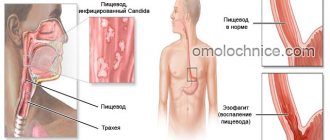
Erosion of the esophagus is a very insidious disease, and its development threatens with serious complications, including cancer. Symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation and nausea are often not a cause for concern in patients who try to treat themselves at home. Doctors insist that if you suspect esophageal erosion, you should not hesitate, but consult a specialist to determine a diagnosis and prescribe a treatment program. With timely treatment, erosive lesions of the esophageal mucosa heal completely without scarring or deformation of the esophageal tube.
- 2 Classification of the disease
- 3 Causes of occurrence
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 Treatment
6.1 Medication
6.1.1 Medicines used for esophageal erosion, pictured
- 6.2.1 Recommended products in the photo
- 6.3.1 Traditional medicine in the photo
What is esophageal erosion
Ulcerative lesions of the digestive system
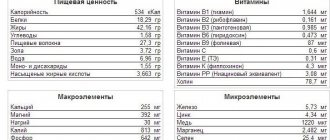
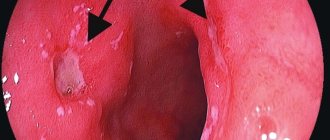
Esophageal erosion is a disease associated with defects of the esophagus, its inner layer, and damage to the mucous membrane due to the action of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. It irritates and corrodes the sensitive mucous membrane of the esophageal tube, which causes inflammation and ulceration.
Methods of examining patients
Erosion can appear unnoticed by humans. Symptoms already appear with severe inflammation. Before treating a person, it is necessary to exclude other pathologies of the digestive system. For this purpose the following studies are carried out:
- FEGDS;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- pH-metry;
- urine and blood tests;
- stool examination for the presence of occult blood;
- biopsy;
- X-ray examination of the esophagus.
To exclude intestinal pathology, a colonoscopy is organized. The simplest and most accessible diagnostic method is esophagoscopy. It is often supplemented by manometry. In the latter case, the contractility of the esophagus is determined. During fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, it is possible to identify the pathology of the stomach and duodenum. This is a traditional diagnostic method for suspected esophagitis and GERD. During the study, a fragment of the mucous membrane is taken. The procedure is necessary to exclude metaplasia and cancer. For subsequent treatment, it is important to determine the acidity of the stomach and the presence of Helicobacter bacteria in the blood. Additionally, an enzyme immunoassay is organized. To exclude cardiac pathology (CHD), electrocardiography is performed.
Classification of the disease
| Due to erosion | |
| Primary type | Secondary type |
| Damage to the mucous membrane is an independent disease | Erosive lesions are a symptom of another disease |
| By type of damage | |
| Malignant changes | Erosions not associated with malignant lesions |
| Erosion of the mucous membrane appears when serious processes of development of Crohn's disease or a malignant tumor occur in the esophagus. | Conditions causing ulceration:
|
Although certain classifications for esophageal erosion have been drawn up, research continues into causative factors and symptoms to more accurately identify the types of disease.
Possible complications
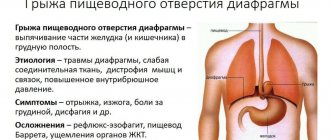
If you ignore the symptoms of the disease and do not seek help from a specialist for a very long time, severe consequences may develop, such as the formation of deep ulcers, perforation of the esophageal wall, bleeding, and the appearance of neoplasms.
Each of these complications can lead to death, so there is no need to delay treatment.
Failure to provide timely assistance when symptoms occur can lead to dangerous consequences:
- open bleeding;
- rupture of a vessel;
- vomiting blood;
- thrombosis;
- the formation of a deep ulcer;
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- problems with swallowing, passing food;
- peritonitis;
- the appearance of a malignant tumor.
Erosion of the esophagus negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. When scar deformities and obstructions appear, the digestive process is disrupted, which can lead to serious complications.
Causes
The reflux of gastric juice into the esophageal tube and the erosion of the mucous membrane by hydrochloric acid leads to the formation of erosions
In most cases, esophageal erosion is a consequence of other diseases that provoke the reflux of hydrochloric acid into the esophageal tube. The appearance of erosion is caused by a sum of factors that create favorable conditions for the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus and further damage to the mucosa.
