What joints does the spinal column include?
The spinal column forms a container for the spinal cord, and it also performs a supporting function for the organs and tissues of the body.
The spinal column consists of 32-34 vertebrae, which are interconnected by various connections:
- Intervertebral discs that connect the vertebral bodies;
- Joints that form between the articular processes of the above and underlying vertebrae;
- Ligaments of the spinal column.
The vertebral arch has seven processes that play a role in the formation of joints: 2 upper articular, 2 lower articular, 2 transverse and spinous.
With the help of the upper and lower articular processes, intervertebral (facet, facet) joints are formed.
With the ribs, the vertebrae form costovertebral joints: with the help of the articular surface of the rib head and the costal fossae of the vertebral bodies, the joints of the rib head are formed, and the costotransverse joints are formed with the help of the articular surface of the tubercle of the rib and the transverse process of the vertebra.
Uncovertebral joints are formed using special hooks on the lateral edges of the cervical vertebrae lll - vll.
These hooks play a role in preventing excessive lateral flexion of the cervical spine.
Near the uncovertebral joints pass the vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord, as well as the nerves that extend from the spinal cord.
Classification
The division of spinal spondyloarthrosis involves several directions:
- development of pathological changes;
- degree of severity;
- the location of the painful manifestation.
Kinds
Destructive processes involving articular joints are of several types:
- Degenerative - the surfaces at the junction of the ribs with the ridge, as well as the intervertebral layer, undergo pathological changes.
- Deforming - characterized by the formation of osteophytes along the edges of the bone structure.
- Ankylosing - severe deformation affects several joints and leads to their destruction.
- Facet - negative changes in the facet joints, and in the joints between the ribs and the vertebral axis.
- Uncovertebral - changes are characteristic of the cervical region, and occur between the first and second fragments of the ridge.
- Dysplastic means severe deformation with subsequent destruction of the joints of the spinal column.
- Polysegmental - joints in several parts of the spine are subject to changes.
Degrees
Spondyloarthrosis is divided according to the degree of development:
- The first is that at the initial stage it does not cause concern to patients; only a random preventive examination can reveal minor pathological changes. The pain is moderate and can be attributed to fatigue after physical activity.
- Second, the first signs of the disease appear, manifested in back fatigue, loss of former mobility, and a feeling of pain. Changes in the fibrous ring (disc protrusion and second degree spondyloarthrosis) can be diagnosed.
- Third, during this period the cartilage tissue becomes inflamed, the bone surface of the joints is affected, osteophytes appear, the ligamentous apparatus is disrupted, the manifestation of pain in spondyloarthrosis of this degree forces the use of blockades using analgesics.
- Fourth, all changes become irreversible. The growths along the edges of the joints increase and lead to complete immobility, problems with blood supply arise, and compression of the nerve endings occurs. Pain at this level is pronounced and constant.
Read more in the article about the degrees of spondyloarthrosis.
The photo shows the degree of development of the pathology:
Localization
The pathology can be localized in different parts of the supporting column and have an appropriate name.
There are spondyloarthrosis:
- Cervical spine or cervicoarthrosis - the formation of bone growths leads to damage to the bone marrow, vertebral artery, and painful sensations in the back of the head, in the shoulders, in the area of the shoulder blades;
- Thoracic spine or dorsarthrosis - in this section the joints are located behind the ribs, this interferes with the examination and detection of pathology; symptoms are mild, vessels are rarely affected;
- Lumbar spine or lumboarthrosis is the most common type of pathology; pain spreads to the buttocks and femoral part of the leg, especially pronounced during all kinds of movements in the lumbar region at the very beginning of body movement;
- The lumbosacral spine - pain appears in the lower part of the lower back, since the cause is a pathology in the formation of the spine, the pain radiates to the lower parts of the body; Possible gait disturbances due to changes in posture.
Mechanism and causes of occurrence ↑
Degenerative changes in the joints of the spine occur when trophism is disrupted.
In cartilage tissue that is not properly supplied with blood, the content of chondroitin sulfate decreases, which is replaced by non-functional substances.
