What is radiculitis and how to treat it is a common question in the neurologist’s office. Radiculitis is a consequence of osteochondrosis, much less often it is the result of various injuries, hernia, and spinal deformities. Lumbar sciatica is the most common, because it is this part of the spine, which is the center of gravity of the body, that bears a large number of loads.
It is believed that radiculitis affects older people, but in recent years it has been diagnosed in people of middle age. Symptoms of sacral radiculitis are most often seen in women after 30 years of age, and in men after 35 years of age. The causes of radiculitis are varied. The disease occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle, various types of stress, and sedentary work.
Causes
Radiculitis can be caused by developmental defects, degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system, or severe physical activity.
One of the common causes of the development of pathology is intervertebral hernia
The most common causes of the development of lumbosacral radiculitis include:
- intervertebral hernias . They cause displacement of the nucleus pulposus and rupture of the fibrous ring, which leads to compression of the spinal roots and the appearance of an inflammatory process, accompanied by symptoms of radiculitis;
- osteochondrosis . Degeneration of the intervertebral discs causes changes in the size of the openings through which the spinal roots pass. With a long course of the disease, bone growths (osteophytes) form on the vertebrae, compressing the roots, and the associated inflammatory process leads to the development of edema, which increases pain;
- spinal injuries . Bruises and fractures contribute to the appearance of deformation and scars, which in turn cause compression of the spinal roots;
- neoplasms in the spinal column . The cause of symptoms of radiculitis can be benign and malignant tumors originating from intervertebral discs, vertebrae, spinal cord and its membranes, neuromas, hemangiomas or metastases. As the tumors grow, they compress the spinal roots, causing pain;
- congenital malformations of the spinal column . According to statistics, they are observed in 50% of children. In 30% of cases, pathologies persist for life. The cause of lower back pain can be spondylolisthesis, as well as deformation or splitting of the vertebral body, when one side becomes higher than the other;
- infectious diseases . The cause of radiculitis can be abscesses in the spine or osteomyelitis;
- diseases of intervertebral joints . Radiculitis is often associated with diseases such as rheumatism, spondyloarthritis, spondyloarthrosis or ankylosing spondylitis;
- external reasons . Symptoms of radiculitis may occur after lifting something heavy, awkward movement, or staying in the same position for a long time or exposure to cold.
Surgical treatment
If the patient’s health does not improve within 3-4 months, the attending physician will suggest treating radiculitis with surgery. The operation is performed if:
- Manifested neurological signs;
- Degenerative changes in the discs;
- Obvious disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
There are several types of surgical intervention. In a minor open surgery, one intervertebral disc pressing on the sciatic nerve is removed. If spinal canal stenosis is detected, and the patient finds it difficult to tolerate the most simplified physical activities, then a laminectomy is prescribed. This surgery removes the bone where the nerve is pinched.
Patients avoid surgical involvement, hoping that sciatica will heal on its own. But at the moment when the patient loses control over urination or finds it difficult to move, forced surgery is performed.
Symptoms of lumbosacral radiculitis
Pain syndrome
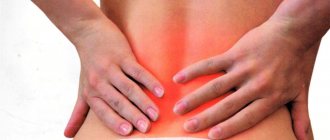
The main symptom of the disease is pain in the lumbar region. It can have a different character: be unexpressed or so sharp and burning that the patient cannot get out of bed and walk. Often with radiculitis of the lumbar region, the pain radiates to the thigh, lower leg or foot.
The main manifestation of radiculitis is pain in the lumbar region
Pain syndrome can occur suddenly, after lifting heavy objects or hypothermia. In response to irritation of the nerve endings, the location of which is the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc, a reflex muscle spasm occurs. An attack of pain can paralyze a person; he freezes in one position for several minutes (may even fall).
At the initial stage of the disease, the pain is unbearable, shooting, throbbing. The duration of the attack can be from several minutes to two hours. The lower back is stiff and the muscles are tense, and the patient cannot bend. The person is afraid to move, lest an awkward movement cause a new attack.
In some cases, with the chronic form of radiculitis, the pain is subacute. It is dull, aching, aggravated by any movement or cough. Pain may radiate to one or both legs. Quite often there is increased tone of the lumbar muscles.
Sensory impairment
Another sign of lumbosacral radiculitis may be impaired sensitivity. Compression of the nerve root leads to numbness in the area of its innervation.
Tactile, pain or temperature sensitivity of the skin may also disappear. Sometimes, when peripheral nerves are affected, a pins and needles, cold, or tingling sensation appears in this area.
Impaired muscle tone
With severe damage to the nerve roots, which is observed in the patient for a long time, muscle tone is disrupted. In severe cases, muscle atrophy may occur.
Impaired sensitivity and movement, unlike pain, occurs only on the side of the damaged nerve root. It is not two-sided.
Symptoms of radiculitis
The main symptom of radiculitis is acute pain, which intensifies with any movement. Patients complain of complete or partial loss of sensation in the area of the affected nerve.
Symptoms of radiculitis also include dizziness, hearing loss, muscle weakness, loss of balance when walking, which is caused by impaired blood supply to the brain.
The disease may be accompanied by dysfunction of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract (most often observed with sacral radiculitis).
Diagnostics
With radiculitis, the patient experiences certain symptoms that indicate the presence of the disease. They are conventionally divided into two groups:
| Group of symptoms | Description |
| Weakening of reflexes | As a result of compression of the nerves, the reflex response of the muscles to irritation becomes weak |
| Symptoms of tension | If a patient who is lying on his back is asked to raise his extended leg up, then he experiences pain in the lower back and back of the thigh, which indicates the presence of radiculitis. When he turns over on his stomach and the doctor tries to lift the limb, pain appears in the front of the thigh |
In order to identify spinal injuries, malformations, or displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, radiography is performed. The presence of intervertebral disc herniation can be determined using computed tomography.
Prognosis for radiculitis
A favorable prognosis is possible in case of timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, including all possible directions. Only with this approach can one expect recovery without fear of relapse. In the case of the development of ischemia and, as a consequence, spinal cord infarction, it is impossible to predict a complete recovery, since the consequence of such complications is often a violation of the motor and sensory functions of the body.
Prevention of radiculitis
Prevention of radiculitis includes measures aimed at maintaining correct posture and strengthening the back muscles. It is recommended to avoid excessive stress on the spine. Correct posture during sleep and wakefulness minimizes the stress experienced by the spinal column. You should not sleep on mattresses that are too hard. Contrary to popular belief, they are capable of distorting the position of the spine and disrupting its function. To avoid this and maintain the natural curve of the spine, it is recommended to pin small pillows under the neck and lower back or use a semi-rigid mattress that can support the natural position of the spine.
