Sore throat (acute tonsillitis) is an inflammatory disease of the tonsils.
It is characterized by an acute course and occurs with a frequency of 50–60 cases per 1000 population per year. Children from 3 to 7 years old are often sick, adults - mainly up to 40 years old. It can be primary or secondary, caused by both bacterial and viral, and sometimes fungal infection. There are many different causes and, accordingly, forms of this disease. Follicular tonsillitis occupies a special place among its primary manifestations. This disease is caused by bacterial flora, so antibiotics are mandatory when carrying out etiotropic treatment.
Reasons for development
The main cause of follicular tonsillitis is infection with pathogenic bacteria, viruses or fungi or autoinfection with one’s own opportunistic microflora, which becomes more active when the tension of local immunity decreases.
The bacterial agents that most often cause follicular tonsillitis include:
- arcanobacteria (most often found in the age group up to 25-30 years);
- Neisseria;
- pneumococci;
- meningococci;
- influenza stick;
- Klebsiella; and etc;
- β-hemolytic streptococcus group A, GABHS (is the cause in more than 50-70% of cases);
- streptococci of groups C and G (along with GABHS cause 30-40% of all cases of sore throat in pediatric practice).
Viruses provoke the development of the disease much less frequently; the main causes of follicular tonsillitis are the following:
- coronavirus;
- influenza and parainfluenza viruses;
- Epstein–Barr virus;
- adenovirus;
- rhinovirus;
- Coxsackievirus A.
In some cases, the disease may be caused by the pathogenic effects of fungi of the genus Candida, usually in association with viruses or bacteria.
Infection of tonsil tissue with pathogenic microflora usually occurs through airborne droplets or nutritional means, but it is also possible through direct contact. In addition to infection from the outside, endogenous infection is possible in the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the ENT area, especially often in chronic tonsillitis (in this case, group A β-hemolytic streptococcus can persist for a long time in the internal structures of the tonsils).
View photos
[collapse]
Antibiotics for sore throat
Before prescribing an antibiotic to a child, the doctor must take a swab from the patient’s throat, which is sown on a nutrient medium and then studies which microorganisms caused the inflammatory process and which antibacterial drugs are best used to treat them.
Sore throat, including follicular tonsillitis, in most cases is caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus or staphylococcus. These microorganisms are highly sensitive to antibiotics from the penicillin group.
Approved drugs for children are:
- Flemoxin Solutab - dispersing tablets that disintegrate when interacting with liquid;
- Amoxiclav – tablets for oral administration;
- Ampicillin – tablets for oral administration;
- Amox – powder for preparing a suspension;
- Amoxicillin - tablets for oral administration.
Infants and preschool children (1-3 years old) are most often prescribed Flemoxin Solutab in the form of dispersing tablets or an antibiotic in the form of a suspension.
These dosage forms have advantages over conventional tablets - the suspension and the resulting solution have a pleasant taste and smell, and the dose of the drug is easy to swallow even for the smallest patient.
Attention! Treatment of follicular tonsillitis in children with antibiotics requires caution, since an incorrectly calculated dose or uncontrolled use of medication can provoke a number of serious complications, among which the most common is colitis - acute inflammation of the large intestine, accompanied by uncontrollable diarrhea and rapid dehydration of the child's body.
Rules for taking antibiotics in children
Follicular tonsillitis in children and treatment with antibiotics requires adherence to clear rules:
- You should not stop treatment without permission as soon as you feel an improvement - if you have not completed the course of antibiotic therapy, it leads to the fact that the infectious agent develops resistance to the drug and all the symptoms of a sore throat return with renewed vigor. The antibiotic previously prescribed by the doctor will no longer have a proper effect on the pathogen, so you will have to select a new, stronger medicine, which in turn increases the risk of developing toxic damage to the liver, kidneys and the development of serious side effects.
- Antibiotics should be taken strictly at the same time.
- It is not recommended to combine antibiotics with other medications, as they often turn out to be incompatible with each other or neutralize the therapeutic effect.
