Arthritis of the knee joint – an inflammatory process of the right or left knee that occurs for various reasons. It occurs in the form of monoarthritis or polyarthritis. Signs of knee arthritis are: pain (whether you are moving or your body is stationary), limited range of motion, swelling in the affected joint, redness of the skin in the inflamed area, pain when palpating with your fingers, and fever.
Diagnosis of arthritis of the knee joint includes X-rays, MRI, ultrasound, thermography, collection of synovial fluid from the diseased joint, biopsy of the synovial membrane, and arthroscopy. Treatment for knee arthritis depends on the conditions and causes of the disease. It may include medication, a course of injections, immobilization of the affected joint, physical therapy, exercise therapy, and sometimes surgery.
According to ICD-10, arthritis of the knee joints has code M17.
Knee arthritis: general information
Arthritis of the knee joint is an acute chronic disease of the knee joint, characterized by degeneration of osteochondral tissue. Of all the joints in the human body, the knee is most likely to suffer from disease, since it has a complex structure and is constantly under stress. According to statistics, knee arthritis accounts for 35-52 percent of all joint inflammatory diseases. It can occur at any age, but people between 40 and 60 years of age are at risk. Prolonged arthritis, as well as arthritis characterized by regular exacerbation, leads to a limitation in the range of motion of the joint or a complete loss of mobility.
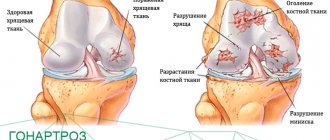
The knee is made up of three bones - the patella, femur and tibia. Their surfaces are covered with cartilage tissue, which serves to weaken the friction force. Ligaments (intra-articular and extra-articular) are responsible for stabilizing the knee, and the menisci are responsible for shock absorption. All components are located in the articular capsule, covered with a fibrous membrane. Inside, the compound bursa has a synovial membrane that produces synovial fluid.
The knee performs the function of support, as well as flexion-extension of the lower limbs and their rotational movement.
How does the disease manifest itself?
This joint disease can only be overcome with complex therapy that can both eliminate pain and eliminate all those processes that caused the development of arthritis. The attending physician's arsenal includes:
- Drug treatment.
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage sessions.
- Physiotherapy.
- In extreme cases, surgical interventions are possible.
What exactly can be used and how to treat the patient is determined only by the doctor. Under no circumstances should you choose measures on your own and try to get rid of arthritis of the joints.
There are five main groups of drugs and you should know about them.
Treatment of this unpleasant joint disease begins with a medication schedule. Usually these are drugs from five large groups.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These are basic formulations that are necessarily prescribed to patients who need to treat joint diseases. They can reduce pain and reduce swelling. Most often these are drugs “Nimesulide”, “Olfen”, “Revmoxicam” and the like. Despite their effectiveness, they cannot be taken for a long time due to a long list of side effects. The most dangerous effects are considered to be on the digestive tract, liver, and the ability to cause bleeding and bronchospasms.
- Steroid hormonal drugs. They are needed to reduce inflammation and pain, and relieve a person from swelling. To treat a knee with them, you need to pump the medicine directly into the joint cavity. The best known drugs are Diprospan, Kenalog and hydrocortisone suspension. However, it must be taken into account that these drugs have even more side effects than non-steroidal drugs.
- Warming gels with ointments. They act directly on the skin and joint area, reduce pain, increase local blood circulation, help treat the knee and return it to normal mobility.
- Chondroprotective medications. Without these drugs, it is almost impossible to cure joints. They are the ones who restore cartilage tissue and put metabolic processes in cartilage in order. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Rumalon, Dona, and Teraflex. It takes several months to take them to notice the medicinal effect.
- Vitamins and various restoratives. To treat joints, a variety of vitamin complexes are necessarily prescribed to help restore metabolism not only throughout the body, but also specifically in the affected joints. The use of group C, B in combination with immunostimulating drugs such as Tactivin or Levamisole helps to normalize the formation of fluid in the joint and increase the elasticity of cartilage tissue.
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe antibiotics, drugs against tuberculosis, and the development of tumors. It all depends on the causes of arthritis of the knee joints, the course of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of each patient.
Knee arthritis is an inflammatory disease. It occurs most often due to increased stress, as well as the influence of infectious diseases on the joints. However, the causes of the development of the disease can also be:
- regular stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- problems with lymph nodes.
A combination of several reasons or even one of them can affect the development of the disease. Arthritis will manifest itself as pain. It can occur both at night and during the day. In addition, the following symptoms may occur:
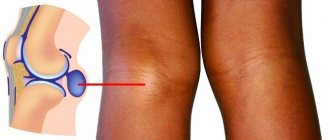
- swelling of the knee;
- joint inflammation;
- redness on the skin near the affected area;
- stiffness of movements;
- knee deformity.
Of course, you shouldn’t wait until cartilage deformation begins. At the first signs, you should seek help from a specialist. After diagnosis, the doctor will decide to prescribe certain medications to relieve symptoms and treat the disease.
Symptoms of the disease fall into several categories. Therefore, each of them should be considered in more detail.
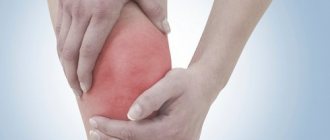
- Local symptoms. These symptoms include pain, swelling and deformity. The pain occurs periodically. If there is more load on the knee, the pain will increase. It can be different, from sharp and stabbing, to dull and pulling. The pain is especially aggravated in the morning, and throughout the day it subsides. In case of infectious infection, the pain can be unbearable.
- Tumor in the knee area. In this case, the knee becomes enlarged and heat is felt under the skin. And the skin on top also becomes hot to the touch. Such changes in the knee joint mean that inflammation has begun.
- Symptoms such as deformation are rare and therefore do not lead to serious consequences and do not impair the functions of the knee joint.
- Extra-articular symptoms. In addition to the above-described symptoms, there are also other symptoms of the disease. Depending on the type of disease, the symptoms vary. For example, with rheumatoid arthritis, weakness occurs, the temperature rises, the person loses weight, the heartbeat accelerates, and sometimes the person sweats a lot.
This disease is typical after suffering from tonsillitis or scarlet fever. In this case, accompanying symptoms are fever or chills.
Arthritis can also cause changes in other organs of the body.
- The eyes are affected by keratitis, keratoconjunctevitis, uviets.
- Shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing appear in the lungs.
- The heart speeds up its rhythm, shortness of breath and pain appear.
