Fungus, or another name for mycosis, is a viral infection with the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, which widely covers all parts of the body, including the feet. Foot fungus is one of the most famous varieties and forms of this disease.
According to statistics, every 5 people are at risk and carry this unfortunate disease. Let's consider the common causes and ways of infection with foot fungus.
Types of mycosis
Mycosis appears due to strong pathogens - saprophyte, moldy fungus, candida and other complex microorganisms.
- Interdigital mycosis is the most popular type, which can infect the entire surface of the lower leg.
- Foot, or moccasin-like - spreads to the soles of the feet, severely injuring the skin and causing moderate pain.
- Ulcerative – accompanied by severe discomfort, itching, burning and peeling of the skin.
Any of these forms of fungus can cause severe complications, so it is important to start treatment as soon as possible.
Why is mycosis of the foot dangerous?
With foot fungus, complications often arise that lead to a deterioration in the patient’s general condition. His body is also not in the best position, because the disease has an extremely negative effect on it.
- Any scratches and wounds, even the smallest and most invisible ones, take much longer to heal than before. Dermatitis and eczema appear more often, and the patient’s recovery is delayed.
- Fungi and their metabolic products cause allergic reactions on the patient’s skin - urticaria, Quincke’s edema.
- The infection easily affects the body, penetrating through cracks in the feet. In addition, this negatively affects the process of treating the fungus itself - the disease becomes more complicated.
- Plantar warts often form on the skin of the feet, requiring additional treatment.
Important!
With weak immunity, the human body is attacked by other viruses. Even a common cold is much more difficult to bear.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of foot fungus are not always noticeable to the human eye, but some changes in the condition of the skin are observed. The subsequent and final stage of the fungal infection is accompanied by severe damage to bone tissue.
If there is any suspicion of a disease, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Main symptoms:
Sloughing of dead skin and severe flaking. Mycosis, which feeds on the important elements of the skin - keratin and protein, causes the upper protective layer of the epidermis to die.
Itching and burning. It is not difficult to notice such a symptom, because it brings severe discomfort.
The smell of rot. Due to infection, many functions in the body are disrupted, including the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Therefore, the feet begin to sweat a lot.
Loss of previous skin color. The beige color is rapidly turning into dark shades of brown, blue and green. This occurs due to the destruction of keratin-containing fibers.
To accurately understand the degree of destruction, you should look on the Internet for photos of foot fungus. You need to pay attention to additional symptoms. Firstly, it is increased temperature in the extremities. Secondly, mycosis destroys strong nails, causing them to break.
About the causative agents of foot fungus
Fungi (dermatophytes) that cause damage to the feet live in warm and damp areas - public showers, locker rooms, baths and swimming pools. They quickly multiply in moist places between the toes and can parasitize on the skin of the feet for a long time without causing disease. If a person has had a fungal infection in the past, there is a high probability that he may get sick again.
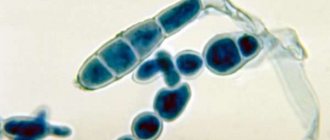
Most often, the disease is caused by the fungus Trichophyton rubrum (red trichophyton), which is difficult to treat. The disease caused by the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes is severe, but responds well to treatment. Much less commonly, mycosis of the feet is caused by Epidermophyton floccosum and yeast fungi. A mixed infection is often detected.
Rice. 1. Trichophyton rubrum (red trichophyton). View under a microscope.
Characteristics of the pathogen Trichophyton rubrum
- Fungi of the genus Trichophyton rubrum penetrate the skin as a result of the destruction of keratin, which occurs under the action of the fungal enzyme keratinase.
- Mannans (polysaccharides) contained in the wall of the pathogen are able to inhibit immune reactions, which makes it resistant to destruction by immune cells.
- Some proteases (enzymes) of Trichophyton rubrum are capable of destroying collagen.
- Fungi produce aphalotoxin-like substances that promote the formation of calluses and hyperkeratosis.
- Under the influence of the fungus, the growth and development of papillomaviruses, which cause the formation of warts on the palms and soles, is enhanced.