- Treatment with antibiotics should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, especially if we are talking about a small child under 3 years old.
Attention! Since antibiotics negatively affect not only pathogenic microorganisms, but also the beneficial intestinal microflora, while taking the drug, the child may have more frequent stools up to 3-4 times a day. In case of complaints of severe abdominal pain and development of diarrhea (up to 6-10 times a day) with the presence of blood or mucus in the stool, you should immediately stop taking the drug and consult a doctor. Such symptoms may signal the development of pseudomembranous colitis, a serious complication.
Symptoms in adults
Harbingers of follicular tonsillitis are inflammation of the mucous membrane of the soft palate, palatine arches, palatine tonsils:
- the patient complains of a sore throat;
- the surface of the tissues of the oral cavity is hyperemic and covered with mucus;
- examination reveals low-grade fever, moderate swelling, swelling of the mucous membrane, regional lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular) are enlarged and painful on palpation.
Within 1-3 days, in the absence of treatment, the first signs appear. A general clinical examination reveals the symptoms of follicular tonsillitis:
- Sharp sore throat, general malaise;
- Febrile temperature, regional lymph nodes are enlarged and painful;
- Pharyngoscopy reveals small blisters (follicles) containing pus, which are visible through the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
A characteristic symptom of follicular tonsillitis is purulent-necrotic areas that are located next to the lacunae. The division of follicular and lacunar tonsillitis is conditional. Typically, pus-filled lacunae and follicles are located nearby. Visually, the lacunar form of tonsillitis appears as stripes on the tonsil, filled with purulent contents.
Follicular sore throat without fever. In the classical view, any inflammation, including follicular tonsillitis, is accompanied by six external signs:
- swelling of the tonsils and surrounding tissue,
- local acidosis (increased tissue acidity),
- local hyperemia (redness of the tonsils),
- hyperthermia (increase in local body temperature),
- dysfunction of the damaged organ,
- pain.
Very often, at an early stage of the disease, the symptoms of follicular tonsillitis are very similar to infectious mononucleosis, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, herpetic tonsillitis, and oral candidiasis.
Secondary angina with mononucleosis is very similar to follicular, although it can also occur as a lacunar angina:
- It begins on the first day of illness or appears on the 5-6th day.
- Also very typical are abdominal pain and enlargement of the liver and spleen, which are not present in primary follicular angina.
- In addition to the high temperature, which flows in waves, the lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. But at the same time, not only the cervical, but also the axillary, occipital, subclavian, and inguinal groups of nodes are affected.
- Mononucleosis is distinguished by blood tests (lymphocytosis, detection of mononuclear leukocytes).
- The diagnosis is confirmed by immunological (detection of antibodies and determination of their titers) and serological blood reactions.
It is especially important to distinguish infectious mononucleosis from follicular tonsillitis; the treatment of these two diseases is radically different. If you have mononucleosis, you should never take antibiotics, and purulent follicular tonsillitis can only be treated with them.
Complications of the pathological process
Among the complications of follicular angina are the following conditions:
- Prolonged intense pain in the throat. They can continue after complete cure of follicular tonsillitis.
- Meningitis. An inflammatory process localized in the area of the dura mater. Causes serious neurological symptoms.
- Endocarditis and myocarditis. Inflammation of the structures of the heart.
- Polyarthritis. Generalized inflammation of the joints. Usually small peripheral.
- Sepsis, also known as blood poisoning, is possible.
A lethal outcome is possible in extreme cases; this is more of a casuistry. Death is much more likely to occur from kidney complications. Read more about the consequences of sore throat in this article.
Symptoms in children
It can be quite difficult to quickly determine the main focus of inflammation in a small child. The following symptoms should alert parents at the initial stage of the disease:
- Redness of the cheeks.
- A sharp jump in temperature above 38° (with a sore throat it is difficult to bring down the temperature).
- Prolonged crying (in infancy).
- Complaints of pain in the throat, head or ear.
- Bad breath.
- Indigestion (diarrhea or vomiting).