- Gastrointestinal tract - abdominal pain, problem with stool, a person is losing weight.
- Changes occur in the kidneys, resulting in kidney failure, swelling, pressure, lower back pain, and problems with urination.
- Blood vessels - systemic vasculitis, Raynaud's syndrome, capillaritis.
Arthritis of the knee joint progresses very slowly, with its manifestations alternating between acute forms and remission, as a result of which the joint itself is damaged and deformed.
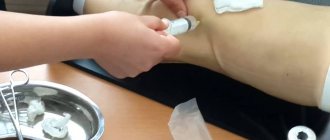
In order to make an accurate diagnosis of arthritis of the knee joint, blood is taken for analysis.
With a general blood test, the patient will have an increased ESR, the number of leukocytes, eosinophils, platelets and anemia.
Due to biochemical analysis, a symptom of rheumatic factor is detected. Also, with an x-ray, the doctor will find that the joint spaces are greatly narrowed, damage and growths have appeared on the bone tissue.
The main symptoms of knee arthritis include pain, swelling and changes in the shape of the joint.
Arthritis pain can vary, but all tend to gradually increase in intensity. At first, these are periodic unpleasant sensations that appear during physical activity or at the end of the day. It is also likely that a “starting” pain syndrome will appear (appears after rest). Arthritis pain is often accompanied by joint stiffness or a general feeling of stiffness in the affected area.
Signs of the inflammatory process in arthritis are standard: edema, swelling, increase in the volume of the diseased joint, redness of the skin, increased temperature, limited range of motion. At an advanced stage, the inability to flex the joint, changes in the shape of the bone, ankylosis, and muscle deformation appear.
We invite you to read: Exercise therapy for hip dysplasia
Depending on the etiology of arthritis, disruption of the functioning of body systems is possible: skin (rash), visual (keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc.), respiratory (pneumonitis, alveolitis), cardiovascular (diseases of the membranes of the heart, heart disease), digestive (enterocolitis), urinary (amyloidosis, chronic renal failure).
The signs of purulent arthritis are somewhat different: chills, fever, headache and muscle pain, disruption of the contour of the joint, a feeling of “fullness” in the affected area. In this case, the pain varies in intensity. It is constant, strong, and does not depend on whether you are moving or resting. In addition, purulent arthritis is accompanied by ligament degeneration, dislocations and sepsis.
Treatment of arthritis of the knee joint at home during the period of acute manifestation of the clinical picture is carried out using medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain - Butadione, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide;
- Corticosteroid tablets, injections to eliminate swelling - Hydrocortisone, Diprospan;
- Chondroprotectors for restoration of articular-cartilaginous tissue, normalization of metabolic processes in the body - Terflex, Artra, Collagen Ultra.
At home, you can use Fastum gel based on ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Ortofen - no more than 2 weeks. If there is no positive result, stop using these medications.
Medication methods for treating pathology at home
Being a manifestation or complication of other diseases, knee arthritis is possible in the following cases:
- In the presence of osteoarthritis. Inflammation of the joint cavity occurs as a result of its deforming lesion, and in addition, destruction of cartilage.
- With the development of rheumatism. This is a general disease of the whole body, which most often negatively affects large joints, as well as the heart.
- If you have psoriasis, which is a disease of the skin and connective tissues.
- With the development of lupus erythematosus (damage to the immune system).
With arthritis of the knee joint, symptoms can be intense, bright or sluggish. Arthritis can be acute. In this case, it begins suddenly, proceeding quite intensely. Or the disease may have a chronic form, when the first signs of the initial stage of the disease are invisible, and it continues for a long time with periodic exacerbations.
How can you determine inflammation of the knee joint? The diagnostic stage is, first of all, the task of the attending physician. Regardless of one or another reason for the development of various forms of arthritis, there are common signs, for example:
- The presence of pain that intensifies during movement.
- The appearance of swelling or swelling in the area of the affected knee.
- The presence of a local increase in temperature.
- The appearance of redness of the skin in the area of inflammation.
- Reducing the range of motion in the affected joint.
Classification
Arthritis of the knee joint does not have a clear classification. From a clinical point of view, it can be acute or chronic.
Based on the cause of occurrence, arthritis is divided into:
- primary (being an independent disease);
- secondary (provoked by other diseases).
Etiology divides arthritis into:
- infectious (specific, nonspecific, infectious-allergic);
- rheumatoid;
- aseptic;
- post-traumatic;
- reactive.
According to the type of inflammatory process, knee arthritis is:
- purulent;
- serous-purulent;
- serous.
Depending on the number of affected joints, the following are distinguished:
- unilateral arthritis;
- symmetrical arthritis.
Treatment of pain without pills and injections
How to “treat” rheumatoid arthritis of the knee? The treatment methods described below do not completely eliminate the neurological disease, but eliminate obsessive pain and excruciating suffering during active physical activity or at rest, especially at night.
Lidocaine patch
Lidocaine stickers will help alleviate human suffering by reducing the pain symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. You can purchase this medicine at any pharmacy chain without a prescription.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that, when absorbed into the skin surface, causes blockade of sodium channels and ensures stabilizing activity of neuronal membranes.
The German Versatis® lidocaine patch, which is glued to the source of pain (the knee joint), will help eliminate pain symptoms. The effect of the drug is 10-12 hours.
Kinesiology taping
Rheumatoid arthritis of the knee is accompanied by muscle weakness. Due to wear and tear of the articular surface, the bones of the lower limb naturally move closer together, which leads to imbalance of the muscles. You can strengthen the musculoskeletal and ligamentous apparatus with special tapes (kinesio tapes). An elastic patch with an acrylic thermoactive coating is applied to the lateral knee ligaments and patella.
Applying tapes will reduce the pain effect, improve blood and lymph flow in the osteoarticular segment, and provide the knee joint with a certain degree of freedom. Kinesiology taping of the knee can be used for 5-7 days.
Use of ointments with capsaicin
There is another substance for external use that effectively eliminates the pain symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joint.