Maintaining correct posture is also very important in everyday work. When picking up objects from the floor, it is recommended to bend your knees without tilting your torso. Thus, the load will move from the back to the legs. It is recommended to avoid uncomfortable positions (long sitting at a table with your head down, sitting in front of the TV with your chin on your chest, etc.). In addition, gymnastics plays a big role in the prevention of radiculitis, helping to strengthen the back muscles, as well as sports and hardening, which increase the body’s resistance to physical stress and hypothermia.
Drug treatment of lumbosacral radiculitis
The patient needs bed rest until the attack of pain is relieved. The lower back should be warmed with a heating pad, a bag of salt or a woolen scarf. When the pain subsides a little and the person begins to get out of bed, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic exercises.
For drug treatment of lumbosacral radiculitis, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, ointments, suppositories, patches or injections are most often used.
Also in complex therapy of the disease, drugs from the group of muscle relaxants and B vitamins are used.
Diclofenac
Diclofenac sodium is the active ingredient of such drugs as Dikloberl, Olfen, Diclak, Almiral, Voltaren, Naklofen. The substance has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. It is most often prescribed for the treatment of radiculitis.
Diclofenac sodium is one of the commonly used drugs for the treatment of radiculitis.
In order to relieve inflammation, diclofenac is prescribed in the form of an injection solution. The drug is injected deep into the gluteal muscle. In case of severe pain, repeated use is allowed no earlier than after 12 hours. Injections are carried out over 3–5 days, and then medications are used in the form of tablets or suppositories.
One tablet or capsule of Diclofenac may contain from 25 to 150 mg of active substance. The drug is taken after meals, according to the instructions. It is not recommended to use the product for people with stomach ulcers, as this can lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
In order to reduce the load on the digestive system, you can use Diclofenac in the form of suppositories.
Ointments and gels based on diclofenac are used externally. They are used 2–4 times a day, depending on the dosage. Since the active substance enters the blood in small quantities, products for external use do not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Meloxicam
Meloxicam (Revmoxicam, Melbek, Movalis) belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drug has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects. It is used for short-term symptomatic treatment of the disease.
Meloxicam is used for short-term symptomatic treatment
Preparations with this active ingredient are produced in the form of injections, tablets and suppositories. In the acute form of the disease, in most cases, Meloxicam is prescribed by injection. The drug is administered intramuscularly once a day. The course of treatment is 3–5 days.
In the chronic form of the pathology, the drug is used in the form of tablets or suppositories for a course of 5 days.
What is acute radiculitis?
In the acute form of radiculitis, painful attacks begin suddenly, and the symptoms are usually pronounced. Inflammation of the roots can occur at different levels of the spine. The inflammatory process affects the inner part of the nerve sheath (extrasheath).
Causes of acute radiculitis
The most common cause of painful attacks of acute radiculitis is sudden, awkward movement or heavy lifting. Such an attack is also called the simple word “lumbago”. Such a lumbago appears when the spine is bent (tilted) with a turn to the side.
The causes of acute radiculitis are divided into two categories: congenital and acquired.
Congenital causes most often include abnormalities in the development of the spine, for example:
- neoplasms of various origins;
- proliferation of fibrous tissue;
- formation of adhesions.
Acquired causes are most often chronic. This group includes all degenerative changes that occur in the joints and vertebrae over a long period of time (spondylosis, osteochondrosis, etc.).
Most often, such changes lead to the appearance of osteophytes (the growth of the vertebrae and the appearance of a kind of spines on them), which compress the spinal roots. These processes lead to the formation of intervertebral hernias and hypertrophy of the yellow ligament.
In addition, acquired causes include infectious diseases of various kinds (tuberculosis, HIV, tick-borne borreliosis, epidural abscess, osteomyelitis), various malignant formations on the spine (tumors, cysts), endocrine and metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, etc.), spinal injuries , hypothermia (and sudden temperature changes) , high physical activity , etc.
The most common forms of acute radiculitis are the lumbosacral and cervical types. It is these parts of the spine that bear the majority of all loads.
Important! An acute attack of radiculitis is not always the first manifestation of the disease; it is quite possible that it is an exacerbation of an already developed pathology, so you should not delay examination and treatment.
Symptoms of acute radiculitis
An acute attack of radiculitis is accompanied by acute pain , which can have different localizations. Depending on the location of pain, we can talk about manifestations of a certain type of radiculitis.
Acute radiculitis of the lumbosacral type
With acute radiculitis of the lumbar spine, most patients experience characteristic pain in the lower back , which is defined as lumbago or, in other words, lumbago. In some cases, pain is felt not only in the back, but also spreads to the sciatic nerve. Pain may affect the ischial region, dorsum of the thigh, and lower leg.
The nature of the pain is sharp, cutting, tearing, shooting, paralyzing the spinal column in the lumbosacral region . At the same time, the patient strives to take a position in which the pain will be reduced as much as possible: most often the patient leans forward or to the side.
Changes also occur : where the tension is localized, the muscles are hypertonic and contracted to the maximum. When palpated, it seems that the muscle is swollen and enlarged. On the relaxed side, the muscles are stretched.
If the root cause of the acute form of radiculitis is deformation of the vertebral bodies and backward displacement of the intervertebral disc, then this can lead to kyphosis, in which it will be quite difficult and painful to straighten or bend over.
When the vertebrae are displaced to the side, scoliosis develops (or worsens). The body is deviated in the direction opposite to the deformity (heterologous scoliosis).
In the case of acute lumbar radiculitis, loss of sensation may rarely occur . If such a symptom occurs, it is only in the area of the outer part of the lower leg. The main symptoms are characterized by hypertonicity of the gluteal and spinal muscles and, accordingly, acute pain in these areas.
Acute radiculitis of the cervicothoracic type
This type of radiculitis is much less common , despite the fact that the mechanism of manifestation is the same as that of the lumbosacral form. Pain syndrome occurs in the neck and can spread to areas where the most affected nerve endings are located. Pain may be accompanied by numbness in the same affected areas.
The pain syndrome spreads to the thoracic and occipital regions, causing symptoms similar to those of a heart attack . In this case, the patient cannot tilt his head back normally.