Fungal spores remain viable for a long time in the external environment. Among skin scales, dermatophytes retain their viability for up to one year. They can remain on the insoles of shoes, socks, stockings or shoes for a long time. When walking, scales from the patient’s feet peel off and end up in the external environment - on the floor, in shoes, socks, stockings, slippers, etc. Dermatophytes most often affect the delicate layers of skin between the toes. They parasitize in the upper keratinized layer of the epidermis and, in the absence of proper treatment, can affect the deeper structures of the skin.
The state of the immune system plays a special role in the development of foot fungus. High immunity inhibits the development of the disease. Relapses of the disease occur in spring and autumn.
Factors predisposing to the development of the disease
Rice. 2. High immunity inhibits the development of foot fungus.
- increased sweating of the feet,
- minor skin damage: cuts, cracks, wounds,
- shoes that are too tight
- disorders of the immune system,
- diseases of the vascular, endocrine system,
- diabetes,
- frequent hypothermia of the legs,
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules,
- stressful situations.
Foot fungus is a common and very unpleasant form of mycosis. It can be recognized by peeling and redness in the sole area and between the toes. The disease is contagious, in the active stage it causes discomfort, and in the advanced stage it causes intractable ulcers and erosions. With a correct diagnosis, fungal pathology on the feet can be successfully cured within six months. The duration of treatment depends on the type of parasitic fungus and the general resistance of the human body.
Causative agents of mycoses of the feet
Mycosis of the feet is caused by various types of molds. Most often we are talking about the following types:
- Trichophyton red (Trichophyton rubrum). It affects the heels and soles, causing thickening of the stratum corneum and the formation of cracks. It reproduces only by division and inhabits the upper layers of dead skin. Keratin is necessary for the fungus to function. This microorganism also causes athlete's foot and ringworm, and also affects the nails.
- Trichophyton interdigitale, Trichophyton interdigitale. It affects the interdigital area and can spread to the entire foot and toes. The second most common pathogen of mycoses. Can produce penicillin.
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Affects armpits, inguinal folds, feet. Causes detachment of entire layers of skin, small cracks, and provokes allergic reactions.
- Candida fungus. Conditional pathogen. With severe immunity impairment, it can affect the skin of the feet more often in the area between the 3rd and 4th or 4th and 5th toes.
Mycosis of the feet is contagious. Pathogenic fungi that provoke these diseases persist in a humid environment and live for some time on bathing and medical supplies, common items, on socks and inside shoes, on sports mats, and on damp floors. It is enough to walk barefoot in a public locker room, in a bathhouse or in a swimming pool where someone infected with a fungus has previously been, and the microorganism will settle on your feet. The only exception in this group is Candida; they live everywhere, even on the skin of a healthy person, and exhibit pathogenic activity only under certain circumstances.
Types and symptoms of foot fungus
Fungus on the legs can cause different clinical pictures - squamous, dyshidrotic, intertriginous, and can cause onychomycosis. These varieties are often combined with each other.
Squamous
The squamous form is mycosis of the legs, which occurs with damage to the foot. The first signs are local redness and peeling of the feet.
[img] alt=”Squamous form of foot fungus” src=”https://skinperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/36468478474854684848568.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”670″ height=”376 ″[/img] This is the initial form, in which peeling begins between the toes, on the sides of the foot, there is no redness, and there is also an unpleasant odor.
Sometimes there is itching, and in some cases the symptoms go unnoticed at all, but the patient spreads a skin fungus.
Dyshidrotic
The dyshidrotic form, or wet fungus, is mycosis of the foot, in which blisters with liquid appear on the sole. They burst, leaving behind ulcers that exude a cloudy liquid. This is a gateway to infection, which, of course, complicates the course of the disease.
