A correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment, but the doctor is not always able to identify the disease based on an examination of the patient and the collected medical history, especially when there are suspicions of diseases of the abdominal organs, which have a complex structure and often have similar symptoms when pathologies develop.
In the modern world of technology, not a single area of medicine can do without informative and high-quality equipment that allows us to identify the slightest disorders and diseases inside our body. One of the most common and accessible diagnostic methods is ultrasound examination, which helps to make the correct diagnosis for many diseases, especially when it comes to possible disorders in the functioning of the abdominal organs. In order for an ultrasound examination to provide maximum information to the doctor, special preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is required, which consists of several stages, which the doctor must inform about on the eve of the examination.
What is ultrasound examination of the peritoneum?
Abdominal ultrasound is a highly informative ultrasound diagnostic technique. It is painless, based on the ability of waves to penetrate tissue and be reflected from them. Radiation passes freely through internal organs that are filled with air. Ultrasonic waves are reflected from all dense structures.
This signal is recorded by the sensor and the data, after processing in the computer, is transmitted to the monitor. The image shows organs, their shape, density and deviations from the norm. At the same time, the retroperitoneal space, pelvic area or kidneys can be examined.
Preparatory activities for diagnosis
Some types of ultrasound examination of internal organs require preliminary preparation. This is done in order to optimize the examination results as much as possible. Preparatory measures are usually not particularly difficult for the patient. The most unpretentious, in this regard, is the study of the thyroid gland, for which special preparation of the body is not required.
Before echocardiography, it is necessary to stop smoking, drink coffee and energy drinks, and limit physical activity. The longest preparatory measures are provided before a general ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys. In order not to distort the final results, three days before the ultrasound scan you need to change your eating behavior and start taking medications.
All foods that cause intense gas formation are excluded from the diet:
Transabdominal pelvic ultrasound
- cabbage;
- beans, lentils, peas and other legumes, and dishes made from them;
- fresh milk;
- baked goods and brown bread;
- pears, apples, grapes, radishes, radishes, cucumbers, tomatoes;
- sweet desserts.
Dietary nutrition involves foods that will be easily absorbed by the body. Portions should not be voluminous, maximum 350 g, every 3-4 hours. To the frequently asked question, is it possible to eat before an ultrasound, the answer is categorically negative. Residues of food will not allow the doctor to examine the organs, or the data will be interpreted incorrectly. Ultrasound is always performed on an empty stomach. Drinking regime before the procedure plays an important role.
The volume of fluid consumed per day should be 1.5 liters. You can drink water, juices and fruit drinks. Green and herbal teas are recommended. Soda and kvass are prohibited, they cause excess gas. The medicinal component of preparation for ultrasound diagnostics consists of taking carminatives (Espumizan, activated carbon) for three days. This is done in order to eliminate excess gases. On the eve of the examination, it is recommended to cleanse the intestines with laxatives (Lavacol, Forlax).
Before any study, drinking alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
How does ultrasound work?
Abdominal ultrasound uses the ability of ultrasound waves to illuminate tissue. They have a high frequency, penetrate the skin and are fully or partially reflected from tissues. The information is transmitted to the machine, which is both a highly sensitive sensor and receives data.
They are transmitted to a computer on which a special program is installed to create a 2 or 3 dimensional image. For a better picture, the air gap is removed between the skin and the highly sensitive device using gel. For scanning, devices operating at 1.8-7.6 MHz are most often used.
Preparing children of different ages
Children are prepared for abdominal ultrasound in the same way as adults, but there are differences in nutrition.
Is it possible for children to eat before an ultrasound and when:
- Infants should refuse the last feeding, that is, two hours before the ultrasound.
- Children from 1 to 4 years old should not eat four hours before.
- Over the age of four years, the last meal should be at least six hours before the abdominal examination.
What organs are checked?
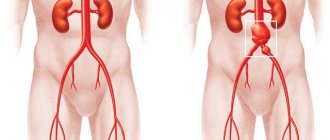
During ultrasound diagnostics, all vessels and aortas that are located in the peritoneum are checked. The kidneys, sections of the ureters, and cellular spaces are examined. Internal organs partially or completely hidden in the peritoneum (and in the space behind and in front of it) are checked:
- The spleen is checked for enlargement, ruptures and internal bleeding. The area of the organ, its thickness, length and width are measured.
