Bloody issues
In the postoperative period, it is necessary to explain to the woman that it is important to monitor discharge from the genital tract, take into account the time of its appearance, the nature of the discharge, its quantity, and whether it is accompanied by changes in well-being.
Bloody discharge after tubal laparoscopy may appear in small quantities in the first few days after surgery. This is normal and should not cause concern. The appearance of these discharges is associated with traumatic damage to the internal genital organs during laparoscopic surgery. As a rule, the discharge is not abundant and is often spotty in nature. Gradually, the discharge normally acquires a sanguineous character, and then becomes mucous, like ordinary leucorrhoea.
If the discharge is cloudy, yellow or greenish, or has an unpleasant odor, you should immediately seek medical help, as it is a sign of an infection.
Brown discharge after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes can be observed both normally, if there is no additional reason to worry, and with pathological processes in the pelvis. In the case of pathology, the discharge has an unpleasant odor and is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, weakness, and chills.
The first menstruation after laparoscopy may not occur on time. Both a delay, sometimes quite long, and premature menstruation are possible. In addition, menstrual blood after tubal laparoscopy is brighter and in greater volume than usual. It is necessary to differentiate the early onset of menstruation with a complication such as bleeding after laparoscopy. during bleeding, the discharge is bright red, with clots, and does not tend to decrease. In this case, the woman notes increased weakness, dizziness, and tachycardia. Bleeding after tubal laparoscopy can be a life-threatening condition and requires urgent medical attention.
Laparoscopy technique
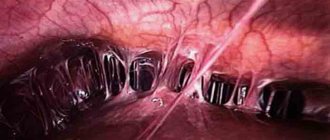
Laparoscopy is performed under sterile conditions in the operating room. The entire operation takes no more than forty minutes. The places where the punctures will be made are processed. Punctures are performed with special devices - trocars. Through one of them, a camera is inserted into the pelvic cavity, which transmits the image to the monitor.
Lighting works in conjunction with the camera. Carbon dioxide is supplied to the abdominal cavity, which moves the uterus. Next, using special devices, the cyst is removed, but if this is not possible, then the entire tube is removed along with the benign neoplasm.
Source: zovmiloserdia.ru
Modern methods
Recently, doctors are increasingly using process automation when carrying out such operations, which allows them to partially eliminate the “human factor” when performing operations.
In this case, minimal blood loss occurs, tissues are traumatized only to the extent necessary for healing. In the postoperative period, due to the action of the system, the pain syndrome is less pronounced. In this case, wound infection is completely excluded. Recovery and healing of wounds occurs several times faster.
When carrying out such operations, a robot is used that has four grippers, with the help of which all manipulations during laparoscopy are carried out. The doctor only controls the actions of the robot, which makes smooth movements that exclude errors.
The risk of complications due to careless movements of the surgeon is completely eliminated here. When using a robotic system, trocars are not used. The punctures are made by the robot itself. In this case, the accuracy of the punctures is much higher than what happens when they are created manually by a surgeon. The only disadvantage of this system is its high price. Therefore, not all clinics are equipped with it. This equipment is available only in large centers.
Diet after tubal laparoscopy
Fallopian tube laparoscopy: diet. Fallopian tube laparoscopy, like any operation, is a certain stressful situation for the body. Therefore, in the postoperative period it is necessary to adhere to a certain diet and diet. The diet after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes should be gentle, the food is light, does not require a lot of energy for digestion, and does not provoke stool disorders and gas formation.
Following nutritional recommendations helps reduce the possibility of postoperative complications associated with the digestive system, and also promotes a speedy recovery. Before laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is performed, you need to find out what you can eat after the operation. This will help the attendants navigate what products can be brought to the patient and what should be limited.
General principles of nutrition in the postoperative period:
- On the first day you can drink still water, then by the end of the first day after surgery - low-fat broths
- Food should be boiled or stewed and have a rough structure so as not to damage the intestinal mucosa. In addition, after intubation, unpleasant sensations in the throat persist and rough food only further injures the already damaged mucous membrane
- Meals should be fractional: you need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions, so as not to overload the digestive tract and not contribute to the processes of decay in the intestines
- Nutrition after tubal laparoscopy should be high in nutrients, especially proteins and vitamins, which improves immunity and speeds up recovery processes.
