- What does a polyp in the uterus look like on an ultrasound?
- Hysteroscopy
- How does a polyp affect menstruation?
- Drug treatment
Uterine polyp is a fairly common gynecological disease that can occur in a woman at any age. More often it is associated with hormonal imbalance and occurs against the background of hyperestrogenism; risk factors also include inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. Less commonly, a polyp in the uterus is associated with psychosomatics, although stress has a great impact on women's health.
Why is a polyp in the uterus dangerous? It can cause severe uterine bleeding, ulcerate, become inflamed, and in 1-2% of cases degenerate into cancer. Therefore, it is recommended to treat it in any case, and the sooner treatment is started, the easier it is to perform. In Moscow, polyp treatment is successfully carried out at the Yusupov Hospital. This is a modern medical center where patients are provided with medical services at the highest level.
Symptoms
The polyp in the uterus at the beginning of its formation does not manifest itself in any way, but over time the woman begins to be bothered by the following symptoms:
- Heavy menstruation;
- Bloody discharge outside the cycle;
- Cramping pain in the abdomen;
- Unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse;
- Difficulty conceiving;
- Temperature (with a uterine polyp, it can occur with the development of inflammation).
Sometimes uterine polyps are asymptomatic and are detected during random medical examinations.
Therefore, do not forget to regularly visit a gynecologist and conduct an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Make an appointment
Types of polyps
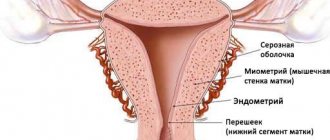
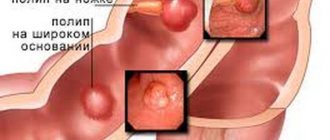
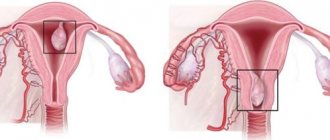
A polyp develops in the uterine cavity from the mucous layer. This is focal endometrial hyperplasia, which is characterized as a pedunculated polyp in the uterus. The neoplasm can be attached to the uterine cavity with the help of a thin connecting growth or have a wide base (in this case, a flat polyp in the uterus is meant). Neoplasms can be single or multiple, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.
This type of benign tumor in most cases is based within the uterine cavity. The following localizations are distinguished:
- Polyp on the back wall of the uterus;
- On the anterior wall of the uterus;
- On the side wall;
- Polyp on the uterine stump;
- Polyp of the cervical canal (rare occurrence).
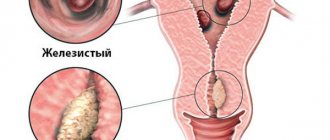
Based on their structure, neoplasms are divided into:
- Ferrous;
- Glandular-fibrous;
- Fibrous;
- Adenomatous.
A glandular polyp in the uterus consists of endometrial tissue, in which glands predominate. A glandular polyp of the uterine body often develops at a young age.
The glandular-fibrous polyp is represented by endometrial glands and fibrous (connective) tissue. Fibrous neoplasms consist largely of dense connective tissue. Fibrous polyps in most cases develop in women of menopausal and premenopausal age.
Polyps in the uterus require urgent treatment as they can cause serious consequences such as anemia, infertility and, in rare cases, cancer.
Adenomatous polyp
Adenomatous neoplasms are formed from glandular epithelium, which exhibits signs of excessive growth and structural restructuring. Such tumors require increased attention, as they have a tendency to malignant degeneration.
An adenomatous polyp is characterized by an abundance of densely located glands. They have numerous branches in the direction of the connective tissue. Sometimes they are located so close to each other that they displace stromal cells and they are not visible even under a microscope. In some dilated glands, the presence of papillary outgrowths towards the lumen is observed, which has the specific name “gland in a gland”.
A uterine polyp with foci of glandular atypia is difficult to identify visually. Therefore, in the case of multiple polyposis, all tumors are removed, and a histological examination is subsequently carried out. If there is an adenomatous uterine polyp with atypia, consultation with an oncologist is necessary to determine further treatment tactics.
Placental polyp
Placental polyp is a special type of neoplasm that forms in the uterine cavity due to retention of placental tissue particles after childbirth, medical abortion or miscarriage. The remnants of the placenta, which is tightly attached to the walls of the uterus, are joined by many blood clots, from which a polyp is formed.
