There are different methods of contraception. Some women protect themselves from unwanted pregnancy using oral contraceptives. Others use a condom, while others resort to injection methods of protection. There are also special patches and rings that prevent the process of fertilization. And not the last place in this list is occupied by the spiral. The Mirena system has been especially popular recently. Not all women experience side effects from its use. Some people simply don’t notice the IUD and consider it an excellent means of contraception.
Description of the spiral
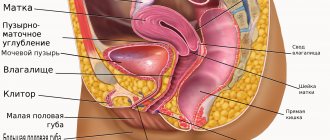
The hormonal intrauterine device is one of the most effective contraceptives. It is made of plastic and has the shape of the letter “T”. On the spiral, the size of which varies from three to five centimeters, there is a small compartment containing the necessary hormone. The essence of this device is that the drug is introduced into the body gradually, in equal doses. What is its effect?
The hormone affects the uterus in such a way that its ability to close is lost. This occurs due to inhibition of the growth of the uterine epithelium, weakening of the function of the glands and self-compaction of cervical mucus. As a result, the fertilized egg cannot reach the uterine cavity, which means pregnancy does not occur.
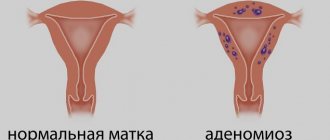
As you can see, many types of hormonal IUDs are abortifacients, since their task is not to prevent the egg from being fertilized, but to limit its access to the uterus. That is, pregnancy occurs, but the development of the fertilized egg stops.
What are the positive and negative aspects of installing a hormonal IUD? Let's find out.
Composition and description
The Mirena intrauterine device not only protects against unwanted pregnancy, but also treats. It contains the hormonal substance levonorgestrel in the amount of 52 ml. The secondary component in the spiral is polydimethylsiloxane elastomer.
The appearance of the intrauterine therapeutic system resembles the letter “T”, placed in a special conductor tube, which has a white core and has an elastomeric hormonal filling. The spiral body is equipped with a loop on one side and two arms on the other. Threads are attached to the loop, with the help of which the spiral is removed from the vagina.
Pros and cons of using a spiral
Before deciding which contraceptive to use, a woman should weigh all the pros and cons of a particular method. Let's discuss them in more detail in the light of our topic.
Positive aspects of the hormonal contraceptive device:
- Almost one hundred percent guarantee of preventing unwanted pregnancy.
- Comfortable to use.
- Local action of the drug.
- Duration of use.
- No discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Therapeutic effect for certain diseases.
The main negative aspects of the hormonal IUD include:
- Expensive installation.
- Existence of side effects.
- Fertility is fully restored only six to twelve months after removal of the device.
- The possibility of installing the IUD is only for those who have children (nulliminating women can be prescribed a contraceptive only for medical reasons).
- The use of hormonal drugs during the treatment of diseases is carried out only after consultation with a specialist.
- Takes some getting used to (some women may experience discomfort at first).
- Lack of protection against sexually transmitted infections.
- Inability to use for certain diseases.
What side effects does the hormonal IUD have?
Mirena: instructions for the spiral
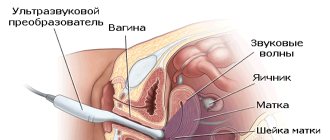
According to the instructions for the Mirena spiral, it should be installed after an examination (ultrasound, colposcopy, blood tests, smears). Installation and removal takes place in a gynecological chair; this may cause minor pain. For engraftment, you should abstain from physical activity and sex for 10 days.
If there are signs of prolapse (bleeding, pain), or the threads (antennae) in the vagina are not detected, then you need to use a condom to protect against pregnancy and consult a doctor.
Preparing for installation
Before installing the spiral, preparation is required to identify possible contraindications and limitations:
- examination by a gynecologist and mammologist;
- vaginal smears;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood test: general, biochemistry with liver and kidney tests, coagulogram (clotting).
Based on the results of the study, the gynecologist can expand this list. As a result of the diagnosis, pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections should be completely excluded, and the cure of all inflammatory diseases should be confirmed.
What day of the cycle is it placed on?
In order to get a reliable contraceptive effect from the first cycle and eliminate the risk of possible pregnancy, it is necessary to insert the IUD 4-5 days from the start of menstruation. Most often, the doctor prescribes installation on the last day of bleeding.
If this time is missed, then the administration should be postponed to the next cycle, since, starting from days 10-13, there is a risk of ovulation and fertilization. Women who have completely stopped menstruation (natural or medicated menopause) can have the IUD inserted on any day.
Menstrual cycle
How is Mirena installed?
Mirena installation takes place at a gynecologist's appointment:
- after determining the expiration date and eliminating damage, the packaging is opened;
- the woman is on a gynecological chair, a speculum is installed in the vagina;
- the cervix is treated with an antimicrobial agent (antiseptic), and then with a local anesthetic.
- the intrauterine system moves through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity, and then it is imperative to lie down for another 30-40 minutes;
- the doctor conducts a control examination; if there are no signs of prolapse or displacement, then the procedure was successful;
- You must come back for your next examination in a month.
Installation of the Mirena coil
Is it painful to insert the IUD?
According to women, inserting the IUD does not hurt; it is reminiscent of taking vaginal smears. There may be discomfort and short-term pain. If there is a high sensitivity to pain, then additional painkillers are administered. After 2.5-3 hours, women’s pain completely disappears.
When, by the end of the first day, a woman notices unpleasant sensations, or while wearing the Mirena they arise during sexual contact or movements, it is important to immediately contact a gynecologist.
Watch this video about the benefits and harms of the intrauterine device:
What not to do after
During the first ten days (10 days) after installation, douching and other therapeutic or diagnostic procedures in the vagina should not be performed. Also during this period restrictions are introduced on:
- sexual contacts,
- hot bath,
- sauna,
- swimming,
- sports,
- lifting weights from 3 kg.
It is necessary to limit strength training and heavy lifting.
All these precautions are important, since the device must be well strengthened in the uterine cavity. After this period, as a rule, women do not feel the presence of Mirena at all. It does not interfere with sex or active movements, but its presence is considered one of the factors that increases the risk of inflammation. Therefore, for the entire period of wearing it is recommended:
- in case of casual sex, changing partners, use a condom to avoid sexually transmitted infections;
- carefully observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- If unusual symptoms appear (pain, itching, burning, bleeding, leucorrhoea, fever), immediately contact a gynecologist, visit him once a year, even if there are no complaints.
If the Mirena coil falls out, what should you do?
If the Mirena device falls out, then it is imperative to use means of protection against unwanted pregnancy - suppositories, vaginal tablets, a condom. It is recommended to immediately visit a gynecologist to rule out fertilization. Even if the IUD is displaced, there is a risk of cessation of contraceptive action.
Signs that may indicate prolapse are:
- pain;
- bloody issues;
- resumption of menstruation after cessation;
- increased menstrual bleeding.
Throughout the entire period of wearing the intrauterine system, it is necessary to periodically check the presence of antennae in the vagina.
When can an IUD be removed?
After five years or at the woman's request, the intrauterine device (IUD) can be removed at any time. This happens more often if complications or severe adverse reactions arise while wearing it (for example, abdominal pain, joint pain, headache, depression).
If the entire period of health remained normal, and for medical reasons the gynecologist recommends continuing to use Mirena, then after 5 years it will be changed to the next one. You must visit the doctor 1-2 cycles before the end of the period in order to undergo an examination before removal.
