Home » Liver cirrhosis
Arkady Belyakov Updated: 03/01/2019 0
Terminal or stage 4 of liver cirrhosis is the final stage of necrotic damage to the organ. As a result of impaired liver function, damage to the brain, nervous system and gastrointestinal tract begins to progress. These negative phenomena lead to the development of a comatose state of the patient and encephalopathy.
End-stage symptoms and signs
Stage 4 liver cirrhosis is characterized by pronounced symptoms (unbearable pain, itching, attacks of hypertension), and the absence of a favorable prognosis for survival. Complete necrosis of organ tissue leads to the patient’s inability to move independently, to structure thoughts, and partial memory loss occurs. The patient becomes apathetic and, due to brain intoxication, depressive states develop.
In addition to impaired brain activity, at the fourth stage of cirrhosis, severe liver failure develops, as a result of which the compensatory function of the liver is disrupted and chronic intoxication of the body occurs, including ammonia. It is the concentration of ammonia salt in the body that leads to even greater liver damage and disruption of the respiratory system.
As a result of these disorders, experts note the following symptoms of the last stage of liver cirrhosis:
- complete refusal to consume food and liquid;
- pronounced weight loss, which is accompanied by exhaustion of the body;
- development of insomnia;
- apathy and depression;
- complete muscle atrophy;
- confusion and memory loss;
- coma.
The terminal stage of cirrhosis is accompanied by concomitant pathologies, which are also signs of this disease:
- Ascites. The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity begins in the earlier stages of cirrhosis, but it is at the terminal stage of the disease that this pathology becomes pronounced.
- Encephalopathy. Chronic hypoxia of the brain leads to disruption of its functioning.
- Jaundice. The last stage of cirrhosis is characterized by a bright dark yellow coloration of the skin and visible mucous membranes.
- Liver failure. The functionality of hepatocytes is impaired, which leads to a sharp drop in the platelet content in the blood, as a result of which the patient experiences heavy bleeding.
- Hepatic coma, which is expressed in depression of the central nervous system, which leads to complete loss of consciousness while all reflexes are preserved.
Features of stage 4 cirrhosis
The disease involves four stages of development:
- the first is initial, which is not yet characterized by biochemical abnormalities;
- the second is subcompensatory, clinical signs of liver dysfunction begin to appear;
- the third is decompensating, the cells of the organ cease to perform their functions, the process develops after several years of pathology;
- fourth - the latter seems to be a further increase in the malaise, a decrease in the size of the liver and the virtual cessation of its functionality.
It is the final stage of this liver disease that is characterized by the formation of dropsy, the occurrence of a complex of neuropsychological disorders, cancer, and the risk of bleeding and life-threatening conditions.
Serious malfunctions in the liver make themselves known by yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes, spider veins on the body, and severe enlargement of the abdomen.
It is sad to say, but this disease cannot be cured. Only supportive liver therapy is indicated, aimed at prolonging the patient’s life.
External signs of the disease
Disturbances in the functioning of all body systems are also reflected in the patient’s appearance. Thus, as a result of the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, the patient’s skin and mucous membranes acquire a rich yellow color. The patient's skin becomes dry and flabby. The doctor notices multiple scratches and bruises. The patient's body takes on a disproportionate appearance - the legs and arms are markedly thin, and the stomach, as if inflated, sticks out.
Xanthomas—neoplasms with fatty inclusions—appear near the patient’s eyes, and the facial skin itself becomes red as a result of the expansion of the capillary network.
The expansion of veins in the abdominal area reaches catastrophic proportions, which gives the abdomen a bluish tint.
General characteristics of the disease
Cirrhosis begins to develop against the background of poor-quality treatment of any form of hepatitis, chronic alcoholism (but not all alcoholics suffer from it), immune disorders, blockage of the bile ducts, toxic damage to cells or hereditary diseases. The choice of control tactics largely depends on identifying the main factors that contributed to the onset of death of liver hepatocytes. The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- A sharp decrease in working capacity.
- Lack of appetite.
- Depressed mood, state of depression.
- Low body weight (sharp weight loss).
- Yellow skin color.
- Accumulation of physiological fluid in the abdominal area.
In the early stages, treatment can be done on an outpatient basis, regularly performing prescribed tests and instrumental examinations. In the last two stages, hospitalization is required, as there is a high probability of rapid development of complications and death.
