Ultrasound examination is considered the most informative diagnostic technique for diseases of the pancreas. It allows you to assess the condition of all structures and parts of the organ, including the Wirsung duct. The main criteria by which a doctor determines diseases and anomalies of the pancreas are echogenicity (the ability to reflect sound), size and appearance of the organ. Sometimes in the ultrasound report you can find a phrase that causes concern in patients: “the Wirsung duct is not visualized.” What does such a conclusion mean, and what pathologies or illnesses may it indicate?
Indications for ultrasound of the pancreas
Since functional disorders of the pancreas are accompanied by a “bouquet” of recognizable symptoms, an experienced doctor will immediately issue a referral for an ultrasound scan after hearing specific complaints from the patient:
- pain in the left hypochondrium;
- girdle pain in the middle part of the abdomen;
- digestive disorders - loose stools, diarrhea of unknown origin, constipation (may alternate or occur systematically, but irregularly);
- nausea, vomiting, often with increased body temperature;
- bloating, flatulence;
- an increase in the organ or a change in its shape revealed by palpation;
- yellowness of the skin;
- increased blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of pathology
The main symptom of the development of pathology is a violation of the digestive processes. Pancreatitis can cause dilation as well as narrowing of areas of the Wirsung duct. Experts call this pattern the chain of lakes syndrome. The contours of the canal become uneven, and solid inclusions, which are calcifications or stones, are found in their lumen. Additional symptoms of the disease are:
- The appearance of severe pain in the hypochondrium area (the fact is that pain, as a rule, is not relieved by antispasmodics and analgesics).
- The occurrence of diarrhea and pasty stools.
- The appearance of nausea, vomiting and weight loss.
- Decreased appetite along with specific signs indicating persistent dilation of the gland canal.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the pancreas
In order for the study to be reliable, it is necessary to carefully prepare for the procedure:
- For 3 days before the ultrasound, adhere to a special diet aimed at reducing fermentation processes in the intestines (prohibition of the consumption of vegetables, fruits, milk and fermented milk products, sweets, baked goods, bread, carbonated drinks and legumes);
- Conduct the study only on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning. If the patient is scheduled for an ultrasound in the afternoon, he must comply with the main condition - the minimum interval between breakfast and the procedure is 6-8 hours;
- Stop chewing gum and smoking before the study (in the morning);
- Take medications that reduce gas formation (Espumizan and its analogues, activated carbon, Enterosgel, Polyphepan, etc.) or enzymes (Mezim Forte, Festal, Pancreatin, Creon, etc. .P.).
- If you have difficulty defecating before the study, you can take a laxative or do a cleansing enema (1–1.5 liters of water at room temperature).
In addition, the following rules must be followed:
- Ultrasound cannot be performed immediately after studies using a contrast agent (irrigoscopy, MRI, CT with contrast), as well as endoscopic manipulations (FGDS, colonoscopy) - this distorts the acoustic response of ultrasound, and, consequently, the observation results.
- If you are taking any medications as part of your current treatment regimen, it is recommended to take them after the ultrasound procedure is completed.
- On the eve of the ultrasound, it is prohibited to take antispasmodics and other medications that reduce smooth muscle tone.
Features and norms of ultrasound of the pancreas
The examination site is covered with a special gel to ensure maximum contact of the sensor with the surface of the skin, after which the doctor slowly moves the device in the central part of the abdomen with a gradual shift to the left hypochondrium.
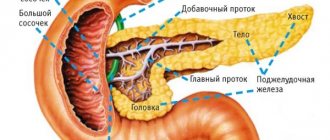
It is in this projection that the pancreas is located, which anatomically consists of three sections:
- Body (width up to 21–25 mm), having a central location relative to the projection of the spinal column, and lying directly under the stomach (hence the name of the organ);
- The head (up to 32–35 mm), slightly protruding to the right relative to the spine and bordering the duodenum;
- Tail (up to 30–35 mm), extending to the left hypochondrium and spleen.
In general, the size of the pancreas can vary; the upper limits of normal are important to determine pathology. Moreover, their limit values do not coincide in different medical sources.
For example, previously a tail width greater than 30 mm was considered a deviation. Today, many gastroenterologists allow a normal increase in this section to 35 mm.
That is why the size of the organ - unless, of course, it exceeds the normal limits to a significant extent - is not a key sign of pathology. The structural and morphological characteristics of the organ, its tissues and boundaries are of utmost importance.
- The contours of the gland should be smooth, clear, with good visualization of both the main parts of the organ and the uncinate process with the isthmus.
- The homogeneity of the structure with minor “errors” in the form of inclusions up to 3 mm indicates the absence of pathologies.
- The echogenicity of the parenchyma (gland tissue) of a healthy organ is not impaired and corresponds to the tissue of the liver and spleen.