What can you eat after tubal laparoscopy:
- Vegetables and fruits, especially baked apples and bananas
- Cream soups
- Chicken broth
- Lean types of meat (veal, chicken) and fish (hake, pollock, pike perch)
- Porridge – buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, rice – with caution
- Whole grain or bran bread
- Cottage cheese and low-fat cream, fermented milk products
- You can drink weak tea, diluted fruit and vegetable juices, still water
The following foods should be limited or excluded from the diet:
- Salty, spicy food
- Pickled products
- Fatty fish (trout, salmon) and meat (pork, lard)
- Smoked meats, fried foods with a high content of oil and fat
- Chocolates, pastries, cakes, fresh pastries
- Foods that contribute to increased gas formation in the intestines - black bread, beets, cabbage, legumes
- Some berries and fruits, such as quince, persimmon, dogwood
- Alcohol, coffee, carbonated drinks
You need to know what you can eat after tubal laparoscopy to prevent constipation. These are products such as fresh kefir, yoghurts without food flavoring and aromatic additives. The bacteria contained in fermented milk products that are beneficial for digestion prevent dysbacteriosis and the problems that accompany it. To improve peristalsis, you can eat dried fruits, including prunes.
It is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of fluid - about 2 liters per day. It can be plain water, fruit drinks, juices, compotes, jelly, weak tea. Excessive fluid intake can lead to the development of edema, which is also undesirable.
Alcohol after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is strictly contraindicated. This is due to many reasons:
- Alcohol toxins lead to intoxication of the body; their removal requires enhanced work of the detoxification system.
- Increased risk of infectious complications
- The combined use of alcohol with medications leads to liver damage and the development of acute toxic hepatitis.
- Regeneration processes slow down, chronic diseases worsen
- Alcohol contributes to blood clotting disorders
- Suppression of the nervous system due to alcohol consumption aggravates the course of the postoperative period
Taking alcohol together with antibiotics is especially dangerous for the liver (since it is where the processes of neutralization and breakdown of toxic substances occur) and kidneys (since they remove dangerous metabolites from the body in the urine). This does not mean that you need to give up alcohol forever, but during the rehabilitation period, complete abstinence from alcohol is necessary.
If a woman smoked before surgery, then in the postoperative period you should also limit yourself to smoking, since nicotine and tar contained in cigarettes can worsen the course of the postoperative period and slow down the regeneration processes.
Ovarian cyst
Nutrition after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst should be as light as possible, but rich in microelements. Since the operation is performed under general anesthesia, the body needs to recover from the stress on the heart and respiratory organs. Therefore, on the first postoperative day, it is prohibited to consume food - drink still mineral water.
Why do doctors recommend sticking to a strict diet on the first day after laparoscopy? Because the patient may vomit, and this threatens to rupture the stitches. In addition, anesthesia causes nausea in many people, so eating will only be harmful. During the first postoperative days, patients eat food only in liquid form.
After abdominal surgery, it is necessary to restore the functionality of the intestine, which could have been injured by medical instruments and the pressure of gas introduced into the abdominal cavity. Therefore, for several days it is not recommended to eat foods that cause increased gas formation:
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- Rye bread;
- fresh fruits.
Also, during the rehabilitation period, you should completely avoid pickles and smoked foods. These foods put a lot of stress on the kidneys and liver, and the body will have difficulty absorbing these foods.
Recommended Products:
- boiled dishes;
- porridge made from semolina, buckwheat and oats;
- baked apples for dessert;
- boiled zucchini, carrots and potatoes.
During the recovery period, you should forget about pasta and sweet pastries. To restore impaired intestinal motility, you should eat more foods rich in fiber.
Important! A gentle diet after ovarian laparoscopy should be discussed with the treating gynecologist.
Low-fat fermented milk products and dried fruits help get rid of possible constipation, which is unacceptable during the recovery period. Any muscle tension in the peritoneum will contribute to the divergence of the internal sutures. To avoid the development of dysbacteriosis, it is necessary to take bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
When can I resume my normal diet? Not earlier than 30 days after laparoscopy. This time will be enough for full rehabilitation.
Even more interesting:
Why is Unidox prescribed to women?
Balls hurt after arousal
Sex after laparoscopy on the fallopian tubes
Sex after tubal laparoscopy is usually allowed no earlier than 3-4 weeks after surgery. It is possible to resume normal sexual activity if the woman feels normal and has not experienced any complications. It is also important that the sexual partner is examined for urogenital infections and is healthy. This is important, since re-infection of a woman can aggravate her condition and negate all treatment results. If laparoscopy was performed to treat infertility, you should not postpone the issue of starting sexual activity for too long, since usually operations to restore tubal patency are effective for several months.
Laparoscopy is a modern, low-traumatic method of performing surgical interventions and diagnostic studies of organs located in the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
Nutrition before laparoscopy - preparation
Before surgery, it is important to prepare the gastrointestinal tract system in order to minimize the risks of complications of the abdominal cavity and adhesions. Compliance with the diet in the preoperative period will provide the surgeon with an open view and access to the organs. There are no strict rules regarding nutrition, but there are a number of tips to help prevent unpleasant consequences, as well as speed up the recovery of the body.
During the week before laparoscopy, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Avoid smoked, fatty, high-carbohydrate foods that cause gas:
- black bread;
- milk;
- beans;
- potato;
- eggs;
- fat meat;
- apples;
- plums;
- cabbage in any form.
