An allergy is the body's reaction to some component that is constantly or occasionally present in the environment. The immune system perceives it as foreign, protective mechanisms are activated: mast cells that produce histamine begin to intensively inject it into the blood. Excess hormone causes unpleasant symptoms.
There are different types of allergies and the differences between the symptoms and the manifestations of other diseases are insignificant.
Allergies: what is it?
The response to the influence of chemical or physical influences is called an allergic reaction or simply allergy. The reason that triggered the activation of the immune system is called an allergen.
Human health is regularly affected by whole groups of different root causes: they do not threaten the state of health, so the protection of the human body simply ignores them. An allergy begins when a catalyst encounters the human body, causing a violent response and activating the immune defense.
In fact, the body is ready to defend itself against seemingly harmless things. The response to such influences can vary in severity from a barely noticeable rash on the skin to damage to organs or tissues.
Anaphylactic shock
When bitten by bees or snakes, some people may experience such a strong and rapid reaction to the allergen that life is threatened. The main symptoms of anaphylactic shock:
- severe shortness of breath;
- rash all over the body;
- blue skin due to insufficient oxygen supply to the blood;
- convulsions;
- blackout;
- involuntary cleansing of the intestines and bladder.
At the first signs of anaphylactic shock, you should urgently seek medical help. If possible, transport the patient to a medical facility yourself. With anaphylactic shock, minutes sometimes count.
Allergy reaction categories
There are several similar categories:
Late hypersensitization
This type of allergic reaction in humans is expressed by the unhurried formation of a response, which manifests itself no less than a few hours after the irritant affects the person. Lymphocytes are involved here, due to which specific substances are produced that provoke a non-standard response.
Allergies such as skin dermatitis, rhinitis, and asthma act as late hypersensitization.
Immune complex type
Allergic effects in this category are associated with IgG and IgM immunoglobulins. Having combined with a provocateur that has entered the circulatory system, they settle in the blood vessels, which leads to severe irritation. Such a response occurs faster than hypersensitization and manifests itself within the next few hours after interaction (from 6 to 12 hours).
This category of allergies includes:
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Lupus erythematosus;
- Conjunctive;
- Glomerulonephritis, etc.
Cytotoxic category
In it, the interaction occurs with the participation of IgG and lgM immunoglobulins, which are capable of killing their own brothers by attacking and destroying the membranes of their cells.
The category of such allergic reactions includes:
- Hemolytic disease and anemia of newborns;
- Thrombocytopenia, etc.
The allergic reaction to the use of medications is expressed in the same way.
Anaphylactic category
The allergic reaction in this case is the most transient. It appears almost instantly after the body interacts with the provoking allergen. The period required for the initiation of the response process to the influence of the stimulus can be measured in just a matter of minutes; lgE and lgG immunoglobulins are involved in this process.
LgE and IgG are located on the outer membrane of cells called mast cells. The result of such an effect is a significant production of histamine and other complex substances, which in turn changes the state of blood vessels, affecting permeability, increasing the latter, the secretion of mucous substances, and reduces the amount of smooth muscle. As a result, a classic protective response of the immune system occurs, known to many.
Well-known models of such allergic reactions include:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Anaphylactic shock;
- Urticaria, etc.
Quincke's edema and asthma
The most dangerous manifestation of allergies is swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat and respiratory tract. The first signs of an allergy are difficulty breathing. It is difficult for the patient to get out; he begins to gasp for air, like a fish thrown ashore.
If first aid is not provided to the patient in time, death is possible. With asthma, severe spasms of the bronchi occur; these manifestations of allergies are accompanied by a dry cough.
What to do at the first symptoms of an allergy:
- if possible, eliminate contact with the allergen;
- call doctors;
- calm the patient, create conditions for proper breathing: open doors and windows, relieve pressure on the neck and chest;
- help the patient take a comfortable position;
- in case of bites, localize the place where the poison spreads (you can apply cold to the area of redness, tie the limb with a tourniquet);
- If the patient has antihistamine drops, sprays, tablets with him, it is necessary to help the allergic person take them. This assistance can be provided before the arrival of doctors.
Step-by-step formation of an allergic reaction
The emergence and development of the immune system response is determined by several stages:
The initial interaction of the antigen with the human cellular structure, activation of protective functions. At this stage, the susceptibility of cells to the attacking factor usually increases; the process in the form of an allergy manifests itself during the second and subsequent penetration of the irritant into the circulatory system.
Allergy treatment - treatment rules, recommendations and main symptoms of the disease (100 photos)
Eye allergies - main causes, manifestations, symptoms of the disease and recommendations for choosing the best drugs (95 photos)
Allergy test: blood sampling and collection of necessary materials for analysis. Decoding the results of the examination
During the second stage, cells called “fat” come into play, their structure is disrupted, and subsequently histamine appears in the circulatory system, causing serious disorders in human tissues and organs.