Often the disease is caused by pathologies of the esophagus. As a rule, they are associated with a hernia formed in the diaphragmatic opening due to the movement of peritoneal organs into the chest area through this opening.
Factors for the development of such hernias:
- weak tone of the muscles of the walls of the esophagus;
- significant shortening of the esophageal tube due to neoplasms or inflammation;
- stretching of the sphincter in the lower part of the esophagus;
- deficiency of fat, which should be under the diaphragm;
- curvature of the thoracic spine (typical of the older generation).
In addition to these pathologies, there are the following causes of erosion:
- traumatic injuries to the esophageal mucosa;
- complications after surgery;
- chemical or thermal burns of the mucous membrane;
- regular negative impact of harmful substances (ethanol, nicotine, heavy metals, particles of welding and foundry gases, chemicals);
- severe mental disorders, prolonged stress conditions;
- diabetes and high blood sugar;
- liver damage, renal failure;
- hereditary anatomical pathologies;
- abrasions, scratches on the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube due to eating spicy or hard foods.
Diet
The diet, in addition to observing the intake and refusal of certain dishes, also includes a number of nutritional rules, the observance of which is mandatory:
- Eating too cold or hot food can worsen the patient's health.
- Doctors recommend drinking 200 ml. milk every time before going to bed.
- While consuming food, you should completely avoid drinking water or other drinks.
- During an exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to exclude from the diet any vegetables or fruits that have not been subject to pre-heat treatment.
- Food should be consumed more often than usual - 6 times. You need to eat in small portions. This will get rid of high acidity.
- During an exacerbation, it is also recommended to take soft, porridge-like foods. These are cream soups, pureed vegetables and fruits, boiled fish, jelly or jelly.
For esophageal erosion, the doctor may prescribe one of the following diets:
- Therapeutic diet 1a - prescribed for exacerbation.
- Therapeutic diet table 1b - prescribed after 10-14 days.
- Diet No. 1 is prescribed after 20 days.
During the period of decline of the disease and recovery, the doctor usually prescribes diet No. 1, but the specialist can make some adjustments to it.
You can consume:
- warm drinks and warm, gentle dishes;
- dairy products;
- steamed chicken or low-fat fish cutlets;
- steamed and boiled dishes in crushed form.
The list of what is not recommended to consume is much wider. It includes:
- fried meats and fish, fried vegetables and fatty foods;
- sauces;
- hot spices;
- ice cream, cold drinks;
- hot dishes;
- dry food without pre-processing;
- soda;
- sour juices and compotes;
- strong drinks.
Even the slightest deviation from the nutritional rules prescribed by the doctor can lead to an immediate deterioration in the patient’s condition. As a preventative measure, it is recommended to quit smoking. Source: gidmed.com
Symptoms
Signs of erosion of the esophageal tube are often very similar to symptoms characteristic of other diseases of the stomach, small intestine and liver, so difficulties often arise with the initial diagnosis. Sometimes the pathology passes for a certain time with erased clinical symptoms.
Manifestations of esophageal erosion:
- burning in the esophagus, lower part of the sternum, stomach;
- obvious pain or discomfort, aggravated by eating (due to hydrochloric acid corroding already damaged areas of the esophagus). When a large number of ulcerations appears, the mucous membrane changes shape and shrinks in places of scarring, which makes it difficult for the food bolus to pass;
- dull or sharp pain, similar to the pain and burning sensation of angina pectoris (in the chest area, abdomen);
- pain and heartburn that appear when changing body position (when bending over, lying on the right side, on the stomach);
- a feeling of heaviness, fullness, pressure, decreasing when standing;
- painful or difficult swallowing or dysphagia (especially severe manifestations are observed when trying to swallow coarse, hard food);
- belching food or air;
- frequent hiccups;
- regurgitation, gagging;
- copious secretion of saliva;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Important! Often, burning sensation in the esophagus and heartburn are treated with disdain, believing that the condition occurs only due to poor nutrition. In this case, patients try to eliminate the burning sensation with baking soda, which brings some relief, but then provokes an even greater release of caustic acid. To relieve heartburn, gastroenterologists advise drinking low-fat milk or water with low-acidity honey.