- The gallbladder's contractility, bile density, and the absence or presence of stones are determined.
- The dimensions and volumes of the pancreas are measured (its body, tail, and head are examined separately), and the pancreatic duct is checked.
- When examining the bladder, the presence or absence of stones is noted, whether there are wall tumors, reflux, or fistulas.
- In the liver, bile ducts, parenchymal structures, veins and large vessels are checked. The dimensions of the organ, its fragments and lobes, and edges are measured.
- In the kidneys, the structure of the parenchyma is scanned, the size and volume of the organ, the condition of the cups and pelvis are measured. Its contractility is recorded.
- Stomach.
During the abdominal ultrasound procedure, a partial examination of the intestines is possible. However, due to the fact that it contains semi-liquid contents and air, it is impossible to completely check the organ. However, ultrasound can detect some dense intestinal fragments (foreign bodies, tumors).
Hepatobiliary system: norm and pathology
The liver, when examined by ultrasound, should be clearly visible and have a high-density, uniform structure. With clear visualization of the lobes and the large vessels supplying them.
An ultrasound scan of the liver can reveal echo signs of inflammation (hepatitis), cirrhosis, primary neoplasms and metastatic tumors. Signs of parasitic liver damage (schistosomiasis, echinocococosis), cysts with serous and purulent contents, and hematomas can also be detected.
Normally, the gallbladder is located under the liver, low echogenic, and pear-shaped. The wall thickness does not exceed 3 mm, the width of the lumen does not exceed 4 cm.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system can reveal changes in the localization of the organ, developmental abnormalities, spastic conditions of the gallbladder and its ducts, changes in size and shape due to congestive or inflammatory processes. Diagnostics shows the presence of foreign inclusions (concriments, cystic formations, tumor processes and abscesses), as well as pathological compression by the tumor in adjacent tissues.
What does the study show?
What is included in an abdominal ultrasound? All organs located in this area are examined. This method helps identify tumors, but ultrasound cannot determine whether they are malignant or benign. Ultrasound also shows:
- fibrosis;
- cysts;
- appendicitis;
- changes in the kidney parenchyma;
- echinococcal parasitic cysts;
- glomerulonephritis;
- amyloidosis;
- jaundice;
- subcapsular rupture of the spleen;
- splenomegaly;
- Hydnephrosis;
- pyeelectasis;
- gastritis;
- stones in the kidneys;
- fatty hepatosis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pyelonephritis;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- non- and calculous cholecystitis;
- renal agnosis;
- stomach ulcer;
- calicopyelectasia;
- alcoholic, infectious and toxic hepatitis;
- organ ruptures.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity reveals swelling and changes in organ volumes. The presence or absence of neoplasms behind the peritoneum is determined. Diagnostics shows some signs of ureteral reflux, vesicouterine or rectal fistulas.
Gallbladder examination
The gallbladder normally has an elongated shape, dimensions within 10x4 cm, wall thickness not exceeding 0.4 cm.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder allows you to diagnose:
- congenital anomalies (double gallbladder, diverticulum, presence of septum, etc.),
- tumors and cholesterol polyps,
- concretions (stones),
- inflammatory changes (manifested by wall thickening of more than 0.4 cm).
Ultrasound allows you to most accurately determine changes in the gallbladder. If chronic and calculous cholecystitis is suspected, the final diagnosis is made by ultrasound examination.
A healthy gallbladder has an oblong shape with a clear echogenic cavity and thin walls.
Signs of changes in the gallbladder are:
- wall thickening,
- deformations, deformations
- the presence of partitions in the cavity,
- heterogeneity of echogenicity of the cavity,
- the presence of individual shapeless foci of echogenicity in the parenchyma surrounding the gallbladder,
- reduction in the size of the gallbladder,
- increase in the size of the gallbladder.
Only three of these seven signs (deformation, presence of partitions and changes in size) are detected by radiography.
Signs of chronic cholecystitis on ultrasound
- Thickening of the gallbladder wall (especially evident on an empty stomach).
- Deformation of the gallbladder is a violation of the normal oval shape of the organ, shapeless contour outlines.
- Scar changes in the cervical area.
- The presence of septa, which are visualization of individual scars and adhesions.
- Fibrous changes in the parenchyma surrounding the gallbladder.