[img] alt=”Dyshidrotic form of foot fungus” src=”https://skinperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/3646347893673573.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”670″ height=”417 ″[/img] The contents of the bubbles include a large number of spores and fungi. When bubbles open, they easily end up in the environment: socks, shoes, floors. You can become infected with fungus almost anywhere - a common locker room or room, gym, swimming pool, sauna, and so on. In this regard, it is always unsafe to use someone else's shoes.
The dyshidrotic form is similar in appearance to eczema and psoriasis.
Intertriginous
This is a foot fungus that prefers the area between the toes. Most often between 3 and 4 or between 4 and 5. In this vulnerable area, a crack first appears, around it there is a whitish area with peeling skin and weeping. With this form, the patient feels a burning sensation and itching, and painful erosions appear in the affected area of the foot.
[img] alt=”Intertriginous form of foot fungus” src=”https://skinperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/346847357546373637574.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”670″ height=”350 ″[/img] Infection with it occurs in places that involve the adoption of various water procedures by a sufficiently large number of people.
The intertriginous form lasts a long time. In winter, symptoms subside, in summer they worsen. As the pathology develops, the skin of the foot becomes loose, loses its protective functions, and becomes vulnerable to streptococci. This leads to the appearance of pustules, redness, swelling, pain, a local increase in temperature, and a deterioration in the quality of life.
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal disease of the feet that is associated with damage to the nail plate. At the first stage, yellowish spots and stripes are noted on the toenails, then there are more such defects.
[img] alt=”Onychomycosis” src=”https://skinperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/78573754764846874573.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”670″ height=”367″[/ img] The infection reaches its greatest spread among elderly people over 65 years of age.
Kinds:
- If the plate does not collapse, it is called normotrophic onychomycosis.
- If the nail thickens and crumbles, it is called the hypertrophic form.
- If it thins and exposes the underlying skin, it is an atrophic form.
When nails are affected by mold fungi, purulent inflammation of the periungual bed develops, the plate acquires a yellow, black, green or brown tint. Usually the fungus affects the 3rd and 4th toes, but in every fourth case it develops on the little toe or big toe.
Other forms
Mycoses of the feet can also take other forms, for example, hyperkeratotic. In this case, the skin becomes covered with a dry red-blue rash, peels off, and plaques and scabs appear. The rash areas thicken and unite into one area of inflammation throughout the foot. In this case, any contact with the affected skin causes pain, the skin on the soles of the feet itches and emits a putrid odor.
How to recognize
Everyone needs to know how the fungus begins in order to start treatment on time. At first, the skin changes are so minor that they do not cause discomfort. You may notice that the skin on your foot has begun to peel, or notice areas of redness, and sometimes feel itching or burning. All these signs may bother you from time to time for several years.
Under favorable conditions, mycosis takes an active form, and then the signs of foot fungus are easy to detect on your own. It is very easy to determine what a fungus on the foot looks like:
- The affected skin becomes rough and thickened.
- The fungus absorbs keratin, destroys the upper layers of the epidermis, which are separated by scales. This peeling of the epithelium is called desquamation. This is accompanied by itching and sometimes an unpleasant odor.
- The affected areas turn red.
- The pattern of the skin furrows becomes sharper, as if you had covered your foot with a layer of powder.
- With the intertriginous form, diaper rash and deep painful cracks appear between the fingers.
- In the dyshidrotic form, a layer of blisters and erosions appears along the arch of the foot and on the interdigital folds.
How to get rid of foot fungus
If you have a fungus on your feet, you will need the help of a specialist - a dermatologist or mycologist. The doctor prescribes tests, determines the type of causative agent of the disease and recommends effective remedies for the fungus. In mild cases, these can be external antimycotics; in severe cases, antimycotic drugs in tablets. Typically, treatment of athlete's foot requires a systematic approach.
Drug therapy
Modern medicine offers to fight foot fungus with the help of external and local antifungal drugs. The doctor chooses the tactics based on the form, severity of the disease and the type of pathogen.
Among the systemic agents that can be used to treat mycosis of the foot, the following drugs are used:
- Griseofulvin is a fungistatic, inhibits the development of pathogenic fungi;
- Terbinafine is a drug with a broad antifungal effect, effective against trichophytons and epidermophytons;
- Fluconazole is a drug active against yeast fungi of the genus Candida;
- Itraconazole is a universal drug that is effective against almost all pathogens.