Capsaicin is an alkali found in red peppers. Based on this organic compound, medicines are produced to relieve pain:
- Nicoflex® Hungarian. Ointment for external use has a combined effect (absorbent effect, local irritant and analgesic). The drug is widely used for myalgia, arthritis, sprains, sciatica, etc. For joint diseases, it is recommended to apply a thin layer of ointment to painful areas no more than once a day. Contraindications and restrictions: violation of the integrity of the skin in the area of therapeutic actions, individual intolerance to the main active ingredient - capsaicin;
- Espol® is an ointment for external use from Nizhpharm JSC (Russia). The drug has a local irritant and analgesic effect due to the extract of capsicum. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the knee no more than 2-3 times a day. To enhance the therapeutic effect, a dry warming bandage is applied over the drug. The duration of treatment should not exceed 7 days. Contraindications: allergic dependence on the active substance, violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of the lesion, pregnancy and breastfeeding in women, children under 7 years of age.
The proposed treatment methods do not eliminate the neurological problem, but only temporarily relieve pain symptoms in rheumatoid arthritis of the knee.
Causes of the disease
Primary arthritis occurs due to various injuries (bruise, meniscus tear, damage to the knee capsule, open wounds), due to which infection enters the joint and causes inflammation. Arthritis can occur as a result of an incorrectly performed puncture or careless surgical intervention.
Secondary arthritis is provoked by systemic diseases (psoriasis, rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.), as well as infections (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, tuberculosis, etc.) and suppuration (furunculosis, osteomyelitis, etc.).
Reactive arthritis of the knee often develops against the background of genitourinary and intestinal diseases.
Acute arthritis is provoked against a broader background of external factors (allergies, infections, vaccinations, hypothermia, childbirth, previous operations).
In addition, knee arthritis is diagnosed in people suffering from hemophilia, gout and malignant tumors. Also at risk are those who have suffered various joint injuries, are overweight, experience frequent, severe physical activity, and suffer from flat feet and joint hypermobility.
Types and forms of the disease
The reasons why this disease occurs are not yet fully understood. Arthritis in people can develop as an independent pathology or be a symptom of other diseases, for example rheumatism. There are primary and secondary forms of this disease. Primary arthritis is considered to be the presence of pathology that occurs independently. The secondary type occurs in the form of a manifestation or complication of other diseases. The primary form includes the following types of disease:
- Septic form. Within this type, inflammation is caused by pus-forming microbes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis affects different groups of joints. For example, knees and so on.
- Post-traumatic form.
- An idiopathic species, the nature of the origin of which is unclear.
Treatment methods for knee arthritis are improving every year.
Symptoms of knee arthritis
The main symptoms of knee arthritis include pain, swelling and changes in the shape of the joint.
Arthritis pain can vary, but all tend to gradually increase in intensity. At first, these are periodic unpleasant sensations that appear during physical activity or at the end of the day. It is also likely that a “starting” pain syndrome will appear (appears after rest). Arthritis pain is often accompanied by joint stiffness or a general feeling of stiffness in the affected area.
Therapeutic measures
Today in medical practice there is no possibility to completely cure gonarthritis. However, early initiation of specific treatment helps to slow down pathological changes in the inflamed joint and prevent its further destruction. Therapeutic measures in this case are as follows:
- To relieve pain in the affected joint, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen) are prescribed.
- If an infectious focus is identified, a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary.
- To reduce the intensity of pain in an inflamed knee, ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects (Virapin, Ketonal, Capsoderma) are used externally.
- In case of significant limitation of mobility and pronounced pain in the knee joint, the attending physician may prescribe intra-articular injections of glucocorticosteroid drugs. Such measures help to eliminate pain in the knee in a short period of time and significantly expand the amplitude of movements performed in it.
- Diet for arthritis of the knee joint also plays a big role in the treatment process and includes the inclusion in the daily diet of foods with a high content of vitamins (A, C, E, group B). Every day you should eat foods such as fish, herbs, fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, cereals, etc. It is necessary to exclude smoked, canned, spicy dishes, marinades from the usual menu, and refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages, as well as coffee and black tea.
- To maintain mobility in the affected joint and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory reaction, the patient must daily perform a complex of physical therapy developed individually for him.
- Additional therapeutic measures include the use of physiotherapy methods and sanatorium-resort treatment.
Daily exercise therapy helps maintain the functionality of the knee joint.
In the absence of a pronounced effect from conservative treatment, the attending physician may decide on the advisability of correcting pathological changes in the knee joint through endoprosthetics surgery.
Maximum improvement of the usual lifestyle, timely treatment of chronic foci of infection in the body and strict adherence to all medical recommendations in the event of an inflammatory reaction in the knee joint help prevent the progression of pathological changes in the structure of its elements.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of arthritis of the knee joint is necessary to establish the causes of the disease, as well as the degree of its severity (first, second, third).
At the first signs of the appearance of this disease, you should contact an arthrologist, rheumatologist, orthopedist, phthisiatrician and even a venereologist.
Blood sampling in acute arthritis will show the following signs of the inflammatory process: leukocytosis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the presence of inflammatory markers and antibodies to infectious pathogens.
An x-ray may reveal bone holes, narrow gaps, and bone degeneration. For a broader diagnosis, they resort to magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound, as well as thermography, arthrography (with contrast) and pneumoarthrography.
An invasive type of diagnosis includes sampling of synovial fluid through a puncture, sometimes a biopsy of the synovial membrane and arthroscopy of the joint.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after examining the patient, studying his medical history, laboratory tests and instrumental examination.
Diagnostics looks like this:
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- joint thermography;
- arthrography with contrast agent;
- pneumoarthrography.
Sometimes invasive techniques are used - arthroscopy, puncture and biopsy of synovial fluid. To differentiate from arthrosis, MRI is prescribed.
Treatment
When treating knee arthritis, it is necessary to reduce the load on the legs or completely immobilize the affected joint.
Treatment with medications includes taking chondroprotectors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the use of gels and ointments, as well as applications, dimexides and antibiotic therapy. In some cases, injections using corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid directly into the joint itself are necessary.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that arthritis caused by syphilis or tuberculosis requires special treatment.
The rehabilitation period involves therapeutic exercises, massage procedures, physiotherapy and acupuncture, and experts also recommend the use of assistive devices (canes, knee pads, orthopedic shoes).
A general recommendation for anyone who suffers from joint disease is to lose weight (to reduce the stress on the joints).
If conventional treatment does not help, surgical intervention is resorted to. It includes methods such as resection, dissection of the synovial membrane, lavage, sanitation of inflammatory foci, arthrotomy and prosthetics of a degenerated joint.
Symptoms and treatment
Damage to the knee joint by rheumatoid arthritis is accompanied by pain that increases with any physical activity. Pain in the joint is accompanied by stiffness, crunching, and limited mobility. It becomes difficult for a person to perform his usual daily work.