If the disc is displaced to the side, then a forced tilt of the head occurs and the formation of a kind of torticollis. In some cases, there is paresis of the fingers on the affected side (the last two fingers are pressed to the palm and bent).
Exacerbation of cervicothoracic radiculitis is a rather long process. It is periodic in nature, and, in contrast to the lumbosacral form, is more extended.
First aid for acute and chronic radiculitis
If you are suddenly struck by an attack of acute radiculitis (or a pain attack of a chronic nature), and there is no opportunity to see a doctor immediately, there are several first aid techniques that can somewhat reduce the pain and hold out until you visit a doctor:
- Secure the affected area with a bandage or thick cloth;
- Ask them to gently support you and place you on your back on a hard surface. At the same time, bend your knees and place a pillow or cushion under them;
- If possible, administer a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug intramuscularly. If this is not possible, then take the tablet form of NSAIDs (Movalis, Voltaren, Indomethacin);
- Add muscle relaxants to treatment (for example, Mydocalm or Baclofen);
- You can use special patches based on NSAIDs. Such patches act slowly, so it is recommended to use them in cases of mild symptoms;
- Take a mild herbal sedative (for example, tincture of valerian or motherwort);
- Apply a warming ointment or gel (Fastum-gel, Ketanol, Finalgon, etc.) to the inflamed area.
Important! These tips are intended for those cases when it is not possible to immediately contact your family doctor or call an ambulance. First aid can help temporarily reduce pain, but it cannot eliminate the root cause of the attack. Therefore, you should definitely contact a specialist who will conduct an examination and prescribe you a comprehensive treatment that can overcome the original cause of the symptoms of radiculitis.
Treatment of acute radiculitis
Did you know that...
Next fact
Both acute and chronic forms of radiculitis are primarily consequences of another disease . Therefore, there is no treatment aimed at eliminating sciatica; the root cause must be treated. Therefore, the first step should be to establish this reason. To do this, you need to see a doctor and undergo an examination.
When the examination shows what exactly is causing acute pain in the back, neck or chest, treatment can begin. Your doctor will prescribe a treatment regimen based on the reasons that cause radiculitis. It will be very difficult to give any specific methods, since there are countless reasons for the appearance of radiculitis.
Standard therapy includes bed rest (in case of exacerbation) or a gentle daily routine, treatment with medications (painkillers, vitamins, muscle relaxants, NSAIDs), massage and physical therapy (a mandatory item in any therapy aimed at treating spinal diseases).
Sometimes acupuncture, vacuum therapy, magnetic puncture, and laser therapy are added to these techniques. But these are purely individual methods; they are not suitable for everyone.
All these methods are aimed at eliminating pain and normalizing blood circulation, as well as inhibiting pathological processes occurring in the spinal column.
Video: “Symptoms and causes of radiculitis”
Find out how heat affects the condition of the back with radiculitis:
- Is it possible to go to the bathhouse with radiculitis and how does heat affect the body during the syndrome?
- You can find out which warming belt for radiculitis is better in the following article
- Description of injectable drugs for radiculitis on the page
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic gymnastics is a universal remedy that allows you to cope with lumbosacral radiculitis at home. In order to achieve a positive result, exercises must be performed regularly.
To achieve the best results, therapeutic exercises must be performed regularly.
A set of exercises for lumbar radiculitis:
- Exercise No. 1: starting position - standing, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the belt. Slowly bend to the right and hold for 4 seconds, then return to the starting position. Repeat the movement in the other direction. The maximum number of bends is 12. If a person does not experience discomfort when bending, the pace can be accelerated;
- exercise No. 2: in the same position, bend forward and backward. At maximum tilt, hold for 2-3 seconds. The exercise should be performed very slowly, without jerking. Repeat it no more than 8 times. If severe discomfort occurs, the exercise should be abandoned;
- Exercise No. 3: standing in the starting position, turn left and right, holding for 3-4 seconds. The exercise is performed 8–10 times;
- exercise No. 4 : perform rotational movements of the body, first from left to right, then from right to left. The maximum number of such exercises is 10 times. Rotations should be smooth, without jerking;
- exercise No. 5: do half squats from the starting position. You can use the back of a chair as a support. The exercise should be repeated 8 times. When half-squatting, you need to inhale, when returning to the starting position, exhale;
- Exercise No. 6: starting position - lying on your back, placing a small cushion under your neck. Bend the leg at the knee, clasp it with your arms and carefully pull the thigh to the chest. The exercise is performed smoothly, repeated 4 times with one leg, then the other.
Diagnosis of radiculitis
X-ray examination of the spine in various forms of radiculitis usually reveals osteochondrosis, which is quite common. Therefore, the examination must be comprehensive. In order to exclude destructive processes in the spine, a spondylogram is indicated. However, it is not able to verify the discogenic etiology of the disease. For lumbosacral radiculitis, a lumbar puncture is performed, which reveals a slight increase in protein content.
To recognize the etiology of radiculitis, a thorough study of the anamnesis, clinical picture, as well as a large amount of paraclinical data (clinical blood test, myelography, spondylogram, cerebrospinal fluid examination, MRI and CT of the spine, etc.) is necessary. It should be noted that with discogenic radiculitis, as a rule, , only one or two roots are affected. And in cases of thoracic radiculitis, vertebrogenic osteochondrosis should be excluded; here the cause of compression of the roots lies in other diseases. In addition, radiculitis must be differentiated from acute myositis of the back muscles.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods will help reduce pain in the lumbar region with radiculitis:
- recipe No. 1: black radish is grated, the finished pulp is wrapped in gauze and applied to the affected area. Cover the top with film and tie it with a warm scarf. The compress can be left overnight. Apply the remedy daily until symptoms resolve;
- recipe No. 2: 3 pods of red hot pepper must be crushed and poured with 100 mg of 96% alcohol, add 20 ml of ammonia and leave the product overnight. The lower back is rubbed with tincture twice a day;
- recipe No. 3: 1 kg of pine shoots should be poured with 5 liters of water and boiled over low heat for a quarter of an hour. The product is infused under the lid for at least three hours. Add a glass of sea salt and a liter of broth to a bath of warm water. Take it within 10–15 minutes. Then the lower back is tied with a woolen scarf;
- recipe No. 4: boil 3 large potatoes with their skins and mash into a paste, add one teaspoon of soda. The resulting pulp is applied to the lower back. Cover the top with compress paper and tie it with a scarf. This compress is left overnight;
- recipe No. 5: cabbage leaves are cut from the middle of the head of cabbage with a knife and pine or rosemary essential oil is applied to the surface. Apply to the lower back, cover with polyethylene and a towel.