Walnut tincture
To treat the esophagus, it is better to use unripe rather than ripe nuts, since they are rich in bioflavonoids, polyunsaturated acids, quinone, and tannins. Using the tincture for erosion will quickly eliminate pain, relieve inflammation, and reduce stomach acidity. It should be used in acute forms of erosive esophagitis, 1 tbsp. l., diluted in 125 ml of water after meals 3 times a day for 14 days. Method for preparing walnut tincture:
- crush 500 g of nuts;
- pour 500 ml of vodka;
- leave to infuse in a dark place for 14 days.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing erosion, a traditional examination scheme is used, similar to the diagnosis of other diseases of internal organs.
- Complaints are collected, anamnesis (medical history) is established, areas of particular pain and other signs are identified: how often attacks of pain occur, at what time, in what position the pain becomes most intense, whether it radiates to the neck, sternum, spine.
- If symptoms worsen, additional research is carried out to identify or exclude tumors of malignant origin.
- In the presence of vomiting, one of the signs of erosion, analyze how its appearance is related to the time of consumption of food. In certain cases, such a symptom is observed with cardiospasm or cancerous tumors in the upper part of the stomach.
- When diagnosing erosion of the esophagus, the condition of its mucous membrane, liver, stomach, pancreas, and nervous system is simultaneously carefully examined.
- To exclude diseases with similar symptoms, existing diseases of the heart, intestines, stomach, lungs, bronchi are assessed, the presence of noises when swallowing saliva and food is detected, and the condition of the neck, chest, and skin is examined.
- Erosive lesions of the esophagus are most often detected by endoscopy, a method that provides the most accurate picture of the disease among the available diagnostic methods.
Treatment
Medication
Medical practice shows that with proper therapy, the prognosis for treating erosion is quite favorable - damaged areas on the mucous membrane of the esophagus are restored, sometimes without the formation of scars.
The basis of therapy is medications that neutralize hydrochloric acid and suppress its abundant secretion.
The following medications are used:
- Prokinetics (Domperidogn, Motilium), facilitating the process of digestion and evacuation of food from the stomach. In the lower part of the esophagus, pressure increases, and the time of contact of hydrochloric acid and peptins with the mucous membrane is reduced.
- Antacids that reduce irritation of the mucous membrane with hydrochloric acid. Almagel, Gastal, Phosphalugel, Vikalin - drugs that belong to this group reduce the severity of heartburn, burning, and belching.
- Alginates (eg Gaviscon), which form a thick foam that coats and protects the lining of the esophageal tube.
- Mucus-forming drugs (Sucralfate, Keal, Venter) protect the affected areas of the mucosa from the action of aggressive hydrochloric acid, bile, pepsin, which can no longer damage the ulcerated surface.
- Proton pump blockers that suppress the formation of hydrochloric acid:
- omeprazole;
- rabeprazole (Pariet);
- lansoprazole;
- esomeprazole (Nexium, Neo-Zext, Emanera) is one of the safest and most effective drugs.
Treatment of an unadvanced disease usually does not last long - with an exacerbation, scarring is completed by 10-12 days, in certain cases it lasts up to 2-3 months.
The chronic form of erosion, as a rule, is protracted; some patients experienced a practically asymptomatic course of the disease, which lasted for several years.
Medicines used for esophageal erosion, pictured
Gaviscon creates a gel protective barrier that protects the mucous membrane from the effects of gastric juice
Omeprazole inhibits the secretion of hydrochloric acid
Almagel chemically neutralizes the effect of hydrochloric acid
Motilium facilitates the digestion process, reducing the time of contact of hydrochloric acid with the mucous membrane
Diet therapy
For esophageal erosion, therapy with drugs and folk remedies gives a positive result only if you follow a therapeutic diet .
Basic Rules:
- eating slowly, eating frequently and in small portions;
- ban on alcoholic drinks;
- eating only warm food, you are not allowed to take anything very cold or hot;
- prohibition on hard, hard foods that scratch the mucous membranes;
- during an exacerbation, the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables that cause gas formation is not allowed;
- Cooking should only be done by baking, boiling, or steaming.
