Home Diseases and treatment Gastroenterology
2 Mar 2020, 20:05 Anna 1 792 No
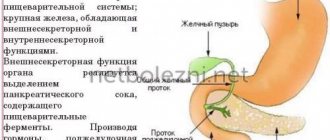
The pancreas is one of the most important organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The gland has exocrine and intrasecretory functions. For digestion, the most significant external secretion is the synthesis of digestive enzymes.
If the secretory function is impaired, a person has problems with digestion and processing of food. In order to understand that it is the pancreas that is affected, a common study such as ultrasound is performed.
Before performing an ultrasound examination, preparation is required on the part of both the doctor and the patient. The accuracy of the research result and, consequently, the diagnosis depend on the thoroughness of preparation.
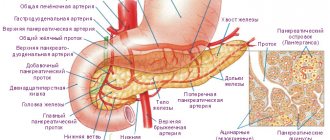
Anatomy of the pancreas
Normally, the pancreas in an adult weighs about 80 grams, has a length of 14-18 cm, a width of about 3-9 cm and a thickness of approximately 2-3 cm.
The pancreas is located in the retroperitoneal space, in the epigastric region, at the level of the first and second lumbar vertebrae, and has an oblong shape, approximately located transverse to the midline. For various pathologies determined by ultrasound, it can have a ring-shaped, spiral, split shape, or have doubled individual parts, an additional lobule.
The main parts of the pancreas are the head, the body in the middle, and the tail, on the far left. The longest part of the pancreas is located to the left of the midline, and the tail near the splenic muscle is usually slightly above the head. The rather complex shape of the pancreas and its close location to nearby structures can make it difficult to recognize, but experienced ultrasound physicians are able to use surrounding structures to determine some of the boundaries of the pancreas. For example, the head and body of the pancreas are located below the liver, in front of the inferior vena cava and aorta, usually located behind the distal part of the stomach. On the far left, the tail of the pancreas is located below the spleen and, accordingly, above the left kidney.
The pancreas has the form of small lobules that produce enzymes for digestion, and pancreatic islets that secrete an important hormone - insulin - into the bloodstream. It is this that allows energy to penetrate every cell of the human body and actively participates in carbohydrate metabolism. Digestive enzymes or pancreatic juice take part in the digestion process and are excreted into the duodenum.
Indications for ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is usually included in a comprehensive examination of all abdominal organs. After all, it is closely related to the functions of other internal organs, mainly the liver. The indication for research is any pathological condition of the digestive system. Many diseases can occur with hidden or completely erased clinical signs. Therefore, once a year it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity for the early detection of many diseases.
The most common conditions for which an ultrasound is recommended:
- prolonged or periodic pain, discomfort in the upper abdomen or left hypochondrium;
- tension in the anterior abdominal wall or local pain in the epigastric region, which was detected by palpation;
- frequent bloating (flatulence), nausea and vomiting that does not provide relief;
- diarrhea (stool disorders), constipation, detection of undigested parts of food in the stool;
- presence of low-grade fever for a long time;
- when observing the patient's yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, deviations of laboratory parameters from the norm;
- with a sharp increase in blood sugar levels and an unreasonable decrease in body weight;
- after an x-ray of the abdominal organs has been performed and changes in size, shape, structure, distortion of contours have been identified, and pneumatosis of the pancreas has been detected;
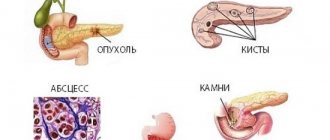
- if you suspect the presence of a cyst, tumor, hematoma, stones, or abscess in the gland.
Mandatory use for abdominal injuries and elective surgeries is indicated.
Possible results
The most common deviations:
- Small pancreas. A symptom, if it is not accompanied by clinical manifestations and other disorders, indicates aging of the organ in elderly patients. Most often, no treatment is required, as it is a normal variant.
- Symptom of lobular pancreas. It is diagnosed when part of the normal tissue of an organ is replaced by fatty tissue. This deviation is indicated by increased echogenicity - on the screen such “fatty” areas look very light compared to normal tissue.
