Purulent paraproctitis can occur in acute or chronic form. In acute cases, abscesses form on the fatty tissue, which hurt, bleed and cause a lot of inconvenience.
Acute purulent paraproctitis includes the following symptoms: pain, suppuration, swelling. When the disease occurs, a fairly large volume of fiber is affected, and sometimes muscles and connective membranes can even be destroyed. It spreads quickly, new tissues are affected, death begins, and swelling increases.
There are several forms of acute purulent paraproctitis , each of which has its own differences, symptoms and methods of treatment.
Forms of the disease and causes of appearance
Acute purulent paraproctitis can be divided into two main large groups: depending on the etiology of occurrence and the localization of infiltrates.
The first group includes the following types of paraproctitis:
- ordinary;
- anaerobic;
- specific;
- traumatic.
The second group includes:
- ischiorectal;
- subcutaneous;
- submucosal;
- retrorectal;
- pelviorectal;
- necrotic.
Most often, the disease begins to develop due to the penetration of various pathogenic organisms into the peri-rectal tissue. Anaerobes, which cause purulent paraproctitis, affect the fiber and rectum so much that it can cause complete tissue necrosis.
Pathogenic microorganisms can enter in two ways:
- with the bloodstream - all local inflammatory processes are associated with the intensive proliferation of bacteria, which then hematogenously enter the fatty tissue. Sometimes any inflammatory process not associated with a specific organ can cause infection (for example, caries);
- contact - when a gland ruptures, which contains a certain secretion, suppuration appears, infection enters the tissue, inflammation and infection occur.
In rare cases, infection can occur as a result of trauma, injury, or surgery. But such situations are extremely rare.
If we talk about risk factors for the occurrence of purulent paraproctitis, we can highlight the main ones:
- persistent problems with bowel movements;
- hemorrhoids and anal fissures;
- weak immune system;
- diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis.
By and large, the disease develops quite rapidly. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, the abscess may open, and this will lead to additional health problems.
What it is
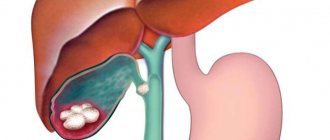
To understand what paraproctitis is, it is necessary to take into account the structural features of the rectum. This organ is the last section of the intestine located in the pelvic cavity. In an adult, the length of the rectum is 15-20 cm. The organ passes into the anus (anus).
The walls of the rectum consist of:
- mucus - this is the inner layer, consisting exclusively of cells that produce mucus;
- muscle layer - consists of muscles that form sphincters that hold back feces;
- the outer layer is the serosa.
These three layers are internal; the outside of the rectum is protected by fatty tissue. When the inflammatory process begins in it, this disease is called acute paraproctitis. With paraproctitis, the infection penetrates into the tissue from the rectum.
Main symptoms
All acute purulent inflammations are characterized by general symptoms, although the disease itself can occur individually:
- a sharp and rapid increase in temperature. If the abscess is deep, the temperature usually rises no higher than 37.5, but if it is close, then in this case an increase to 38-39 degrees is possible;
- general weakness, deterioration of health, intoxication of the body;
- pain in the affected area, which intensifies during bowel movements;
- redness in the buttocks, pain when touching them.
Pain, temperature - all these are the first and main signs of the disease. You should not put off visiting a doctor, because this can result in quite unpleasant and disastrous consequences.
Treatment
When diagnosed with “acute purulent paraproctitis,” surgical intervention is most often necessary. If the operation is not carried out in a timely manner, this can lead to consequences, and they will not always be the most pleasant:
- self-healing - release of pus to the outside, healing of the wound. This happens extremely rarely, so you shouldn’t hope and wait, this is, of course, an ideal option, but not everyone is lucky, so it’s not worth the risk;
- the release of pus inside, its spread through the tissues, infection - pus can enter the blood, and in this case the prognosis is extremely unfavorable;
- the pus comes out, but not completely, a chronic focus is created, the patient suffers from constant relapses of the disease;
- full of pus from the source of inflammation, but the wound does not heal - pathogenic bacteria can constantly enter it, the inflammatory process is constantly getting worse. The prognosis is unfavorable.
If an operation is prescribed, you should under no circumstances refuse it, this can lead to the following consequences:
- development of phlegmon and penetration of infection into deeper tissues of the body;
- pelvioperitonitis;
- spread of infection into the abdominal cavity, development of peritonitis;
- purulent melting of organs - if pus penetrates inside;
- thrombosis;
- sepsis.
If surgical intervention is not carried out in a timely manner, the acute form of the disease will become chronic, and then more serious consequences and health problems simply cannot be avoided.
Methods of therapy
The chronic type of paraproctitis can only be removed surgically. But treatment of the disease is possible using traditional methods.
It is recommended to treat paraproctitis without surgery
- medications;
- folk methods;
- maintaining a proper balanced diet.
The goals of treating paraproctitis at home are to eliminate the symptoms and the causes of the pathology. Surgical intervention is contraindicated for young and elderly people, patients with chronic diseases in remission.
Medications
The use of medications is effective at the early stage of detection of the disease. Treatment of paraproctitis at home involves the use of:
- antibacterial drugs;
- painkillers;
- rectal suppositories, suppositories;
- external ointments, gels.
Taking medications is aimed at eliminating spasms, itching of the anus after bowel movement, normalizing stool, eliminating pathogenic bacteria and infections.