Stages of development of intervertebral spondyloarthrosis:
- Atrophy of the cartilage tissue of the joint;
- Degenerative changes in cartilage, resulting in loss of proteoglycans and death of chondrocytes;
- Cartilage loses elasticity. This process begins from the center and then spreads to the periphery of the cartilage;
- The articular surfaces of the bones are exposed;
- Periarticular bone tissue undergoes sclerosis (subchondral sclerosis);
- The joint capsule undergoes an inflammatory reaction, which is provoked by fragments of cartilage floating in the synovial fluid;
- Along the edges of the articular surfaces, growths of bone tissue appear - marginal osteophytes.
The causes of spondyloarthrosis are divided into two groups:
- External reasons. They are characterized by a discrepancy between the load on the joints of the spine and their ability to withstand this load, injury to the spinal column, and excess body weight.
- Internal reasons. Such factors include hereditary predisposition, defects in the development of the musculoskeletal system, autoimmune pathology, in which antibodies are produced to one’s own cartilage tissue, as well as metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus and gout.
There are the following predisposing factors for the development of the disease:
- age over 65 years;
- female gender, since estrogens, which are maximally produced during menopause, affect the development of osteoarthritis;
- increased content of adipose tissue, in which sex hormones are produced that affect the development of arthrosis;
- high bone mass, characteristic of professional athletes, also promotes the production of estrogen;
- identified cases of common spondyloarthrosis within the same family.
Worried about foot pain?
One possible cause of such pain is tendinitis. Find out what foot tendonitis is in our article. What are the symptoms of lumbar spondylolisthesis? The answer is here.
Characteristics of the disease
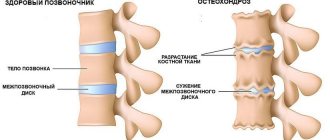
Spondyloarthrosis is a chronic disease and can develop asymptomatically for a long time. It is a lesion of the facet joints of the spine with the formation of bone spurs along the edges of the vertebrae. At the initial stage, degenerative changes affect only the cartilage tissue: the cartilage between the vertebrae becomes thinner, loses its elasticity and can no longer perform shock-absorbing functions.
The disease is characterized by damage to cartilage and bone tissue with subsequent formation of growths along the edge of the vertebrae
Massage pillow for neck and shoulders
Subsequently, if no measures are taken, the process of destruction covers the bone tissue in the periarticular areas, as well as the ligaments and muscles of the spine. Gradually, bone growths form on the joints, which cause the patient some discomfort when turning and tilting the head. The more the disease progresses, the stronger the pain when moving the neck, and only at rest does a person feel relief.
The disease manifests itself as severe neck pain and limited motor functions.
Main symptoms and signs ↑
Spondyloarthrosis of the facet joints is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Morning stiffness of the spine is associated with a person’s immobility during sleep. The duration of stiffness is approximately 30 minutes;
- Pain occurs when moving, and as the disease progresses, it also occurs at rest. Articular cartilage does not have pain sensitivity, so pain occurs when other components of the joint are involved in the pathological process;
- In the later stages, the patient may hear a “crunch” in the joints of the spine, which is associated with the appearance of a large number of osteophytes;
- Changes in weather can cause pain in the affected joints;
- Restriction of mobility up to the occurrence of tendon-muscular contractures.
Spondyloarthrosis of the costovertebral joints is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the area of the affected joints during movements with initial spondyloarthrosis, and in later stages at rest;
- Limitations of movement in the joint;
- Neuritis of the affected area;
- Discomfort and pain may appear in response to changes in atmospheric pressure;
- In later stages, atrophy of the surrounding muscles may occur.
Spondyloarthrosis of the uncovertebral joints is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain along the distribution of nerves arising from the cervical segments of the spinal cord;
- Impaired blood supply to the brain, which manifests itself as headaches, ringing in the ears, decreased memory, and blurred vision. In severe cases, cerebral ischemia occurs.
