Acidosis is a condition of the body that occurs as a result of certain etiological factors and is characterized by a violation of the acid-base balance. This disorder can occur in both adults and children. Metabolic acidosis, like other forms of this pathological process, can lead not only to complications, but also to death. Therefore, self-medication is unacceptable - you need to seek medical help.
Online consultation on the disease “Acidosis”. Ask a question to the specialists for free: Endocrinologist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Mild forms of this pathological process can be asymptomatic: in some cases, the patient may be bothered by short bouts of nausea, weakness and dizziness. In general, acidosis does not have specific symptoms that would allow one to accurately identify such a disorder without diagnosis.
For diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental methods of examining the patient are used. Treatment will be aimed at eliminating the underlying factor, and the acidosis itself will be relieved through symptomatic therapy. Acidosis in children is treated in the same way as in adults - in both cases hospitalization is required.
It is inappropriate to talk about any unambiguous prognosis in this case, since the outcome of therapy will depend on many factors, including: the underlying factor in the development of such a condition, general clinical indicators of the patient, age, personal and family history (in some cases).
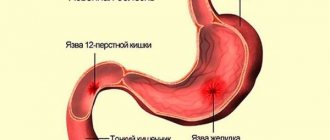
Acid-base balance
Description
Acidosis is usually called an increase in the acidic environment in the blood and tissues of the body compared to the norm, while the pH decreases.
If the shift occurs by 0.3, acidotic coma develops, and by 0.4, death occurs. If a person refuses to eat, so-called internal nutrition begins to occur using secondary tissues and fats. After a while, acidosis reaches maximum levels, ketone cells are converted into amino acids, and an acidotic crisis occurs. Alkalosis is considered to be an increase in alkaline substances in the body with an increase in pH value. If the shift occurs by 0.2, the functioning of all body systems occurs.
Acidosis and alkalosis
You will be interested in: "Anaferon" adult: instructions for use, analogues and reviews
Most of all diseases that develop in the human body can greatly affect the balance of acids and the internal environment. Because of this, a condition such as acidosis (acidification) or alkalosis (alkalinization) may occur. In the presence of a compensated form of acidosis and alkalosis, the absolute amount of carbonic acid changes, but their quantitative ratio is normal. Problems of the decompensated type cause changes to shift towards acids or towards bases.
Causes of acidosis
Acidosis is not an independent disease, but a symptom that can develop in many diseases and pathological conditions, including:
- life-threatening conditions (clinical death and post-resuscitation illness, shock, multiple organ failure, sepsis);
- lung diseases (severe asthma, pneumothorax, sleep apnea);
- neuromuscular disorders (Guillain-Barré syndrome, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, myasthenia gravis);
- infectious diseases (botulism);
- renal failure;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- starvation;
- dehydration (dehydration);
- complicated pregnancy;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- intestinal fistulas;
- intestinal dysbiosis (excessive synthesis of D-lactate by intestinal microflora);
- alcohol intoxication;
- drug overdose;
- poisoning with methyl alcohol (methanol), antifreeze, ethylene glycol, as well as salicylates and some other drugs.
Long-term excessive physical stress (hard exhausting work, intense training) can lead to metabolic acidosis.
Main causes of metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a common pathology in pediatric practice. Acute severe metabolic acidosis generally has the same causes and manifestations as in adults, while chronic acidosis leads to rickets and growth retardation.
Most cases of metabolic acidosis encountered by pediatricians are lactic acidosis caused by shock during critical illness of various etiologies.
The presence of a large accumulation of acidic products during acidosis can be caused by various reasons.
Factors influencing the development of acidosis can be both external and internal. External causes of acidosis include inhalation of air or vapors with a high carbon dioxide content.
Internal causes include functional disorders of body systems that affect metabolic processes and the removal of organic acid products.
The causes of the development of acidosis can be certain processes in the body: diabetes mellitus, circulatory disorders, tumor processes, pregnancy, hypoglycemia, hypoxic conditions of various origins, disorders of the kidneys, intoxication, fasting, side effects of medications, etc. In some cases, obvious reasons, leading to acidosis are not determined.
Regardless of the cause that caused it, acidosis negatively affects the entire body of the patient. The worst prognosis for severe acidosis is shock or death.
The consequences of acidosis can be dehydration, blood thickening, thrombosis, unstable blood pressure, myocardial, liver, spleen, etc., functional disorders in the blood circulation of the brain and metabolic processes in it, i.e. the state of acidosis entails disruption of the activity of all vital organs.
Acidosis is not a disease, but only a condition of the body caused by an imbalance in the acid-base balance, which occurred as a result of insufficient excretion and oxidation of organic acids. As a rule, these products are eliminated quickly during normal functioning of the body. Only in some diseases and conditions do they come out slowly. The most common causes of acidosis are:
- respiratory failure due to pneumonia (pneumonia), emphysema (pathological expansion of the air spaces of the distal bronchioles) of the lungs, hypoventilation (rare shallow breathing);
- malignant neoplasms;
- fasting, diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- hypoglycemia (low blood glucose levels);
- renal failure;
- smoking;
- loss of appetite, poisoning, other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract);
- pregnancy;
- dehydration of the body;
- poisoning with harmful substances;
- oxygen starvation (with myocardial infarction, heart failure, anemia, shock);
- loss of bicarbonate (acid salts of carbonic acid) by the kidneys;
- use of drugs (calcium chloride, salicylates and others);
- conditions of the body that provoke metabolic disorders (circulatory failure, diabetes mellitus, febrile conditions).
Alkalosis and acidosis can occur due to various reasons, depending on their type. Acidosis appears in diseases that are accompanied by a feverish state, since organic acids are retained in the body. Acetone and acetoacetic acid appear in the urine. In severe cases, coma occurs.
The same type of food and a poor diet, dehydration, and elevated ambient temperatures can also provoke alkalosis. With brain injuries, when vomiting and hypercapnia appear, this pathology also develops. Metabolic alkalosis occurs when the body loses hydrogen ions through excessive vomiting or taking medications that increase diuresis, or long-term intake of mineral water.
Acidosis is not an independent disease. This condition of the body indicates the presence of certain problems and can be caused by the following factors:
- bad habits (tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse);
- constant diets, fasting;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- conditions in which metabolic processes in the body are disrupted (fever, circulatory failure, diabetes and a number of others);
- respiratory failure;
- pregnancy;
- cancer;
- long-term uncontrolled use of certain medications (calcium chloride, salicylates and a number of others);
- dehydration of the body;
- oxygen starvation in heart failure, anemia, shock;
- renal failure;
- hypoglycemia;
- poisoning of the body with substances, the breakdown of which leads to the formation of large amounts of acids.
In some cases, the causes of acidosis cannot be determined.
This condition cannot develop without cause. There are many negative factors that can provoke acid-base imbalance:
- Kidney diseases, which are associated primarily with damage to the renal tubules. This happens with kidney failure and other conditions.
- Taking certain medications containing salicylates, calcium or ammonium chlorides, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and others.
- Circulatory disorders (especially in the pulmonary circulation), accompanied by blood stagnation, for example, such as left ventricular failure or pulmonary edema.
- Severe respiratory failure, developing with diseases such as pneumonia, obstructive pulmonary diseases, emphysema, pulmonary embolism, hypoventilation. In such conditions, carbon dioxide is not fully released during exhalation.
- Poisoning of the body with certain substances that are transformed into acids during metabolism.
- Loss of bicarbonate bases along with gastric juices. This happens with severe vomiting or diarrhea, as well as after surgery or with certain pathologies of the digestive tract (pyloric stenosis).
- Diseases and conditions leading to disturbances in the body's metabolic processes: diabetes, fever, disturbances in hematopoietic or circulatory processes.
- Bad habits, especially alcohol abuse and smoking.
- Inadequate nutrition (diet, fasting, refusal of certain foods).
- Poisoning.
- The appearance of malignant neoplasms.
- Acidosis can develop during pregnancy (for example, as a result of severe toxicosis).
- Low blood glucose levels, called hypoglycemia.
- Dehydration (extreme heat, excessive sweating, or not drinking enough fluids).
- Lack of oxygen. This condition can occur with severe stress and certain mental disorders (panic attacks), with anemia or heart failure.
Violation of the acid-base balance occurs as a result of insufficient oxidation and excretion of organic acids. In general, in a healthy person these products are eliminated from the body quite quickly. For certain diseases and conditions (for example, during pregnancy, intestinal disorders, fasting, febrile illnesses, etc.