- The Wirsung duct should be clearly visualized without being dilated.
Ultrasound of the pancreas for pancreatitis
Acute and chronic inflammation of the pancreas are the most common diseases among those examined.
Pancreatitis develops predominantly in a diffuse manner, and is accompanied by a general increase in the size of the organ, a change in echogenicity, and an expansion of the Wirsung duct.
With the development of acute pancreatitis, the pathological condition worsens - the swelling spreads to the adjacent tissues, the clarity of the contours of the gland is disrupted, a significant expansion of the Wirsung duct occurs, and compression of the celiac vessels occurs.
An acute condition in the absence of timely medical care is dangerous due to complications occurring in the form of necrotization (tissue decay) or abscess. The first sign of necrotic changes is the visualization of pseudocysts on ultrasound.
Chronic pancreatitis has its own specific picture of ultrasound observation - a slight increase in the organ, a violation of the clarity of its contours, heterogeneity of the parenchyma and uneven expansion of the Wirsung duct.
There are frequent cases of local inflammation, acute or chronic, in which all of the above signs are noted on ultrasound, but within a section or fragment of the gland.
In this case, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the root cause and differentiate an abscess or inflammation from a tumor.
Treatment
Treatment of diffuse changes detected in the pancreas can be carried out using conservative and surgical methods. The choice of the correct treatment tactics largely depends on the nature of the pathology, the presence of concomitant diseases and the general condition of the patient.
Often, due to untimely diagnosis and treatment, echogenic signs are irreversible and do not undergo reverse development.
Restoring the normal structure of the organ is possible only with timely, adequate therapy and compliance with all specialist recommendations.
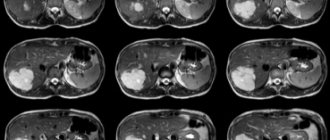
Ultrasound of the pancreas for tumors
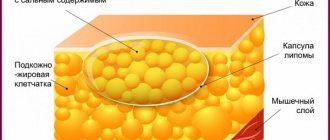
Benign formations of the pancreas are very diverse. They are classified according to their histological structure - hemangiomas (vascular), fibromas and lipomas (connective tissue), adenomas and cystadenomas (epithelial), insulinomas (glandular), etc.
Increasing in size, such pathologies are visualized on ultrasound as formations with smooth contours. Determining the cellular structure of a tumor using ultrasound is problematic, so additional procedures are required - CT, MRI, elastography, etc.
Ultrasound observation has proven itself well in identifying pancreatic cysts - thanks to the liquid filling, the formation is well visualized, which allows one to obtain information about the nature of the contents, size, and the presence of septa.
Ultrasound takes a leading place in the primary detection of pancreatic cancer. There are signs by which an experienced specialist can draw preliminary conclusions about the degree of malignancy (malignancy) of the formation.
First of all, the doctor examines the regional (closest) lymph nodes for their enlargement, changes in structure, and metastasis. Evaluates the clarity of the contours of the formation - malignant tumors often have uneven, unclear contours.
As a rule, additional scanning of blood vessels - Doppler sonography - is required, since cancerous tumors are characterized by an increase in the intensity of blood flow in adjacent areas.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function
When pancreatitis is detected, the doctor usually checks the condition of the gallbladder - these two organs are not only “connected” by a common duct, but are also functionally dependent on each other.
Often chronic pancreatitis is provoked by disturbances in the normal motility of the gallbladder; sometimes, on the contrary, inflammation of the gland can lead to the development of acute cholecystitis.
In the morning, on an empty stomach, the bladder is clearly visualized, being filled with bile. This is a hollow organ, measuring from 3x6 to 5x10 cm. Normally, it should not have kinks or structural anomalies. Wall thickness – up to 4 mm. The development of cholecystitis is indicated by an increase in the size of the bladder and thickening of the walls due to edema.
In the cavity of the gallbladder, ultrasound observation can detect stones, both single and multiple. Formations called polyps may be observed on the walls of the organ.
To assess the functional state of the gallbladder, ultrasound observation is carried out in 4 stages:
- on an empty stomach;
- 10 minutes after the test meal;
- two control observations with an interval of 15 minutes.
If normal motility is maintained, the gallbladder should shrink by 60–70% within 45 minutes of examination. The discrepancy between the indicators and the norm is a sign of a violation of the contractile function of the organ.
Ultrasound examination is considered the most informative diagnostic technique for diseases of the pancreas. It allows you to assess the condition of all structures and parts of the organ, including the Wirsung duct. The main criteria by which a doctor determines diseases and anomalies of the pancreas are echogenicity (the ability to reflect sound), size and appearance of the organ. Sometimes in the ultrasound report you can find a phrase that causes concern in patients: “the Wirsung duct is not visualized.” What does such a conclusion mean, and what pathologies or illnesses may it indicate?