- Brachial and cervical neuritis.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of spondyloarthrosis are determined by the stages of development of the pathological condition of the spinal joints. They help determine the course of the disease. Timely diagnosis and treatment of spondyloarthrosis makes it possible to prevent complications caused by degenerative changes in the tissues of the spinal column. The clinical picture of the disease does not differ in pronounced symptoms. The list characterizing the symptoms of spondyloarthrosis at the initial stage of its development includes:
- pain in the area of the spinal column that occurs during static loads in the form of prolonged standing or sitting and localized in places of partial degenerative dystrophy of the intervertebral joints;
- the appearance of discomfort in the back.
During the transition of spondyloarthrosis, treatment of which should begin after the appearance of its first symptoms, from the initial stage to more severe forms of development, weakness and numbness of the limbs, headaches, dysfunction of the visual system, hearing, coordination of movements and balance in the surrounding space are noted. Such symptoms of spondyloarthrosis are compression of the nerve trunks, the vertebral artery and a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Diagnostic methods ↑
The diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis is made on the basis of a medical history, characteristic complaints, and palpation examination of the affected joint, which reveals pain, muscle contracture, and sometimes swelling and redness.
The range of motion of the spine is determined, and the limitation of mobility is judged from it.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing this disease include:
X-ray examination
It is often decisive in making the diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis.
On an x-ray, it is more difficult to recognize arthrosis of the joints of the spine than damage to larger joints.
The joints of the spine are distinguished by their small size.
However, the radiological classification of the stages of osteoarthritis also applies to them:
- absence of radiological signs;
- dubious signs;
- minimal manifestations in the form of slight narrowing of the joint spaces and isolated osteophytes;
- moderate manifestations in the form of progression of narrowing of the joint space and multiple osteophytes;
- pronounced manifestations are characterized by an almost complete absence of joint space and rough osteophytes.
Photo: lumbar spondyloarthrosis
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A method based on the properties of hydrogen protons to emit radio waves.
The maximum number of returned radio waves will be observed in tissues with a large number of hydrogen atoms, i.e. with a high percentage of water.
Damaged joints contain very little water, so joints with spondyloarthrosis will be darkened.
Photo: cervical spondyloarthrosis
CT (computed tomography)
This is a method of layer-by-layer examination of the body - the CT machine operator sets the distance between the slices.
To examine vertebral joints, it is necessary to set a minimum distance to accurately determine the presence of osteophytes and marginal osteosclerosis.
Does spondyloarthritis disease require sick leave or disability?
Does spondyloarthritis disease require sick leave or disability?
As mentioned above, with spondyloarthrosis, a disability group is assigned, which depends on the clinical picture of the pathology, inflammatory processes, and functionality of the joints. Disability may be assigned after an examination. In the first group of disabilities, work is prohibited.
A sick leave certificate for spondylarthrosis is issued if a person has limited motor activity due to pain and inflammation. In this case, the doctor prescribes medication in the form of a blockade or tablets. When the pain subsides, the person returns to work.
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis ↑
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis is aimed at reducing pain impulses, restoring the range of motion in the joint and its functionality, reducing the progress of the pathological process and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Non-drug methods of combating spondyloarthritis include:
- Physiotherapy. Physical activity helps maintain the functionality of the spinal joints. In this case, the loads should be dynamic, and loads on the spinal axis should be excluded. The exercises are best performed in a lying or sitting position. Swimming is the best option for physical activity. It is necessary to perform exercises to strengthen the back muscles.
- Loss of body weight.
- The use of orthopedic corsets. These devices help reduce pain symptoms.
- Procedures with temperature effects. Outside the acute stage, it is advisable to use cold or heat, which will help relieve pain for a while.
- Ultrasound therapy. Reduces symptoms and improves joint function. The procedures are prescribed during the remission stage.
- Blockades. To reduce radicular pain and neuritis, intercostal nerve blockade can be used.
- Reflexology. Some authors suggest the use of reflexology, but for spondyloarthrosis it is an unconventional method of treatment.