The onset of the disease corresponds to acute or subacute clinical symptoms, which last several months or years. Joint syndrome is accompanied by morning stiffness and lasts from 30 minutes to one hour. Similar sensations occur at night. Spontaneous or constant pain increases with movement.
Lecture not on the topic of RA treatment:
Symptoms and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee depend on the degree of destruction of the articular cartilage (see table).
| Progression of rheumatoid arthritis | Main symptomatic signs |
| Rheumatoid arthritis stage 1 | The initial stage is characterized by periarticular swelling of the synovial capsule, pain in the joints with minor physical exertion, redness of the arthritic area, and a local increase in temperature |
| Rheumatoid arthritis stage 2 | The rapid division of connective tissue cells leads to compaction of the synovial membrane, which significantly affects the motor activity of the affected joint |
| Rheumatoid arthritis grade 3 | The released enzymes of the inflammatory cells spread to nearby bone segments and cartilage tissue, which leads to their deformation. Increased pain, partial loss of motor functions of the knee joint become more pronounced |
Clinical symptoms may have extra-articular manifestations when the vital organs of the cardiovascular, endocrine, genitourinary, and respiratory systems are affected.
The therapeutic response to rheumatoid arthritis of the knee is not clear-cut. It depends on the cause-and-effect factor of joint damage. If the mechanism of development of the disease involves an infectious component, the introduction of drugs with antibacterial activity is required.
In the case of a hereditary form of clinical pathology, the course of treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroid drugs, chondroprotectors, physiotherapy, and manual treatment. Dietary nutrition, physical therapy, massage, and sanatorium treatment are mandatory for successful recovery.
Drug therapy
The systemic basis of drug treatment includes drugs with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory activity (NSAIDs):
- Melokvitis® is a Russian medicinal product. The solution for intramuscular administration has antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. The dosage form with the active ingredient – meloxicam – is recommended for all types of joint diseases of a degenerative-inflammatory nature: rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, any type of deforming arthrosis. Contraindications: gastric ulcer, liver and kidney disorders, patient's adolescence under 16 years of age;
- Ibuklin® is very effective . The medicine has all the properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory groups. The main active ingredients of the pharmaceutical product are ibuprofen and paracetamol. Contraindications: systemic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary and respiratory systems;
- Popular drugs with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory activity include a solution for intramuscular administration, Injectran® Russian. Thanks to the active substance - chondroitin sodium sulfate - the drug regulates phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the cartilage structure, slows down the loss of calcium and bone tissue resorption. Contraindications: individual intolerance to the active biochemical substance, pregnancy and lactation.
The use of glucocosteroids, chondroprotectors and other medications for basic therapy is considered by the attending physician individually, taking into account the patient’s age, gender, and the degree of complexity of the neurological pathology.
All pharmacological combinations are presented for informational purposes and are not intended as treatments without the direct prescription of a consulting specialist.
Report on the topic of drug treatment:
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine remains the safest and no less effective method of treatment, which, in combination with official therapy, significantly improves the patient’s condition, provided that all doctor’s instructions are strictly followed.
Several formulations that are most effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joint at the initial stage of inflammation:
- Recipe No. 1 from raw potatoes. Dip the grated (with skin) potatoes into hot water for a few seconds and apply to the damaged area of the knee. The medicinal mixture is additionally fixed with cellophane film and warm woolen cloth;
- recipe number 2 . You can eliminate acute pain using a weak solution of table vinegar. The food product is mixed with warm water in a proportional ratio of 1:2 and applied to the joint as a warming compress. This procedure is performed before going to bed;
- recipe number 3 . Onion peel (1/2 cup) is brewed with 200 ml of water. After cooling to a comfortable temperature, gauze or a medical bandage is moistened in a medicinal solution and applied to the knee joint;
- recipe number 4 . Honey and black radish juice will help relieve pain. To a tablespoon of juice add 20 g of honey and a tablespoon of baking soda. All ingredients are mixed and applied to the sore spot as a compress. Already in the morning, there is an increase in vitality, as the oppressive stiffness in the joints recedes, and a noticeable relaxation of the muscles is felt;
- recipe number 5 . A compression mixture of vodka, honey and mustard powder will give an excellent result. To prepare a homemade medicine, you need 100 ml of vodka or diluted alcohol, a tablespoon of a natural beekeeping product and a teaspoon of dry mustard powder. The whole mixture is mixed and infused for 1.5-2 hours in a dry place. This medicine is lubricated on the sore joint and left for 10-12 hours. Fixation with cling film and woolen cloth is required.
These traditional medicine recipes are recommended in the absence of an allergic reaction to the active medicinal components.
The traditional treatment program for rheumatoid arthritis can include daily pine or salt baths, which will relieve the inflammatory reaction and calm the human nervous system.
A home physiotherapy treatment can be a clay and paraffin wrap for the knee joint. Such treatment procedures are performed 30-40 minutes before bedtime.
Exercise therapy
The therapeutic complex of gymnastics and physical education is determined by the attending physician. It is worth starting physical therapy after the exacerbation has passed. The goals of gymnastics are:
- increasing the degree of elasticity of ligaments;
- muscle strengthening;
- normalization of metabolism through adjustment of blood circulation intensity;
- general improvement in well-being.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Some therapeutic methods are used exclusively if there is relief from pain, including inflammation. Among them there are methods borrowed from Tibetan medicine:
- Carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Performing massage and self-massage in order to relax the muscular frame of the knees and increase blood circulation.
- The use of pharmacopuncture, in which the patient is administered medications to biologically active areas of the back in minimal dosages. It is also advisable to perform acupuncture.
- Carrying out auriculotherapy, in which needles are inserted into active points on the ears.
- Performing a physical therapy complex.
- Carrying out sanatorium-resort rehabilitation.
Depending on the stage of knee arthritis, symptoms and treatment vary. Among other things, the following physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed:
- Phonophoresis with hydrocortisone.
- Performing paraffin applications.
- Use of magnet, quartz and laser.
- UHF therapy.
- Taking radon or hydrogen sulfide baths.
Special gymnastics and massage are effectively used to restore joint mobility. These methods can be used only after stopping the acute form of the disease.
Effective exercises for knee arthritis:
- Bridge;
- Bike;
- Butterfly (the closest approximation to the lotus position, only the feet are flattened towards each other);
- Swinging your leg back and forth while sitting on a chair;
- Raise your legs parallel to the floor, hold each limb suspended for 5 seconds.
