Causes of varicocele
The causes of varicocele disease in men have not been precisely established to date.
- Most often the disease manifests itself during puberty. In most cases, the development of varicocele is explained by congenital predisposition and individual characteristics in the structure of the male genital organs.
- Most often, the disease appears due to a lack of connective tissue. A deficiency of such tissue leads to the fact that the veins lack a special valve that prevents the reverse flow of blood. Normally, blood flows towards the heart. In the case where the valve is missing, the blood flows back, that is, down towards the scrotum. Because of this, congestion occurs in the veins, and the vein gradually expands. As a result, the testicle appears to be immersed in venous tissue and plexuses, which causes the temperature in the testicle to increase. This process interferes with the production of sperm, since the production of seminal fluid requires a temperature lower than normal body temperature. Thus, in men suffering from varicocele, sperm production stops.
- Sometimes, due to excessive venous pressure and elevated temperature, autoimmune inflammation develops in the testicle, which also disrupts sperm production and leads to infertility.
- The cause of varicocele in men can also be due to prolonged (and systematic) physical activity. In this case, we are talking about excessive loads that increase blood flow in the veins.
- Varicocele becomes a consequence of other diseases in which intra-abdominal pressure greatly increases.
- Thrombosis or excessive pressure on the renal veins is also often a factor in the development of varicocele. That is why quite often this disease occurs in men who suffer from kidney cancer.
Varicocele - diagnosis and treatment
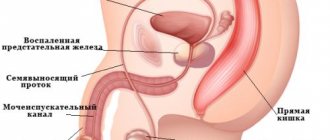
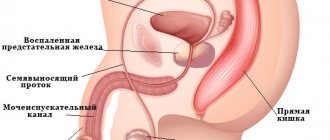
Varicocele is a varicose vein in the testicle and spermatic cord. Varicocele is one of the most common diseases among men, which often leads to very unpleasant consequences.
Causes of varicocele
Varicocele develops as a result of two reasons.
1. Congenital weakness of the vascular wall. Most often, varicocele develops as a result of a genetic predisposition to this type of problem. Almost always, one of the relatives of a patient with varicocele has varicose veins of the extremities, flat feet, heart valve defects, phimosis or other manifestations of connective tissue insufficiency. Often these diseases accompany each other.
2. Increased blood pressure in the veins of the pelvis or scrotum. In fact, it is more of a predisposing factor than a cause of the disease. But sometimes there are such pronounced anatomical changes leading to increased pressure in the veins that this factor becomes the cause of varicocele. The testicular vein can bend, be pinched by other vessels, pass through folds of tissue, etc. All this leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the vein and, as a result, an increase in pressure in it.
Less commonly, an increase in blood pressure in a vein is caused by general phenomena - chronic constipation or diarrhea, heavy lifting, tension in the abdominal muscles, etc. These factors can contribute to the development of varicocele, but are unlikely to cause the disease.
Why and how does varicocele disease occur?
The veins of the scrotum carry blood from the testicle and surrounding tissues to the heart. In this case, blood flows from bottom to top, against gravity. Normally, the reverse flow of blood through the veins is prevented by a special valve apparatus in the venous wall. When the veins dilate, these valves stop working, as a result of which the blood begins to make so-called “pendulum-like movements” in the vein. As a result, blood flow slows down sharply, and the blood supply to the testicle as a whole suffers.
Impaired blood supply to the testicle leads to the fact that its oxygen-depleted tissues begin to function worse. In addition, testicular temperature is normally several degrees lower than body temperature. With varicocele, the testicle is surrounded by a plexus of dilated veins, its temperature becomes equal to body temperature, and the function is inhibited even more. All this leads to the appearance of symptoms of the disease.
Degrees of development of varicocele
Based on how dilated the veins of the testicle and spermatic cord are, 4 degrees of varicocele are distinguished.
1st degree - testicular veins cannot be palpated by hand, their varicose veins are determined only instrumentally (ultrasound, Dopplerography). 2nd degree - dilation of the veins can be felt in a standing position; in a lying position, the varicocele is not detected. 3rd degree - dilated veins can be felt both in a standing and lying position. 4th degree - dilated veins of the testicle and spermatic cord are visible to the naked eye. Most often, varicocele develops in young men during puberty, quickly reaches a certain degree and no longer progresses. It is extremely rare that one degree of varicocele passes into another.
Almost always, varicocele is left-sided. It is very rare to encounter a bilateral varicocele, and it is extremely rare that a varicocele develops on the right.
Manifestations of varicocele
As already mentioned, with varicocele, testicular function suffers. This can manifest itself in two ways - either pain or discomfort occurs in the testicles, or the man becomes infertile.
The described symptoms occur differently in different men with varicocele. If we take all men suffering from varicocele as 100%, then half of them will not have any manifestations of the disease, 25% will experience discomfort in the testicle and 25% will suffer from infertility. Moreover, these numbers do not depend in any way on the stage of the disease.
Pain in the testicles with varicocele.
Most often, pain or discomfort is of a pulling, pressing nature; patients often describe this condition as heaviness in the scrotum. Typically, these sensations are not present all the time, but appear after physical activity, sexual intercourse, thermal procedures, or after a long period of inactivity.
It is not at all necessary that unpleasant sensations in the scrotum with a left-sided varicocele appear on the left. Most often, patients find it difficult to determine in which half they are more pronounced, and often the pain is localized mainly on the right.
Infertility and varicocele.
Among all men suffering from infertility, varicocele is observed in 40% of them. However, it is relatively rare that varicocele manifests itself with any other symptoms. Therefore, all men whose sperm count does not correspond to the norm must undergo an examination in this regard.
Violation of the blood supply to testicular tissue and its thermoregulation leads to inhibition of the function of the spermatogenic epithelium. As a result, the number of sperm in the spermogram may decrease, their motility and morphology may deteriorate. But this is not all the mechanisms of infertility with varicocele.
Testicular tissue belongs to the category of so-called barrier tissues. This means that normally the body's immune system never encounters testicular tissue and is not “familiar” with it. With a varicocele, the venous wall may no longer act as a barrier. In this case, immune factors reach the testicular tissue and begin to perceive it as foreign tissue. The so-called aseptic autoimmune inflammation develops. It is expressed more strongly the better the immune system of a man’s body is. The worst thing here is that the antibodies produced also affect the healthy testicle, causing the same inflammation in it.
Asymptomatic varicocele.