Diagnostics and tests
When diagnosing cirrhosis of the last stage, specialists, as well as in determining compensated and decompensated cirrhosis, conduct an external examination of the patient and manual examination of the organ by palpation.
When diagnosing a disease in a laboratory, experts focus on blood tests based on the five criteria below:
- AST and ALT (aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase);
- lactodehydrogenase;
- alkaline phosphatase;
- gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Stage 4 of the disease is characterized by an increase in the level of ALT and AST in the patient’s blood by more than 5 times.
This is interesting to know! If liver pathology is suspected, it is necessary to undergo tests for ALT and AST. Determination of these enzymes makes it possible to determine the volume and depth of liver damage.
For all patients, without exception, the doctor prescribes a referral for a biochemical blood test, which in terminal cirrhosis shows critically elevated levels of bilirubin, globulin, and liver enzymes. However, not all indicators increase in cirrhosis. As cells die, the levels of cholesterol, albumin and prothrombin in the blood rapidly drop.
Quite often, when diagnosing the final stage of cirrhosis, doctors resort to additional procedures:
- Liver biopsy is a procedure for analyzing part of the liver to identify the nature of the lesion and the degree of proliferation of fibrous tissue.
- Parancethesis is an effective technique for removing excess fluid accumulated in the abdominal cavity.
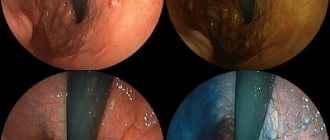
- Endoscopic examination is carried out to assess damage not only to the liver, but also to other internal organs.
Stages of pathology
The stages of the disease are determined by the extent of organ damage and the degree of development of complications. The stage of the disease is determined after a comprehensive examination. The condition is assessed according to five parameters, with a certain number of points assigned to each. The total score is compared with the Child-Turcotte-Pugh scale, where:
- class A denotes disease compensation (baseline period);
- class B – subcompensation (moderate stage);
- class C – decompensation.
Child-Turcotte-Pugh Rating Scale
A score of more than 15 indicates the fourth terminal stage, aggravated by complications, which ends in inevitable death.
The initial or compensated stage of the disease may be asymptomatic. The patient's main sensations are dysania (sleep disorder), physical weakness, loss of appetite, heaviness in the epigastric region. The second stage of pathology development, or the stage of subcompensation, is characterized by more pronounced symptoms.
In the third stage (decompensation), the liver cells completely hypertrophy into fibrous scars, and the gland loses the ability to perform functional duties. Characteristic symptoms intensify. Numerous severe complications develop, leaving the patient no chance of survival. Decompensated cirrhosis of the liver, in most cases, ends in hepatic coma. The final (terminal) stage of the disease develops rapidly due to progressive complications. The result is the death of the patient.
End stage treatment
Treatment of liver cirrhosis at the last stage is extremely ineffective and is aimed at reducing the level of bilirubin in the blood (treatment of a disease such as jaundice), preventing the progression of encephalopathy and ascites, and viral diseases.
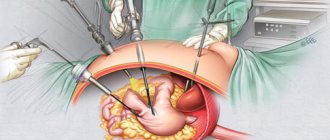
An alternative treatment option is to transplant a healthy organ to the patient. However, this surgical intervention has a number of contraindications and is extremely difficult to perform.
Doctors place the main emphasis in the treatment of the last stage of liver cirrhosis on preventing the occurrence of concomitant diseases. Methods and regimens for taking medications at this stage of the disease are selected strictly individually.
Development mechanism
Depending on the cause that influenced the development of the pathology, there are several main types of cirrhosis of the liver:
- Viral. Occurs against the background of incorrect treatment (or lack thereof) of viral hepatitis (A, B, C).
- Medicinal (pharmacological). Develops due to long-term use of medications.
- Metabolic and nutritional. It is a complication of chronic endocrine and hormonal pathologies.
- Alcoholic or toxic. Progresses due to regular excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Congenital. It is formed in the fetus during intrauterine development under the influence of teratogenic factors or due to unfavorable genetics.
- Biliary (primary and secondary). It develops, in the first case, due to autoimmune processes, in the second, against the background of severe diseases of the hepatobiliary system.
- Cryptogenic. Has no clear cause.
In essence, liver cirrhosis is the transformation of working living cells (hepatocytes) into connective scar tissue, under the influence of the negative factors listed above. To the question of whether it is possible to cure cirrhosis and return liver cells to their functionality, medicine, unfortunately, gives a negative answer.
