Home → Services → Ovarian cancer: it is important to intensify chemotherapy
In Russia, Israel, and Germany, ovarian cancer begins to be treated with surgery. The uterus with appendages, greater omentum, and visible manifestations of the tumor are removed. If surgery is unlikely, then chemotherapy is started. This is because ovarian cancer does not respond well to chemo. Particularly low effectiveness of chemotherapy is observed in mucinous and clear cell ovarian cancer.
If after 2-3 courses of chemotherapy as part of standard treatment according to compulsory medical insurance there is no noticeable positive dynamics, improvement in well-being, reduction in tumor size and metastases, then you should think about the need to intensify chemotherapy with heating. Further continuation of standard chemotherapy in the absence of dynamics, even with a change in chemotherapy drugs, will only lead to drug resistance of ovarian cancer.
Surgery for borderline tumors and stage 1
When it comes to treating borderline tumors or early stage ovarian cancer, surgery is often the only treatment needed. The extent of the intervention varies from resection of one ovary and one fallopian tube to a complete abdominal hysterectomy .
Minimal surgical intervention is performed if treatment is necessary for a young patient with a borderline tumor or stage 1a ovarian cancer - in this case, the uterus and one of the ovaries are preserved intact, and the patient retains reproductive function. In patients with stage 1b or 1c cancer, as well as women in menopause or who are not interested in having children, resection of both ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and cervix is performed.
In this case, the surgeon will also excise the omentum - adipose tissue located in close proximity to the ovaries. Samples of other tissues, such as lymph nodes, may be taken to determine whether the cancer has spread. In addition, “peritoneal washes” will be performed - the surgeon will place a special liquid into the patient’s abdominal cavity, part of which will be sent for examination to determine the presence of cancer cells.
If it is difficult to determine at what stage of development the oncological process is before surgery, the surgeon can remove only the damaged ovary and fallopian tube, taking many samples of surrounding tissue. Depending on the result of the biopsy, additional surgery may be performed to remove the uterus, fallopian tube, remaining ovary and omentum.
After surgery, if the tumor was not completely removed or there is a suspicion that some cancer cells were not removed, a course of chemotherapy is given.
To the beginning ⇑
Psychological recovery
“How to live further after removal of the uterus, what will my life be like?” - this is the question that torments women. Uncertainty about the correctness of their decision, sexual dysfunction, infertility - these are just some of the fears of patients who agreed to have their uterus removed.
To avoid these problems, first, take your psychological preoperative preparation seriously. A positive attitude and optimism are the main guarantees of the success of the operation and the speedy completion of the recovery period. Choose a surgeon you truly trust. Mutual understanding between doctor and patient is very important for treatment and your future life.
Secondly, do not close yourself off or isolate yourself from loved ones. You will need the support of your loved ones and family very much at the right time. Have fun with friends, do your favorite thing. In a word, do everything to distract yourself from unpleasant thoughts and fears.
Third, don't put too much emphasis on the operation. Thousands of women undergo hysterectomy every day, and their lives continue in the same direction. Modern treatment methods involve preserving the ovaries, and if the ovaries are removed, taking hormone replacement therapy. In this regard, menopause as such is not observed, as are other hormonal disorders. A full sexual life is restored within 3 months.
Stage 2 and 3
If the ovarian cancer has already spread, surgery will be performed in which the doctor will remove both ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and uterus, and as much of the tumor as possible. During the procedure, the surgeon may also take biopsies or remove some of the lymph nodes located in the pelvis or abdomen. In addition, doctors will remove the omentum and may remove the appendix and part of the peritoneum.
If the oncological process has spread to the intestines, then a small part of it can be removed, after which the integrity of the intestine is restored. In rare cases, the two ends cannot be connected, in which case the upper part of the intestine is connected to the peritoneal wall - a colostomy or ileostomy is performed.
In some patients, treatment may be supplemented with a course of chemotherapy, which can be performed both before and after surgery. In the first case, as the patient completes the course of drug treatment, a control computed tomography scan will be performed - if it shows that the size of the tumor has been reduced to acceptable levels, surgery will be performed.
This approach makes it possible to increase the efficiency of surgical intervention and significantly simplify its implementation. After surgery, the goal of drug treatment is to destroy any malignant cells that for some reason were not removed during surgery.
To the beginning ⇑
Prevention of long-term complications
Long-term complications include:
- Early menopause (menopause).
- Adhesive disease or extensive adhesions in the pelvic cavity.
- Osteoporosis.
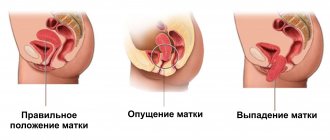
- Prolapse of the pelvic organs, vaginal prolapse.
Climax
Menopause as a result of ovarian hysterectomy is surgical. Its course is much more severe than the natural one.