- A week in advance, start taking activated carbon three times a day after meals, 2 tablets.
- Start eating fermented milk products with a minimum percentage of fat, cereals, fish, broths.
- Use valerian, sedative or sleeping pills if necessary.
On the eve of laparoscopic surgery, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Take laxatives or do enemas for two days before the intervention.
- You can only eat liquid porridge for lunch, and only water for dinner.
- Food and water are prohibited 17-20 hours before surgery.
- If you are very thirsty, you are allowed to rinse your mouth with water and lemon or citric acid.
Important! If the diet is not followed, there may be a risk of food getting into the respiratory tract of the patient being operated on.
Main stages of laparoscopy
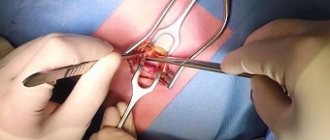
- General anesthesia is used to perform laparoscopy. Small incisions (about two centimeters long) are made on the skin, after which they are deepened using a blunt probe, thereby preventing damage to internal organs.
- One operation usually requires three or four holes. The introduction of sterile surgical instruments is carried out through special tubes inserted into the holes.
- To straighten the abdomen and provide maximum access to the internal organs, carbon dioxide is injected through one tube.
- A video camera and surgical instruments are inserted into other tubes.
- The video camera transmits the image of the operated organs to the monitor screen, which provides the doctor performing the operation with visual control over his actions.
- After all necessary actions have been completed, the instruments are removed and sutures are applied to the incision sites.
Benefits of laparoscopy
- Laparoscopy is characterized by minor tissue trauma, in contrast to conventional operations, for which large incisions are made.
- The rehabilitation period after laparoscopy is easier and shorter. Within a few hours after laparoscopy, the patient is allowed to get up and walk.
- The risk of complications (wound infection, adhesions, suture dehiscence) is significantly reduced.
- After laparoscopy there are no large scars or scars.
Types of laparoscopic operations
Laparoscopy is used to perform surgical interventions aimed at removing or restoring affected organs. Today, the following operations are performed using this method:
- remove the gallbladder (for patients with cholecystitis and cholelithiasis);
- the appendix is removed;
- remove the kidneys, bladder and ureter, or restore their functions;
- the fallopian tubes are removed or tied (sterilization);
- remove an ectopic pregnancy;
- treat endometriosis;
- treat PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome);
- treat hernias;
- perform surgical interventions on the liver, stomach and pancreas;
- examine and remove ovarian cysts;
- remove uterine fibroids;
- remove the adhesive process in the fallopian tubes;
- diagnose and stop internal bleeding.
Contraindications for surgery
Fallopian tube laparoscopy is contraindicated if:
- oncological diseases of the pelvic organs, when there is a risk of new metastases;
- poor blood clotting;
- severe systemic pathologies in the acute stage - diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine and respiratory systems, liver and kidney failure;
- severe exhaustion or shock of the patient;
- excessively short fallopian tubes (less than 4 cm) as a result of previous operations;
- diaphragm hernia.
Important! Sometimes laparoscopy is performed despite contraindications. It is prescribed when there is a threat to the patient’s life. For example, in case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fallopian tubes will have to be removed, regardless of possible complications.
There are also relative contraindications to therapeutic or diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes. The operation is carried out after their elimination, or under the supervision of a specialized specialist.
Such restrictions include:
- obesity;
- acute infectious diseases;
- high pressure;
- diabetes;
- severe adhesive disease.
Preparation for laparoscopy
Preparation for laparoscopic surgery is discussed between the doctor and the patient individually. The following actions are recommended:
- refusal to eat food 8 hours before the intervention;
- administering a cleansing enema several hours before the operation;
- epilation of the abdomen (if laparoscopy is performed on men).
Before the operation, the patient must inform the doctor about the medications he is taking. Due to the effect of some medications (aspirin, contraceptives) on hemocoagulation, their use before laparoscopy is strictly contraindicated.
Possible development of complications after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a method characterized by a minimal risk of developing dangerous complications. As a rule, this operation is easily tolerated, and recovery after laparoscopy is quick.
You should consult a doctor after discharge from the hospital as soon as possible if the following symptoms appear:
- high temperature, chills;
- fainting (loss of consciousness);
- increased pain in the abdominal area, nausea, vomiting that does not stop for several hours;
- swelling, suppuration or redness in the suture area;
- bleeding from wounds;
- urinary disorders
Recovery period after laparoscopy
Most often, the patient recovers within a few days after laparoscopy, and sometimes can even be discharged on the day of the operation.
After laparoscopy, the patient may complain of intense pain in the abdomen and in the area of postoperative wounds, which intensifies with movement. This is considered normal. To relieve pain, painkillers may be prescribed.
In some cases, bloating, nausea, and general weakness may occur. To eliminate severe bloating, medications that include simethicone are prescribed.