Removing the Mirena coil
If Mirena is removed as planned, and not due to urgent indications for removal, then the gynecologist often schedules a visit on the last day of menstrual bleeding (if it continues).
On the gynecological chair, after treatment with an antiseptic solution and anesthetic, the cervical canal is widened and Mirena is removed by the antennae. This may be accompanied by slight soreness and a brief episode of dizziness. At the same time, if necessary, the doctor installs a new IUD.
Removal of the IUD
Negative consequences
Side effects of the hormonal IUD are:
- The likelihood of bleeding.
- The appearance of benign cysts on the ovaries (which may go away on their own).
- Possibility of ectopic pregnancy.
- Painful sensations in the mammary glands.
- Various pathological changes in the organs of the reproductive system.
- Irritability, bad mood, depression.
- Pain in the pelvic organs.
- Frequent headaches.
According to various studies, many of the above symptoms occur during the initial period of action of the hormone and disappear immediately after the body gets used to it.
What about birth control pills? Are they effective in the fight against unwanted pregnancy? Do they have a negative impact? And what is better to choose: pills or spirals?
Side effects
Side effects occur in the first months of use; their manifestations bother women for no more than six months. During this time, it is important to be observed by a gynecologist, who will note whether the treatment is effective. If the side effects are minor, but have been bothering you for more than six months, then this is a reason to cancel.
Adverse reactions of the body occur mainly due to hormonal changes in the body. Despite the fact that the dose of the active component is small, it can cause discomfort. At first, the following reactions from the body are possible:
- nausea and changes in taste preferences;
- headaches, up to severe migraines;
- impaired ability to concentrate;
- the occurrence of scanty blood discharge at a time when menstruation should not occur;
- violation of cyclicity, frequency of menstruation;
- change in the abundance of discharge during critical days;
- the appearance of rough areas in the mammary glands (can be isolated or very pronounced);
- changes in the skin (the appearance of acne, rashes, blackheads, blackheads);
- increased greasiness of the epidermis and scalp.
There are other negative reactions, but they are extremely rare. These include disorders of the psycho-emotional background, in particular, frequent mood swings, the occurrence of depressive and unconditional states. It is also possible for a small cystic type to form in the ovaries. If any adverse reactions are detected, a woman should immediately contact a gynecologist. In this case, the spiral should be removed and another method of treatment should be chosen, for example, hormonal tablets with a lower concentration of the active substance.
There are many negative reactions, but in 98 percent of cases they all go away after several months of use. The woman’s hormonal background stabilizes and the body begins to work as before. After six months, patients forget about the gynecological problems that bother them and get used to the installed Mirena contraceptive-therapeutic device.
Hormonal drugs
The age-old question: “Intrauterine device or hormonal pills - which is better?” - should be decided based on your views and preferences. What can be taken into account?
First of all, you should know that hormonal contraceptives are very different both in composition and in their principle of action. Some of them have an abortifacient effect (they make the lining of the uterus so thin that a newly formed embryo cannot attach to it), while others thicken the uterine mucus so that it does not allow the sperm to be fertilized.
Are there pros and cons to the birth control “pill”? Of course, and here are some of them.
Flaws. These include an inconvenient dosage schedule, which can be missed or forgotten, and then the likelihood of pregnancy will increase. As well as a number of side effects similar to the side effects of the spiral.
Advantages. This advantage of medicines includes the formation of a woman’s hormonal levels, including the stabilization of the menstrual cycle, which relieves the “weaker sex” of pain during “critical days”, and can also have a beneficial effect on appearance (the condition of the skin and hair).
Another important positive feature of the tablets is that their use prevents the development of tumors in the female genital organs and prevents the occurrence of ectopic pregnancy. Moreover, hormones in the form of medications do not affect basic reproductive functions - the likelihood of conception is restored almost immediately after stopping contraception.
So, the advantages, disadvantages and negative consequences of hormonal IUDs have been determined, and the decision to install this type of contraception has been accepted and approved. What should you do next?
Mirena therapeutic spiral: indications for installation
Indications for installation of the Mirena therapeutic coil are fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, endometriosis, estrogen therapy for menopause. In all these cases, the intensity of uterine bleeding decreases. If you have a polyp, you must first remove it, examine it for cancer, and after eliminating it, insert an IUD.
For fibroids
For fibroids (tumors growing in the muscle layer of the uterus), Mirena helps get rid of the main symptom – uterine bleeding. For 2-3 months you can expect their volume to decrease, and then they are usually completely absent. This effect is the most important, but at the same time the sensitivity of the uterus to the action of estrogen and progesterone also decreases, slows down the growth of existing nodes and prevents the formation of new ones.
Types of fibroids
Not all types of fibroids can be treated with a spiral - it is contraindicated for a tumor that is located in the submucosal layer, that is, the direction of its growth is the uterine cavity (submucosal). Installation is not recommended for cervical fibroids, as well as for node sizes exceeding 2.5-3 cm. In the latter case, it is possible to first reduce its volume by creating an artificial menopause (with drugs).
For endometriosis
When the endometrium grows outside the uterine cavity (endometriosis), the introduction of Mirena helps:
- stop feeding the lesions, they gradually decrease, then die and are replaced by connective tissue;
- reduce blood loss;
- prevent iron deficiency anemia;
- relieve pain in the lower abdomen;
- prevent the emergence of new areas.
During menopause
A gynecologist may recommend Mirena upon the onset of menopause due to age or after surgery to remove the ovaries for:
- prevention of endometrial thickening while taking estrogen (replacement therapy);
- reducing bleeding, normalizing blood composition after anemia;
- preventing cancerous changes in the inner layer of the uterus.
For endometrial hyperplasia
Mirena, due to the content of levonorgestrel, has a positive effect on the growth (hyperplasia) of the endometrium: its cyclic changes stop, blood flow decreases - the vascular networks become empty, the arteries thicken and become clogged with blood clots. This leads to a gradual thinning of the inner layer and stopping bleeding.
The same effect is observed with long-term use of female sex hormones (estrogens), so the IUD is placed in women, among other things, to prevent hyperplasia.
For polyps
A polyp is a growth inside the uterine cavity. If it is present, Mirena cannot be installed. This is why it is so important to undergo a full examination before using the IUD. If such a formation is suspected, a diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is prescribed. If, according to histology (tissue examination), cancer is excluded, then the hormonal IUD is allowed to be used; it can prevent the re-formation of the polyp.
Is the IUD used as a contraceptive?
The Mirena spiral as a contraceptive is recognized as the most reliable. It prevents pregnancy both mechanically and hormonally. The risk of fertilization over 5 years does not exceed 0.7%. This is almost 80 times higher than that of suppositories and condoms.
The use of Mirena has an advantage over tablets, since the penetration of levonorgestrel into the blood is minimal. In the absence of restrictions on its use, it is successfully used as a contraceptive, but this method is not recommended for women who have not given birth.
Can it be installed and worn during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Mirena cannot be used during pregnancy, but it is not contraindicated during breastfeeding . When using a spiral, it is important for women to consider:
- this is a reliable means of contraception, but there is a risk of prolapse from the uterine cavity;
- while wearing the IUD, there may be no bleeding, and the effect of the progesterone analogue is often accompanied by symptoms of conception (nausea, pain in the mammary glands), if these symptoms arise suddenly, and if there is any doubt, you should consult a gynecologist;
- if pregnancy has occurred and the IUD remains in the uterine cavity, then it must be removed; if this is not done, then miscarriage, premature birth, infection, blood poisoning may occur;
- during the period of removal of the IUD, spontaneous abortion often occurs;
- pregnancy with Mirena will occur with the threat of excess hair growth in girls; the possibility of other pathologies cannot be excluded, since there are very few such cases.