If the removal was carried out without amputation of the appendages and ovaries, then signs of menopause are not observed or they are erased. Clear signs of menopause are observed in women who have had their uterus and ovaries amputated. The first symptoms appear within a month after surgery.
During the maturation of eggs, the ovaries cyclically produce hormones that maintain normal hormonal levels and emotional state. With natural menopause, the decrease in the production of these hormones by the ovaries occurs gradually, the symptoms are more easily tolerated. During surgical menopause, against the background of normal hormone production, the ovaries are abruptly removed, which negatively affects the functioning of all body systems. The symptoms of menopause are the following:
- Tides.
- Increased sweating.
- Emotional instability.
- Decreased mood, depression.
- Disorders of skin appendages - hair and nails.
- Vaginal dryness syndrome.
To prevent menopause, the patient is prescribed hormonal drugs, taking into account the initial hormonal background. Monophasic and biphasic combined oral contraceptives, gestagen and progesterone preparations are suitable for this. They are taken according to a certain schedule, every day, at the same time of day. The course of treatment is from 2 years.
Adhesive disease
Since removal of the uterus and ovaries is an extensive and radical abdominal operation, the occurrence of adhesions is observed in 90% of cases. Adhesions are fibrous strands of rough connective tissue that, when distributed widely, “solder” together the internal organs of the abdominal cavity. As a result, organ functions are impaired. In severe cases, adhesive disease is fatal.
To prevent the formation of adhesions, undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs at least 2 times in the first year after surgery. Massage the lower abdomen. Helps in preventing adhesions and early activation. Therefore, do not give up light physical activity (walking, cycling) and gymnastics, do light exercises every morning.
Osteoporosis
This disease also often complicates the lives of patients. The occurrence of the disease is associated with a decrease in the level of estrogen in the blood. Estrogens are hormones produced by the ovaries during the menstrual cycle. These hormones retain calcium inside the bone, preventing it from entering the general bloodstream. When estrogen decreases, calcium is washed out of bone tissue, which leads to fragility and brittleness of bones, frequent fractures and dislocations.
To prevent osteoporosis, take hormonal medications regularly and eat right. Include fermented milk products and calcium-rich drinks in your diet every day. Food should be rich in vitamins. In parallel with this, a course of vitamin therapy is carried out with calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D3 or multivitamin combinations. Do exercises every day.
Prolapse of organs and vaginal prolapse are associated with impaired tone of the perineal muscles. For prevention, each patient needs to do exercises daily to strengthen the muscles of the perineum. In the first months, it is forbidden to lift heavy things or engage in heavy physical labor.
Stage 4
In this case, the operation is performed to reduce the size of the malignant tumor and alleviate the symptomatic manifestations of the disease, prolong the patient’s life and improve her quality of life. Chemotherapy treatment may be given before and/or after surgery.
In some cases, surgery cannot be performed - for example, if the cancer progresses too quickly, or if the patient's health condition does not allow surgery. In this case, the main treatment method is chemotherapy, which subsequently (if there is a good response to medications) can be supplemented with surgery.
To the beginning ⇑
How to eat properly if you have ovarian cancer
When it comes to treating oncology, the simplest vegetables and fruits become highly important for the body. To restore your health faster, it is recommended to listen to your doctor’s prescriptions and adhere to proper nutrition.
Advice! The diet is developed in combination with the chemicals used.
Nutrition for ovarian cancer should be gentle and not contain roughage. Often the patient does not want to eat at all due to lack of appetite and apathy, however, this must be done. The specific diet for each patient will be different depending on the state of health, however, there are general rules.
Diet after ovarian chemotherapy
The diet should be varied, but it is better to stick to vegetarian food. For example, grain products, vegetables and fruits are good options. Diet for stage 1 ovarian cancer includes foods rich in plant elements. The diet after chemotherapy looks like this:
- Freshly squeezed carrot or beet juices.
- Vegetable or cereal soups in low-fat broth.
- Viscous buckwheat porridge.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Yogurts, kefir.
- Curd casseroles.
Advice! Drinking clean water is one of the key rules when dieting.
Doctors also advise spending more time outdoors.
What not to eat if you have ovarian cancer
Nutrition for stage 3 ovarian cancer or any other stage of the disease, as well as after chemotherapy, will be soft and healthy. It should not include the following products:
- smoked sausages, boiled sausages,
- refined oil,
- products made from premium flour,
- spices,
- rough food
- fat meat.
The purpose of the diet is not only to improve health, but also to saturate the weakened body with useful substances from certain foods.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After surgery, patients are advised to start moving as soon as possible - as a rule, doctors advise taking walks the very next day after the operation. During the time during which the patient is in bed, it is very important to regularly perform physical exercises that put stress on the legs - this is necessary to prevent thrombosis. It is also recommended to perform special breathing exercises that help prevent the development of lower respiratory tract infections. The patient will be introduced to the technique of performing the exercises by a physiotherapist or nurse. Also, in order to prevent the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities, the patient may be prescribed to wear compression stockings for the first day after surgery.
Droppers and drainage
During the first day after surgery, the patient receives all the necessary nutrients through intravenous infusion. The ability to eat light food usually returns the next day - approximately 48 hours after the end of the operation.
Also, a special catheter may be placed in the patient’s bladder to allow urine to drain into a special bag. The catheter will be removed a day or two after the operation.
To drain excess fluid from the postoperative wound, one or two drainage hoses can be placed in the area of the intervention, which are removed after a few days.
Postoperative wound care
If the patient has undergone more extensive surgery than the removal of one ovary and one fallopian tube, then the post-operative wound extends from the pubic hairline to the area just above the navel. The wound is closed with a surgical suture and/or special staples. Seven days after surgery, sutures are usually removed, but some stitches do not need to be removed - they dissolve on their own. The wound is usually covered with a bandage for the first few days.
Pain control
After the operation, the patient may experience some discomfort and pain. Painkillers are used to control these factors.
In the early days after major surgery, the patient will usually need a strong painkiller such as morphine. She can receive it either injectively (with the help of nurses) or using a special pump connected to a catheter placed in the arm - in this case, the help of a nurse is not required.
In some cases, a technique such as epidural anesthesia is used to relieve pain. In this case, a special tube is placed in the patient’s epidural space, through which a painkiller is continuously supplied for some time after the operation - such permanent anesthesia can significantly reduce the intensity of pain.
Extract
Most women who have surgery for ovarian cancer can go home 4-10 days after surgery. In some cases, before discharge, the patient may need to remove stitches or special staples that tighten the edges of the postoperative wound. Some patients may require some assistance - for example, women who have undergone major surgery may find it difficult to get home on their own or, for example, climb several flights of stairs. In this case, patients are advised to seek help from relatives or social workers. Difficulties may also arise with aspects of daily life such as cleaning the house, cooking, caring for oneself, and performing work duties.
Patients are advised to avoid strenuous physical activity and heavy lifting for at least the first three months after hospital discharge. It is also strongly recommended not to drive for at least a month and a half after surgery. In addition, during the first time, wearing a seat belt may cause some inconvenience to the patient - in this case, it is recommended to refuse any trips until the problem disappears.
To the beginning ⇑
Consequences and life after surgery
Return to sexual activity
One of the most frequently asked questions by patients before undergoing a hysterectomy is: “How will this surgery affect my sex life?” First of all, you should take into account the fact that it will take at least a month and a half for the surgical wound to heal - during this time, sexual intercourse is strictly undesirable.
Most patients who have undergone a hysterectomy do not experience any problems during sexual intercourse - we can say that the operation has not affected their sex life in any way. However, some women who have undergone this surgery note that the volume of their vagina has decreased somewhat, as well as the fact that its inclination has changed somewhat. This may cause the sensations experienced during sexual intercourse to be different from those before the operation. In some cases, low-intensity pain may occur, which will subside over time.
There is also a common misconception that cancer can be passed on to a partner during sexual intercourse. This is absolutely false - sexual contact is completely safe, cancer is not transmitted sexually.
Early menopause
In young patients, surgery to remove the ovaries will result in an early onset of menopause. Physically, this is manifested by the presence of the following factors:
- Short-term hot flashes (instant sensation of heat, which in some cases is accompanied by sweating and redness of the face);
- Dry skin;
- Vaginal dryness (can lead to difficulties during sexual intercourse);
- Decreased sex drive.
Discomfort that occurs during sexual intercourse can be reduced by using lubricants, which can be purchased at any pharmacy or purchased online.
Also, some patients may be prescribed hormone replacement therapy after treatment for ovarian cancer. This therapy may help reduce some of the problems associated with early menopause.
Fertility
Very often, patients find it difficult to come to terms with the fact that after a hysterectomy they can no longer have children. The patient's fears that she has lost part of her feminine nature may also be a cause for concern. All these emotions are natural and understandable; one way or another, you have to get used to them. Patients are encouraged to discuss any fears or concerns with relatives, friends or a psychologist. Separately, it should be noted all kinds of psychological support organizations for women who are unable to have children.
Chemotherapy for uterine sarcoma
Treatment of local uterine sarcomas always begins with the surgical stage. For leiomyosarcoma, the issue of preventive chemotherapy is decided individually. As a rule, it is carried out for any prevalence, except for stage 1, but even then if there are no morphological signs of an unfavorable course. The optimal regimen includes 6 courses of anthracycline drugs or a combination of gemcitabine with docetaxel.
With the progression of the disease or with initially widespread uterine sarcoma, regimens including anthracyclines, taxanes, gemcitabine, trabectedin, as well as a number of other chemo- and targeted drugs are used.
Specialists at the European Clinic will select the optimal treatment program and determine which drug will give the maximum result in order to change the life prognosis.
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.