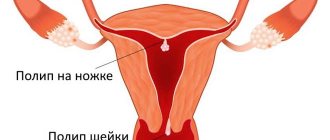
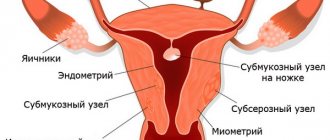
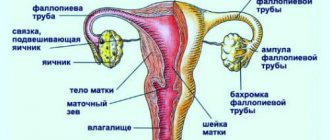
Duplication of the uterus is a congenital developmental anomaly in which there are different options for dividing the main reproductive organ of a woman into 2 parts. Pathology is one of the causes of infertility and menstrual dysfunction.
The causes of abnormal development of the uterus are most often harmful factors affecting a pregnant woman when carrying a female fetus. Primary detection of the disease is possible with an ultrasound scan, but for better visualization of the malformation, an MRI of the pelvis should be done. This is especially important against the background of habitual miscarriage, infertility and preparation for surgical intervention.
Types of uterine duplication
Causes of the anomaly
Duplication of the uterus and other defects of the female genitourinary organs occur in no more than 1% of women (0.3-0.9%). The reproductive and urinary system is formed in utero from one embryonic germ, which can cause the formation of several types of defects (a double uterus is often combined with a double kidney or other types of congenital pathology of the urinary system). Abnormal intrauterine development of the genitourinary organs in a girl occurs against the background of the following causative factors:
- genetic disorders;
- complicated pregnancy in the mother (threat of miscarriage, gestosis, malnutrition, intrauterine infection);
- long-term use of toxic medications during pregnancy;
- occupational hazard in a pregnant woman;
- severe diseases of internal organs in the expectant mother.
It is often impossible to accurately identify the main cause that led to the occurrence of intrauterine pathology in a girl. Therefore, in all cases when a girl or woman is found to have congenital anomalies in the reproductive system, it is necessary to conduct a full examination to identify malformations of neighboring organs. It is optimal to use the MRI method for this, with which you can obtain maximum useful information about all genitourinary organs.
What is a bicornuate uterus?
Duplication of the uterus and vagina is a type of structure in which the organ is divided by a septum into two chambers. Depending on the severity of anatomical changes, physiological processes in the organ, including pregnancy, can occur in different ways. The causes of such disorders may be viral and bacterial diseases, pharmacological agents, addictions, and occupational hazards. The influence of teratogenic factors is especially dangerous during the critical period of fetal development (8-16 weeks of gestation).
Uterus doubling options
Malformation of the uterus is almost always combined with pathology of the cervix and vagina. There are several possible types of congenital uterine anomalies.
| Variant of malformation | Description |
| Full doubling | 2 uteruses and 2 vaginas are completely separated and separated from each other |
| Incomplete doubling | 2 isolated parts of the reproductive organs (uterus and vagina) in a certain area are connected by a fibromuscular septum |
| Complete doubling with one vagina | 2 uteruses, 2 cervixes and 1 vagina |
| Double organ with one cervix and vagina | 2 uteruses, but the cervix and vagina are presented in 1 version |
| Duplication of the uterus with a rudimentary horn | One half of the organ looks normal, and the second is underdeveloped and is represented by a defective cavity |
| Two-horned | The uterine cavity is deformed in the upper part, partially dividing the organ into 2 halves |
| Saddle | The fundus of the uterus is moderately deformed without dividing the organ into 2 parts |
| Internal partition | A thin fibrous septum inside the uterus separates the organ completely or partially |
It is not always the case that a young woman experiences typical symptoms and manifestations, so a congenital defect in the reproductive system is discovered by chance at the stage of preconception preparation or during an examination for infertility. The asymptomatic course of the disease is especially common with erased and unexpressed variants of doubling (bicornuate, saddle-shaped). It is much worse if the anomaly of the genital organs is combined with a delay in the outflow of menstrual blood: in this case, typical symptoms will become the basis for an accurate diagnosis.
Features of the female body with a bifurcated uterus
The pathology begins during the period of embryonic development.
