Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis are varied. Determining the disease is not difficult. Despite the fact that candidiasis is a disease caused by opportunistic flora, it cannot be avoided without proper treatment.
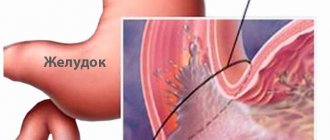
Intestinal candidiasis is a pathological condition of the gastrointestinal tract caused by pathogenic mycoses of the genus Candida. Normally, microorganisms are found in the normal flora of a healthy person. The development of the disease occurs against the background of uncontrollable growth of fungi. The appearance of symptoms is due to the negative influence of candida waste products.
Symptoms of the disease
The main manifestation of thrush in the intestines will be severe pain, in addition to which you should pay attention to the following signs of invasion:
- bloating becomes chronic;
- patients complain of heaviness in the epigastric region (stomach);
- after eating, intestinal spasms are observed;
- impaired intestinal motor function (diarrhea);
- low-grade body temperature (from 37 to 37.50);
- patients complain of lack of appetite;
- impurities of blood and pus are found in the stool;
- in the anal area and stool you can find a cheesy discharge with a foul odor;
- after bowel movement there is no feeling of relief;
- pain during defecation;
- false urge to defecate;
- a rash appears on the skin.
In addition to the primary signs of pathology, fatigue, insomnia and various forms of skin diseases (acne, dermatitis, urticaria) may appear.
Regardless of the severity of the clinical picture, intestinal candidiasis can be easily determined by an experienced doctor (gastroenterologist).
As the pathological spread of fungi progresses, all symptoms intensify. Lack of treatment allows the pathology to spread to various parts, most often the disease affects the genitourinary organs and the oral cavity. In addition to spreading, candidiasis provokes an exacerbation of existing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The transition of thrush from the intestines to the genitals in a woman has the following symptoms:
- cheesy discharge is detected on the genitals and underwear, having an unpleasant odor;
- unbearable itching of the vagina, turning into a burning sensation, can be observed at rest, during urination or sexual intercourse;
- in severe forms of the disease, menstrual function may be impaired; long-term infection can cause secondary infertility.
Symptoms in men are not very different:
- itching and burning of the penis and scrotum;
- discharge of a cheesy nature (outwardly reminiscent of cottage cheese);
- disturbance of urination, pathogenic fungi are detected in the urine (visually the urine has a cloudy whitish sediment).
Intestinal infection with candida fungus has a pronounced clinical picture
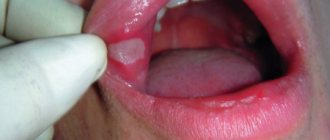
When the oral cavity is affected, inflammation of the mucous membrane, a white coating that can be easily removed with a spatula or gauze swab, and pain during eating are determined.
Advice. When identifying the first signs of intestinal candidiasis (or simply long-lasting pain), you should contact a gastroenterologist in order to find out the cause of the negative sensations and timely treatment of the infection.
What is intestinal candida?
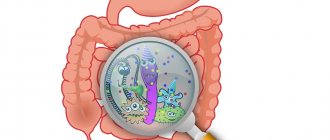
Intestinal candida is an infection that occurs when the bacteria in our intestines become unbalanced and increase in size.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
Why is this happening? This intestinal infection usually affects those people who eat a lot of carbohydrates, refined foods, alcohol, processed foods, etc. This type of diet also feeds bacteria and, by destroying sources of short-chain fatty acids, causes intestinal gas and swelling.
Other types of bacteria can also break down bile salts before the body can use them, which is why our body doesn't absorb fat well and causes problems like diarrhea.
Additionally, a third type of bacteria can produce toxins that damage the lining of the small intestine, preventing the body from absorbing essential nutrients.
Reasons for the development of candidiasis
Intestinal fungus does not cause problems if the immune response is good. For the development of the disease, certain conditions are necessary that favor the development of mycosis:
- decreased resistance of the body to the development of pathogenic flora under unfavorable environmental conditions (sudden time zone changes, temperature changes, high or low humidity);
- chronic infections;
- diseases of internal organs;
- immunodeficiency (congenital or acquired);
- uncontrolled treatment with antibiotics;
- suppression of immunity during the treatment of oncological processes (chemotherapy or radiation);
- imbalance in the hormonal background (the cause may be diseases of the endocrine system, hormone intake, menopause, pregnancy);
- malnutrition (favorable conditions for candidiasis are created by lovers of flour products with a rare and inconsistent diet).
Uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs is the most common cause of candidiasis.
Important. Candidiasis develops only against the background of a weakened immune response of the body. Which indicates the need for an integrated approach to the treatment of pathology. In addition to the use of antifungal agents, a necessary condition for recovery is the elimination of the root cause of the pathological growth of candida.
Prognosis and prevention
Intestinal candidiasis is a dangerous disorder of the digestive system because it can develop in the human body for a long time without any special symptoms. However, these symptoms should not be underestimated as they can lead to the development of autoimmune diseases and mental disorders.
Prevention of intestinal dysbiosis will be a nutritious and varied diet, limiting the consumption of simple carbohydrates. Patients at risk of developing intestinal candidiasis require close attention, that is, an annual preventive examination. Take care of yourself and always be healthy!
https://youtu.be/tt55HIwJ3dY
Treatment
Only a doctor can determine how to treat intestinal candidiasis. Elimination of pathology should be comprehensive and carried out in two directions:
- stopping the growth of mycoses and destroying the already expanded network;
- treatment of a disease that causes a decrease in immunity.