Causes of radiculitis
Before you figure out how to cure sciatica in the lower back, it is worth establishing the causes of the disease. If previously it was believed that radiculitis occurs on its own , leading to inflammation and damage to the radicular nerves, now doctors agree that radiculitis is a radicular syndrome , and treatment should begin with determining the root cause. More often it occurs against the background of other pathologies, degenerative changes in the spinal column.
The main causes of the disease:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Hypothermia.
- Spinal damage.
- Serious infections.
- Hernias.
- Deformation of intervertebral discs.
- Salt deposits.
- Deformation of the spinal column.
- Spinal stenosis.
- Tumors.
- Metabolism problems.
- Great physical activity.
- Stress.
- Age after 45 years.
Athletes or manual workers also often suffer from radiculitis in the lumbosacral region.
Prevention of radiculitis
In order to prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary:
- do gymnastics and strengthen your back muscles. Physical exercises begin with minimal loads, then increase them;
- go swimming. For people with spinal diseases, this is one of the best sports;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- visit the bathhouse and sauna;
- sleep on a hard, flat surface.
In most cases, lumbosacral radiculitis is treated at home. The indication for hospitalization is severe pain syndrome, when the pain is not relieved with the help of medications and folk remedies.
If symptoms of radiculitis are detected, you should consult a neurologist or traumatologist.
Classification of radiculitis
Depending on the topography of the inflammatory process, radiculitis is divided into a number of forms:
- lumbosacral,
- chest,
- cervical,
which in turn can have a chronic or acute form. In addition, there are primary radiculitis (toxic, infectious origin) and secondary, caused by abnormalities of the spine and spinal cord. With meningoradiculitis, the inflammatory process develops simultaneously in the roots of the spinal nerve. and membranes of the spinal cord.
Reasons for development
Lumbosacral radiculitis can occur for a variety of reasons. Predisposing factors are increased load on the lumbar region (heavy lifting), hypothermia, consequences of injuries, curvature of the spine (scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis), advanced herniated intervertebral discs, and the formation of osteophytes (bone growths) on the vertebrae. But still, radiculitis pain most often appears against the background of osteochondrosis, a degenerative disease in which the elasticity of the intervertebral discs is lost and the distance between the vertebrae is reduced. As a result, when the body turns unsuccessfully, the nerve roots are compressed, pain occurs and lumbosacral radiculitis develops.
The pain syndrome associated with sacral radiculitis is so strong and acute that a person almost completely loses motor abilities. At the slightest attempt to lean forward, tears appear in the eyes. It’s not for nothing that many people call radiculitis pain “lumbago.” When you sneeze or cough, the intensity of the pain only increases. In the first minutes of an attack, a person, even in a supine position, cannot find a suitable position for a long time that could reduce severe pain. Subsequently, taking a forced position, the patient lies with his leg bent on the affected side. If a person is placed on his back and his leg is raised on the affected side, the diseased nerve is stretched. This action again causes sharp pain in the lumbar and gluteal regions (Lasegue symptom). With lumbosacral radiculitis, a person cannot sit down or stand up for a long time. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by low-grade fever and increased sensitivity to cold. At the slightest physical or nervous stress, the pain attack appears again.
Read also: Abscess of the elbow joint
The treatment process for lumbosacral radiculitis should be comprehensive: combine drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage (with the exception of manual therapy, which can only be used upon the patient’s final recovery). In the acute stage of the disease, first of all, it is necessary to relieve pain. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, mainly in the form of injections - Ibuprofen, Ketonal, Diclofenac, Indomethacin. In case of particularly severe pain, injections of the drug Ketanov help well. Novocaine blockades and medicinal electrophoresis with dicaine and phenol are also carried out. For muscle relaxation, muscle relaxants are additionally prescribed - Baclofen, Sirdalud, Mydocalm. Of course, treatment of sacral radiculitis is not complete without the use of external ointments, which can be analgesic (Voltaren, Nurofen), warming (Amizartron, Viprosal) and locally irritating (Capsicam, Finalgon). Drug treatment is combined with vitamin therapy: a course of vitamin B12 injections is given.
The complex of rehabilitation measures for lumbosacral radiculitis also includes physiotherapeutic procedures (galvanic currents, ultrasound), massage of the lumbar region, physical therapy, mud applications, hydrogen sulfide baths. In order to increase the distance between the vertebrae and release pinched nerve endings, the spinal traction technique is used. During the period of remission, it is very useful to purchase a ticket to a sanatorium-resort treatment, where the patient will be provided with a full course of necessary procedures.
In order not to encounter sacral radiculitis in life, the symptoms and treatment of this disease, it is necessary to protect the spine in every possible way: avoid lifting heavy objects, hypothermia, stress, monitor your posture, and train the lumbar muscle corset. Be healthy!
general characteristics
Radiculitis of the lumbosacral region most often causes back pain. According to statistics, it occurs in 10% of adults. Usually this disease is secondary and develops in the presence of other pathologies of the spine. Therefore, some experts consider radiculitis to be a symptom complex, a consequence of degenerative diseases, most often osteochondrosis. But pain can be caused by changes in the joints, discs or musculo-ligamentous apparatus. Sometimes inflammation of the nerve roots develops on its own, for example, due to infection, alcohol intoxication or severe hypothermia.
Radiculopathy of the lumbosacral spine, better known as radiculitis, is common mainly in people 35-50 years old. Moreover, the pathology occurs more often in men. This is due to the fact that it appears due to increased stress on the lower back or hypothermia. People who spend long periods of time sitting in a sitting position, doing work on their feet, or having to lift heavy objects are susceptible to radiculitis. Representatives of certain professions have a particularly high risk of developing sciatica. These are loaders, builders, drivers, agricultural workers, as well as athletes.
Usually, after the first attack of radiculitis, which occurs after an injury, when performing a sudden movement or lifting a heavy object, the disease is not cured at all, but becomes chronic. If the patient behaves correctly, relapses can be rare - once every 2-3 years. But most often the pathology worsens several times a year.