When breastfeeding, you can neglect the amount of hormone that penetrates into the blood and then through breast milk to the baby. You should regularly check the presence of the device, since during sucking the released oxytocin provokes uterine contractions. This increases the risk of Mirena falling out.
Watch this video about contraception during breastfeeding:
Installation of a contraceptive
The installation of the hormonal IUD must take place under sterile conditions. The manipulation is carried out by an experienced doctor. If these conditions are met, the intrauterine device will not cause pain, and the risk of infection of the uterine cavity will be minimized.
Is it necessary to undergo any procedures or examinations before installing the IUD? Certainly.
First of all, the possibility of pregnancy should be excluded (for this there is a specialized test or a specific blood and urine test). You will also need to undergo universal tests: general blood/urinalysis, vaginal smear and gynecological ultrasound. If a woman is sick with any chronic diseases, consultations with specialists will be required.
Now let's move on to the next question: what types of hormonal IUDs are there and how do they differ from each other?
Hormonal intrauterine device Mirena: changes in the body
The hormonal intrauterine device Mirena causes irregular or increased menstruation in the first 3 cycles. Bloody discharge is normally possible in the first 3-5 days after installation and removal.
How is your period going?
In the first three months, there is a gradual decrease in the formation of hormones, so during this period there are different types of bleeding:
- irregular,
- reinforced,
- meager,
- between the next menstruation.
After 3 cycles, blood loss should decrease as the layer that is shed (the endometrium) becomes thinner. For many women, menstruation disappears completely. The gynecologist usually warns about this effect; it is considered normal.
Seeing a doctor is necessary if after 4-5 months the bleeding remains heavy or there is intermenstrual bleeding.
Discharge after installation of the Mirena coil
Since a foreign object is inserted into the cervix and uterine cavity, discharge may be brown or red after Mirena installation, but it is usually spotty and goes away on its own within 3-5 days. Signs of complications (infection) are:
- unpleasant odor;
- discharge of scarlet or dark blood, as during menstruation;
- blood clots;
- the appearance of pus.
At the same time, body temperature may rise and pain in the lower abdomen may increase.
If Mirena bleeds after removing the IUD
After the IUD is removed, Mirena may bleed for the first 3-5 days. The discharge is normally not intense, spotting, and painless. As a rule, normal menstruation returns from cycle 3-4. Uterine bleeding rarely occurs in the first months, since the endometrium grows gradually. Such a reaction is possible if, instead of the prescribed 5 years, Mirena was in place for much longer. Any bleeding due to pain or fever requires clarification of the cause from a gynecologist.
What is Mirena
This type of contraceptive is securely fixed in the woman’s uterus due to its “T”-shaped design. A thread loop is placed on the lower edge of the product to make it easy to remove the system from the body.
The device contains fifty-two milligrams of a white hormone (levonorgestrel), which slowly penetrates the body through a special membrane.
The contraceptive begins to act immediately after installation. Released directly into the uterine cavity, the gestagen acts predominantly locally. In this case, a fairly high concentration of levonorgestrel is achieved directly in the endometrium.
Like other hormonal IUDs, Mirena suppresses the activity of the uterine epithelium and reduces sperm mobility. Over the course of several months, transformation occurs in the endometrium, which leads to infrequent bleeding and ultimately to a shortening of the menstrual cycle or its complete cancellation.
Are there any contraindications to the use of this method of contraception? Yes, and we’ll talk about this below.
Mirena spiral: features of the IUD
Mirena is a spiral that releases a hormone similar to natural progesterone. It inhibits the growth of the inner layer of the uterus, reduces bleeding, prevents the growth of fibroids and unwanted pregnancy. Set for 5 years, price 12-12.8 thousand rubles, 1.9-2.3 thousand hryvnia.
What does it look like
Mirena looks like a white letter T about 3 cm in size. This is the main part of the hormonal device that is placed in the uterine cavity. On the white polyethylene body there is a reservoir for the hormone; it is gradually released through the membrane at a pre-calculated rate. A loop and threads are attached to the T-shaped base, through which Mirena is removed. The second part of the system is an insertion device (tube, piston, slider, handle).
Compound
Mirena contains levonorgestrel. It is similar in action to the female sex hormone progesterone. Due to it, two processes occur simultaneously - treatment of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterus) and strengthening of the contraceptive effect of the IUD. The total amount of levonorgestrel is 52 mcg. It is released at a rate of 20 mcg per 24 hours, but after five years the release into the uterine cavity drops by half.
All other components are auxiliary:
- polymer core with high elasticity (flexibility) and viscosity;
- shell made of polymer material with silicon dioxide;
- plastic housing with barium sulfate;
- thin brown threads (antennae).
We recommend reading about how menstruation occurs during and after the IUD. From the article you will learn about the effect of the IUD on the reproductive system, installation of the IUD, and the timing of the onset of menstruation with the IUD. And here is more information about treatment options for hyperplasia without curettage.
Action of Mirena
The action of Mirena occurs simultaneously in two directions - therapeutic and pregnancy prevention. The first is manifested in the following changes:
- the thickness of the inner layer - the endometrium - decreases, its nutrition deteriorates, cell division is inhibited, the response to female hormones (estrogens, progesterone) decreases;
- uterine bleeding decreases by 95% after a year, and may disappear while the device is in the uterus, this helps restore the composition of the blood;
- prevents further growth of tumors (fibroids) of the muscle layer.
The contraceptive effect is provided by several processes at different levels:
- pituitary gland (gland of the brain) – the production of luteinizing hormone decreases, it is responsible for the process of release of the egg from the follicle;
- endometrium - Mirena prevents its cyclical changes, reduces its thickness, which prevents the fertilized egg from attaching;
- cervix – sperm motility decreases, mucus becomes thicker;
- fallopian tubes - relaxes the walls, reduces the speed of movement of the egg.
As a result, either ovulation (and, accordingly, conception) does not occur at all, or the spiral interferes with the attachment of the fertilized egg.
Manufacturer
The manufacturer of the original Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is the Bayer Schering Pharma concern. Its factories are located in Germany and Finland.
When should you not install Mirena?
The Mirena hormonal device should not be used if:
- There is a possibility of pregnancy.
- There are inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs or in the urinary system.
- Chronic sexually transmitted infections appear.
- Oncological, precancerous conditions of the uterus or mammary glands are noted.
- There is a history of thrombosis.
- There are serious liver diseases.
- There is an allergic reaction to the components of the spiral.
Description of the product
The Mirena intrauterine device (IUD) is the latest achievement in the field of gynecology and obstetrics. Finland is a manufacturing country, which certainly inspires confidence and indicates the high quality of the drug.
Composition and principle of action
Mirena looks like the letter T and is an elastic core filled with an active hormonal substance. The body is covered with a special membrane for dosed release of the active component. Additionally, it has a built-in loop with medical threads, with the help of which the spiral is removed after use. The product itself is placed in a guide tube, which allows for painless installation.
The synthetic hormone levonorgestrel is a medicinal substance located inside the core. It begins to enter the female body immediately after the IUD is installed in the uterus. In the first years, the average release rate is up to 20 mcg. By the fifth year, the levels gradually decrease to 10 mcg. In total, the Mirena IUD contains 52 mg of levonorgestrel.
The drug is designed in such a way that the hormone has only a local effect. Thus, the released substance does not spread beyond the endometrial layer covering the uterus. The concentration of the drug in the muscle layer is extremely low (less than 1%). And the hormone practically does not penetrate into the blood, so it is not capable of having any serious negative effects on the body.