Complications of the disease
Most complications that occur with terminal cirrhosis are fatal. Experts have identified several of the most common pathological conditions:
- sudden and heavy internal bleeding resulting from varicose veins;
- proliferation of atypical cells in liver tissue;
- lesions caused by an infectious nature.
Also, the terminal stage of liver cirrhosis leads to the likelihood of PVT (portal vein thrombosis), proliferation of cancer cells, hepatic coma, complete impotence and gynecomastia in men.
Causes of cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is a predominantly male disease. This is explained by the fact that most of the causes leading to cirrhosis occur in men. Thus, pathology develops with alcohol abuse, drug addiction, consumption of fatty foods, and exposure to toxins on the body. The disease is provoked by various types of hepatitis and fatty liver disease. Much less often, hereditary diseases and metabolic disorders lead to cirrhosis - congenital fibrosis, hemochromatosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, autoimmune disorders. How long people live with stage 4 liver cirrhosis also depends on the cause of the disease.
Forecast
Statistics show that even with a liver transplant, the maximum life expectancy for a patient with cirrhosis is 2 years.
This is interesting! The probability of the patient’s body rejecting someone else’s liver is more than 50%.
How many people live with late-stage liver cirrhosis without the use of surgical treatments? The patient can live from several weeks to 1 year. The prognosis is not good, especially if bacterial infection or damage to the brain and spinal cord develops against the background of cirrhosis.
How long do people live with stage 4?
The course of stage 4 disease is characterized by many complications. It is in this case that the disease renders the liver completely inactive, so the prognosis is unfavorable. A person with this diagnosis can live no more than 3 years. But if the central nervous system is damaged, then life will not last more than a year.
Therefore, it is very important to detect liver cirrhosis as quickly as possible. You should also take preventive measures, avoid interaction with toxic substances and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Disease prevention
To prevent complete destruction of the liver and protect yourself from the fatal consequences of cirrhosis, you need to listen to your body and do not delay visiting a doctor. An important aspect in the prevention of cirrhosis is avoiding alcohol-containing products, and men, especially after 40 years, should definitely undergo an ultrasound of the liver at least once a year and take a blood test to determine the level of liver enzymes.
Proper nutrition, regular exercise and careful attention to your body are factors that will help you live a long life without cirrhosis of the liver.
Therapy for hepatitis C
The fourth degree is irreversible. Therefore, the problem can only be solved surgically. The result is an organ transplant. The procedure requires careful and complex preparation. But the forecast is disappointing. Not everyone can endure the procedure. In addition, the wait for a donor is very long. Even if the operation was successful, the patient must take special medications throughout his life. They suppress the immune system, which helps prevent rejection of the new organ.
If the queue is very long, then conservative treatment is prescribed, aimed at preventing the occurrence of serious complications and alleviating the patient’s condition. It is important to ensure that the degree of damage does not increase. Otherwise the prognosis is very poor. It is important to pay attention to taking medications that can improve the situation:
- Antiviral. The course is aimed at eliminating the root cause that led to fibrosis. Doctors recommend paying attention to new generation products.
- Hepatoprotectors. Their action is aimed at protecting the liver from various negative factors. Hofitol and Essentiale are often prescribed.
- Immunomodulators and vitamins. Improves the functioning of the body and activates its protective functions. This allows him to more easily endure the pathological process.
It is important to follow a special diet. Smoked, fried, salted, spicy and pickled foods are excluded from the diet. Instead, it is recommended to eat as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible. Preference should be given to boiled, baked or steamed food. Drinks containing alcohol are prohibited. This also applies to drugs. You should also avoid medications that negatively affect the liver.
Folk remedies are widely used in therapy. Before using such medications, you should consult your doctor. Self-medication will lead to serious consequences and worsening of the liver condition. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor based on the results of the examination. Compliance with important recommendations and regulations will extend your life.
Liver cirrhosis stage I
At this stage, the patient often has no idea about the development of the pathology and does not experience negative feelings. Sometimes, when drinking alcohol or eating unhealthy (fatty and spicy) foods, you may experience slight heaviness under the ribs, a bitter taste and dry mouth, and signs of mild dyspepsia.
However, these signs are an alarming signal of the onset of an inflammatory process, leading to the formation of fibrous areas that separate the healthy parts of the liver from the affected ones.
Simultaneously with inflammation, fatty degeneration of cells occurs in the liver, preventing the normal functioning of blood vessels.