There are many reasons for the incorrect placement of an organ. In the first stages, under the influence of negative environmental factors, the embryonic uterus forms very slowly. This leads to the fact that the woman ends up with two uterine cavities. This type of pathology is the most common.
If the developmental deviation was too strong, then the uterine cervix, and even the vagina, can double in size. Most women with this pathology are not even aware of its presence.
Developmental anomalies are diagnosed during pregnancy using ultrasound examination.
The abnormal structure of the organ does not affect the menstrual cycle and egg maturation. However, pregnancy often comes with complications. Therefore, women with two uteruses require closer medical supervision.
Often such a pregnancy requires hospital stay throughout the entire period of the child's development.
Symptoms of congenital pathology
Manifestations of congenital pathology depend on the form of uterine duplication. There are 2 groups of defects possible:
No retention of menstrual blood in the uterine cavity
The vast majority of congenital anomalies of the uterus are represented by defects in which a woman has normal periods. With a regular cycle, women who do not have an intimate life will not have any symptoms or unpleasant manifestations of congenital pathology. With the onset of sexual activity, problems may arise associated with the act of love, which happens with a double vagina against the background of complete doubling. The main symptoms occur in women who want to give birth to a baby. With uterine abnormalities without menstrual problems, the following manifestations are possible:
- threat of miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy;
- spontaneous abortion in the early stages;
- late miscarriages;
- habitual miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- infertility.
In all cases of prematurity or in the absence of a desired pregnancy, it is necessary to do a full examination, starting with safe and highly informative examination methods (ultrasound and MRI).
Duplication of the uterus is an unpleasant malformation of organs
Defects with delayed blood outflow
The lack of communication between one part of the uterus and the cervix and vagina is the reason for the retention of menstrual blood and the appearance of the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain associated with menstrual periods;
- detection of a tumor-like formation gradually increasing in size in the lower abdomen.
Typically, such symptoms occur when the uterus is doubled with a functioning rudimentary horn. If the underdeveloped area of the double organ communicates with the cervix, then the following problems are possible:
- bleeding before and after menstruation;
- heavy periods;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Any types of defects can lead to the formation of genital endometriosis with typical symptoms.
Duplication of the uterus and pregnancy
Symptoms
The presence of two separate uteruses and vaginas may not cause clinical manifestations and can be diagnosed during a routine gynecological examination, ultrasound, or surgery. In the case of complete doubling of the uterus and vagina in combination with aplasia or atresia of one vaginal cavity, 3-6 months after the first menstruation, a picture of hematocolpos, hematometra, hematosalpinx develops on the side of the separate cavity. In this case, the symptoms are characterized by severe bursting pain in the lower abdomen, which cannot be relieved by antispasmodics and painkillers. With a saddle uterus and intrauterine septum, clinical manifestations in adolescence are usually absent. If there is a fistula tract in the intervaginal septum, menstrual blood can partially flow through the full vagina. When a secondary infection occurs, pyocolpos, pyometra, and pyosalpinx are often formed. Patients with a fistula opening in the intervaginal septum experience constant bleeding or purulent leucorrhoea from the genital tract. The combination of uterine doubling with ovarian hypofunction may be accompanied by algodismenorrhea, amenorrhea, and infertility. If one or two uterine cavities are complete, pregnancy is possible, but usually occurs with the threat of spontaneous abortion and premature birth. Childbirth with a double uterus is often complicated by incoordination or weakness of labor, heavy postpartum bleeding, and lochiometer.
Duplication of the uterus and pregnancy
The desired conception against the background of complete doubling of the reproductive organ is quite possible. Pregnancy begins on the side where the egg is released from the ovary. The beginning of pregnancy may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- menstrual-like reaction during pregnancy (a woman experiences scanty bleeding on the days of her expected period);
- brown discharge in the first months of pregnancy (rejection of the endometrium from the part of the uterus where there is no fertilized egg);
- nagging pain in the abdomen.
All these manifestations are similar to typical symptoms of a threatened miscarriage, so the doctor will prescribe maintenance treatment or refer you to the hospital. If no serious problems arise in the first stages of fetal development, then the woman, with constant monitoring and treatment, carries the fetus to term and gives birth to a healthy baby.