- Deterioration in coordination of movements.
- Redness of the throat, white or yellowish coating on the tongue.
- Manifestation of moodiness with a sharp decline in physical activity (in older children).
- Confusion to the point of fainting is possible.
In children, the disease develops rapidly and occurs in a more acute form, so at the first symptoms it is necessary to call an ambulance, which will quickly take the child to an infectious diseases hospital. Calling a local physician in this case is inappropriate, because greatly enlarged tonsils can block the airways and cause suffocation.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations of purulent follicular tonsillitis can be divided into two groups. The first includes reactions from the body’s immune system. During its normal functioning, they will definitely be present. The second includes reactions caused directly by the pathogen. They can vary in strength, duration depending on its type, or be completely absent. In the first case, the following symptoms are observed:
- Heat. With follicular angina it can reach 39-40°.
- Severe sore throat , worsening when swallowing and often spreading to the ear.
- Enlargement of local lymph nodes , possibly the spleen.
- Salivation (increased salivation).
The second group of symptoms include:
- General malaise and weakness.
- Chills and fever.
- Headache, pain in the lower back, pain in the heart.
- Diarrhea, vomiting.
In childhood, these symptoms may be added to:
- Cramps.
- Changes in voice tones, nasality.
- Changes in behavior, forgetfulness, confusion.
Follicular tonsillitis in children is more severe. All clinical manifestations are usually more pronounced than in adult patients.
Symptoms of the follicular form are similar to the clinical manifestations of lacunar tonsillitis, but are more pronounced. Some experts combine both diseases into one - purulent tonsillitis, believing that these forms are only different stages of the inflammatory process. Hence the similarity between treatment and diagnosis.
Complications and prognosis
Untimely, unprofessional treatment, the use of antibiotics to which this type of pathogenic flora has developed resistance, and reduced immunity of the patient are the main reasons contributing to the occurrence of complications.
Most often it occurs:
- rheumatism;
- streptococcal meningitis;
- gastrointestinal tract damage;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- formation of phlegmon;
- pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- sepsis;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- otitis;
- swelling of the larynx.
The prognosis of the disease largely depends on how to treat follicular tonsillitis and how timely medical care is provided. At the first manifestations of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What does the disease look like and features?
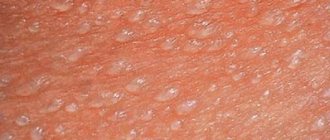
In order to recognize the disease, you need to know what follicular tonsillitis looks like. With it, the tonsils, which can be easily seen in the mirror on both sides of the root of the tongue, are covered with small white foci of inflammation, see photo 1.
Photo 1
It is important to differentiate follicular tonsillitis from lacunar tonsillitis. The latter is an accumulation of purulent contents in the lacunae of the tonsils, which are located deeper in the tissues. Follicular tonsillitis involves the formation of small follicles on the surface of the tonsils.
This is what lacunar tonsillitis looks like, see photo 2, it is important not to confuse follicular from lacunar.
Photo 2
It is important to know about the following features of the pathology:
- most often it occurs in the cold season;
- the cause of its occurrence can be not only general, but also local hypothermia: for example, eating ice cream;
- Statistically, this form of sore throat is more common during the first contact with the causative virus.
How to treat follicular sore throat
Effective treatment of sore throat with medications is impossible without strict adherence to the following instructions at home:
- Bed rest, refusal to stay outside for 5-6 days to avoid a sharp deterioration.
- The diet should consist of homogeneous food without spices, such as porridge, broths, purees and soups.
- Regular gargling, 7-10 times a day, will clear the throat of purulent discharge that remains after the follicle matures and opens.
- The room where the patient is located must be cleaned and ventilated daily.
- Drink plenty of warm drinks, especially still mineral water, milk with soda, herbal teas with rose hips, chamomile and sage. In order not to injure the inflamed mucosa, the temperature of the liquid should not be too high.