Depending on the type of affected nerves, the cause of their compression, as well as the symptoms manifested, several types of lumbosacral radiculopathy are distinguished:
- lumbago is characterized by acute shooting pain in the lower back, which makes a person freeze in a bent position;
- lumbodynia is a painful condition that lasts several months;
- sciatica is a type of radiculitis associated with damage to the sciatic nerve, and pain occurs not in the back, but in the buttock, thigh, and lower leg;
- lumbar sciatica is a pathology that combines manifestations of lumbago and sciatica;
- When intervertebral discs are herniated, leading to compression of the nerve roots, a condition called discogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy develops.
A lumbago in the lower back can occur when bending sharply forward
Preventive actions
It is recommended to swim more
The instructions look like this:
- Perform physical therapy exercises. Therapeutic gymnastics strengthens muscles, which leads to the creation of a natural muscle corset. The load on the spine is removed.
- Pay attention to water procedures. It is recommended to swim in natural reservoirs and do water aerobics. It is important to avoid hypothermia. You should refrain from sudden movements.
- Fight excess weight. You need to give up fatty and sweet foods.
- When starting heavy physical labor, wear a corset. You cannot stay in an inclined position for a long time.
- Watch your posture. Exercise regularly.
Types of radiculitis
The lumbar (lumbar) spine is the most common location for sciatica. But besides him, there are others:
- Cervical (or cervical). Process at the level of the first 4 cervical segments of the spinal cord.
- Cervico-brachial. When the 4th to 6th cervical segments of the spinal cord are affected.
- Cervicothoracic. The process affects segments from 6 cervical to 1 thoracic.
- Thoracic (thoracic) – at the level of the thoracic segments.
The exact location of the disease can be determined based on clinical manifestations and examination by a doctor.
First aid for an attack of lumbar radiculitis
It is important to call a doctor if symptoms of acute radiculitis develop. Do not make sudden movements on your own, so as not to increase the feeling of pain, call someone close to help
The correct thing to do during an attack is:
Secure your lower back using a bandage belt, fabric, sheet or any other means currently at hand. Place the patient on a hard surface (for example, a hard bed). At the same time, be extremely careful. It is necessary to support the patient, allow him to lean on you with his hand. Lay correctly on the bed on your back, place a pillow or bolster under your lower limbs
During an attack, it is important to maintain bed rest. It is necessary to relieve the pain attack. If you have the skill to administer intramuscular injections, it is necessary to administer drugs from the NSAID group (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Examples of drugs: ibuprofen (Nurofen), diclofenac (Voltaren), nimesulide (Nise, Nimesil, Nimulid), meloxicam (Movalis), indomethacin. If you do not have the skill to administer injections, you need to give the drugs in tablet form, in accordance with the instructions for use. It is possible to use a patch with an anti-inflammatory component in the composition, for example, a Voltaren patch containing diclofenac, or Nanoplast (containing magnetic powder). It provides gradual administration of the drug throughout the day. This method of pain relief is suitable for people with mild symptoms of the disease. Be sure to reassure the patient. If necessary, you can use valerian or motherwort preparations, in tinctures or tablets. Apply anti-inflammatory ointments or gels to the area where pain is felt: containing diclofenac (Voltaren Emulgel 1 and 2%), ibuprofen (Nurofen gel, Dolgit), ketoprofen derivatives (Fastumgel, Bystrumgel, Ketonal), nimesulide (Nise gel). It is recommended to use ointments with a warming effect, since pain relief occurs due to improved blood circulation, relieving swelling and the irritating effect of the components. For example, you can use: Finalgon, Capsicam. Also gels with a combined effect: Dolobene or Fitobene and others. Preparations of B vitamins (Neuromultivit, Milgamma compositum, Neurodiclovit: B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12) in combination with diclofenac).
Nutrition
To prevent the load on the spine from being too high, it is necessary to get rid of extra pounds and prevent their appearance. To do this, you need to follow a special diet; in addition, proper nutrition supports the normal functioning of the entire body, strengthens the immune defense and enriches it with nutrients.
The essence of the diet:
- reduce the amount of salt in the diet;
- eat vegetables and fruits;
- include dairy products in the daily menu;
- reduce the consumption of canned food and sausages and be sure to prepare dishes with lean meat;
- limit the consumption of sauces, fatty and fried foods;
- give up alcohol and coffee;
- Compote, apple nectar, lemon and honey are useful for radiculitis.
To ease the pain
In this world there are ardent fans and no less ardent opponents of painkillers. Just in case, let us remind you: extremes do not lead to good. Uncontrolled use of painkillers can give a person a huge range of complications. But at the same time, it has been scientifically proven that a person who is in an optimistic mood recovers better and copes with the disease faster. And it is almost impossible to radiate optimism while suffering from pain. Therefore, in reasonable doses and strictly as prescribed by the doctor, painkillers are very, very useful.
For radiculitis, as a rule, analgesic drugs are prescribed in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. Moreover, at the beginning of the disease, when the pain is especially severe, the drug will have to be used in the form of injections, and then you can switch to tablets. In addition, the therapy is supplemented with muscle relaxants - drugs that make the muscles relax. They help break the vicious circle: pain causes muscle spasm, and spasm causes pain. Novocaine blockades provide a good anti-pain effect.
Disease prevention
To avoid getting lumbar radiculitis either in adulthood or throughout your life, you should take some precautions and follow the following recommendations. Life should be active, filled with movement. You should eat right. If a person has chronic diseases of the spine, he must always wear a special corset. It is recommended to promptly treat any viral diseases. It is necessary to harden the body and regularly undergo preventive treatment in a sanatorium. It is important to follow a daily routine; you need to sleep on a hard mattress.
By following these simple preventive measures, you will protect yourself from the manifestations of radiculitis and other diseases. Be healthy!
Which doctor treats lumbar radiculitis?
Treatment of radiculitis is carried out by a neurologist or neurologist. If there are no such specialists in your local clinic, you should contact a therapist.
Since an attack of radiculitis often completely immobilizes a person, before going to a medical facility or the arrival of a doctor, he needs the support of those who are nearby.
First aid for lumbar radiculitis includes:
- immobilization of the spine with a corset, bandage or tight sling;
- placing the victim in a horizontal position with slightly elevated limbs;
- pain relief with Ortofen and Diclofenac tablets.
The back of a person in a horizontal position should not bend. For this, a patient with an acute attack of radiculitis is placed on a board, plywood or simply on the floor.
First aid
With radiculitis, awkward, sudden movement, hypothermia leads to pain. It is so strong that a person is afraid to take a deep breath so as not to provoke its intensification. He needs help getting to bed. If the floor is warm, then it is better to lie down on it, as the pain subsides faster when lying on a hard surface.