The Wirsung duct is not visualized: what does this mean?
Ultrasound picture
Modifications of the pancreas (disturbance of the organ parenchyma) can be caused by various causative factors. They are visible during an ultrasound examination, which allows you to assess the size and structure of the parenchyma, see the contours, the presence of pathologies, as well as the condition of the pancreatic ducts. Signs of individual diseases diagnosed during the examination also show possible deviations that may affect the Wirsung pancreatic duct.
By the way, it is worth noting that many healthy people may experience symptoms of diffuse changes associated with the environmental situation and the consumption of products with various preservatives and stabilizers.
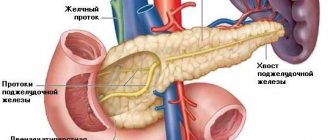
What is the duct of Wirsung?
The Wirsung (pancreatic) duct is the main trunk of the pancreas, into which small, secondary ducts flow. It stretches from the tail of the organ through its entire body, reaches the back, and is about 20 cm in length, and the width differs depending on the area - at the beginning about 2 mm, then 2-3 mm, and at the end, where The sphincter of Oddi is located, the diameter can reach 4 mm. The shape of the canal almost exactly follows the shape of the pancreas, but sometimes it can be ring-shaped or S-shaped.
The structure of the Wirsung duct depends on the characteristic features of the human body - in most people it connects with the common bile duct (common bile duct) and ends in the duodenum.
Location of the duct of Wirsung
There are four types of highway merging:
- The common bile duct and Wirsung duct flow into the duodenum, forming something like an ampulla, and the intestinal sphincter, when contracted, completely closes them (occurs in 55% of people);
- the ducts connect next to the duodenum, but do not merge together (observed in 33% of cases);
- the lines merge at some distance from the intestine, but end in it and touch the walls (8.5% of cases);
- ducts empty into the intestine independently of each other (4%).
Diameter of Wirsung's duct is normal
The role of the pancreas is unusually great. This organ of external exocrine and internal endocrine secretion is involved in the digestive process and regulation of lipid, carbohydrate and protein metabolism in the body. Problems in the functioning of the organ are reflected in the condition of the Wirsung duct. Acute inflammation of the gland is expressed by its expansion, and in chronic pancreatitis its expansion is observed, alternating with areas of stenosis of narrowings. With diseases of the gland, changes occur in the excretory duct, which are detected using modern diagnostic methods. The main pancreatic duct stretches along the entire length of the pancreas, reaching its posterior surface.
Indications for ultrasound of the pancreas
Indications for ultrasound examination of the pancreas include:
- pain localized in the left hypochondrium or radiating to this area, which lasts for several weeks;
- discomfort, heaviness or heartburn that occurs even after eating a small amount of food;
- the appearance of a yellow tint to the skin and mucous membranes;
- dysfunction of the digestive system, accompanied by constipation or diarrhea.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
If any of the above symptoms appear, the patient needs a comprehensive diagnosis of all organs involved in the digestive process, including the pancreas.
Important! The work of the pancreas is closely related to the activity of the liver, therefore, if there are any unpleasant sensations in the liver area, it is necessary to check the pancreas.
Other methods
Other diagnostic methods include:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal area (i.e. sonography).
- Performing computed tomography.
- Taking general laboratory tests of blood, urine, and feces to assess the functional status of the digestive system and the entire body as a whole.
They also conduct a preliminary conversation with the patient as part of the initial appointment with a gastroenterologist, during which they take a detailed anamnesis, finding out the details of the symptoms.
You may be interested in: Coloproctology: what is it, methods of diagnosis and treatment
Preparing for an ultrasound examination of the pancreas
As a rule, ultrasound examination does not require special preparation from the patient, but the pancreas is anatomically located next to hollow organs (stomach, intestines), so the diagnostic results can be distorted by air entering from there. To avoid inaccuracies during an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, the patient must properly prepare for the procedure.
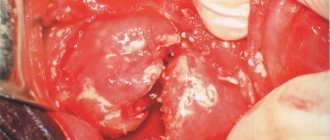
This is what an inflamed pancreas looks like
The study is best carried out in the morning - at this time the indicators will be the most informative. It is recommended to refrain from eating for 12 hours before the diagnosis, and for several days to exclude the consumption of carbonated drinks, baked goods, fresh bread, legumes and other foods that can cause gas formation. If an ultrasound is performed without prior preparation, the accuracy of the results can decrease by 40%.
Ultrasound of the pancreas: norms and pathologies
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor examines the pancreas with a special sensor, and an image appears on the screen, from which one can judge its condition. There are several indicators that allow you to determine the norms and pathologies in the structure of the organ.