Drug therapy includes drugs that can be included in two large groups:
- Fast-acting remedies. Their use leads to minimization of pain symptoms. These include analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tramadol.
- Slow-acting agents. Their action is aimed at restoring the structure of the cartilage tissue of the vertebral joints. These include chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine, diacerein, soy or avocado unsaponifiables.
Fast-acting drugs are designed to reduce the symptoms of the disease:
- Analgesics. They are first-line drugs for pain relief. These include paracetamol. It is prescribed no more than 4 g/day. A relatively harmless drug when used for two years.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Most often used in practice. Their use is advisable in the absence of the desired effect from paracetamol. When prescribing this group of drugs, it is necessary to rely on concomitant pathology. This group of drugs has a large number of side effects on the cardiovascular, digestive and kidney systems. Taking these drugs for spondyloarthrosis should be started only during periods of increased pain.
- Opioid pain medications. Prescribed if there is no effect from the previous groups. Tramadol is prescribed at 50-200 mg per day. Taking opiates should be short-term.
- Corticosteroids. The use of corticosteroids is prescribed when the disease progresses with a significant limitation in the range of motion in the joints.
If there are contraindications for prescribing systemic drugs, topical agents in the form of ointments, gels, and creams are used.
Slow-acting drugs have chondroprotective properties.
The duration of the therapeutic effect varies from 2 to 8 weeks.
Representatives of this group:
- Chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine are components of articular cartilage. To have an effect, these chondroprotective drugs need to reach a high concentration in the synovial fluid of the joints. Trade names of these drugs: structum, teraflex, dona, chondromed, etc.
- Unsaponifiable compounds from soy and avocado promote the synthesis of substances that stimulate collagen production by chondrocytes. These drugs reduce pain impulses.
Surgical treatment methods are used extremely rarely.
Has your child been diagnosed with Schinz disease? You will find a lot of information on this issue on our website. Why do osteophytes of vertebral bodies appear? The answer is here.
What is vertebral artery syndrome? Find out here.
Facet syndrome: what is dangerous and how to treat it
The bones, cartilage, and ligaments in the spine work together to protect the spinal cord, support the weight of the upper body, and facilitate movement. Each component of this complex system depends on the others. Because of this, any, even the most minor, pathology can ultimately lead to chronic pain and difficulties with movement.
Facet syndrome occurs when there is an uneven load on the intervertebral (facet, also known as facet) joints. Typically, this condition occurs as a result of a decrease in the height and volume of the intervertebral disc due to spondyloarthrosis and other degenerative processes. The facet joints become inflamed and can cause pain and stiffness.
Although every part of the spine can be affected by facet syndrome, it most often affects the lumbar region of the spine (lower back). This makes sense since the lower back carries a significant amount of stress from everyday life. Increased load on the facet joints leads to rapid wear of the cartilage, stretching of the joint capsules, the formation of osteophytes and cramping acute pain with any load on the spine. Exacerbation of pain is observed after long periods of inactivity. Patients also complain of a crunching sound when moving.
Treatment is medicinal
Many over-the-counter medications can reduce the inflammation caused by facet syndrome and allow patients to undergo physical therapy and other long-term care programs.
Localized injections of painkillers may also provide long-term relief from discomfort associated with movement. Sometimes these injections have to be done for 6 months.
Muscle relaxants can be used to reduce localized muscle spasms.
After the painful symptoms of facet syndrome have been brought under control with medication, the doctor may refer the patient to exercise therapy to strengthen the lumbar spine and associated muscles.
Stretching exercises aimed at restoring the correct pelvic tilt are very useful; Therefore, special attention should be paid to stretching those muscles that cause excessive anterior pelvic tilt (eg, hip flexors and lumbar extensors).
Stretching should not be limited to just these muscles, because all the muscles associated with the lumbar spine and pelvis can be out of balance, and regular stretching will help restore normal movement in the lumbar spine and pelvis. Stretching done through dynamic postural movements (such as yoga poses) is especially beneficial because it helps restore balance to the muscles of the lumbar spine and pelvis.