Thus, the causes of acidosis, or more precisely, the factors that accompany the development of this condition, can be:
- Pregnancy;
- Strict diets, fasting;
- Smoking, alcohol abuse;
- Poisoning and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Diseases characterized by metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, febrile conditions, etc.);
- Dehydration of the body (regardless of the cause that caused it);
- Malignant formations;
- Oxygen starvation (for heart failure, states of shock, anemia);
- Kidney failure;
- Poisoning by chemicals, the metabolism of which can lead to the formation of excess acids;
- Respiratory failure in severe form (with emphysema, pneumonia, hypoventilation, etc.);
- Kidney loss of bicarbonate;
- Hypoglycemia (a condition characterized by a decrease in blood glucose levels);
- Circulatory failure (for example, with pulmonary edema);
- Taking certain medications (for example, calcium chloride, salicylates, etc.).
It is worth noting that it is not always possible to determine the cause of acidosis.
Types of metabolic acidosis
Diagnosing a specific form of pathology is very important - this allows not only to find out the cause of its development, but also to determine the optimal medical tactics. At the moment, doctors use 2 main classifications that help make a diagnosis.
The first reflects the connection with diabetes. It is necessary to determine whether a patient has this disease before starting treatment, since metabolic acidosis in diabetes mellitus has its own characteristics. Its therapy necessarily includes correction of glucose (sugar) levels. Without this nuance, any other treatment procedures will be ineffective.
The criterion for the second classification is the type of poisoning of the body. Various acids can increase in human blood, the most dangerous of which are lactic acid and ketone bodies (acetone, butyric acids). Depending on the “acidifying” substance, the following are distinguished:
- Ketoacidosis. The presence of hydroxybutyric acids and acetone is noted in the patient’s blood. Often develops against the background of diabetes, but can also occur with other diseases;
- Lactic acidosis. Accompanied by an increase in the concentration of lactic acid. It can occur with a large number of diseases, including due to dysfunction of the liver or kidneys, the development of a severe infection, poisoning, etc.;
- Combined form. It often occurs in people with high sugar levels and in the presence of provoking factors. The latter may include severe stress, physical overload, infectious diseases and a number of other conditions.
The reasons for the occurrence of various forms are somewhat different from each other. They need to be known in order to quickly guess the type of disease and correctly treat metabolic acidosis.
Lactic acidosis
This pathology is accompanied by the accumulation of large amounts of lactic acid in the blood. The disease is of two types: A and B. In the first type, oxygen is completely absent in the tissues, in the second case this is not observed. This disease is inherent in those who have shortening of the small intestine. In this case, bacteria produce not only enzymes and lactic acid, which causes the development of acidosis, which can lead to coma. Lactic acidosis can be caused by leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, epilepsy, bacteremia, exposure to toxins, and medications.
Classification
Due to the fact that a disorder of this nature can be the result of a fairly large number of diseases, the classification is also quite broad.
If we consider the factor of origin, then the following types of acidosis are distinguished:
- respiratory acidosis (respiratory acidosis) - in this case, the pathological condition develops due to the fact that a person inhales a large amount of carbon dioxide;
- non-respiratory – due to an excess of non-volatile acids and other compounds;
- mixed type - combines the clinical pictures and etiology of the two forms described above.
In turn, the non-respiratory form is divided into the following subtypes:
- excretory acidosis;
- acute metabolic acidosis;
- exogenous.
Based on the pH level, three forms of this pathological process are distinguished:
- compensated acidosis;
- decompensated acidosis;
- subcompensated.
The most severe stage is decompensated, since there is a high risk of developing not only complications, but also death.
The classification of the disorder by causative factor is also considered:
- gas acidosis;
- non-gas acidosis;
- diabetic acidosis;
- lactic acidosis (lactic acidosis);
- hyperchloremic acidosis;
- blood acidosis;
- tubular acidosis;
- tubular acidosis;
- lactic acidosis (rumen acidosis).
Depending on the nature of the course, this disorder can be acute or chronic. However, it should be noted that the chronic form is quite rare, since the lack of treatment for the acute form can lead to the death of the patient.
Blood condition with acidosis
Signs
Metabolic acidosis may not cause significant symptoms if the acidemia is mild and develops slowly. In other cases, its symptoms are nonspecific, that is, they are characteristic of many conditions.
Significant and/or rapidly developing acidemia is manifested by nausea and vomiting, and an increasing deterioration in health. Characteristic signs include hyperventilation due to hyperpnea (inhalation becomes slow and deep, but the frequency of inhalations does not increase - the so-called Kussmaul breathing) due to the action of compensatory processes.
Slowly developing (chronic) acidemia leads to bone demineralization.
Possible signs of acidosis include:
- deterioration of myocardial function, determined by a decrease in stroke and minute blood volume, as well as a decrease in sensitivity to the action of inotropic and vasopressor drugs;
- decreased peripheral vascular resistance;
- hyperkalemia;
- spasm of arterioles of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, which is accompanied by a decrease in intestinal motility and diuresis;
- decreased surfactant synthesis;
- development of seizures.
Since these signs are nonspecific, they should be assessed with attention to historical data that indicate the possible occurrence of acidosis:
- prolonged diarrhea;
- diagnosed diabetes mellitus or indications of its possible presence (increased thirst, polyuria, weight loss, epigastric pain, etc.);
- malnutrition, starvation;
- renal failure (nocturia, polyuria, weight loss, itching);
- taking certain medications (for example, salicylates) or consuming toxic substances (for example, methanol);
- visual disturbances, increased photosensitivity, loss of visual fields;
- kidney stone disease;
- signs of intoxication.
Classification according to hydrogen index
The pH value plays a big role in the body. Its norm ranges from 7.25 to 7.44. If this indicator is exceeded or, on the contrary, falls, then the protein loses its natural properties, enzymes begin to function worse and cell destruction occurs. These processes can cause destruction of the body. Based on the pH level, the described state is divided into:
- compensated - the blood pH shifts towards the lower norm - 7.35 (in most cases not accompanied by any special symptoms);
- subcompensated - the acid level increases, the pH reaches 7.29-7.35 (symptoms may include shortness of breath, diarrhea, arrhythmia, vomiting);
- decompensated - the pH level drops below 7.29, and problems arise with the digestive system, heart and brain.
You may be interested in: 5 exercises of Tibetan monks - a simple way to restore health and prolong youth. Benefits, detailed description of the complex, rules of implementation
Acidosis: symptoms
Symptoms of acidosis are difficult to differentiate from signs of various diseases, and in mild forms they are not at all associated with a violation of acid-base balance.
Symptoms of mild acidosis may include:
- Short-term nausea and vomiting;
- General malaise;
- Fatigue;
More severe conditions of acidosis may be accompanied by:
- Cardiac arrhythmia;
- Central nervous system disorders: lethargy, dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, loss of consciousness;
- Shortness of breath;
- Hyperpnea (increased depth of breathing and then its frequency);
- Increased heart rate;
- Signs of a decrease in the volume of extracellular fluid (ECF), especially with diabetic acidosis;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Increasing deafness.
Severe acidosis can lead to circular shock, which develops as a result of impaired myocardial contractility and the response of peripheral vessels to catecholamines.
Manifestations of imbalance in the human body are difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of other diseases. As a rule, with a mild form of acidosis, a person cannot even suspect a shift in the acid-base balance. Therefore, only an experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. Although there are general signs of acidosis in humans:
- short-term vomiting, nausea;
- loss of consciousness;
- general malaise;
- dizziness;
- cardiac arrhythmia (impaired rhythm and heart rate);
- dyspnea;
- increased blood pressure (blood pressure);
- drowsiness;
- increasing stupor
- increased heart rate;
- lethargy;
- confusion;
- state of shock;
- hyperpnea (increased frequency and depth of breathing).
In children
As a rule, acidosis in children occurs when there is a large combustion of fats as a result of the lack of carbohydrates. This often happens when a child has diabetes or poor diet. Other causes of acid-base imbalance in children are diarrhea, kidney failure, poor intestinal absorption, and Addison's disease. The main symptoms of acidosis in a child are:
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy;
- depressed state of the central nervous system (CNS);
- rapid breathing;
- stupor;
- disturbance of peripheral microcirculation (pallor, marbling of the skin);
- stomach problems;
- diarrhea, vomiting, leading to dehydration;
- Diabetics have a characteristic rotten odor from the mouth;
- headache;
- heat.