The legs must be bent at the knees, placing a cushion or rolled blanket under them. If cervical radiculitis worsens, you should place a thin pillow under your head. In some cases, the pain goes away by lying on your side with your legs bent.
Taking 1-2 tablets of any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) - Diclofenac, Nurofen, Nise or applying Voltaren, Fastum, Ketorol gels will help improve your well-being. To relieve pain, you need to wrap your neck or lower back in a woolen cloth, but cold should not be used to provide first aid.
Clinical manifestations of an acute attack of radiculitis
The main symptoms are typical for the disease; when they appear, it is necessary to provide first aid and then immediately consult a doctor. An attack can be triggered by hypothermia, overheating, injury, a sharp turn of the body or a sharp tilt of the body followed by heavy lifting. An acute attack of radiculitis is characterized by:
- A person experiences severe pain, it is burning, sharp, “shooting” in nature, and radiates along the nerve. The patient can neither sit nor lie down. Takes a forced position in order to relieve pain. The pain does not go away on its own.
- Weakness of the back muscles, decreased tone, feeling of heaviness and discomfort.
- Feeling of numbness, crawling, tingling, loss of sensitivity to pain, temperature.
The above symptoms can be found in all types of radiculitis. The lumbar type is distinguished by the localization of pain in the lumbar region and irradiation (radiates to the buttocks, thighs, and groin area). Most often, the patient has to take a forced position, for example, half-bent to the side. Sometimes, due to severe pain, the patient cannot straighten up without assistance and experiences pain when coughing or sneezing.
Increased temperature with radiculitis
For inflammatory disease of the spinal cord roots, along with the occurrence of pain, the appearance of elevated temperature is typical, but not more than 37–37.2 degrees. If the temperature rises above the permissible values, you should urgently go to a specialist, as this may indicate an infection.
Also, under the mask of radiculitis, serious renal pathologies (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis) can be hidden, which also manifest themselves as severe pain in the lumbar region and fever. In addition, it is possible to suspect other diseases localized in the spine, which are characterized by a rise in temperature (rheumatic diseases, spinal tuberculosis, tumors, osteomyelitis).
Symptoms
Based on data provided by the National Center for Population Health Statistics in the United States, the most common cause of loss of work activity in a person under the age of 45 is back pain.
Every third person of this age has symptoms of radiculitis caused by chronic causes.
The severity of the pain syndrome depends on the level of damage to the nerve roots and their location.
Symptoms of radiculitis have signs of the pathology that causes it. In the vast majority of cases, the cause is osteochondrosis.
The main symptoms of radiculitis are as follows:
- Painful symptoms in the area where the damage is located: piercing or dull pain, burning sensation in the tissues at the site of inflammation;
- Stiffness in movements. Intuitive bending of the knees during sleep or when trying to sit down or stand up. There may be numbness of the limbs, spontaneous elementary muscle movements - muscle tics;
- With cervical radiculitis, the following may be observed: dizziness, decreased visual acuity and hearing;
- Sacral radiculitis - pain in the lower back often radiates to strong shooting pains in the legs or the so-called symptoms of lumbago.
You may also experience redness of the skin, sweating, tingling and a feeling of “floaters” under the skin.
The pain can appear suddenly or subside. In the acute phase, symptoms can last from several days to several weeks.
What are the first symptoms?
Oh, you will never forget this moment and will never confuse it with anything. As a rule, after physical activity or sitting under air conditioning or just in a draft (in the heat it’s so refreshing, it’s a thrill!) you suddenly feel a sharp sharp pain in one of the above places, as if a nail was driven into your back.
However, sometimes the pain may be mild at first and increase over the course of several hours. As a result, you get a significant disadvantage to the ability to move in general or move individual parts of the body, for example, the head (depending on the location of the inflammation). Radiculitis can also be caused by osteochondrosis and trauma. How was it for me? Yes, in different ways.
The first time I just decided to take off my jacket in November to get some air. Then the cervicothoracic wound started. Another time, after lifting something heavy, I bent down to tie my shoelaces. And when I straightened up, I realized that it was no longer possible for me to bend down. And after three or four hours I was just lying on the bed and all I could do was turn my head and move my arms. Any attempts to move the torso or legs led to wild pain along the entire spine.
Treatment with and without tablets
Treatment of radiculitis in the acute period requires bed rest, the duration of which is determined by the doctor. It is important to use a bed that has an optimal ratio of hardness and softness at the same time. Special orthopedic mattresses sold in medical equipment stores have these properties.
Such a mattress allows you to correctly distribute a person’s weight during sleep and maintains the spine in an anatomically normal position throughout the night. In addition, during the acute period it is important to ensure immobility of the affected part of the spine. For this purpose, your doctor may prescribe wearing a rigid fixing lumbar corset, which can also be purchased at medical equipment stores. In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures (ultraviolet irradiation, Bernard currents, UHF, electrophoresis with proserine, laser therapy) are prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. Acupuncture sessions can relieve pain and at the same time help the spine recover.
Forms
The intensity and nature of pain depends on the form of radiculitis.
Acute
Acute radiculitis develops very quickly. The cause of a pinched nerve ending can be awkward movement, sudden lifting of weights, or hypothermia. All these are so-called correctable conditions of the spine, after the elimination of which the patient’s well-being quickly returns to normal.
Rest and conservative treatment will help get rid of an attack of acute radiculitis. Recovery usually occurs within 2–3 weeks.
Chronic
Chronic radiculitis develops with complete disregard for the acute form, when the patient does not comply with prescribed recommendations or completely refuses therapy, dulling the pain with anesthetics.
The cause of the pathology is permanent disorders in the spine that do not disappear over time - osteoporosis, scoliosis, intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis.
The chronic form usually occurs in waves, with remissions and frequent relapses (3-4 times a year). Exacerbation of radiculitis can be caused by minor physical activity, mild hypothermia, long walking or standing, and a respiratory infection.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture sessions are carried out to eliminate both acute and mild pain due to radiculitis. Thin, short needles made of steel, silver, and gold are installed on biological active points of the human body. These reflexogenic zones are located not only along the spinal column, but also on the arms, legs, and earlobes. After the needles are inserted, with only mild discomfort, impulses are sent to the central nervous system. In response to them, substances with analgesic, anti-inflammatory properties, as well as endorphins are produced.
Symptomatic picture
The main symptom of radiculitis, by definition, is pain in the affected area. It manifests itself as periodic strong shooting pains, which many people compare to electric shocks.