When choosing treatment tactics for the condition, the doctor takes into account the form of the disease, the severity, the risk of a complicated course, the state of the immune system and the underlying disease that gave rise to thrush.
Antimycotic treatment
To stop the development of fungus in the intestines, antimycotic drugs are prescribed (impact on the growth of candida). When choosing a remedy, preference is given to a topical drug (the most commonly used form is rectal suppositories). The most commonly used:
- Nystatin;
- Levorin;
- Pimafucin.
Pimafucin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that acts in the intestinal lumen without affecting systemic blood flow.
For severe forms of infection, systemic drugs are used: Fluconazole, Itraconazole, and others. These medications may be prescribed in the form of tablets (orally), solutions (intravenously), or suppositories (rectally). A combination of forms of local and systemic influence is possible.
Important. The choice of drug and treatment regimen is selected individually. The use of rectal suppositories should only be after a carefully carried out hygienic procedure (you should wash with baby soap without any additives).
Treatment of dysbiosis
In addition to destroying Candida fungi in the intestines, treatment of the disease is impossible without restoring healthy intestinal microflora.
When choosing prebiotics and prebiotics at the time of antifungal therapy, drug stability should be taken into account. This group helps eliminate intestinal dysbiosis, which leads to normalization of the digestive system. Drugs suitable for normalizing microflora after antimycotic therapy:
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Acylact;
- Biosporin;
- Linux.
Application of enzymes
To relieve symptoms during treatment of gastrointestinal thrush, a gastroenterologist may prescribe enzymes. The rapid breakdown of food under the influence of enzymatic action allows the patient to relieve flatulence and improve intestinal motor function.
Immunity restoration
When the body's immune response decreases, immunocorrective or immunomodulatory drugs are included in fungal therapy. The choice of medications is made by an immunologist after determining the level of imbalance and identifying the cause of the pathology.
Traditional therapy methods
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis with folk remedies is auxiliary and is selected by a specialist.
Important. Self-medication of thrush with folk remedies can have irreversible consequences, especially during pregnancy and in the treatment of young children.
Sea buckthorn oil
Taking sea buckthorn oil helps against fungal infections of the intestines. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, this remedy stimulates the immune system (strengthens the body's resistance) and has a protective effect on the irritated walls of the digestive tract.
This remedy has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect, is rich in vitamins that strengthen the immune system and promotes the rapid restoration of tissues damaged by inflammation
Sea buckthorn oil is considered one of the best traditional medicines that triggers the mechanism of tissue regeneration (healing and restoration). Take 1-2 teaspoons per day (depending on the patient’s build) for up to 10 days during meals.
Advice. To improve the absorption of sea buckthorn oil, include more raw vegetables in your diet.
Baking soda and iodine
For local treatment of thrush, baths in a soda solution with potassium permanganate are used. Washing the external genitalia when infected with fungus is also effective.
It is recommended to carry out the procedure 2-3 times a day. For a bath or wash, you will need to dissolve 1 teaspoon of table soda and iodine in 1 liter of boiled and cooled water.
The course of treatment is at least 10 days. Even if symptoms disappear after the first procedures. This will prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Herbal decoctions
From plant materials, you can choose drugs that have anti-inflammatory, regenerating or immunocorrective properties.
The most common intake is white chamomile, sage, St. John's wort, oak bark, bird cherry, pomegranate peels, black currant leaves, etc.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a person's Candida infection is difficult due to the fact that many people experience non-invasive candidiasis and transient candidiasis - conditions in which pathogenic Candida fungi are present in the body, but their rapid growth is blocked by the immune system. A detailed blood test for severe intestinal candidiasis can only detect a significant decrease in the level of lymphocytes, erythrocytes and leukocytes.
At the first symptoms of the disease, you should contact a general practitioner, who will refer the patient with candidiasis to a consultation with an endoscopist. This specialist, depending on the symptoms, will choose the optimal method for examining the intestines. Endoscopy is a diagnostic method based on visual examination of the colon cavity using an optical device inserted into the organ. This research method can detect inflammation of the mucous membrane and ulcerative-necrotic tissue lesions.
Articles on the topic
- Antifungal tablets - inexpensive but effective drugs
- Fungus in the throat - signs and manifestations, analysis, drugs and folk remedies
- Yeast fungi in the stool of an adult during analysis
An effective research method is endoscopic biopsy, during which a biopath (a section of intestinal tissue) is taken and its bacteriological and cytological examination is carried out. In this case, the taken material is inoculated onto a nutrient medium. A positive result of the analysis is the identification of pseudomycelium - a filamentous form of candida that penetrates into the tissue structures of the human body, on the basis of which a diagnosis is made: intestinal candidiasis.
Yeast fungi in the intestines are also detected using bacteriological examination of stool. Its main task is to identify cultures of microorganisms and determine the causative agent of the disease using the reaction of fungi to antimiotics. If there are more than 1000 colony-forming units of various pathological flora per gram of test material, candidal dysbiosis is diagnosed.
How to treat this problem?
One of the first recommendations for treating intestinal candida is to reduce carbohydrates and avoid refined foods such as sugar and flour. You should also avoid drinking alcohol and consult your doctor for specific drug treatment. Antibiotics are usually prescribed. Published by econet.ru.
Ask a question about the topic of the article here
The materials are for informational purposes only. Remember, self-medication is life-threatening; be sure to consult a doctor for advice.
PS And remember, just by changing your consumption, we are changing the world together! © econet