- Heterogeneity in the image of the gallbladder cavity is a sign of stones or papillomas. The image of stones is easily diagnosed by the presence of a “shadow path” behind them. The papilloma does not shift when the patient’s body position changes.
- An increase in the size of the gallbladder indicates a decrease in excretory function as a result of cicatricial changes or partial obstruction due to inflammation of the major duodenal papilla.
- A reduction in the size of the gallbladder may be the result of scar changes due to chronic cholecystitis or congenital hypoplasia.
Signs of blocked bile ducts
Undilated bile ducts have a diameter of 1-2 mm and are normally not visible. The diameter of the common bile duct is an important indicator of bile duct obstruction, even more important than the diameter of the intrahepatic bile ducts.
Normally, the diameter of the common bile duct is 4-5 mm. A diameter of 6 mm indicates dilation of the bile ducts.
The diameter of the extrahepatic bile ducts increases with age and in patients who have undergone surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Therefore, their increase is not always a sign of blockage. An accurate diagnosis can be made by repeat scanning after ingesting fatty meat foods or internal administration of cholecystokinin. If the diameter of the duct does not change in size after repeated scanning, then there is a blockage of the duct.
Indications for ultrasound
The reasons for performing an ultrasound scan of the pancreas are deviations from normal values in a blood test and girdle pain. A bladder scan is done when urination is painful and difficult, and sediment and salts appear in the urine. The examination is carried out when:
- painful constant sensations in the lumbar region;
- hypertension;
- painful urination;
- chronic form of pancreatitis;
- damage to abdominal organs;
- all types of hepatitis;
- suspected Addisson's disease;
- the appearance of cysts in the peritoneum;
- swelling;
- an increase in the size of the spleen;
- jaundice;
- suspected Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- abdominal injury;
- after car accidents;
An abdominal ultrasound may be done if signs appear:
- throbbing and abdominal pain;
- excessive gas formation;
- belly growth;
- stable elevated temperature that is not associated with colds;
- heaviness and discomfort under the ribs on the right;
- dyspeptic syndrome, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, heartburn, loss of appetite;
- hypersalivation;
- distension of the stomach, nagging pain after meals;
- bitterness in the mouth.
An abdominal ultrasound is prescribed to assess damage to the genitourinary system after inflammation and changes during pregnancy. Ultrasound scanning is performed when tumors are suspected or to monitor already detected diseases. As a preventative measure, it is advisable to do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs twice a year.
Colon cleansing before abdominal ultrasound
To obtain reliable ultrasound results, doctors often recommend bowel cleansing on the eve of the procedure. This procedure can be carried out using an enema, but recently most people prefer an alternative method of cleansing the intestines - taking laxative medications: Senade, Senadexin or the drug Fortrans, which must be taken depending on body weight. 1 tablet or one sachet of laxative is designed for 20 kg of human body weight. As a laxative, you can also take drugs such as: “Normaze”, “Dufalak”, “Prelaxan”. Before using any laxative, you should read the instructions for use or consult your doctor.
Preparing for an ultrasound
If a person is taking medication, this should be reported to the doctor before the procedure. Before it, the intestines are cleansed. Four days before the ultrasound, they begin to drink medications and herbs that reduce gas formation and improve food digestion.
During the preparatory period, you can drink Espumisan, activated carbon, or other drugs prescribed by your doctor. Take 2 tablets three times a day, before meals. For persistent constipation, an enema is performed two days before the procedure. It can be recommended by your doctor on the day of the ultrasound. You cannot undergo a colonoscopy before the examination.
For three days before the ultrasound, you should adhere to a strict diet. You need to eat 5-6 times a day, but in small portions. The diet should include barley and oatmeal, buckwheat. Before the examination, all foods that cause flatulence are excluded. Accumulated gases can distort the results of the study. Excluded from the menu:
- peas;
- dairy products;
- fresh juices;
- black bread;
- chocolate and other sweets;
- White cabbage;
- milk and yoghurts;
- fried food;
- fat meat;
- raw fruits and vegetables;
- excessively salty foods;
- flour and confectionery masterpieces;
- spicy food;
- alcohol;
- soda.