This is the most common variant of the disease. Most cases of varicocele are asymptomatic and do not bother the person in any way. Many men live with varicocele all their lives, have children and do not know anything about this disease. Often, a varicocele turns out to be an accidental discovery during an examination or a comprehensive examination (checkup) for a completely different reason.
As already mentioned, varicocele rarely progresses, so if there are no symptoms of the disease, then they most likely will not appear. However, the opposite often happens - older men experience pain in the testicles or changes in the spermogram associated with varicocele.
Diagnosis of varicocele
Starting from the second degree, varicocele is detected by a urologist during examination. If the enlargement of the veins is significant and the diagnosis leaves no doubt, then no additional examination is required. If the degree of varicocele is small, then a special examination is necessary.
Ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound of the scrotum.
If a varicocele is suspected, ultrasound or Dopplerography must be performed in two positions of the patient - lying and standing. If this is not done, the examination loses all meaning.
Which examination method to choose does not matter much. Doppler sonography is more accurate and allows you to definitively confirm or refute the diagnosis. However, an ultrasound scan of the scrotum performed by a competent specialist also dispels all doubts about the diagnosis of varicocele.
Dopplerography or ultrasound of the scrotum in lying and standing positions must be performed for all men with infertility and pain in the testicles.
In addition to all that has been said, in case of varicocele a spermogram must be taken.
Treatment of varicocele
There are only surgical methods for treating varicocele. If you hear somewhere about treating varicocele without surgery, do not believe it; there is no effective treatment for varicocele without surgery.
Surgery for varicocele must be performed if the disease manifests itself as pain in the scrotum or infertility. In both cases, getting rid of varicocele is the only way to get rid of the manifestations of the disease.
If nothing bothers a man with varicocele, the need for surgery is a controversial issue. It is usually decided based on the possibility of infertility. If a man still expects to have children, then it is better to have an operation; if not, then you can do without it. Most often, it turns out that if a varicocele is found in a teenager or a young man, then it makes sense to get rid of the disease, but if we are talking about an older man, then this is not necessary.
There are several types of operations for varicocele, and they are all divided into two types.
=> 1 type. The essence of this type of operation is to completely ligate, cut or remove the varicose vein.
The following happens. Before the operation, blood flow through the vein was slow. After the operation it stops completely. For the body, this situation is stressful, and this stress leads to the opening of new pathways for the outflow of blood from the testicle. As a rule, the superficial veins of the scrotum are involved.
The advantages of operations of this type are: relative ease of execution, minimal volume of surgical intervention, minimal time spent in hospital, lower cost compared to operations of the second type.
Disadvantages: relatively high percentage of relapses and non-physiological nature of the operation.
Relapses during operations of the first type are due to the fact that the veins in each person are located individually and can vary within a very wide range. If a branch comes off from a varicose vein, and during the operation this branch is not noticed and is not tied up, the operation will not give any result. This is usually called a relapse of the disease, but in fact it is simply the ineffectiveness of treatment.
For different operations of the first type, the percentage of relapses is different, depending on the type of operation it ranges from 10% to 40%.
The second drawback is the non-physiological nature of these operations. As already mentioned, the result of the operation is the complete cessation of blood flow through the dilated vein. As a result, the testicle is left without blood circulation, and under the influence of this stress, new pathways for blood discharge are opened.
This process takes about a week. During this week, the testicle often begins to hurt, and if there was pain in the testicle before, it noticeably intensifies. There is also evidence that during these events, the barrier between testicular tissue and the immune system may be disrupted, as a result of which antisperm antibodies appear in the blood, and the man develops or progresses infertility.
There are quite a few types of type 1 operations for varicocele. The more common ones are the Ivanissevich operation, the Marmar operation and the endoscopic operation.
=> 2nd type. During this type of operation, the veins of the testicle are completely removed, and then they are restored - plastic surgery. This type of operation is represented by only one type of operation, which is called microsurgical testicular revascularization.
The advantage of this operation is that immediately after the operation normal blood circulation is restored to the testicle. Varicose veins are completely removed, and recurrence of the disease is completely excluded. After microsurgical revascularization of the testicle, the patient does not experience pain for a week, as with type 1 operations.
Disadvantages of the operation: high complexity of the surgical intervention, longer hospital stay, higher cost of the operation.
Choosing a surgical method for varicocele
The choice of surgical method should be based on the manifestations of the disease on the one hand and financial capabilities on the other. The final choice of surgical method is made jointly by the patient and the doctor who will perform the operation. But very often the patient himself is excluded from the choice of surgical method and is not provided with complete information.
Therefore, we will consider here the most frequently occurring cases.
1. Varicocele is accompanied by severe pain in the scrotum area. In this case, microsurgical testicular revascularization is the optimal choice. With all other methods of surgery, a significant increase in pain is possible in the postoperative period.
2. Varicocele is accompanied by moderate pain or discomfort in the scrotum. Microsurgical testicular revascularization remains the most acceptable procedure. But in general, any method of surgery is suitable, you just need to be prepared for an increase in these sensations in the first week after surgery.
3. Varicocele is accompanied by changes in the spermogram. The only correct choice is microsurgical testicular revascularization. Other methods of surgery can lead to progression of infertility.
4. Varicocele is asymptomatic, discovered by chance, the patient is a young man who expects to have children in the future. The operation must be performed; the choice of method depends only on the patient’s capabilities. Preference should be given to either microsurgical testicular revascularization or endoscopic surgery.
5. Varicocele is asymptomatic, the patient is a middle-aged man who does not expect to have any more children. The need for treatment in such a situation is highly questioned, since nothing prevents one from continuing to live with this disease. If the patient insists on surgery, any method of treatment is quite suitable.
6. Recurrence of varicocele after previous operations. Repeated intervention is required, the most optimal is endoscopic surgery, microsurgical revascularization can also be performed.
7. Bilateral varicocele. Endoscopic surgery will allow you to get rid of the disease in one stage of the operation; all other methods require separate intervention for the right and left sides. But in case of development of infertility or severe pain in the scrotum, the choice should be microsurgical revascularization of the testicle.
Prevention of varicocele
Varicocele develops mainly due to an anatomical or genetic predisposition to this disease. Therefore, we are not talking about any special prevention of varicocele. After the end of puberty (19-20 years old), it makes sense to undergo an examination by a urologist, and if no signs of varicocele are found, you don’t have to worry about this.
