discomfort. Otherwise, there is a risk of sudden torsion of the leg with subsequent inflammation. In addition, with a teratoma, a woman is at risk of complicated pregnancy.
Immature dermoid cysts have a poor prognosis. They undergo long-term treatment followed by constant monitoring of the condition.
There is no specific prevention that would guarantee the absence of the development of ovarian dermoid cysts. The main actions are aimed at reducing the risk of abnormal pregnancy in order to prevent the development of a pathological process in the fetus. They include a healthy lifestyle before and during pregnancy, a balanced diet, the absence of bad habits, and a responsible attitude towards your health.
At the Yusupov Hospital, you can undergo regular gynecological examinations, which will allow you to suspect pathology in time. Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide consultations to women planning a pregnancy to eliminate possible risks for the mother and unborn child.
Author
Yulia Vladimirovna Kuznetsova
Oncologist
How is it diagnosed?
The tumor is diagnosed during a gynecological examination. A round, elastic, painless formation can be felt on the ovary. It is mobile and located on the side of the anterior edge of the uterus. Then additional research :
- The most informative diagnostic method is ultrasound. With its help, the size of the formation, wall thickness, and blood supply are determined.
- If there is doubt about the diagnosis, a CT or MRI is prescribed. Using layer-by-layer photographs of the tumor, you can verify its benign nature.
- A blood test for tumor markers is required to exclude oncological processes.
- Laparoscopy is the most reliable method. Using the camera, you can obtain an accurate image of the tumor and differentiate it from other types.
- If inflammation and suppuration are suspected, a puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix is performed.
What it is?
Ovarian dermoid cyst belongs to the group of teratomas, tumors whose development is associated with impaired embryogenesis.
Its distinctive feature is its capsular structure, which indicates the maturity of the teratoma.
Inside this thick-walled cyst you can find teeth, hair, skin cells, liver, brain and other elements that are normally present in other parts of the body.
In oncological practice, among cysts of other types, the probability of the appearance of ovarian dermoid is about 15%. This benign formation can very rarely transform into squamous cell carcinoma. The risk of malignancy is 1-3%. Typically, women who develop a dermoid cyst in their body do not notice its manifestations. Only when it reaches a large size does symptoms appear. This type of tumor can grow up to 15 cm or even more.
A dermoid cyst can form on both the left and right ovary; its treatment does not change.
Treatment methods
There is a high risk of the cyst degenerating into cancer.
Therefore, when a dermoid is detected, doctors insist on its surgical removal . The large size of the tumor causes significant discomfort to the patient. However, there are some conditions where surgical treatment is not possible, for example:
- In childhood. If a cyst is diagnosed in a girl, but is small in size and does not cause discomfort, the doctor chooses a wait-and-see approach with regular ultrasound monitoring.
- In the presence of other diseases of the genital area in the acute period. First, concomitant diseases are treated, and then the issue of surgery is decided.
- During pregnancy. If the cyst does not put pressure on other organs and does not interfere with the development of the fetus, it is not touched. Monitoring the condition of the tumor is mandatory.
Unfortunately, you cannot do without surgery - drug treatment and the use of folk remedies cannot in any way affect the disappearance of such a cyst. In medical practice, not a single case of its spontaneous resorption has been recorded.
The use of hormonal drugs can only aggravate the situation, provoke tumor growth and its malignant degeneration.
Therefore, surgical removal of the cyst is the standard treatment for mature teratoma. If the formation is uncomplicated, the laparoscopic method of removal is used. The extent of surgical intervention depends on the patient’s age, her desire to have a child, and the size of the cyst.
Click to view (do not watch for the impressionable)
There are 4 types of surgery:
- Cystectomy. The formation is removed without affecting healthy tissue. In this case, all functions of the ovary are preserved. Such an intervention is possible with small sizes, uncomplicated course of the disease and the patient’s young age.
- Wedge resection. The tumor is excised along with the affected ovarian tissue. This is indicated when the cyst size is more than 5 cm and the pedicle is torsed. Then the functions of the ovary will gradually be restored.
- Ovariectomy. The cyst is removed along with the affected ovary. Indications are suppuration, necrosis. Such operations are performed on mature women during menopause.
- Adnexectomy. In the case of a malignant process, all reproductive organs and nearby lymph nodes must be removed.
In the postoperative period, the woman is prescribed the following medications:
- Antibiotics. To prevent the inflammatory process.
- Hormonal agents. They help normalize hormone levels and restore fertility.
- When immunity decreases, the use of immunomodulators is indicated.
- Vitamins strengthen the body and promote rapid recovery.
Ovarian dermoid cyst - symptoms and treatment
→ Home treatment → Women's diseases → Ovarian cyst
Dermoid cyst - what is it?
Mature teratoma, dermoid, dermoid cyst is a benign neoplasm in the ovarian tissue, diagnosed in every fifth woman with cysts.
The tumor looks like a round or oval lump, has a smooth surface, and can reach 12–15 cm in diameter.
Inside the neoplasm there are several layers of epithelium, a mass of jelly-like consistency, various derivatives of the skin are present (hence the name of the cyst): hair, subcutaneous fatty tissue, teeth, and other tissues.
