Dibothriocephalosis (another name is diphyllobothriasis) is a helminthic infestation from the group of cestodoses caused by the larvae of Diphyllobothrium - a broad tapeworm. The parasitic disease occurs with primary damage to the gastrointestinal tract, signs of megaloblastic anemia (deficiency of vitamins B12 and folic acid). Treatment of diphyllobothriasis is complex and includes a health-improving diet, vitamin supplements, and narrow-spectrum antiparasitic agents. Let's look at how infection occurs and what symptoms indicate worms in the human body.
Briefly about helminth
The causative agent of the invasion is a tapeworm of the species Diphyllobothrium latum, Diphyllobothrium pacificum and Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense. The helminth is quite large and can reach 12 m in length. The tapeworm consists of a flattened head (scolex), a body and 2 suction slits (bothrium). The structure of the worm is formed from many (300–4000) proglottids (segments).
Helminth eggs have an oval shape and are reliably protected by a two-layer coating. The larvae are small in size and invisible to the eye. Their average values are from 50 to 60 microns. Helminth eggs are visible only under a microscope. The broad tapeworm lives up to 25 years. Located in the body of an intermediate or primary host, the worm lays eggs, causing severe intoxication and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
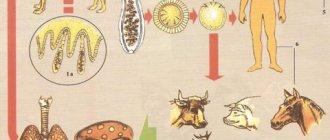
The helminth has a complex ontogeny. For its full ripening, a fresh water environment is needed. In this case, the temperature favorable for the development of the worm is from +10 to +20 degrees. The helminth migrates using 3 intermediate carriers. After the larva reaches the embryonic state, the worm emerges from the egg and is immediately swallowed by the first host, a freshwater crustacean (daphnia or cyclops).
Further, the infected crustaceans enter the fish’s stomach through the food chain, and from there move into the muscle tissue and eggs. In them, the helminth goes through several stages of development, completing its growth and reproduction in the body of the final host - a person, cat, dog, pig or wild animal that feeds on fish.
Sloth eggs are released into the environment through the excrement of the carrier.
Helminth larvae are resistant to adverse atmospheric factors (cold and heat). However, temperatures of + 200 C° and salt water are detrimental to sloth. This fact explains the absence of foci of helminth infection in countries with hot climates and in sea waters. In the body, the wide tapeworm can exist for decades.
Causes
A person becomes infected with the causative agent of the disease by consuming raw fish containing tapeworm larvae. In addition to humans, the definitive hosts of the parasite are dogs, cats, walruses, seals and other animals. After entering the intestine, the larva begins to grow and develop. Over time (about 3-6 weeks), it turns into a sexually mature individual capable of producing eggs. Eggs are produced in each segment of the worm and are then passed in the stool. Sometimes the whole worm or parts of it can be seen in the stool.
The causative agent of diphyllobothriasis is the adult broad tapeworm. The average length is 10 m. Life expectancy is up to 20 years.
Etiology of the disease
A person becomes infected with the parasite through eating fish that have larvae inside. Most often this concerns pike, ruff, perch and burbot. Penetrating orally into the stomach, the helminth moves throughout the gastrointestinal tract, settling on the walls of the mucous membrane, internal organs and subcutaneous tissue.
At the end of its ontogenesis, tapeworm eggs enter the environment with human waste products, after which they are absorbed into the ground or end up in a reservoir.
The incubation period of the broad tapeworm lasts from 1.5 months to several years. In this regard, detecting a “settler” is not easy.
The helminth appears only at the last stage of development. Its symptom complex is nonspecific and mimics various types of disease, which significantly complicates the diagnosis of the disease and timely provision of medical care to the patient. The number of eggs released by a sexually mature female tapeworm can reach 2 million.
Reasons for appearance
Those who live in regions with a temperate, cold climate (mainly in the northern hemisphere) and developed fisheries in fresh water bodies are more predisposed to diphyllobothriasis. The definitive hosts of the parasite are fish-eating animals and humans. Intermediate hosts are cyclops crustaceans and freshwater fish (salmon, perch, pike, ruffe, burbot and others).