The mechanism of operation of the IUD is similar to the action of hormonal implants, combined oral contraceptives and contraceptive injections. The action of all these drugs is aimed at blocking the release of the egg from the ovary (ovulation process) and preventing the development of the uterine mucosa, which ultimately leads to difficulty in implantation of the fertilized egg.
After installation of the device in the uterus, endometrial restructuring begins, lasting several months. During this period, spotting, irregular discharge appears. Then there is a significant decrease in the number of menstruation or even their complete cessation.
Indications and contraindications
Any contraceptive is used to prevent pregnancy, and in some cases, IUDs are used to stop heavy menstrual bleeding that occurs for unknown reasons. Before installing the IUD, the presence of neoplasms in the female genital area should be excluded.
Mirena is often used to prevent endometrial hyperplasia. For example, in women with severe menopause or after surgery to remove the ovaries. But it is also used for the treatment of menstrual disorders, which are expressed in severe blood loss during menstruation.
The Mirena hormonal device is a contraceptive for internal use, so it is used for inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. These include:
- inflammatory processes in the cervix and pelvis;
- endometritis that appeared after childbirth;
- an infection that spreads to the lower region of the genitourinary system;
- abortion performed within 3-4 months of installation of the IUD.
The indication for removal of the IUD is the development of acute inflammation in the pelvic organs, which cannot be treated. Therefore, the IUD is contraindicated in those with a predisposition to infectious diseases and poor functioning of the immune system, as well as in women who often change sexual partners. As protection against pregnancy, the product is not suitable for the following pathologies of the body and cervix:
- fibromyoma;
- cancer;
- dysplasia.
Changes in the anatomical structure of the uterus are another contraindication.
The active component of the spiral passes through the liver, breaking down in it. Therefore, it is not recommended for organ diseases such as cirrhosis, acute hepatitis or cancer.
Although levonorgestrel does not have a systemic effect on the body, this hormone is still contraindicated in all gestagen-dependent malignancies, for example, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and other similar dangerous conditions. Contraindications to installing Mirena are also:
- migraine;
- diabetes;
- stroke;
- heart attack;
- thrombophlebitis;
- persistent increase in blood pressure.
The IUD should not be used during pregnancy or sensitivity to the active component. In any case, only a specialist decides on installing Mirena after all diagnostic studies.
Side effects
The instructions for the product indicate that unwanted effects that appear after using the intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD) Mirena do not require treatment; as a rule, they disappear on their own a few months after installation. Main negative reactions:
- Long menstruation. About 10% of women complain of copious and prolonged bleeding, as well as spotting.
- Changes in the central nervous system. Most often, patients report headaches, increased irritability and nervousness, and frequent mood swings. Back pain may occur.
- Changes in the gastrointestinal tract. After installation of the IUD, in the first days you may experience abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and lack of appetite.
If the body is overly sensitive to the active substance, then systemic changes may develop. For example, acne, dermatitis or acne appear, breasts “swell”, and body weight increases. You should consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- absence of menstruation for 1.5–2 months;
- prolonged pain in the lower abdomen;
- fever, chills, night hot flashes;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- changes in the color, odor and volume of vaginal discharge;
- heavy menstruation.
How to install Mirena
As noted above, an IUD should be installed by a gynecologist. After a careful examination and examinations, the doctor will install Mirena in his office, and will do it quickly and painlessly. If a woman has a low pain threshold, she may be given a local anesthetic.
When is the best time to carry out this manipulation? During the first week after the start of the critical days, when the likelihood of getting pregnant was reduced to zero.
Does Mirena have side effects? Of course, like other hormonal IUDs.
Is Mirena effective?
Reviews from doctors about the use of the drug are mixed. Not all gynecologists believe that inserting an IUD is justified in the long term. There is no reliable evidence that Mirena effectively suppresses the spread of endometriosis. The drug is inferior in its effect to other representatives of hormonal drugs - gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, drugs based on dienogest. Levonorgestrel only temporarily suppresses the growth of heterotopias. After removal of the IUD, the disease returns quite quickly. Relapse is possible a year after completion of therapy.
Practicing gynecologists note that Mirena is good as symptomatic therapy. With the IUD, the woman’s condition improves:
- The volume and duration of menstrual flow decreases. Some women experience amenorrhea - a complete absence of menstruation;
- Intermenstrual bleeding stops;
- The intensity of the pain syndrome decreases;
- The risk of developing uterine bleeding is reduced.
The use of Mirena helps reduce the volume of menstruation.
Mirena helps treat anemia, a condition in which the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood decreases. With the IUD, the volume of blood loss decreases and red blood counts are restored. Habitual weakness goes away and performance increases. 3-4 months after insertion of the IUD, a woman can stop taking iron supplements to correct anemia.
It is important to know
Anemia is diagnosed by a blood test. The doctor can stop iron-containing drugs after obtaining good results. You cannot stop taking the medicine yourself, based only on subjective sensations. With prolonged anemia, the body adapts to new conditions, and often the disease is asymptomatic.
In what situations does Mirena not work on endometriosis lesions?
- Adenomyosis III-IV degree;
- Large endometriotic ovarian cysts;
- Multiple foci of endometriosis in the pelvic cavity.
It is also useful to read: Intestinal endometriosis and its treatment
In advanced situations, the hormonal system is ineffective. Mirena cannot cope with large lesions and widespread process. It is necessary to take other drugs - dienogest, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Gn-RH). After a course of therapy with strong drugs, Mirena can be installed for several years. Levonorgestrel will suppress the growth of remaining lesions and prevent relapse of the disease.
Mirena is ineffective in localizing multiple endometriotic lesions in the pelvic cavity.
The effectiveness of Mirena also increases after surgical treatment. First, the doctor removes areas of endometriosis in the ovaries, fallopian tubes and peritoneum. After laparoscopy, an intrauterine device is installed. This scheme allows you to remove the largest lesions surgically and suppress the growth of remaining heterotopias conservatively.
On a note
Mirena is not used as a means to prevent endometriosis. There is no reliable evidence that the use of an intrauterine hormonal system in healthy women prevents the development of pathological lesions in the future. It can be assumed that Mirena delays the time of manifestation of the disease. COCs and oral gestagens have the same effect.
Bad influence
What undesirable consequences can this hormonal IUD have? The harm to the body caused by Mirena is usually temporary and minimal. First of all this:
- acne;
- nausea;
- weight gain;
- headache;
- sudden mood swings;
- absence of menstruation, minimization of discharge;
- decreased sexual activity;
- pain in the spine.
Such symptoms are rare and disappear soon. If the discomfort and accompanying unpleasant sensations do not go away, you should consult a doctor.
Is it possible to place the Mirena hormonal device immediately after childbirth?
Side effects when taking Mirena
More than 10% of women experience uterine bleeding , oligo- and amenorrhea. In addition, there may be a disturbance in the intensity of menstrual bleeding. However, such side effects gradually disappear during the first months after the installation of MPS.
Decreased mood, lack of libido, and the appearance of acne are extremely rare. From the digestive system, bloating, nausea, and abdominal pain may occur. In 1% of cases, there is an increase in body weight.
Childbirth and breastfeeding
It is not recommended to install an intrauterine contraceptive immediately after delivery. This is due to an increase in the volume of the uterus, which can provoke rapid prolapse of the device. According to the instructions, it should take about two months (and in some cases more) before the uterus returns to its original size and the gynecologist allows the introduction of Mirena.