Feelings of weakness, nausea, loss of appetite and increased urge to urinate go away on their own within 2-3 days after laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy
Previous topics
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
A chat of those who have already undergone laparoscopy is here:
Pregnant girlfriends and babies after lapara - 4
Survey for those who have had laparoscopy
Table with data on laparoscopy
Many thanks to Lesik-mama 2012 for systematizing the information on the topic “Laparoscopy”.
We kindly ask everyone to read all the information below first, so as not to clutter the new topic with questions, the answers to which are contained on the first page.
The topic is devoted only to Laparoscopy, i.e. directly to the operation itself.
All questions regarding diagnoses identified during laparoscopy and methods of their treatment are included in the appropriate topics. For example, Endometriosis
If you would like to ask a question to a direct forum participant and your question does not relate to laparoscopy, you can do this through personal correspondence or in the appropriate topic.
———————————————————-
Laparoscopy
- this is one of the types of modern surgical operations when, without an incision, using optical instruments (gastroscope or laparoscope), the doctor can examine organs from the inside. Laparoscopy, literally translated, is an examination of the abdominal organs. Laparoscopy is performed to examine the abdominal and pelvic organs and diagnose certain diseases, and, depending on the pathology, for surgical treatment.
Highlight
diagnostic and operative laparoscopy.
Diagnostic laparoscopy
is a surgical research technique in which the doctor examines the abdominal organs with his own eye without making large incisions on the abdominal wall. During laparoscopy, you can directly see the woman’s internal genital organs with the eye and, thanks to this, obtain comprehensive information about their condition. During diagnostic laparoscopy, after examining the abdominal organs, the doctor confirms or rejects any diagnosis, or checks, for example, the patency of the fallopian tubes.
At
During surgical laparoscopy, the doctor eliminates the detected pathological changes.
Laparoscopic gynecology is a new possibility for the effective treatment of gynecological diseases, allowing to minimize recovery time and leaving no cosmetic defects.
What operations can be done with laparoscopy?
Using laparoscopic access, you can perform almost all operations that are performed in the open way, i.e. using a cut. Solving some surgical problems, such as eliminating genital endometriosis, is generally impossible without the use of laparoscopy. This technology has opened a new era in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility, allowing for significant improvements in results. Timely detection and removal of ovarian cysts using laparoscopic access has significantly reduced the incidence of ovarian cancer. The degree of development and implementation of endoscopic technology is the key to the quality of medical services provided. This must be taken into account when choosing a gynecological hospital.
Indications for laparoscopy
- Infertility for a year with regular sexual activity without contraception. Before performing laparoscopy, the woman must be examined, and her husband must also have a spermogram done to rule out male factor infertility. In case of hormonal pathology, a woman is referred for laparoscopy if treatment is ineffective within 1–2 years. In case of infertility with a regular menstrual cycle, organic pathology is detected during laparoscopy in 75% of women.
— Chronic pelvic pain, if there is a suspicion of endometriosis or adhesions
— Ovarian tumors
— Polycystic ovary syndrome (if hormonal therapy is ineffective).
— Endometriosis of the uterine appendages or peritoneum
— Uterine fibroids (usually small nodes of fibroids located on the surface of the uterus are removed using laparoscopic access)
— Voluntary surgical sterilization (tubal ligation)
Laparoscopy in extreme situations
— Suspicion of an ectopic (tubal) pregnancy.
— Suspicion of ovarian apoplexy.
— Suspicion of uterine perforation.
— Suspicion of torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian tumor.
— Suspicion of rupture of an ovarian cyst or pyosalpinx.
— Acute inflammation of the uterine appendages in the absence of effect from complex conservative therapy within 12-48 hours.
— Loss of the Navy.
Now let's look at these readings in more detail.
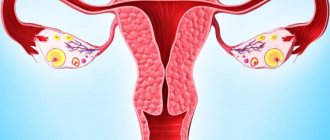
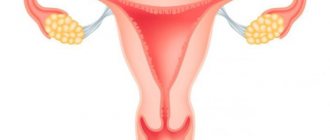
The fallopian tubes
Sterilization.
In this operation, the fallopian tubes are cut or burned with a bipolar current and then divided. This type of contraception is recognized as the most reliable, but, unfortunately, irreversible, therefore it is used for patients over 35 years of age who already have at least 2 children.
Ectopic pregnancy.
In 98% it is a tubal pregnancy. This means that the fertilized egg is located in the lumen of the fallopian tube. Ectopic pregnancy is a condition that threatens intra-abdominal bleeding, so it must be operated on, and urgently. During operations for tubal pregnancy, 2 main methods are used - in the first, the tube is cut lengthwise, the fertilized egg is removed from the lumen of the tube, and the tube is left in place. In another option, the tube is removed immediately, regardless of the timing of the detected tubal pregnancy, considering that the tube is already affected and the next pregnancy will again be ectopic.
