In medicine, reflux esophagitis is referred to as GERD. The disease occurs with many symptoms and occurs due to disturbances in the digestive tract. However, it is noted that a common manifestation of the disease is cough during GERD at any stage. The symptom can accompany the disease either independently or in combination with other manifestations. If reflux esophagitis is not treated in a timely manner, and it occurs along with a cough, then unpleasant complications arise. In this case, respiratory tract pathologies can appear.
Causes
The mechanism by which this symptom occurs is based on the fact that hydrochloric acid irritates cough receptors located along the entire length of the respiratory tract, including those located in the upper sections.
A characteristic feature of such a cough, which occurs with gastric pathology, is that it is unproductive and also annoying. This is due to the fact that sputum is not produced. The occurrence of cough is purely due to chemical irritation of the receptors.
The most common is a combination of reflux esophagitis and cough. It is this pathology that causes coughing in most patients.
The main diseases of the digestive tract that are accompanied by this symptom are:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. This pathology is associated with impaired motility of the digestive tract. The development of gastroesophageal reflux disease occurs when the smooth muscles of the stomach contract improperly, and food moves not to the duodenum, but back to the esophagus.
- Hyperacid gastritis. This disease is associated with the proliferation of various areas of the mucous membrane on which special G cells are located. It is these cells that are responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid, which is the main component of gastric juice. This disease is characterized by heartburn and cough.
- Peptic ulcer disease. Almost always, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is accompanied by an increase in acidity.
- Esophagitis. A cough with esophagitis can appear regardless of food intake, which is the result of an inflammatory process.
- Duodenitis.
- Pathologies of the biliary tract or pancreas.
All these diseases are accompanied by increased acidity of the gastric environment. It is acids that are the etiological factor that leads to the appearance of the symptom.
It is worth noting that stomach cough does not appear in all patients. An important point is the presence of increased sensitivity of receptors to acids.
What is the cause of cough with reflux esophagitis?
Primarily, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs due to the reflux of oxidized food in small quantities into the esophagus, which leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms. The patient often experiences heartburn or belching. However, some complain of a dry cough. The appearance of this sign is considered dangerous. Therefore, it is necessary to treat all symptoms.
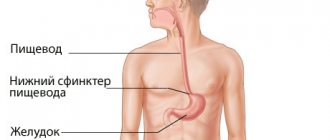
The formation of a cough with GERD is associated with the reflux of food into the esophagus due to incomplete closure of the lumen or valve between the two organs. Impaired function of the lower esophageal sphincter is associated with:
- with increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- due to weakening of the muscle epithelium near the esophageal sphincter;
- with mechanical damage or compression;
- with increased pressure in the stomach;
- due to frequent consumption of junk food;
- due to excess weight.
Cough due to GERD often occurs in pregnant women. The appearance of the sign is associated with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
How does spasm appear during illness?
Depending on the irritation factor, there are 3 categories, which is why cough develops with reflux esophagitis. These options include:
- complications of the underlying disease;
- mild irritation of the vagus nerve (vagus);
- compression of the trachea.
If the patient has started reflux esophagitis, then unpleasant consequences often occur. In Barrett's esophagus, tissue degeneration occurs. Then the epithelium becomes tumor-like. The danger of complications lies in the growth of tumors into the lumen of the esophagus. When the tumor reaches this place, it further grows and enlarges. This leads to difficulty breathing and subsequently coughing.
Irritation of nerve fibers during esophagitis occurs due to the ingress of stomach contents. This causes a constant cough due to reflux.
The disease causes damage to the walls of the esophagus. The lumen begins to change and increase. This is due to swelling due to the inflammatory process. This causes compression of the trachea, which causes coughing. The process occurs when reflux esophagitis is started or occurs in a severe form.
The causes of cough in esophagitis are associated with the intake of irritating substances that are used for viral diseases and colds. These medications include those that increase the production of bronchial secretions. When a spasm occurs, the substances protect and retain mucus in the bronchi. If this secretion remains in the body, then frequent coughing occurs.
However, the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus causes inflammation due to aggressive substances. In this case, biologically active elements are released. Then the lungs are damaged due to aggressive processed substances, and not from oxidized products.
Sometimes external compression of the lungs occurs. In this case, the cause of the cough reflex is a hiatal hernia, where the diaphragm passes. This lumen is referred to as the continuation of the esophageal tube into the chest cavity. When a hernia appears, compression of the lungs occurs. As a result, a cough occurs.