Avoid smoking; chewing gum and hard candies can cause stomach cramps. Food should be steamed or boiled. Adding salt to dishes is kept to a minimum. Allowed:
- lean fish;
- oatmeal, buckwheat, millet, boiled in water;
- low-fat soups (for example, chicken or vegetable);
- hard cheeses;
- chicken meat;
- unsweetened tea;
- beef;
- hard boiled eggs.
The last time you can eat before the ultrasound is twenty hours. On the day of the procedure, eating is allowed only after the examination. You can drink during the day, but stop drinking any liquids a couple of hours before the ultrasound.
If the kidneys and bladder are examined, then the patient, on the contrary, should drink a lot. Immediately before scanning, drink 1.5-2 liters of water. You need to drink very slowly so that as little air as possible gets into the stomach with the liquid. It can provoke distortion of the results.
How to prepare for an ultrasound examination
An abdominal ultrasound is a procedure that you should prepare for in advance to ensure accurate results. For example, if a woman on the eve of the examination consumed foods that caused flatulence, then after an ultrasound, this fact will cause difficulties in visualizing the spleen, pancreas, liver or biliary structure. Or if the patient is taking medications, then you need to stop taking them or warn the specialist who will conduct the ultrasound examination.
It is especially necessary to take the diagnosis of the pelvis seriously: before undergoing an ultrasound, you need to cleanse the intestines, and a few days before you start drinking herbs and medications that improve digestion and reduce gas formation: tea made from lemon balm, mint, chamomile, ginger. If the examination is required for a child, it is advisable to also put him on a diet on the eve of the ultrasound. A couple of days before the appointed date, give him enzymes (festal, activated carbon) to avoid flatulence during the ultrasound examination.
How many days in advance should you start the diet?
Patients always ask whether it is possible to eat before an abdominal ultrasound? Yes, but doctors warn that for three days before the procedure you need to follow a special balanced diet. It is advisable to eat every three to four hours, and there should be at least 4 meals. It is recommended to eat low-fat cheese, meat, and fish. Your daily diet must include grain porridges: buckwheat, oatmeal, barley. 1 boiled egg per day will harmoniously complement your diet.
- Ultrasound of the intestine - what it shows and how it is done. How to prepare for an ultrasound examination of the large and small intestine
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity - preparation, indications for the study, performance and interpretation of results
- How is a prostate ultrasound performed in men?
What not to eat before the test
On the eve of the ultrasound, a diet is prescribed so that the research conclusions are correct, because ultrasound waves will not be able to pass through the air in the stomach. Before undergoing the procedure, you should avoid any products that contribute to gas formation: dairy and fermented milk, baked goods, raw vegetables, sweets, carbonated drinks. You also need to give up too salty, spicy and fatty foods, and immediately before the procedure - from alcohol, smoking, chewing gum, and candy, so as not to provoke stomach cramps.
How far in advance can you eat on the day of an ultrasound?
The cleaner the body is on the day of the ultrasound, the more accurate the diagnosis will be, and, as a result, the more effective the treatment and faster the recovery. A short-term diet before an abdominal ultrasound will help improve the condition of the whole body, which is important for both men and women. The day before the procedure, you need to have dinner no later than 19:00, and you cannot eat anything on the day of the ultrasound.
Should I drink before an abdominal ultrasound?
During the diet, 2-3 days before the ultrasound, doctors recommend drinking herbal infusions, weak tea or non-carbonated water, but not more than 1.5 liters per day. You should not drink anything on the day of the ultrasound. It is recommended not to drink for several hours before the procedure so that the digestive system is completely empty. But this does not create much inconvenience for patients, since most doctors prescribe an ultrasound in the morning, and after the examination they are allowed to drink and eat as much as they want.
If an ultrasound of the kidneys or bladder is planned, preparation for the procedure includes the use of water for the acoustic window, so the patient is instructed to drink plenty of fluids. But we must take into account that you need to drink non-carbonated drinks slowly, without swallowing a lot of air, so that during the examination it does not form a space in the stomach that will not allow the device to correctly read the information.
Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics
An abdominal ultrasound does not take long. The patient lies down on the couch in the position required by the doctor. If it is the liver, then the patient is placed on his left side or stomach up. A conductive gel is then applied to the skin to improve ultrasound transmission.
The study is carried out with a small sensor. It moves around the body in the desired area. An image appears on the computer monitor. According to it, the doctor evaluates:
- general condition, structure, size of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity;
- presence or absence of neoplasms;
- location of organs.