The patient may recover within 5 days, but it is not recommended to immediately go to work or visit public places. The immune system needs time to recover after an illness. Doctors recommend protecting the body from contact with the external environment for 10 days. Healthy sleep, proper rest, a balanced diet, vegetables and fruits will help improve your health.
Various treatment options for the disease
All patients with follicular sore throat must be kept in bed. Drinks and food should be moderately warm, without spicy additives. In case of uncomplicated course of the disease, doctors prescribe topical medications, gradually adding more effective drugs in the form of tablets or intramuscular injections. If the disease does not go away, the need for surgical intervention is decided.
To prevent complications, young patients must stay in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor. To treat them, the same drugs are used, but with lower dosages, since antibiotics and hormones have a serious effect on the liver. During the recovery period, physiotherapy is used: UHF procedures, ultrasound and magnetic fields.
Video: Doctor Komarovsky talks about the fight against illness in children
Drug therapy for follicular tonsillitis
All drugs prescribed to treat the disease are divided into 2 groups: local and systemic. The former are used in the form of sprays and rinses, allowing you to fight the external manifestations of the disease. The latter are used in the form of tablets, capsules or solutions for intramuscular administration in more severe cases of the disease.
All pharmaceuticals have certain dosages. Do not think that the more medication you take, the sooner the effect will occur. While working in emergency medicine, I had to deal with the fact that a patient significantly exceeded the recommended dosage of the medicine. The man lost consciousness and almost choked on vomit. Medics who arrived at the scene washed the gastrointestinal tract and hospitalized the victim in the hospital. Due to drug intoxication, he developed acute renal failure, which subsequently led to disability.
Means for local therapy:
- Antiseptic rinse solutions allow you to remove plaque on the surface of the tonsils and clean the oral cavity. For this purpose, Furacilin, Miramistin, potassium permanganate, and Chlorhexidine are prescribed.
- Sprays with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and analgesic effects. It is recommended to apply them several times a day immediately after rinsing. The most popular products in this group include: Hexoral, Stopangin, Hexasprey, Ingalipt, Kameton, Lugol spray.
Photo gallery: drugs for local treatment of the disease
Lugol spray can also be used in small patients
Hexoral has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect
Miramistin irrigates the throat, effectively clearing plaque
Medicines for systemic therapy:
- Antipyretics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to normalize temperature and also effectively treat headaches. These include Paracetamol, Ketotifen, Askofen, Ibuklin, Ibuprofen, Tamoxifen, Nise, Nimesulide, Celecoxib, Rofecoxib.
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve swelling of soft tissues and make swallowing easier. For this purpose, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Cortef, Laticort are prescribed.
- Antibacterial agents cause the death of pathogenic bacteria that cause the disease. The most common of them are Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Ceftriaxone, Flemoxin Solutab, Vancomycin.
- Antifungal drugs are prescribed when sore throat is of fungal origin. These include Griseofulvin, Pimafucin, Natamycin, Fluconazole.
- Antiviral agents kill viruses that cause the disease. For this, Cycloferon, Viferon, Acyclovir, Ganciclovir are prescribed.
Photo gallery: drugs for systemic therapy
Paracetamol normalizes body temperature
Augmentin kills bacteria
Viferon kills viruses and strengthens the immune system
Traditional treatment of the disease
To get rid of the main symptoms of pathology, the use of natural recipes is allowed. They cannot destroy the causative agents of the disease, but they effectively cope with such manifestations of follicular tonsillitis as sore throat, swelling of soft tissues, and bad breath. It is recommended to use folk remedies as additional techniques, since they have virtually no contraindications for use.
The most popular natural recipes for treating the disease:
- decoctions for rinsing based on chamomile, calendula, lungwort, birch buds, oak bark;
- boiled water with honey, iodine and salt;
- tinctures of rose hips, anise, calamus;
- compresses with onion and garlic juice, plantain and burdock leaves;
- fruit drinks with the addition of strawberries, blueberries, rowan berries, chokeberries, and cherries.