The causative agent of diphyllobothriasis in the mature stage parasitizes in the small intestines of humans or animals predisposed to it, after which helminth eggs are released into the external environment with their feces. The eggs fall into the water and after 2-5 weeks the embryos appear, which are swallowed by freshwater crustaceans. Further development of the embryos into the form of procercoids occurs in the muscles, fiber, liver, and tissues of fish that feed on crustaceans. Here the helminths move into their next form of development, which is dangerous for humans.
Infection with diphyllobothriasis occurs due to the consumption of raw, poorly processed, lightly salted infected fish and its caviar. You can also become infected with diphyllobothriasis through knives, dishes, and boards used to cut infected fish.
Complications
Helminthiasis cannot be ignored. Its constant toxic activity not only provokes discomfort and changes in the patient’s well-being, but also leads to the development of serious negative health consequences:
- Tissue necrosis and atrophic processes of the gastrointestinal mucosa, in the places of attachment of the scolex of the wide tapeworm;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract due to damage to nerve endings by the parasite;
- Disorders of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the intestinal microflora (trophism);
- Allergies of varying intensity, as a result of sensitization of the body to helminth waste products;
- Development of megaloblastic anemia due to adsorption of vitamins B1, B12 and B6 by tapeworm;
- Funicular myelosis - chronic, dystrophic damage to the spinal cord;
- Intestinal obstruction leading to intestinal obstruction;
- Depression;
- Strengthening segmental reflexes (hyperreflexia);
- Paresthesia;
- Damage to the walls of the large intestine (perforation), causing the development of abdominal inflammation (peritonitis);
- Anemia.
As a rule, diphyllobothriasis does not pose a threat to the patient’s life. But in some cases, with multiple accumulations of parasites or their long stay in the body, a severe form of anemia and pathological changes in the functioning of the nervous system develop.
Without proper treatment, the patient may die.
Symptoms
Since the tapeworm attaches to and feeds on the tissues that make up the wall of the human intestine, first of all, the patient experiences a dysfunction of this organ. At first, this may manifest itself as discomfort in the abdominal area. Later, the clinical picture may be supplemented by bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract and impaired ability of the stomach to produce gastric juice.
Diphyllobothriasis does not immediately make itself felt. This is explained by the fact that once the worm enters the human body, it takes some time to mature. Thus, symptoms may appear only after a period of twenty to sixty days. After this, the first signs of infection appear, which are similar to the symptoms of normal intoxication of the body:
- headache;
- constant weakness;
- deterioration of memory and attention;
- nausea;
- severe dizziness;
- loose stool.
If such a worm is not detected when the first symptoms appear, then the health of the infected person will only worsen, since the parasite “eats away” many nutrients from the body of its owner (vitamin B12 is excellent for increasing its fertility). A lack of this vitamin in the body leads to the formation of a small number of red blood cells, which contain an excess of hemoglobin. These factors cause the taste buds of the tongue to smooth out, causing it to acquire a rich red color and cracks to appear on it.
Due to a lack of nutrients and vitamins in the body, there is numbness in the lower extremities and muscle weakness, due to which gait may be impaired. Paralysis and loss of sensation may develop. In the later stages of disease progression, these processes begin to affect the upper limbs.
A pronounced symptom of diphyllobothriasis is the appearance of scarlet allergic spots on a person’s skin, but the rest of the skin is very pale. Characteristically, this symptom occurs only in the first year of the parasite’s life. If its duration exceeds this period, then the allergic reaction goes away because the body stops responding to the presence of the parasite.
Wide tapeworm
While listening to the heart, murmurs and rapid heartbeat are heard. When the worm is large, the spleen and liver become enlarged. A worm of this size can cause intestinal obstruction. Doctors note that if diphyllobothriasis occurs latently, this indicates that the disease has become chronic. In this case, the manifestation of symptoms is periodic (periods of exacerbation alternate with periods of subsidence). But often only intoxication of the body and allergic reactions are observed.