Gymnastics is performed in the morning and evening, in a lying or sitting position. Regular exercise is an excellent prevention of muscle stagnation. If pain occurs, exercise should be stopped.
A therapeutic technique is performed after gymnastics, duration is 15 minutes, 2 times a day. It is useful to knead the knee area, stroking the back of the hand, massaging the side surface, rubbing the skin in a spiral. Finish the procedure with light stroking.
Diet
Proper nutrition is very important for joint health. If you suffer from arthritis, your diet should consist of:
- Omega-3, 6, 9 fatty acids (sea fish, flaxseed and rapeseed oil);
- spices (ginger and turmeric);
- plant foods (stewed vegetables, fresh fruits, nuts, seeds);
- honey;
- liquids in the form of medicinal tinctures, fruit drinks and natural juices.
It is necessary to exclude:
- alcohol;
- animal proteins;
- salt and hot seasonings;
- strong coffee and tea.
Treatment with folk remedies
Despite the skeptical attitude of representatives of official medicine towards folk remedies, some of them successfully cope with their task. During preparation, you should strictly adhere to the recipe and do not exceed the recommended amount of ingredients.
Compresses
Compress is a therapeutic bandage for the knee joint. In folk medicine, this is the name for a mixture of ingredients that is applied to the painful area. A plastic film and thick fabric are placed on top of it to enhance the warming effect. The bandage is fixed on the knee with gauze or elastic bandage.
Arthritis of the knee joints can be treated using a variety of folk remedies. You just need to take into account that the attending physician must know about all planned procedures and approve them. In no case should you limit yourself to healer’s recipes and heal joints only with them. Folk remedies include a variety of preparations from plant or animal materials.
- An ointment made from pork fat (0.5 kg), eggs (4 pieces), grated ginger (50 g), table vinegar (350 ml) is considered quite effective. It must be infused for three days and only then rubbed on the joints before bed.
- A compress of aloe leaves (2 pieces) mixed with brewer's yeast (a tablespoon) is considered an effective remedy for pain and inflammation. This paste is applied to the knee and kept for half an hour.
- Having previously smeared the sore joint with sunflower oil, you can apply a medicinal mixture of alcohol (1 tablespoon), honey (1.5 tablespoons) and radish juice (a third of a spoon) for forty minutes. Keep it for no longer than half an hour.
- It is also recommended to drink a special herbal infusion three times a day for a month: buckthorn bark is mixed with calamus, licorice and dandelion rhizomes. All herbs are taken in equal proportions. You should drink 100 ml at a time.
Knee arthritis should be treated not with traditional medicine alone, but with a combination of medications, special gymnastics and physiotherapeutic procedures. This is the only way to guarantee the patient’s cure and his return to his usual active life.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
Arthritis can also be treated with folk remedies, in combination with the main treatment. For treatment, compresses created according to ancient recipes are used. Here are a few of them:
- One of the effective folk remedies is using aloe compress. For this compress you will need aloe that is at least 4-5 years old; the leaves are crushed into a paste, brewer's yeast is added and applied to the sore spot. The compress is usually applied at night for three days. Then a short break and re-treatment with a compress.
- Black radish is a good folk remedy. For this recipe, you need to take a third of the black radish and squeeze the juice out of it, add a spoonful of ethyl alcohol and one and a half spoonfuls of honey. Next, lubricate the knee with vegetable oil and apply the mixture. It is good to wrap your knee with a warm scarf. Treatment should last for ten days.
- Arthritis can be treated with barberry tincture. To do this, pour 50 grams of barberry root with half a liter of vodka and leave for 10 days. Take the medicine orally, 20 drops per spoon of water before meals for a month.
- To treat the knee joint, you can prepare an ointment. This folk remedy is no worse. Pharmaceutical ointments. Melt half a kilogram of pork fat, add 4 eggs along with the shells. 350 grams of vinegar and 50 grams of ginger. Mix everything thoroughly and leave for three days. This folk remedy should be applied to the knee in a thin layer at night.
Folk recipes
Treatment of arthritis of the knee joint with folk remedies consists of the use of ointments, rubbing and compresses. These methods have almost no contraindications, and the positive side is that they can be used at home.
Compresses
- Warm up a cabbage leaf and brush with honey. Place the resulting compress on the sore spot, wrap it with film and a warm bandage, and leave it overnight.
- Beat an egg with two tablespoons of salt and pat dry with a bandage. Wrap your knee. As soon as the bandage is dry, rub it with any medicinal ointment. Repeat this manipulation two times.
- Apply a mixture of kefir and chalk to the sore spot, wrap in a warm towel. Leave overnight.
- Cut aloe leaves, dilute with black radish juice. Apply to the sore joint for forty minutes, wrap with film and bandage.
- Pour 5 garlic cloves with 500 ml of vodka. Let it brew for a week in a dark place. Strain. Drink 1 teaspoon before meals.
- Blot the bandage with a 50% dimexide solution. Leave on the sore spot for an hour. Repeat the procedure every day for 14 days.
- Warm up a burdock leaf, apply it to the sore spot, wrap it in film and a warm towel. Leave the compress on overnight.
Baths
Cut spruce branches, pour boiling water, let cool. Once the temperature becomes comfortable, lower your legs for half an hour. Repeat every day for two weeks.
Bee venom
Apitoxin therapy is not exactly a popular method today, but our ancestors used it. Bee venom strengthens immune defense, normalizes metabolism and hormonal levels, and reduces cholesterol levels. However, now this technique should only be used in the presence of a specialist.
Remember the main thing: it is impossible to cure the disease without the help of a doctor, but folk remedies will help slow down its progression.
Causes and symptoms of knee inflammation
reading information
Arthritis is based on pathological changes in the joints due to the development of an inflammatory process. When we talk about knee arthritis, we mean a disease associated with inflammation of the knee joint and the periarticular areas of one or both limbs. In medicine, this disease is called gonitis or gonarthritis.
Gonit has several forms of flow:
- The primary form of arthritis occurs on its own, that is, as an independent disease.
- The secondary form of the disease is a complication of another disease.
Depending on the cause, arthritis of the knee joint can be:
- rheumatic;
- reactive;
- post-traumatic;
- infectious;
- juvenile rheumatoid;
- septic;
- idiopathic, etc.
