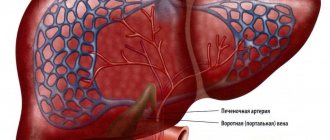
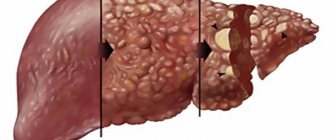
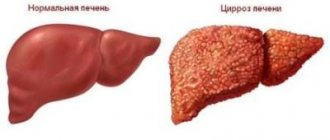
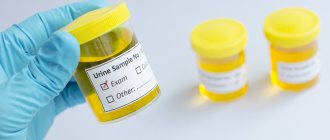
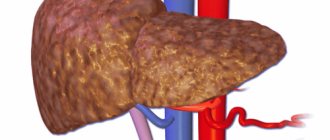
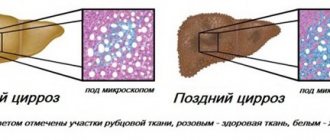
In cirrhosis, due to the action of damaging factors, the connective tissue, which forms the protective framework for liver cells, grows due to inelastic coarse fibers. This leads to the displacement of healthy liver cells and to inhibition of organ function. The progression of the disease is indicated by many characteristic signs, among which the most eloquent are the results of laboratory tests. First of all, the color of urine is studied, since with cirrhosis of the liver it changes noticeably.
Why changes happen
Cirrhosis refers to chronic liver diseases.
When the disease occurs, liver cells die and are replaced by connective tissue. As the disease progresses, it becomes more and more difficult for the liver to perform its functions and, in the end, it finally stops functioning. As a result, death occurs. With the development of cirrhosis, the mechanism of hemoglobin breakdown described above is disrupted.
- The binding of bilirubin slows down and more and more of it remains in free form.
- Unbound bilirubin does not enter the intestines and continues to circulate in the blood.
- Bilirubin excretion now occurs almost entirely through the kidneys. As a result, the formation of stercobilin does not occur in the intestines.
Thus, due to liver dysfunction, the amount of pigment in stool that determines its color decreases. In urine, on the contrary, bilirubin accumulates. As a result, changes in their color occur. In case of cirrhosis of the liver, urine darkens and gradually acquires a color like that of dark beers.
It should be understood that without careful laboratory tests it is impossible to determine liver cirrhosis. After all, urine can change its color under the influence of other factors. This can happen after eating a number of foods, such as beets. Some medications can also affect its color.
Cirrhosis is a disease that can be avoided if you lead a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to remember what factors are predetermining its occurrence. First of all, this is an excessive passion for alcohol. About 40% of patients with cirrhosis are alcoholics.
The danger of viral infection should not be ruled out. Therefore, it is necessary to get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
You should also not overload the liver by eating fatty and fried foods.
Further development of the disease
At the next stage of development of cirrhosis (subcompensation), an inevitable increase in destructive processes occurs, but a considerable part of the liver functions is still preserved.
The initial signs of liver cirrhosis are accompanied by new symptoms, which in themselves can often be considered as a secondary disease.
Namely:
- severe weight loss;
- discomfort, pain in the right hypochondrium, bitter taste in the mouth;
- periodic mild nausea, flatulence, belching of air or eaten food, alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- heaviness in the upper abdomen, a feeling of fullness even after eating a small amount of food;
- memory loss, impaired concentration;
- in women - deviations in the menstrual cycle, in men - erectile dysfunction;
- dryness and decreased elasticity of the skin;
- baldness (including legs and groin areas);
- sometimes pain in the back, ribs
Fatigue becomes excessive, a person feels drowsy even after a long sleep, and performance decreases. Often, patients leave themselves without treatment, attributing the first signs of liver cirrhosis to habitual gastritis or a stone in the bile ducts.
Further, the disease receives more and more distinct signs. And although it is generally accepted that there are no specific symptoms that are characteristic only of cirrhosis, there are those that most likely indicate liver damage.