This pathology is very common among those who resorted to artificial termination of pregnancy or suffered a spontaneous abortion. The presence of endometrial polyps increases the likelihood of miscarriage by 5-8 times. Treatment of placental polyp is carried out surgically.
Polyps on the wall of the uterus: definition
One of the most common neoplasms in the uterus are polyps. They are exclusively benign in origin. If there is gradual damage to the entire uterine cavity, namely the mucous membrane, the multiple presence of polyps is called polyposis.
The base is divided into two types. Either the polyp has a thin stalk, or its base is thickened. Also, according to localization, these formations can be divided into: polyp on the anterior wall of the uterus, on the back, polyp of the cervical canal.
Why is an endometrial polyp in the uterus dangerous?
The most dangerous clinical manifestation of a polyp in the uterus is bleeding. In addition to this unpleasant symptom, a sick woman may be diagnosed with pain and lack of pregnancy. To stop this pathology it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. Other treatment methods are not particularly effective.
As practice shows, more than ten percent of women come with the problem of polyps in the uterus. This is a serious disease that affects both young, nulliparous girls and women of retirement age. Currently, even teenagers who have not entered into sexual activity come to the clinic with this disease; endometrial polyps are also found in the uterus of a nulliparous woman. What kind of disease is this? How to recognize it? What are its symptoms and treatments?
Polyps in the uterus are pathological neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the uterus. It is a benign tumor. A woman may have one or several polyps in the uterine cavity. In appearance it resembles a mushroom, and its size ranges from one and a half millimeters to several centimeters.
Are there polyps in the uterus? In order to identify this unpleasant pathology, it is necessary to resort to a histological research method. Also, for diagnosis, you need to visit a gynecologist for an examination, undergo an ultrasound method and hysteroscopy. Polyps of the uterine cavity can be detected in completely different sizes, depending on time. Typical is the identification of a polyp of endometrioid origin along with a polyp in the cervix of the organ.
Causes of endometrial polyp in the uterus
The reasons that led to this pathological process are constant processes of inflammation of the endometrium, as well as certain hormonal disorders. Based on this, this disease can overtake any woman, regardless of her age. One of the branches of medicine that deals with this issue is gynecology. Polyps in the uterus - reviews regarding treatment are extremely positive.
The average statistical indicators provide us with the fact that the pathological process is diagnosed in 15% of women. Leading doctors have proven that the appearance of a polyp in a woman is a condition that can later develop into a cancerous process. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend removing the endometrial polyp in the uterus to prevent cancer.
Symptoms of a polyp of the uterine body
When a woman has one polyp, clinical manifestations may be completely absent. But if there is extensive damage to the mucous membrane, then symptoms will arise that will worsen the quality of life. The patient suffers enormous discomfort and constant pain.
Can a polyp in the uterus be malignant?
Most women who are diagnosed with a single endometrial polyp of the uterine cavity make a huge mistake. They do not go to a gynecologist for further treatment. This is absolutely wrong. There is a huge risk of a polyp, because if the disease is not stopped, then the process of malignancy (cancer) may begin. It is imperative to carry out therapeutic measures for existing pathology.
Are polyps in the uterus dangerous?
Polyps can provoke dangerous processes: the formation of polyps in the uterus can cause difficulty conceiving a child.
Polyp in the uterus - the cause of infertility
- Even if you manage to get pregnant, there is a high risk of losing the fetus.
- Absolute infertility.
- The occurrence of heavy bleeding from the uterus. This is especially typical during a woman’s menstrual cycle. If bleeding is not stopped in time, irreversible processes may occur, even death.
- Premature expulsion of the placenta at the time of pregnancy. There is a terrible threat of losing the child and causing bleeding.
- Uterine polyps can cause compression of the fetus, which can result in hypoxia in the child. If the process is not stopped in time, the fetus can be lost.
It is necessary to understand that cervical polyps are no less dangerous than endometrial polyps themselves. Therefore, it is necessary to stop the disease as soon as possible; the uterine polyp can be safely removed.
There are different types of polyps in the uterus. But regardless of the type, it is necessary to treat and not avoid the recommendations of a gynecologist. In order to study the varieties in detail, we will look below.