Large toxic breath - the main sign of acidosis, as a rule, rarely occurs in newborns. Only when there is a metabolic type of acid-base imbalance, the breathing of babies becomes irregular and incorrect. With respiratory distress syndrome (respiratory failure), accompanied by a mixed severe type of acidosis, the child’s breathing becomes paradoxical - pendulum-like air movements appear from the lung on the healthy side to the opposite side and back.
Clinical manifestations of this condition of the body can be very diverse. They depend on what disease led to the development of acidosis and the severity of acidosis.
The main symptoms are:
- from the muscular system - suppression of reflexes, decreased tone, weakness, convulsions;
- from the cardiovascular system - arrhythmia, tachycardia, pressure drops;
- from the urinary system - frequent urination;
- on the part of the respiratory system - shortness of breath, increased breathing, smell of ammonia from the mouth;
- from the gastrointestinal tract - loose stools, nausea, vomiting;
- from the nervous system - dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy, headaches, stupor, loss of consciousness.
A mild degree of the disease may not manifest itself clinically. Mixed forms of acidosis often lead to shock, since the pathological changes in this case are more severe than in the respiratory or metabolic form of the disease.
The following types of alkalosis are distinguished:
- Exogenous occurs as a result of the entry into the blood of drugs or substances that increase pH.
- Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is increased ventilation of the lungs, which leads to the excretion of large amounts of carbon dioxide. This is observed with brain damage, exposure to toxins and large blood loss.
- Excretory occurs when gastric juice is lost due to the formation of fistulas in the stomach, incessant vomiting, and in diseases of the kidneys and endocrine system.
- Metabolic alkalosis occurs when electrolyte metabolism is disrupted. Often observed after operations, in people suffering from rickets.
- Mixed manifests itself in a combination of several types of alkalosis. Occurs with hypoxia, vomiting, and brain injuries.
With this disorder, a decrease in cerebral blood flow and blood pressure is observed. Nervous and muscle excitability increases, convulsions may develop, and constipation is also observed. Respiratory alkalosis provokes a decrease in mental performance, dizziness and fainting occur, and the activity of the respiratory center decreases.
Symptoms may also include weakness, thirst, lack of appetite, drowsiness, and mental retardation. If help is not provided in time, coma may occur. With metabolic alkalosis, edema may appear, Burnet's syndrome develops, in which apathy, aversion to dairy products, skin itching, conjunctivitis, renal failure develop, and polyuria or polydipsia develops.
This type of disorder provokes lethargy, rapid breathing, a state of stupor and stupor, which can result in shock and death. Sometimes the patient experiences nausea, vomiting, and hyperpnea. With acidosis, there is a high risk of arrhythmia, a decrease in pressure is observed, which can result in disturbances in metabolic processes in the brain.
Also, acidosis, the symptoms and treatment of which we are considering, can provoke dehydration and the formation of heart disease. In its acute form, the disease manifests itself as indigestion, circulatory disorders, and general lethargy.
Therapy in this case should be comprehensive. Treatment should help eliminate the causes of the pathology. Thus, gas alkalosis is treated with mixtures containing carbon dioxide, the patient is given inhalations and Seduxen is prescribed. Non-gas alkaloses are treated depending on their type. Usually they use ammonium, insulin, etc.
In addition to specific treatment for pathologies such as acidosis and blood alkalosis, therapy is prescribed aimed at eliminating concomitant ailments that caused the pathologies.
Mild forms of acidosis do not give any characteristic clinical picture. It is quite difficult to differentiate acidosis from other diseases, because symptoms of acidosis do not indicate the development of acid-base balance disorders in the body. The presence of general malaise, mild nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath and palpitations, increased blood pressure, disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system should be alarming and serve as a reason to contact a medical facility.
Diagnosis of acidosis is carried out on the basis of an analysis of the results of the pH of arterial blood; for analysis, blood is taken from the radial artery at the wrist. To determine the causes of acidosis, the amount of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate in the blood is checked. When studying anamnesis, to diagnose acidosis, the patient’s previous condition and illnesses are taken into account.
Diagnosis of acidosis is also carried out based on the pH level in the urine, serum electrolytes and blood gas composition are examined. Other tests are also done to determine the cause of acidosis.
Why is acidosis dangerous?
This is a serious complication that can occur due to severe infections, diabetes, impaired liver function, kidney function, and a number of other pathologies. “Acidification” of the blood causes a number of additional disturbances in the functioning of organs and tissues, among which the most dangerous are:
- Damage to cells throughout the body. A large amount of free acids corrodes the outer membrane of cells, which leads to disruption of their functions. Since toxins are distributed to all organs and tissues, pathological changes can be very diverse;
- Respiratory disorders. Oxygen in the body is alkali in its chemical role. Therefore, patients are characterized by deep, frequent breathing - this is how the body tries to reduce acidity. Unfortunately, this process leads to narrowing of cerebral blood vessels and increased blood pressure. As a result, the person’s condition only worsens and increases the risk of hemorrhages in various organs;
- Increased blood pressure. The mechanism of occurrence is associated with the presence of breathing disorders;
- Damage to the digestive organs. In most patients, acute metabolic acidosis causes abdominal pain, stool disorders and other dyspeptic symptoms. With this disorder, aggressive substances such as acetone and hydroxybutyric acid are often formed, which corrode the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus and intestines. In some cases, patients even experience bleeding from these organs;
- Depression of consciousness. Toxins produced by the body negatively affect the nerves and brain matter. In mild cases, the patient may experience irritability, weakness, drowsiness, and in severe cases, coma;
- Heart dysfunction. Damage to cells and nervous tissue, imbalance of microelements and a number of other factors inevitably affect the myocardium. In the first stages, this effect can manifest itself as frequent and strong heartbeats and rhythm disturbances. In severe cases of pathology, heart contractions weaken and become more rare. The final stage is cardiac arrest.
All of these disorders can not only worsen your health, but also pose a threat to life. That is why the first signs of the disease must be detected and treated as early as possible.
Diagnostics
If any of the symptoms of acid-base imbalance occur, a person should definitely consult a doctor. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. To do this, the doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic methods:
- blood test for serum electrolytes (blood is taken from an artery);
- urine pH level analysis;
- blood gas analysis (arterial blood is taken from the radial artery at the wrist, but venous blood does not allow an accurate determination of the pH level).
As a rule, all blood tests (for the level of serum electrolytes and gas composition) show both the presence of the disorder itself in the body and its type (metabolic, respiratory and others). Often, to determine the factors causing acidosis, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic methods (urinalysis, ultrasound).
The diagnosis is made based on a blood pH test. It is also important to establish the causes of acidosis. To do this, the doctor interviews the patient, studies his medical history, conducts an examination, and prescribes additional tests.
In addition to blood tests, the pH level is determined in a urine test. In addition, studies of blood gas composition, serum electrolytes and a number of other studies are carried out.
Diagnosing alkalosis and acidosis is easy. To do this, urine is tested for pH and blood to determine its gas and electrolyte composition. The diagnosis of alkalosis is based on the patient’s clinical data and determines the presence of chloride in the urine. To detect acidosis, a test using ammonium or calcium chloride is used, and blood and plasma are examined for gas composition and electrolyte levels.
Kussmaul breathing in combination with other signs allows one to suspect metabolic acidosis. To confirm the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- blood test for electrolytes and gases;
- blood test for ketone bodies (helps in determining diabetic, alcoholic and malnutrition-induced acidosis);
- determination of plasma lactate level;
- determination of anion gap in blood and urine;
- clinical blood test (possible acidosis due to sepsis may be indicated by leukopenia or leukocytosis, anemia may be accompanied by lactic acidosis).
If acidosis due to renal failure is suspected, the following is additionally determined:
- plasma renin activity;
- plasma aldosterone;
- transtubular potassium gradient;
- fractional excretion of bicarbonate, and some others.
The following hardware diagnostic methods are used:
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys;
- measurement of blood pressure, heartbeat, etc.
As mentioned above, the symptoms of acidosis are not specific. In addition, they are very often masked by signs of the underlying disease, so the diagnosis cannot always be established immediately.
For an accurate diagnosis, patients undergo the following studies:
- Blood test to determine the pH level in the urine;
- Arterial blood analysis for the presence of serum electrolytes;
- Analysis of arterial blood to determine its gas composition.
The last two studies allow us to determine not only whether a person has acidosis, but also its type (respiratory or metabolic).
A number of additional studies may be needed to determine the cause of acidosis.
Acidosis can be detected using blood and urine tests, since their composition will certainly change.