Aerobic exercises such as walking or cycling have also worked well for facet syndrome. They need to be done for 20 to 30 minutes a day.
Massage can be beneficial for both short-term and long-term pain relief from facet syndrome. Some evidence suggests that massage, when combined with exercise therapy and physical therapy over a period of a year, may actually reduce the need for pain medications.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy for facet syndrome includes instruction in correct posture and body positioning during daily activities to protect injured joints and reduce painful symptoms.
Cryotherapy, ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis and radiofrequency ablation can help relax the muscles and reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease.
A fixing orthopedic semi-rigid corset for the lower back allows you to maintain the spine in the correct fixed position, preventing displacement of the vertebrae and relieving the spine of part of the load. Ideally, the corset should be selected for the patient by an orthopedic specialist.
Treatment with folk remedies
To reduce blood flow to the affected area and provide temporary pain relief, you can apply an ice pack to the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes.
The essential fatty acids found in fish are an effective supplement for treating back pain. Essential fatty acids are the “building blocks” that make up fats and oils.
Read also: Stress arthritis
They are essential for muscle recovery and increase the production and activity of anti-inflammatory substances, which help control pain and inflammation in the joints. Therefore, fish must be in the diet of people who have been diagnosed with facet syndrome.
Prevention
Exercise aimed at strengthening the back muscles, losing extra pounds and increasing the flexibility of the body helps reduce the load placed on the spine and prevent facet syndrome.
Buying the right shoes, avoiding too much stress on the spine and maintaining correct posture (even while sleeping, with the help of an orthopedic mattress and pillow) are also effective measures to prevent the development of facet joint disease.
Frequently asked questions ↑
The diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis and the army - are they compatible?
A patient with spondyloarthrosis is not suitable for military service if the diagnosis indicates osteochondrosis with damage to at least three intervertebral discs, or the occurrence of pain when performing physical work.
A prerequisite is documentary evidence of multiple visits to the clinic for this disease.
Does the disease occur in children?
Spondyloarthrosis can occur in children. Congenital defects in the development of cartilage tissue and collagen lead to rapid aging of the cartilage of the vertebral joints.
As the child develops, the load on the spine changes. Therefore, manifestations of spondyloarthrosis in children occur in preschool or primary school age, when the child is most active.
How do pregnancy and childbirth affect the development of the disease?
During pregnancy, large amounts of estrogen are produced - this hormone prevents spontaneous abortion and promotes the normal course of pregnancy.
Estrogen plays a big role in the occurrence and progression of arthrosis, therefore, during pregnancy, exacerbations of existing spondyloarthrosis often occur.
In addition, the woman gains weight, which increases the load on the spinal column. After childbirth, estrogen levels decrease and the disease goes into remission.
Is it possible to go to fitness?
Adequate physical activity is very beneficial for patients with spondyloarthrosis.
Fitness is a set of exercises that allow a person to keep in shape, develop coordination, and train the cardiovascular system.
In fitness, there are no strictly defined exercises that everyone must adhere to, so for a person with spondyloarthrosis it is necessary to select a number of exercises individually, taking into account the specifics of the disease.
When performing exercises, there should be no sharp pain; it is necessary to exclude exercises with static load.
Will going to the bathhouse be harmful?
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, visiting the bathhouse is not recommended.
Thermal exposure promotes a sharp flow of blood, which leads to hyperemia and swelling of the compressed nerves. As a result, the symptoms of the disease progress.
Visiting a bathhouse or sauna is acceptable during the remission stage, when there is no pronounced pain syndrome. In this case, heat will be beneficial. But we must not forget the important rule: “everything is good in moderation.”
Severity
Deforming spondyloarthrosis is classified depending on the severity of damage to the facet joints. The degree of the disease always becomes one of the main criteria when determining treatment tactics.
1st degree
The disease begins to develop asymptomatically. Sometimes mild discomfort occurs when staying in one body position for a long time. They are also provoked by increased physical activity, for example, heavy lifting or sports training. In most cases, patients explain the appearance of these sensations by muscle fatigue and are in no hurry to see a doctor.