Photo gallery: folk remedies for fighting follicular sore throat at home
Chamomile relieves swelling
Rowan has an antiseptic effect
Calamus relieves sore throat
Surgical methods to eliminate the problem
Reddened and changed tonsils are a source of constant chronic infection. With a prolonged course of the inflammatory process, follicular tonsillitis will occur again and again, which is why doctors have to resort to surgery. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- inflammatory changes in the tonsils;
- recurrent sore throat;
- personal desire of the patient;
- pregnancy planning.
The operation is not performed if the victim’s condition is extremely serious (coma, shock), if he is under the influence of alcohol or drugs, or if chronic diseases are exacerbating. Currently, two methods are used to eliminate the problem:
- Complete removal of tonsils. To do this, the patient is given anesthesia, which reduces sensitivity. The doctor uses a special clamp to pull back and fix the formation, squeezing the blood vessels. The tonsil is cut off with a scalpel, after which it is sent for histological examination to the laboratory.
The operation to remove tonsils takes no more than an hour
- Removal of purulent contents. The tonsil is also fixed, but only an incision is made on its surface. Using a tube, purulent masses and plugs are sucked out. The doctor uses a large syringe with an antiseptic to rinse the area.
In the absence of contraindications to surgical intervention, complications are minimized. If the patient violates the diet by immediately eating spicy or too hot food, bleeding may occur at the wound site. The addition of a secondary infection is extremely rare.
Drug treatment
Medications for follicular tonsillitis are prescribed:
- vitamins (increase resistance to infection);
- antihistamines (Suprastin, etc.) that reduce sensitization to streptococcus;
- antipyretics (for children, Paracetamol in syrup or suppositories, at high temperatures, injections of analgin and diphenhydramine). Although pediatricians often prescribe Nurofen as an analgesic and antipyretic, this drug is strictly prohibited for children under 2 years of age, and its use for children under 12 years of age is relatively unsafe;
- antibiotics are advisable in almost all cases due to the proliferation of bacteria on damaged tonsils (penicillins Amoxicillin/Augmentin, macrolides Sumamed/Azithromycin/Clarithromycin, cephalosporins Cephalexin/Cefazolin).
Forecast
The prognosis for treatment of follicular tonsillitis is favorable if there are no complications in the form of diseases:
- kidney,
- hearts,
- joints.
Follicular tonsillitis is a pathology that affects both children and adults. With quickly and correctly prescribed treatment, it lasts 10-14 days, leaving no serious consequences. But in order to be sure that there is no risk to your health, you need to take a second smear from the larynx some time after recovery.
Treatment of follicular tonsillitis with antibiotics
Before prescribing the drug, it is recommended to culture the mucus or pus from the surface of the tonsils to determine the sensitivity of the microbial flora to the drug.
If you are not allergic to antibiotics, you need to use:
- First-line drugs, which are penicillins (inhibitor-protected or semi-synthetic). These are broad-spectrum drugs that are very effective in the fight against streptococci and staphylococci. The course of penicillin should be at least 10 days. Drugs in this group include Ecoclav, Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Amoxicillin.
- The secondary series of antibiotics are macrolides. Josamycin, Klacid (clarithromycin, Azithromycin (Hemomycin, Azitrox, Sumamed). The course of taking these drugs should be limited to 5 days, since the drugs tend to accumulate in the blood, so this course will provide 10 days of exposure to bacteria in the body.
The effectiveness of antibacterial therapy is assessed after 72 hours by improving general well-being and lowering the temperature. For this purpose, the patient is visited daily by a doctor for the first three days. If there is no effect from using an antibiotic, switch to another group of drugs.
View photos
[collapse]
Diagnostics
When examining the surface of the pharynx using a pharyngoscope, the doctor may find:
- Enlargement of the tonsils, their redness.
- The presence of infiltration, protrusion of follicles through the surface of the epithelium in the form of yellow dots up to 3 mm in size.
- After the peak of the disease, erosions remain on the surface of the tonsils (small scars formed after the opening of the abscesses).
When conducting a biochemical blood test, the following is detected:
- Increase in the number of leukocytes to 12-15*10⁹/l.