Reasons for the appearance of the tumor
There is no reliable information about the reasons for the appearance of polyps. There are several possible causes of the formation of focal endometrial hyperplasia, including:
- Hormonal dysfunction (formed when there is a large amount of estrogens and a lack of progesterone in the second phase of the menstrual cycle). This is why polyps are most often diagnosed between the ages of forty and fifty, shortly before menopause;
- Infections - chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs: previous endometritis (inflammation of the intrauterine membrane), cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of the uterine appendages);
- Endometrial trauma (abortion, diagnostic curettage);
- Obesity;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Stress.
What causes polyps to form?
The health of the endometrium depends entirely on the hormonal balance of a woman. An increase in the body's level of the hormones estrogen and progesterone produced by the ovaries without a reason (pregnancy) can lead to the formation of pathological growths in the uterus. The concentration of female hormones may increase due to:
- chronic stress;
- presence of infectious diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine glands (pancreas, thyroid and adrenal glands).
Also, the proliferation of tissue lining the uterine cavity may be the body’s response to mechanical injuries, for example:
- abortions;
- diagnostic curettage;
- wearing an intrauterine device for more than five years.
Polyps of placental origin can occur both after unsuccessful abortions and after childbirth and spontaneous miscarriages.
This disease can also develop due to a woman’s decreased immunity.
Polyp in the uterus and pregnancy
Very often, a polyp is called a “natural contraceptive”, since if it is present, it is quite difficult for a woman to become pregnant. The neoplasm prevents the implantation of a fertilized egg, and even if this occurs, it can provoke a miscarriage. As a result, the woman is diagnosed with infertility or recurrent miscarriage. In addition, a large tumor will cause pain during sexual intercourse, which will negatively affect a woman’s libido.
Therefore, during pregnancy planning, this pathology should be completely treated in order to reduce the risks of adverse events.
Make an appointment
Diagnostics
After symptoms of pathology appear (heavy menstruation, bleeding outside the cycle, pain in the lower abdomen), you should consult a gynecologist. Polyps can also be detected at an early stage during a routine examination. Therefore, it is important to visit a gynecologist at least once a year.
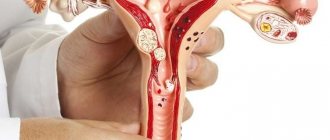
To diagnose neoplasms, the doctor will perform a gynecological examination with palpation of the uterus and prescribe an ultrasound. A polyp in the uterus on ultrasound looks like an oval or round growth, usually on a stalk. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the expansion of the uterine cavity and local thickening of the endometrium.
A more informative diagnostic method is hysteroscopy of a uterine polyp. During this procedure, the doctor observes neoplasms in the uterine cavity of various locations. They can have a smooth or knotty surface and are pink in color. Neoplasms can be red if inflammation has begun in them, or grayish with individual patches of variegated color if the polyp’s nutrition is disrupted and a necrotic process develops.
Determining the type of polyp by appearance (glandular, fibrous or adenomatous) is quite difficult. Therefore, it is removed for further histological examination.
What does a polyp in the uterus look like on an ultrasound?
Ultrasound examination is the most accessible and highly informative method for identifying tumors in the uterus. Based on the results obtained, the gynecologist draws up a description of the polyp in the uterus using ultrasound. A polyp in the uterus is a neoplasm growing from the endometrium.
The polyp has a simple structure, it is formed by a body and a stalk, attaching the formation to the wall of the uterus. In the photo of a uterine polyp on ultrasound, with this pathology, echo signs in the uterine cavity change, the oval or round shape of the neoplasm and its homogeneity can be seen.
An ultrasound examination for suspected polyps in the uterus at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using transvaginal and transabdominal sensors. Modern equipment allows specialists to accurately identify tumors in the uterus and conduct further research on them.
Histology
Histological examination of polyps is carried out to determine the nature of the formation and select further treatment tactics. This procedure is prescribed to women after a uterine polyp is detected on ultrasound. During diagnostic curettage of the endometrium, the specialist obtains tissue samples that are used for histological examination.
The histology of a uterine polyp allows one to identify cancer cells at an early stage before the first symptoms of the disease appear. The resulting sample is fixed by a specialist using ethanol or formaldehyde, then the tissue undergoes further processing and staining. After completing these steps, the specialist examines the tissue under a high-precision microscope.
What are polyps?