Important! The probability of this neoplasm degenerating into a malignant tumor is low and is about 2%.
The reasons for the occurrence of such a cyst are not fully understood, but it is formed during the formation of the fetus. Against the background of stress, hormonal imbalance, inflammation and trauma to the abdomen, pathological changes in tissues develop during pregnancy, which becomes the cause of neoplasms.
ICD 10 code – D27
Symptoms
At the initial stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, no signs or pathological changes are observed. The tumor is most often discovered accidentally during an ultrasound or examination by a gynecologist. Deterioration in well-being is observed when the tumor reaches a significant size and causes symptoms in nearby organs that are compressed by the tumor.
Signs of pathology:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- there is a constant feeling of heaviness in the stomach, a feeling of fullness arises, it can inflate and increase in volume;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- bowel disorder is replaced by constipation.
Important! The presence of teratoma does not affect hormonal levels and the female cycle.
With a dermoid cyst, the disease can occur in an acute form - the temperature rises sharply, abdominal pain becomes acute, and severe weakness appears. When the leg of the tumor is twisted, an “acute abdomen” syndrome occurs, high temperature, severe pain that radiates to the leg.
Diagnostics
The tumor is easily palpable during examination on a gynecological chair - the doctor determines the presence of a round, movable formation that does not cause pain.
To be more informative and confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to do a pelvic ultrasound. The study helps determine the size of the tumor, the thickness of the teratoma capsule, and the density of the internal contents.
MRI and computer diagnostics are used as additional methods.
If the disease occurs in an acute form, symptoms of an “acute abdomen” occur, and urgent diagnostic laparoscopy is prescribed.
Signs of a dermoid cyst may resemble an ectopic pregnancy, so you should take a pregnancy test. To exclude the presence of malignant neoplasms, in case of mature teratoma, a study of tumor markers is carried out.
Treatment without surgery
A dermoid cyst does not resolve on its own because it contains not only fluid, but also various solid elements. Therefore, drug therapy and treatment with folk remedies are ineffective; such methods are used in rare cases.
When doctors postpone surgery:
- age up to 12 years - if the tumor does not interfere with the development and health of the girl, its size does not change, then doctors choose a wait-and-see approach, which involves regular visits to the gynecologist and ultrasound examinations;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of infectious diseases, inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system - first, drug treatment of the corresponding pathology is carried out, then surgery is performed;
- other contraindications to surgery.
As maintenance therapy, the drug Duphaston and oral contraceptives (Zhanine, Logest) can be prescribed. It is imperative to take vitamin complexes, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial medications.
To prevent tumor growth, you can prepare an herbal mixture - mix 10 g of viburnum bark, flaxseed, calendula inflorescences, add 20 g of birch leaves. Brew 220 ml of boiling water for 6 g of the mixture, simmer for 10 minutes in a water bath. Filter the medicine, divide into 5-6 equal portions, drink throughout the day. Continue treatment for 3 weeks, then take a break for 10 days.
Surgical treatment
Surgery to remove an ovarian dermoid cyst is considered the most effective treatment for the disease. The type of surgical intervention is chosen based on the woman’s age and the degree of development of the pathology.
Types of surgical intervention:
- Removal of a neoplasm without excision of undamaged tissue (cystectomy) - while the ovary itself is not affected, its integral structure and functionality are preserved. This treatment method is effective for small tumors when the cyst has not spread deep into the tissue. After 5–7 months, the scar from the operation is almost invisible, and the woman can plan a pregnancy.
- Wedge resection - the tumor is removed along with damaged tissue. The operation is performed to remove cysts, the size of which is in the range of 5–7 cm, when the base of the tumor is torsed. Within 12 months, the damaged ovary fully restores its functionality.
- Removal of one or both ovaries (oophorectomy) - a surgical method is indicated for women who do not plan to have children in the future, during menopause, in case of tumor rupture, necrosis of ovarian tissue, twisting of the pedicle, accumulation of pus in the tumor cavity.
- Supravaginal hysterectomy – removal of the uterus, tubes and ovaries.
Most often, the operation is performed using laparoscopy - the doctor makes several small incisions into which he inserts a video camera and instruments. The duration of the operation is within an hour, after 4-6 days the woman can be discharged from the hospital, further treatment will be carried out on an outpatient basis. Excised tissues are necessarily sent for histological examination.
Treatment after surgery includes hormonal therapy; it will take 6–12 months for the body to fully recover. Negative consequences after surgery are rare, the most typical are endometriosis, disturbances in the hormonal system, and infertility. Relapses occur when the tumor is not completely removed.
Important! After removal of a dermoid tumor, reproductive, menstrual and sexual function is rarely impaired.
Ovarian dermoid cyst and pregnancy
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause intensive growth of teratoma. Is an ovarian dermoid cyst removed? If the formation does not impair the functioning of nearby organs, then treatment is postponed until the postpartum period. When diagnosed with an ovarian dermoid cyst, a woman will be under special monitoring by a gynecologist throughout her pregnancy.