Over time:
- the pain dulls, a feeling of numbness, goosebumps, tingling appears;
- then, over the area of the affected spinal nerve, skin sensitivity becomes dull or completely disappears - pain, temperature, tactile;
- As the inflammatory process further spreads along the nerve, muscle fiber weakness occurs and reflexes disappear.
2-3 weeks after the debut or relapse of radicular syndrome, atrophy of paretic muscles is possible. With the infectious nature of radiculopathy, both local and general body temperature may rise.
In addition to pain and local disorders, other manifestations of radiculopathy depend on the location of the lesion
Typical symptoms and signs of radiculitis:
- In the case of pathological processes in the cervical spine , most often they occur in 5-8 spinal nerves, the pain syndrome spreads to the back of the head, the upper region of the chest, scapula, and shoulder. A person cannot turn his head to the painful side and tilt it back. Torticollis, as well as numbness and sluggishness of fine motor skills of the hand, are possible. How to recognize which roots are inflamed? Testing your reflexes will help. Problems with the 5th and 6th nerves reduce the biceps reflex, and problems with the 7th and 8th reduce the triceps reflex. Inflammation of the 8th cervical nerve is also characterized by dry and marbled skin and a cold hand.
One of the signs of cervicothoracic radiculopathy (C8) is Bernard-Horner syndrome
- Radiculopathy of the thoracic roots and spinal nerves is rare, and is usually a consequence of herpes zoster, and osteochondrosis ranks only second in the list of causes. Pain from the spine radiates to the area between the ribs. Patients often bend their back in the painful direction, lifting one shoulder up, and try to constantly remain in this position. Thoracolumbar radiculopathy is characterized by the Neri stretch symptom - involuntary supination of the hand and forearm, which occurs when the arm is passively flexed on the affected side.
- With lumbosacral radiculitis, patients involuntarily take antalgic positions, which help reduce pain. The gait changes. Pain appears or intensifies when sneezing and coughing, as well as when sharply bringing the sore leg to the side. How to check for lumbosacral radicular syndrome? There are more than 12 reflex tests for this. Here are the 2 most popular:
- bowing symptom - a person cannot bend forward due to acute pain in the buttock and back of the thigh;
- Langers' symptom - a person lying on his back, legs should be straight, cannot touch his chin to his chest due to a lumbago that occurs in the lower back.
With a long course of lumbosacral radiculitis with frequent episodes of relapses, the skin on the affected leg becomes like marble, the hair on it falls out or begins to grow more actively, it becomes cold or, on the contrary, sweats in isolation, the nails become covered with lines.
Attention. Quite often, renal colic is disguised as lumbar or lumbosacral radicular syndrome. However, the latter have a distinctive feature - the presence of pain in the groin and/external genitalia.
The standard instrumental examination to clarify the diagnosis of Radiculopathy is radiography in 2 projections - anterior and lateral.
However, today doctors prefer to receive information after MRI. The price of such an examination is several times more expensive, but it is a hundred times more informative.
Risk group
The most susceptible to radiculitis are people whose profession involves increased stress on the spine, in particular loaders, miners, dentists, and professional athletes. In addition, truck drivers and mental workers who spend whole days at the computer are at risk.
But if employees of mental work often go to yoga or qigong, support their body with useful physical activity, go to resorts where they can swim and restore their spine, then truck drivers and people who work hard in mines can suffer from severe osteochondrosis for years , endure pain, drink painkillers and destroy your spine. Such work, coupled with a neglectful attitude towards the spine, plus heavy lifting, stress, hypothermia, infections, metabolic disorders - this is a direct road to sciatica.
Diagnostic methods ↑
After examination, studying the manifestations of diseases and checking the reflex activity of the patient, the doctor may prescribe:
- X-ray examination , which allows us to assess the degree of degenerative changes in bone structures;
- magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography to identify compression of nerve roots, assess the condition of the ligamentous apparatus and intervertebral discs;
- electromagnetography , which allows you to determine the degree of damage to the nerve fibers themselves.
If the doctor decides to prescribe a course of manual therapy to the patient, then before treatment it is recommended:
- do a general blood and urine test
- undergo densitometry (test for osteoporosis).
If necessary, the patient may also be prescribed an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and electrocardiography of the heart.
Treatment method
In order for radiculitis to recede as quickly as possible, it is necessary to take a comprehensive approach to the treatment of this pathology. It is very important to contact a qualified doctor as soon as possible, who will select the most effective treatment regimen. Typically, treatment for radiculitis consists of the following measures:
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce pain;
- Complete bed rest - exclusion of physical activity for several days significantly speeds up the recovery process;
- Therapy with muscle relaxants - medications that relieve spasms. For radiculitis, they restore pinched nerve endings;
- Traction is a procedure for stretching the spine, thanks to which it is possible to increase the clearance between the discs;
- Psychological correction - consists of taking antidepressants and sedatives, thanks to which it is possible to improve the functioning of the nervous system;
- Therapeutic exercise – allows you to improve blood circulation throughout the body, which has a positive effect on the spine;
- Manual therapy and physiotherapy are procedures that strengthen the body and increase its vital energy.
To get rid of radiculitis in a short time, you need to consult your doctor as soon as possible. A specialist will be able to select the most suitable and effective medications for you, thanks to which you will get rid of pain in just a few days.
You should not waste time on self-medication, this can lead to serious complications.
Treatment with traditional recipes
Alternative treatment methods will help you cope with the initial stages of radiculitis. They have been tested for centuries, their effectiveness is confirmed by numerous reviews. Keep in mind that before starting such therapy, it is best to consult with your doctor - he needs to assess the condition of the spinal column and determine whether individual components of the chosen medication will affect your body.
The most popular recipes are:
- Elderberry decoction is one of the most effective remedies against radiculitis. To prepare it, you will need to pour 2-3 tablespoons of dry berries with 2 cups of boiling water, after which they continue to be kept on low heat for 10 minutes. After this time, the broth is infused for about an hour, filtered and poured into a glass container. The medicine is taken 100 ml before each meal.
- When the first signs of radiculitis appear, you need to start making special compresses. With their help, it is possible to warm up the back, due to which the pinched nerve endings begin to expand. Keep in mind that this is a radical method of influence; before starting treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor. To warm up, you can use special corsets and belts.