These are small nodules ranging in size from a few millimeters to 3 cm. In most cases, they are no more than 1 cm in diameter. Polyps can be single or multiple. They resemble burgundy-violet or yellowish small cylinders with a porous surface. The vessels are clearly visible through their thin shell.
Where do polyps come from? Scientists have not yet fully elucidated this issue. But many theories have been put forward. The main causes are considered to be hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes.
What procedures can detect polyps? The most accessible and painless method is ultrasound. The most accurate results are obtained by testing using a sensor that is inserted into the vagina. But if a detailed examination is necessary, the doctor may prescribe a hysteroscopy. In this procedure, a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the uterine cavity. Using the same device, you can take pieces of tissue for examination (biopsy). In some cases, special contrast agents are injected into the uterus and an x-ray is taken.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method and management tactics for a patient with endometrial polyposis is influenced by many factors: the size of the formation, its structure, the condition of the uterine mucosa (endometrium), the woman’s age, the presence of concomitant pathologies, etc. Therefore, to achieve the desired result and eliminate the problem, therapy must have an integrated approach.
Treatment of uterine polyps is successfully performed at the Yusupov Hospital. Here a woman can undergo a full course of therapy with consultations from doctors of various specialties (gynecologists, endocrinologists, oncologists). Treatment is carried out in compliance with international standards of evidence-based medicine and is highly effective.
Make an appointment
Causes, diagnosis and treatment of uterine polyp
An endometrial polyp is a benign formation in the uterine cavity. If there are many such formations in the organ, then they speak of uterine polyposis. Neoplasms grow from the basal inner layer of the endometrium. It affects women of both reproductive age and menopause. With uterine polyposis, hyperplasia of the mucous membrane occurs. Under the influence of mutagenic factors, polyps can become malignant, that is, degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
Types of polyps
First of all, let's talk about what cells polyps consist of and what their structure is. A polyp usually consists of epithelial cells. It has parts such as a body and a leg. The following types of polyps are distinguished:
• glandular; • fibrous; • glandular-fibrous; • adenomatous.
The glandular polyp of the endometrium, which is treated in gynecology, consists of a base and glandular epithelium. A fibrous endometrial polyp is made up of connective tissue cells. Glandular fibrous polyps include both connective tissue elements and glandular epithelial cells. The main elements of adenomatous polyps are also glandular epithelium, but upon histological examination they contain cells that have signs of atypia.
Etiological factors for polyp formation
Uterine polyposis is a multifactorial disease that develops under the influence of many causes. The formation of polyps of the uterine mucosa occurs due to the following points:
• imbalance between the hormones progesterone and estrogens; • chronic trauma to the endometrium with the intrauterine device; • frequent diagnostic curettage or termination of pregnancy; • childbirth during which the placenta is not completely removed, as well as miscarriages and frequent abortions; • some somatic diseases accompanied by hormonal imbalance; • reduction of specific and non-specific protective factors; • uncontrolled arterial hypertension, • some infectious diseases and inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of endometrial polyps
A woman may not always suspect that she has endometrial hyperplasia or polyp. Small polyps do not manifest themselves in any way. A woman can contact a gynecologist about some complaints or come for a routine examination, and he will find a polyp. Sometimes this pathology is detected on ultrasound. However, in most cases, with uterine polyps, you can detect a sufficient number of pathognomonic symptoms that allow you to suspect something is wrong.
What are the most characteristic symptoms of endometrial polyps? First of all, the woman complains of cramping pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during coitus or appears immediately after intercourse. In patients of reproductive age with an unchanged cycle, the intensity and volume of discharge during menstruation increases.
Menorrhagia quite often leads to anemia. The woman feels constantly tired, she is bothered by headaches and general weakness. The skin and visible mucous membranes become pale, and dark circles can be seen under the eyes. Nails also begin to break and hair falls out. Hypotension and tachycardia lead to dizziness and collapsed states.
Postmenopausal women may experience discharge from the genital tract once or twice, to which she does not pay any attention. If the polyp becomes large, leucorrhoea may appear. After coitus, scanty discharge mixed with blood is possible.
Endometrial polyp and pregnancy
Pregnancy with a uterine endometrial polyp is always problematic. Women suffering from uterine polyposis cannot conceive. If conception occurs, it is unlikely that the embryo will be able to implant into the pathologically altered uterine mucosa. Well, in the case when pregnancy does occur, the risk of miscarriage is high.