If a woman is breastfeeding, this is not a reason to refuse contraception. The fact is that the hormone acting in a spiral will in no case spread through the blood vessels and be absorbed into the milk. As mentioned above, the principle of action of Mirena is the local distribution of the main substance.
Is it possible to install an IUD after a miscarriage or abortion? Sometimes this can be done on the same day, sometimes a week later. Be that as it may, the decision is made by the attending gynecologist after a detailed examination of the patient.
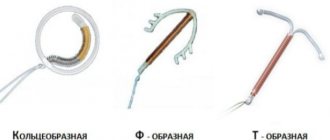
Types of intrauterine devices
In gynecological practice, a variety of spirals are used, which differ primarily in shape. The intrauterine system can be loop- and ring-shaped, in the shape of a spiral or umbrella, in the shape of the letter F. But still, devices in the shape of the letter T are more popular.
The materials from which intrauterine contraception is made also differ: copper, silver, gold, plastic. The size of the contraceptive is selected individually for each woman and depends on the anatomical characteristics of the patient.
The intrauterine device can be hormonal and non-hormonal. In the first case, the contraceptive effect is provided by the hormone contained in the stem of the device, which is released in small quantities. But even a low dose of the hormone causes thickening of the mucous layer of the uterine cavity and prevents the penetration of male germ cells. Spirals made of copper and silver belong to the second, non-hormonal type and have an inhibitory effect on sperm. The attending gynecologist will help you find out whether the IUD is hormonal (this or that model).
Spiral falling out
Although Mirena is installed for at least five years, sometimes there are cases of it being dropped without permission. How can this be determined?
For example, during menstruation, you should carefully examine pads and tampons in order to notice a fallen device. In addition, any change in the position of the spiral will be indicated by poor health or pain experienced by the woman.
Why can a helix self-remove? This happens quite rarely, often during the first stages of installation of the intrauterine system and most often in nulliparous women. The reasons for this phenomenon have not been scientifically determined or substantiated.
It has been precisely proven that neither vomiting, nor diarrhea, nor playing sports, nor drinking alcohol affect the partial or complete slipping of the Mirena from the uterine cavity.
Yes, the hormonal IUD is an effective remedy against pregnancy. But what to do if fertilization does occur?
Contraindications
Like any effective medical device, IUDs also have contraindications.
- Current pregnancy
- Sexual infections, cystitis
- Suspicion of oncology of the reproductive system
- Bleeding of unknown etiology
- The uterus is deformed due to the presence of a large fibroid node or a tumor of other (non-oncological) origin
- Severe liver damage
- Allergic incompatibility with the composition of the contraceptive
- Old age (over 65)
- Thromboembolism, thrombophlebitis, other vascular pathologies
- Severe forms of migraine with temporary asymmetric vision loss
In addition, there is a list of diseases in which the installation of an intrauterine system is problematic:
- Diabetes mellitus of any type.
- A heart attack noted in a personal medical record, regardless of its statute of limitations.
- Severe hypertension.
- Migraine, headaches of unknown etiology.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Pathologies of heart valves.
For women on this list, if they decide to install an intrauterine device, and the doctor has not found any obvious reasons for refusing this procedure, they need to carefully monitor all sudden changes in their well-being.
Pregnancy and Mirena
It is worth mentioning here that pregnancy occurs extremely rarely when using an intrauterine contraceptive. However, if this happens, it is recommended to do an ultrasound as soon as possible to determine the place where the fetus is attached.
If the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus, the IUD should be removed. This will prevent the development of a threat to the child's development.
If Mirena is deeply embedded in the placenta, then it is not recommended to remove it so as not to harm the fetus.
The birth of a healthy child is practically not affected by whether the hormonal IUD remains in the uterus or not. In such incidents, a pattern is impossible: cases of the birth of both healthy children and those with pathologies were observed. It is still difficult to determine whether abnormalities in fetal development are a consequence of the presence of the contraceptive in the uterus or whether it was influenced by other, more objective factors.
Advantages and disadvantages of the hormonal system
The hormone IUD has advantages over other medications:
- Life time. An IUD is placed once every 5 years. The cost of Mirena is 10-14 thousand rubles, but the price is worth it. A woman spends about 200 rubles a month on treatment. This is significantly less than when using other drugs;
- Low dosage of the hormone. The IUD releases only 20 mcg of levonorgestrel daily. The drug immediately enters the uterine cavity and does not pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The likelihood of systemic effects on the body is lower than when taking other hormonal drugs. Overdose is impossible;
- Reliable contraception. Mirena changes the structure of the uterine mucosa, increases the viscosity of cervical mucus and interferes with the advancement of sperm. In some women, levonorgestrel suppresses ovulation. There is no need to think about additional contraception during treatment.
Mirena is considered one of the most reliable means of contraception.
Mirena's motto: “Set it and forget it.” You no longer have to think about how not to miss a pill. There is no need to give injections every month. You should only visit your doctor regularly - once a year or more often if indicated for a follow-up examination.
Disadvantages of the IUD:
- It can only be placed and removed by a doctor. You cannot introduce or remove the drug yourself without a special tool;
- Involves interference in the uterine cavity and can lead to the development of aseptic inflammation;
- Increases the risk of genital tract infection;
- Sometimes it interferes during sex. If the partner feels the threads of the spiral during sexual intercourse, they need to be trimmed. The problem can be easily resolved by visiting a doctor;
- Not suitable for women planning pregnancy in the next year. Mirena can be removed at any time, but if a woman is not inclined to use it for several years, it is better to change the drug;
- Has an abortifacient effect. Mirena does not suppress ovulation in all women, and it is possible to conceive a child. But the IUD prevents implantation of the fertilized egg, and a miscarriage occurs. Due to moral convictions, the IUD is not suitable for every woman;
- Long adaptation period – up to 6 months. Unpleasant side effects in the first six months after the introduction of the spiral often become a reason to discontinue the drug;
One of the negative aspects of using the Mirena IUD may be a long-term adaptation to the contraceptive with pain.
- Temporary effect. After removal of the IUD, relapse of the disease is possible.
Removal of the IUD
Since the validity of Mirena is limited to five years, after this period the system is removed and, at the woman’s request, a new one is installed. If necessary, the spiral can be removed earlier.
This is very easy to do. On any day of the menstrual cycle, you should contact your treating gynecologist, who will carefully pull out the Mirena, grasping its threads with special forceps.
After such a procedure, the doctor is obliged to check the integrity and integrity of the system. If some element is missing (for example, the core containing the hormone has slipped out), the specialist will carry out the necessary manipulations to remove them from the body.
Is it possible to get pregnant immediately after taking off the contraceptive? In some cases, this may happen as early as the next month. Often, the body will need some time to adapt to the function of childbearing. Sometimes this period can last a whole year.
Mode of application
The therapeutic effect of Mirena after insertion into the uterine cavity lasts for 5 years. The system is in sterile packaging, which is opened immediately before installation. If the packaging has external defects, it should be disposed of as medical waste.
It is advisable that the Mirena spiral be installed by a specialist who has already had experience working with it. Before administering the drug, he must inform the patient about the effectiveness and possible side effects. But he also prescribes diagnostic tests:
- examination of the mammary glands and pelvic organs;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- cervical smear analysis.
It is necessary to exclude genital infectious diseases and pregnancy. It is especially important to determine the size and position of the uterus. A correctly positioned Mirena coil in the fundus of the uterus evenly distributes the hormone to the endometrial area. As a result, maximum effectiveness of the product is achieved. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the attached instructions, because the installation technique for different IUDs is different.
