Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a procedure that causes fear in many patients. Fear of pain and discomfort makes you put off visiting a doctor, thereby putting your health at risk. Is it painful to have a gastroscopy? This question interests many. There are several recommendations regarding how to make this procedure easier and how to properly prepare for it.
Preparation
To obtain the most accurate results of EGD, it is very important for the prospective patient to prepare in advance. A person should warn the doctor about the presence of allergies to local anesthetics and tell them about regularly taking any medications. The patient is also obliged to warn the specialist about existing chronic diseases associated with breathing, heart, and blood. There are several basic conditions that must be met before performing esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Is it possible to drink water
It is necessary that the preparation for the examination of the stomach in the morning is complete, otherwise the results of the study may be erroneous. Many patients are interested in whether it is allowed to drink liquid before visiting the EGD diagnostic room. You cannot drink alcohol, tea, coffee, juices or other drinks. If thirst is significant, then you can drink no more than 100 ml of ordinary purified water 3 hours before the procedure.
Also, three to four days before the expected day of the FGDS, you need to adhere to a special diet. The consumption of alcoholic beverages, spicy and fatty foods is prohibited. You should limit the amount of spices, seasonings, and salt in your diet. The menu must include the following products: milk, eggs, broths (chicken, vegetable), vegetables (boiled, steamed). The day before endogastroscopy, it is advisable not to eat fish, cereals, meat, or any flour products.
The upper part of the digestive tract and the entire viewing area must be free of food. This is explained by the fact that the fibrogastroduodenoscope is inserted first into the pharynx and then into the stomach. Considering these nuances, you should not eat at least 8-10 hours before gastroscopy. If EFGS is scheduled for the morning, then it is better to have dinner before 6 pm, using light, easily digestible food. When gastroenteroscopy is scheduled for the afternoon, you can have a little snack in the morning.
How is gastroscopy done?
Before starting FGDS, the patient is given an injection with a sedative (relaxing, hypnotic) drug. Sometimes local anesthesia is given to the root of the tongue and pharynx using a spray with an anesthetic effect. In some cases, FGS is performed using general anesthesia. Scheme for diagnosing the gastrointestinal tract:
- The patient should lie on his left side, while slightly pulling his knees towards his stomach.
- If the manipulation is performed under general anesthesia, the person lies on his back.
- A mouthpiece is inserted into the oral cavity - a special device that helps you swallow the tube easily and without interference.
- With the gradual introduction of the fibrogastroduodenoscope inside, the patient makes swallowing movements. You need to breathe deeply through your nose. If a significant gag reflex is observed, the tube is removed.
- The doctor performs a gastrointestinal examination while operating equipment. If necessary, instruments are inserted into the device to collect tissue (biopsy).
- After a thorough examination and analysis of the obtained material, the patient is given an accurate, detailed diagnosis.
FGDS under anesthesia
Due to the unpleasant symptoms that accompany the procedure, patients prefer anesthesia. Often, preparation for EGD involves the use of muscle relaxants, which improve the effect of anesthesia. Endoscopic examination under anesthesia is an excellent option for people who are afraid to undergo this procedure.
Especially for those patients who are physically or psychologically not ready to swallow a tube, there is an absolutely painless alternative - capsule gastroendoscopy. The procedure provides an excellent chance to effectively examine the digestive system, examining it from the oral cavity to the anus. This modern type of FGDS is carried out using a very small computerized capsule. It consists of a tiny video camera, a transmitter and a light bulb.
The patient swallows a unique tablet with water. The capsule moves through the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Its travel time is approximately 7-8 hours. In this case, the person does not need to be under the supervision of doctors; he can calmly go home and lead his normal daily life.
After the end of the gastroscopy, the patient comes to the doctor so that the latter can read the diagnostic information from the capsule. A special sensor is attached to him in the stomach area. This device “takes out” information data from the video tablet and transmits it to a computer monitor. Two to three days after the examination, the capsule leaves the body naturally. There are several contraindications for which the procedure is prohibited:
- pregnancy period;
- the patient's age is less than 12 years;
- if you have a pacemaker;
- problems with intestinal patency.
Gastroscopy (the simplified name of the procedure) is prescribed in the clinic for pathologies of the upper gastrointestinal tract, but is mandatory for people over 40, and is also strongly recommended in the presence of complaints and symptoms of “anxiety”, such as:
- bleeding;
- weight loss;
- swallowing disorder;
- anemia;
- regularly recurring vomiting;
- frequent chest pain;
- suffocation.