External solutions that can be prescribed are solutions, ointments and creams for foot fungus - Griseofulvin, Terbinafine, Sertaconazole, Econazole, Clotrimazole, Natamycin, Naftifina hydrochloride, Bifosin, Vishnevsky's balsamic liniment, Levomekol, Miramistin, Stop Active, Formidron, Iodinol, Mycocid.
In difficult cases, hardware therapy for mycosis of the feet using an erbium laser is prescribed. It cauterizes the mycelium and eliminates the visible symptoms of the fungus. After the laser, a course of drug therapy is carried out.
Additionally, vitamins and immunostimulants may be recommended. When complicated by a bacterial infection, therapy includes antibiotics. If a fungal infection occurs against the background of chronic infections or skin diseases that create a burden on the immune system, then treatment of the underlying disease is carried out in parallel. When mycosis is combined with allergic reactions of the body, antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
On the feet, mycosis is often combined with damage to the nail plate. To kill nail fungus, sometimes they are simply removed. This can be done surgically in an operating room or using patches and ointments that destroy the structure of the nail plate. The nail will grow back in about six months.
Folk remedies
Among the folk remedies that can be used to treat skin fungus on the legs, the following are effective:
- Foot baths with a solution of boric acid, apple cider vinegar or peroxide. The product is prepared at the rate of 20 g of active ingredient per 1 liter of boiled water. The procedure is carried out for 30 minutes daily until signs of recovery.
- To quickly get rid of early signs of fungus, combine baths with an antibacterial scrub, which is prepared from equal amounts of soda and salt with the addition of a few drops of celandine, tea tree or wormwood oil. Rub the mixture into the soles of your feet, paying special attention to your heels and between your toes.
- Tar soap helps a lot with foot fungus. It relieves inflammation and kills bacteria. Treat your skin with soap foam and leave the product on for 5 minutes, then rinse and apply foot cream or Zinc ointment. Use within 14 days.
These remedies are good because they do not have side effects. But they are best used as an addition to the main therapy prescribed by a doctor. During pregnancy, treatment is generally not recommended. The main therapy is prescribed after childbirth and lactation.
Features of care and diet therapy
If you have the initial stage of mycosis, you can only use external remedies, but this is associated with certain difficulties. With mycosis, the skin becomes rough, thickens, cracks, and this prevents the penetration of antifungal agents. Therefore, every patient with mycosis should learn to regularly care for their feet and nails:
- The keratinized, thickened and cracked skin of the feet should be treated with a sanding blade and scrub.
- Nail plates should be trimmed and filed.
- After the procedures, thoroughly disinfect your hands, as well as scissors, cosmetic files and other tools used.
To effectively treat skin fungus, it is necessary to follow a diet that excludes foods that are favorable to pathogens. First of all, these are sugar, yeast and products that contain them in large quantities. It is recommended to reduce the amount of fat in the diet and increase fluid intake.
[img] alt=”The doctor warns” src=”https://skinperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/4423444.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”770″ height=”330″[ /img] A sudden transition to a new food system can cause flatulence and bloating in the intestines due to a lack of usual enzymes. Symptoms of indigestion will disappear as your body gets used to the new diet.
The ban includes baked goods, white rice, pastries, alcohol, carbonated drinks, white flour pasta, fast food, sugary fruits (raisins, grapes, bananas), peanuts, smoked foods, potatoes.
The diet should include:
- dairy products;
- lean meat;
- dark rice;
- eggs;
- durum pasta;
- porridge;
- fruit and vegetable juices;
- greenery;
- garlic, onion;
- fresh fruits, vegetables, berries;
- walnuts;
- beans, peas, beans;
- black or gray bread.
Prevention of infection and possible consequences
An advanced form of the fungus can lead to serious consequences. Mycosis creates favorable conditions for the formation of plantar warts and causes increased allergic readiness of the body.