Under certain circumstances, the esophagus can compress the trachea. This process occurs when tumors or inflamed lesions form on the lining of the esophagus. Under this condition, the tissues swell. The inflammation process can put pressure on the trachea and provoke a cough reflex.
Symptoms
Each disease has its own time of cough onset. A cough with GERD appears immediately after eating, and with diseases of the stomach or duodenum - 1-2 hours after eating.
In addition, the cough may appear at night, regardless of food intake. This is due to the fact that in some diseases, gastric juice is produced even at night. This condition is extremely dangerous, as it can lead to the formation of ulcers. If ulcers have already been diagnosed, the risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation of the ulcer increases significantly.
Interesting! Burning sensation in the throat: lesions, treatment and prevention
A cough from the stomach has the following characteristics:
- Dry. With gastrointestinal pathology, the cough will always be unproductive.
- Nasty, not bringing relief. The duration of coughing attacks can reach an hour. The longest attacks occur at night.
- The appearance of bloody sputum. During prolonged attacks, a violation of the integrity of the bronchial mucosa may occur, which will lead to the release of a small amount of blood.
Additional symptoms and the treatment needed to get rid of them depend on the underlying pathology. This may be pain in various parts of the abdomen, dyspepsia (vomiting, bowel movements, nausea), belching, deterioration in general condition, increased body temperature.
In some cases, patients develop cough and heartburn after eating, which is considered an important diagnostic criterion.
The appearance of such a symptom requires contacting a medical institution, where a comprehensive examination and selection of etiotropic treatment will be carried out.
Symptoms of reflux disease
Determine that reflux cough does not affect the respiratory system if you observe your body. Among the signs of reflux, the symptoms are:
· Heartburn. It doesn't always appear. For example, it may occur after intense physical exertion, when sharply bending forward, after eating a large amount of liquid food, while lying in a horizontal position;
· Belching. It often has a sour or bitter aftertaste. In some cases, its consequences are nausea and vomiting;
· Swallowing disorder. The patient has difficulty swallowing. This pathology develops due to loss of muscle tone or due to severe narrowing of the esophagus;
· Other symptoms: chest pain, heaviness in the stomach after eating, increased salivation, bad breath, hoarse voice.
We recommend reading - What to do about heartburn when coughing?
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for a cough reflex against the background of gastric pathology are quite long, since when a cough occurs, attention is first paid to the respiratory system. Only in the absence of pathology of the lungs or bronchi, doctors pay attention to the digestive tract.
A set of diagnostic measures consists of those examination methods, the purpose of which is to identify the cause of its occurrence, as well as to exclude diseases of the respiratory system:
- General laboratory tests. Carrying out blood and urine tests almost always makes it possible to exclude respiratory pathology. The most important criterion in a general blood test is the level of leukocytes. In case of stomach diseases, the level of leukocytes will be normal, and pulmonary pathology is always accompanied by high leukocytosis.
- Biochemistry of blood. This test is performed to confirm diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. The results of this analysis pay attention to the levels of bilirubin, amylase and alkaline phosphatase. These substances are always elevated during inflammatory processes of the gallbladder and pancreas.
- Plain radiography of the chest organs. This examination is carried out to exclude diseases of the respiratory system.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to identify pathologies of an inflammatory or non-inflammatory nature. Most often, ultrasound is performed if cholecystitis or pancreatitis is suspected.
- Gastroscopy. Endoscopic methods are the basis for diagnosing diseases of the digestive tract. Using gastroscopy, you can visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. This examination requires special medication and psychological preparation.
Interesting! Can there be heartburn from honey: the benefits and harms of sweets
- Duodenal sounding. Probing is carried out to assess the secretory function of the stomach, pancreas and gall bladder. The most common phenomenon that is diagnosed during such an examination is hyperfunction of the glandular cells of the stomach or insufficient amount of bile.
The duration of the examination for such symptoms can take a fairly long period of time due to the fact that cough is not a characteristic manifestation of pathology of the digestive tract.
During diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate cough due to reflux with the following diseases:
- Asthmatic cough and bronchial asthma.
- Obstructive bronchitis.
- Damage to lung tissue.
The most important differential criterion is the absence of sputum. In addition, examination of the respiratory system does not reveal foci of inflammation in the bronchi and lungs.
Some more causes of reflux
Most often, esophagitis appears due to violations of the diet and food intake. However, there is another cause of GERD – increased intra-abdominal pressure. This condition can be caused either by wearing uncomfortable and tight clothes, or by the appearance of somatic pathology. Pathologies of internal organs cause increased pressure inside the abdomen, which compresses the diaphragm. In turn, it puts pressure on the gastroesophageal sphincter, causing its insolvency.