As a complication, arthritis of the knee joint develops after illnesses such as rheumatism, psoriasis, osteoarthritis, etc.
Depending on the location of the source of inflammation, arthritis of the knees is divided into cartilaginous (bone) and synovial.
According to the course of the disease, arthritis of the knees is divided into acute and chronic. Some scientists also identify a subacute form of the disease. Symptoms of acute arthritis of the knee joint are always violent, rapidly progressing, sudden, and in the chronic form they are sluggish.
How to prevent the development of symptoms of periarthritis of the knee joint?
A disease such as periarthritis of the knee joint is quite common. If you do not start treating it, you may face more serious problems. Inflammation of the periarticular soft...
Any training for this disease can be carried out only after the pain has been relieved and the inflammation has been eliminated, otherwise the joints may not be healed, but only harmed. It is advisable to carry out all exercises while lying on the floor or hard bed. It is advisable to perform each exercise six to eight times, carefully monitoring your own condition. The appearance of sharp pain is a signal about the need to stop gymnastics.
- Lie on your back, pull your arms up, straighten your legs. Stretch in opposite directions, thus stretching and straightening the joint areas.
- Lying down, stretch your toes and heels alternately.
- Lie down, straighten your legs. Carefully make circles with your feet.
- Take turns raising straight legs.
- Classic exercise "Bicycle". It can be performed with either bent or straight legs.
- “Butterfly” movement: lie on your back, put your feet together and try to spread your legs to the sides, while raising your head.
- The usual “Bridge”: lift the pelvic area, leaning only on the shoulders and heels.
Symptoms
This pathological process can manifest itself not only in the form of general disorders, because there are also local symptoms associated only with the knee joint. Here is a list of the main disorders observed in arthritis:
- Swelling of the joint, accompanied by the accumulation of fluid, which always leads to disorders associated with joint mobility, this is especially pronounced during exercise, as well as when squatting and walking on an inclined plane;
- Feeling of some heaviness in the knee joint;
- Sprain;
- Severely increased sweating;
- Significant increase in size of lymph nodes;
- General weakness, causing fatigue, as well as drowsiness, decreased performance and poor appetite;
- Fever and chills;
- Severe redness of the skin in the area of the knee joint and even a strong increase in temperature in this area;
- Severe pain in the knee area, which intensifies with movement due to muscle or ligament tension;
- Changing the shape of a limb;
- The occurrence of abscesses;
- Atrophic processes occurring in muscles;
- Joint erosion;
- Soft tissue necrosis.
If you notice manifestations of this kind together, and even separately, then you should immediately contact a specialist, because it is necessary to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin therapy while the pathological changes are still reversible.
Provoking factors
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs in people due to disruption of the immune system.
The following factors can give impetus to the development of pathology:
- severe allergic reaction – especially common in children;
- serious metabolic disorders;
- severe infectious diseases;
- traumatic lesions of the joints, in which there was severe inflammation;
- severe form of psoriasis;
- severe purulent processes in the body;
- systemic autoimmune diseases.
Whatever the cause of the pathology, it has a chronic course, and all therapy is aimed only at eliminating symptoms and reducing the rate of progression of the disease. According to statistics, pathology occurs more often in women than in men, and first appears at a young age. The disease is especially severe in women and leads to serious complications.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine, successfully used at home, is an excellent addition to traditional treatment methods. In order to treat arthritis of the knee joint at home, anti-inflammatory decoctions are used, which are prepared from medicinal herbs.
Let's look at the most popular traditional methods for treating knee arthritis.
The preparation of tinctures, compresses and homemade ointments is often used, which with proven effectiveness relieve pain, helping to reduce acute inflammation and being an excellent prevention of certain complications.
A remedy made from fresh cabbage, coltsfoot or burdock, as well as honey, works well. A large sheet is washed with hot water and slightly heated in the oven. Then cuts are made on it with a knife. Honey should be applied over the entire surface. After this, the sheet is applied to the knee. You need to wear a warming bandage on top. Use before bed every day. Relieves swelling and inflammation well.
Treatment of knee arthritis with folk remedies is most often a lengthy process.
We will also provide another recipe. The potatoes are washed, finely chopped, poured with boiling water and heated to 39 °C. The resulting pulp is applied to a cotton cloth 2 cm thick. Then it is applied to the inflamed joint.
Chestnut and lilac tincture is very effective as a pain reliever. Dry or fresh raw materials and vodka are used. Infuse in a warm, dark place for three weeks. Rub the infusion on the joints.
The symptoms of knee arthritis are very similar to arthrosis. The treatment of these diseases is also not much different.
It is strictly forbidden to use folk remedies to treat children, pregnant and breastfeeding women. If there is pathology of internal organs (liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract) accompanying arthritis of the knee joint, it is undesirable to use tinctures, infusions, decoctions, and herbal teas. Compresses, ointments, baths are contraindicated for abrasions, cracks, burns, infectious and allergic rashes.
What to do at home for knee arthritis?
During an exacerbation, you need to see a doctor and avoid putting stress on the inflamed knee. In order for the condition to improve as quickly as possible, you should take all medications recommended by your doctor at home, and do therapeutic exercises as your condition improves. You should also reconsider your lifestyle and give up everything that worsens recovery:
- smoking;
- taking alcohol and drugs;
- hot spices and hot dishes (their use aggravates the side effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hormonal drugs on the gastric mucosa, which can lead to the formation of ulcers or erosions).
You should also reconsider your diet and normalize your body weight, reducing the number of calories consumed due to fatty and refined foods. On the doctor’s recommendation, you can take medicinal baths at home (the doctor will tell you which substance to use) or make warm compresses on the knee.
What can you take orally?
- Elderberry (dried flowers) in the proportion of 1 tbsp. l. for 1 liter of water. Heat on fire for 15 minutes. Leave for 45 minutes, then strain. Dilute with boiled water to the initial volume. Dosage: 1 glass 3 times a day.
- Birch sap is effective. Gathered in the spring. Stored in the refrigerator. Take 1 glass three times a day.
- Tincture of nettle leaves. Take a tablespoon three times a day. Preparation: 200 ml boiling water and 1 tsp. raw materials. Leave for two hours.
We looked at traditional treatment for knee arthritis. Now let's find out how to prevent this disease.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women and men
Rheumatoid arthritis in women has more intense symptoms than in men. It is quite difficult to confuse pathology with the symptoms of another disease, and therefore a doctor, even before conducting tests, can make a preliminary diagnosis quite easily. The disease tends to symmetrically affect the joints, and therefore, after the knee joint on one side begins to deteriorate, pathology develops in the second knee. Impairments can also develop in both knees at the same time.