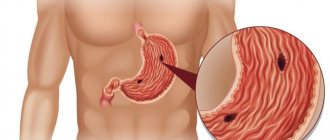
This study is used to diagnose diseases of the stomach, esophagus, and intestines. At the same time, modern technology makes it possible to conduct video recording, take biopsy material, and stain suspicious areas to exclude or confirm oncological pathology. An additional function of the study is the ability to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
FGDS can be not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic procedure in cases where endoscopic hemostasis (stopping bleeding), removal of polyps or sclerosis of dilated veins of the esophagus or stomach is performed.
There is no need for special training. It is enough to eliminate food and water intake for 10 hours, and also not smoke. If it is intended to determine acidity, then 5-6 days before stopping taking medications that affect it (both reducing and stimulating).
We are talking about the following drugs:
- Antisecretory (lowering Ph): proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, lanzoprazole, rabeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole), anticholinergics, H2 blockers, bismuth preparations.
- Stimulating and replacing Ph (preparations based on plantain, bitterness, as well as: gastric juice, hydrochloric acid, acedin-pepsin).
FGDS is strongly not recommended in the acute period of myocardial and cerebral infarction, as well as in patients suffering from severe attacks of bronchial asthma, mental illness, and bleeding disorders.
In case of urgent indications, manipulation in a hospital setting is allowed.
Patients often ask whether it is possible to do FGDS during menstruation? We answer that this condition is not one of the absolute or indirect contraindications. So it's possible.
For children
Almost all children do not like therapeutic and diagnostic measures. Gastroendoscopy for a child is a difficult test, so it should be prepared in advance. Before starting the procedure, as a rule, children are injected with a little atropine to calm and relax the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
When the anesthesia takes effect, the examination can begin. The child is placed on his left side, while the patient's back should be straight. A towel or diaper is placed under the patient's chin to absorb saliva, which is released abundantly during the diagnostic procedure. The baby is swaddled during EGD. Scheme of implementation of children's diagnostic measures:
- A small patient's mouthpiece is inserted into his mouth so that it is constantly open.
- Next, the endoscope tube is carefully and gradually inserted. The probe is immersed inside during each exhalation of the child.
- When the device enters the patient's stomach, its movement is stopped.
- The specialist carefully examines the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The gastroscope is slowly and carefully removed.
Why is this procedure so popular?
Thanks to colonoscopy, it has become possible to detect various tumors in the colon. This method is much more effective than others, as it allows you to detect cancer at an early stage, polyps and other neoplasms, even in the most inaccessible places. The procedure gained such capabilities thanks to the highly sensitive probe of the colonoscope. Its length reaches 160 cm and allows you to examine most of the intestine. The procedure, performed by an endoscopist or proctologist, is absolutely safe and minimizes the possibility of internal burns, since cold light is used.
The duration of the study is no more than half an hour
. The procedure is usually completed by reaching the cecum. The probe is inserted into the anus manually and the advancement of the flexible tube is accompanied by air supply. In this case, the doctor controls the position of the device by palpation of the abdomen.
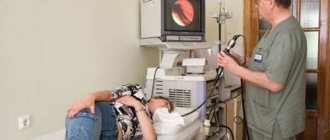
How FGDS is carried out: description
During the procedure, the patient is placed on his side; before this, the pharynx is treated with an anesthetic solution to reduce discomfort during the examination. A mouthpiece is inserted into the mouth to prevent biting of the device.
The patient needs to listen carefully to the doctor’s instructions and calmly follow them: breathe deeply and calmly through the nose, do not swing your limbs, do not try to grab something that should not be grabbed.
The manipulation is performed by an endoscopist.
| Procedure name | Approximate cost of the procedure in rubles |
| EFGDS classic | 1500-5000 |
| Gastroendoscopy under any type of anesthesia | 6000-10500 |
| Gastroscopy biopsy histology | 2000-3500 |
| EFGDS Express method Helicobacter pylori | 700-1000 |
WHY IS THE RESEARCH CARRIED OUT?
Gastroscopic examination has extremely great potential, so this procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- With the development of inflammatory reactions of the esophagus.
- When the lumen of the lungs narrows.
- For oncological pathologies of the stomach.
- For peptic ulcers.
Gastroscopy has too many indications for its implementation, so we list the main points of what the study can prevent:
- Determine the source of infection.
- Find out the reasons for the development of some symptomatic abnormalities.
- Monitor the condition of organs after surgery.
- Investigate the healing processes of stomach ulcers.
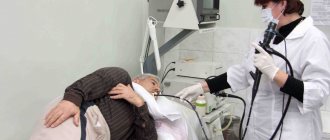
How is the gastroscopy procedure performed?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy - which is what gastroscopy is officially called - must be carried out in a room equipped for such procedures. It must be performed by a gastroenterologist who specializes in conducting such studies.