Acid-base balance of the human body
The ratio of alkali and acid in any solution is called acid-base balance (ABC). It is characterized by a special indicator - pH (from the English power Hidrogen - “hydrogen power”), which names the number of hydrogen atoms in the solution. A neutral environment is an indicator of 7.0; if the level is lower, the environment is more acidic; if the level is higher, it is alkaline. With the right proportion of acids, the pH of the blood is 7.365, which means it is slightly alkaline. Achieving the necessary balance is a complex process, but it can be achieved through good habits.
How to check the acid-base balance of the body?
You can find out about the state of the body by the state of the blood. ARB varies depending on age, physical activity, metabolic type and other factors. Those who care about their health are interested in the question: how to determine the acid-base balance of the body? You can do this in several ways:
- Using special electronic devices
- at home or in medical institutions. The device takes the required amount of blood from the artery and displays the result on the screen. - Indicator paper
is another simple device. When it gets into an alkaline or acidic solution, it changes its color, indicating a deviation from the norm. - Conjunctival staining
can relatively accurately determine ASC. The darker it is, the higher the alkalinity. Scarlet color indicates normal pH. - By measuring pressure (lower) and pulse
, you can also determine the pH of the blood - the norm or deviation will show their ratio. When the pressure is greater than the pulse, this indicates the alkalinity of the blood; if less, it indicates its acidity.
Symptoms of alkalosis
Since metabolic acidosis is not an independent disease, but only one of the symptoms of another, underlying disease, etiotropic therapy is aimed at the underlying disease.
With decompensated, and in some cases with subcompensated form of metabolic acidosis, parenteral and then oral administration of buffer solutions containing sodium bicarbonate, glucose solution, and sodium chloride is indicated. Acesol, Disol, Trisol solutions may be prescribed to help eliminate electrolyte imbalance.
Trisol is a drug for the treatment of decompensated metabolic acidosis
In severe conditions, resuscitation, hemodialysis, and artificial ventilation are performed.
Due to the fact that the described condition is the result of a disruption in the functioning of body systems, the goal of treating acidosis is to eliminate the factors that became the trigger. In particular, we are talking about the treatment of underlying diseases, pathological conditions or dysfunctions, which provoked a shift in the acid-base balance of the body.
Correction of severe forms of acidosis involves:
- Elimination of the provoking factor;
- Normalization of hemodynamics: improvement of rheological properties of blood, restoration of microcirculation, elimination of hypovolemia;
- Correction of electrolyte metabolism;
- Elimination of hypoproteinemia;
- Improving renal blood flow;
- Strengthening the hydrocarbonate buffer system;
- Improving oxidative processes in tissues by introducing ascorbic acid, glucose, riboxin, thiamine, insulin, pyridoxine;
- Improving pulmonary ventilation (switching to artificial ventilation in extreme cases).
Targeted correction of the acid-base state by introducing buffer solutions is carried out only at a pH level of less than 7.25 (with decompensated acidosis).
Symptomatic treatment of acidosis involves drinking plenty of fluids, ingesting soda, as well as eliminating associated symptoms (malaise, nausea, arrhythmia, high blood pressure, etc.). In case of poisoning, drugs are prescribed that remove toxic substances from the body; in severe cases, dialysis is performed.
Treatment of acidosis in children is similar to the treatment of this condition in adults.
Treatment consists of eliminating the dysfunction or underlying disease that provoked the development of acidosis.
In the metabolic form of the disease, therapy for metabolic disorders and intravenous fluid administration are indicated. In severe forms of acidosis, solutions containing sodium bicarbonate are prescribed. This is done to increase the pH level in the body to 7.2 or higher.
In addition, solutions of sodium chloride or glucose are used. When severe symptoms appear, measures are taken to relieve them. If acidosis is caused by poisoning of the body, then, first of all, it is necessary to remove toxins.
In our online store you can purchase the following drugs for the treatment of acidosis, which can be used as part of complex therapy for this disease:
- Beta-Carotene;
- V-Complex;
- Green Formula;
- Calcium/Magnesium Chelate;
- OsteoComplex.
Before using this or that product, you should consult your doctor.
Due to the fact that the appearance of acidosis is caused by a disruption in the functioning of the body's systems, treatment of this condition is reduced to the treatment of the underlying disease or dysfunction that provoked a shift in the acid-base balance. Acidosis of any kind can lead to critical conditions of the body, so it is necessary to seek help from a specialist if symptoms appear. As a rule, correction of severe forms of pathology involves:
- strengthening the buffer hydrocarbonate system;
- improvement of pulmonary ventilation;
- elimination of hypoproteinemia (decrease in protein concentration in blood plasma);
- normalization of hemodynamics: elimination of hypovolemia (decreased blood volume), restoration of microcirculation;
- improvement of oxidative processes by introducing glucose, pyridoxine, ascorbic acid, Thiamine, Riboxin, Insulin;
- correction of electrolyte metabolism;
- elimination of the provoking factor;
- improvement of renal blood flow.
Symptomatic treatment of the disease involves ingesting sodium bicarbonate (soda), drinking plenty of fluids, and eliminating associated symptoms (nausea, malaise, arrhythmias). In case of poisoning, drugs are prescribed that remove toxins from the body; in severe cases, dialysis (cleansing) is performed. With a moderate disorder, it is necessary to limit the consumption of protein foods. Drug treatment includes the use of calcium carbonate.
To treat metabolic disorders, nicotinic and glutamic acids and Cocarboxylase are prescribed. For acute forms of acidosis, rehydration salt is used. Dimephosphone is also often used to correct the pathological condition. In the treatment of lactic acidosis, the drug Dichloroacetate is used, which activates a complex of enzymes. In addition, the patient must maintain a proper and balanced diet and avoid coffee and alcohol.
If the acidosis is moderate, no specific treatment is prescribed. They only recommend sticking to a diet, excluding protein foods from the diet. In other forms, patients are given intravenous saline solutions and potassium chloride is prescribed. If a patient has adrenal hyperfunction, the underlying disease is treated. In the presence of Barter's syndrome, prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors are used.
Therapy is mainly aimed at preventing the development of anemia, hypovolemia, and correcting the respiratory process. For this, alkali solutions are used. Acidosis is treated with drugs such as Trisamine, Nicotinic acid, Riboflavin, Carnitine, Lipoic acid, and so on. It is also necessary to properly organize your diet and consume foods that help remove toxins from the body.
Principles of treatment
Correcting metabolic acidosis is quite a difficult task even for an experienced doctor. Each patient suspected of having this disease is asked to be hospitalized, as they need constant monitoring, regular intravenous infusions of solutions and periodic examinations.
All treatment goals can be divided into two groups - restoration of normal blood acidity and elimination of the cause of the pathology.
pH restoration
First of all, doctors are trying to find out what disease led to the development of the pathology. If it is diabetes, therapy to lower glucose levels with insulin and medications begins immediately. If a severe infection develops, complex treatment is carried out using antibacterial/antiviral drugs. If a decrease in pH has caused severe damage to an organ, the attending physician tries to restore its function or replace it with the help of medications and instrumental techniques (for example, hemodialysis).
Simultaneously with the measures listed above, infusion therapy is required - drip intravenous infusion of solutions. The choice of solution depends on the type:
| Form of pathology | Features of infusion therapy | Optimal solutions |
| Diabetic ketoacidosis | In patients with this condition, it is necessary to replenish the loss of fluid and beneficial microelements. However, solutions containing glucose are contraindicated for use. | Preparations containing electrolytes: potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, etc.
|
| Lactic acidosis | The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the lack of fluid, reduce the concentration of lactic acid and restore the deficiency of alkalis. | |
| Nondiabetic ketoacidosis | With this form, solutions with an anti-ketone effect are indicated. In addition, they must replenish the deficiency of glucose (if any) and fluid. | The optimal drug for therapy (in the absence of contraindications) is a 20-40% glucose solution. Additionally, it is possible to use the drugs Reosorbilact and Xylate, which effectively remove acetone and butyric acids from the blood. |
Infusion therapy in children is carried out according to the same principles as in adults. The main thing is to correctly determine the cause and variant of the disease. The only difference is the volume of intravenous infusions - the child requires significantly less fluids. Doctors calculate the required amount based on body weight.