Repeated examination is necessary after insertion of the IUD in 3-10 weeks. If no deviations are observed, then the doctor is visited once a year.
In nulliparous women, the system should be installed within a week from the start of menstruation. The IUD can be used immediately after an abortion performed in the first trimester of pregnancy. Patients who have given birth are recommended to insert the IUD no earlier than 2 months after natural birth.
If insertion is accompanied by severe pain or bleeding during installation, an ultrasound scan should be performed to rule out perforation.
The spiral is removed using threads that are grabbed with a medical instrument. If the threads are not visible, the doctor removes the spiral with a special hook for removing the IUD. During this procedure, the cervical canal may need to be dilated.
The Mirena system is removed 5 years after insertion. A new spiral can be installed immediately after removing the old one. To prevent pregnancy, it is better to remove it during menstruation if the cycle is maintained. If removal occurs in the middle of the cycle, then there is a chance of becoming pregnant during this period with unprotected sexual intercourse.
Installation and removal of Mirena may be accompanied by pain and minor bleeding. Usually all these signs disappear after the procedure.
On practice
What are the real opinions regarding the use of hormonal IUDs? Reviews about this are quite ambiguous and contradictory.
First of all, many patients are not satisfied with the abortifacient effect of some types of hormonal IUDs, as well as their negative effect on the skin and weight. However, the last negative effect can be easily eliminated - experts recommend that women with IUDs move more and give up sweets, flour and fatty foods.
Others are very satisfied with the chosen contraceptive method and are happy to note the absence or minimization of menstruation, ease of use and favorable cost (if you calculate the total price of birth control pills over a five-year period, then installing the IUD no longer looks so expensive).
Gynecologists also cannot clearly agree on the use of an IUD. They confirm a fairly high level of protection and some healing properties of the spiral, but note that it should be installed carefully, after a thorough diagnosis.
Moreover, experts unanimously declare that if any unpleasant or painful sensations occur after the installation of a hormonal IUD, a woman should urgently see her doctor.
How it works
The active substance of the spiral belongs to gestagens. Hormone:
- blocks the growth of the endometrium;
- prevents cancer cells from multiplying;
- normalizes the balance between estrogen and progesterone;
- does not affect the normal functioning of the ovaries;
- blocks the appearance of pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- reduces the symptoms of menopause;
- protects against unwanted conception;
- acts as an excellent means of preventing the growth of the endometrium during menopause and endometriosis.
After installing the system, the woman’s body receives a certain dose of levonorgestrel (20 mcg) every day. By the end of the five-year period of use, this figure drops to 10 mcg per day. It is important to note that almost the entire dose of the hormone is concentrated in the endometrium, and the hormone content in the blood does not exceed a microdose.
The active substance does not begin to enter the blood immediately. This happens in about an hour, and after 14 days the blood contains the highest concentration of levonorgestrel, but this figure depends on the woman’s weight. If a woman weighs no more than 54 kilograms, then this figure will be 1.5 times more.
According to reviews, after installation of the system, unstable spotting discharge may be observed, but only during the first few months. This is due to the restructuring of the endometrium, after which the duration and volume of bleeding is significantly reduced. And sometimes they stop altogether.
Who is the IUD not suitable for?
This is a very convenient method of contraception, suitable for almost everyone: women over 40 and young girls. If previously it was believed that the IUD could be placed only after childbirth, today gynecologists recommend it for nulliparous women. Use is also possible after a cesarean section, but only 3 months after the operation.
Due to the constant presence of a foreign body inside the uterus, the cervix is always slightly open, which means it is more accessible to pathogens. In this regard, the use of the spiral is contraindicated in case of inflammation or infectious diseases, including chronic ones.
Gynecologists do not recommend uterine contraception for women with acute and cancerous pathologies of the genitourinary system, as well as with severe heart and vascular defects.
Other contraindications include:
- previous ectopic pregnancy;
- cervical dysplasia;
- anemia and pathologies of hemostasis;
- diseases of the endocrine system, including diabetes;
- deviations in the structure of the uterus.
Scheme for using the IUD
The intrauterine device is installed by a gynecologist. Stages of IUD insertion:
- Control examination of the external genitalia and bimanual examination;
- Treatment of the external genitalia with antiseptics;
- Installation of gynecological speculum;
- Assessment of the patency of the cervical canal and the length of the uterine cavity with a probe;
- Introduction of the spiral along the conductor;
- Removing the conductor. The spiral remains in the uterine cavity.
Scheme of introduction of the intrauterine hormonal system Mirena.
According to patient reviews, insertion of an intrauterine device is a painless procedure. A slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen may occur during the installation of the IUD and in the first days after the procedure. Discomfort inevitably occurs when using a gynecological instrument. No anesthesia is required. The entire procedure takes no more than 15 minutes and is often performed under ultrasound guidance.
If well tolerated, Mirena is removed after 5 years. The gynecologist removes the IUD. No additional preparation is required. According to indications, the spiral is removed earlier:
- Pregnancy planning;
- Pregnancy with an IUD. In the early stages, you can try to remove the IUD without harm to the child;
- The development of negative side effects, against which it is impossible to continue treatment with levonorgestrel;
- Complications after installation of the spiral.
After removing the device, the menstrual cycle is restored after 1-2 months, fertility – after 3-12 months.
Reviews from women about the use of a hormonal IUD
Reviews from women about the use of Mirena are varied. Negative comments are associated with the adaptation period. In the first 6 months, many women notice the appearance of spotting between periods. Menstruation remains heavy and long. Over time, the body adapts to levonorgestrel, menstruation decreases until amenorrhea. The condition improves, and many patients agree to re-install the IUD after 5 years.
Positive comments are associated with good regulation of the cycle after an adaptation period. Against the background of Mirena, periods become scanty. Blood loss decreases, hemoglobin in the blood increases, and general condition improves. The threat of uterine bleeding due to endometriosis disappears. After removal of the IUD, no growth of lesions is observed for at least another 6 months (usually up to a year).
Among all the reviews, comments from women over 40 are of particular interest. Not all drugs are suitable for this category of patients. COCs are rarely prescribed due to the high risk of thrombosis. Surgery is not always available and is associated with health risks. Mirena is becoming a good alternative to other drugs, albeit with less effectiveness (compared to dienogest and GnRH agonists).
Mirena is often prescribed to women over 40 years of age, since its action has minimal risks for the health of this category of women.
Reviews:
I got Mirena for the first time when I was 40 years old. Everything was great, there were no side effects. The condition gradually returned to normal, the ovarian cysts disappeared. I also drank hogweed and other herbs. At the age of 45, I got the IUD for the second time and reached menopause. Now everything is fine, I survived menopause and didn’t even notice, I didn’t gain any weight.
Alisa, 53 years old
After an examination, the gynecologist found endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia, 3 cm fibroids, an ovarian cyst and papillomas on the cervix. I was treated with Buserelin for 7 months, then put Mirena on for a year. It didn’t help, I had to have surgery. The uterus and appendages were removed. The doctor says it was on time, since the histology showed precancerous changes.
Natalia, 45 years old
I've been using Mirena for almost 5 years, and I'm going to change to a new one. No signs of menopause yet. My periods are short on Mirena. Only libido has decreased, but this may not only be from the spiral. I have endometriosis and fibroids - without worsening.
Svetlana, 47 years old
Mirena is a good hormonal drug used to treat endometriosis in the initial stages of the disease. In the later stages, it is prescribed after surgical treatment or taking other strong drugs. Approved for use during reproductive age after childbirth. Mirena can be used in women over 40 years of age.