The examination lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. The duration of the scan depends on the quality of preparation and the individual characteristics of the body. If necessary, attention is focused on suspicious points that require more careful study.
How they do it and how much it costs
The procedure is almost always performed externally; in exceptional cases, the ultrasound receptor sensor must be placed inside the vagina (in women) or rectum (in men). Otherwise, this is the least invasive technique, which is especially important when examining children.
To study the condition of blood vessels and the nature of blood flow in the abdominal cavity, a relatively new form of ultrasound is prescribed - Dopplerography. The sensitive sensor is capable of measuring the length of the ultrasonic wave reflected from a dynamic object.
In private clinics, the lower price limit for ultrasound of internal organs is 500 rubles, the average range is from 1 to 2 thousand rubles. As a rule, subjects do not have to buy the gel themselves; for reference, its price is in the range of 100-200 rubles per liter (varies based on viscosity, delivery conditions and the presence of additional components, such as hypoallergenic aloe vera extract). Ultrasound also includes negligible trivial expenses - wipes to remove gel from the skin, shoe covers, and so on.
For children
Ultrasound screening is recommended to be done at a very early age in order to identify deviations from the norm - it examines the internal organs (including brain structures) of the child, its tissues, cartilage and joints. The preparatory measures are always the same: the child is placed on his back or side, a sound-conducting gel is applied to the skin in the area under study and sensors are placed, after which the procedure begins.
When analyzing the condition of the joints, they scan in several phases, changing the position of the limbs (in a bent and unbent state, moving the leg and arm to the side) in order to collect a comprehensive picture.
For adults
For adults, the situation is little different: the patient lies on his back or side, a gel is applied to the skin, a sensor is applied, and scanning begins. It is not accompanied by vibrations, tingling or other unpleasant sensations (except in possible cases in the presence of irritation or injury - but this is no longer the fault of the equipment). Periodically, you may need to hold your breath for a few seconds to improve visibility.
The average duration of an ultrasound is 10-20 minutes.
How often can an ultrasound of internal organs be done?
Given the extremely weak effect of ultrasound on cells and tissues - at least in the context of clinical settings, when the intensity of the sound waves is low - ultrasound cannot directly generate any side effects, and there is no “ceiling” on the number of times a complex ECHO can be done internal organs. On the other hand, frequent repeated preparation - restricting the diet, measures to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract and others - sooner or later can lead to exhaustion, imbalance and deficiency of substances in the body, so you should carefully schedule a visit to the doctor. For preventive purposes, the norm for ultrasound is no more than once a year (provided there are no chronic conditions that require more frequent screening).
Interpretation of ultrasound results of OBP
For each organ or system there are certain standards - size, density, etc. Their deviations may indicate specific diseases.
Liver
Increased echo density of the liver (presence of small lesions) indicates fatty hepatosis. The edges of the organ are rounded. Due to its compaction in the final stages of the disease, the portal vessels become completely invisible.
Cirrhosis of the liver is determined by enlargement of the organ and dilation of the veins. In this case, uneven contours are visible, the lower edge is rounded. A large focal increase in density is noted. Fluid accumulates in the abdomen.
Enlargement of the organ, rounding of its edges and dilation of veins may indicate pulmonary diseases or heart pathologies. If the echo structure is disturbed, this may be a sign of neoplasms, cysts, abscesses.
Gallbladder
Thickening of the gallbladder wall indicates acute cholecystitis. The size of the organ is any. The wall may have a “double” contour. Peritonitis is indicated by fluid spilling around the bladder.
The walls of the organ also appear thickened in the chronic form of cholecystitis. At the same time, the contours maintain density and clarity. Acoustic shadow, thickening of the gallbladder wall, uneven contours - everything speaks of calculous cholecystitis. An increase in the width of the ducts indicates the presence of stones.
Pancreas
A decrease in the echo density of the pancreas is observed in acute pancreatitis. Its chronic form or oncology is indicated by an increase and expansion of the duct. Additional signs include “ragged” edges of the contours, pits on the surface of the organ, compression of the aorta or displacement of the vena cava.
Spleen
Diseases of the blood and liver are reflected in the spleen in the form of its increase in size. Tissue compactions indicate the death of some area. The image clearly shows organ ruptures due to trauma.