Spondyloarthrosis of the 1st degree is often diagnosed accidentally during a medical examination. This allows you to quickly begin treatment and avoid the development of irreversible complications.
2nd degree
Ignoring the first symptoms of spondyloarthrosis causes further destruction of the facet joints. There is pain in the back. While they are unstable, dull, aching, pressing, clearly localized. Soreness often appears in the morning and is accompanied by stiffness of movement. If you touch the source of pain, you will feel swelling of the skin due to the formation of inflammatory edema.
In grade 2 pathology, the cartilage layer is already severely damaged. Therefore, any sudden, awkward movement (tilt, turn) can provoke a sharp, piercing pain - a “lumbago”.
3rd degree
With grade 3 spondyloarthrosis, pain becomes constant. They are sharp when moving, dull when at rest. The cause of pain is not only joint damage, but also muscle spasms and inflammatory swelling that put pressure on sensitive nerve endings. The joint spaces gradually grow together, which leads to ankylosis - complete or partial immobilization. Steadily increasing stiffness seriously worsens not only the physical, but also the psycho-emotional state of the patient.
Stenosis.
What causes the development of spondyloarthrosis
Spodyloarthrosis can develop in a person regardless of his age. Often the cause of the development of this disease in children may be incorrect posture, and in older people - concomitant diseases of the musculoskeletal system or spine, such as osteochondrosis.
The main reasons for the development of the disease can be considered:
- injuries and congenital abnormalities in the development of the spine;
- microtraumas of the spine that are chronic;
- poor posture;
- permanent loads on the spine;
- metabolic disorder.
Constant loads to which the spinal column is subjected should be understood not only as work associated with constant presence at the computer or a sedentary lifestyle, but also as loads associated with professional sports.
Another reason for the development of spondyloarthrosis is considered to be flat feet. This is due to the fact that people with flat feet have impaired gait and, as a result, the load on the spine is distributed incorrectly. If flat feet are not treated promptly, it can later lead to spondyloarthrosis.
The cause of such a disease may be previously suffered or existing diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
The most likely cause is considered to be osteochondrosis, which destroys the intervertebral discs.
Complications
It is impossible to completely cure ankylosing spondylitis. It is only possible to stop the progression of the disease and reduce the symptoms. If treatment is not treated in time, serious complications may occur. In addition to damage to the joints and spine, the disease affects the organs of vision. Developing:
- episcleritis;
- iridocyclitis;
- iritis;
- uveitis;
- glaucoma;
- cataract;
- complete loss of vision.
A serious disease affects other systems, causing the development of:
- pulmonary dysfunction, fibrosis;
- secondary amyloidosis, nephropathy – kidney pathologies;
- diseases of the heart, blood vessels - conduction disorders, valve defects, myocarditis;
- respiratory system problems;
- compression fracture;
- spinal cord damage;
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- hemodynamic disorders;
- atlantoaxillary subluxation;
- a condition that guarantees disability.
Where to look for the disease?
Experts distinguish three levels of localization of the disease:
- Cervical region. The patient experiences pain in the neck area, which can be felt in the back of the head and shoulder blades.
- Thoracic department. Due to the limited mobility of this department, spondyloarthrosis rarely develops to a clearly defined degree.
- Lumbar section. The area most vulnerable to disease. The pain syndrome extends not only to the lower back, but also to the hips and buttocks.
Cervical Thoracic Lumbar
In addition, there is polysegmental spondyloarthrosis, which affects several vertebral segments simultaneously. The L4 S1 segment is where polysegmental spondyloarthrosis most often occurs.
Main reasons
There are an impressive number of causes that cause the disease:
- reaching old age. The passing years negatively affect the tissues of the facet joints;
- genetically determined spinal abnormalities;
- spinal injuries that lead to negative consequences for the facet joints;
- a hypodynamic lifestyle associated with sedentary work and, accordingly, a long stay in one position;
- failure to maintain correct posture;
- excess body weight;
- disruption of metabolic processes;
- flat feet, causing spinal load disorders.