If you already have a varicocele, you should try to avoid heavy physical activity and problems with bowel movements. Both lead to increased intra-abdominal pressure and, as a result, blood pressure in the veins of the pelvis, which can lead to progression of the disease.
For testicular pain caused by varicocele, cold applied to the scrotal area and the use of vasoconstrictor drugs can help. On the contrary, vasodilating medications and heat are contraindicated in such a situation.
It is also recommended to check for hidden sexually transmitted infections and a complete check of the male genitourinary system ( checkup ).
This can be done by making an appointment with the urologists of the “ Dr. Filatov Clinic ” by calling:
(812) 312-65-65 and 716-26-86
Symptoms of varicocele in men
The main symptom of varicocele is nagging pain. Such pain can be felt both in the area of one testicle and in both testicles at once. In addition, pain can be felt throughout the entire scrotum, and sometimes spreads to the entire groin area. As a rule, the pain becomes worse when a man plays sports, especially if the sport involves heavy physical exertion. Also, pain can be especially noticeable during sexual intercourse and immediately after it.
Capsules for potency Erostone
Using the drug increases sexual desire, strengthens erections, prolongs sexual intercourse and enhances orgasm!
Read more…
In addition to pain, you can notice a clear increase in the size of the scrotum or one of the testicles. Periodically, patients experience prolapse of the scrotum or left testicle. These signs indicate the development of pathology, which in turn can lead to infertility in the absence of proper treatment.
Sometimes a varicocele may not appear at all. For example, this often happens during puberty in teenage boys. In such cases, the disease is discovered completely by accident during an examination of the genital organs. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo an examination and comprehensive examination by a urologist at least once a year.
Complications
Complications of untreated varicocele are irreversible and consist of only two conditions:
- Infertility - due to a slowdown in blood flow from the testicles, constant tissue ischemia occurs with an increase in temperature in the scrotum area. This negatively affects spermatogenesis, which can subsequently lead to complete aspermia;
- Testicular atrophy is a direct result of varicose veins of the spermatic cord, the consequence of which is infertility and a decrease in the size of the testicles.
Postoperative complications also occur. But they are usually reversible and easily amenable to drug correction.
Surgery using direct access or a laparoscope can lead to the following complications:
- Infection;
- Hydrocele (swelling of the surrounding tissues of the testicle, lining of the scrotum due to trauma);
- Recurrence of varicocele;
- Damage to the artery in the spermatic cord.
Percutaneous embolization also has a number of complications:
- Allergic reaction to components of embolization or sclerotherapy;
- Thrombophlebitis;
- Damage to nearby vessels;
- Introduction of infectious agents into the pelvic cavity.
Stages of disease development
There are three stages of development of testicular varicocele in men.
- At the first stage, it is quite difficult to determine the presence of the disease. It can only be detected by touch when the patient is in an upright position. As a rule, the first stage of varicocele development does not cause much discomfort, so few men seek help from a specialist at this time.
- In the second stage, varicose veins can be seen in the testicular area. As a rule, to diagnose the disease at the second stage, it is not even necessary to palpate the testicles, since the expansion is visible to the naked eye. In this case, no significant changes in the testicles are detected.
- The third stage of varicocele, in addition to obvious dilation of the veins, is also characterized by an increase in the size of one or two testicles. In addition, when palpated, a change in the consistency of the testicles can be observed.
To make a diagnosis, as a rule, an additional analysis of seminal fluid is performed, which allows one to determine the stage of development of the disease and the presence or absence of infertility in a man. With varicocele, sperm motility is greatly reduced, so the presence of pathology is immediately visible.
Symptoms of varicocele
Symptoms of varicocele vary depending on the stage of the disease.
Grade 1 varicocele is usually invisible to the patient. The disease is detected during a medical examination (by palpation when the patient strains in an upright position).
Grade 2 varicocele is usually a consequence of an advanced first stage. Visually noticeable dilated veins descend in the form of clusters below the lower pole of the testicle. Upon examination, asymmetry is revealed: the testicle on the affected side descends, and, accordingly, half of the scrotum sags. The patient may experience pain of varying intensity (from a slight discomfort when walking to acute pain or burning in the scrotum, similar to neuralgia). Patients may also complain of decreased sexual function.
Grade 3 varicocele is characterized by constant pain, enlargement of the scrotum due to numerous “clusters” of veins that descend significantly below the lower pole of the testicle. This stage is almost always accompanied by impaired spermatogenesis.
Varicocele in men is often the cause of decreased sperm production and quality. Therefore, the consequences of varicocele are infertility and testicular atrophy.
Methods for treating varicocele in men
Like any enlarged veins, treating varicocele in men without surgery is simply impossible. However, if we take into account that in the early stages the disease is hidden, then only the presence of a certain discomfort becomes an indication for surgery. For example, surgical intervention is necessary if a man experiences pain. When pain prevents a man from living a normal sex life, doctors prescribe surgery.
Gel for penis enlargement for only 147 rubles!
"Titan Gel" - guaranteed penis enlargement. With Titan Gel you will always be in full combat readiness mode!
Read more…
Also, the indication for surgery is male infertility. If the reason for the inability to conceive is a varicocele, the only way to solve this problem is to have surgery to correct the problem.
Sometimes the reason for sending a man for surgery is only aesthetic discomfort caused by prolapse of the scrotum or an increase in the size of the testicles. If a man is concerned about the appearance of his genitals, he may also be sent for surgery.
In addition, doctors often recommend eliminating varicocele surgically in adolescents, since later after puberty the young man may develop other pathologies of the genital organs, as well as infertility.
Today there are several options for performing the operation:
- Operation using the Ivanissevich method . The essence of the surgical intervention is that the specialist makes an incision in the area between the lower ribs and the pelvic bones; there is a small depression in this area. This operation is otherwise called open. Then, incisions are also made in the tendons and muscle tissue to get to the veins. This is to locate the testicular vein and then tie it off to prevent blood from pooling in the testicular area.
- Operation via mini-access . This operation is performed by doctors through a small incision in the area where the spermatic cord exits. This zone is located one centimeter away from the base of the man's penis. After the incision is made, the surgeon finds the veins of the spermatic cord inside, which he ligates. Thanks to these measures, the blood flows through the veins located on the surface.
- Endoscopy . Operations of this type are increasingly used in modern surgery. In the surgical method of eliminating varicocele in men, three punctures are made. The first one in the navel area is for inserting a miniature camera. The next two punctures are necessary to insert tools - scissors and clamps. Thanks to the camera, the surgeon can see everything that happens under the skin in the abdominal cavity. Using clamps, the specialist locates the testicular veins and ties them with surgical thread. Sometimes titanium brackets are used for the same purposes.