Specific symptoms:
- jaundiced skin tone; The whites of the eyes and mucous membranes also turn yellow. Sometimes jaundice appears brightly, but it can also be mild;
- skin itching; the symptom develops due to the entry of bile acids into small vessels under the skin. (Normally, bile acids are constantly produced and processed by the liver; if the organ is damaged, their amount becomes excessive);
- redness of the palmar surface (the so-called “liver palms”), hands or some fingertips (palmar erythema); this is caused by an increased level of bilirubin in the blood;
- small, red interlacing of vessels (“stars”). Their typical location is in the shoulder girdle due to expansion (hypertension) of the superior vena cava;
- bruises of varying sizes, often for no apparent reason (both due to blood clotting disorders and weak blood vessels); minor spontaneous hemorrhages and nosebleeds may occur;
- periodic fevers, despite the absence of colds, elevated temperature (up to 38°C);
- the patient feels that the liver is “interfering” with him; by touch one can determine its enlargement and thickening, lumpiness; a sharp, protruding leading edge is noticeable (40% of cases);
- a person easily catches infectious diseases;
- a blue vascular pattern appears on the abdomen, reminiscent of intertwined branches (“jellyfish head”);
- hemorrhoids with bleeding and varicose veins;
- bright pink and even crimson color of the tongue; the tongue itself is smooth and shiny, as if varnished;
- cloudy and brown urine and light-colored feces;
- In men, the mammary glands become noticeably enlarged (gynecomastia).
We suggest you read: How much beer is healthy to drink per day?
Often, a patient with cirrhosis can also be recognized by the bright color of the skin, the unnaturally smooth border of the lips - they look like “varnished”. Their bright red color and the appearance of “stars” are associated with an excess of estrogen and serotonin in the blood.
The abdomen may bulge due to the accumulation of water in the abdominal cavity. Against the backdrop of severe weight loss, this becomes especially noticeable. The skin of a typical patient with cirrhosis is dry, pigmented, and traces of scratching are visible. A person may notice intolerance to fatty foods and alcoholic drinks.
As for such a common symptom as jaundice, it must be said that for patients with alcoholic cirrhosis at the very beginning it manifests itself only in 12% of cases, becoming noticeable in the terminal stage.
Thus, knowing how liver cirrhosis manifests itself, in the presence of a complex of similar symptoms, it can be distinguished from other diseases.
How the disease develops
There are 3 stages of the disease:
Compensated cirrhosis has very few symptoms that only a person who values his health can notice:
- Changed color of urine to the color of dark beer;
- Blood escaping from the gums when brushing teeth, bleeding from the nose are signs of a blood cell clotting disorder;
- Discoloration or black stool, blood, alternating diarrhea and constipation are a consequence of insufficient production of bile enzymes involved in the digestion of food;
- Fatigue, drowsiness, decreased performance.
With subcompensatory cirrhosis, you can still return to normal life if you consult a doctor in time and notice the following signs:
- Nausea, loss of appetite, indigestion, alternating constipation and loose stools;
- Loss of strength, severe weight loss;
- Aching pain on the right, abdominal enlargement is associated with stretching of the liver due to the inflammatory process.
Decompensated cirrhosis of the liver is characterized by symptoms:
- Itching of the skin, which manifests itself mainly at night, dry skin;
- Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum;
- Decreased libido, in men the figure becomes effeminate;
- Thin blood provokes subcutaneous hemorrhages with the slightest pressure on the body;
- The palms and feet change color - they become covered with red spots;
- The skin of the body and the whites of the eyes turn yellow.
Change in urine color in the treatment of liver cirrhosis
With proper treatment of liver cirrhosis, the color of urine will also change. Gradually it should lighten and return to normal, and the patient begins to feel much better. The liver is the only human organ prone to self-healing, so timely and competent therapy can work wonders in this case.
When confirming the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, doctors immediately prohibit the patient from drinking alcohol and put him on a therapeutic (sometimes salt-free) diet. These two factors are decisive for the success of treatment, which can be independently monitored by changes in urine color. The patient’s life expectancy in this case depends only on how much he follows all the doctors’ advice and what lifestyle he chooses for himself.
In case of liver cirrhosis, therapy can be prescribed in a strictly individual form, since its choice is influenced by factors such as age (at an advanced age, doctors make a conclusion about the duration of the disease, besides, older people are less responsive to therapy, and their liver cells are not so actively recover, like in young people), gender of the patient, since with female cirrhosis more severe lesions are observed, the presence of other diseases that worsen the prognosis of cirrhosis (hepatitis, AIDS and others).
We suggest you read: Signs of liver cirrhosis in men and women
When a patient is in the last stage of the disease, doctors must recommend liver transplantation, since otherwise everything will be fatal. But it is important to remember that even an organ transplant will not bear fruit if you continue to drink alcohol.