Bibliography
VAS – visual analogue scale
DDT – diadynamic therapy
DS – facet joints
EHF – extremely high frequency therapy
CT – computed tomography
Exercise therapy – physical therapy
IVD - intervertebral disc
MRI – magnetic resonance imaging
MSCT – multi-slice computed tomography
NSAIDs – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
SMS – spinal motion segment
Microwave – ultra high frequency therapy
TPF – transpedicular fixation
UFO - ultraviolet irradiation
Image intensifier – electron-optical converter
ODI – Oswestry disability index – functional disability index for the lumbar spine
PLIF – posterior lumbar interbody fusion – posterior lumbar interbody fusion
TLIF – transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion – transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion
- Lutsik A.A., Sadova M.A. Krutko A.V., Epifantsev A.G., Bondarenko G.Yu. Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine - Novosibirsk: Science, 2012 - 264 p.
- Sold A.I. Lumbar spondyloarthrosis / A.I. Sold. – Kharkov, 1992. – P. 96.
- Orlov Yu.A., Kosinov A.E., Tkach A.I. Pain syndrome in stenosis of the lumbar spinal canal // Issues. neurosurgery. - 1987. - No.2. — P.60–63.
- Lutsik A.A. Compression syndromes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Novosibirsk, 1977.
- Zharkov P.L., Zharkov A.P., Bubnovsky S.M. “LUMBAR” PAIN MOSCOW, 2001
- Algunbaev, PA Modern concept of clinical and radiological diagnosis of dystrophic pathology of the spine / PA Algunbaev, I. I. Kamanin // Vertebroneurology. – 1998. – No. 1. – P. 10–13.
- Shatrova V.P. Treatment and rehabilitation of patients with injuries and diseases of the spine: Diss. ...doc. honey. Sciences /V.P. Shatrova. – M. 2012. 148 p. 60 ill.
- Shatrova V.P., Aganesov A.G., Zharova T.A. – An integrated approach to the treatment of pain in patients with injuries and diseases of the spine // Palliative care and rehabilitation, 2011, No. 1, p. 1-5.
- Shatrova V.P., Aganesov A.G. – Principles of rehabilitation of patients with injuries and diseases of the spine // Moscow Surgical Journal, 2011, No. 3, p. 25-31.
- Sorokovikov V.A., Koshkareva Z.V., Larionov S.N., Gorbunov A.V., Sklyarenko O.V., Potapov V.E., Negreeva M.B., Kopylov V.S. – Experience in the treatment of patients with herniated intervertebral discs at the lumbar level Bulletin of the All-Russian Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, 2013, 5 (93) P. 91-94
- Shatrova V.P., Aganesov A.G., Zharova T.A. – Rehabilitation treatment after reconstructive operations on the spine // Palliative care and rehabilitation, 2011, No. 2, p. 23-27.
- Mannion A., Denzler R., Dvorak J. A randomized controlled trial of post operative rehabilitation after surgical decompression of the lumbar spine. European Spine Journal. 2007, vol.16, pp. 1101-1107.
- Can A., Gunendi Z., Suleyman Can S. The effects of early aerobic exercise after single-level lumbar microdiscectomy: a prospective, controlled trial. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2010, vol.46, pp. 489-495.
- Kulikov A.G., Luppova I.V., Makarova I.N., Makarova M.R., Frolov D.V., Voronina D.D., Mikhaleva A.V., Udovichenko S.A. – Principles of early restorative treatment of patients after minimally invasive operations for discogenic radiculopathies // Textbook – M. 2019.
DETAILS: Ossification nuclei of the hip joints - Orthopedist.info
Sensational discovery of doctors
Therapy for spondyloarthrosis is aimed at eliminating all symptoms and preventing its spread to healthy facet joints. In the acute and subacute periods, to reduce the load on the spine, wearing semi-rigid orthoses or Shants collars is recommended.