The teratoma itself does not affect the development of the fetus in any way, and the woman’s well-being does not deteriorate. But the growing uterus displaces the internal organs, which can cause strangulation of the cyst - the stalk of the tumor will twist, and the tumor may rupture. Therefore, doctors sometimes recommend that expectant mothers remove the tumor laparoscopically after 4 months of pregnancy.
Important! After removal of the tumor, you can plan a pregnancy no earlier than six months later.
An ovarian dermoid cyst is a benign neoplasm that forms at the stage of intrauterine development. An effective treatment is removal of the tumor. Otherwise, complications may arise in the form of twisting of the leg, suppuration of the contents, and in very rare cases the cyst may degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Source: https://lechim-prosto.ru/dermoidnaya-kista-yaichnika-simptomy-prichiny-lechenie.html
Symptoms
As previously noted, ovarian dermoid cysts grow over a long period of time.
The patient does not notice any changes in her state of health.
The neoplasm does not affect the woman’s hormonal background and is not malignant, so its manifestations appear only when it reaches a large size.
Then the cyst begins to compress the structures surrounding it, causing the girl’s condition to worsen.
Symptoms include:
- Bursting pain and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen . Painful sensations may radiate to the lower back or rectum. During physical exertion, torsion of the cyst pedicle may occur. A sign of this will be the appearance of severe and sharp pain;
- Stool disorders - due to compression of the intestines by the tumor, peristalsis is disrupted. Constipation with flatulence or diarrhea develops;
- Dysuric disorders - they are caused by the pressure of the cyst on the bladder. Frequent urination is most often observed;
- Intoxication syndrome - occurs with inflammation or suppuration of the cyst, manifested by general weakness, increased body temperature, increased sweating, impaired consciousness;
- Anemic syndrome - as the tumor increases in size, it requires more blood supply and nutrition, due to which, in rare cases, the patient may develop anemia. The cyst may also contain tissues that synthesize antigenically modified red blood cells. Because of this, autoimmune disorders and anemia are formed.
Dermoid cyst on ultrasound
This type of examination allows you to accurately assess the condition of the affected organ and provides accurate information about the formation of the tumor. Ultrasound examination allows you to identify the localization of the dermoid, determine the volume, contents of the capsule, and the effect of the neoplasm on neighboring organs. The dermoid cyst of the brow ridge, as well as dermoids localized in other areas, are determined in real time (3D, 4D projections). Ultrasound is a necessary research method for differentiating perineal dermoid cyst and mesenchymoma.
Causes
To understand how a dermoid cyst was formed, it is necessary to recall some aspects of embryogenesis, because it is during the period of fetal development that disturbances occur that contribute to the appearance of a neoplasm in the future. After the fusion of the sperm and egg in the resulting zygote, rapid cell division begins to occur, from which three main embryonic layers subsequently arise - ectodermal, mesodermal and endodermal.
Each of them will further turn into certain tissues of the developing organism. External or internal factors can cause a failure in the differentiation of cells located in these sheets. As a result, a specific cell type will be partially deposited in a place where it should not be.
Features during pregnancy
What to do if a pregnant woman is diagnosed with such a tumor?
Again, everything will depend on the size of the tumor.
If she is small, this will not affect the course of pregnancy in any way.
It should be noted that with hormonal changes that occur in a woman’s body during pregnancy, activation of dermoid growth is possible. When the cyst grows to 10 cm or more, the risk of complications increases, so it should be removed.
It is recommended to plan to conceive a child if you have a history of surgery to remove a cyst, at least 6 months after treatment.
Diagnostics
A cystic tumor with a thick wall, containing mucus and various tissues, can be determined during examination and objective examination.
If it is large, the specialist may notice some asymmetry of the abdomen.
Upon palpation, an elastic, mobile, round formation is determined.
If the size of the cyst is small, ultrasound visualizes a formation with a thick shell, the contents of which are heterogeneous, the echogenicity is different, and inclusions and calcifications are also detected.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe magnetic resonance and computed tomography. If malignancy is suspected (degeneration of a benign neoplasm into cancer), it is possible to donate blood for analysis aimed at identifying tumor markers.
Characteristic symptoms
Mature teratomas develop very slowly and may remain asymptomatic for many years. More often, women learn about the presence of a cyst during a medical examination with a gynecologist or an ultrasound scan.
The progression of dermoid growth can cause the appearance of certain symptoms. The formation tissue gradually squeezes out the ovarian tissue. The cyst begins to disrupt the blood circulation in the organ, compressing blood vessels and nerve fibers.
Common signs of a dermoid cyst:
- nagging pain, which may have unclear localization,
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach,
- frequent, difficult diuresis, which may be accompanied by burning and pain,
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract,
- increase in abdominal volume.
If complications occur, the clinical picture may be supplemented by other symptoms. When the cyst stem is twisted, the following are observed:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen,
- pain can radiate to the lower extremities, intestines,
- heat,
- pain in the abdominal wall when touched.
On a note! If the dermoid undergoes an inflammatory process, then the woman’s temperature rises sharply, loss of strength, general weakness, and fever appear.