- Testicular revascularization . This operation involves transplanting a vein from the testicle to the epigastric vein. Thanks to this intervention, normal blood flow is restored in the testicular area.
These types of operations do not take much time and are very common nowadays. Most often, doctors refer patients for endoscopy, since in this case there is minimal surgical intervention, and the operation itself takes only 20-30 minutes.
Treatment
The main treatment that can correct the situation is surgical. Drug therapy is selected only to relieve symptoms. It may delay the need for surgery, but it will not prevent a person from developing varicocele.
Drug therapy
Drug multicomponent therapy always accompanies treatment:
- The first stage of varicocele, which does not yet require a surgical solution to the problem;
- Relief of symptoms during preparation for surgery;
- Early and late postoperative periods for faster recovery of the body;
- Preventive courses.
The main arsenal of drug therapy is based on painkillers and venotonics.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and non-narcotic and narcotic analgesics are used as painkillers.
In addition to the analgesic effect, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have anti-inflammatory, normothermic and antiplatelet effects. It is better to use second-generation drugs that have selective inhibition of COX-2. Among the representatives it is worth highlighting Nimesulide, Meloxicam, Celecoxib, Etodolac.
Analgesics only relieve the symptom of pain, as they block the transmission of impulses from pain receptors. Ketoprofen, Nalbufin, Nalbuk, Ketanov cope well with the task. They are used both in the postoperative period and for pain relief before surgery.
Venotonics are taken in the first stages of varicocele to delay the pathological process and after surgery in the later stages of the rehabilitation period. Prominent representatives that have proven their effectiveness are Detralex and Aescusan.
Throughout the entire preoperative period and from the 10th day of the postoperative period, it is mandatory to use drugs to improve the microvasculature and rheological properties of blood. Trental, Pentoxifylline, Orbiflex, Agapurin will help with this.
Do not forget about auxiliary vitamin therapy. To quickly restore and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, you will need a sufficient intake of vitamins B, C, A and E.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is carried out only according to indications and is the only solution for varicose veins not only of the spermatic cord, but also of any organ.
Indications for the operation:
- Constant pain in the groin and scrotum;
- Progressive enlargement of the veins in the scrotum;
- Cosmetic defect;
- Gradual reduction of one testicle in relation to the other during the patient's puberty;
- Asthenozoospermia (immobility and low mobility of sperm in the test ejaculate) and oligospermia (insufficient number of sperm in 1 ml of ejaculate);
- Signs of male infertility.
There are 3 main directions in which the operation is performed. Ultimately, the essence of surgery is:
- Raising the testicle;
- Excision and removal of varicose veins;
- Embolization or sclerosis of varicose veins of the spermatic cord.
Recovery after varicocele surgery
As a rule, it takes 5-10 days for a man’s body to recover after surgery to eliminate varicocele. In the first two days it is not recommended to do anything at all. It is advisable to spend this time in bed. In addition, in the postoperative period it is advisable to exclude any physical activity.
You can return to a normal lifestyle, as well as to playing sports, after two weeks after the operation. It is advisable to gradually increase the load and carefully monitor the condition of your body. If there is any deterioration or if pain occurs, you should immediately stop playing sports.
During the week after surgery, a man is prohibited from lifting weights exceeding 4.5 kilograms. In addition, you should not take a bath or visit a bathhouse or sauna for at least 5 days after surgery. Bandages that will be applied to the patient immediately after surgery should not be wet or removed for two days. Next, the doctor will inform you about the schedule for dressings, if they are necessary.
After two days from the day of surgery, you need to gradually start moving. It is not recommended to lie in one place all the time; this can lead to the development of constipation and other digestive problems. In addition, it is advisable to eat soft, low-fat and light foods in the first days. Of course, sexual relations in the postoperative period are completely excluded.
Classification
According to the World Health Organization classification, there are three degrees of varicocele:
Stages and degrees of varicocele.
- 1 degree - changes in the veins cannot yet be determined visually or by palpation; pathology is determined only using the Valsalva maneuver;
- 2nd degree - varicose veins are still not noticeable visually, but are already well defined to the touch;
- 3rd degree - pathological changes in the veins are determined in the scrotum with the naked eye and are easily palpated during examination.
Varicocele is also divided into primary and secondary. In the second case, there is a specific reason for the development of the disease: obstruction by a blood clot or compression of the testicular vein by an inflammatory infiltrate or tumor. Some classifications distinguish 4 stages of varicocele progression. Each of them has its own symptoms.
Why do you need surgery for varicocele?
In the absence of proper treatment, varicocele in men can experience the most unpleasant consequences. Firstly, varicocele is the cause of infertility in men. This is the most common factor in reducing sperm motility, resulting in many men being unable to conceive.
In addition, often varicocele on the left in men leads to the development of various congestion in the testicles and other organs of the reproductive system. Such stagnation leads to the development of various inflammations and even infections.
Many people wonder what to do when they detect signs of varicocele in men. The answer in this case is simple. The first thing you need to do is see a doctor for an examination. You should not delay this, since varicocele often becomes the cause of many other diseases, including infertility.
Diagnosis of varicocele
Diagnosis of varicocele does not seem difficult. A urologist can detect abnormally dilated veins in the scrotum during a physical examination using palpation. An ultrasound examination of the scrotum can also be performed to rule out other causes of varicose veins (for example, an abdominal tumor may be pressing on the spermatic vein).
A spermogram is also required.
Prevention
Prevention of varicocele is a regular examination by a urologist, which should be carried out at least once a year. A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will also help to avoid diseases of the reproductive system. Sports activities are necessary for any man, however, the load should be moderate.
Article taken from the site: vozhak.info
Gel for penis enlargement for only 147 rubles!
"Titan Gel" - guaranteed penis enlargement. With Titan Gel you will always be in full combat readiness mode!
Read more…
Reasons for development
Representatives of the stronger half of humanity who have been diagnosed with testicular varicose veins are interested in what varicocele is and why it appears.
Varicocele develops for the following reasons:
- congestion in the pelvic organs;
- heavy physical labor associated with regular dragging of heavy objects;
- lack of constant sex life;
- surgical intervention on the genitourinary system;
- injuries to the abdominal cavity and genital organs as a result of sporting events, fights, accidents;
- renal vein thrombosis or kidney tumor;
- poor functioning of venous valves or their complete failure;
- weak vessel walls;
- increased blood pressure in the veins of the pelvis and scrotum.