It is possible to cure paraproctitis without surgery using antibacterial agents. The drugs Cefepime, Betasporin, Amoxicillin and others reduce inflammation and swelling of the anal canal, prevent the occurrence of fistulas, remove pathogenic microbes, and eliminate symptoms of intoxication. Effective drugs that reduce pain are antispasmodics Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Ketolorac.
Treatment of paraproctitis without surgery is effective with the help of rectal suppositories Relief, Olestezin, Anuzol, etc., which eliminate the symptoms of the disease and have an antibacterial effect on the affected areas of the rectum. External ointments Levomekol, Levosin, Vishnevsky are used to reduce the inflammatory process.
Traditional methods
Treatment of paraproctitis with folk remedies is possible:
- baths;
- lotions, compresses;
- rectal suppositories;
- infusions, decoctions;
- microenemas.
It is recommended to treat paraproctitis at home with the help of herbal preparations, including chamomile, string, calendula, yarrow, as well as mumiyo and food products used daily.
Baths
Thermal baths and lotions are an effective method of treating paraproctitis and diseases of the pelvic organs with folk remedies. The procedures have an anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect on the affected areas of the rectum.
The main rule is to maintain the temperature of the water, which should not be hot to avoid an increase in purulent formation. The main components used to achieve an effective result are mumiyo, herbal preparations (chain, oregano, oak bark), soda and salt, milk and garlic.
To prepare the bath, the selected components are dissolved in warm water. A decoction is first made from solid ingredients, such as tree resin, and then added to the liquid. The procedure takes at least 15 minutes until the water cools down once a day for several weeks.
Lotions, compresses
It is possible to cure paraproctitis with the help of compresses and lotions. The main rule is to create a temperature regime for deep penetration of the active components. To do this, it is recommended to place a plastic bag or thick paper on the main components of the compress.
Operation
After surgery, complete recovery occurs in 90% of cases. Most often, the operation is carried out quickly and easily - initially you need to open and clean the inflammation, then remove the connection to the rectum.
In some cases, it is not possible to perform the operation at once. This can happen for various reasons. In such cases, the purulent focus is first cleaned, and after some time it is removed.
The operation does not require any special preparation; moreover, it is most often carried out according to indications and in the serious condition of the patient, in emergency conditions. Surgical intervention requires precision and compliance with all rules; it must be carried out by an experienced proctologist.
The operation requires complete muscle relaxation, so it is performed under anesthesia. The simplest operation for subcutaneous paraproctitis - in this case, an incision is made, pus is released, all connecting bridges are removed, the wound is drained or tamponed. Usually an experienced proctologist carries out both stages at once. If the doctor doubts his abilities, he can postpone the second stage of the intervention for several days or weeks.
Methods for diagnosing paraproctitis
Diagnosis of paraproctitis is a mandatory and important medical measure, allowing a specialist to most accurately determine the form and stage of the disease. Only based on the results obtained during diagnosis, a proctologist can prescribe an effective treatment for the inflammatory process in the rectum to the patient.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by proctological and surgical specialists. Using the patient’s clinical picture and complaints as a basis, the specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis. A proctologist or surgeon must differentiate paraproctitis from a festering benign tumor and intestinal tumors, and the subcutaneous form of inflammation from a boil.
Diagnostic methods such as manual and instrumental examination, as well as sigmoidoscopy and some other manipulations, are not performed because they are very painful. They can be used only in some cases, always under anesthesia on the operating table, usually before the operation.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, an ultrasound of the perineum with a rectal sensor, computed tomography, fistulography - x-rays are performed to identify tumors and fistulas in the rectum.
Postoperative period
Although the operation itself is not complicated and does not require special preparation, after it is carried out it is necessary to follow some rules and recommendations of the doctor.
First of all, the patient is not discharged from the hospital immediately. He must spend several days in the hospital so that doctors can observe him and assess his health. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and painkillers if necessary. Dressings are performed, which are usually very painful.
Diet is an important step on the road to recovery. During the postoperative period, it is important not to overstrain the muscles and sphincter during bowel movements. The patient can eat semolina or rice porridge with water, drink tea, kefir. Other fermented milk products, baked vegetables and fruits are gradually added. You can only diversify the menu gradually; you shouldn’t do it all at once. Alcohol, salty, fried, fatty foods are strictly prohibited. If three days after the operation there is no normal stool, the patient is given a cleansing enema.
After discharge, the patient takes care of himself - makes dressings and treats the wound with antiseptic agents (hydrogen peroxide is suitable). After defecation, the bandages must be changed and the wound thoroughly cleaned.
The period of incapacity for work after surgery is no more than 10 days, although complete recovery and wound healing occurs only after a month.
Prevention
No one is immune from the disease. If you are at risk, it is necessary to promptly treat all concomitant diseases. It is necessary to eat right and improve your bowel movements - this will also help to significantly reduce the risk of developing this disease.
If you have frequent constipation, you should not get too carried away with laxatives or enemas - all this can also lead to the development of pathology. For prevention, you can regularly perform simple physical exercises that prevent blood stagnation in the pelvic organs.
If symptoms of purulent acute paraproctitis appear, do not be afraid to go to the doctor. Fears can harm your health and make the situation worse. If the disease is advanced, treatment will be difficult and ongoing, and the consequences may be irreversible.