- Rubbing your back with black pepper tincture will help you get rid of back discomfort. To prepare it, you need to take 100 ml of vodka, to which add 10 grams of allspice black pepper. Leave the tincture for one week in a dark place, then use the prepared solution to rub your back.
Therapeutic exercises for radiculitis
To prevent frequent relapses of radiculitis, it is necessary to engage in physical activity. Special physical exercises help normalize blood circulation in the body, so that nerve fibers function normally. The most important physical exercises are:
- Place your feet together, clasp your hands in front of your body. Lift them up, bend - return to the starting position;
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart and place your hands on your waist. Bend in different directions until painful sensations appear;
- Lie on your back, place your arms along your body. Raise your left arm and leg up, then change to the right side;
- Kneel in cat pose, arch your back, alternately lift your left and right legs;
- Stand on your feet, place your arms along your body. Smoothly transfer your body weight from toe to heel, repeat this exercise as often as possible;
- Sit on the edge of a chair, place your arms behind your back, and keep your legs at right angles. Do the scissors exercise.
Massage
Therapeutic massage is prescribed after the end of the acute period of illness and is selected for each patient individually, sometimes through a combination of its different types - tonic, acupressure, vacuum, relaxing, etc.
The massage complex is intended to relieve specific pathologies of the patient, improve blood circulation and restore weakened muscle corset around the spine.
Some forms of massage lead to complete muscle relaxation and the release of endorphins into the blood - natural painkillers produced by the body.
How to treat the disease?
How to treat lumbosacral radiculitis? Therapy is selected individually for each patient, based on the clinical picture and symptoms, stage and cause of the inflammatory process.
Treatment of the disease is complex, which includes taking medications, undergoing physiotherapy, visiting a massage and physical therapy room.
What is sacral radiculitis, symptoms and treatment of this disease - these are the questions patients ask their doctor. Typically, a conservative treatment method involves maintaining bed rest if the disease begins to worsen, wearing a corset, taking pills and various external medications, and using muscle relaxants.
Injections are prescribed and spinal traction is performed. Physiotherapeutic procedures help get rid of pain and take preventive measures for chronic radiculitis. You can strengthen the muscles of the spine with the help of physical therapy. You can either exercise in a special institution or do the exercises at home.
Other treatments for sciatica
In addition to drug treatment and taking medications for inflammation in the lumbar region and radiculitis, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, water therapy) can be prescribed . During treatment, patients are also recommended bed rest to maintain heat and magnetic therapy to restore blood circulation.
Sometimes traction is prescribed, in which a person lies on a flat surface for about 15 minutes. This is done to restore the nerve roots and relieve pain.
If an infection is present, antibiotics are prescribed in addition to treatment. And if the effect of treatment of radiculitis is absent for more than two months, then surgery is prescribed.
Video about how to relieve pain from radiculitis:
Gymnastic exercises for radiculitis
Gymnastic exercises and the course are chosen only under the supervision of a doctor, depending on the problem.
If you follow all treatment recommendations, you can achieve this effect.:
- Strengthening the spine.
- Reduced pressure.
- Posture correction.
- Increased space between spinal discs.
- Restoration of blood circulation.
Set of exercises
It is important that exercises for radiculitis are performed constantly, every day, but the load is moderate and controlled. Performing gymnastics reduces the risk of relapse. Also, do not start gymnastics until pain in the lower back is relieved.
Most often, exercises during treatment are performed using two methods:
- Exercises in the “lying” position , at the same time it is necessary to perform turns, pull the knees to the chest, raise and lower the pelvis.
- Exercises in the “on all fours” position , along with this you arch your back, raise and tighten your arms.
Efficiency increases when the patient visits the pool together, where it is easier to perform exercises and the muscles relax faster.
Massage for radiculitis
Massage for radiculitis in the lumbar region is prescribed only after pain has been relieved, the main symptoms have been relieved and the causes have been relieved.
With the help of massage you can achieve this effect:
- Improving blood circulation and metabolism in cells.
- Muscle relaxation.
- Anesthesia.
- Relieving swelling and tension.
- Relieving pain syndrome.
A massage can only be performed by a specialist who selects the duration of the course and the type of manipulation. Most often, vacuum and cupping massage and acupuncture are combined, and the total duration for radiculitis is three months.
Folk remedies
You can also resort to traditional medicine in case of exacerbation of radiculitis, but before that, consult a therapist.
The most commonly used recipes are:
- Prepare a warming tincture . To do this, mix a bottle of triple cologne, five pieces of red pepper and a bottle of iodine. The mixture is infused for at least a day, then you need to rub the affected area every day and cover it with a warm scarf.
- Take baths with horseradish, St. John's wort , which relieve inflammation and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- In case of hypothermia, inflammation and infection in the body, it is necessary to prepare a decoction for oral administration . Mix a tablespoon of oregano, willow and coltsfoot, two glasses of water. After this, warm the broth for 15 minutes and take it hot once a day.
Also, after treatment, you can do inhalation or visit a bathhouse, adding St. John's wort, sea buckthorn, and pine cones to the water. You can prepare rubbings based on poisons and poisonous plants for treatment and relief of lower back pain.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of recurrence of radiculitis, it is necessary to follow all preventive measures. It is very important to pay special attention to posture - this can be done by strengthening the muscle corset and wearing special devices. Thanks to this, you will be able to reduce the load on the spinal column, as well as establish its normal functioning.
Many experts recommend that patients use special mattresses and place small cushions under their back and neck.
Exercise regularly, thanks to which you will be able to build your muscle frame. Special gymnastics is of greatest importance. You can do hardening, which increases the body's immune abilities. In addition, this will prepare him for possible hypothermia.
Try to lead a healthy lifestyle, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of all organs and systems. With an integrated approach to prevention, the risk of relapse will be extremely small.
Complications
The consequences of lumbar radiculitis can be very unpleasant. The disease causes severe pain, as a result of which a person’s performance is significantly reduced. Radiculitis can also lead to spinal cord infarction or paralysis of the limbs.
In any case, if lumbar radiculitis is not cured, each of the complications will make a disabled person out of a healthy person, so it is extremely important not to delay diagnosis and treatment, the tactics of which should be determined by the attending physician and exclude independence.
Manual therapy
The chiropractor begins treatment procedures only after studying X-ray and MRI data and examining the spine using superficial and deep palpation. He works with his fingers directly on the cause of inflammation of the nerve roots - displaced discs, deformed vertebrae. After installing them in an anatomical position, the spaces between the vertebral bodies increase. This helps eliminate not only pain, but also neurological disorders.