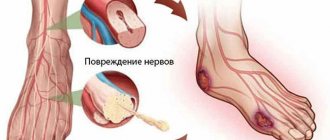
The disease is contagious. When asked whether the fungus can spread to other parts of the body, medicine answers unequivocally - it can. Due to itching, the patient scratches his feet, and dead, affected skin particles accumulate under the nails. This way the fungus can spread to the stomach, arm or other part. Scratching, especially with dyshidrotic mycosis, leads to secondary infection of damaged skin. In severe cases, this can cause sepsis.
To prevent the spread of fungus, disinfect your shoes and socks regularly. Buy a spray with Formaldehyde, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin or other antibacterial drugs and irrigate the inner surface of your wardrobe items. Clothing and the bathroom also need to be disinfected.
If you strengthen your hygiene measures and carefully follow your doctor's recommendations, you can defeat the fungus and protect your loved ones from infection. In the future, follow measures to prevent foot fungus - wash your feet more often and change your socks. Use individual shoes for each family member, refuse to use non-disposable shared shoes in public places and when visiting. Do not go barefoot in locker rooms, bathhouses, or swimming pools. These simple tips will help keep your feet healthy.
Prevention
Of course, it is better to prevent fungus than to deal with its consequences for a long time.
How to protect yourself from fungus:
- Before each visit to the pool, sauna, gym or other place where you need to take off your shoes, it is important to treat the skin of your feet with a protective cream. These are “Zdorov” wax, Teymurov paste and other preparations.
- At the first signs of fungus (itching, redness, peeling), you need to generously lubricate your feet with salicylic ointment. It has a strong antibacterial effect and moisturizes the skin. Instead, chamois or streptocide are also suitable;
- To strengthen the skin and ensure local immunity, a recipe for a prophylactic mixture based on onions is suitable. One onion is ground with two tablespoons of honey. The resulting paste is applied to the skin of the feet and palms. It is advisable to leave the mask on for 30 minutes. Repeat every other day;
- Treat your shoes regularly, wash them if possible and dry them in the fresh air. It is not necessary to use special compounds for this. Most products can be wiped from the inside with alcohol or other antibacterial solutions.
Folk remedies
Medical and folk remedies for foot fungus should coexist harmoniously with each other, but it is important to always adhere to the opinion of doctors. There are certain drugs that cannot be used with some of grandma's recipes.
Cleansing baths and antiseptic. Every day you should perform water treatments for your feet in products such as boric acid, hydrogen peroxide. After a half-hour bath, you need to wipe your feet with an antiseptic.
Tar soap, which contains tar from the birch tree. Soap is ideal as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory assistant in the fight against the virus.
Compresses with butter and crushed garlic. Should be performed until healing.
Homemade high fat sour cream. You can simply lubricate the affected areas with it. To ensure that the sour cream is well absorbed, you should wrap your feet in cling film and put on a warm sock.
Allergy pills are the most effective broad-spectrum medications. The best manufacturers and characteristics of optimal anti-allergenic products
Wen on the body - the reasons for its appearance and who to contact with the problem. 130 photos and videos of treatment and removal of wen
Allergy symptoms - first manifestations, causes of allergies, taking broad-spectrum drugs and targeted treatment (120 photos)
Modern methods of treating foot fungus today can be afforded by everyone without exception, because there are quite cheap but effective drugs. And we also cannot exclude folk methods that our ancestors once used.
Treatment of foot fungus
Mycosis of the feet is difficult to treat due to impaired cellular immunity. Antifungal agents are difficult to overcome the stratum corneum of the sole, and fungi located in the nail plates (with simultaneous lesions) serve as a constant source of infection. When treating foot fungus, old proven remedies and modern antifungal drugs are used, which are divided into drugs that stop the growth of fungi and drugs that kill them. Some of these drugs are obtained synthetically, others are natural. There are narrow- and broad-spectrum antifungal drugs. In addition, different forms of the disease have their own nuances of treatment, so only a doctor can choose the right treatment.