In difficult cases of infertility associated with uterine duplication, IVF is performed. After a full examination, including MRI, the fertilized “in vitro” egg is implanted in that part of the future fetal sac where conditions for gestation are most optimal.
Fetal development with incomplete duplication of the uterus
Treatment
Surgical tactics in the case of complete doubling of the uterus and partial aplasia of one vagina are indicated in cases of impaired outflow of menstrual blood. In this case, during the vaginal stage, the vaginal walls are dissected to form a connection between the functioning and closed cavities, the hematocolpos is opened and drained, and the vagina is sanitized. At the laparoscopic stage, the relative position of the uterus is clarified, the hematometra and hematosalpinx are emptied, and the abdominal cavity is sanitized. In case of hymenal atresia, an X-shaped incision of the hymen and elimination of hematocolpos is performed under local anesthesia. Surgical gynecology considers the identification of an additional closed horn as an indication for hysterectomy - extirpation of the rudimentary uterus with preservation of the ovary and fallopian tube. The presence of an intrauterine septum is an indication for methoroplasty only in cases of reproductive dysfunction. When the uterus is doubled with complete or partial aplasia of both vaginas, various methods of colpoelogation and peritoneal colpopoiesis are used.
Diagnosis of uterine duplication
The main methods for identifying various types of abnormal structure of the reproductive system are the following studies:
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- hysteroscopy;
- MRI;
- laparoscopy.
At the first stage of the examination, preference is given to non-traumatic methods - ultrasound and MRI. The doctor can easily detect a saddle-shaped and bicornuate uterus with an ultrasound scan. Endoscopic techniques are optimal when combining diagnosis and treatment.
Visual examination of the inner surface of the uterus (hysteroscopy) allows you to detect the septum and immediately remove the developmental anomaly. External examination of the uterus during laparoscopy is combined with an operation to remove a non-functioning part of the organ in the presence of a rudimentary horn.
What will a tomography show when the uterus is doubled?
Diagnostics
In the complex of step-by-step diagnostics of duplication of the uterus and vagina, a medical history, gynecological (including rectoabdominal) examination, vaginoscopy (colposcopy), hysteroscopy, ultrasound or MRI of the pelvis, ultrasound and CT scan of the kidneys, and laparoscopy are carried out. Complete duplication of the vagina and cervix can be visually determined during a gynecological examination and vaginoscopy. With aplasia of one vagina, only a full-fledged vagina is available for examination, in the dome of which one cervix is identified. Vaginoscopy during uterine duplication and aplasia of the accessory vagina reveals a protrusion in the area of the lateral vaginal wall; Rectoabdominal examination reveals hematocolpos and hematometra in the form of a tumor-like immobile formation of a tight-elastic consistency. In the presence of a fistula tract, an increase in purulent discharge is noted during a rectoabdominal examination. With a rudimentary closed horn, one vagina and one cervix are revealed, but rectoabdominal examination allows palpation of a painful formation near the uterus, which tends to increase during menstruation; hematosalpinx is also detected on its side. Ultrasound of the pelvis with typical forms of uterine duplication makes it possible to determine the size of both cavities, the size of the hematocolpos and hematometers. An obligatory stage of diagnosis is an ultrasound of the kidneys to assess their condition. For atypical forms of uterine duplication, it is advisable to perform MRI of the pelvis, hysteroscopy and laparoscopy. Duplication of the uterus and vagina often leads to diagnostic errors and, as a result, unnecessary interventions - appendectomy, tubectomy or removal of appendages, bougienage of the cervical canal and vagina. If pathology of the urinary system and kidneys is detected, consultation with a urologist or nephrologist is necessary.
MRI for double uterus
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the reproductive and urinary organs. MRI examination is indicated in the following cases:
- for all types of defects with a delay in the outflow of menstrual blood;
- to diagnose the causes of uterine infertility;
- at the stage of prenatal preparation after untimely termination of a desired pregnancy;
- with defects of the external genitalia that create difficulties in intimate life;
- with congenital anomalies of the urinary organs;
- in case of doubts and suspicions after ultrasound diagnostics.