Features of therapy for individual forms
Since each form has different pathological mechanisms, some aspects of their treatment differ from each other. In this section we present the most important principles that must be followed when prescribing therapy:
- For lactic acidosis, in addition to infusion therapy, B vitamins (thiamine, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin) must be prescribed every 12 hours. These substances improve metabolism and help normalize acidity. To combat the lack of air, patients are given continuous oxygen inhalation through a mask or nasal prongs. In case of severe acidosis, when the level of lactic acid increases 4-5 times, doctors can “cleanse” the blood - hemodialysis;
- In case of ketoacidosis without diabetes, it is recommended to prescribe drugs that restore the functioning of the digestive system (Domperidone, Metoclopramide) as an addition to standard therapy. This will reduce fluid loss through vomiting and improve food digestion. Feeding must be done orally (using a gastric tube or frequent split feedings). It should be high in calories, high in carbohydrates and low in fat. Vitamin therapy is also indicated for patients;
- For diabetic ketoacidosis, the main treatment is insulin administration. Reducing sugar concentrations and sufficient intravenous infusions are the most effective methods of therapy. After these measures, in most cases, the pH is restored to normal values and the patient’s well-being improves.
Treatment of a child is carried out according to the same principles as therapy for an adult patient. However, it should be remembered that children are more susceptible to any disease, especially those accompanied by changes in acidity. Therefore, timely hospitalization and properly provided medical care are especially important for them.
Prevention of acidosis
Prevention consists of preventing the development of pathological conditions accompanied by metabolic acidosis, and if they have developed, in their timely and adequate treatment.
Violations of the acid-base balance can be avoided if you watch your diet, walk more in the fresh air and give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol). In addition, to prevent acidosis, the following recommendations must be followed:
- promptly treat any metabolic disorders;
- raw plant foods should predominate in the diet;
- You must drink at least two liters of clean water;
- You should play sports to improve blood supply to all organs and normalize the functioning of the respiratory system;
- to quickly relieve symptoms of poisoning, you can drink a soda solution;
- It is necessary to control the quality of drinking water and monitor the level of its hardness (saturation with minerals).
Acidosis, the symptoms and treatments for which are described above, can be prevented. To reduce the likelihood of developing the disease, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Healthy food;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- drink enough fluids;
- control the hardness and quality of drinking water;
- promptly treat pathologies associated with metabolic disorders;
- lead an active lifestyle, engage in physical exercise;
- do not abuse caffeine-containing drinks;
- timely sanitization of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- undergo regular preventive examinations of the body.
Health to you!
First of all, the patient needs to establish a lifestyle, observing sleep and diet. Bad habits should be eliminated; it is recommended to eat fruits and vegetables. This all contributes to the prevention of pathologies such as alkalosis and acidosis. But proper nutrition alone is not enough; moderate physical activity is needed.
Doctors recommend undergoing a medical examination once a year for the purpose of prevention. To balance BER, you need to know that mineral water and milk increase the level of alkalis, while tea and coffee, sweets and meat increase the level of acids. Therefore, such products should be consumed in moderation.
To prevent acidosis, it is necessary to take a very careful approach to the issue of a balanced diet and timely treatment of existing diseases. White bread, eggs, cheeses, meat, animal fats, eaten without restrictions, do more harm than good. Therefore, to prevent acidosis, it is necessary to use these products in moderation. Do not abuse coffee and alcohol. It is advisable to consume as many vegetables and fruits raw as possible.
Prerequisites for preventing acidosis are preventive visits to the doctor and careful treatment of already acquired diseases.
Prevention
Preventive recommendations for such a violation are as follows:
- proper nutrition - in this case it means a balanced diet, timely consumption of food, avoidance of the habit of washing down food with drinks;
- avoidance of too much alcoholic drinks, you should quit smoking if such a habit occurs;
- it is necessary to treat all diseases promptly and correctly, since any pathological process can lead to serious complications;
- it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, which will help avoid frequent cases of infectious and inflammatory pathologies;
- eliminate stress, nervous experiences, abstract from negative moral influences;
- monitor your weight;
- drink enough liquid per day (liquid meals and alcohol do not count);
- use vitamin-mineral complexes.
During pregnancy, this condition can be excluded if you follow the recommendations of doctors and lead a healthy lifestyle. In addition, it would be useful to systematically undergo a preventive medical examination, especially if your personal history includes diseases that are included in the etiological list.
Consequences and complications
Complications of metabolic acidosis can include:
- dehydration;
- decrease in circulating blood volume;
- increased blood clotting, accompanied by a risk of thrombosis;
- circulatory disorders (including such serious ones as myocardial infarction, infarction of parenchymal organs, peripheral thrombosis, stroke);
- arterial hypo- and hypertension;
- disturbance of brain functions;
- coma;
- death.
Correct nutrition
To avoid acidosis, you should think about proper nutrition. The reason for the disturbed acid-base balance is most often the so-called one-sided diet, in which one type of food predominates in the diet: meat, dough products, confectionery. However, diet alone for acidosis is not a sufficient solution. Doctors also recommend playing sports and leading an active lifestyle. The fact is that moderate physical activity promotes excellent ventilation of the lungs, which is why the body is supplied with a large volume of oxygen. All this favors acid metabolism.
You may be interested in: What do blue lenses look like on brown eyes?
To get rid of acidosis and restore the acid-base balance, it is recommended to regularly drink plenty of fluids, still mineral water and add such products to your menu;
- not too fatty meat;
- porridge, in particular oatmeal and buckwheat;
- green tea, herbal decoctions and infusions;
- fresh vegetables, fruits and berries;
- whole grains and whole grains;
- rice broth.
During the period of treatment for this disorder, you should not “indulge” in rich broths, borscht with sauerkraut and sorrel, hot sauces, marinades and appetizers. Also reduce the amount of fast carbohydrates in your diet, since during their digestion a large amount of acids are formed. Products that you should forget about for a while include:
- potato;
- confectionery and bakery products;
- pasta;
- animal fats;
- carbonated drinks;
- sausage products, frankfurters and small sausages;
- alcoholic and alcoholic beverages;
- coffee and black tea;
- crackers and chips.
Complication
Severe metabolic acidosis at the terminal stage causes depression of the respiratory center. Hyperventilation is replaced by weak, shallow breathing. Hypoxia of the brain develops, leading to loss of consciousness and coma. The activity of the kidneys and liver is impaired, and multiple organ failure occurs.
The consequences of metabolic acidosis if untimely or incorrectly treated can be quite dangerous. Initially, the bones begin to release minerals. In this case, the acidity decreases somewhat, but as a result, a person may develop osteoporosis. The damage also affects cartilage, resulting in a sharply increased risk of osteoarthritis.
As a result of increased uric acid levels, a person develops gout, which causes severe joint pain. In addition, acidosis can provoke diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- impaired renal function;
- hypertension;
- formation of kidney stones;
- dysfunction of the immune system.
Violation of acidity is often accompanied by severe hunger, apathy, fatigue, deterioration of skin condition, severe hair loss, increased sweating and brittle nails. In the most severe cases, there may be a state of shock. This can lead to death, especially if the patient is not provided with timely assistance.
What should be the analysis indicators?
If metabolic acidosis is suspected, blood values are taken into account first to make an accurate diagnosis. In the presence of the disease, are such indications observed? How:
- pH shift to the acidic side;
- increased serum potassium levels;
- increased levels of chlorides.
However, it is worth noting that in this case the total content of carbon dioxide in the blood serum decreases sharply, urine is always acidic, even with normal kidney function. Based on the results of the examination, a final diagnosis is made and subsequent treatment is prescribed.
Causes
The development of lactic acidosis can be caused by hypoxia that occurs in skeletal muscles due to prolonged physical overexertion. Also, the pathological process can develop with diabetes mellitus, malignant neoplasms, infectious and inflammatory diseases, respiratory failure, myocardial infarction, acute intestinal or lung infarction, renal failure, chronic liver diseases, massive bleeding, severe injuries, chronic alcoholism.
Alkalosis and acidosis can occur due to various reasons, depending on their type. Acidosis appears in diseases that are accompanied by a feverish state, since organic acids are retained in the body. Acetone and acetoacetic acid appear in the urine. In severe cases, coma occurs.
The same type of food and a poor diet, dehydration, and elevated ambient temperatures can also provoke alkalosis. With brain injuries, when vomiting and hypercapnia appear, this pathology also develops. Metabolic alkalosis occurs when the body loses hydrogen ions through excessive vomiting or taking medications that increase diuresis, or long-term intake of mineral water.
Acidosis is a violation of the acid-base balance, in which the acidity of the blood increases and the pH drops below 7.35, hence the accumulation of harmful products in the body and depression of consciousness. The natural ending is coma and then death.