Cirrhosis of the liver is a deadly disease; the patient should voice any changes in his own well-being to the doctor so as not to miss the line after which no treatment will bring results. In the last stages or in severe forms complicated by concomitant diseases, patients are prescribed an inpatient treatment regimen.
The color of urine is a direct indicator of the success of the chosen treatment. If disorders in the disease are quickly diagnosed, the level of the dye in the urine will gradually return to normal. The liver is capable of effective regeneration, restoration of not only the tissue structure, but also the functionality of the organ.
The attending physician prescribes studies indicating liver cirrhosis to confirm the presumptive diagnosis:
- general analysis of urine, indicating changes in its color, transparency, concentration, and chemical composition;
- a blood test to look for general signs of inflammation in the body;
- blood tests for biochemical detection of enzymes - indicators of cellular destruction;
- stool analysis for the presence of bile enzymes.
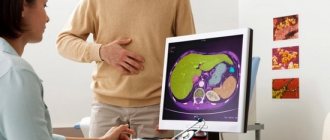
Laboratory methods are complemented by ultrasound of the affected liver so that the chosen treatment is as effective as possible.
The color of urine is a symptom not only of the development of pathology, but also a sign of successful therapy. Properly selected treatment slows down destructive processes in the body, and gradually the composition of urine returns to normal.
A diseased liver has an amazing ability to restore its structure and functionality. But only healthy organ tissues are subject to regeneration, so it is very important to diagnose liver cirrhosis in the early stages.
Factors that affect the color of urination
The color of urine depends on the concentration of pigments: urochromes, urozein, urobilin, uroerythrin, urates.
In a healthy person, it has a light yellow or slightly yellowish tint, called straw by doctors. The composition and color of urine can change during the day depending on physiological reasons and a number of pathologies:
Grandmother's recipe for the treatment of Alcoholism To get out of binge drinking you need every day... Reviews My story bezalkogolya.ru
Treatment of alcoholism according to the method of Elena Malysheva Alcoholism can be cured! It is necessary every day... Elena Malysheva’s website Interview with a doctor malisheva.ru
How to save your husband from binge drinking? Real story To get rid of binge drinking without the knowledge of an alcoholic... Official website Recovery zapoyu.net
You need to pay attention to the color of your urine
- taking medications (antibiotics, vitamins);
- volume of liquid drunk;
- physical activity;
- weather conditions (heat, humidity);
- eating foods that can color urine (beets, carrots, blackberries, blueberries, cherries, oranges, strong tea);
- intoxication of the body by parasites;
- metabolic problems, possible pathologies of the kidneys, liver and other diseases.
Urine of an unnatural color most often serves as an indicator of the presence of dangerous pathologies in the human body. If there are traces of pus or blood in the urine, or an unpleasant odor is felt after visiting the toilet, then you must urgently seek medical help and get tested.
Complications
Due to cirrhosis of the liver, disorders develop in other organs. “{amp}gt; Hepatorenal syndrome. This syndrome appears when the kidneys are damaged. Quite often, kidney failure begins to develop. At the same time, bleeding from the esophagus and stomach only intensifies. And:
- high blood pressure;
- rapid development of oliguria;
- azotemia. It indicates severe liver damage and possible imminent death. In this condition, the concentration of nitrogenous products in the blood is increased due to protein metabolism.
At the last, terminal stage of cirrhosis, the liver experiences almost complete degeneration and loses its functions.
Manifestations of the disease take on not just the character of individual external symptoms, but represent quite severe conditions.
The cause of brain dysfunction in cirrhosis is the powerful effect of toxins that the patient’s liver is not able to neutralize.
Signs of brain damage:
- deterioration of memory and speed of thinking
- disturbances of consciousness and intelligence, changes in behavior
- nerve and muscle disorders
Patients may sleep for days and stay awake all night. Irritability and inability to concentrate turns them off from the normal rhythm of life.
Hepatic encephalopathy is sometimes impossible to determine by yourself, and it is detected by a doctor using special tests. At extreme levels of development, it can cause coma (unconsciousness).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Cognac and cola – a mix that is becoming more and more popular
With cirrhosis, excess salt and water accumulate in the body. At first, only the legs and then the entire abdominal area swell.
Swelling, which often appears in the evening, is called spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Their reason is the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the abdominal part.
This complication is life-threatening, although in half of the cases it occurs without symptoms. The general condition may worsen: fever with chills, abdominal pain, problems with appetite and diarrhea may appear.