Diagnostic methods
To establish diphyllobothriasis, a differential diagnostic method is used. The most informative studies in this sense are:
- Collecting an epidemiological history - the patient’s area of residence, his culinary preferences, frequency
- Eating lightly salted or raw fish, etc.;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Biochemical analysis to determine the level of bilirubin, transaminases (AST and ALT), protein and its fractions;
- Study of gastric secretions;
- Fecal analysis for worm eggs, which allows you to isolate fragments of the parasite;
- Anal swab for bacterial microscopic analysis;
- PCR method;
- Serotological diagnostic technologies aimed at searching for antibodies;
- Blood sample for ESR, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia and anemia.
Also, given the similarity of the symptoms of helminthiasis with a number of other diseases, the patient may be prescribed additional tests.
Diphyllobothriasis is always approached in a comprehensive manner, since no type of analysis is exhaustive for making a final diagnosis. An infectious disease specialist treats helminthiasis.
Traditional medicine tips
Man lives on earth for several thousand years, and all this time his body becomes a favorable environment for infection with helminths. Perhaps in ancient times people were not familiar with parasites, but the methods given to modern man by ancient folk medicine are still effective today. It is the means that have been proven over centuries that are presented here.
Pregnant and lactating women should take these medications with caution. Some may burn the milk or have a negative effect on the baby or fetus in the womb.
Ancient healers and healers, when identifying strange worms in human feces, recommended consuming:
- milk with garlic;
- dry pumpkin seeds;
- walnuts;
- infusions and decoctions of St. John's wort, tansy;
- onion or juice from it;
- sagebrush;
- thyme;
- pomegranate fruits;
- male varieties of fern.
Milk and garlic
A rather strange combination, but this is the remedy that will help neutralize this enemy. More than one generation of humanity has been saved by this burning, fragrant plant from many diseases. Garlic is inevitable death for the tapeworm. This reaction is easily explained by the presence of a large amount of essential oils and phytoncides in garlic, which is responsible for its pungent aroma. The effect of these components on parasites can be compared to the effect of high temperature. They just burn out.
Both sour and fresh milk are used to prepare the product. One tablespoon of chopped garlic (can be squeezed through a crush) is diluted in a glass of sour milk. The mixture is left for 6-8 hours. It is advisable to stir the solution several times during this time. It is better to prepare it in the evening. In the morning, divide the entire volume by the number of meals and drink in equal parts half an hour before meals.
With fresh milk, the solution is prepared a little differently. Pour one glass of milk into an enamel pan. Pass 5 cloves of garlic through a crush and add to the milk. Bring to a boil, reduce heat and simmer for about 10 minutes. Then cool, do not strain and put in the refrigerator. Take four times a day half an hour before meals. It is desirable that there is a feeling of hunger. Therefore, exclude any kind of snacks at this time. Course – 7 days.
Pumpkin seeds
The most common remedy in the fight against parasites. It is recommended as a safe and effective remedy for children and adults. The main thing is that the seeds are raw, but well dried naturally.
Pumpkin seeds contain the active substance cucurbitin, which is a real poison not only for tapeworms, but also for most other helminths. From the gastrointestinal tract, the substance enters the blood and paralyzes the parasite, after which it dies and comes out.
Despite the fact that pumpkin and its seeds are an original Slavic vegetable, the remedy was discovered by Tibetan monks. And it is they who advise, for greater effect, to consume the seeds together with the peel, if possible. Since it is in the peel that the largest amount of cucurbitin is concentrated.
The seeds must be taken on an empty stomach. For an adult, the daily dose is 300 grams, for children - no more than 100. Doctors recommend combining this remedy with garlic treatment to obtain a faster effect.
Conclusion
Whatever remedy is chosen, it must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Each human body is individual. What suits one person may not be accepted by another, causing allergic reactions or side effects, even if it is a traditional medicine.
It is equally important to observe basic hygiene standards. Equipment and cutting boards for fish cannot be used for cutting and slicing other products.
If this cannot be done, then at least wash everything thoroughly after the fish and treat it with boiling water. Be healthy!
https://youtube.com/watch?v=7Rmc53Hqy5I
Therapy
Deworming is not a pleasant procedure. If the disease is mild and there are no complications, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. But in case of poor test results and serious condition, the patient is subject to urgent hospitalization and inpatient treatment. The wide tapeworm is removed from the body in stages, using anthelmintic drugs and a vitamin complex.
The following medications have the most effective antiparasitic effect against tapeworm:
- Phenasal/Iomesan/Vermitin;
- Mebendazole;
- Paramomycin;
- Praziquantel;
- Azinox;
- Biltricide.
The medications are quite specific and are used according to a certain pattern, often after meals. The daily dose of tablets is prescribed to the patient individually, based on the clinical picture and study results. The diet during treatment consists of liquid, easily digestible food.
The second stage involves replenishing the vitamin deficiency. To do this, the patient is given intramuscular injections of Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12), Ferronate, Hemofer, Ferroplect, Aktiferrin, Hematogen and other iron injections daily.
The third stage is the prevention of helminthiasis. The most common way to prevent diphyllobothriasis in this case is peeled pumpkin seeds, filled with a small amount of water and mixed with a few tablespoons of honey. The product is highly effective and is taken on an empty stomach 1 hour before meals.
But the effect of the drugs is aimed only at paralyzing the helminth in order to detach it from the intestinal walls. The process of final elimination of the parasite is completed by cleansing the body with the help of laxatives and agents that enhance intestinal motility.
To properly carry out the procedure for removing helminths, special preparation of the gastrointestinal tract is necessary. Common enemas and weak saline solutions are used as approved flushing methods. The manipulation itself to extract the wide tapeworm must be carried out very carefully.
Since the helminth's body is quite long, pulling it is not recommended. Otherwise, the scolex may come off, and part of the tapeworm may remain inside the organ.
In a situation with intestinal obstruction, immediate surgical intervention is indicated. Upon completion of the course of treatment, the patient is advised to undergo regular preventive examination for the presence of worm eggs. If residual helminthic material is detected, re-treatment is recommended.
Treatment of infection
The main method of treatment is medication. Folk recipes are auxiliary. They help you recover faster and reduce symptoms of the disease. Surgery is used in cases where intestinal obstruction is diagnosed.
The main method of treating diphyllobothriasis is medication.
Drug therapy
A fairly simple and effective treatment is the prescription of antiparasitic drugs:
- A single dose of Praziquantel is 5-10 mg per 1 kg of weight (for adults and children). Taken orally.
- A single dosage of Niclosamide is 50 mg per 1 kg of weight (but not more than 2 g) for children, 2 g at a time for adults.
- Treatment with Biltricide is carried out once at an average dosage of 25 mg per 1 kg of weight.
All of these drugs are quite effective in treating parasitic infections. No additional diet is required. Most often, positive reviews are found after Biltricide therapy.
The anti-worm drug Biltricide is available in the form of film-coated tablets.
Biltricide is available in the form of film-coated tablets. The active ingredient is praziquantel, effective against cestodes and trematodes.
The death of helminths after taking Biltricide is explained by the effect of the drug on parasites:
- The product increases the permeability of tapeworm cell membranes for calcium ions. As a result, the helminth's muscles contract.
- Biltricide prevents the absorption of glucose by worm cells. Glycogen levels in parasites drop.
- Under the influence of chemical processes provoked by Biltricide, lactic acid compounds are actively released in the body of helminths. Death is coming.
Biltricide is quickly and completely absorbed. Metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys. Like all antiparasitic drugs, it easily passes through the blood-brain barrier and passes into breast milk. It is not recommended to treat infection during pregnancy and breastfeeding with special synthetic agents.
Biltricide is best taken in the evening. To treat diphyllobothriasis, a single dose is sufficient.
Patient reviews report that anthelmintic drugs can cause the following side effects:
- nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- dizzy and headache;
- I have a stomachache;
- concerns about increased drowsiness;
- muscle pain, cramps;
- heart rhythm failure;
- allergic rash.
If adverse reactions occur, treatment should not be stopped.
Anthelmintic drugs can cause abnormal heart rhythms.
And the drug therapy regimen in most cases is elementary: a single dose of a tablet of Biltricide, Praziquantel, Niclosamide, etc.
Traditional methods
Diphyllobothriasis cannot be completely cured only through folk recipes. This is a complementary therapy. Popular folk recipes:
- Male fern extract. It is highly effective. Treatment is accompanied by laxatives and cleansing enemas, an antiparasitic diet (limit fats, spicy foods, light dinner). The capsules are very toxic.
- Pumpkin seeds. Make a tincture of water, which is taken on an empty stomach. According to user reviews, for maximum effect, you need to use a saline laxative after three hours, and after half an hour, do an enema.
In case of severe anemia and pronounced manifestations of the disease, vitamin complexes, probiotics and painkillers are prescribed. If diphyllobothriasis is accompanied by constipation, the patient is given laxatives.
After 1 and 3 months, the effectiveness of the therapy is monitored. If the test for diphyllobothriasis is negative, a repeat course is not required. The prognosis is favorable. There may be insufficient immunity for some time.
Infection of people with diphyllobothriasis occurs due to the consumption of diseased fish in a raw, insufficiently heat-treated form. The causative agent of the infection is tapeworm. The parasite lives for a very long time, so the disease takes a chronic form. Often there are no signs.
The main and effective method of therapy is taking antiparasitic drugs. To reduce symptoms and provide additional effects on helminths, traditional methods are used. Patients leave positive reviews about the use of male fern and pumpkin seed extract.
Prevention
Unfortunately, humans do not have natural immunity to the pathogens of diphyllobothriasis. Therefore, the risk of re-infection remains high. By observing precautions, you can protect yourself from infection with diphyllobothriasis and prevent the possibility of relapses in the future.
Effective measures to prevent helminthiasis include:
- High-quality heat treatment of fish and seafood. Any product must be well fried or baked. Cooking time for fish dishes is at least 20 minutes. In the case of pickling raw fish, the percentage of salt must be 9%. Always store seafood only in the freezer or at a temperature of -15 Cº, but no more than a day.
- Before eating delicacies made from raw fish - sushi or sashimi - make sure that the product has been properly processed by the manufacturer.
- Avoid eating half-baked fish from your diet. You should also be careful with smoked and marinated fish, especially home-cooked fish.
- Wash tools and cutting boards thoroughly after working with raw, especially diseased, fish.
In addition, local control authorities in areas with a potential risk of infection are required to conduct regular sanitary and epidemiological inspections of fishing cooperatives and specialized food enterprises, hygienic monitoring of the cleanliness of reservoirs and wastewater, control over the disinfection of fish before its release for sale, periodic examination of persons Those at risk include fishermen, food industry workers, and river vessel crews.
Not the least role in the prevention of diphyllobothriasis is given to sanitary and preventive work with the population.
How to avoid infection with diphyllobothriasis?
To prevent infection in food, it is recommended to consume well-cooked or fried fish, well-salted freshwater fish caviar. You need to know that when salted, the larvae die after 2-7 days (the variability of time is due to the concentration of the saline solution).
Helminth eggs die when salted for 30 minutes, if the mass fraction of the cooking powder is 10% of the weight of the salted product. If the salt percentage is five, then the parasite eggs die after six hours, if three - only after 48 hours.
The larvae die when deep frozen. Death at -18 degrees occurs within 2-4 days, and at -6 - within a week. Other preventive measures include avoiding consumption of any raw fish; when cutting it, all hygiene rules must be observed.
If characteristic signs appear, you should contact a medical facility. First of all, they contact a therapist, the doctor issues a referral for a stool sample. Treatment is prescribed by an infectious disease specialist. Sometimes an additional consultation with a hematologist is required. If intestinal obstruction has developed, the treatment is carried out by a surgeon.