Lymphatic structures
If the lymphatic structures are normal, they are not visible during an ultrasound. Enlarged nodes indicate infection, malignant tumors, and metastases.
After the abdominal ultrasound procedure, a conclusion is made that describes in detail what diseases the echo signs resemble. If a specific organ is examined and no deviations from the norm were observed, it is written that the echo symptom did not reveal any pathology.
Ultrasound is an effective and accurate method for determining changes in internal organs and systems. The procedure helps determine the development of oncology and other serious diseases. The method is painless and has virtually no contraindications.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity: norms and interpretation of results
- What will a heart ultrasound show? What diseases will it detect?
- Ultrasound of the adrenal glands
- Normal kidney sizes according to ultrasound in adults and children
- Ultrasound of the pancreas
- Ultrasound of the liver. Preparation for the procedure
Norm and pathology in ultrasound diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract
Normally, the intestine is moderately echogenic and has uneven edges of the mucosa. The abdominal cavity has no fluid inclusions, the walls of the stomach are not thickened or ulcerated. As a result of an ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract, the following can be detected: ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines, intestinal obstruction, diverticulosis, oncopathology, cystic formations of the esophagus, abscesses of the stomach or intestines. As well as echo signs of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity as a result of injury to a section of the intestine, rupture of the appendix, urinary or gallbladder, etc.
What is included in the examination
Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity involves the examination of all organs located in this area.
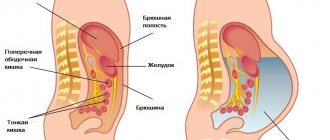
The diaphragm closes the abdominal cavity at the top; the back muscles, tissue and spine are located at the back. In front are the abdominal muscles, and below are the skeletal system and pelvic muscles.
The inner surface of the abdominal cavity is covered by a thin layer of tissue with a mass of nerve endings, called the peritoneum.
Ultrasound of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space allows not only to carefully examine the organs of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system, but also to evaluate the blood vessels located here.
Important! It is not possible to thoroughly examine hollow organs (stomach, intestines) using ultrasound. Other methods are used to diagnose them.
The abdominal ultrasound complex includes examination of the following areas:
- Liver;
- Pancreas;
- Spleen;
- Gallbladder.
The organs of the retroperitoneal space are also examined: kidneys, bladder, ureters, lymph nodes and blood vessels of this area.
It will be possible to visualize the ureters only if they are enlarged, since these organs are hollow.
Ultrasound examination is used quite often, both in routine examinations and in emergency situations.
The duration of the procedure is no more than 15-20 minutes. It is performed by an ultrasound specialist and assisted by a nurse, who fills out the study protocol.
Important! An ultrasound scan is not accompanied by pain or discomfort.
A special conductive gel is applied to the contact sensor. For the procedure, the patient lies on his back on the couch. If necessary, he is turned on his side and asked to hold his breath for a few seconds.
Using a special sensor, which is connected to the monitor of the ultrasound machine, the doctor receives an image and the necessary information, which is entered into the protocol. Immediately after the study, the patient can eat and lead a normal lifestyle, without restrictions.
Normal indicators of organs of OBP and deviations
The study protocol prescribes the norms for abdominal ultrasound, indicating age and gender distinctions, so even the patient himself can see any inconsistencies in his form.
Liver and gallbladder
Due to close contact and interaction, these two organs are examined almost simultaneously and always together. Most of the diseases of these two organs are interrelated, and they affect a significant part of the population not only in our country. Therefore, the liver and gall bladder are subjected to the most scrupulous study.
Diet before ultrasound of the abdominal organs
The normal dimensions of the natural filter - the liver - for an adult are:
- right lobe: length up to 5 cm, thickness 12–13 cm;
- left lobe: height up to 10 cm, thickness up to 7 cm;
- oblique vertical size – up to 15 cm.
If diagnostic materials indicate increased echogenicity of liver tissue, it is understood that this organ is characterized by an increase in the ability to reflect ultrasonic waves. This phenomenon is characteristic of hepatosis - changes in the quality and quantity of liver fat cells. In extreme stages of this disease, ultrasound cannot detect hepatic vessels.