Acidosis itself is not considered a disease; it is a critically dangerous condition, but it is secondary. Refers to a symptomatic complex, a syndrome of a specific disorder.
In some cases, situational surges in acidity are possible, even though they are within the normal range.
In most clinical situations, urgent treatment is required. The underlying disease that caused such a formidable symptom is subject to correction, as well as the elimination of excess acidity, a symptomatic measure.
Both activities take place in a hospital setting, often as part of resuscitation efforts.
Development mechanism
The process has a complex origin. The pathogenesis is based on the inability of the body's buffer systems, primarily blood, to normalize the acidity of the environment. Typically, even healthy people experience pH fluctuations; an adequate value is in the range from 7.35 to 7.38.
Minor deviations in both directions are possible, but short-term. This is also not considered critical.
When the pH drops below 7.35 on a long-term basis, changes in the functioning of organs develop: breathing and cardiac activity suffer, the nervous system is depressed, which ends in death without treatment.
Dynamic balance becomes impossible in a group of disorders. There are several mechanisms for the development of acidosis:
- Excessive acidification of the blood due to the intake of large amounts of gases rich in carbon compounds. For example, when exposed to smoke for a long time, in a stuffy room, with a lack of O2, possibly in high mountains. This is a relatively uncommon cause.
- Hormonal imbalance, accumulation of protein breakdown products in the body. Typically, this problem occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- The development of a gestational variant of the disorder is possible. They talk about it when the waste products of the fetus poison the mother’s body, when self-regulation and cleansing of the latter is impossible. It occurs mainly in women with somatic pathologies (renal, cardiac, respiratory failure), also in cases of multiple births and severe gestation.
There are other options. Acidosis does not always have a pathological origin. Normally, healthy people experience changes in the acidity of the blood and urine.
There are several reasons for this:
- Intense stress triggers biochemical reactions involving cortisol, adrenaline and others. The result is a temporary pH drop.
- The problem is also observed against the background of excessive physical activity.
- After surgery.
- With an ill-formed diet with a large amount of carbohydrates, protein with a minimum amount of coarse fiber.
Each situation is subject to individual assessment.
Acidosis does not always present pronounced symptoms, especially if the acidity is slightly increased.
But the disorder has the unpleasant property of progressing quickly, within a matter of hours, leading to coma and death. You need to be on your guard.
Classification
The disorder can be divided in several ways. Upon admission of a patient, doctors urgently examine the extent of the disorder. This involves assessing blood and urine.
The types are named according to the criterion:
- Compensated form. Accompanied by relatively normal acidity levels of up to 7.35. There are no symptoms or any signs yet, the patient is completely fine and does not suspect a problem. In this state, acidosis is usually not noticeable and the person is admitted to the hospital for another reason.
- Subcompensation gives a pH level in the range of up to 7.25, which is much more dangerous. The body is still coping, buffer systems partially correct the acidity level, but functional impairments are already present. From the heart, blood vessels, respiratory system. The central nervous system is still normal; headache, nausea, and vomiting are possible. Reflexive, not bringing relief. Without treatment, the pathological condition very quickly moves to the next stage.
- Decompensation of acidosis. Acidity levels are below 7.25, and abnormalities in the functioning of the brain and digestive tract occur. Breathing is shallow, gas exchange is significantly impaired. The phenomena of depression of consciousness and coma are rapidly increasing. Without urgent correction, death cannot be avoided.
Another way to classify acidosis is to evaluate its origin. Without elaborating this criterion, it is impossible to begin quality treatment.
Exogenous form
It is caused by the entry into the body of a large amount of acid in its pure form or substances that can be converted into acid during metabolic processes. If the buffer systems are working properly, the situation is unlikely.
Among the routes of entry of substances, the main one is considered to be nutritional. Food.
Respiratory acidosis
It's gas. It occurs more often and occurs as a result of the ingestion of dangerous mixtures from the surrounding air and environment into the body. For example, when you are in a burning room, there is a lack of oxygen in a room or office.
The same is observed with chest injuries. Carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood, which causes an imbalance in the dynamic balance.
Respiratory acidosis most often leads to rapid changes in the lungs, endocrine system, central nervous system, coma and death.
Excretory form
Accompanied by the inability to remove protein breakdown products and acidic substances due to insufficient filtering function of the kidneys.
The same problem occurs if the concentration of alkaline compounds drops. This often happens with dysfunction of the digestive tract. Recovery involves correction of the main diagnosis.
Associated with insufficient metabolism. Develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and pathologies of infectious origin.
The dysfunctions are deep and systemic. Therefore, treatment may take a little longer.
A special case of the metabolic form of the disorder is lactic acidosis, caused by a drop in insulin levels and, as a result, a complex biochemical reaction with the formation of a large amount of organic acid.
The pathogenesis (origin) is based not on one, but on several factors.
All of these types of acidosis are dangerous and, without treatment, in approximately 87% of cases end in the death of the patient.
Compensated forms can regress on their own, but this does not always happen. There is no need to count on luck.
The clinical picture is determined by the type of disorder.
The respiratory form is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Dizziness. Occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen concentration. Accompanied by disturbance of orientation in space, unsteadiness of gait. In difficult cases, the patient takes a lying position to ease the symptom.
- Shallow shallow breathing. A typical sign of respiratory acidosis. However, such an increase in movements does not lead to compensation; hypoxia (oxygen starvation) increases.
- Change in skin tone to pale. Cyanosis.
- With the long-term existence of the pathological process, the phenomena intensify. Cardiac signs occur: tachycardia, increased number of contractions per minute, arrhythmia. Jumps in blood pressure that are not subject to qualitative correction.
- Objectively, in addition, changes in urea levels are detected, calcium concentration drops, which leads to muscle spasms and cramps.
- In terms of diagnosis, the respiratory form is the simplest; the causes are obvious even with a superficial examination.
- Metabolic acidosis from the beginning gives cardiovascular manifestations:
- Tachycardia. Increase in the number of contractions per minute. At the same time, although the volume of pumped blood increases, the effect is minimal. Because there is not enough oxygen.
- Arrhythmias of other types. When excessive load on the myocardium occurs, group extrasystole or ventricular fibrillation occurs. Which is extremely dangerous. Against the background of such changes, the contractile, pumping function decreases.
- A characteristic symptom of acidosis in adults is increased breathing. The depth of movements increases while the frequency is formally preserved. Based on such a sign of acidosis as the nature of gas exchange, the doctor estimates the type of pathology, this saves time during further examination.
- Dizziness. Inability to navigate in space.
- Nausea and vomiting. Rare. Most often one-time, reflex.
- Impaired consciousness. When the pathological process worsens, all forms of the disorder cause depression of the central nervous system.
At first, this manifests itself as a “wobbly” body, weakness, drowsiness, a decrease in the speed of reaction to stimuli: a call, physical impact, a request, etc. Then loss of consciousness occurs.
Treatment of acidosis
Since acidosis practically does not manifest itself, treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of its occurrence. However, the phenomenon itself is not ignored. Acidosis is treated with protein foods in mild forms. Medicines include sodium bicarbonate orally for mild cases or intravenously for severe cases. Calcium carbonate is prescribed if it is necessary to limit the amount of sodium and for hypocalcemia.
Metabolic acidosis is treated:
- Sodium bicarbonate.
- Nicotinic acid.
- Cocarboxylase.
- Riboflavin mononucleotide.
- Glutamic acid.
- Dichloroacetate.
For pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract, Rehydration salt and Dimephosphone are taken orally.
The main emphasis is on proper nutrition. During treatment you should avoid coffee and alcoholic beverages. Fruits, vegetable fats, berries, fresh vegetables are taken along with white bread, pasta, and animal fats. It is actively recommended to take a decoction of rice to remove toxins, waste and other harmful elements.
Lactic acidosis in diabetes mellitus symptoms, treatment
Lactic acidosis is a dangerous pathological condition that occurs when large amounts of lactic acid enter the blood. In this case, the body cannot cope with sufficient excretion, which is why it accumulates. This causes a serious disturbance in the acid-base balance. The body ceases to cope with the negative changes occurring, and the development of lactic acidosis begins.
Pathology can be diagnosed in healthy people (for certain reasons), as well as in patients with diabetes. In the second case, lactic acidosis (ketoacidosis, diabetic acidosis) is often the result of uncontrolled diabetes.
As a result, the body begins to produce organic acids (ketone bodies) in large quantities. For diabetics, this condition is extremely dangerous, as it can cause hyperlactic acidemic coma.