Adhesions around the fallopian tubes
(peritubar adhesions). They are coagulated with electric forceps (bipolar coagulator) and then cut with scissors. Such adhesions occur after operations (after abdominal operations - in 90 - 95% of cases, after laparoscopy - very rarely), after sexually transmitted infections, mainly chlamydia. The adhesive process is the most common factor of infertility and is called tubo-peritoneal factor of infertility.
Tubal patency disorders
- an important factor in infertility. The operation is confirmed by passing a bright blue solution through the pipes. If the part of the fallopian tube farthest from the uterus, located near the ovary, is sealed, manipulations are carried out to restore the patency of the tubes, which quite often lead to pregnancy (according to some data, up to 30% of cases with an unexpressed adhesive process).
Hydrosalpinx
- accumulation of liquid in the cavity of the pipe, in which the outer hole is sealed - the “exit”, while the pipe turns into a bag of liquid, which is an ideal environment for the development of bacteria. The affected tube is non-functional and dangerous for the patient, as it can become inflamed, twisted, which will cause acute pain, prevent pregnancy, and also worsen the quality of the endometrium. Therefore, such fallopian tubes must be removed laparoscopically.
Ovaries
are also a classic object of laparoscopic intervention.
Ovarian cysts
: are divided into functional (follicular or corpus luteum), which go away on their own within a few months, and organic, which must be removed, since these cysts can grow, torsion of the ovary enlarged due to the cyst is possible, rupture of the cysts, impaired blood supply are possible cysts, cyst degeneration. During laparoscopy, they try to remove the cyst from the capsule, preserving the ovarian tissue as much as possible.
Ovarian torsion
- possible due to the fact that the ovary has a long “leg”, that is, ligaments with which it is attached to the wall of the pelvis. When torsion occurs, the blood supply to the ovary sharply decreases, which disrupts its nutrition, causing the so-called “acute abdomen” syndrome - acute pain, which is the basis for emergency hospitalization and surgery.
Apoplexy
, i.e. bleeding from the ovary, usually occurs in the middle of the cycle - at the time of ovulation, with frequent acute pain in the lower abdomen, for which the patient is hospitalized and operated on - the ovary is sutured or the bleeding site is coagulated.
Polycystic ovary syndrome ( PCOS )
, described by Stein and Leventhal back in the 30s of the twentieth century. Classic signs are absence of menstruation or irregular menstruation from the moment they appear, excess weight, excess hair growth. One of the most common causes of infertility. With this syndrome, the ovaries are large, round, with a thick capsule and many small follicles. Laparoscopy is a recognized method of treating infertility in patients with PCOS who have failed conservative treatment. There are many laparoscopic treatment techniques. Classic methods include wedge resection, in which a sector resembling a piece of watermelon is excised from the ovary along the long axis. Recently, more gentle techniques have been used, for example, point coagulation of the ovarian surface (monopolar coagulation of the capsule), after which points remain on the surface of the ovary, reducing the density of the capsule. After such operations, most patients ovulate within several months. During this time, called the “light period”, infertility treatment is intensively carried out. If infertility treatment is unsuccessful during this period, IVF is recommended to patients.
Uterus
Uterine fibroids
- a benign hormone-dependent tumor of the uterus, consisting of smooth muscle cells, altered cells of the myometrium - the main layer of the uterus. Occurs in 25-40% of women, according to various studies. In a significant proportion of women, fibroids do not manifest themselves in any way and are discovered by chance during routine examinations. Fibroids can cause infertility, especially if the fibroids are large enough - more than 3-4 cm. With such sizes, fibroids can deform the uterine cavity, worsen the condition of the endometrium, and in a certain location can block the entrance to the fallopian tube. In addition to infertility, indications for removal of uterine fibroids are: rapid growth of fibroids, large tumor sizes, disruption of neighboring organs, for example, urination problems, constipation, bleeding caused by fibroids. With laparoscopy, there are much more opportunities to perform a conservative myomectomy, that is, to remove fibroid nodes from the thickness of the uterine wall, thus leaving the uterus in the body.
Malformations of the uterus, such as a bicornuate uterus. Often with this shape of the uterus it is impossible to carry a pregnancy. The developed classical operations to restore the shape of the uterus are successfully used in laparoscopy.