Products allowed for consumption:
- pureed vegetable soups with cream or sour cream;
- steamed fish, meat cutlets or boiled meat in minced form;
- jelly made from sweet fruits, berries, oatmeal jelly;
- kefir, yoghurt, curdled milk, low-fat milk, sour cream, hard and processed cheese;
- cottage cheese of low acidity and fat content;
- baked cheesecakes, dumplings, cottage cheese casseroles;
- egg dishes: omelettes, poached eggs, soft-boiled eggs, egg soufflé with minced meat;
- side dishes from well-cooked cereals;
- pasta, noodles and casseroles made from them;
- boiled potatoes, mashed potatoes;
- boiled, baked vegetables (carrots, cauliflower, white cabbage, zucchini, peeled eggplant, beans, soft peas with delicate skin, broccoli);
- baked apples with jam (not sour);
- watermelon, melon, cherries, grapes (without skin), bananas, blueberries and ripe strawberries, strawberries only of sweet varieties;
- boiled dried fruits (in compotes);
- soufflé, marmalade, marshmallow;
- baked goods without a hard crust.
Recommended products in the photo
Steam cutlets
Dairy products
Omelette
Boiled vegetables
Mashed potatoes
Avoid foods that provoke excessive production of hydrochloric acid from the diet:
- hot, smoked, salty, spicy and fatty dishes;
- coffee, hot chocolate, strong tea, sparkling water, any cold drinks;
- chocolate, especially dark varieties;
- citrus fruits and any sour fruits;
- fried meat, strong broths;
- pickles, marinades;
- nuts, seeds;
- caramel, dried fruits;
- spices (you can use vanilla, cinnamon).
Photo gallery of prohibited products
Coffee
Currant
Grilled meat
Ice cream
Pepper
Smoked meats
Nuts
Citrus
Chocolate
Folk remedies
Before starting to use home methods, it is necessary to obtain the advice of a gastroenterologist, otherwise it is difficult to predict the result of the simultaneous use of herbs and medications. Their possible incompatibility can easily cause harm instead of benefit.
The most famous safe folk methods:
- Using fresh potato juice. It is necessary to take 50 ml of juice half an hour before meals 3-4 times a day for 8 weeks. Repeat the course every 4 months. In case of exacerbation of erosion, this potato “medicine” quickly reduces inflammation, alleviates pain, and promotes rapid healing of damage.
- Carrot juice perfectly restores tissues affected by erosion. Drink 70 ml of juice 2 times a day. They also use a potato-carrot mixture, making a cocktail from an equal amount of ingredients.
- For damage to the esophagus, an infusion of dill, St. John's wort, chamomile, marigold, linden flowers, valerian root, immortelle and fennel has healing properties. Crushed herbs (a tablespoon of the mixture) are poured into a glass of boiling water and drunk 50 ml 3-4 times a day. The infusion relieves inflammation and kills pathogenic microflora.
- A good way is to take sea buckthorn oil (a teaspoon 2 times a day 20 minutes before meals). The course lasts 6-8 weeks.
- Medicinal collection: the roots of comfrey and valerian are mixed with wormwood, burdock, tartar, cocklebur, and viburnum flowers. They take equal shares. A mixture of 30 g is brewed with a liter of boiling water, leaving for at least 12 hours. Drink 2/3 cup before meals. One of the herbs is comfrey, a powerful natural regenerative healing agent.
- Flaxseed mucilage. For 1 share of seeds, take 30 parts of boiling water, and leave the mixture for about 30 minutes. Drink mucus one tablespoon at a time. Mucus gently envelops the inner wall of the esophagus, eliminates pain, and accelerates tissue restoration. It is a natural replacement for Almagel and Phosphalugel, acting just as quickly, but without causing addiction.
Traditional medicine in the photo
Dill
pharmaceutical camomile
Flax-seed
Propolis
Comfrey
Calendula
Potato juice
carrot juice
Doctors recommend using traditional methods of therapy during the period of weakening of the disease and after treatment with medications.
Honey
Honey therapy will help increase the intensity of tissue regeneration and reduce the inflammatory process in the esophagus. This unique product will improve your general condition and strengthen the body's protective functions. To treat erosion, it is better to use rapeseed or buckwheat honey. Directions for use:
- In the morning on an empty stomach, hold 1 tsp in your mouth. honey until completely dissolved (treatment can be continued for a long time);
- consume 3-4 times/day, 1 tbsp. l. between meals;
- add 1 tsp to warm milk, water, herbal infusions.