The undoubted advantages of MRI are the safety and high information content of the examination: the absence of radiation exposure and the identification of precise anatomical changes in the reproductive system become the main factors for the mandatory use of magnetic resonance imaging for congenital anomalies of the genitourinary organs.
On our website you can find up-to-date information about MRI clinics, choose a place for a diagnostic study, make an appointment online or by phone, find out the exact cost and select the optimal time for the examination. You can also undergo an MRI at the price you specify yourself - details here.
Uterus division - incomplete removal
Treatment of the anomaly
Abnormalities of the uterus in most cases do not require any therapy. But, if the pathology causes menstrual dysfunction or makes it difficult to conceive or bear, then treatment is necessary. If the outflow of menstrual fluid is disrupted, metroplasty is used, which consists of dissecting the uterine septum and forming a common cavity. In this case, the vagina is sanitized.
Hysteroscopy allows you to obtain information about the shape of the septum and cavities. In the postoperative period, estrogen-containing drugs (Divigel transdermal) are prescribed to prevent the formation of synechiae. Plastic surgery is necessary for patients suffering from partial aplasia (when one horn forms a closed space). In this case, the surgeon creates a single cavity by cutting the septum. To sanitize the cervix, drainage and treatment with antibiotic solutions are used.
In the period after surgery, 2 weeks of physical and sexual rest are recommended. Pharmacotherapy includes: Trental 100 mg/4 times a day, Tocopherol 200 mg twice a day, Vita-melatonin tablet before bedtime. In addition, Betadine vaginally 1 suppository for 12 days.
Treatment of uterine duplication
In the absence of problems with the outflow of menstrual blood, duplication of the uterus does not require mandatory surgical intervention. The saddle and bicornuate form of the pathology extremely rarely leads to serious consequences, being an unpleasant feature of the main reproductive organ.
If difficulties arise during intimate life, infertility and pathology with retention of menstrual blood, surgery will be required.
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- complete duplication of the uterus, in which a woman has an abnormal vaginal structure;
- the presence of a closed rudimentary uterine horn;
- an open and underdeveloped part of the double uterus, in which an ectopic pregnancy can occur;
- habitual miscarriages associated with doubling of the uterine cavity;
- septum in the uterus;
- a combination of uterine defects and gynecological diseases (endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cysts).
The choice of surgical technique is individual and depends on the woman’s desire to bear and give birth to a child. In most cases, it is quite possible to preserve a woman’s reproductive function and ensure the absence of problems in her intimate life.
4.Treatment
The decision on the need, plan and extent of surgical intervention (obviously, drug treatment in this case is absurd) is made on the basis of the clinical picture and a number of individual characteristics of a particular case. Of greatest importance is the volume of the single uterine cavity (excluding bifurcated “horns”), as well as the history of pregnancy, childbirth, artificial and spontaneous abortions. In some cases, surgical correction is indicated, in others it is recommended to resort to in vitro fertilization or surrogacy, in others the anomaly has virtually no effect on fertility and reproductive function, i.e. It is quite advisable to limit ourselves to observation tactics.
Fusion
Another multifaceted pathology leading to recurrent miscarriage, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain is
. The frequency of this disease has been increasing recently. The causes are inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, abortion, diagnostic curettage and violation of the period of use of intrauterine contraceptives.
For treatment, hysteroscopy and mechanical dissection of the fused areas are used.
To prevent recurrence of synechiae, which can occur independently and after removal of the septum in the uterus, you can use an intrauterine device (IUD). The separation of the anterior and posterior walls of the cavity with the product promotes better regeneration of the endometrium.
However, intrauterine levonorgestrel releasing systems are not recommended due to the suppressive effect of hormones on the endometrium. T-shaped models are too small for consistent wall separation. To prevent complications of synechiae, it is better to use a copper coil after removing the septum in the uterus. The trapezoidal IUD was the best choice for this purpose, but is no longer available on the global market.