Quite often, women regard bleeding that occurs as a result of a polyp as a threat of early miscarriage. In any case, a woman who has uterine bleeding should consult a specialist. One thing is clear: in any case, if there is uterine bleeding, a woman should consult a gynecologist.
After removal of the endometrial polyp, pregnancy is possible. Treatment of endometrial polyp with folk remedies should be carried out only in the presence of small tumors. After such treatment, the chances of getting pregnant increase.
Methods for diagnosing endometrial polyp
First of all, the gynecologist to whom the woman turned for a consultation should interview her. After collecting an anamnesis, the patient is examined, including a bimanual gynecological examination. Next, the woman is looked at in the mirrors. During such an examination, endometrial polyps can be detected, which are located in the neck of the cervical canal. In the future, the following research methods are used:
• hysteroscopy; • echoscopy of the uterus (ultrasound) using a vaginal sensor; • biopsy followed by histological examination of the drug; • CT and MRI (if indicated).
Hysteroscopy is a diagnostic method that is performed under general anesthesia. The doctor inserts an optical camera into the uterine cavity and examines the endometrium using fiber optics. During this manipulation, it is possible to remove the polyp.
In some cases, using a hysteroscope, a piece of tissue is taken from a suspicious area of the uterine mucosa, which is sent for histological examination. This allows us to exclude the malignant nature of the neoplasm. The most modern way of taking material for endometrial examination is pipel biopsy. This method is the most painless, safe and shortest in time.
A pipel is a special plastic tube, thin in diameter, which has a small piston. With its help, the endometrium is absorbed for the upcoming study of the material. The entire procedure lasts no more than thirty seconds.
A uterine polyp can be seen during an ultrasound examination, which is performed using a vaginal probe. This allows a preliminary diagnosis to be made. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are performed for multiple polyps.
Treatment methods for endometrial polyposis
In most cases, surgery is performed to treat endometrial polyps. A uterine polyp can be removed during hysteroscopy. The doctor removes the pathology and scrapes the uterine mucosa under the control of a hysteroscope camera. If he finds a large polyp, he can simply unscrew it. After the endometrial polyp is removed, the resulting material is sent to a histology laboratory. The polyp attachment site is cauterized with either liquid nitrogen or an electrocoagulator.
You can also perform laser coagulation or cryodestruction of the polyp. After treatment of the endometrial polyp, on the third day after its removal, a control echoscopy of the uterus is performed. And what tactics to choose in the future, the doctor will determine after receiving the results of histological examination.
If histology reveals a fibrous endometrial polyp, treatment is completed. If it turns out that the patient has a fibroglandular endometrial polyp, treatment is prescribed to normalize hormonal levels. In the presence of glandular and fibroglandular neoplasms, a patient of any age should be prescribed hormonal drugs.
For women under thirty years of age, combined oral contraceptives are prescribed for the treatment of endometrial polyps. Patients after thirty years of age should be prescribed gestagens. If a woman does not plan to become pregnant within the next five years, it is advisable for her to have the Mirena hormonal device installed.
A more stringent approach to the treatment of adenomatous polyp. If the patient is before or in menopause, then she is offered to undergo hysterectomy (removal). If malignancy of the polyp or dyshormonal disorders is suspected, the uterus and ovaries should be removed. If a woman is of reproductive age and is planning a pregnancy, then surgery should be postponed and hormonal therapy should be tried.
In the postoperative period, antibiotics are prescribed for prophylactic purposes to prevent infectious complications. For ten days, a woman must adhere to a diet: eat low-calorie foods.
Alternative treatment for endometrial polyp
Often women have a question: is it possible to treat an endometrial polyp with folk remedies? In principle, this is possible. But first you need to contact a gynecologist, undergo an appropriate examination, and perform a histological examination. Only after this, together with your doctor, should you decide on treatment tactics.
What is the traditional treatment for endometrial polyp? Traditional medicine offers many methods for treating this disease. So, douching is carried out with a decoction of celandine, St. John's wort, calendula, and bodyaga. They say that a decoction of hemlock, infusions of shiitake or chaca mushrooms, which a woman should also douche with, help with uterine polyps.