Today we will talk about lactic acidosis in diabetes mellitus, we will find out the symptoms, treatment of this pathology, and also learn about preventive measures. We will begin our topic with a description of its characteristics:
Signs of diabetes
Very often, nothing predicts the appearance of lactic acidosis. However, in a very short time, in just a few hours, symptoms of acute pathology appear. The earliest ones include: pain in the muscles and behind the sternum, a state of apathy, drowsiness (insomnia), rapid breathing.
Attention! Next, the main symptom of lactic acidosis develops - cardiovascular failure, complicated by high acidity. Further, as the pathology progresses, abdominal pain appears, accompanied by nausea and vomiting
If the necessary treatment measures are not taken, the patient's condition will deteriorate greatly.
There is a slow reaction. A person reacts little to the surrounding reality, then stops noticing it altogether. The patient experiences involuntary muscle contractions, convulsions, decreased activity and motor activity.
With further development of lactic acidosis, a coma occurs. Its harbinger is the appearance of intermittent breathing followed by loss of consciousness.
Treatment of the condition
With this dangerous complication of diabetes, the patient needs urgent medical attention. When placed in a medical institution, he is given a drip of sodium bicarbonate solution. At the same time, the level of potassium in the blood is constantly monitored.
A patient suffering from diabetes is prescribed additional insulin injections. If necessary, the daily dosage is adjusted, or the drug used is replaced. Also used in treatment is a carboxylase solution, which is administered intravenously by drip. If prescribed by a doctor, it is possible to administer blood plasma. Treatment is with heparin (in small doses).
Prevention of the condition
Lactic acidosis, the symptoms and treatment that we discussed with you today, can always be prevented. To do this, use the following recommendations:
- First of all, a patient with diabetes should take into account the effect of medications that reduce sugar on the body. In the absence of certain side diseases, these drugs effectively cope with their task and do not cause any negative consequences.
- However, if any disease occurs, infectious, viral, even a cold, the body’s reaction to a drug that lowers sugar can be unpredictable. Therefore, in such cases, a diabetic patient is advised to consult with his or her doctor.
- In particular, lactic acidosis can occur due to the intake of biguanides. Therefore, the doctor prescribes its dosage strictly individually. The patient must strictly follow these instructions and comply with all medical recommendations.
- In addition, it is necessary to carefully monitor the dynamics of the development of the disease, visit a doctor regularly, and take the necessary tests on time. At the slightest suspicion of the development of lactic acidosis, it is necessary to visit an endocrinologist as soon as possible. Be healthy!
Symptoms
Symptoms of metabolic acidosis
The symptoms of metabolic acidosis directly depend on the disease that provoked the onset of the pathology.
The main manifestations are:
- increased breathing;
- constant nausea and vomiting, which does not improve the general condition of a person;
- shortness of breath that occurs even at rest;
- extreme weakness;
- painful pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- slow heart rate;
- decreased blood tone values;
- dizziness;
- lethargy;
- attacks of loss of consciousness;
- seizures;
- drowsiness;
- feeling of lack of air;
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- shock or coma.
It should be noted that in some cases external manifestations may be completely absent.
If the following symptoms occur, it is necessary to take the patient to a medical facility as soon as possible or call an ambulance at home:
- deep and frequent breathing;
- severe weakness - to such an extent that the victim cannot get out of bed;
- fainting;
- confusion.
In such situations, all diagnostic and therapeutic measures are carried out in intensive care conditions.
Causes of lactic acidosis
- hereditary metabolic disorders (methylmalonic acidemia, glycogenosis type 1);
- parenteral (bypassing the gastrointestinal tract) administration of large doses of fructose;
- consumption of ethylene glycol or methanol;
- pheochromocytoma (adrenal tumor);
- complicated infectious diseases;
- severe damage to the liver and kidneys;
- excessive intake of salicylates;
- carbon monoxide poisoning;
- chronic alcoholism;
- massive bleeding;
- cyanide poisoning;
- state of shock;
- taking biguanides;
- acute anemia;
- epilepsy.
Lactic acidosis in diabetes mellitus
Among the etiological reasons, long-term use of biguanides occupies a special place. Even a small dose of these drugs (subject to the presence of renal or hepatic dysfunction) can provoke the appearance of lactic acidosis.
Almost half of the cases of lactic acidosis development occur in patients with diabetes mellitus.
When treating a patient with biguanides, the development of lactic acidosis occurs due to impaired penetration of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) through the membranes of cellular mitochondria. In this case, pyruvate actively begins to be converted into lactate. Excess lactic acid enters the blood, then to the liver, where lactic acid is reformed into glycogen. If the liver cannot cope with its job, lactic acidosis develops.
Additional provoking factors
Provoking factors influencing an excess of lactic acid in the body during diabetes mellitus may be the following reasons:
- muscle hypoxia (oxygen starvation) during intense physical activity;
- general respiratory failure (dysfunction);
- lack of vitamins (in particular group B);
- alcohol intoxication;
- severe myocardial infarction;
- kidney dysfunction;
- acute bleeding;
- age from 65 years;
- pregnancy.
Hypoxia
The main trigger for the development of lactic acidosis is oxygen starvation (hypoxia). Under conditions of severe oxygen deficiency, active accumulation of lactic acid occurs (provokes the accumulation of lactate and increases anaerobic glycolysis).
With the oxygen-free division of carbohydrates, the activity of the enzyme responsible for the conversion of pyruvic acid into acetyl coenzyme A decreases. In this case, pyruvic acid is converted into lactate (lactic acid), which leads to lactic acidosis.
General rules and methods of treatment
If a complication of type 2 diabetes develops, urgent medical attention is needed. It is not always possible to predict the development of severe complications of diabetes. The patient’s life depends on the awareness of loved ones who were nearby at the time of increasing signs of lactic acidosis and the qualifications of the doctors providing assistance.
First, you need to eliminate hypoxia and manifestations of acidosis, stabilize the main life support systems
It is important to bring the patient out of shock and ventilate the lungs. If a diabetic is unconscious, then urgent intubation is needed to supply oxygen to the body cells
Doctors eliminate excess blood acidity and neutralize the negative effects of excess lactic acid using a solution of sodium bicarbonate. The procedures are carried out daily until the main indicators in the body are stabilized. In one day, the patient receives no more than two liters of an alkaline solution.
Additionally, short-acting insulin with glucose, cardiotonics and vasotonics are prescribed to normalize the functions of the heart and vascular system. During treatment, blood tests are needed to assess potassium concentration and blood pH.
Learn about the prevention of diabetes in children and adults, and also read useful recommendations from experts.
The rules and features of following a diet for thyroid hypothyroidism are described in this article.
Go to https://vse-o-gormonah.com/hormones/testosteron/kak-ponizit-u-zhenshin.html and read information about the causes of high testosterone in women, as well as how to lower the hormone levels naturally .
The next stage is detoxification therapy:
- intravenous administration of carboxylase;
- correction of insulin therapy;
- administration of blood plasma;
- to eliminate DIC syndrome, small doses of heparin are prescribed;
- administration of rheopolyglucin.
After stabilization of the condition and normalization of vital signs, the patient is in the hospital. Be sure to follow a diet, monitor the dynamics of glucose concentrations and blood acidity levels, measure blood pressure
Upon returning home, you need to follow the endocrinologist’s prescriptions, take hypoglycemic drugs with caution, and always use traditional or.
General information
Metabolic acidosis (MA) or acidemia is a condition associated with a change in the activity of biologically significant proteins against the background of a shift in acid base balance to the acidic side. Develops in severe somatic diseases, some poisonings, shocks of any origin. Moderate acidemia is not accompanied by clinical symptoms.
When the cause of the failure is eliminated, the normal state of the internal environment is restored without medical intervention. Severe acidosis requires treatment in the ICU due to the high risk of respiratory and cardiovascular accidents. Patients need constant hardware monitoring of vital signs, daily and sometimes hourly blood sampling for laboratory tests.
How is lactic acidosis treated?
Lactic acidosis, or lactic acidosis, is a condition in which the level of lactic acid in a person's blood rises too quickly. This acid is not eliminated as quickly as it accumulates, and the person's blood becomes too acidic. Lactic acidosis can be dangerous, and those who experience it may need medical attention.
Treatment for this condition may require hospitalization, intravenous hydration, medications or antiacid agents, and sometimes even kidney treatments that help eliminate lactic acid from the blood. The choice of the most appropriate treatment often depends on the severity of lactic acidosis, as well as the underlying cause.