Main signs of pathology:
- in the morning there is stiffness in the sore joint, which completely disappears after 2-3 hours of activity;
- knee pain after intense physical activity. With severe destruction of articular tissues, pain of pronounced intensity appears in the second half of the night and, reaching a peak in the morning, persists until lunch. By evening the pain disappears;
- severe weakness in the diseased joint - disrupts its normal functioning and prevents full movement;
- swelling of the lymph nodes - first located as close as possible to the knee, and then regional;
- an increase in temperature to insignificant levels at the time of exacerbation of the disease and its complete normalization during periods of remission;
- deterioration in sleep quality due to pain;
- change in taste preferences.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms intensify, and during exacerbations the patient’s condition seriously deteriorates. Gradually, other joints, as well as the cardiovascular system, are involved in the pathological process. This process is especially rapid if there is no therapy.
In advanced forms of the disease, all manifestations of pathology are divided into local and general.
| Local (symptoms from the knee joint) | General symptoms |
| Swelling of the knee | Persistent chills |
| Deformation of the joint, which is noticeable from the side | Stably elevated heart rate and regular heart pain |
| Intense pain | Sweating |
| Mobility impairment | Weight loss |
Consequences
Advanced stages of the disease lead to irreparable changes in the joint.
If you identify the disease in a timely manner and do not delay treatment, the prognosis for recovery is positive. Otherwise, the patient risks getting the following complications:
- inflammation and destruction of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus;
- muscle tissue dystrophy;
- formation of cystic growths;
- complete immobilization of the limb;
- disability.
Dangerous complications develop with rheumatoid arthritis. In this case, internal organs suffer - the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, liver.
Causes
Diagnosis of joint diseases is fraught with some difficulties, since the inflammatory process develops gradually, accompanied by slow degeneration of cartilage tissue. Nonspecific symptoms indicate the disease at the time of its manifestation, but there are dozens of possible reasons for its development: post-traumatic, infectious, autoimmune, parasitic, etc. Even a simple rubella vaccine can provoke arthritis. Therefore, it is extremely difficult to make a clear and comprehensive etiological classification, and the cause of arthritis of the knee joint is determined individually after differential diagnosis.
| Type of relay protection | Cause | |
| P | Osteoarthritis | genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders |
| Rheumatoid | idiopathic etiology with possible autoimmune pathogenesis | |
| Gouty | metabolic disorder causing deposition of uric acid salts in the joints | |
| Still's disease | hereditary causes, but there is evidence of the influence of viruses and bacteria on the course of the disease | |
| IN | "Lupus" | damage occurs to all structures and organs where there is connective tissue |
| Scleroderma | pathogenesis similar to lupus arthritis, but the epidermis is predominantly affected | |
| Enteropathic | degeneration of cartilage tissue is associated with inflammation in the intestines (ulcers, colitis, dysentery, celiac disease, etc.) | |
| Tuberculous | arthritis is a complication of tuberculosis, although joint pain may increase even after treatment of the underlying disease | |
| Reactive | develops as a consequence of infectious diseases, mainly intestinal (salmonellosis, shigellosis) and urogenital (chlamydia, gonorrhea) | |
| Hemochromatic | joint degeneration occurs due to abnormal accumulation of iron in the body |
Designations in the table:
- (P) - primary arthritis;
- (B) - secondary arthritis.
The division of arthritis into primary and secondary is very arbitrary, since it is possible to find cause-and-effect relationships between the manifestations of certain diseases, but their exact etiological mechanisms have not been fully established. For example, in hemochromatosis, arthritis is caused by the accumulation of iron in tissues and joints, but what exactly causes this anomaly is not known for certain.
In most cases, the main cause of arthritis of the knee joint is injury with infection in the synovial area. If there is a genetic predisposition to this disease, it can develop under the influence of trigger factors.
Etiology:
- Infectious
- Autoimmune
- Post-traumatic
- Idiopathic
- Bacterial staphylococcus;
- streptococci;
- gram-negative bacteria;
- gonococci;
- hemophilus influenzae, etc.
- parvoviruses;
- schistosomiasis;
Leaving aside the specific etiology, we can identify the following factors against the background of which the knee joint develops:
- old age and associated metabolic disorders;
- weakened immunity and the presence of chronic diseases;
- injuries and severe hypothermia;
- professional factor;
- hormonal disorders associated with diabetes and obesity;
- transmission of severe infectious diseases;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Studies have shown that a sedentary lifestyle causes joints to “rust”, that is, rapid atrophy of cartilage tissue occurs. Therefore, to prevent arthritis, daily exercise or regular visits to the pool are simply necessary.
Prediction and prevention
The consequences of arthritis depend on the timely intervention of doctors - competent diagnosis and the immediate treatment process. The extent to which the patient adheres to the recommendations received is also of great importance.
Knee arthritis can be prevented by:
- avoid injury;
- do not overexert yourself physically;
- do not get too cold;
- keep your body weight within normal limits.
Prevention of secondary arthritis differs from the above requirements. It requires high-quality treatment of existing infectious and rheumatic diseases.
As the main methods for the prevention and prevention of complications of such a pathology as arthritis, we will name the following measures that are aimed at eliminating the main causes of this painful illness:
- A person should avoid getting cold feet. It is especially important to avoid keeping your feet in cold water for long periods of time.
- If your work involves standing for a long time or sitting for a long time, for example at a computer, it is recommended to take short breaks and set aside some time for short warm-ups or walking.
- It is very important to follow a diet, especially during treatment of arthritis and arthrosis of the knee joint. In addition, fight excess weight if you have it.
- You should always boost your immunity by leading a healthy lifestyle, hardening yourself and taking vitamins.
- It is extremely important to overcome bad habits.
It is, of course, up to the doctor to decide exactly how to treat arthritis of the knee joint in each specific situation. But the healing process itself largely depends on the patient himself. If a person strictly follows the recommendations given by the doctor and is attentive to his health, then he will have every chance of a full recovery. However, the possibility of completely curing this disease cannot be ruled out.
We reviewed the symptoms of knee arthritis and treatment with folk remedies, as well as traditional therapy for this disease.