Moreover, the first pattern of disease development is typical for men, especially those who abuse alcohol, and the second - for women who do not adhere to healthy eating standards. The main condition for prolonging life is timely diagnosis, which is carried out using a liver biopsy or biochemical analysis.
Liver fibrosis, what is it, causes, symptoms, can it be cured, how to treat it
- Classification of liver fibrosis: definition, its pathological processes, reversibility and diagnosis.
- Liver fibrosis: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, causes and prevention
Fibrosis, or fibrogenesis, is a complex of various dynamic processes in the liver and, mainly, damage to hepatocytes (the main liver cells) resulting from necrotic inflammation and activation of the stellate cells of the organ. Stellate cells, along with portal fibroblasts and bone marrow myofibroblasts, produce collagen in the damaged liver, one of the most abundant proteins in the human body. In a healthy liver, stellate cells remain passive, but alcohol and other toxic substances, as well as hepatitis viruses, set them in motion. When active, they begin to produce fibrogenic cytokines, such as TGF-beta1, angiotensin II and leptin, which damage liver hepatocytes and thereby lead to the appearance and development of fibrosis.
A change in the state of stellate cells is the beginning of fibrogenesis, while the progression of the process entails liver cirrhosis, liver failure, and portal hypertension, which can most often be eliminated only through organ transplantation.
Degrees of liver fibrosis
Liver fibrosis has 5 degrees, or stages: F0, F1, F2, F3, F4 (cirrhosis). With viral hepatitis C, on average, they change every 5 years, but in the later stages the rate of development of the disease increases. It is possible to determine its degree - the most effective method is a functional liver biopsy, which can be repeated 3 to 5 years after the initial procedure to obtain more accurate results.
Progression of fibrosis
The rate at which fibrosis develops depends on many factors and varies markedly between patients. Mainly, its progression is determined by the intensity of the inflammatory process in the liver. However, factors such as
- infection at an older age (at the same time, a direct connection between the viral load and the rate of development of fibrogenesis has not yet been discovered);
- male gender;
- alcohol abuse;
- weakened immune system;
- fatty liver;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- high levels of ALT (alanine aminotransferase, an enzyme found mainly in the liver and kidneys and involved in the metabolism of amino acids).
Treatment of liver fibrosis
Recently it was found that the process of inflammation of the connective tissues of the liver is reversible, therefore, it can be treated therapeutically. Newer antifibrotic drugs can stop the accumulation of fibrogenic cells and/or prevent the deposition of extracellular matrix proteins. However, although many therapeutic interventions are effective in the laboratory, their effectiveness and safety in real life in patients has not yet been proven. In viral hepatitis, treatment of fibrosis is aimed at eliminating the causes of its occurrence, but antiviral therapy can only help if a stable virological response is achieved in the patient.
Degrees of fibrosis
In the usually long course of liver fibrosis, five stages are distinguished - from zero to four. Liver fibrosis grade 4 corresponds to cirrhosis. The process of disease development is not linear and unevenly distributed, and can be stopped with treatment and lifestyle changes, regardless of the degree of liver fibrosis that has developed.
On average, with viral hepatitis, long-term alcohol and other intoxications, liver fibrosis of the 1st degree, then liver fibrosis of the 2nd degree, develops in about five years.
But further, in the absence of treatment, the persistence of unfavorable factors, and also in old age, the process accelerates, and grade 3 liver fibrosis can turn into cirrhosis in 1-2 years.
In men, fibrous replacement of liver cells occurs faster than in women. The presence of fatty hepatosis can also speed up the process. With parasitic infestations (shigellosis and others), the transition from stage to stage occurs faster.
STEP 3: The more scars, the closer to cirrhosis
If you don't treat fibrosis, you risk progressing to the next stage, called cirrhosis. It can take a long time for cirrhosis to occur, anywhere from 10 to 30 years. But it is also possible for the disease to develop rapidly – literally within a few years. Depends on what caused the liver damage (fat deposits, alcohol, virus, parasitic infection) and what resources the body has to fight the disease.
Unfortunately, patients often find out about liver problems only at this almost irreversible stage. The disease can be “rolled back” only when it is in its infancy.
“The most dangerous thing is the accumulation of fat in the liver. This is where the legs of osteoporosis, infertility and even cancer grow.” Pavel Bogomolov, head of the hepatology department of the Moscow Regional Research Institute (MONIKI), spoke about the dangers of violent feasts, regular overeating and lack of physical activity.