Endometriosis
- a common disease in women of childbearing age. In this disease, cells similar to the cells of the endometrium, that is, the lining of the uterus, are found outside the uterus, for example, on the peritoneum of the pelvic cavity, on the fallopian tubes, on the ovaries. These cells grow, form microcysts, and eventually cause fusion of the pelvic organs. Growing on the ovaries, these cells often lead to the appearance of endometrioid cysts. In addition, endometriosis is a very common cause of infertility, even in the so-called minor forms. It is now generally accepted that the basis for the development of endometriosis is the entry of endometrial cells during menstruation with blood through the fallopian tubes into the abdominal cavity. The peculiarity of this disease is that it cannot be reliably diagnosed using conventional methods. Indirect signs of endometriosis are spotting before and after menstruation, pain when examined in a chair, and periodic pain during sexual activity. According to the WHO (World Health Organization), laparoscopy is recognized as the only reliable method for diagnosing endometriosis. During the operation, the foci of endometriotic ovarian cysts are destroyed. A two-stage treatment regimen for endometriosis is recognized as the most effective: surgery, and after it, patients receive the drugs Differelin, or Zoladex, or Decapeptil for several months. If a patient undergoes IVF after such an operation, she may be prescribed a super-long protocol: stimulation of ovulation after several months of taking such drugs.
Infertility
. According to the WHO classification, the cause of infertility cannot be fully established until diagnostic or therapeutic laparoscopy has been performed. Laparoscopy is indicated for patients in whom hysterosalpingography (x-ray examination) determines the patency of the fallopian tubes, as well as for patients who, despite confirmed tubal patency, have a regular menstrual cycle, normal hormonal levels, the husband has a normal spermogram, and pregnancy does not occur. And also, of course, for patients who have uterine tumors, adnexal cysts, or there is a suspicion of adhesions in the pelvis. In addition, if a patient with hydrosalpinx undergoes IVF, she is strongly recommended to remove the diseased tube, since, against the background of stimulation, the hydrosalpinx often empties into the uterine cavity, affecting the endometrium, preventing implantation, and negatively affecting the embryos.
Contraindications to laparoscopy
Absolute contraindications
for laparoscopy are diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems in the stage of decompensation, shock and coma, cachexia (severe exhaustion), disorders of the blood coagulation system, hernia of the anterior abdominal wall or diaphragm.
Relative contraindications
— Obesity III-IV degree
— Pronounced adhesions after operations on the abdominal organs
— Significant amount of blood in the abdominal cavity (1-2 l)
— Significant size of the pathological formation of the internal genital organs
— Malignant tumor of the ovaries
- Cervical cancer
Contraindications for elective surgery
are acute infectious diseases suffered less than 1 month before surgery, deviations in clinical laboratory tests (usually in these cases the patient is sent to a therapist to decide on the possibility of surgery and the need for further examination), bronchial asthma with frequent exacerbations, hypertension illness with high blood pressure.
How is laparoscopic surgery performed?
Laparoscopy is almost always performed under general anesthesia. During laparoscopy, only endotracheal anesthesia is used: during the operation, the patient’s lungs breathe through a tube using a special breathing apparatus. Endotracheal anesthesia is the most common type of anesthesia in the world. The use of other types of anesthesia during laparoscopy is impossible, since during the operation gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity, which “presses” on the diaphragm from below, which leads to the fact that the lungs cannot breathe on their own. As soon as the operation is over, the tube is removed, the anesthesiologist “wakes up” the patient, and the anesthesia ends.
First, a small hole is made in the patient's navel and gas is injected into the abdominal cavity. This is done for the following reason. Typically, the abdominal wall is pressed tightly against our organs, which makes diagnosis and treatment much more difficult. In order for the abdominal wall to rise above the organs and the doctor to see them better, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. At the same time, an empty space appears in the abdominal cavity, like in a balloon, which is necessary for the doctor’s work.
After filling the abdominal cavity with gas, a laparoscope is inserted - a telescopic tube containing a lens system and usually attached to a video camera. An optical cable illuminated by a “cold” light source (halogen or xenon lamp) is also attached to the tube. This allows you to view the image of the abdominal organs and the surgeon’s manipulations during the operation on a special TV screen with high magnification and record the progress of the operation.
Next, the surgeon makes 2 more small punctures of the anterior abdominal wall, 5 and 10 millimeters in diameter (as thick as a ballpoint pen). Unlike a traditional (laparotomy) 15 to 20 centimeter incision in the anterior abdominal wall, these punctures do not traumatize the muscle tissue, so patients experience much less pain after surgery and can usually return to normal life within one week. Through these punctures, special instruments (manipulators) necessary to perform the operation are inserted into the abdominal cavity.
Painful sensations in the puncture area disappear, as a rule, after 1-2 days, after which the patient does not experience the discomfort characteristic of the postoperative period of traditional surgical operations. The patient is discharged home 2-3 days after the operation, and can return to a full life after 5-6 days. However, medical supervision is necessary throughout the entire recovery period to avoid complications.
Advantages of laparoscopic operations
Their low morbidity
Short stay of patients in hospital (2-3 days)
Rapid restoration of health and ability to work after interventions
Carrying out the operation under multiple magnification makes it possible to carry out any surgical intervention more accurately and less traumaticly.
Minimal trauma to the anterior abdominal wall contributes to the rapid restoration of the functions of all organs and systems: breathing, activity of the cardiovascular system, motor-evacuation function of the intestines and bladder.