The basis of treatment for foot fungus is:
- The use of general and local antifungal drugs.
- The use of drugs that improve blood circulation in the small vessels of the extremities and the treatment of concomitant diseases.
- Antifungal treatment of personal belongings and household items to prevent re-infection.
Treatment of foot fungus with systemic drugs
Treatment of foot fungus with tablets and injections is used for moderate and severe cases of the disease. Taking them increases the chances of cure, but requires constant medical supervision due to a number of side effects. To treat foot fungus, 2 groups of antimycotic tablet drugs are used:
- Group 1 of drugs (azoles) is represented by intraconazole (orungal), fluconazole, ketocornazole;
- Group 2 drugs (allylaminamines) are represented by terbinafine and naftifine.
Intraconazole and terbinafine are today the drugs of choice for the treatment of foot fungus. They quickly penetrate the stratum corneum of the skin and remain there for a long time.
The selection of doses of antifungal drugs and determination of the duration of treatment is carried out only by a doctor.
If the disease is combined with skin lesions in other parts of the body, the doctor will decide to prescribe more powerful antifungal drugs.
Rice. 11. Antifungal drug of systemic action of the azole group.
Rice. 12. Antifungal drug of systemic action of the allylamine amine group.
Treatment of foot fungus with topical drugs
Foot fungus is a very common disease. A doctor’s arsenal includes many medications, such as old, well-proven ones, as well as new drugs that are available in the form of ointments, creams, lotions, sprays, drops and powder. They are easily applied to the skin.
- When swelling, skin damage and weeping occur, antifungal drugs with corticosteroids are used (Triderm cream, Mikozolon, Lotriderm, etc.). The simultaneous use of Lamisil spray gives a good effect.
- When acute inflammatory phenomena subside, drugs that kill fungi (fungicides) are used. The group of azoles for topical use is represented by Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Bifonazole, Econazole, Isocanazole, etc. The group of allylamine amines is represented by Naftifine and Terbinafine (Lamisil).
Rice. 13. Antifungal drug with corticosteroid.
Rice. 14. Antifungal cream.
A modern drug for the treatment of foot fungus Lamisil
- Lamisil is highly active against all types of fungi, including yeast and mold.
- Lamisil exhibits high activity in the treatment of complications of the disease and allergic rashes.
- The drug is available in the form of a spray, gel (Lamisil Dermgel), cream and film-forming solution (Lamisil Uno), which ensures maximum comfort of its use.
- The drug is used to prevent disease and treat shoes.
- Lamisil restores skin pH and skin hydration levels.
- Promotes epithelization of skin lesions with cracks.
- When using Lamisil Uno, the film covering the skin of the feet lasts up to 72 hours, ensuring that the drug reaches the stratum corneum of the skin for a long time.
- The clinical effectiveness of the drug reaches 72%.
Rice. 15. The photo shows a modern drug for the treatment of foot fungus Lamisil gel and Lamisil cream.
Rice. 16. The photo shows a modern drug for the treatment of foot fungus, Lamisil Uno solution and Lamisil spray.
Pathogenetic therapy
Pathogenetic therapy drugs are prescribed for any pathology. With their help, the effectiveness of treatment increases and adverse reactions decrease. If you have a fungal infection of the foot, you must:
- correct immunological disorders,
- reduce allergic manifestations,
- make up for the lack of sulfur, which is found in eggs, cottage cheese, herbs, etc.,
- take vitamins of group A.
Timely initiation and correctly selected treatment for foot fungus will allow you to achieve a healthy appearance in the shortest possible time, eliminate the feeling of discomfort and improve your general condition.
Reasons for treatment failure
The main reason for the ineffectiveness of treatment for foot fungus is a violation of the treatment regimen on the part of the patient.
- More than a third of patients consider their disease not serious and refuse treatment.
- About 70% of patients do not believe that the prescribed treatment will bring a positive result.
- Half of the patients are not satisfied with the previous treatment.