The final stage is characterized by visible allergy symptoms. For example, characteristic sneezing, copious mucus secretion, and much more occur. This is the body’s response to the active entry of histamine into the blood, as well as other substances similar to it.
Basics of first aid for allergies at home
First aid for allergies should begin with the provision of therapeutic procedures at home before the doctor arrives. If a person is aware of the presence of an inadequate immune system response, he should always have emergency medicine for allergies at home.
Elimination of the pathogenic effects of the allergen
To eliminate the gradual deterioration of well-being, first aid for allergies at home should begin with eliminating the effect of the potential allergen. For example, they remove the sick animal or close the windows to prevent pollen from getting in. If the symptom arose due to a food product, it should be completely excluded from your diet.
Desensitization of the body (symptom relief)
Thanks to emergency care for acute allergic reactions, it is impossible to completely eliminate the disease, so before going to a medical facility, the task arises - to try to remove or at least reduce the main symptoms of an allergic manifestation. After eliminating contact with the allergen, treatment continues with the use of antihistamines (see in more detail “Antihistamines in the treatment of allergies: mechanism of action and classification”), as well as sorbents (Polysorb, Enterosgel, Smecta, etc.). First aid for severe forms of drug allergies is reduced to the use of antihistamines.
The following methods are used to administer an antihistamine:
- orally (tablets, suspensions) – first aid for food allergies;
- locally (drops, sprays, creams, ointments) – allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis;
- intravenously or intramuscularly (emergency help for allergies).
Intravenous or intramuscular administration of drugs is used for severe allergic reactions.
What to do if you don’t have a first aid kit at hand
What to do if a sudden allergic reaction occurs? An allergic reaction can be temporarily stopped only with the help of antiallergic medications. Improvised tools do not work here.
What to do about skin allergies? It is recommended to cool the affected area of the body to reduce itching, irritation, and swelling.
The exception is an attack of suffocation. In this case, it is impossible to do without the help of doctors, so it is necessary to deliver the patient to a medical facility as soon as possible.
What is strictly forbidden to do if an allergic reaction occurs suddenly?
First aid for an allergic reaction must be carried out according to all rules. If a person does not know what to do with an allergy, it is better not to resort to treatment, but to wait for a specialist. There is a list of the most common mistakes that should not be made, especially when providing first aid for acute allergic reactions:
- using an expired antihistamine;
- administering drugs intravenously or intramuscularly not according to the rules (unsterile conditions, secondary use of a syringe);
- self-performing laryngectomy in case of suffocation by an inexperienced person;
- the use of foreign drugs, such as painkillers, which can enhance the immune response;
- lack of contact with a specialist, especially in cases of acute allergic reaction.
If a person is aware of the increased response of the immune system, he should always carry medicine with him so that he can receive first aid for allergies. First aid for acute allergic reactions should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
Allergic symptoms
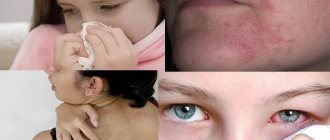
In addition to the specific symptoms characteristic of this or that type of allergy in adults and children, there are general symptoms:
- Redness of the eyes;
- Swelling of the mucous membranes, copious mucous discharge;
- Characteristic discomfort in the ear canals, hearing loss;
- Swelling of the upper respiratory tract, frequent, intermittent whistling breathing, can lead to bronchial asthma;
- Severe migraine, manifested on both sides;
- Redness and itching of the skin, the development of urticaria, eczema, then the elbows, cheeks, sides, and groin area are mainly affected.
Symptoms
Allergy symptoms in adults and children are different and they depend, first of all, on the irritant that provoked a response in the body. If we talk about the general signs of an allergic reaction, the following should be highlighted:
- violation of body thermoregulation (temperature can rise to 37.9 degrees);
- chills;
- overexcitation or, conversely, lethargy;
- clouding of consciousness;
- pale skin;
- hypotension.
Important! In severe forms, angioedema and anaphylactic shock may be signs of an allergic reaction.
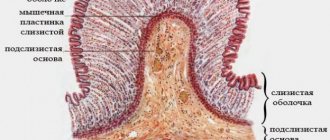
Local signs
Local signs of allergies in adults and children in most cases manifest themselves in the gastrointestinal tract, mucous membranes of the nose and eyes, lungs and skin. In this case, most often local signs of allergy appear in the form of a rash, which is complemented by redness of the skin, a feeling of dryness, burning and excessive susceptibility to changes in air temperature.
Allergic spots can appear only on certain areas of the body, for example, cheeks, neck, arms, etc., or cover all skin. They can merge and migrate, that is, first appear in one part of the body, then disappear and appear in another.
Allergy sufferers quite often complain when allergies occur to disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, which manifests itself in the form of abdominal pain, nausea, flatulence and diarrhea. In addition, allergization quite often manifests itself in damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes. It is noted:
- redness of the eyeballs;
- active lacrimation;
- hyperemia of the eyelids.
General symptoms may also include the larynx, nose and bronchi. In this case, the patient has:
- sore throat;
- dry mouth;
- runny nose and problems with nasal breathing;
- wheezing in the sternum;
- paroxysmal dry cough.
Respiratory tract allergy is the most severe and dangerous form of allergic reaction, as it can lead to swelling of the lumens of the respiratory tract and their complete closure, which will cause asphyxia.
Allergy to insect bites
This type of allergic reaction is also the most common, especially among young children. In this case, the allergen is the saliva and venom of the insect, which it injects into the skin when it bites.
It is not difficult to determine an allergy to insect bites. As a rule, it has a pronounced symptomatic picture, which is often supplemented by angioedema or anaphylactic shock. In the first case, there is rapidly developing swelling in the neck and face, resulting in a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx and attacks of suffocation.
Important! If a patient experiences symptoms of Quincke's edema, he needs urgent help. He must be immediately taken to the nearest medical facility or an ambulance team must be called to the scene. Long-term angioedema can lead to complete obstruction of the airways, which can be fatal.
Anaphylactic shock manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- sharp excitement, followed by depression of consciousness;
- drop in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- shortness of breath;
- rapid breathing.
Important! Anaphylactic shock can also be fatal in a matter of minutes. Therefore, a patient who exhibits signs of anaphylactic shock also requires emergency medical care.
Speaking about how to recognize an allergy to an insect bite, we cannot help but mention the local signs of an allergic reaction. When it occurs, the skin at the site of the bite becomes swollen and red, and the patient complains of a feeling of heat, burning and itching in this area. As a rule, these symptoms occur within 5-10 minutes after the bite. The skin allergy lasts for several hours.
Allergy to ultraviolet rays
Allergies to ultraviolet radiation are also not uncommon. Its primary symptoms may appear immediately when the skin is exposed to direct sunlight or after a few hours. Moreover, its symptoms most often appear in those parts of the body that have been in contact with the sun's rays. The most common signs of a sun allergy are red spots and blisters on the body.
It should be noted that there are some foods and medications that increase the body's sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and contribute to the fact that a person begins to develop a chronic allergy to ultraviolet rays. These include:
- vegetables and herbs - St. John's wort, yarrow, parsley, dill, carrots and others;
- medications – tetracycline, NSAIDs, sulfonamide antibacterial agents, vitamin E.
Allergy to sperm
Recently, cases have become more frequent when women experience allergic conditions when male seminal fluid enters her body. There are several reasons for this:
- infectious diseases of the urogenital tract;
- hereditary predisposition;
- promiscuous sex life.
Allergy to sperm manifests itself in different ways. Most often these are local inflammations, expressed by rash, hyperemia and itching. In rare cases, an allergy to male seminal fluid can result in long-term infertility.
Food allergies
Food is the most powerful allergen, which provokes the development of allergic reactions in more than half of allergy sufferers. The symptoms they exhibit can be very different. Among them, the most common are:
- vomiting and nausea;
- dry cough;
- rashes like urticaria;
- hoarseness of voice;
- shortness of breath and wheezing in the lungs;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx and tongue;
- dizziness;
- pale skin.
It should be noted that there is a certain group of products that contains the most allergens. These include:
- chicken and quail eggs;
- all types of nuts;
- milk (most often cow's milk);
- soy;
- fish;
- seafood;
- wheat;
- chocolate;
- citrus fruit.
Children may also experience skin manifestations of food allergies in the form of a rash and the appearance of an “orange peel” on the cheeks. In most cases, citrus fruits and chocolate give this reaction. At the same time, it should be noted that most often the parents themselves are to blame for the development of food allergies in a child by introducing early complementary foods.
Prevention of this type of allergy involves the complete exclusion of foods that provoke such a reaction in the body.
Heat allergy
Heat allergies are extremely rare in people. It is characterized by rashes on the skin similar to urticaria - blisters appear on the skin, accompanied by severe itching. It manifests itself when the body is exposed to hot temperatures and is often combined with an allergy to the sun.
Allergy to animals
A fairly common type of allergic reaction is animal allergy. Moreover, it occurs not only on fur, but also on saliva, urine, and secretions of the sebaceous glands. The main signs of developing an allergy to animals are attacks of dry cough, choking and nasal congestion.
If the body has such a reaction, a person should constantly take antihistamines and take preventive measures, which include:
- regular cleaning of the tray;
- wet cleaning of the room where the animal is located;
- a ban on letting a pet into the bedroom where an allergic person sleeps;
- washing the animal daily.
Important! To prevent frequent attacks of an allergic reaction to an animal, experts advise giving the pet to another owner.
Viral allergy
Viral allergies occur against the background of such serious diseases as:
- plague;
- tuberculosis;
- dysentery;
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- brucellosis;
- typhus
Signs of such an allergy can vary widely. The most common among them are:
- skin manifestations - rash, itching, redness of the skin;
- allergic rhinitis;
- tearfulness;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - diarrhea, nausea, increased gas formation, cramps, etc.;
- labored breathing;
- anaphylactic shock.
The consequences of developing a viral allergy can also be very different. Therefore, when it occurs, the patient must be immediately taken to a specialized institution.
Photos of types of allergies
Diagnosis of allergic symptoms in adults
An adult can independently eliminate the allergen - to do this, you need to listen to your body, remember what contributed to the allergic reaction: food products, contact with animals, toxic substances and other types of antigens.
It is not difficult for an adult to eliminate food allergies: it is necessary to remove possible allergens—frequently consumed foods—from the nutritious diet. After a few days, a reaction is noticeable - a decrease or resumption of symptoms.
Article on the topic: Causes of atopic dermatitis in children and methods of its treatment
In the absence of symptoms, foods should be introduced into the diet gradually and separately to notice the body’s reaction to the product.
If you have an allergic reaction to household chemicals, jewelry, or cosmetics, you should do the same: stop washing clothes with powder that is the suspected allergen, do not wear clothes or jewelry with the metal to which you are likely allergic.
If an allergic reaction occurs after putting an item into use, eating food, or contacting an animal, it is necessary to permanently eliminate the allergen to prevent aggravated conditions.
When starting treatment, an adult needs to visit an allergist, who will collect an anamnesis from the patient’s words, take into account heredity, and refer all necessary tests.
Diagnosis of allergic symptoms
Hay fever (hay fever)
This is an allergic reaction caused by plant pollen. Characterized by inflammatory changes in the mucous membranes of the nose (rhinitis) and eyes (conjunctivitis).
Hay fever can manifest itself as urticaria, dermatitis, and Quincke's edema. Most often it manifests itself as pollen-induced bronchial asthma.
Hay fever is characterized by a hereditary predisposition, especially if the allergy is a common illness for both parents.
Hay fever manifests itself as itching and redness of the eyelids. There is sand in the eyes, they water, a severe runny nose appears, and attacks of uncontrollable sneezing appear. It becomes difficult to breathe through your nose.
At the same time, the patient may feel itching of the palate, pharynx and nasal cavity. Hay fever is seasonal. It coincides with the flowering period of wind-pollinated plants, the pollen of which is very small.
Plants that are brightly colored, have a pleasant scent, and are pollinated by insects rarely cause hay fever.
When to see a doctor? If allergy symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only an allergist can clarify the diagnosis. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment. In case of a severe allergic reaction, you must call an ambulance.
Immune system: structure and functions
The immune system is responsible for the constancy of the internal environment of the body. This means that everything foreign that has penetrated from the external environment (bacteria, viruses, parasites) or appeared during life (cells that have become atypical due to genetic damage) must be neutralized. The immune system has the ability to distinguish “self” from “foreign” and take measures to destroy the latter.
The structure of the immune system is very complex, it includes individual organs (thymus, spleen), islands of lymphoid tissue scattered throughout the body (lymph nodes, pharyngeal lymphoid ring, intestinal nodes, etc.), blood cells (various types of lymphocytes) and antibodies (special protein molecules).
Some parts of the immune system are responsible for recognizing foreign structures (antigens), others have the ability to remember their structure, and others ensure the production of antibodies to neutralize them.
Under normal (physiological) conditions, an antigen (for example, the smallpox virus), when it first enters the body, causes a reaction from the immune system - it is recognized, its structure is analyzed and remembered by memory cells, and antibodies are produced to it and remain in the blood plasma. The next arrival of the same antigen leads to an immediate attack by pre-synthesized antibodies and its rapid neutralization - thus, the disease does not occur.
In addition to antibodies, cellular structures (T-lymphocytes) that are capable of secreting enzymes that destroy the antigen also take part in the immune reaction.
Pathogenesis
Most drugs are chemical compounds that have a simpler structure than proteins.
For the immune system, such drugs are not antigens (foreign substances for the body that can cause the formation of antibodies).
Defective antigens (haptens) can be:
- the drug in unchanged form;
- impurities (additional substances);
- products of drug breakdown in the body.
The drug can act as an antigen and cause an allergic reaction only after certain transformations:
- formation of a form capable of binding to proteins;
- connection with proteins of a given organism;
- The response of the immune system is the formation of antibodies.
The basis of LA is the development of hypersensitivity of the body to the formed antigen due to the changed immune reactivity of the body.
The reaction develops mainly after the drug (or its component) re-enters the body.
Special (immune-competent) cells recognize it as a foreign substance, and antigen-antibody complexes are formed, which “trigger” the development of allergies.
Few drugs are full-fledged antigens that can cause an immune reaction without transformation:
- medicinal serums;
- hormones;
- immunoglobulins
Factors influencing the occurrence of hypersensitivity:
- properties of the drug itself;
- method of drug administration;
- long-term use of the same drug;
- combined use of drugs;
- presence of allergic diseases;
- endocrine pathology;
- chronic infections.
Patients with changes in enzyme activity, liver pathology with impaired liver function, and metabolic disorders are especially susceptible to the development of sensitization.
This explains cases of reactions to a drug that was well tolerated over a long period.
The dose of the drug that enters the body does not affect the development of LA: it can appear in some cases after inhalation of vapors of the drug or ingestion of a microscopic amount of it.
It is safer to take the medicine internally.
When applied topically, the most pronounced sensitization develops.
The most severe reactions occur when drugs are administered intravenously.
Specifics of traditional allergy treatment
The effectiveness of therapy for the body’s negative reaction to a particular stimulus lies in identifying the cause of the disease. It is worth noting that any allergen causes an increase in histamine. This substance in the human body provokes a rash, itching, and disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, stomach, and respiratory tract. Consequently, antihistamines (Tavegil, Diphenhydramine, Diazolin, Pipolfen) are used in the treatment of allergies with medications. Such drugs belong to first generation therapies. They are prescribed to be taken on a daily basis to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Antihistamines are prescribed by the doctor. He determines the timing of treatment and dose.
The second generation of antihistamine drugs include Claritin, Zyrtec, Astemizole. Their difference from the previous medicine is that they do not cause drowsiness and lethargy in the nervous system.
Attention! Long-term use of drugs that suppress histamine production is not recommended. This can provoke addiction, and the occurrence of allergies is even more intense.
To relieve swelling and spasm in the respiratory organs, vasodilators are used. Their main action is as follows:
- cough decreases;
- breathing becomes easier;
- shortness of breath disappears, wheezing in the bronchi and lungs is eliminated.
The most common medications used in complex therapy are: Salmeterol, Theophylline, Albuterol. These drugs help relax the soft tissues of the bronchi and make breathing easier in a short time.
Vasodilator medications also include anticholinergics. They are auxiliary agents in the complex therapy of allergies, but can be used as independent medications.
In drug treatment for a negative reaction of the body to irritants, anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They are used for asthma, eczema, watery eyes, and rhinitis. The most popular remedies are steroid medications (tablets, drops, ointments). Corticosteroids (injections, inhalations, drops) help well. Such drugs are well suited in those moments when you need to provide first aid for exacerbation of allergies (asthma).
For children with allergic conjunctivitis, the famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky recommends lecrolin, cromoglin, and high-chrome. These drugs can be used for a long time, they do not harm.
Traditional treatment may use antibiotics. Cetrin helps with allergic rhinitis. It is worth noting that before deciding how to treat allergies, the doctor must find out whether the patient has drug intolerance. Therefore, self-medication with antibiotics is not recommended.
Features of various types of disease
Skin dermatitis may differ in symptoms depending on the type of disease.
If toxicdermia develops, then redness and swelling are noted on the surface of the skin. Papules and erythema may form. They become sources of severe itching and burning. A person may feel unwell, have a fever, chills and clouding of consciousness.
With atopic dermatitis, symptoms are expressed in the form of itching and burning. They are identified in combination with respiratory diseases, household and food allergies.
Skin dermatitis in the form of erythema is characterized by purple spots. They may vary in size. The size of each varies between 2–8 mm.
Symptoms of allergic skin dermatitis may vary depending on the type of disease.
What to do if you have allergic reactions
It is believed that allergic diseases, in which the body's immune reaction is accompanied by damage to its own tissues, affect on average about 10% of the world's population. Let's take a closer look at what it is and what to do in case of allergic reactions.
What are the types of allergic reactions?
Types of allergic reactions vary in severity. According to the severity of the course, allergic reactions can be divided as follows:
- mild and moderate severity - itching, urticaria, allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Quincke's edema;
- severe - anaphylactic shock.
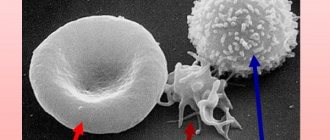
Patients with an immediate allergic reaction (anaphylaxis, atopic bronchial asthma, urticaria, Quincke's edema, hay fever, allergic rhinitis) often require emergency care. With this pathology, foreign substances (antigens) stimulate lymphocytes, which turn into plasmacytes, that is, cells that produce antibodies. Antibodies attach to the surface of mast cells, which become sensitized. When the antigen re-enters the body on the surface of mast cells, it interacts with the antibody, this leads to the destruction (degranulation) of mast cells and the release of biologically active substances from them - allergy mediators (histamine, serotonin, prostaglandins, etc.).
Types of allergic reactions
Anaphylactic shock - the most dangerous clinical variant of an acute allergic reaction - is most often observed after the administration of penicillin, but it can also occur after the use of other antibiotics, sulfonamides, medicinal serums, radiopaque agents, etc., as well as after insect bites.
Immediately after the injection (or after 20-40 minutes), the patient experiences a feeling of tightness in the chest, dizziness, headache, anxiety, agitation or depression, severe weakness, a feeling of heat in the body, skin rashes and itching, and rhinorrhea. At the same time, suffocation and dry hacking cough occur, caused by the development of bronchospasm or laryngeal edema with stridor breathing.
In severe cases of allergic reactions, symptoms of shock are expressed: pallor and marbled skin coloring, acrocyanosis; the limbs become cold, the pulse is thready or cannot be felt, blood pressure drops or is not detected. In anaphylactic shock, a drop in blood pressure can be combined with the development of a coma. Convulsions with foam from the mouth and involuntary urination are a consequence of severe cerebral hypoxia. In such cases, death may occur within a few minutes after the onset of shock. In less severe cases, patients experience symptoms of fainting, combined with mild bronchospasm and a drop in blood pressure.
Quincke's edema is angioedema (local or widespread) of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and mucous membranes. Angioedema of the larynx is manifested by cough, hoarseness, suffocation, wheezing, and possible death from asphyxia; swelling of the gastrointestinal tract is accompanied by intestinal colic, nausea, vomiting (the cause of diagnostic errors and unjustified surgical interventions).
Urticaria is a sudden onset lesion of the superficial part of the skin with the formation of sharply defined round blisters with raised erythematous scalloped edges and a pale center, accompanied by severe itching. A rash due to allergic reactions can persist for 1 to 3 days, leaving no pigmentation.
Allergic rhinitis - swelling of the nasal mucosa, secretion of copious watery mucous secretions, nasal congestion, burning sensation in the conjunctiva and pharynx, lacrimation.
Hay fever (hay fever) is a seasonal allergic reaction to plant pollen, manifested by acute conjunctivitis and rhinitis.
What to do in case of allergic reactions: emergency care
Emergency care for allergic reactions, in particular anaphylactic shock, should be provided without delay. A dose of 0.3 - 0.5 ml of a 0.1% solution of adrenaline is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly; if necessary, injections are repeated every 20 minutes for an hour. Adrenaline causes constriction of blood vessels in the skin, abdominal organs, skeletal muscles, and relaxes the muscles of the bronchi.
Correction of arterial hypotension and replenishment of circulating blood volume is carried out using transfusion of saline and colloid solutions (500-1000 ml). With the development of bronchospasm, aminophylline and inhalation of beta-adrenergic agonists (salbutamol, alupent) are indicated.
At the same time, for allergic reactions, 125-250 mg of hydrocortisone or 60-150 mg of prednisolone are administered intravenously. Steroid hormones do not have an immediate effect, but prevent relapses of the reaction. Glucocorticoids suppress the development of immune cells (lymphocytes, plasma cells) and reduce the production of antibodies, prevent the degranulation of mast cells and the release of allergy mediators from them and have an effect opposite to the effects of allergy mediators - a decrease in vascular permeability, an increase in blood pressure, etc.
What to do in case of allergic reactions: drug therapy
Antihistamines - H1-histamine blockers - are competitive antagonists of histamine released from mast cells, and their affinity for H1-histamine receptors is much lower than that of histamine itself. Therefore, antihistamines do not displace histamine bound to receptors; they block receptors that are not occupied or released by histamine. Accordingly, H1-histamine blockers are most effective for the prevention of allergic reactions, and in the case of an already developed reaction, they prevent reactions to the release of new portions of histamine. Thus, H1-histamine blockers are used for allergic reactions only as an additional means to reduce the duration and prevent relapses of the reaction. For allergic reactions, it is preferable to use drugs such as terfenadine, Zyrtec, astemizole - modern, highly active antihistamines with a minimum number of side effects.
When providing emergency care to patients with anaphylactic shock, speed and accuracy in completing prescriptions is required. Therefore, it is necessary to have appropriate sets of medications and disposable syringes and droppers in treatment rooms of clinics, ambulances, nursing stations and paramedic stations. After emergency care, the patient should be hospitalized and observed in a hospital.
The principles of treating angioedema are the same as those for anaphylactic shock. For mild allergic reactions (urticaria, hay fever, allergic rhinitis), antihistamines and ketotifen are prescribed, a drug that suppresses the release of biologically active substances (histamine, leukotrienes, slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis).
© Olga Vasilyeva for astromeridian.ru
Homeopathy treatment
If you take the treatment of allergies seriously, it is recommended to use not only medications, but also alternative medicine. The most common is homeopathy. This method is the treatment of allergies by taking medications in very small doses, which in large proportions are allergens to the immune system.
Homeopathy includes the following medications:
- Allium sulfur is used for inflammatory processes in the eyes, lips, and nasal mucosa.
- Sabadilla is used in case of throat problems (sore throat, sore throat), runny nose.
- Pulsatilla is a drug that helps reduce mucous discharge, which can cause discomfort to the patient for a long time.
Note! Homeopathy completely eradicates allergic reactions. This method helps to alleviate the patient’s condition and eliminate the symptoms of pathology.
Dr. Komarovsky does not recommend resorting to homeopathy in the treatment of allergies in children. It is better to visit an allergist to take all the necessary tests and tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Why do allergy symptoms appear?
The basis of an allergic reaction is the hypersensitivity of the human body. In 1963, British doctors presented a classification of such reactions and identified 4 types of hypersensitivity. Type 1 (anaphylactic) includes typical allergies and their manifestations. Everything is described as follows: upon initial contact with an antigen (irritant), the immune system produces IgE-type reagins, which connect with basophilic and mast cells. Repeated contact provokes the binding of reagin to antibodies and causes subsequent cell degranulation. As a result, inflammatory mediators are released in the cells, the main one of which is histamine.
Note that the symptoms of an allergic reaction are complex and depend on a number of factors, such as the characteristics of the patient’s body, the intensity of exposure to the allergen, the presence of external exogenous influence (for example, a man-made factor), the frequency of exposure to allergens, as well as the phase of the immune response. Let's pay attention to the last factor - with allergies there can be a phase of early and late immune response. In other words, phases can be characterized as a period of time during which one or another clinical picture is formed. The first signs of allergy are the same in all cases (since the mechanism of occurrence is similar in all people), but later manifestations of allergies depend on the type of allergen.
What are the types of allergic reactions?
The types of allergic reactions are classified according to the clinical picture and mechanism of development. There are four types in total.
- Allergic reactions of immediate type or anaphylactic. They are characteristic of urticaria, childhood food allergies, allergic rhinitis, anaphylactic shock. With this type of reaction, histamine is released in large quantities and has a pronounced physiological effect: respiratory failure, surges in blood pressure, interruptions in heart function, confusion, and circulatory disorders.
- Cytotoxic type of allergic reaction. It occurs with hemolytic anemia, Rh conflicts, and the administration of vaccines and medications. With this type of allergic reaction, antibodies attack antigens that are located in the body's own cells; during complex biochemical processes, cytotoxins are formed - cell-destroying substances. As a result, cell membranes are destroyed and cytolysis occurs - cell death.
- Immunocomplex type of reaction. Observed with the introduction of serums, dermatitis. Immune complexes of molecules of antigens and antibodies to it settle on the walls of capillaries, increase their permeability and destroy them.
- Delayed allergic reaction or type 4 allergic reaction. Characteristic of rhinitis, bronchial asthma. Antigens are attacked not by antibodies, but by T-lymphocytes accumulated over a certain period of time.
Some researchers identify a fifth type. Type 5 allergic reactions – stimulating hypersensitivity reactions. Antibodies are produced not to an antigen, but to cellular receptors for hormone molecules, or to the hormones themselves. The normal concentration of the hormone decreases and the hormone molecules are destroyed by antibodies.
Classification
In medicine, allergic reactions are distinguished depending on the time of their occurrence, the characteristics of the mechanisms of the immune system, etc. The most used classification is according to which allergic reactions are divided into delayed or immediate types. Its basis is the time of allergy occurrence after contact with the pathogen.
According to the classification, the reaction:
- immediate type - appears within 15–20 minutes;
- delayed type - develops a day or two after exposure to the allergen. The disadvantage of this division is the inability to cover the diverse manifestations of the disease. There are cases when the reaction occurs 6 or 18 hours after contact. Based on this classification, it is difficult to attribute such phenomena to a specific type.
A widespread classification is based on the principle of pathogenesis, that is, the peculiarities of the mechanisms of damage to cells of the immune system.
There are 4 types of allergic reactions:
- anaphylactic;
- cytotoxic;
- Arthus;
- delayed hypersensitivity.
Allergic reaction type I is also called atopic, immediate type reaction, anaphylactic or reaginic. It occurs within 15–20 minutes. after interaction of reagin antibodies with allergens. As a result, mediators (biologically active substances) are released into the body, from which the clinical picture of a type 1 reaction can be seen. These substances include serotonin, heparin, prostaglandin, histamine, leukotrienes, etc.
The second type is most often associated with drug allergies, which develop due to hypersensitivity to medications. The result of an allergic reaction is the combination of antibodies with modified cells, which leads to the destruction and removal of the latter.
Hypersensitivity of the third type (precitipin, or immunocomplex) develops as a result of the combination of immunoglobulin and antigen, which together leads to tissue damage and inflammation. The cause of the reaction is soluble proteins that re-enter the body in large quantities. Such cases include vaccinations, transfusions of blood plasma or serum, infection with blood plasma fungi or microbes. The development of the reaction is facilitated by the formation of proteins in the body during tumors, helminthiases, infections and other pathological processes.
The occurrence of type 3 reactions may indicate the development of arthritis, serum sickness, visculitis, alveolitis, Arthus phenomenon, periarteritis nodosa, etc.
Allergic reactions of type IV, or infectious-allergic, cell-mediated, tuberculin, delayed, arise due to the interaction of T-lymphocytes and macrophages with carriers of a foreign antigen. These reactions make themselves felt during contact dermatitis of an allergic nature, rheumatoid arthritis, salmonellosis, leprosy, tuberculosis and other pathologies.
Allergies are provoked by microorganisms that cause brucellosis, tuberculosis, leprosy, salmonellosis, streptococci, pneumococci, fungi, viruses, helminths, tumor cells, altered body proteins (amyloids and collagens), haptens, etc. Clinical manifestations of reactions are different, but most often infectious -allergic, in the form of conjunctivitis or dermatitis.
Types of allergens
There is no single classification of substances that lead to allergies yet. They are mainly classified according to the route of penetration into the human body and their occurrence:
- industrial: chemicals (dyes, oils, resins, tannins);
- household (dust, mites);
- animal origin (secrets: saliva, urine, gland secretions; hair and dander, mainly from domestic animals);
- pollen (pollen from grasses and trees);
- insect (insect poisons);
- fungal (fungal microorganisms that enter with food or by air);
- medicinal (complete or haptens, that is, released as a result of the metabolism of drugs in the body);
- food: haptens, glycoproteins and polypeptides contained in seafood, honey, cow's milk and other products.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is based on the following criteria:
- the appearance of clinical manifestations after using the drug;
- hereditary predisposition
- similarity of symptoms with other allergic diseases;
- the presence in the past of similar reactions to a medication with a similar composition or structure;
- disappearance of symptoms (or noticeable improvement) after discontinuation of the drug.
Diagnosis in some cases (with the simultaneous use of a number of drugs) is difficult when it is not possible to reliably establish the connection between the appearance of symptoms and a specific drug.
In cases where the origin of the symptoms is not clear, or the patient does not know which drug there was a previous reaction to, laboratory diagnostic methods are used (detection of specific IgE class antibodies to drugs).
The level of IgE can be determined using the enzyme immunoassay method and the radioallergosorbent test.
It eliminates the risk of complications, but is less sensitive and requires special equipment.
However, the imperfection of laboratory tests does not allow us to exclude with 100% certainty the possibility of hypersensitivity to the drug if the result is negative. The reliability of the study does not exceed 85%.
Skin tests to confirm LA in the acute period are not used due to the high risk of developing a severe form of allergy.
They are also contraindicated in the presence of a history of anaphylactic shock, in children under 6 years of age, and during pregnancy.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, you need to keep your home clean.
The room should not contain:
- fluff;
- ticks;
- dust.
In case of any contact with dusty objects, you need to cover your nose - you can use a mask or bandage for this.
If you have a reaction to pets, it is not recommended to keep them in your home.
If you have allergies to medications, you need to have a special card with you indicating this information.
People with severe forms need to warn family members and colleagues about this. It is also necessary to inform doctors about this.
Find out the common causes of neck allergies. How to take prednisolone for allergies? Read on.
How is an allergy skin prick test done? The answer is here.
Taking anamnesis for diagnosis and treatment
A detailed medical history allows you to select the optimal safe diagnostic method without the risk of provoking anaphylactic shock, as well as adjust treatment taking into account individual characteristics. The main points of the survey when collecting anamnesis:
- Information about the presence of bronchial asthma or allergies in close relatives determines hereditary predisposition.
- Data on the manifestation of allergies in the patient during different life periods.
- Identifying a typical set of symptoms.
- Presence/absence of seasonality in the manifestation of allergic reactions.
- The patient’s diet, his household habits, preferences.
- Presence of reactions to vaccinations.
- General signs of sensitization: roughness and dryness of the skin, a characteristic “geographical” tongue.