In later stages, numerous scars and tissue compression lead to a significant accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. The load on the kidneys becomes enormous, which is noticeable by urinary retention and dark, brownish urine.
This syndrome is called portal hypertension and is extremely dangerous, leading not only to a specific “pattern” on the chest and abdomen, but to serious bleeding and ascites.
As a result of bleeding, vomiting occurs, which looks like coffee grounds mixed with blood. Accompanying symptoms are dizziness, fainting or loss of consciousness. Bleeding may occur around the liver, esophagus, or stomach.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment is prescribed depending on the stage of cirrhosis and the extent of liver damage, the presence and nature of complications. As a rule, intensive drug therapy is indicated together with diet No. 5. It is possible to perform surgery through anastomosis and ligation of the hepatic artery. Self-medication is strongly discouraged due to the severity of the disease. Cirrhosis of the liver is incurable.
Cirrhosis is a serious disease in which liver tissue dies and scars form. Due to fibrous formations, the functions of the organ are impaired; it is not able to fully participate in digestion, cleanse the body of toxins, or synthesize fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
The gradual death of the liver lobes ultimately ends fatally. Cirrhosis occurs more often in men after 40 years of age. The main causes are chronic viral hepatitis and alcoholism. If both factors are combined, cirrhosis develops rapidly and has a particularly severe course. Rarely, cirrhosis is provoked by impaired outflow of bile, a side effect of medications. There are also cases when the cause of cirrhosis is not detected.
Manifestations of cirrhosis in the early stages
At the onset of the disease or the compensation stage, signs of liver cirrhosis often go unnoticed. At this time, the destruction of blood vessels, parenchyma and inflammatory-necrotic processes are not yet so strong.
Outwardly, this may resemble a condition that doctors usually call asthenic syndrome:
- general malaise;
- rapid fatigue and weakness;
- difficulty concentrating;
- decreased appetite.
Unfortunately, at this stage people are in no hurry to see specialists, although biochemical tests would not be difficult to establish the presence of cirrhosis.
Types of cirrhosis
There are 3 more types of liver cirrhosis, which are classified according to their clinical course, since not everyone has the same course of this disease. There are portal, biliary hypertrophic and mixed types of cirrhosis. Treatment is also different. The portal type is characterized by an increase in pressure in the hepatic venous system. Signs of this type of liver cirrhosis: “{amp}gt;
- bleeding from the nose and during bowel movements;
- blood impurities in vomit;
- loose stools;
- bloating;
- abdominal enlargement due to ascites. Also because of this, a venous network appears around the navel;
- weight loss resulting in complete cachexia;
- loose skin;
- low blood pressure.
It is characteristic that in the portal stage of cirrhosis the patient does not have jaundice. This cirrhosis can last from 6 months to 2 years. As a result of this type of disease, hepatic coma often occurs, and death can occur from acute bleeding.
Biliary hypertrophic cirrhosis is longer lasting, so it is considered favorable. It lasts from 5 to 8 years. Symptoms of biliary type liver cirrhosis:
- yellowness of the skin;
- xanthelasmas (yellowish growths), which are localized on the eyelids, chest, face;
- severe itching.
These symptoms are caused by stagnation of bile and a high concentration of bile pigments in the blood. Death in biliary cirrhosis occurs from bleeding.
The mixed type is the most severe form of cirrhosis, since it occurs with complications and symptoms are present from both portal and biliary cirrhosis.
Laboratory test results
After the consultation, the doctor will refer the patient for diagnostics - laboratory, instrumental. The following diagnostic measures are considered basic for making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment:
- UAC. A blood test reveals a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells due to impaired absorption of B12 and folic acid. The number of platelets responsible for stopping bleeding (clotting) is also reduced. Increased ESR, which indicates inflammation;
- liver tests. A decrease in albumin, an increase in bilirubin, and an increase in the activity of AST, ALT, and GGTP are detected. Kidney function indicators – urea, creatinine – increase. Glucose levels also increase;
- OAM. A urine test reveals many red blood cells and white blood cells. Proteinuria is observed - the kidneys filter the protein and excrete it in the urine. Sugar is also detected in the urine;
- Ultrasound. The study reveals an enlargement of the spleen and liver. The structure of the liver tissue is heterogeneous; there are regeneration nodes. The pressure in the portal vein increases. The kidneys are enlarged, the tissues are heterogeneous and light.
The results of tests and diagnostic equipment help the hepatologist establish the stage, nature of the disease, and choose the right treatment.