- Up to 70% of patients stop treatment when a positive result is achieved and no longer come to see a doctor to monitor for cure.
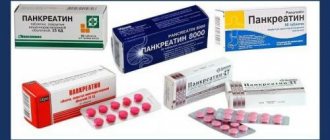
Anti-fungal agent - “Terbinafine”
A drug that is characterized by a relatively low price, but is highly effective in combating fungal infections, is Terbinafine. The basis of this drug is a chemical substance - allylamine. Available in aluminum tubes in dosages of 15 - 30 ml. The cost varies between 200 rubles.
Terbinafine
Instructions for use:
- The area prone to contamination should be cleaned and dried. Afterwards the product is applied. It is worth noting that the substance should be applied not only to areas affected by infection, but also to healthy areas adjacent to them.
- Repeat the procedures twice a day.
More on Med-Gribok.Ru:
Garlic against nail fungus
Powered by Inline
Possible complications and consequences
Complications of foot fungus can include:
- development of combined (multiple) sensitization, increased allergic readiness;
- secondary infection of damaged skin, up to the development of sepsis in severe cases;
- formation of plantar warts;
- onychomycosis.
When assessing gender and age differences, a more frequent susceptibility to foot fungus in men was clearly revealed (1.5–3 times), and a predominance of older and elderly patients among patients.
Consequences of foot fungus
The area of the affected surface occupies a significant part of the foot. When infected with yeast fungus of the feet, the patient is considered a carrier of a contagious disease. Regardless of the stage and degree of infection of the skin of the legs, the patient becomes a constant spreader of the infection. The body's protective factor decreases, the infection spreads through the blood to organs and tissues. In this regard, damage to the lymph nodes and the appearance of severe weakness are possible. Patients may experience sharp pain when moving. Purulent inflammation in the cells or erysipelas are recognized as frequent consequences of fungal diseases.
Fungal disease in some cases leads to the development of allergic processes with a chronic course. Treatment is only possible with the use of antifungal drugs. Before starting treatment procedures, it will be necessary to eliminate the inflammatory reaction and swelling. Compresses containing Vaseline, salicylic acid and milk mixture are prescribed. The compress is applied for 2 days, then the diseased skin tissue is easily removed.
Treatment with salicylic petroleum jelly is prescribed for treating sore areas of the skin. The duration of the procedures is at least 8 days, 3 times a day.
The drugs used for topical use are: Lokoid or Advantan - substances from the group of corticosteroids. It is possible to prescribe sulfur ointment and tar ointment to relieve the inflammatory reaction. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor. Clotrimazole cream is prescribed 3 to 4 times a day for a month. Treatment is carried out under the control of tests.
Diprosalik, Tigboderm - these drugs are used in complex treatment together with the prescription of ointments and creams. These medications relieve itching and allergic factors.
Together with combined medications, feet are treated with Castellani solution or simple iodine. The duration of the procedures is at least two weeks. To lubricate cracks, Lugol's solution and Betadine are used, also in the form of a solution. It is possible to treat with compresses with a drying property, for example, copper sulfate.
Severe forms of yeast fungus should be treated with systemic medications. For example, Orungal 100 mg for a month, 200 mg for a week, then repeated courses of treatment are required. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed: Griseofulvin (taken until negative tests for the presence of fungi are obtained), antiallergic drugs Erius, Kestin, Cetrin are used as additional treatment. As an antifungal agent, Fluconazole 150 mg is widely used - the daily dosage of the drug, after 2 days Fluconazole in the same dose should be repeated.
Treatment of fungal diseases is required in conjunction with the prescription of sedative and strengthening medications: any multivitamins, vitamins and minerals. When a streptococcal or bacterial infection occurs, antibacterial drugs are added to the treatment.
Symptoms
Initially, there is itching of the skin and tingling in the affected areas. The areas where the rash appears are characterized by a slight increase in temperature. Over time, small bubbles of a dense structure begin to appear in the thickness of the epidermis. During maturation they merge or open. Microcracks appear on the surface of the skin. If infection gets inside these ruptures, serious pathologies can develop. Purulent development and enlargement of the lymph nodes may begin inside the blisters.