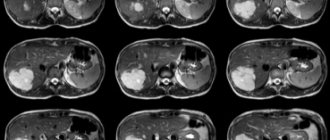
- Diffuse changes in the pancreas detected on ultrasound indicate inflammation of the organ. The main signs are increased size of the gland, changes in its structure, the presence of compactions and foci of inflammatory processes. Ultrasound shows alternating dark and light areas, which indicates problems such as pancreatitis, lipomatosis, and endocrine pathologies. This may also indicate disturbances in the blood supply system of the organ due to atherosclerosis, surgical procedures, or due to constant stress in the patient.
- The head of the gland is significantly enlarged (there is a tumor), the pancreatic duct is dilated. These symptoms indicate pathologies such as inflammation of the head of the organ, pancreatic cancer, pseudocyst.
- The organ is enlarged, but unevenly - may indicate pancreatitis.
- Thickening in the area of the gland body indicates the onset of a tumor process in the area of the head of the organ.
The evaluation and interpretation of ultrasound results is done by the doctor immediately after the examination. This process may take 10-15 minutes. The presence of a disease is usually indicated not by individual deviations, but by a combination of several factors. Usually, if a doctor discovers one or more abnormalities in the physical characteristics of the pancreas, other examinations, studies and tests are mandatory.
Minor fluctuations in the values of various parameters from the generally accepted norm are not signs of pathology.
Conclusion
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas makes it possible to diagnose most diseases and pathologies of the organ in the early stages. Since the gland is located deep in the abdominal cavity, it is quite difficult to visualize it entirely. Therefore, the patient must adhere to the diet and advice that the doctor will give him on the eve of the examination. Thus, the likelihood of obtaining the most reliable and informative data on the condition of the organ increases by 40%.
All detailed data on the size, shape and condition of the organ are recorded in a specialist’s report. Normal pancreas:
- located next to the spleen and liver;
- has the shape of the letter S;
- looks uniform, has no obvious defects;
- has clear contours;
- easy to visualize: head, body, tail are visible.
The size and other parameters of the pancreas may differ from standard indicators for adults and children of a certain age. But this is not always a reason for making a diagnosis. Diseases are usually indicated by a combination of various deviations from the norm. An ultrasound scan can identify a specific organ defect.
Preparing for the study
Ultrasound of the pancreas can be performed both routinely and as an emergency in acute conditions. When carrying out a planned procedure, it is necessary to follow some rules and prepare for this procedure. After all, the most problematic thing during ultrasound examination is the presence of air in adjacent hollow organs. It is he who can interfere with a detailed study, distort visualization and expose the patient to an incorrect diagnosis. Doctors recommend undergoing pancreatic diagnostics, preferably in the morning. After all, it is during this half of the day, following all the rules and recommendations, that you can get the most accurate results.
During routine diagnostics, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet three days before the procedure. It is advisable to exclude foods that cause fermentation and bloating in the intestines, and do not consume foods rich in fiber and whole milk. The day before the test, it is recommended to take a laxative to cleanse the stomach and intestines. For twelve hours before the planned ultrasound examination, you must refrain from eating and drinking water, avoid taking medications, and prohibit smoking. Carbonated drinks should not be consumed as they cause excess gas formation. This can specifically affect the results and spoil the ultrasound visualization.
In case of emergency indications for an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, the patient does not need preparation. But this can reduce the information content to approximately 40%.
How should you prepare for diagnosis?
The attending physician who has given the patient a referral for examination should give advice - what should not be eaten before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and why, whether the procedure is carried out on an empty stomach or not, whether it is possible to drink water before an ultrasound and how much. You need to eat in small fractional portions, preferably take food at three-hour intervals, and you cannot drink it down. Before an abdominal ultrasound, you can drink purified or still mineral water, weak and unsweetened tea either 1 hour before a meal or 40 minutes after it.
During the day you need to drink 1.5 liters of liquid. Now let's look at the detailed recommendations. 3 days before the test, it is necessary to completely avoid eating food that increases the formation of gases in the intestines.
- baked goods – cookies, pastries, cakes, buns, pies;
- black bread;
- candies and chocolate;
- fatty fish and poultry;
- pork;
- legumes;
- sausages;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- sweet carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- juices;
- smoked meats and spices;
- mushrooms;
- pickled vegetables;
- strong coffee;
- milk.
The evening before the procedure, until 20.00, a light dinner is allowed; it should not include fish and meat products (even dietary ones). If the patient is prone to constipation, before 16.00 you need to take a drug that stimulates bowel movements (Senade, Senadexin) or administer a Bissacodil rectal suppository. If the patient does not tolerate laxatives well, a cleansing enema is prescribed 12 hours before the diagnostic session.
Method of performing ultrasound of the pancreas
Sonography of the pancreas is a completely painless and highly informative, accessible procedure for most patients. In addition, it takes very little time - about ten minutes. It is necessary to free the abdominal area from clothing; it is on this area that the doctor will apply a special gel called mediagel. And then he will conduct an examination with an ultrasound sensor. The patient should lie quietly, first on his back, and later, with the doctor’s permission, turn on his right and left side to examine the pancreas from all sides. The ultrasound specialist examines the gland while holding the breath while inhaling to the maximum and while the patient is breathing calmly. He must also decipher the diagnostic results and give the patient a complete report and pictures of the pancreas.
During this procedure, the position of the pancreas in relation to the vessels and spinal column, the structure of the pancreatic ducts and the gland itself, shape and size are studied.
The doctor will immediately be able to see whether the gland is compacted or swollen, whether calcifications are present, whether there is an inflammatory process or not, whether pathological formations, cysts and pseudocysts are present.
If the inflammatory process has already been present for a long time, then the pancreas can significantly decrease in size, scar tissue can grow, fat deposits can increase, the capsule of the internal organ thickens, and the echogenicity of the gland increases.
How the research works
During an ultrasound diagnosis of the abdominal organs, the examinee is placed on a hospital couch. The doctor, using a probe across the abdomen, performs a scan of the organs. The real-time image is displayed on the device screen.
During the ultrasound, it is necessary that the bladder is full. Fullness of the urinary tract will create pressure in the ureter and pelvis. This condition allows you not to resort to contrast - the presence of fluid in the bladder significantly improves image visualization. Therefore, before an ultrasound examination of the kidneys, you will need to drink 1 liter of liquid about an hour before the procedure.
Before the procedure, you will be laid on a couch, and a special ultrasound gel will be applied to the skin in the study area, providing a continuous signal and the necessary acoustic contact to prevent air from entering. During an ultrasound, the doctor will move a special device with a sensor that sends high-frequency ultrasound waves over the area to be examined.
When the device is placed on the abdomen at the test site, the ultrasound transducer begins to send signals. Ultrasound easily passes through the skin and tissues of internal organs and other natural barriers, after which it is reflected from the organs and returned back to the transducer, which transmits the data to the screen in the form of a digital image.
Ultrasound of the bladder (transabdominal) is a completely painless procedure. The patient sits on the couch, and the doctor examines the abdominal area with an external sensor.
To prevent the development and avoid complications of the diseases described above, the doctor at the Medspravka Plus MC prescribes an ultrasound of the mammary glands for the following symptoms and complaints of the patient:
- enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit area;
- swelling and compaction in the mammary glands, in the armpits, in the area of the shoulders on the chest side;
- wrinkled, inverted, swollen or hardened nipples;
- peeling of the skin in the mammary glands;
- bloody or purulent discharge;
- changes in the volume, shape or structure of the mammary gland;
- pain and discomfort in the glandular area;
- formation of depressions in the mammary glands when raising the arms up.
In addition to the listed symptoms, ultrasound diagnostics of the mammary glands is mandatory for women before or after operations to enlarge, reduce or remove (full or partial) the breast. Ultrasound diagnostics can be used to monitor the position of the needle when performing a biopsy.
During an ultrasound examination, the patient lies down on a hospital couch and a special gel is applied to the chest area. The doctor, pressing the sensor on the chest area, moves it across all quadrants of the mammary gland. In patients with pathologically enlarged breast size (gigantomastia), the examination is performed in a standing or sitting position.
Indicators of a healthy pancreas
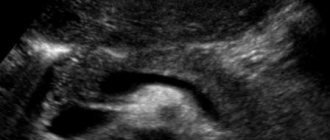
With an ultrasound scan, the doctor will normally see a “sausage-shaped”, S-shaped pancreas. It will have clear and even edges, have a homogeneous, fine-grained or coarse-grained structure, the vascular pattern will be visible on the screen without deformation, the central duct of the gland - the Wirsung duct will not be enlarged (normally - 1.5-2.5 millimeters). It looks like a thin hypoechoic tube; it can decrease in diameter in the tail and be larger in the region of the head of the gland.
The size of this organ varies depending on the age and body weight of patients, with varying amounts of fat. The older the person, the less iron and the more echogenic it will be during scanning. A study was conducted in which 50% of people had increased echogenicity of the pancreas, and in children, on the contrary, it was decreased. An indicator of a healthy pancreas is its uniform structure.
In an adult, the size of the head of the gland can be from 18 to 30 millimeters, the body - from 10 to 22 millimeters, and the tail - from 20 to 30 millimeters. In children, everything will depend on the height, weight and age of the child: the body is from 7 to 14 mm, the head of the gland is from 12 to 21 mm, and the tail is from 11 to 25 mm.
Contraindications and restrictions
Ultrasound diagnostics has no contraindications and is prescribed even to children and women during the period of feeding and childbearing.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder has no contraindications or limitations. However, the procedure should be postponed if there are open wounds on the skin in the area to be examined.
Ultrasound of the pancreas has no contraindications or limitations. It is an absolutely safe research method and does not involve radiation exposure.
Ultrasound scanning of the veins of the lower extremities is completely safe and does not cause any discomfort; there are no contraindications.
Ultrasound diagnostics today is one of the safest methods for examining the mammary glands and has no contraindications.
Ultrasound of the pancreas for various pathologies
For pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas and can be easily detected using an ultrasound scan. After all, it is the acute onset of this disease that greatly affects the structure, size, and structure of the gland tissues. The disease occurs in several stages and each stage, of course, will have its own characteristics.
Pancreatitis can be total, focal, segmental. They can be distinguished from each other by determining the echogenicity of the organ. A change in echogenicity can occur both in the entire gland and only in a certain part of it.
Initially, the pancreas will actively increase in size, the contours will be distorted, and the central duct will expand. As the gland enlarges, compression of large vessels will occur and the nutrition of neighboring organs will be disrupted, with an increase in echogenicity in them. The liver and gall bladder will also enlarge.
In the last stages of this serious disease, an experienced doctor will be able to consider when the necrotic stage will progress, organ tissue will disintegrate, and there may be the presence of pseudocysts or foci with abscesses in the area of the walls of the abdominal cavity.
What is the preparation before an ultrasound of the abdominal organs?
The main goal of preparatory measures for ultrasound scanning is to ensure complete visualization of internal organs - this will allow the diagnostician to fully assess their condition. Most often, the examination is carried out in the morning, in some cases - in the afternoon. A patient who has adequately prepared for the diagnostic procedure can be absolutely confident in making an accurate diagnosis.
When preparing for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, the following points are considered the basic rules. You should not eat or drink 8–10 hours before the examination.
An exception is the diagnosis of the genitourinary organs - 1.5 hours before the procedure you need to drink about 1 liter of still water (drinking coffee and tea is contraindicated) and not urinate.
Three days before the study, the patient must eat a special diet - the essence of the diet is to prevent contraction of smooth muscles, minimize gas formation and irritation of the mucous membranes. Smoking is prohibited 2 hours in advance - nicotine causes spasms of the stomach and gall bladder. Before the session, you are not allowed to use chewing gum or breath freshening lozenges.
Ultrasound is not performed after an X-ray examination with a contrast agent, as well as colonoscopy (assessing the condition of the internal surfaces of the large intestine using an endoscope) and fibrogastroduodenoscopy (a method for examining the upper digestive tract). Diagnostics should be carried out at intervals of two days.
You need to worry about cleansing the intestines - do an enema or take a laxative 12 hours before the session. Failure to comply with any rule must be reported to the diagnostician, otherwise he may inaccurately interpret the resulting image. In addition, it is very important to provide him with information about the medications he is taking, especially antispasmodics - Dibazole, Papaverine, Drotaverine. If possible, it is better to avoid using them.
The number of hours of fasting before testing for children differs:
- up to 1 year – you can’t eat for three hours before an ultrasound;
- up to 3 years – four;
- up to 12 years – from 6 to 8 hours.
A child should not drink water for one hour before an abdominal ultrasound.