Causes of pathology
Typically, disorders of this type occur during embryogenesis, which can be caused by the external influence of pathogenic, genetic, and endocrine factors. During normal development of a child, the distal ducts combine, and VG parts and MT structures are formed. The VH part develops due to the convergence of the caudal segment of the Müller ducts, the cloaca, and the urogenital sinus.
When the doubling of the uterus is observed in the above area, union does not occur during embryogenesis, causing certain anomalies in the development of the child. The occurrence is usually accompanied by disorders of the urinary system.
Unfavorable changes in the full development of the embryo can occur for a variety of reasons:
- poor nutrition during pregnancy, lack of vitamins, which also affects the embryo;
- infectious diseases that a woman suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, during the formation of the embryo;
- taking medications that negatively affect the fetus;
- endocrine disorders;
- severe toxicosis at the beginning of pregnancy;
- constant stress;
- intoxication due to the use of harmful substances, tobacco and alcohol during pregnancy.
Also, the embryo may not develop properly due to unfavorable hereditary factors, so it is worth paying special attention to patients who have previously had such anomalies in their family. Pathological development of the reproductive organs is often observed with concomitant insufficient kidney function.
Classification and reasons
Duplication of the uterus has its own classification, which was identified solely on the basis of abnormal development.
Doubling classification:
- complete or insufficient development (one-horned uterus without a horn of a rudimentary type, underdeveloped);
- problems with the canals (one-horned with a vestigial horn);
- incomplete fusion of ducts (double and bicornuate);
- partial reabsorption of the septum (arcuate and septal).
It has been proven that such a pathology is an abnormal formation associated with problems in the embryonic development of the fetus. Unfavorable changes occur in the environmental conditions in which the fetus develops, for example, nutrition, gas exchange and other harmful factors that adversely affect the pregnant woman’s body.
Improper development of the embryo can be caused by the following factors:
- infections during pregnancy in the early stages, at this stage the formation of the uterus in the fetus occurs;
- unbalanced, unhealthy diet, when the embryo does not receive enough minerals, vitamins and enzymes necessary for normal development;
- taking teratogenic drugs;
- problems with the endocrine system - diabetes, imbalance in ovarian function, hypothyroidism;
- excessive stress, depression and psycho-emotional stress;
- severe toxicosis, which began from the very first days of pregnancy;
- intoxication of the body.
Genetics, that is, heredity, is also important. Therefore, if organ doubling has already been observed in a related family, it is necessary to plan a pregnancy and first obtain specialist advice.
Close connection between the rudiments of the genital organs together with the urinary tract and kidneys. Therefore, the fetus may often exhibit not only a doubling of the uterus, but also a doubling of the kidneys.
Characteristic symptoms and diagnosis
The manifestation of pathology depends on its characteristics, classification and intensity, as well as on the individual characteristics of each woman’s body.
Let's look at the most common reasons that will help identify the problem:
- A woman may feel fullness in the lower abdomen. This symptom can appear in girls during puberty and disappear after 3 months.
- Vaginal discharge in the middle of the cycle is not too profuse, brown spotting, sometimes with such symptoms it reveals a fistulous tract in the septum that overlaps the two vaginas.
- Systematic bloody discharge and leucorrhoea mixed with pus is detected with a fistula or secondary infection; pyometra and pyosalpinx can occur against the background of sexually transmitted infections.
- Women who have given birth experience weak labor activity, bleeding after labor and incoordination. Sometimes you can find out about two uteruses after childbirth.
- Suspicion or confirmed diagnosis – infertility.
- Impossibility of pregnancy and spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle, not always.
- Pain in the lower abdomen of a cramping nature.
In order to establish or confirm the diagnosis, the specialist must order a complete examination of all reproductive organs.
List of diagnostic measures:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and kidneys;
- MRI of the abdominal cavity and kidneys;
- gynecological examinations, together with retoabdominal;
- laparoscopy;
- hysteroscopy;
- colcoscopy;
- compiling a medical history and studying test results.
Important! An experienced obstetrician-gynecologist will be able to identify the abnormality during a routine examination in the chair.