During the wound healing period, there is no pain, which eliminates the need to prescribe strong painkillers.
In addition, there are no postoperative scars, which are observed during conventional incision operations.
Possible complications during laparoscopy
Complications during laparoscopy are possible, as with any other medical procedure. But they are rare - according to various sources, 0.5-7%.
Complications are possible during anesthesia; when inserting a camera and instruments, organ injuries are possible, and damage to a vessel on the abdominal wall at the puncture site is also possible. When the abdomen is “inflated,” gas may be introduced into the subcutaneous fat (subcutaneous emphysema). Complications may also arise during manipulations in the abdominal cavity, such as injury to organs and large vessels). If bleeding is not stopped sufficiently, bleeding may also occur in the postoperative period.
Preoperative preparation
Before carrying out a planned operation, you need to undergo a certain number of examinations. The patient either undergoes them in the hospital or enters the department with ready-made tests (the second option is preferable, as it reduces the number of days the patient spends in the hospital).
Sample list of tests (ATTENTION! If necessary, the scope of the examination can be changed by your attending physician)
1. General blood test
2. General urine test
3. Coalogram
4. Biochemical blood test (sugar, bilirubin, total protein, urea)
All these tests are valid for 10 days before surgery.
5. Blood type, although upon admission to the hospital it is necessarily redefined.
6. Testing for syphilis (RW), HIV, hepatitis B and C (HbSAg and ATHCV) – valid for 3 months.
7. Vaginal flora smear – valid for 10 days.
8. ECG – shelf life 1 month.
9. Fluorography no more than six months old.
10. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
11. Therapist's conclusion.
If the patient has any pathology of the cardiovascular, respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, then consultation with related specialists is necessary to develop tactics for managing the patient in the pre- and postoperative periods, as well as to assess the presence of contraindications for laparoscopy .
In the cycle in which the operation is performed, it is necessary to protect against pregnancy using non-hormonal means (@#$%&om).
Before the operation, the patient signs a consent for the operation, which states that the doctor explained to her what the scope of surgical treatment will be (for example, with ovarian cysts, it is possible to remove the cyst, remove the cyst with part of the ovary, in some cases, remove the entire ovary), what complications are possible . Also, before the operation, a conversation is held with the anesthesiologist, who explains what kind of medicinal preparation for the operation will be carried out (to stabilize the psycho-emotional status, prevent thrombosis and bleeding), and the patient also gives her consent to anesthesia.
Before surgery, the gastrointestinal tract must be cleansed, since a swollen intestine makes it difficult to see and blocks access to the genitals, increasing the risk of intestinal injury. A cleansing enema is performed the evening before and the morning of the operation. The day before the operation, you can eat until 18:00, and you can drink water until 22:00. On the day of surgery, you should not eat or drink anything. It is also recommended to limit foods that cause flatulence (bloating) 3-4 days before surgery (brown bread, cabbage, legumes).
In preparation for surgery, it is necessary to shave the hair in the lower abdomen and perineum.
According to indications, before surgery, the patient puts on anti-varicose stockings on her legs or performs elastic bandaging. After the operation, the patient wears these stockings for at least another week, preferably two. This is necessary because during surgery, microthrombi may form in the veins of the legs, and in the absence of elastic compression, these thrombi enter the general bloodstream; the most dangerous is their entry into the vessels of the lungs and heart.
When is the operation performed?
As a rule, laparoscopy can be performed on any day of the cycle, just not during menstruation. This is due to the fact that bleeding increases during menstruation and there is a risk of increased blood loss during surgery. In addition, the operation cannot be performed against the background of acute inflammatory processes (acute respiratory infections, herpes, etc.). The most optimal time to perform a laparoscopic examination for infertility is after ovulation (with a 28-day cycle - from the 15th to 25th day of the cycle), and for some operations - the first phase of the cycle (immediately after menstruation). The day of surgery depends on the diagnosis with which the patient undergoes surgery.
After laparoscopy
Compared to conventional surgery, laparoscopy is less traumatic (muscles and other tissues are less damaged). For this reason, there are fewer restrictions on your physical activity than you might expect. Walking is allowed and even encouraged within a few hours after surgery. Start with short walks, gradually increasing the distance and duration. There is no need to follow a strict diet. Painkillers should be taken as directed by your doctor.
Most frequently asked questions
1. How long does laparoscopy take?
It depends on what pathology this operation is performed for. If this is separation of adhesions or coagulation of foci of endometriosis of moderate complexity, then laparoscopy lasts about 40 minutes.
If the patient has multiple uterine fibroids and it is necessary to remove all myomatous nodes, then the duration of the operation can be 1.5-2 hours.
Laparoscopy is a jewelry operation that is performed under high magnification and very carefully to reduce the degree of tissue trauma and the amount of blood loss.