In particular, if gastroesophageal reflux disease is suspected, it is recommended to check the condition of the liver and its portal vein. Increased intra-abdominal pressure may be due to ascites (fluid in the abdominal cavity). It is quite easy to detect using ultrasound. If ascites is confirmed, it is necessary to perform a puncture of the abdomen and remove fluid, as well as establish the causes of the pathology. This will help reduce blood pressure and eliminate the symptoms of GERD.
Seeing a therapist is necessary if you have a persistent cough.
Treatment
In order to get rid of such an unpleasant manifestation, treatment of stomach cough should be aimed directly at eliminating the disease that led to its occurrence. Thus, different groups of drugs can be used, depending on the pathology.
Antacids
Antacids are drugs that reduce acidity in the stomach. Today, there are two main types of antacids: absorbable and non-absorbable.
The mechanism of action of absorbed antacids is based on the fact that the active substance, entering the stomach, reacts with hydrochloric acid and neutralizes it. During this reaction, various chemical compounds are formed that can be absorbed into the blood.
This feature is the main disadvantage of such drugs, since long-term use can lead to intoxication of the body. But the main advantage of absorbable antacids is that they extremely quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms, such as stomach cough or heartburn.
The most primitive remedy that belongs to this group is baking soda. The newest drugs in this class include Rennie, Bourget's mixture and magnesium carbonate. When they are used, the effect occurs after a few minutes, but its duration is insignificant.
The use of non-absorbable antacids is more relevant. Their effect occurs after a longer period of time, but the lasting effect lasts for several hours. The main representatives of this group are Maalox and Almagel.
The use of such drugs is practically safe, since their action is limited to the stomach cavity. The products of the chemical reaction, during which the acid is neutralized, are not absorbed into the blood. In addition, they have an enveloping effect, which protects the mucous membrane from the harmful effects of acid.
Interesting! Why does heartburn occur after eating: causes of pathology
The use of such drugs is permissible even during pregnancy and breastfeeding. They help get rid of not only cough due to GERD, but also heartburn.
Antibiotics
In some cases, stomach cough is a symptom of infectious diseases of the digestive system. In this case, broad-spectrum antibiotics or selective drugs should be used. The prescription of antibiotics requires the use of additional agents, the purpose of which is to protect the normal intestinal microflora, as well as the vagina.
For this purpose, live yoghurts and antifungal agents are prescribed.
In some cases, stomach cough needs to be treated promptly. Indications for surgery are for peptic ulcer disease, as well as for the development of complications.
Diet
The appearance of symptoms of stomach cough requires adherence to a diet, which helps reduce the likelihood of repeated attacks.
To do this, the patient should follow the following recommendations:
- Frequent meals in small portions. Thanks to this nutritional scheme, food will be located exclusively in the pyloric part of the stomach, which almost completely eliminates the risk of it refluxing into the esophagus. As a result, you can get rid of cough with reflux esophagitis without the use of medications.
- Refusal of sour, hot and spicy foods. These products significantly increase the acidity of gastric juice, which makes coughing attacks more pronounced.
- Eating food with an alkaline environment. This mainly includes drinks such as milk and soda mineral waters.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of cough in diseases of the digestive system, it is necessary to promptly diagnose and treat the underlying pathology.
Thanks to this, the risk of such a symptom occurring will be minimal. In addition, the patient will be provided with the most favorable outcome.
The appearance of cough in diseases of the stomach and lower esophagus is a rare occurrence. But it causes discomfort and inconvenience for patients. If you experience an unreasonable cough after eating, you should contact a gastroenterologist to undergo examination and begin treatment.
Time of occurrence
Many people do not associate coughing with eating. However, it is still observed. The easiest way to notice it is 20-30 minutes after eating; it is after this amount of time that active digestion of foods begins. Excessive amounts of food and incompetence of the gastroesophageal sphincter cause reflux.
It is after a short amount of time after eating that symptoms such as:
- discomfort in the upper abdomen;
- heartburn;
- cough.
The appearance of a cough after eating should be alarming
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, some will have all the symptoms, while others will have only one.
Reflux can also occur on an empty stomach. If a person has not eaten anything for 3-4 hours, but sees or hears food, gastric juice begins to be intensively produced. In this case, the pH of the stomach changes towards an acidic environment. There is a reflux of juice from the stomach into the esophagus. This reflux may also be accompanied by coughing and rumbling in the stomach.