In the severe stage of the disease, the following features will be observed:
- general weakness of the body;
- headache;
- decreased appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits;
- fever symptoms;
- tingling and moderate itching;
- soreness;
- the presence of obvious cracks and peeling.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms. These include: fungal infection, scabies, psoriasis, dyshidrotic eczema.
Signs
Initial symptoms do not always force the patient to pay due attention, but as the disease progresses, the clinical picture changes. In this case, it becomes impossible to ignore the disease. It is not recommended to start the disease; it is advisable to start therapy at the first damage to the skin or when cracks appear on the leg. The picture of infection depending on the stage:
- First stage: small areas are affected, does not cause discomfort.
- Second stage: the affected areas expand, if you look at the photo, they look like they are covered with plaque, the nails begin to break.
- Third stage: accompanied by itching, pain, blisters.
Causes
Infection with a fungal infection occurs through direct contact with it. The disease can easily be caught in public places: a sauna or bathhouse, a locker room in a gym, a swimming pool, and so on (especially if you take someone else’s shoes or walk barefoot). Sometimes the fungus gets on the skin when using improperly disinfected pedicure tools. Often the disease is caused by the following types of pathogenic organisms:
- Trichophyton Mentagrophytes (Trichophyton mentagrophytes): athlete's foot;
- Trichophyton interdigitale (Trichophyton interdigitale): develops between the toes, spreads to the entire foot);
- Trichophyton Rubrum (Trichophyton rubrum): rubrophytosis of the skin;
- Candida albicans (Candida albicans): candidiasis.
There are a number of factors that significantly increase the chances of contracting mycosis:
- Wearing tight, uncomfortable, low-quality shoes that constantly injure your feet.
- Severe sweating of the feet or walking for a long time in wet shoes (moisture contributes to the active development of a fungal infection).
- Severe forms of immunodeficiency.
- Pathologies that lead to changes in normal blood circulation in the legs (varicose veins, diabetes mellitus, thrombophlebitis and similar diseases).
Diagnostics
To diagnose foot fungus, the following laboratory tests are performed:
- microscopic examination of material obtained from the surface of areas of peeling or weeping under a light microscope;
- sowing the obtained material on a nutrient medium in order to determine the species of the pathogen;
- polymerase chain reaction (detection of DNA fragments of pathogenic fungi).
To diagnose foot fungus, a microscopic examination of material from the surface of the lesions is performed.
Forms in which fungal infection of the feet manifests itself
The speed of recovery and the effectiveness of treatment generally depend on the drugs selected for treatment. The sooner the disease is identified and the right drug is prescribed, the more noticeable the effect of its use will be. Of course, before starting treatment, a consultation with a medical specialist is required, who will assess the degree of development of the disease and prescribe a suitable inexpensive but effective remedy.
Here is an overview of the possible forms in which the disease manifests itself:
Intertriginous form
The first symptoms appear a week to a week and a half after the infection begins to develop. The area that is primarily susceptible to the appearance of fungus is the gap between the third - fourth / fourth - fifth toes. The skin begins to turn red, then small flaky scales form on its surface.
There is one peculiarity - due to the intensive process of sweat secretion, which, in turn, is called the greenhouse effect, the affected area of the skin increases in size and loosens as it further moisturizes. As a result, the mild itching already present at this moment becomes unbearable. Everything happens accompanied by a burning sensation. In particular, when a fungal infection appears on the foot, there is a possibility of infection of the nails. Therefore, you should not forget about this long-suffering area and, while undergoing a course of treatment, you should at least occasionally treat it.
Hyperkeratotic form
The infection spreads mainly to the pads of the toes. Cases of damage to the heel areas are quite exclusive. The skin becomes much drier and thicker. This effect is accompanied by the appearance of a “pattern” formed by small grooves.
More on Med-Gribok.Ru:
Iodine for nail fungus
Powered by Inline