Healers also recommend inserting tampons with garlic into the vagina and taking decoctions of various herbs orally. Endometrial polyp can be treated with folk remedies, but it is not a fact that the treatment will be successful. And don’t forget that endometrial polyps can become malignant. Therefore, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a gynecologist.
If you need diagnosis or treatment of endometrial polyps, contact the IVF Center Nalchik. Our specialists will conduct the necessary examination and offer the least traumatic treatment method. We take an individual approach to the treatment of uterine polyps.
Indications for surgery
In some situations, doctors may insist on the prompt removal of polyps when:
- Detection of adenomatous polyps, which are especially prone to malignancy;
- Detection of a large uterine polyp (indication for surgery >20 millimeters);
- High probability of complications (bleeding, inflammation);
- There is a clear deterioration in the patient's condition.
The highest quality and most popular methods of surgical removal of a polyp in the uterus is hysteroscopy followed by curettage of the cavity and cervix. Also recently, an innovative technique for removing uterine polyps has appeared - laser surgery.
Hysteroscopy
The most common operation to remove a polyp in the uterus. During hysteroscopy, all polyps are removed, and the place where their legs are attached is cauterized with electrocoagulation to prevent relapse. According to reviews from many patients, this procedure is painless and low-traumatic in comparison with conservative curettage of the uterine cavity.
When performing hysteroscopy, a fiberscope is inserted into the vagina - a flexible tube with an attached video camera that transmits an image to a monitor. After visualization of the polyp, it is removed and sent to the laboratory for histological examination. The entire procedure lasts 10-15 minutes. It is performed under intravenous anesthesia, without tracheal intubation.
Curettage of the uterine cavity
Curettage of the uterine cavity can accompany hysteroscopy or serve as a separate method for surgical removal of an endometrial polyp. This procedure is recommended to be carried out several days before the onset of menstruation. During the operation, the gynecologist dilates the cervix and uses a special loop to scrape out polyps from the walls of the uterus. The resulting material is sent for histological examination.
Laser surgery to remove uterine polyps
Removing a uterine polyp using laser surgery does not leave scars on the tissue and allows you to preserve a woman’s reproductive function. In modern medical centers, such as the Yusupov Hospital, you can undergo a full diagnostic examination and then remove the formation on the same day. Since this procedure only takes a couple of minutes, the patient does not need to go to the hospital. After removal of a polyp in the uterus, spotting from the vagina may appear in the postoperative period, which will disappear completely over time.
Hysterectomy
In the presence of adenomatous formations with atypia, more radical treatment will be required, which may require removal of the uterus. Hysterectomy is prescribed in case of oncological suspicion and the degeneration of the pathology into cancer.
Treatment of endometrial polyps
curettage of the uterine cavity
The main method of treating a polyp is surgical removal, which can be done during hysteroscopy or by curettage of the uterine cavity. It is important to remove not only the polyp itself, but also its vascular pedicle, which, with non-radical surgery, can become a source of relapse of the disease. After the polyp is removed, the leg is coagulated using a laser, electric current, or liquid nitrogen.
Curettage of the uterine cavity when removing a polyp is necessary to monitor the condition of the endometrium, removal of other parts of it that can also be hyperplastic, and the resulting material is necessarily sent for histological examination.
ablation of the uterine mucosa
Ablation (resection) of the uterine mucosa is considered a gentle method of treatment for recurrent polyps. This procedure removes the entire inner layer of the uterus, making it nearly impossible to get pregnant later. Ablation is applicable for women over 35 years of age who already have and/or do not plan to have children in the future.
If the listed methods for removing a polyp do not lead to a complete cure, and relapses occur again, as well as when atypia of polyp cells is detected in menopausal women, doctors are forced to resort to the most radical method of treatment - removal of the uterus. In cases where the polyp has signs of malignancy, removal of the appendages is also justified. Such oncological alertness helps to avoid the development of cancer in patients at risk.
Women of reproductive age after removal of endometrial polyps need hormonal therapy aimed at normalizing the menstrual cycle. For glandular polyps, patients of reproductive age can be prescribed combined oral contraceptives according to the usual contraceptive regimen (Lindinet, Logest, Silest). Premenopausal women are better off using progestin drugs (duphaston, norkolut), since the estrogen component of contraceptives can increase the proliferation of endometrial cells. Hormone therapy is prescribed for a period of up to 6-9 months and under mandatory periodic ultrasound control.