2. When can you get out of bed and start eating? When are stitches removed? When can you have sex?
As a rule, after laparoscopy you can get up in the evening on the day of the operation. The next day, a fairly active lifestyle is recommended: the patient should move and eat smaller meals in order to recover faster. Discomfort after surgery is mainly due to the fact that a small amount of gas remains in the abdominal cavity and is then gradually absorbed and “dissolved”. The gas that remains can cause pain in the muscles of the neck, abdomen and even legs. In order to speed up the absorption process, movement and normal bowel function are necessary.
Sutures are removed 7-9 days after surgery.
Sexual activity is permitted one month after laparoscopy. Physical activity should be limited in the first 2-3 weeks.
3. When can you start trying to get pregnant after surgery?
If laparoscopy was performed for adhesions in the pelvis, which was the cause of infertility, then you can start trying to get pregnant a month after menstruation.
If laparoscopy was performed for endometriosis and additional treatment is required in the postoperative period, then it is necessary to wait until the end of treatment and only then plan a pregnancy.
After conservative myomectomy, pregnancy is prohibited for 6-8 months, depending on the size of the myomatous node, which was removed during laparoscopy.
For this period of time, sometimes it is even necessary to prescribe contraceptives, since pregnancy during this period is very dangerous and uterine rupture can occur. Strict pregnancy protection is recommended for such patients.
4. When can you go to work?
According to standards, sick leave on average after laparoscopy is given for 7 days. As a rule, by this point, patients can already work calmly (only if their work does not involve heavy physical labor). Some business women, with relatively small volumes of surgery, begin work within 3-4 days after the operation.
Menstruation and discharge after laparoscopy
After a laparoscopic operation aimed at treating or diagnosing gynecological diseases, scanty mucous or bloody vaginal discharge may be observed, which can last 10-14 days. This is not a cause for concern.
Severe bloody vaginal discharge may be a concern, as it may indicate internal bleeding.
After laparoscopy, menstrual irregularities may occur: menstruation may not occur on time and may be delayed for several days or weeks. This is also considered normal.
How long after laparoscopy can you get pregnant?
Doctors recommend planning to conceive a child immediately after completion of rehabilitation. Pregnancy after laparoscopy is more likely to occur within 2-3 months. At the same time, a woman must constantly monitor changes in her body. If the fallopian tubes are partially obstructed, ectopic pregnancy may occur, which requires immediate invasive intervention.
Menstruation after laparoscopy, subject to all rules of asepsis and antisepsis, should occur at the usual time. However, some deviations may be observed within 2-3 months. Prolonged menstrual disorder after laparoscopy requires monitoring by the attending physician. Such manifestations usually indicate that the procedure was performed without taking the necessary precautions.
When to plan a pregnancy after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is often prescribed as a diagnostic and therapeutic method for diseases that are accompanied by infertility (endometriosis, fibroids, adhesions, ovarian cysts, polycystic ovary syndrome, reconstruction of the fallopian tubes, etc.). If the operation was successful, you can plan a pregnancy a few months after the operation.
Due to the fact that not only surgery is used to treat infertility, but also conservative therapy, which involves taking medications that affect female reproductive function, pregnancy planning should be discussed with the attending physician who has studied the patient’s medical history.
Successful pregnancy depends on what factors caused infertility before treatment, as well as on how effective the treatment was.
Is pregnancy possible after tubal laparoscopy? A specific, but at the same time very relevant question among women who are faced with a similar problem. Laparoscopy in modern gynecology is the safest and most effective method of combating infertility due to the formation of adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes. From this publication you will learn what this procedure is, and also read reviews from people who have encountered a similar problem.
Fallopian tube laparoscopy and its consequences
Laparoscopy is a common operation in the field of gynecology. It has a huge number of indications, and the vast majority of patients are women who have difficulty getting pregnant.
For reference! According to statistics, every 4th woman suffering from infertility has a problem caused by pathology of the female reproductive system, and every second woman has a problem due to obstruction of the fallopian tubes, infectious diseases, and the consequences of surgical interventions in the past.
The essence of laparoscopy is to operate on the pelvic organs using special equipment through several narrow holes. It is low-traumatic, so recovery after laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes occurs practically without complications and in a relatively short period of time.
When is the operation performed?
Disturbances in the anatomy of the fallopian tubes are rarely congenital. They usually occur as a result of inflammation, surgery, urogenital infections or long-term use of intrauterine contraceptives. The cause of the pathology may be abortion.
Fallopian tube laparoscopy is required for:
- Formation of adhesions around or inside an organ;
- Accumulations of fluid (exudate);
- The appearance of cystic formations;
- Adenomyosis;
- Endometriosis;
- Tumors.
During the operation, the doctor may prescribe chromohydroturbation - a patency test. To do this, a sterile dye solution is injected into the uterus through a catheter. If the tubes are passable, the solution passes through, flowing into the abdominal cavity.