- Shift of the leukocyte formula towards neutrophils.
- Increased number of eosinophils.
- Increase in ESR to 30-40 mm/h.
With tonsillitis of a viral nature, pronounced leukocytosis may not be detected. This is due to the specificity of the immune response to certain pathogens.
It is worth noting that tests to determine the nature of the pathogen are rarely carried out and turn out to be quite lengthy (for example, bacterial culture takes several days). Therefore, the doctor usually prescribes antibiotics a priori, without finding out what is causing the sore throat. Although the development of simpler and more convenient tests is already underway. The study is currently being carried out by the Israeli company MeMed. In the blood of patients, 17 proteins involved in inflammation, specific for various infections, are determined. As Immunology-allergy writes: “The combined test is suitable for the differential diagnosis of bacterial and viral infections, regardless of the location of the infection.” This means that in the near future it will be possible to determine the nature of the causative agent of a sore throat in a matter of minutes.
Physiotherapy
To carry out the procedures, special emitter devices are used. At home, an infrared lamp is usually used. Its main effect is heating, which leads to dilation of blood vessels and stimulation of regeneration processes.
Ultraviolet light is used in hospital settings. Exposure to radiation is usually combined with inhalation of drugs, since, according to some data, it improves tissue permeability. In addition, ultraviolet light has a bactericidal effect.
Also, for angina, microwave and UHF, electric current is used. To achieve the desired effect, a set of procedures is required, the average course duration is 5-7 days. The use of physiotherapy for sore throats in children is widespread, including for preventive purposes.
Possible complications
The follicular type of disease can lead to the development of various complications affecting different organs and systems of the body, including:
- It is possible to develop inflammation of the tissue behind the throat, followed by sepsis .
- Streptococci, getting on the heart , destroy their tissue .
- When streptococci are abundant in the body, defense mechanisms begin to produce large quantities of antibodies to them. They affect not only pathogenic microflora, but also their own tissues with a cellular structure similar to that of sore throat pathogens.
- Kidney damage often occurs , which most often has no symptoms and only after a few years manifests itself in the form of glomerulonephritis in a chronic form.
- Immediately after recovery, in some patients, complications may affect the joints , which manifests itself in noticeable pain and swelling in the affected tissues.
- Sometimes, after an illness, people develop rheumatism .
Surgery
In some cases, to get rid of follicular tonsillitis, surgical and semi-surgical methods of disposal may be required. The latter method is used for frequent occurrence of diseases that lead to changes in the tonsils and pathological complications. The semi-surgical method is practiced as an additional measure during drug therapy, helping to remove pus from the tonsils. These methods include: galvanocaustics and diathermocoagulation. The hardware method is used to cut and cleanse the tonsils from pus in case of chronic tonsillitis.
A more radical method is tonsillectomy or tonsillectomy. In most cases, the tonsils are removed completely, but if they are large, partial excision may be performed. Indications for tonsillectomy include failure of conservative treatment. The operation is carried out no earlier than 3 weeks after suffering from follicular tonsillitis.
Transmission routes
The causative agent of follicular sore throat can be transmitted in many ways:
- airborne (aerosol);
- fecal-oral (through food, water);
- contact-household (through objects that have been in the hands of an infected person).
It is important to understand that not every person infected with a sore throat pathogen has any idea about it. The infection can circulate in the body asymptomatically if the functioning of its immune system prevents the infection from causing the active stage of the disease. At the same time, a person may well be a source of infection for any people around him, whose immunity works worse at the time of contact with the carrier.
Prevention
No special measures have been developed to prevent the development of follicular tonsillitis. General recommendations are as follows:
- Isolation of the patient because the disease is contagious.
- Elimination of traumatic factors if present (dust, air pollution).
- A diet rich in vitamin C.
- Maintaining a stable immune system through hardening procedures and eliminating stress.