If an adenomatous polyp or signs of atypia are detected in a patient of reproductive age, hormonal drugs are prescribed on a continuous basis, more often antigonadotropins (Zoladex, Danazol). These medications lead to complete inhibition of the hormonal function of the ovaries, as a result of which there is no growth and maturation of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle, and, therefore, the likelihood of a recurrent hyperplastic process is minimal. During the treatment, pregnancy will not occur, but after treatment, if the result is positive, the woman can plan to conceive.
A conservative approach, even in the case of dangerous polyps in terms of the risk of malignancy in young women, allows not only to preserve the uterus, but also to realize reproductive function.
Fibrous polyps during menopause, naturally, do not require hormone therapy, and surgery is sufficient to cure. In the case of atypical changes in this category of patients, the question of the need for complete removal of the uterus is always raised.
It is important to remember: the sooner a woman consults a doctor, the easier it will be to treat the existing pathology. Detection of a polyp of the uterine body in the early stages allows you to get rid of the formation in a short time, while maintaining reproductive function. Self-medication, expectant management, and the hope that the polyp will “come out on its own” lead to an increase in formation and an increase in the risk of malignant transformation. The polyp is quite firmly attached to the wall of the uterus, so only the hand of a surgeon can remove it efficiently and radically.
Treatment with folk remedies for endometrial polyps is permissible only in combination with traditional medicine and only in consultation with the attending physician. Medicinal plants that can be used include chamomile flowers, nettle leaves, oak bark, and rose hips, which have antiseptic and hemostatic properties. It is better to avoid douching and vaginal tampons with herbs, garlic, and alcohol tinctures recommended by many healers, since there is a risk of an allergic reaction and damage to the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, and the benefit in treating a polyp is questionable.
If unusual symptoms from the reproductive system appear, it is better not to self-medicate and not to rely on traditional medicine. The first step is to contact a specialist who will make an accurate diagnosis and choose the most optimal and effective treatment method, allowing a woman to maintain hormonal and reproductive function to the extent that she needs. Timely attendance at the antenatal clinic helps not only in the successful treatment of hyperplastic processes, it is also very important for the prevention of uterine cancer. After successful treatment of an endometrial polyp, clinical observation is necessary for a year with regular examinations and ultrasound examination of the uterus.
https://youtu.be/-5vPOywACA4
Preparing for polypectomy
Women undergoing polypectomy require careful preparation. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients can undergo all the necessary examinations and undergo the appropriate tests. Preparation for removal of a polyp in the uterus includes:
- Consultation with a gynecologist, therapist, anesthesiologist;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Vaginal smears for flora and cytology;
- Electrocardiogram and fluorography.
In the presence of an active inflammatory process, surgery is performed only after a course of appropriate therapy.
Make an appointment
What is not recommended to use?
When using non-surgical treatment for polyps in the uterus, you cannot combine official and traditional medicine without consulting a doctor. This can lead to poisoning and other unpleasant consequences.
Also during treatment it is prohibited:
- sit in a hot bath, visit a sauna;
- drink medications based on aspirin and other blood thinners.
IMPORTANT! Any treatment of polyps in the uterus is incompatible with alcohol consumption. This threatens bleeding!
It is also advisable to exclude all mucus-forming foods from the diet - white bread, confectionery, sugar, chocolate, cheese, preservatives.
Bloody discharge after surgery
Due to trauma to the uterine mucosa after surgery, spotting and spasmodic pain may be observed for several days from the place where the polyp in the uterus was removed.
Bloody discharge can be observed for several days, but heavy bleeding can only be a concern in the first hours after surgery.
How does a polyp affect menstruation?
Menstruation after removal of an endometrial polyp in the uterus is irregular and may differ significantly from normal menstruation. The restoration of the cycle usually occurs within a month and a half, but it can be regulated within three to four months. The consequences of removing a polyp in the uterus will depend on whether there was a violation of the surgical technique or other complications directly during the manipulation.
Possible complications
The consequences of an endometrial polyp in the uterus include:
- Anemia. This complication develops with prolonged, heavy bleeding.
- Infertility. Occurs with large polyps or anovulatory cycles.
- Malignancy of the polyp. Characteristic of adenomatous forms of the disease.