An interesting video about installing the Mirena hormonal system with comments from a specialist and a patient
Up to what age can IUD be inserted?
There are no age restrictions for using an IUD. An intrauterine device can be installed in a woman of reproductive age from 18 to 49 years old or before the onset of menopause. Although experts have different opinions about the age at which an intrauterine device should be placed.
It is believed that nulliparous women and women over 40 are not recommended to use the IUD for pregnancy. For those who have not given birth - due to complications (ectopic pregnancy, inflammation of the genital organs and, as a result, infertility in the future), and for those of “age” - allegedly due to the risk of cancer.
The installation of an IUD in itself in women over 45 years of age does not increase the risk of developing cancer. It’s just that in this age category, the likelihood of developing various kinds of pathologies already increases due to lifestyle, habits, and careless attitude towards one’s health, but these problems do not arise because of the IUD.
You are 45 years of age or older. You can safely use an IUD if:
- You have regular periods;
- you have a permanent and only sexual partner;
- Your doctor does not find any contraindications to inserting an IUD.
You are a young girl of 18 years old or a young nulliparous woman. There are restrictions on your use of this method of contraception. But there are situations when another type of protection against unwanted pregnancy is not suitable or is contraindicated. Consult your doctor - there are always exceptions to every rule. A specialist will select a spiral that is less “harmful” for you.
What types of IUDs exist today?
Intrauterine devices can differ significantly from each other in shape and material from which they are made. Their contraceptive effect and safety for a woman’s health will depend on these factors.
The most common types of IUDs by shape:
- "T" shapes. Spirals of this shape are the most common at the moment. They are very convenient for insertion, designed taking into account the characteristics of the female genital organs and do not cause any significant discomfort. There is a small risk of spontaneous loss.
- "Ring". High contraceptive effect, low probability of loss. However, many women experience serious discomfort during insertion of the IUD. You may also experience painful periods.
- Semi-oval (F-shaped). The main advantage of this form of IUD is its secure attachment in the uterine cavity, eliminating frequent prolapses. In addition, it is easily administered, without causing painful drainage in women. The disadvantages include the rather high cost of most models.
Photo gallery: IUDs of different shapes
Based on the material from which the intrauterine device is made, they are divided into the following generations:
- First generation IUD. The products were made of inert plastic, but their contraceptive effect was quite low. In addition, quite often there were cases of side effects in the form of the development of inflammatory processes. The first generation IUDs were banned in most countries of the world in the late eighties of the last century.
- Second generation IUD. These spirals are produced containing inert metals. At first it was copper. Subsequently, models with gold and silver began to be produced. They provide a good contraceptive effect and a low likelihood of side effects.
The presence of metals in the composition of the product allows you to create an acidic environment in the uterine cavity, as a result of which sperm activity is greatly inhibited
After childbirth
The IUD is allowed to be used in the postpartum period 30-40 days after the birth of the child. Wearing the IUD does not in any way affect the health of the baby during breastfeeding. The active components only affect the amount of breast milk produced.
Levonorgestrel during feeding enters the child's body at 0.15%. Therefore, it is not harmful to health.
The spiral also helps to quickly restore the tone of the uterus after childbirth, reduce pain during menstruation, and eliminate the risk of progression of fibroids and cancerous tumors in the uterus.
When the IUD is inserted: does the cycle affect the day the IUD is inserted?
Most often, the installation of an IUD, regardless of the type of device and the age of the woman, is carried out either on the first day of menstruation or immediately after the end of menstruation. In this case, there is complete confidence that the woman is not pregnant. In addition, the cervical external pharynx, through which the anti-pregnancy device will be inserted, is in a slightly open state, which greatly facilitates the procedure for inserting the IUD and reduces unpleasant or painful sensations.
This is especially important if the IUD is installed in a young nulliparous woman. Because the main difference between the cervix in women who have given birth and women who have not given birth is the shape of the external pharynx. Before childbirth, it has a dotted appearance, and after childbirth, it has a slit-like shape. Typically, inserting the IUD into the uterus in women who have given birth does not encounter any difficulties, which is facilitated by the structure of the cervical canal. But for nulliparous women, it is necessary that the external opening of the cervix be slightly open. This occurs on any day of menstruation.
The IUD is allowed to be inserted immediately or within 3-5 days after a medical abortion or spontaneous miscarriage, but only if there is no bleeding or signs of inflammation. If the IUD is not installed within the specified period, then it is necessary to reschedule the procedure for the next period.
An intrauterine device is usually installed after childbirth after 6-8 weeks, and after a cesarean section - after 6 months.
The insertion of an IUD is possible on any day of the cycle, but the following conditions must be met:
- absence of pregnancy;
- absence of inflammatory diseases and bleeding at the time of IUD installation.
Healthy women with no history of gynecological diseases can have an IUD containing copper, silver or gold. The shape of the spiral does not matter. Women suffering from endometriosis or having uterine fibroids should give preference to the Mirena hormonal system.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the device include:
- Effective therapeutic effect;
- Long-term protection against fertilization;
- Mild effect of active substances on organs;
- Rapid restoration of reproductive functions;
- Quick installation;
- Prevention and treatment of various types of pathologies.
Minuses:
- The price of one spiral is from 12 thousand rubles;
- There is a risk of menorrhagia;
- High risk of inflammation with frequent changes of sexual partner;
- If the device is installed incorrectly, internal bleeding may occur;
- Heavy periods after insertion;
- Does not protect against infectious pathologies.
What is the drug
The Mirena hormonal coil consists of a core filled with hormonal-elastomer content, located on a T-shaped body. The contraceptive is covered with a membrane on top that gradually releases hormonal contents in the amount of 20 mcg per 24 hours. The rate of excretion gradually decreases and after 5 years it is 10 mcg per 24 hours.
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 —>
There is a loop at the free end of the body; threads are attached to it to help remove the spiral. This entire structure is placed in a conductor tube.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 —>
Composition of the Mirena spiral: one contraceptive contains 52 mg of levonorgestrel. In addition, the composition includes 52 mg of polydimethyleloxane elastomer, a neutral substance that acts as a reservoir for the drug.
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
The package contains one contraceptive. The internal contents of the package are sterile, so do not install the spiral if the outer covering is damaged.
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
Which spiral is better
The correct answer to this question can only be given by a gynecologist observing a woman, after assessing the following factors:
- physiological parameters, in particular the size of the cervix;
- existing diseases of the reproductive system - uterine fibroids, endometriosis, chronic inflammatory pathologies;
- the presence of childbirth, termination of pregnancy, medical curettage;
- the nature of menstruation - regularity, scanty or heavy discharge;
- individual intolerance to components.
Before installing a contraceptive, the patient must undergo a smear test for flora and undergo an ultrasound scan of the uterus and appendages.
When choosing between hormonal and non-hormonal IUDs, the gynecologist relies on the wishes of the woman herself, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. Thus, LNG drugs are not recommended for acute and oncological diseases of the reproductive system, and for pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Copper-containing IUDs should not be chosen by women with heavy and painful menstruation, anemia, or allergies to metals.
If we are talking about the recommended form of intrauterine contraceptive, then although most modern IUDs are T-shaped, this type is not suitable for everyone due to the individual characteristics of the structure of the uterus. So, a gynecologist will advise someone to choose ring or semi-oval spirals, since thanks to their microscopic protrusions they are securely attached to the uterine walls.