Hypoechoic areas of the liver on ultrasound
Exceeding the normal size of the liver and the presence of fluid in it in most cases indicate the development of cirrhosis. In this case, the expansion of venous vessels (especially the portal vein) is visualized, the shape and contours of the liver change. If an increase in liver parameters is detected on an ultrasound scan of the liver, its contours become rounded and the large vena cava expands, the patient is asked to inhale, and if the diameter of the vessel does not decrease, then the presence of pulmonary and cardiac diseases is likely.
Structural changes in the liver in several areas of different nature may be evidence of the occurrence of various pathological processes. This is observed in cancer, cystic formations and abscesses. In parallel with the liver, the gallbladder is also being studied. The normal level of this organ and its ducts in an adult healthy person has the following characteristics:
- shape: round, oval or pear-shaped;
- dimensions: width – 3–5 cm, length – 6–10 cm;
- walls: smooth, without changes or growths;
- The thickness of the walls of the organ itself is 4 mm.
If there are areas of growth in the gallbladder, ultrasound diagnostics will show them in the form of shadows. Such changes often indicate the presence of stones in the organ cavity. Oncological neoplasms can also be visualized as growths attached to the walls of the bladder. Based on the results obtained, an experienced specialist can determine the nature (benign or malignant) and size of the formed pathology.
An ultrasound examination can detect symptoms of inflammatory processes in the organ. This is indicated by a decrease or increase in its size, as well as thickening of the walls. Such changes indicate the development of acute cholecystitis. In the chronic course of the disease, during the procedure, compaction of the walls and contours is visualized, while the latter have clearly defined boundaries.
In case of combined inflammation with the formation of stones, called calculous cholecystitis, the uneven boundaries of the edges of the bladder and the shadows from them are visualized using ultrasound. Among other things, the procedure allows you to diagnose a condition dangerous to human health, characterized by the presence of fluid - ascites. This indicates the development of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) and requires urgent surgical assistance. Another case that requires emergency surgery is when the bile duct is blocked by a stone.
With such a pathology, an expansion of the bile duct will be visible on ultrasound, which will enable the doctor to diagnose it.
Changes in the gallbladder on an ultrasound image in chronic cholecystitis
Pancreas
Examination of this organ helps to detect the presence of inflammatory and oncological processes in it. Normal parameters of the pancreas in an adult are:
- head – up to 3.5 cm,
- body – up to 2.5 cm,
- tail – up to 3 cm,
- contours are smooth,
- structure – homogeneous,
- sufficient echogenicity,
- no growths,
- The diameter of the gland duct is 1.5–2 mm.
Which organs are being examined?
The examination allows you to determine the presence of the source of the problem.
Organs examined:
- Liver. This organ is examined first. Based on the results of the study, it is possible to diagnose hepatosis, cirrhosis, tumors and cysts;
- Gallbladder and ducts. The doctor evaluates the patency of the ducts, the presence of polyps, the condition of the walls of the organ, the presence of stones in the gall bladder;
- The stomach is examined only for the presence of neoplasms;
- Pancreas. If possible, all lobes are examined. It is possible to diagnose pancreatitis, tumor and pancreatic necrosis;
- Spleen. The doctor evaluates the structure, location and size of the organ, eliminating the possibility of neoplasms, cysts, and inflammatory processes;
- Intestines. Usually only the large intestine is examined. If formations or polyps can be detected, the patient is sent for additional examination;
- Kidneys. Their placement, relative position and size are assessed. Inflammations, tumors, cysts and conglomerates can be diagnosed;
- Bladder. The specialist looks at the shape, size, condition of the walls, as well as the contents of the organ;
- Vessels. It is mandatory to evaluate the abdominal aorta and large vessels feeding the organs. Blood flow and the condition of the vascular wall are also established;
- The lymph nodes. The doctor looks at their size. Enlargement of this organ is characteristic of oncological pathologies.
In women it looks like the uterus, in men it looks like the prostate gland. Despite the fact that these organs are located in the pelvis, they are still examined. Ultrasound can detect tumors or inflammation.
Results and possible complications
Ultrasound examination is considered today the simplest, most accessible and widespread method of examination. This is not surprising, because it is ultrasound of the abdominal cavity during pregnancy or pathologies that allows you to thoroughly see the condition of the internal organs.