When asked by a patient whether it is possible to become pregnant if there is an endometrial polyp in the uterus, doctors answer differently. Some believe that pregnancy is quite possible with this disease. Other experts say that single or multiple (polyposis) endometrial tumors are the cause of infertility. Thus, there is no clear answer to the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with a polyp in the uterus.
If a woman still manages to become pregnant with endometrial hyperplasia, then her risk of miscarriage or various abnormalities of fetal development increases. Therefore, the polyp must be removed before pregnancy.
Conservative treatment
Treatment of polyps is carried out not only surgically, but also conservatively. Drug treatment can be suggested by a doctor in the absence of painful symptoms and large size of the formation. But this method does not exclude constant gynecological monitoring and regular additional diagnostic measures.
Treatment of uterine polyp without surgery also includes undergoing a number of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Electrophoresis with the use of medications;
- Electrical stimulation technique;
- Laser therapy.
Indications for one or another type of conservative complex therapy depend on many reasons, among which are:
- No complications;
- Mild symptomatic picture;
- Slight and slow growth of benign growth in the uterine cavity;
- The presence of contraindications for a woman to undergo surgical removal of a polyp.
Drug treatment
The main stage of treatment for polypous growths of the endometrium is the use of hormonal drugs (COCs and gestagens).
The formation of a pathological process in the uterine cavity in 70% of cases is associated with a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body, which leads to excessive production of estrogen. Hormonal contraceptives eliminate pain in the lower abdomen and quickly stop uterine bleeding. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the treatment of endometrial polyps if the formation of a benign process occurred against the background of the presence of a sexually transmitted disease, chronic inflammation (adnexitis, cervicitis, oophoritis). The combination of these two classes of medications gives the most effective and high-quality results.
Vaginal suppositories for polyps in the uterus are also one of the methods of drug therapy for this disease. Suppositories have a number of advantages over other types of therapy. The active substance exerts its therapeutic effect directly on the pathological focus, quickly penetrating through the mucous membrane of the vaginal wall, bypassing the liver and kidneys.
Treatment of uterine polyps also includes the use of a vitamin complex and drugs with a high iron content to prevent anemia.
Varieties
Based on the structural features and composition of cells, endometrial polyps are divided into several types:
- endometrial glandular polyp. It consists of stroma and glands and is most often observed in women of childbearing age;
- endometrial fibrous polyp. The composition of this formation is dominated by connective tissues and is extremely rare in older women;
- endometrial glandular fibrous polyp. Consists of a small amount of glands and connective tissue, occurs in women after 35 years of age;
- adenomatous endometrial polyp (precancerous). It consists of glandular epithelium, but at the same time has atypical cells.
Forecast
Uterine polyps are prone to recurrence. Therefore, after their removal, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist for a preventive visit twice a year.
In 1.5% of cases, recurrent growths of the uterus are susceptible to malignant degeneration. According to statistics, adenomatous polyps are most often associated with the development of endometrial cancer. Based on this, after the course of treatment, patients remain at the dispensary with a gynecologist for observation.
If uterine polyposis is left untreated, infertility and anemia develop. The presence of such a pathology in the anamnesis provokes miscarriages, which is of particular importance when planning pregnancy.
Prevention
There is currently no specific prevention of polyps in the uterus. To reduce the risk of developing gynecological diseases, it is recommended to take general measures to maintain health:
- Balanced diet;
- No bad habits;
- Moderate physical activity.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo not only treatment of gynecological diseases, but also preventive examinations. Doctors will perform the necessary examinations and give recommendations for long-term preservation of women's health. You can make an appointment with hospital specialists by phone.
Make an appointment
Author
Liana Nazimovna Aminova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, oncologist, candidate of medical sciences
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Cherenkov V. G. Clinical oncology. — 3rd ed. - M.: Medical book, 2010. - 434 p. — ISBN 978-5-91894-002-0.
- Shirokorad V.I., Makhson A.N., Yadykov O.A. The state of oncourological care in Moscow // Oncourology. - 2013. - No. 4. - P. 10-13.
- Volosyanko M.I. Traditional and natural methods of preventing and treating cancer, Aquarium, 1994
- John Niederhuber, James Armitage, James Doroshow, Michael Kastan, Joel Tepper Abeloff's Clinical Oncology - 5th Edition, eMEDICAL BOOKS, 2013