Modern studies conducted by phlebologists have identified the causes of primary and secondary varicocele. Primary varicocele on the left develops due to the anatomical location of the veins on this side of the scrotum relative to each other, disruption of the formation of the inferior vena cava during intrauterine development, underdevelopment, absence or insufficiency of the valves of the venous plexus, inferiority of the connective tissue from which the vein wall is formed.
Secondary varicocele develops as a result of various neoplasms of a benign and malignant nature in the kidneys, retroperitoneum, pelvis, and diseases of blood vessels and organs located at the level of the scrotum and groin.
Scientists have found that being overweight can reduce the risk of varicocele, while being tall can increase it.
Treatment and prevention
If a diagnosis of varicocele in men is made, we have explained what it is, all that remains is to understand the features of the treatment of this disease. If the pathology is asymptomatic, that is, it is at the initial stage, then it does not need to be treated. The surgeon will give the patient recommendations regarding measures to eliminate blood stagnation in the pelvis. It is important to give up heavy physical work and eliminate constipation. Elderly patients are advised to wear a special support bandage for the scrotum area.
If pain occurs, there is infertility, a change in the shape of the scrotum or impaired spermatogenesis, the pathology requires treatment.
The operation will help eliminate the disease in stages 2 and 3. There are several methods of surgical treatment of pathology:
- Operation Palomo;
- Marmara method;
- Ivanissevich operation;
- endoscopic surgical treatment;
- X-ray endovascular venous occlusion.
After surgical treatment, the disease completely resolves. The prognosis is favorable even with advanced disease. Irreversible consequences occur only with testicular atrophy, so if you have the slightest discomfort in this area, consult a doctor. After treatment, reproductive functions and testicular function are completely restored.
General characteristics of the disease
Venous lesions of the testicles and vas deferens indicate disruption of the semilunar folds. Their normal functioning is the organization of reverse blood flow with the exception of platelet stagnation in the scrotum. Poor circulation is observed due to the detection of pathology of the venous leaflets on the inside of their walls. An organism that is exposed to prolonged physical work while in an upright position and does not have a strong immune system is at risk of developing varicocele. Stagnation of blood leads to stretching of the elastic venous walls. Therefore, in some places there is the appearance of serious compactions, swelling and inflammation of adjacent tissues. As the process intensifies, pain is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort that haunts movement. Over time, the disease begins to progress.
Varicocele does not pose a particular health risk, but is a major threat to infertility.
This pathology is associated with organic disorders of the body, since it affects the performance of venous channels, which leads to oxygen starvation of Leydig cells, responsible for the production of male hormones, and a lack of oxygen in Sertoli cells, responsible for the maturation of male germ cells. To identify the disease and provide qualified assistance, contact a urologist, andrologist or surgeon, who will promptly diagnose the stage and prescribe appropriate treatment to restore reproductive function.
How dangerous is varicocele for a man?
Varicocele is a pathological condition that develops due to impaired blood flow from testicular tissue. The veins that form the pampiniform plexuses become wider and swell, resulting in swelling of the tissues of the scrotum and testicles.
Statistics show that varicocele affects about 15% of men. The process of varicocele formation is similar to varicose veins of the lower extremities, and enlarged testicular veins look exactly the same as varicose veins on the extremities. They can swell and become visible through the skin, acquiring a knotty, twisting shape. The severity of the disease may worsen over time.
Classification of varicocele
The disease is classified depending on the severity of the pathological process. The World Health Organization offers the following classification of varicocele:
- I degree – dilation of the veins in the scrotum is not visible or palpable;
- II degree – the veins are visible, but can be easily palpated;
- III degree – dilation of the veins is clearly visible due to their protrusion through the skin, the veins are well palpated.
Possible complications
A dangerous complication of the disease is testicular atrophy, as well as deterioration of spermatogenesis, characterized by a decrease in the number of healthy sperm in semen. With testicular atrophy, irreversible disorders can develop in its tissues that damage the epithelium of the seminiferous tubules, and the testicle shrinks and takes on a soft consistency. When spermatogenesis is impaired, the number of sperm in the seminal fluid decreases and their motility decreases. The result is a complete or partial disruption of a man’s reproductive function and the development of infertility.
Causes of varicocele and its symptoms
The main cause of varicocele is considered to be intravascular valve dysfunction.
Valve defects can cause impaired blood flow and congestion in the venous pampiniform plexus. In addition, today doctors consider varicocele not only as an independent disease, but also as one of the manifestations of genetic disorders in the development of the renal veins or a disease acquired during life.
It is worth noting that any diseases of the inguinal canal, scrotum and abdominal cavity, leading to compression of the spermatic cord, can serve as the beginning for the development of impaired blood outflow, and as a result, to varicocele.
It is also worth considering the following factors that can lead to impaired spermatogenesis:
- excessive production of the hormone hydrocortisone;
- disruption of the barrier between the testicular tissues and the blood circulating in them;
- disturbances in the production of various pituitary hormones;
- increase in testicular temperature.
When examining the scrotum, dilation of the veins of the pampiniform plexus may be detected. A man may feel heaviness or pain in the scrotum. During physical activity, sitting or standing, the patient's condition may worsen. If the patient moves to a lying position, the symptoms disappear.
How is varicocele diagnosed abroad?
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor conducts an initial examination of the patient’s scrotum. This allows you to determine the severity of the disease. Further, foreign clinics recommend performing an ultrasound using Doppler ultrasound. This study is carried out with the patient standing and lying down. During an ultrasound examination, a Valsalva maneuver :
- when the patient is in an upright position, the veins in the testicles increase;
- if the patient is in a supine position, the vein decreases in size.
Urine tests are then performed before and after exercise. The following studies are also recommended for patients with varicocele:
- retrograde renal venography , which is performed after the injection of a contrast agent into the veins of the testicles;
- hormonal profile examination , which may include checking the concentrations of testosterone, prolactin, estradiol, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone;
- semiological examination or semen examination , which may detect a decrease in the number of motile sperm and an increase in the number of unhealthy sperm.
Effective methods of treating varicocele abroad
In foreign clinics, treatment of varicocele is planned individually for each patient. If there are no pronounced symptoms, doctors recommend limiting yourself only to medical observation of the disease.
Surgery on varicocele abroad is performed only in cases where the patient is bothered by severe pain, signs of testicular atrophy or impaired spermatogenesis.
How is it treated in Israel?
Medical treatment of this disease is based on the severity of the process and the presence of characteristic symptoms. In severe cases, when the disease is advanced, surgery is performed. Surgical intervention for varicocele in Israeli clinics is carried out using dissection of varicose veins, which helps restore the physiological outflow of blood in the veins of the scrotum.
The most effective surgical treatment for varicocele is performed in Israel. The operation does not require the use of general anesthesia and further hospitalization of the patient. The doctor makes a small incision in the skin in the scrotum area and excises and/or completely removes the enlarged areas of the veins. This operation helps normalize the flow of blood from the testicle. Doctors recommend performing a spermogram several months after surgery, which allows you to assess the number and degree of sperm motility.
Varicocele surgery is sometimes preventive in nature, and its goal is to prevent irreversible infertility.
New methods of treating varicocele are used at Meir MC
In addition to surgery for varicocele, the Meir Clinic actively uses non-traditional methods for treating this disease. The effectiveness of drug treatment for varicocele has already been proven in practice. Such treatment can be prescribed after the patient’s surgery in order to normalize spermatogenesis. The most often prescribed is a complex of vitamins and dietary supplements containing zinc and selenium. Sometimes hormonal medications may be prescribed. Currently, microsurgical methods for the treatment of varicocele are successfully used at Meir MC. This reduces the risk of relapse or complications after surgery
https://www.meir-health.ru/lechenie-varicocele.aspx
Signs of varicocele
Many men do not experience any symptoms of varicocele for a long time.
And only during a routine medical examination or after visiting a doctor with the problem of conceiving a child, the disease can be detected. In some cases, a sign of varicocele is a feeling of heaviness in the testicle or a dull pain that increases throughout the day, especially in hot weather or after exercise. In addition, enlarged veins or swelling in the scrotum, as well as testicular shrinkage, are common symptoms of the disease.
Main symptoms:
- infertility;
- swelling in the scrotum;
- recurring pain in the testicles;
- noticeably enlarged or twisted veins in the scrotum;
- decrease in testicular volume (in rare cases).
Diagnostic methods
How to determine varicocele? First, the doctor examines the patient and palpates the testicles. During the examination, the patient is in a standing position. The plexus of veins in the scrotum resembles a bunch of grapes.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, the Vulsalva test is used. The man is asked to push. This causes an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity. Enlarged blood vessels can be seen with the naked eye.
It is possible to restore erectile function! Proven FOLK CARE ... Reviews My story spotenciey.ru
Treatment of PROSTATITIS using a new method To restore the functions of the prostate, you need every day... Website Interview with a doctor bezprostatita.ru
The problem of the small size of the dignity has been solved. The mechanism of erection has been revealed... Official website Recovery bigbigrazmer.ru
Several methods are used to carry out diagnostics:
- Blood is drawn to determine the amount of hormones. The disease is accompanied by impaired testosterone production. This affects the reproductive function of a man.
- The march test allows doctors to determine the number of red blood cells in the fluid. A positive result indicates pathology of the renal vein.
- Ultrasound is considered one of the most accurate methods for detecting varicoceles.
- If additional questions arise, the patient is referred for venography. The procedure consists of an X-ray examination of the vessels of the scrotum. For this purpose, a special contrast agent is used, which is injected into the vessels. The method is so accurate that it allows you to determine varicocele, even if the patient does not feel discomfort in the testicles.
- To analyze the seminal fluid, the patient is sent for a spermogram. After deciphering the study indicators, the doctor chooses a treatment method.
- You can find out about damage to the walls of blood vessels in the affected area using Doppler ultrasound.
- MRI of the groin area allows you to assess the condition of tissues and blood vessels. The method is considered quite expensive. It is used in cases where other methods do not provide the necessary information. On the monitor screen, a specialist can identify all areas of blood vessels affected by varicocele.
Spermogram after varicocele shows changes in the patient’s ejaculate
Possible postoperative complications
The male disease responds well to treatment, so relapses occur infrequently. Postoperative complications appear mainly after embolization and laparoscopy:
- atrophy of the gonads;
- lymphostasis of the scrotum;
- hydrocele;
- hematoma in the groin;
- swelling of the scrotum.
The probability of complications after open surgery does not exceed 1%. After installing an embolus in a vein, allergic reactions and perforation of the vascular walls are possible.
POTENTIAL HAZARD
This pathology does not pose a danger to a man’s health. A lethal outcome due to the development of the disease is practically impossible, but only if the patient does not have other diseases in an advanced form against the background of the development of varicocele.
- However, intervention must be carried out in a timely manner, since the disease poses a risk to the patient’s reproductive system.
- In this case, the appearance of infertility is a frequent complication of the pathology.
- However, in the absence of intervention, there is a possibility of developing more dangerous processes - testicular atrophy, inflammation and other phenomena.
Thus, the disease does not threaten the patient’s life, but the disease must be treated in a timely manner. It is not recommended to independently eliminate the pathology, since the lack of information about the causes of varicocele development significantly reduces the effectiveness of home therapy.
lebolab.ru/illness/varicocele/razvitie-varikocele-u-muzhchin-chto-eto-takoe.html
Diagnostics
Typically, testicular varicocele is diagnosed in boys, adolescents, and young men during preventive, sports medical examinations or before military conscription. Men also often do not realize that they have a varicocele, and they only find out what it is by consulting a doctor when they experience pain or testicular asymmetry.
The main diagnostic techniques for varicocele are shown in the table.
| PROCEDURE NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Valsalva maneuver. | Examination of the veins, carried out while straining in a standing position. By inspection and palpation, the thickness of the spermatic cords in a relaxed state is determined. The patient is then asked to tense his abs. As a result of tension, the pressure in the intraperitoneal space increases, and the blood supply to the testicles increases. In the presence of varicocele, enlarged veins of the spermatic cord appear on the side of the diseased testicle, as well as soft nodules along it. |
| Ultrasound and Dopplerography (USGD). | Ultrasound is used to assess how disrupted the blood flow in the testicles is and how severe the stagnation of blood in the veins is. The study is carried out in a standing and lying position. |
| Thermography. | This is the detection of varicocele using a thermal imager. |
| Thermography. | A non-invasive test that detects a local increase in testicular temperature due to varicose veins. |
| Phlebography. | Examination of veins after injection of a dye into them. Using an ultrasound machine, you can see on the monitor the places of venous expansion. |
| Spermogram. | This research technique allows you to determine the quality of sperm. Namely, its consistency, the number of sperm in 1 ml, the volume of ejaculate, the percentage of active, inactive, inactive, and dead sperm. |
Varicocele - what is it?
Varicocele is an enlargement of the veins of the spermatic cord and testicles. There are usually three degrees of varicocele.
- First degree varicocele: dilated veins can be felt in a standing position; when the boy lies down, they disappear. The child is not bothered by anything.
- Second degree varicocele: the child complains of pain in the scrotum, burning sensation. The veins are visible, they descend below the testicle, the scrotum is asymmetrical. The testicle itself feels no different from a healthy one.
- Third degree varicocele: the veins “hang” in clusters in the scrotum, the testicle is small and soft. In this case, spermatogenesis is often disrupted, and testicular atrophy may develop.
Varicocele is a fairly common disease; it occurs on average in 10-15% of men. As a rule, it can occur during puberty and later, so do not forget that for a boy a visit to a urologist or andrologist should be made as mandatory as a dentist or gynecologist for women. As they say, it is better to detect all troubles in advance, and not when it is “too late to drink Borjomi.”
Fun fact: varicoceles usually develop on the left side. Much less common is bilateral varicocele or right-sided varicocele. This is most likely due to the different outflow of venous blood from the right and left testicles: the vein from the left testicle travels a greater distance before entering a large vessel. As a result, the venous pressure on the left is higher, which provides the prerequisites for the development of varicose veins.
Why is varicocele dangerous?
Varicocele in itself is not dangerous. You can live and work normally with it - especially if it does not cause concern. The main problem is the typical complications of this disease, male infertility.
With varicocele, the nutrition of the testicle is disrupted, which can lead to its atrophy. In addition, the network of venous vessels around the testicle creates a kind of “cushion” that interferes with the normal outflow of heat. For normal spermatogenesis, a relatively low temperature is required: from 32.5 to 34.4 degrees. With varicocele, the temperature is higher, because of this the formation of sperm is disrupted or stops completely.
Another possible complication of varicocele: immune inflammation of the testicle.
Treatment of varicocele.
Unfortunately, varicocele cannot be cured without surgery - only surgical treatment methods are really effective. The need for treatment is decided individually. Naturally, if varicocele bothers you and manifests itself as pain in the scrotum or infertility, then treatment is necessary.
If nothing bothers a man with varicocele, then the need for surgery is a controversial issue. Usually, if a man still expects to have children, then it is better to treat the varicocele and perform an operation, but if a varicocele is found in an elderly man, for whom the issue of procreation is no longer so relevant, then it is possible to do without surgery. Since we are talking about teenagers, it makes sense to get treatment: you need grandchildren, right?
Currently, there are several main methods of treating varicocele. In this case, all treatment methods are divided into two large groups: obstructive methods and non-obstructive ones (which do not interfere with venous blood flow).
Obstructive methods of treating varicocele include several types of operations. The first is open surgery. During this procedure, the varicose vein is completely ligated or removed. The operation is performed through incisions 3-5 cm long. The second method is endoscopic (laparoscopic) surgery. Three small punctures are made on the patient’s abdomen, an endoscope is inserted through one of them, and then the surgeon ties the “bad” vein of the affected testicle. The operation takes 15-20 minutes. Compared to open surgery, endoscopic surgery does not require special preparation; it is easier for the patient: no blood is lost, and the person recovers quickly. In addition, there will be no long scars either.
Another method of treating varicocele: sclerotherapy of the affected venous cord. A catheter is inserted through a puncture into the affected vein and a sclerosing substance is injected, causing a cessation of blood flow through the vessel.
All these methods (and some others, for example, Palomo, Marmara) belong to the obstructive method, that is, they interrupt venous blood flow.
In this case, varicocele is eliminated, but the venous outflow of blood from the testicle does not always improve, and accordingly, the temperature does not improve.
There is another approach to the treatment of varicocele, non-obstructive, normalizing venous outflow: the formation of venous anastomoses. Anastomoses are connections between blood vessels. Thus, the purpose of forming venous anastomoses is to create artificial pathways for venous outflow of blood from the testicle.
The choice of treatment method must, of course, be carried out jointly with specialists. As a rule, the treatment prognosis is quite successful, especially when it comes to adolescents whose testicles have not yet undergone changes due to varicocele.
https://ourboys.ru/varicocele
Which doctor should I contact?
At stage 1, the disease is discovered by chance during a routine appointment, since it does not cause discomfort. If there is pain and discomfort in the groin, consult a urologist. If necessary, he will refer you for examination to a surgeon, phlebologist or andrologist. A urologist also gives a referral for tests.
A phlebologist is a specialized specialist
which deals with the diagnosis of venous disorders of the lower extremities. An andrologist diagnoses diseases of the genital organs in men. A urologist, to a greater extent, studies abnormalities of the urinary system. Consultation with a surgeon is required if surgical treatment is planned.
Varicocele treatment without surgery
Varcocele is a disease associated with disruption of the testicular vein, which is responsible for the blood supply to the testicles. With excess blood flow and slow outflow, the vein becomes tense, its walls stretch and deform. Most often, left-sided varicocele is observed; the right testicle is affected much less frequently.
In some cases, a right-sided form is possible. Over time, the affected testicle decreases in size, the scrotum sags, and the patient experiences pain and discomfort. Some urologists believe that an advanced form of varicocele can cause male infertility.
Usually the disease is diagnosed in the second stage, when the patient begins to notice slight asymmetry of the testicles and swollen veins.
At the onset of the disease, there are practically no symptoms. When there is a rush of blood, a dull or nagging pain is possible; when a nerve is pinched, it becomes sharp, but quickly disappears.
If you notice any alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
The patient is examined, a spermogram is prescribed, and testicle measurements are taken.
In the first or second stage, the doctor does not recommend radical intervention.
Typically, the patient is prescribed supportive medications, a therapeutic diet, and strengthening exercises. It is necessary to undergo examination and tests every six months.
If the disease worsens, surgery may be necessary, but if the patient's condition does not worsen, he can successfully continue drug therapy.
Next, how to treat varicocele without surgery?
Localization in the testicle
Varicocele is divided into types according to localization: left-sided (88% of cases), right-sided (3%), bilateral (9%):
- Left-handed . Most often, pain occurs in men on the left, where the renal vein is located, which is in contact with nearby vessels that were compressing it. This is explained by the physiological structure of the genital organs and the blood vessels in them.
- Right-handed . Varicocele on the right is very rare and does not have pronounced symptoms. The present discomfort, expressed by nagging pain, appears only after physical exertion.
This pathology is not considered an independent disease. Its manifestations are influenced by a genetic disorder or the acquisition of venous insufficiency, which is provoked by poor diet, sedentary work or lack of physical activity.
- Bilateral . It is caused by disorders that are provoked by the expansion of the veins between the testicle and the inguinal ring. Painful symptoms are more pronounced on the left side, due to the significant length of the venous trunk, so the disease is often diagnosed as left-sided.
Photos of varicocele on the left, right and both testicles are presented below. It is not recommended for the faint of heart, nor is it recommended for minors!
Surgery
If testicular varicose veins have developed in men, treatment involves the need to eliminate damaged areas of the veins. In this case, different techniques are used. The choice is made taking into account the stage of the disease, the clinical picture, the condition of the blood vessels and the presence of contraindications to performing surgery using one method or another.
Important information: What consequences and complications will occur in men if varicocele (varicose veins of the testicle) is not treated?
Operation Ivanissevich
This method of surgical intervention was common in the recent past; today more modern techniques are used. In order to get rid of damaged veins, ligation of a vessel whose walls are deformed is performed. Then it is crossed.
This measure is considered effective in cases where testicular varicose veins provoke reflux. The reverse flow of blood stops. This operation requires general anesthesia. An incision up to 5 cm long is made on the skin. Through it, ligation and intersection of the vein in the iliac region are carried out.
Marmara method
This option is superior to the previous one, because in this case a small incision is made - up to 2 cm. Considering that in this case less tissue is damaged, recovery occurs faster. The principles of this method and the Ivanissevich operation are similar. If the varicocele on the right has significantly developed, an incision is made in the groin area, the spermatic cord is removed, and the veins are trimmed and divided. The probability of relapse is no more than 5%.
Laparoscopic varicocelectomy
When performing such an operation, it becomes possible to save the artery. However, this method has several disadvantages:
- the risk of adhesions increases;
- there is a need for intubation anesthesia;
- the likelihood of bleeding increases.
This method is more often used for bilateral scrotal lesions. If varicocele manifestations occur on the left or only on the right, other, more effective methods can be considered.
Laser surgery
In this case, surgery is performed with minimal tissue damage. For this, local anesthesia is sufficient. The patient can go home a few hours after the operation. When using a laser, the vessels are sealed together under the influence of high temperatures, which prevents the development of complications such as bleeding. Scars do not form during healing. This method of treating varicocele involves rapid recovery.
Moreover, this operation is characterized by minimal coagulative necrosis, which is important given the high sensitivity of the tissues in the groin area. The level of pain is low. Another advantage is the high precision of laser movements when performing manipulations.
Vein disease of the right testicle
Varicocele on the right occurs only in males and is expressed in reflux (improper outflow of blood) and swelling of the veins in the right testicle.
Pathology is not an independent disease, but just a genetic anomaly of the vascular system.
The disease has no noticeable nature and obvious symptoms. Discomfort is observed, but does not bother the person.
Varicocele of the right testicle is classified:
- First degree – the veins are not visible and cannot be felt.
- Second degree – the veins are easily palpable.
- Third degree - severe pain and blood vessels come out.
The disease is diagnosed by examination, palpation of the testicles, ultrasound and x-ray.
By the way, varicocele on the right provokes testicular hydrocele and male infertility.
Based on the results of a complete examination, the attending physician determines the need for surgery. It all depends on the specific case.
If a varicocele has developed due to a hernia or extensive inflammation, then you should first get rid of these diseases that disrupt the venous outflow.
To eliminate such a varicocele, surgery will be required. Modern surgery lasts no more than 30 minutes and the patient can return home the next day.
During a varicocelectomy (microsurgical operation), a small incision is made in the area of the inguinal canal and therapeutic manipulations are performed through it. If during the period of remission you follow the doctor’s recommendations, then a relapse is excluded.
The conservative approach and folk remedies are not effective, so you should not waste time on them. Such treatment is possible if the disease appears in older men, when the onset of infertility is not of particular importance.
Among the operations, the most common is the Ivanissevich operation. It is based on ligation of the affected testicular vein.
After a successful operation, testicular function is restored and male fertility (ability to fertilize) improves.
Advice! Often this pathology is asymptomatic and painless. But the absence of bad sensations does not mean that the disease does not require emergency treatment. This disease does not shorten life, but affects the possibility of conceiving children. Male infertility is considered the most terrible complication of the disease.
Consequences of varicocele
Varicose veins of the testicles are not a fatal disease.
But you should know what varicocele affects.
With varicocele, the consequences of impaired blood flow in the testicles lead to their overheating.
This affects the quality of sperm and can also lead to infertility and testicular atrophy.
Statistics say that a third of men with this disease become unable to conceive a child.
Often, during consultations with women on infertility, the doctor identifies male varicocele disease, although no factors of inhibition of potency or discomfort during sexual intercourse arose.
Does varicocele affect potency? As a rule, no.
The doctor will tell the patient diagnosed with varicocele what to do in the current situation in order to restore the functions of spermatogenesis. Symptoms and treatment are interrelated. The choice of treatment method will depend on the severity of the manifestations.
Video: “How does varicocele affect potency?”
Prognosis for varicocele
In men, varicocele can be completely cured by surgery. The prognosis for treatment is favorable even in advanced cases. An irreversible process can only occur when testicular atrophy has begun. Therefore, do not be shy, do not tolerate discomfort or pain in the scrotum, and contact a urologist or surgeon if unpleasant symptoms appear. Modern surgical techniques make it possible to completely get rid of varicose veins of the spermatic cord without any complications.
After timely treatment, the functioning of the testicles and the reproductive function of a man are restored in full.
Diagnosis of the disease: Valsalva maneuver and other methods
The Valsalva maneuver for varicocele allows you to assess the condition of the testicular veins. This is a special breathing technique used to identify diseases of various types. Taking a deep breath, after a few seconds the patient exhales air into the narrow opening of the mouthpiece. With the help of respiratory manipulations, the degree of incompetence of the venous vessels is determined. Usually, it is not difficult for a doctor to diagnose varicocele by visual examination. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental research methods are prescribed: ultrasound of the scrotum, ultrasound of male organs with Doppler, phlebography, spermogram analysis.