Simple, fast and relatively cheap
The use of intrauterine devices (IUDs) against unwanted pregnancies is rightfully considered one of the most effective methods of birth control. True, due to female anatomical features and the complexity of installation, an IUD can only be inserted into the uterus by a gynecologist and only if there are indications for such installation.
5 advantages of spiral contraception:
- Greater efficiency of the method. There are no more than 0.01% cases of pregnancy with a correctly installed IUD.
- Rapid return to fertility after removal of the IUD.
- Does not need to be combined with another contraceptive (except for condoms used as a means of protection against STDs)
- After fixing the uterine device in place, only one follow-up visit to the gynecologist is required to make sure that the device is installed correctly and that the device is not rejected by the body.
- When installing a progestin-containing intrauterine device, pain during menstruation is guaranteed to disappear.
The Mirena hormonal device is easy to install, inexpensive and always available.
When not to use the drug
Contraindications to the Mirena coil:
p, blockquote 58,0,0,0,0 —>
- pregnancy or uncertainty about its absence;
- infections of the urinary and genital organs;
- precancerous conditions (cervical intraneoplasia grade 2-3) and cervical cancer;
- malignant tumor of the uterus and mammary gland;
- uterine bleeding of unknown origin;
- deformation of the uterine cavity, including fibroids; The Mirena spiral for uterine fibroids can be installed when the nodes are small in size, located in the thickness of the myometrium or under the peritoneum;
- tumors and other severe liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- age over 65 years;
- individual intolerance;
- thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the veins), thromboembolism of other organs, suspicion of systemic lupus erythematosus.
The Mirena system can be used with great caution in the following situations:
p, blockquote 59,0,0,0,0 —>
- transient ischemic attacks, migraine, attacks of intense headache;
- high blood pressure numbers;
- previous myocardial infarction;
- severe circulatory failure;
- heart defects and other valvular lesions due to the risk of infective endocarditis;
- diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2, especially with high blood glucose levels and complications.
If pregnancy occurs while using the IUD, the contraceptive is carefully removed. If this is not possible, the woman is offered to terminate the pregnancy. The development of the fetus in the uterus, where there is a foreign body, can lead to septic abortion in the 2nd trimester, purulent postpartum endometritis and other serious complications. If the pregnancy can be maintained, the child is usually born without significant developmental abnormalities. Although there is a high concentration of levonorgestrel in the uterine cavity, it rarely affects the fetus by causing virilization (increased male characteristics) because the developing baby is protected by the placenta and membranes.
p, blockquote 60,0,0,0,0 —> p, blockquote 61,0,0,0,1 —>
A woman should consult a doctor if she experiences the following symptoms:
- absence of menstruation for one and a half months to exclude pregnancy;
- prolonged pain in the lower abdomen;
- chills with fever, drenching sweats at night;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- discharge from the genital tract that is unusual in volume, color or smell;
- an increase in the volume of blood released during menstruation (a sign of spiral expulsion).
Mechanism of action of intrauterine drug
Mirena is a local hormonal contraceptive containing small doses of Levonorgestrel (a progesterone drug that is gradually released and has a multifaceted effect on the female body). The spiral is inserted into the uterus and affects gynecological diseases as follows:
- changes in hormonal balance with suppression of estrogenic activity, which predominates in endometriosis and uterine fibroids;
- inhibition of ovulation;
- decreased function of the corpus luteum;
- thinning of the inner lining of the uterus, which causes scanty menstruation or a complete absence of menstrual periods;
- changes in the permeability of cervical mucus and suppression of the activity of sperm entering the genital tract;
- deterioration of blood flow in the endometrium.
Mirena for endometriosis is a reliable contraception and treatment of the disease. Reviews from women using this method indicate relief from painful and heavy menstruation. During the entire 5 years of using the intrauterine hormonal system, you don’t have to worry - an unwanted pregnancy will not occur.
Introduction of the spiral
The insertion of the IUD should be carried out by a well-trained specialist.
p, blockquote 35,0,0,0,0 —>
Necessary research before installing the system:
p, blockquote 36,0,0,0,0 —>
- general blood and urine tests;
- determining the level of human chorionic gonadotropin to exclude pregnancy;
- gynecological examination, two-hand examination;
- examination and examination of the mammary glands;
- analysis of a smear from the surface of the cervix;
- tests for infections transmitted through sexual contact;
- ultrasound examination of the uterus and its appendages;
- extended colposcopy.
The contraceptive is administered in the absence of inflammation of the genitourinary organs, satisfactory general condition, normal body temperature.
p, blockquote 37,0,0,0,0 —>
Technique for inserting the Mirena spiral
A vaginal speculum is inserted, and the cervix is treated with an antiseptic using a tampon. A conductor - a thin plastic tube - is placed into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal, and the spiral itself is passed inside it. You should carefully monitor the correct location of the “arms” of the drug in the uterus to prevent spontaneous release - expulsion of the spiral.
p, blockquote 38,0,0,0,0 —>
Is it painful to install the Mirena system?
p, blockquote 39,0,0,0,0 —>
The insertion of the IUD may be sensitive, but there is no severe pain. With increased pain sensitivity, local anesthesia of the cervix is not excluded. If the cervical canal is narrowed or there are other obstacles, it is better not to install the contraceptive “forcibly”. In this case, it is better to dilate the cervical canal under local anesthesia. The Mirena coil is thicker than usual because it contains a reservoir of hormonal agents.
p, blockquote 40,0,0,0,0 —>
After administering the product, the woman rests for half an hour. At this time, she may experience dizziness, weakness, sweating, and decreased blood pressure. If these signs persist after 30 minutes, an ultrasound examination is performed to ensure that the device is correctly positioned in the uterus. If it is not located as needed, it is removed.
p, blockquote 41,0,0,0,0 —>
During the first days after administration of the product, skin itching, urticaria and other allergic manifestations may appear. In this case, the woman should consult a doctor. Sometimes allergies can be treated with medication. In more severe cases, the coil may need to be removed.
p, blockquote 42,0,0,0,0 —>
A woman should come for a follow-up examination in a month, then in six months, and then annually.
p, blockquote 43,0,0,0,0 —>
If the instructions for use are strictly followed, no complications are observed after the introduction of the Mirena system.
p, blockquote 44,0,0,0,0 —>
After each menstruation, the patient must be taught to check the presence of IUD threads in the vagina so as not to miss the expulsion (“loss”) of the contraceptive. If such a condition is suspected, an ultrasound examination should be performed.
p, blockquote 45,0,0,1,0 —>
p, blockquote 46,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 47,0,0,0,0 —>
Benefits of use
Unlike hormonal contraceptives or simple spirals, Mirena has many advantages:
- The prolapse of the IUD is extremely rare , because the hormone relaxes the uterus, and it does not push out the foreign body.
- Stopping menstrual bleeding.
- The use of Mirena prevents the development of inflammatory diseases .
- The contraceptive effect is almost 100%. After five years of use, only seven women out of a thousand become pregnant.
- Has a local therapeutic effect: prevents the growth and development of endometrioid cysts and fibroids.
- Pregnancy after removal of the IUD occurs within the first year.
- It is used by women of different ages: nulliparous, during lactation and during menopause.
After installation
After inserting the IUD, patients complain that menstruation decreases or stops completely.
When using the device, the disappearance of menstruation is normal. The core of the device contains hormones that stop the growth of the endometrium. Therefore, menstruation becomes scanty or stops altogether.
The opposite effect is also possible after the installation of an IUD; the amount of menstruation released may increase by 2-3 times. Heavy discharge is observed during the first 40-50 days. There is no need to worry, this is also a normal reaction to the release of hormones into the female body.