Tags: arthritis, disease, cure, knee, treatment, joint
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Performing gymnastic exercises
Therapeutic gymnastics can be easily performed by a person at home. But at the same time, it is extremely important to do without making any sudden movements, avoiding excessive loads. They should be excluded in everyday life as well. Gentle stretching exercises help cure arthritis very well. As practice shows, they are very useful.
Let's look at a number of basic and effective exercises that can help stop arthritis of the knee joint and can serve as a preventative measure for this disease.
- Warm up. To warm up, a person must stand up straight and put his feet together. Next you need to place your hands on your knees. Then you should perform several rotational movements with your knees in one direction and then in the other. While performing such rotations, a slight feeling of pain may occur, which is considered normal. If the pain turns out to be sharp or gradually intensifies, then it is not advisable for the patient to do gymnastics.
- You need to sit on a chair and place your feet at some distance from each other. Next, you should lift one leg, moving it to the side and holding it in this position for about ten seconds. Then return to the starting position. The described exercise should also be done with the other leg.
- Lie on the floor, on your back. Next, you need to pull the knee of one leg towards your chest, holding in this position for several seconds. Then you need to straighten this leg vertically up, after which it should be lowered to the floor. The described exercise should also be done with the other leg.
The number of repetitions of each of the above exercises at the very beginning of training should not exceed five. If even a smaller number of such approaches causes discomfort, the load should be reduced to a minimum. In the future, as training progresses, the number of gymnastic approaches can be increased to ten.
Effective treatment with folk remedies for arthritis of the knee joint.
Prevention
Here are the main preventive measures that will help avoid the development of this disease:
- Eliminate any health problems in a timely manner by consulting a doctor (especially for diseases associated with the spine and feet);
- Do sports regularly, but try not to put too much strain on the knee joint (swimming is ideal);
- Perform physical therapy exercises;
- Follow the diet prescribed by your doctor;
- Do not allow infectious diseases to develop to serious stages (they should not become chronic);
- Try to maintain your posture;
- Contact a specialist if you experience any discomfort in the area of the knee joints, do not waste time.
Rheumatoid
This form of pathology is characterized by bilateral, symmetrical involvement of joints in the inflammatory process. Rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joint at an early stage begins to manifest itself as fatigue, asthenia, excessive sweating, low-grade fever, and morning stiffness. The pathology usually debuts with a sudden change in weather, excessive physical activity, the onset of puberty, after childbirth or during natural menopause. Exudate accumulates in the joint cavity, causing an increase in the size of the knee. The following signs of rheumatoid disease are also observed:
- sharp palpation pain;
- motor restrictions;
- local hyperemia and hyperthermia of the skin.
Articular symptoms are combined with extra-articular symptoms. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory organs, nervous and urinary systems is disrupted.
Infectious
Infectious pathology always manifests itself acutely, with severe symptoms, especially with the accumulation of purulent exudate. The knee increases in size, turns red, and becomes hot. Pain occurs not only while walking, but also at rest. At night they are “tugging”, piercing, pressing. The clinical picture of nonspecific infectious arthritis also includes the following signs:
- when pressing on the joint, pain is felt;
- the area of inflammatory edema gradually increases;
- the contours of the knee joint change.
To reduce the severity of pain, a person takes a forced position, his gait and posture change. After some time, he loses the ability to fully lean on his foot. Gonococcal specific arthritis differs from other forms by the involvement of the skin in the pathological process. Multiple rashes form on them - petechiae, papules, pustules, hemorrhagic vesicles.
Infectious arthritis of the knee joint is almost always accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication of the body: muscle pain, fever, chills, and neurological disorders. Children experience dyspeptic disorders: nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite.
Reactive
Rheumatologists and orthopedists are helped to diagnose reactive arthritis by the presence in the clinical picture of the so-called classical triad of specific signs. A couple of weeks after infection, symptoms of urethritis appear - the urge to empty the bladder becomes more frequent, and pain and burning are felt when urinating. Soon they are joined by clinical manifestations of conjunctivitis: redness of the mucous membranes of the eyes, lacrimation. And only then does arthritis manifest itself with pain in the knee joints, swelling, increased local temperature, and redness of the skin. Signs of pathology persist for several months, and then their intensity gradually decreases. A typical form of reactive disease is Reiter's disease.
Even “advanced” ARTHRITIS can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day.
Pathology does not go away without leaving a trace. If a person neglects medical care, joint deformation occurs and partial or complete ankylosis occurs. In some cases, untreated uveitis (inflammation of various parts of the choroid) leads to the development of cataracts.
Read also: Foods for arthritis
Arthrosis-arthritis of the knee joint is asymptomatic at the initial stage of development. A person is bothered only by minor discomfort, attributed to ordinary fatigue. Therefore, in the vast majority of cases, gonarthrosis of the knee joint is diagnosed at stages 2-3, when destructive-degenerative changes have affected a significant part of the cartilaginous tissue. Patients complain to the doctor about morning swelling of the knee and stiffness of movement, which disappears within an hour. The following clinical manifestations are characteristic of gonarthrosis:
Post-traumatic arthritis has a progressive course.
The muscles that stabilize the knee joint gradually weaken, and contracture often develops, significantly limiting movement. Bone osteophytes begin to form, compressing blood vessels and sensitive nerve endings.
Diagnosis of knee arthritis
For a correct diagnosis, one cannot rely only on symptoms; for this it is necessary to conduct a number of diagnostic tests:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- Analysis of urine;
- radiography;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- arthroscopy.
Blood analysis
Clinical blood testing is an important and necessary method for diagnosing knee arthritis. The blood picture shows an increase in ESR, an increased number of leukocytes, eosinophils, platelets, and a decrease in hemoglobin.
A biological blood test detects markers of the inflammatory process: seromucoid, some immunoglobulins, rheumatoid factors and C-reactive protein. If the level of reactive protein is higher than normal, then arthritis of the knee joint is diagnosed.
X-ray
An X-ray examination can determine the extent of damage to the knee joint. The x-ray shows periarticular osteoporosis, narrowing of the joint space, erosions and nodes in the bone tissue.
Ultrasound and MRI
An ultrasound examination is performed to determine the condition of the soft tissues of the joints. MRI is usually performed as an additional test for a complete diagnosis of the whole body.
Arthroscopy
A diagnostic method that involves inserting a flexible endoscope under the skin into the joint cavity. Using this method, you can monitor the condition of the joint and detect changes in the joint cavity. The study is carried out under anesthesia, and is prescribed in rare, exceptional cases.