Which doctor should I contact with symptoms of spondyloarthrosis? It all depends on the form of the disease. If it was caused by injuries, then it is better to make an appointment with a traumatologist. If there is an inflammatory nature, then a rheumatologist will help. If the cause is unknown, then experts recommend going to a neurologist who deals with all pathologies of the spine.
After various studies, doctors found a sensational way to successfully affect the joints.
Prevention measures
To prevent the primary development of spondyloarthrosis, its exacerbations and progression, it is recommended to follow a number of simple rules:
- Losing excess weight and combating obesity;
- Regular exercise or light physical activity (fitness, exercise equipment, etc.);
- Rational and balanced nutrition (adequate distribution of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, intake of vitamins and minerals);
- Prevention of injuries;
- Walking in fresh air (at least 5 km daily);
- Correct distribution of the load on the spine;
- Correctly selected mattress and pillow;
- Wearing orthopedic shoes.
The more recommended points are regularly followed, the lower the risk of developing spondyloarthrosis.
The best preventive measures are daily exercise therapy and a full medical examination every 6-12 months. Vertebrologists and orthopedists recommend, if necessary, to lose weight, quit smoking and alcohol abuse.
If a person asks the question “How to treat spondyloarthrosis?”, then the question of prevention will most likely also seem significant.
Ways to prevent the occurrence of such an unpleasant disease are quite simple and accessible to everyone. It is important to monitor how much stress your body is under and try to avoid injury. Be sure to ensure correct posture. A straight back is not only elegant and beautiful, but also beneficial for the musculoskeletal system.
Choose comfortable shoes to avoid flat feet. Save yourself from physical inactivity! Yes, many people have to do sedentary work, but your health is in your hands.
Try to provide yourself with optimal physical activity. You don't have to be a gym fan; just take a walk on your way to work or home. Watch your weight. Obesity has never made anyone more beautiful or healthier.
With excess body weight, not only your appearance suffers, but also your cardiovascular system, joints, and spine. During the day, do five-minute gymnastic exercises and carefully perform bends, twists, and scissors.
And most importantly, do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. The doctor will tell you how to cure spondyloarthrosis. Trust the professionals and be healthy!
Prevention of spondyloarthrosis consists of eliminating increased loads on the spine, controlling body weight, and correcting nutrition. Orthopedists, neurologists, and vertebrologists also recommend giving up smoking and drinking alcohol, which negatively affect metabolism and the condition of blood vessels.
Preventive measures for the risk of spondyloarthrosis include the following measures, which should also be carried out in remission:
- Physical training. Sometimes simple exercises and light exercises are enough to improve the situation. Experts recommend swimming.
- Dieting. Spinal diseases are sometimes caused by excess weight.
- Massage. From time to time you need to take massage courses.
Spondyloarthrosis: which sanatoriums treat?
Sanatoriums offer a set of measures aimed at preventing the development of the disease and improving the patient’s quality of life. Procedures are carried out using heat and cold, and ultrasound sessions are performed. Physical therapy will help strengthen the back muscles, improve metabolism and develop joints.
Which sanatoriums treat spondyloarthrosis? Here are a few medical and health institutions:
- "Staraya Russa" - Novgorod region.
- "Naftalan" is the city of Ganja in Azerbaijan.
- "Hot Key" - Krasnodar region.
It is worth noting that spondyloarthrosis can be treated in any sanatorium whose profile is aimed at treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system. There are such sanatoriums in almost every city in Russia:
- Bakirovo;
- Yeisk;
- Nalchik;
- Pyatigorsk;
- Ust-Kachka;
- Kemeri;
- Keys;
- Krasnousolsk;
- Nemirov.
Spondyloarthrosis: which sanatoriums treat this disease?
Also specialized in the treatment of spondyloarthrosis are the Sergievskie Mineral Waters sanatorium in the Samara region and the Chapaev sanatorium in the Ershovsky district of the Saratov region.
Timely consultation with a doctor is the key to a successful fight against the disease. Don't self-medicate!