Athletes often experience episodes of lactic acidosis as a result of intense training. During intense work, muscles are able to use oxygen so quickly that the body does not have time to replenish its reserves.
Advice! Without enough oxygen to process lactic acid, lactic acid accumulates in the blood, causing shortness of breath and a burning sensation and fatigue in the muscles. This form of lactic acidosis is mild and usually does not require any treatment other than resting the muscles.
When the athlete rests, the body usually begins to recover on its own and no lasting or severe effects occur.
Lactic acidosis due to diabetes mellitus
In some cases, treatment for lactic acidosis is necessary. A person may develop this condition due to a genetic disorder, a disease that causes a lack of oxygen in the body, severe bleeding, severe infection, and sometimes diabetes. It may even occur as a side effect of certain medications, particularly those used to treat diabetes and immune system deficiencies.
In such cases, a person may experience fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. Some patients also experience:
- pain and bloating in the abdominal area
- decreased appetite
- liver edema
- poor liver function or
When severe cases of lactic acidosis develop, doctors usually do tests to determine its cause and decide on treatment. Sometimes treatment involves stopping the drug that is contributing to the condition.
In addition, doctors may administer intravenous saline and prescribe kidney dialysis, which helps eliminate lactic acid from the blood; it also helps remove the drug from the body that could be causing the problem. Antibiotics are used to treat possible blood poisoning, and sodium bicarbonate is used to neutralize the acid. In severe cases, treatment for lactic acidosis may include oxygen therapy.
Lactic acidosis what is it
Lactic acidosis is a disorder of glucose metabolism, which leads to increased blood acidity, and as a result, destruction of blood vessels, pathology of nervous activity, and the development of hyperlactic acidemic coma.
Normally, glucose entering the blood penetrates the cells and is broken down into water and carbon dioxide. In this case, energy is released, which provides all the functions of the human body. During the conversion process, more than a dozen chemical reactions occur with carbohydrates, each of which requires certain conditions. The key enzymes that ensure this process are activated by insulin. If due to diabetes there is not enough of it, the breakdown of glucose is inhibited at the stage of pyruvate formation, which is converted in large quantities into lactate.
In healthy people, the normal level of lactate in the blood is less than 1 mmol/l; its excess is utilized by the liver and kidneys. If the intake of lactic acid into the blood exceeds the ability of the organs to remove it, a shift in the acid-base balance of the blood occurs to the acidic side, which leads to the development of lactic acidosis.
When lactate in the blood accumulates more than 4 mmol/l, the gradual increase in acidity becomes abrupt. Strengthening the situation in an acidic environment worsens the situation. Disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism are accompanied by distortions in protein and fat metabolism, the level of fatty acids in the blood increases, metabolic products accumulate, and intoxication occurs. The body is no longer able to break out of this circle on its own.
Even doctors cannot always stabilize this condition, and without medical help, severe lactic acidosis always ends in death.
Carrying out prevention
The diet should be rich in vegetables, lactic acid products, and low-sugar fruits. Not recommended for use:
- cereals;
- bakery products;
- sweet fruits.
You will have to exclude alcohol, sugar, sausage, and fruit juices containing sugar. Freshly squeezed juices are allowed in small quantities
A meal schedule is important. It should be given at the same time every day, just like insulin injections.
Medicines
- The tablets should be taken at the same time every day. Independent replacement or discontinuation of medications is prohibited. Only a doctor can make such changes.
- Inject insulin in different places so that the injection in the same place is not repeated often. Keep the area where the drug is administered clean.
- Moderate physical activity. Walking, cleaning, light running - contribute to better absorption of glucose.
- Strict daily routine. Work, rest, getting up, taking medications are done at a certain time.
- Don't overwork yourself mentally and physically.
special instructions
Carry a diabetes card with you. Try not to get sick with viral diseases
Complications can lead to a coma. Always have candy or a few pieces of sugar with you in case of hypoglycemia. Regularly visit the doctor and take the necessary tests. Pay attention to alarming symptoms and seek medical help as soon as possible.. By adhering to these rules, you can live a normal, fulfilling life for many years
By adhering to these rules, you can live a normal, fulfilling life for many years.
- diseases of the respiratory system (for example, bronchial asthma, emphysema, pulmonary fibrosis and other lung diseases);
- respiratory failure (for example, caused by rib fractures);
- diabetes;
- chronic kidney diseases.
In addition, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- eat a balanced diet, pay attention to physical activity;
- drink enough water (about 2 liters per day);
- drink alcohol in moderation;
- give up nicotine completely.
Symptoms
Lactic acidosis develops quite quickly, but its first signs may be dyspeptic disorders, muscle pain, and angina pain. A distinctive feature is the lack of effect from taking analgesics.
It is often possible to suspect that this is lactic acidosis due to such symptoms in patients with diabetes as anxiety, weakness, adynamia, headache, nausea, vomiting, arterial hypotension up to collapse, acute abdomen, drowsiness, turning into a state of stupor, stupor and coma, anuria due to impaired renal perfusion.
The skin is pale, cyanotic, the pulse is frequent and small. Cardiovascular failure, arterial hypotension, shortness of breath, compensatory hyperventilation, and Kussmaul breathing progress.
Unfortunately, there are no specific distinguishing signs of lactic acidosis, so the diagnosis of lactic acidosis is always difficult.
Given its fairly rapid development, which is not typical for hyperglycemic states, it is important to quickly distinguish lactic acidosis from hypoglycemic loss of consciousness.
Table - Differential diagnostic signs of hyper- and hypoglycemic conditions
| Sign | Hypoglycemia | Hyperglycemia |
| Start | Rapid (minutes) | Slower (hours – days) |
| Skin, mucous membranes | Wet, pale | Dry |
| Muscle tone | Increased or normal | Reduced |
| Stomach | No signs of pathology | Bloated, painful |
| Arterial pressure | Stable | Reduced |
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms associated with acidosis are often masked by accompanying progressive illnesses, so abnormal changes in pH balance are not identified for an extended period of time.
Signs of acidosis in a person with a mild form of pathology may be absent; accordingly, people whose blood has high acidity do not consult a doctor due to the absence of complaints.
Severe and moderate stages of acidosis in adults and children are accompanied by:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
- chronic fatigue syndrome,
- deep, rapid breathing,
- bronchial spasms,
- belching,
- arrhythmia, hypertension, hypotension,
- sweating,
- puffiness, change in color (blueness, redness, paleness) of the face,
- neurological disturbances (fog, loss of consciousness, lethargy, dizziness, drowsiness, apathy, drowsiness, depressed reflexes),
- circulatory shock
- comatose states.
Symptoms worsen as blood pH decreases. When the level reaches 6.8, the patient's condition is considered incompatible with life.
Therapy
Since acidosis occurs due to impaired functioning of the body's systems and organs, the course of treatment is based on the treatment of the disease or dysfunction that led to a shift in the acid-base balance. Any type of acidosis can significantly weaken the body, so at the first suspicion of this pathology, rush to visit a specialist. Typically, treatment of complex forms of acidosis includes the following items:
- improvement of pulmonary ventilation;
- decrease in the amount of protein in the blood plasma;
- strengthening the buffer hydrocarbonate system;
- restoration of blood microcirculation, reduction of its volume;
- normalization of oxidation processes by introducing glucose, ascorbic acid, Riboxin, Pyridoxine, Thiamine, Insulin;
- elimination of the cause of pathology;
- normalization of electrolyte metabolism;
- improving blood flow in the kidneys.
To eliminate symptoms, treatment of acidosis involves the following: ingesting a certain amount of soda (sodium bicarbonate); increased drinking; elimination of additional symptoms such as arrhythmia, nausea, lethargy. If poisoning is detected, medications are prescribed to remove toxic substances from the body; in especially severe situations, it is necessary to cleanse the body. If the acidosis has not become acute, it is worth reducing the consumption of protein foods. An excellent medication is calcium carbonate.
To get rid of metabolic acidosis, glutamic and nicotinic acids, as well as cocarboxylase, are prescribed. Acute forms of acidosis must be treated with rehydration salts. Even if the acid-base balance is disturbed, take Dichloroacetate, which activates enzymes. In addition to medications, the patient should eat a balanced diet and eliminate alcohol and coffee from the diet.
On a note! When treating symptoms of acidosis, the ratio of acids and alkalis must be monitored. For this purpose, an ionogram is constantly taken during therapy.