It is necessary to treat follicular tonsillitis comprehensively, using all available means. You should not neglect even those methods that do not give quick results (for example, from the arsenal of traditional medicine), since they often improve the general condition of the body and increase its resistance to infection.
Predisposing factors
Predisposing factors are circumstances that significantly increase the risk of developing the disease. In this case, it is appropriate to talk about factors that increase the possibility of infection against the background of reduced activity of the immune system:
- local hypothermia;
- general hypothermia;
- avitaminosis;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- staying in crowded places during epidemics;
- minor injuries to the mucous membrane of the throat.
Knowing about these factors is important in order to carry out timely prevention aimed at restoring the body's defenses. For example, a child has less chance of developing follicular tonsillitis if he avoids hypothermia and refuses to eat ice cream in the winter.
Physiotherapy
In severe cases of the disease, when the body finds it difficult to cope with the disease, the doctor may prescribe a course of physiotherapy. The main types of physiotherapy include:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser treatment;
- ultraviolet irradiation of the tonsils;
- electrophoresis;
- Phototherapy of the lymph nodes and neck area.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used only after acute symptoms have reduced. Physiotherapy is contraindicated in the presence of high fever and a large number of purulent plugs in the tonsils.
Treatment of sore throat
If the bacterial origin of the disease is confirmed, treatment begins with antibiotics. Starting drugs - penicillins, including protected ones (Amoxiclav); macrolides (Azithromycin or analogues), cephalosporins and carbapenems are often prescribed.
If fungi are detected in smears, antimycotics (antifungal agents) are prescribed - Fluconazole and its analogues. For viral (herpetic) sore throat, the drugs Tiloron and Acyclovir are effective.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Impact on the tonsils using physiotherapeutic methods in the acute period is contraindicated; physiotherapy is carried out during the period of convalescence (recovery), after the disappearance of acute symptoms.
FUF of the pharynx is used - irradiation of the tonsils with short-wave ultraviolet radiation. Ultraphonophoresis of tonsils with antiseptics is often used in ENT practice. The area of the lymph nodes can be affected using SMT or microwave - this helps to reduce them to normal size.
For patients suffering from frequent exacerbations of tonsillitis and other chronic diseases of the ENT organs, spa treatment is recommended during a period of relative well-being, when there are no signs of acute inflammation. Preference should be given to seaside resort areas.
Rinsing and irrigation
In the acute period, you can gargle with solutions of antiseptics: furatsilin, miramistin, an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine, Lugol's solution or peroxide. Rinsing reduces the inflammatory process, washing away some of the pathogens and the toxins they produce.
Gargling for sore throat is one of the components of treatment. Care must be taken when gargling and irrigating the throat - do not allow the solution to get into the trachea!
At the initial stage of the disease, you can use combination drugs containing an antibiotic and an antiseptic: Hexoral, Stopangin or Stomatidin. To reduce sore throat, sprays and lozenges with an anesthetic effect are used: Grammidin, Septolete, Teraflu LAR and similar drugs.
Lubricating the mucous membranes of the tonsils
Among patients, it is believed that lubricating the tonsils for sore throat has a good therapeutic effect. The mechanism of action is explained by the fact that when the tonsils are lubricated with oil-containing products, their surface is better treated. The oil supposedly ensures longer contact of the medicinal substance with the mucous membranes.
In fact, the effectiveness of lubrication is highly questionable - any substance applied to the tonsils is very quickly swallowed by the patient. In addition, the procedure itself for lubricating the tonsils is quite unpleasant, and children tolerate it especially poorly. For lubrication, Lugol's solution, oil with propolis, glycerin with collargol and tannin, carotoline, and aloe juice are used.
The effectiveness of lubricating the tonsils for sore throat is not much higher than irrigation or rinsing, so the use of this method remains at the discretion of the patient.
Lubricating the tonsils during follicular tonsillitis can be dangerous - strong pressure can lead to traumatization of the tonsils, which will cause a large amount of toxins to enter the blood. After this procedure, the temperature may rise sharply and severe general weakness may develop.