Before starting the procedure, you will be asked to gargle with a local anesthetic solution. After three minutes, the mucous membrane of the mouth and pharynx loses sensitivity, and the procedure can begin. A special mouthpiece is inserted into the patient's mouth, through which the device itself is passed.
The most difficult thing for the doctor and the patient is passing the endoscope from the throat to the esophagus. At this stage it is better not to rush. The endoscope is slowly inserted directly into the stomach under the visual supervision of a physician. Air is supplied through the device to straighten the walls of the stomach. When the device is already in the stomach, the doctor has the opportunity to carefully examine the entire surface of the organ and, if necessary, take material for research.
Gastroscopy during pregnancy
Pregnant women are not prohibited from performing EGD; it does not pose a danger to the unborn child and mother. True, there is one important condition (so as not to cause complications): manipulation can be done exclusively in the first three months of pregnancy and the beginning of the second trimester. If we talk about anesthesia for the procedure, then during pregnancy only lidocaine is used topically, in the form of a spray. Indications for FGS in patients in the following position:
- confirmation/refutation of the formation of malignant tumors;
- identifying sources of bleeding in the stomach;
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed in the presence of signs of gastrointestinal diseases, when other diagnostic methods give a negative interpretation (in the first trimester of pregnancy).
| It is carried out only for emergency indications, when the risk to the mother’s health exceeds the risk to the child. Restrictions on the procedure are due to: 1 – With the influence of lidocaine during local anesthesia of the throat used for gastroscopy. |
In any period of pregnancy, anesthesia can harm the developing fetus. It is important to know that despite the fact that the placenta itself has the ability to neutralize some anesthetic drugs to some extent, this ability is not unlimited. Especially when, for various reasons, the barrier function of the placenta is impaired.
Anesthesia can slow down cell growth and disrupt biochemical reactions that occur during cell division. This is especially dangerous in the first trimester, when the formation of all organs and systems of the body occurs.
Exposure to certain drugs can slow down the metabolism between mother and baby. There may be disturbances in placental and uterine blood flow, which impairs fetal nutrition.
2 – During the procedure, tension occurs in the abdominal wall, which can tone the uterus.
This is especially undesirable in the third trimester (after the 28th week) due to increased excitability of the uterus, as well as “squeezing” of the abdominal organs by the uterus, which makes the examination itself difficult.
Is it worth doing FGDS for prevention?
Very often, a patient who complains to a gastroenterologist asks before gastroscopy how many times a year FGDS can be done and whether it is harmful to the body. The constant development of technologies, including medical ones, creates more informative examination tools and less and less discomfort for the patient. Now the diameter of some umbrellas is only 1-2 cm, while maintaining the ability to communicate and swallow during the FGD process.
Important! It is recommended not to perform gastroscopy in cases where the patient has any disease of the upper respiratory tract (laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis). This is primarily due to the additional mechanical effect on the inflamed areas of the throat as a result of its implementation.
How many times gastroscopy of the stomach is done is determined only by the doctor, based on the patient’s condition. For preventive purposes more than once every 10 months. It is not recommended to conduct FGDS without apparent reasons. If an examination is prescribed by a specialist, it is carried out not only for prevention, but also for diagnosis, so you need to be examined on time and without fear of harm from gastroscopy.
Alternative diagnostic methods (gastroscopy without a probe)
As an option for the rich but faint of heart, there is capsule video endoscopy. During the manipulation, it is not the probe that is swallowed, but a capsule that transmits a video signal.
X-ray and graphography of the gastrointestinal tract differ from gastroscopy primarily in that the condition of the mucous membrane is diagnosed worse, but spasms, motility disorders, and hernias are better visible. These procedures complement, but do not replace, FGDS.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QmCeXUabM9Q{amp}amp;modestbranding=0{amp}amp;controls=1{amp}amp;rel=0{amp}amp;showinfo=1{amp} amp;enablejsapi=1{amp}amp;origin=
A less informative option compared to FGDS, but many times more comfortable, is a gastropanel (blood test) for diagnosing stomach problems.
Possible risks
Complications during this procedure are extremely rare. And they are associated primarily with the fault of the patient himself, who does not follow the specialist’s recommendations, and also as a result of the anatomical features of the internal organs.
Possible consequences:
- Allergic reactions in the presence of intolerance to certain components;
- Puncture with an endoscope;
- Ingestion of infection;
- The development of short-term bleeding as a result of microtrauma of the intestine or other organ.
In some cases, upon completion of such a diagnosis, the patient may feel a feeling of nausea, sore throat and difficulty swallowing. However, these symptoms go away on their own after 1-2 days and are not a cause for concern.
Gastroscopy is a safe and effective procedure that allows you to make a diagnosis with high accuracy. It is carried out with the frequency that is necessary, in the opinion of the attending physician.