Wirsung duct on ultrasound
- In a healthy person, the body of the pancreas has a homogeneous structure (minor inclusions no larger than 3 mm are allowed), clear and even contours, and is located in the center relative to the spinal column, exactly under the stomach.
- The brightness and intensity of the image on the monitor depends on the echogenicity of the organ, that is, the ability of its tissues to reflect sound waves - normally the echogenicity of the pancreas is the same as that of the spleen and liver.
- An organ should be clearly visualized on an ultrasound so that the doctor can determine the size of all its parts. The width of the body in the absence of pathologies is 21-25 mm, the head – 32-35 mm, the tail – 30-35 mm.
To assess the large vessels that are located next to the pancreas and supply it with blood, an additional duplex scan of the organ is performed. Interpretation of diagnostic results is carried out taking into account all indicators and is carried out exclusively by the attending physician.
Anatomical variability of the Wirsung duct
With pancreatitis, tumor processes and other diseases of the pancreas, the contours of the organ become blurred, uneven, it increases in size, and echogenicity significantly increases or, conversely, decreases. Sometimes changes are observed in the entire organ, and sometimes in its individual segments.
For reference! The size of the pancreas largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body, and can vary significantly from person to person. When making a diagnosis, as a rule, the upper limits of normal are taken into account, but in the absence of serious changes in the structure of tissues and biochemical blood tests, exceeding them does not indicate the presence of pathologies.
Video - Anatomy of the pancreas
Causes
The causes of the pathology basically coincide with the causes of pancreatitis and other lesions of the pancreas. Since it is possible to determine the cause of inflammatory processes in a given organ only in 70% of all clinical situations, sometimes the etiology (nature) of pathological changes remains a mystery.
Factors that can provoke abnormal expansion of the canal may include:
- Surgical operations on the biliary tract and stomach;
- Diseases of the duodenum;
- Traumatic injuries to the abdominal cavity;
- Regular alcohol consumption;
- Exposure to certain medications (antibiotics, estrogens);
- Infectious diseases;
- Hormonal imbalances.
In some cases, abnormal expansion of the duct diameter is due to a genetic predisposition: the development of hereditary pancreatitis leads to changes in associated tissues and organs.
Wirsung duct on ultrasound
Changes in the Wirsung duct are one of the most informative diagnostic criteria for determining pancreatic diseases. Normally, it is clearly visualized on the monitor, has a width of about 2 mm and an even shape, which depends on the characteristics of the body.
It should be noted that the phrase “The Wirsung duct is not visualized” in the ultrasound protocol does not always indicate pathologies of the pancreas - sometimes this can occur due to the characteristic structure of the organ and its deep location in the human body. According to medical statistics, it is possible to clearly visualize the Wirsung duct only in 56-80% of cases - in other people this is impossible. But changes in the contours of the canal, its expansion or narrowing indicate the presence of diseases that require immediate treatment.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
| Disease | Changes in Wirsung's duct |
| Pancreatitis | Expansion of the canal along its entire length or in some areas, thickening of the walls, uneven contours, the presence of calcifications |
| Cystosis | The appearance of areas of expansion and narrowing, the presence of cysts and calcifications |
| Giardiasis | Thickening of the canal walls |
| Tumor diseases | Blockage of the duct or narrowing in one place |
| Cystic fibrosis | Multiple areas of narrowing, blockage in the area of the head of the organ, stone formation |
Sometimes the functions of the pancreatic duct are disrupted due to congenital anomalies of its structure - bifurcation, splitting, etc.
Pancreatic tumor
Important! If it is impossible to visualize the Wirsung duct on ultrasound, and assessing its condition and functioning is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis, patients are prescribed additional research methods - endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, sonography, computed tomography.
The condition of the Wirsung duct is one of the most effective diagnostic criteria that allows you to identify disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas. For any changes in this part of the organ, the patient requires a comprehensive diagnosis and properly prescribed treatment, otherwise dysfunction of the digestive system can lead to serious consequences.
Prevention of organ dysfunction
To protect yourself from various diseases that are associated with disruption of the duct of Wirsung, you must:
- Completely get rid of all bad habits.
- Preference should be given to foods low in sugar, fat, salt and cholesterol.
- It is necessary to eat a varied diet that contains plenty of fresh vegetables, grains and fruits.
- You need to drink about two liters of water daily.
- From time to time you need to arrange fasting days for yourself.
- It is very important to play any sport.
- You should always get proper rest (namely, sleep at least eight hours a day) and avoid stressful situations.
- It is necessary to promptly treat infectious and viral diseases.
- During the autumn and winter periods, be sure to take complex vitamins.
The normal state of the duct is of great importance for many processes occurring in the human body. When the channel parameters deviate from the norm, a huge number of chronic or acute pathologies can occur. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor your health, maintaining in every possible way the normal functioning of absolutely all internal organs.