Inhalations
The use of any inhalations for this disease is devoid of practical meaning. When using a nebulizer, such a fine suspension of the drug is formed that it is completely inhaled into the lungs. Of course, some part settles on the tonsils, but it is very insignificant. Rinsing for sore throat is much more effective than inhalation.
Against the background of inhalation through a nebulizer for sore throat, there is always a risk of bacteria entering the lungs with the development of bronchitis or pneumonia.
Pills
Antibiotics
In tablets for angina, etiotropic treatment is prescribed, that is, antibiotics. Sumamed, Augmentin, Amoxiclav are the most famous drugs for angina. Only a doctor should select the dosage - when self-medicating, there is a high probability of using an inadequate dose, which can lead to unpleasant, potentially dangerous complications.
Lozenges and antipyretics
In addition to antibiotics, tablets are prescribed to relieve sore throats, but such tablets are not drunk, but dissolved in the mouth. Examples of lozenges: Faringosept, Lizobakt, Strepsils and others. In addition, adult patients may be prescribed antipyretic tablets (paracetamol). In children, it is preferable to use NSAIDs in syrup form.
Antihistamines and vitamins
In the treatment of sore throat, antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil) are used. For general strengthening purposes, vitamins (ascorbic acid, multivitamin complexes in tablets) and immunomodulators (Viferon and its analogues) are prescribed. If complications from internal organs occur, consultation with a specialist is required: a cardiologist or nephrologist, who can prescribe additional specific therapy.
Injections and IVs
Children with acute purulent tonsillitis must be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. Adults can be treated at home, but if severe intoxication occurs, they may also be hospitalized.
In a hospital setting, for severe cases of the disease, antibacterial drugs can be prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections. At high temperatures and severe intoxication, intravenous infusions (“infusions”) of medications or fluids are sometimes prescribed for detoxification purposes and to replenish fluid deficiency.
For a course of treatment with droppers, glucose solution (for children), Ringer's solution, lactosol and other polyionic solutions are usually prescribed. Antihistamines and antipyretics can also be given by injection. In severe cases of the disease, the parenteral route of drug administration is much preferable.
Tonsil removal
A single case of follicular tonsillitis is not a reason to remove tonsils. The question of such an operation arises in cases where a person experiences too frequent exacerbations - more than 5 times a year. In this case, tonsillectomy should be considered as an option for the prevention of tonsillitis, but all possible consequences should be taken into account. The operation is performed exclusively during the “cold” period, when there are no signs of inflammation.
Exercise therapy
Physical therapy for acute inflammation is contraindicated, but doctors recommend it as a preventive measure. It is especially useful to carry out exercise therapy in sanatorium treatment conditions. It has been noted that children who have completed a full course of such treatment in seaside sanatoriums suffer from tonsillitis 3.5 times less often.
Diet
During the period of acute inflammation of the tonsils, eating is very difficult due to severe pain when swallowing. Therefore, all food should be gentle so that the patient experiences as little pain as possible. Before eating, any food can be put through a blender to give it a mushy consistency - such food is easier to swallow.
As for the qualitative composition of the diet, extractive products (spices, pickles, canned food) should be excluded. It is recommended to drink as much liquid as possible: juices, compotes, decoctions. It is not advisable to consume dairy products during a sore throat.
Treatment with folk remedies
You should use traditional methods for self-treatment of sore throat at home only after consultation with a doctor and complete etiopathogenetic treatment (antibiotics). As a means of traditional medicine, it is allowed to gargle and rinse the mouth with decoctions of herbs with an antiseptic effect - chamomile or calendula. Rinsing with herbal decoctions can be done every 2-3 hours.
Recommendations
During the treatment of sore throat, it is recommended to observe strict bed rest. Any physical activity is limited, and body temperature is carefully monitored: raising it above 38.5°C is a direct indication for taking an antipyretic. It is not recommended to drink cold drinks and get too cold - this increases the risk of complications.
During a sore throat, it is very important to adhere to a protective treatment regimen. As doctors say, a sore throat needs to be “rested.” