An endocrinologist treats this disease.
Need more information?
Thank you for your request. Your application is accepted. Our specialist will contact you shortly
Need more information?
Did not find an answer to your question?
Leave a request and our specialists will advise you.
Thank you for your request. Your application is accepted. Our specialist will contact you shortly
By clicking on the button, you consent to the processing of your personal data
Thank you for your request. Your application is accepted. Our specialist will contact you shortly
Hyperandrogenism in women is an endocrinopathy in which the synthesis and activity of androgen hormones (male sex steroids) increases in the female body. According to statistics, hyperandrogenism occurs in 8% of teenage girls and 23% of women of the fertile period. Endocrine pathology leads to multiple changes in a woman’s body, including obvious external disorders, loss of fertility, libido, and metabolic disorders.
The medical department employs a whole team of highly qualified specialists. Our staff includes experienced gynecologists, endocrinologists and reproductive specialists. We have all known technologies for diagnosing and identifying the causes of female hyperandrogenism. The joint work of the clinic’s specialists is aimed at selecting optimal treatment tactics, comprehensive preservation and maintenance of women’s health.
Hyperandrogenism: what is this syndrome?
Hyperandrogenism in women is a condition in which an increased level of androgens is determined in the blood, and clinical data of an excess of male sex hormones are also recorded.
Most women with hyperandrogenism have polycystic ovary syndrome. However, there are other possible causes of this condition that must be ruled out before a diagnosis of PCOS can be made.
Relative hyperandrogenism, whose ICD 10 code is, for example, E70-E90, is eliminated with the help of measures aimed at normalizing metabolism.
As for hyperandrogenism caused by endocrine diseases, aesthetic elimination of manifestations will not be enough to solve the underlying problem. In almost all cases, the results of appearance correction are short-lived.
On the other hand, if dermatological diseases are not eliminated, clinical hyperandrogenism in girls may worsen. Due to untimely diagnosis of pathology, serious diseases of the endocrine glands may be discovered in the future. The treatment of diseases with increased levels of male sex hormones in the blood is approached in a comprehensive manner, only under this condition the diagnosis of hyperandrogenism is eliminated.
https://youtu.be/_di1DcFGefA
Prevention of hyperandrogenism
This disease does not have any specific preventive measures. However, the main points aimed at maintaining balance and health of the body include a correct lifestyle, giving up bad habits, a balanced diet and systematic exercise.
Every woman should know and remember that excessive weight loss can lead to hormonal imbalance and contribute to the development of not only hyperandrogenism syndrome, but also other diseases of the endocrine system. Sports should also be moderate, because professional sports often push women to use steroids, leading to various health problems.
The main thing is to remember that often your health is in your own hands and following the doctor’s recommendations can solve all problems. Hypoandrogenism is a complex disease that requires comprehensive treatment.
https://youtu.be/kfDz5aArkWY
Causes
Hyperandrogenism syndrome is a fairly large group of endocrine pathologies, which can be caused by various pathological and genetic mechanisms, united by similar clinical symptoms. The disease is characterized by excessive production of androgens (male sex hormones), as well as an increase in their quality and activity.
The most common conditions associated with this diagnosis are:
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome (a pathology in which the ovaries cannot perform their functions due to numerous cysts);
- ovarian stromal tecomatosis;
- idiopathic hirsutism;
- virilizing tumor and some other pathologies.
The following main reasons can be identified:
- presence of adrenal tumors;
- improper production of a special enzyme that synthesizes androgens, resulting in their excessive accumulation in the body;
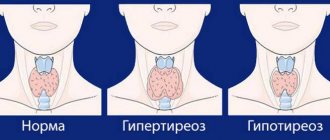
- pathologies of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), pituitary tumors;
- diseases and malfunctions of the ovaries, provoking excessive production of androgens;
- obesity in childhood;
- long-term use of steroids during professional strength sports;
- genetic predisposition.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries, enlargement of the adrenal cortex, hypersensitivity of skin cells to the effects of testosterone, tumors of the reproductive and thyroid glands, pathology may develop in childhood.
Congenital hyperandrogenism sometimes makes it impossible to accurately determine the sex of a born child. A girl may have large labia and a clitoris enlarged to the size of a penis. The appearance of the internal genital organs is normal.
One of the varieties of adrenogenital syndrome is the salt-wasting form. The disease is hereditary and is usually detected in the first months of a child’s life. As a result of unsatisfactory functioning of the adrenal glands, girls experience vomiting, diarrhea, and convulsions.
In older age, hyperandrogenism causes excess hair growth throughout the body, delayed formation of mammary glands and the appearance of the first menstruation.
Why do women need male hormones?
Androgens - male sex hormones (testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone and others) - are synthesized in the female body by the ovaries and adrenal cortex. In the female body they are necessary for: -production of female hormones - estrogens; -maintaining fat and carbohydrate metabolism; -formation and maintenance of sexual desire (libido); - normal formation and distribution of muscle tissue; -prevention of osteoporosis during menopause.
An increase in the concentration of male sex hormones in teenage girls and women of reproductive age leads to the development of hyperandrogenism syndrome, which is characterized by changes in appearance, menstrual cycle and metabolic disorders.
Kinds
In gynecological practice, there are several types of hyperandrogenic conditions, which differ from each other in etiology, course and symptoms. Endocrine pathology can be either congenital or acquired. Primary hyperandrogenism, not associated with other diseases and functional disorders, is caused by disorders of pituitary regulation; secondary is a consequence of concomitant pathologies.
Based on the specifics of manifestation, absolute and relative types of hyperandrogenism are distinguished. The absolute form is characterized by an increase in the level of male hormones in a woman’s blood serum and, depending on the source of androgen hypersecretion, is divided into three categories:
- ovarian or ovarian;
- adrenal, or adrenal gland;
- mixed - signs of the ovarian and adrenal forms are simultaneously present.
Relative hyperandrogenism occurs against the background of normal levels of male hormones with excessive sensitivity of target tissues to sex steroids or increased transformation of the latter into metabolically active forms. A separate category includes iatrogenic hyperandrogenic conditions that develop as a result of prolonged use of hormonal drugs.
The rapid development of signs of virilization in an adult woman gives reason to suspect an androgen-producing tumor of the ovary or adrenal gland.
Types of pathology
Since various organs are responsible for the production of male sex hormones in the female body, varieties of the disease are also distinguished depending on which producing glands have lost normal functionality.
Adrenal
Adrenogenital syndrome in women is caused genetically and is associated with a deficiency in the body of the enzyme C21-hydroxylase, the function of which is to participate in the production of male sex hormones by the adrenal cortex. Pathology occurs only when the gene responsible for the formation of this enzyme is damaged in both chromosomes of the sixth pair.
The manifestation of pronounced male traits is a consequence of a congenital pathology of the adrenal cortex and is called adrenogenital syndrome. The disease is hereditary in an autosomal recessive manner.
Under normal conditions, enzyme deficiency can be compensated by the functions of other hormone-producing organs, but in stressful situations, the adrenal glands begin increased synthesis of male sex hormones. Such stress can be neuro-emotional overstrain, the beginning of sexual life, pregnancy.
Such pathological processes cause disorders of the ovaries:
- amenorrhea caused by suppression of follicle maturation;
- inability to ovulate and menstrual irregularities;
- maturation of an egg with an undeveloped corpus luteum.
The consequence of the adrenal form of hyperandrogenism is infertility and a high probability of spontaneous abortion.
Ovarian
This form of the disease occurs most often; its occurrence is due to hereditary or acquired pathologies of the female organs of endocrine secretion.
The main reason for the failure of the secretory function of the ovaries, as a result of which they begin to intensify the production of androgens, is polycystic disease, which is diagnosed in every fifth woman of childbearing age.
Also, ovarian-type hyperandrogenism can be triggered by a disorder in the pituitary-hypothalamus system.
Another common cause of the disease is the presence of hormone-active ovarian tumors, which stimulate increased synthesis of male sex hormones. This etiology of the disease is characterized by the sudden acute appearance of a complex of symptoms and their rapid development.
Mixed genesis
In some cases, women are diagnosed with simultaneous dysfunction of the adrenal glands and ovaries. This form of hyperandrogenism is associated with dysfunction of the hypothalamus and disruptions of a neuroendocrine nature, and disorders of the nervous system and vegetative-vascular dystonia are usually observed. With this type of disease, lipid metabolism disorders and metabolic problems are often observed.
Peripheral and central
Excessive production of androgens can be associated with disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, various diseases of infectious origin and intoxication of the body. All these negative factors have a suppressive effect on the process of follicle maturation due to a lack of follicle-stimulating hormone.
About adrenal hyperandrogenism, watch this video:
https://youtu.be/Cccvm6vgs5I
Symptoms of hyperandrogenism in women + photos
Among all the symptoms indicating the presence of pathology, the most common are:
- Hirsutism or, in other words, idiopathic hyperandrogenism. There are pathologies in the ICD that can cause excessive hair growth in women. Male pattern hair is the most common sign of hyperandrogenism. If the hair on the body can grow thickly, then on the head, on the contrary, there may be bald patches;
- Excessive dry skin and acne are more considered a cosmetic defect that accompanies the course of the main problem;
- If polycystic ovary syndrome develops, a woman may face problems such as opso-oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea and infertility;
- Obesity may indicate ovarian pathology. This problem can also happen due to a malfunction of the adrenal glands;
- Cushing's syndrome may develop, in which the muscles of the arms, legs, and abdomen atrophy. In addition, the skin becomes inelastic and flabby;
- The risk of infection increases, which is caused by decreased immunity;
- The process of glucose absorption is disrupted. Most often this occurs due to damage to the adrenal glands or ovaries;
- A significant symptom is the formation of irregularly shaped genitals. In particular, this applies to clitoral hypertrophy, partial fusion of the labia majora and other pathologies. Such problems can be identified immediately after the birth of a girl;
- Damage to the retina of the eye, which is not accompanied by an inflammatory process.
There are also symptoms that reveal mild hyperandrogenism. The forum is filled with the opinions of different women who believe that this pathology is accompanied by constant depression, drowsiness and fatigue. All this can be explained by a violation of the secretion of glucocorticoids from the adrenal glands.
In the photo there is hyperandrogenism on a woman’s face
Symptoms of hyperandrogenism in teenage girls
Hyperandrogenism in children and adolescents has several differences. Firstly, if a child had congenital adrenogenital syndrome, then he may have pseudohermaphroditism. These girls have an increase in the size of their genital organs, especially the clitoris and labia.
Most often, symptoms of hyperandrogenism in a child debut with oily seborrhea. It begins with the fact that the fatty glands of the skin (mainly the head and neck) begin to intensively produce their secretion. Therefore, the child’s integuments become shiny due to their excessive secretion. There is also often a blockage of the gland ducts, which contributes to the addition of a bacterial infection and the development of local inflammation.