There is no need to wait several days for results; they are visible during the procedure itself. Ultrasound examination is carried out in real time , so the results are known immediately. During the examination, the doctor announces the results, which the nurse writes down in the protocol. Based on this document, the attending physician can make an opinion.
If you properly prepare before an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the results can be obtained as accurately as possible.
On the screen you can see deformation of internal organs, enlargement or reduction of the spleen and liver.
It should be noted that there are a number of diseases that develop asymptomatically .
Ultrasound will help identify benign and malignant neoplasms. This will allow you to start treatment in a timely manner.
This way you can avoid many complications.
Important! Ultrasound examination is one of the most common today due to its effectiveness and accessibility. An abdominal ultrasound is done very quickly and, most importantly, painlessly. Such procedures make it possible to identify many pathologies and abnormalities.
To get accurate results, you need to properly prepare for the procedure. Preparation prior to abdominal ultrasound allows you to obtain the most accurate examination results. The first thing you need to do is come early in the morning, this will increase the effectiveness of the result.
Spleen examination
Ultrasound rarely reveals diseases of this organ, since pathologies of the spleen are rare. Normal indicators are the following parameters:
- length - 10-12 cm;
- width and thickness - approximately 5 cm;
- the vein is located at the gate of the organ;
- structure without formations.
An enlarged organ indicates problems with the liver or hematopoiesis, as well as infection and parasitic diseases. If pockets of compaction are noticeable, this indicates a splenic infarction, which forms after bruises or due to blockage of the splenic vein by a thrombus.
Recommended Diet
To identify functional or pathological processes in organs, it is important to adhere to a diet. It is best to include in the menu:
- boiled, steamed or baked chicken, beef or fish;
- one hard-boiled egg;
- pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal cooked in water;
- hard cheeses;
- low-fat light soups or broths.
It is advisable to eat small portions every 3 hours. For drinking, use weak tea or regular still water. 3-5 hours before the procedure itself, abstain from food. If the examination does not begin until after noon, then you can eat a light breakfast.
Preparation for examination of female genital organs
When examining the uterus and appendages, deviations from the norm can be noticed. In order for the results to be objective, everything should be done correctly for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Whether or not you come to the procedure on an empty stomach does not matter. But it is important that the bladder is full, this way the organs will be better visible. An hour before the procedure, you need to drink a liter of liquid.
Ultrasound examination is the most informative way to diagnose pathologies of various types. But for the results to be more accurate, it is in the patient’s interests to listen to the doctor’s recommendations and carry out all the steps to prepare for the ultrasound.
Diagnosis of the pancreas
During an examination of an organ, the doctor evaluates its contours and size. Malignant and benign formations are visible. Before preparing for the procedure, you should find out from a specialist whether an abdominal ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach or not. Namely the pancreas. On the day of the procedure, it is advisable to take a laxative on an empty stomach and not eat or drink anything. Usually, when preparing, the doctor advises you to avoid foods rich in protein. You can drink water, but you cannot drink alcohol or harmful drinks.
Spleen examination
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of the spleen in the human body. This organ is located in the abdominal cavity and destroys those blood cells that have been used up, transforms hemoglobin into hemosiderin and bilirubin, acts as a source of red blood cells and lymphocytes, produces the necessary antibodies, and also serves as an excellent barrier to various foreign particles or bacteria.
The spleen is a rather “delicate” organ, because it senses any changes affecting all organs located in the abdominal cavity and immediately suffers from them. That is why it is advisable to perform liver ultrasound in the following cases:
- if congenital defects are suspected;
- with damage to the peritoneum;
- for cancer and chronic diseases;
- for leukemia;
- for infectious diseases: hepatitis, typhus, mononucleosis, etc.;
- if the formation of neoplasms is suspected.
Examination of the spleen can be performed during routine examinations. Ultrasound makes it possible to detect the presence of a spleen in a patient (sometimes people can be born without it), to determine how “correct” its structure, location, stability of fixation is, whether the size is optimal, whether there is a heart attack or other lesions. Some of these indicators help determine the development of other diseases. For example, an enlarged spleen, that is, splenomegaly, may be a sign of:
- jaundice;
- leukopenia;
- infections;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
This is what an abdominal ultrasound shows in a child.
In some cases, the disease can develop almost unnoticed by a person. The patient may experience only minor negative symptoms, which are often not given any significance. But even minimal deviations in any organ can become a source of serious illness.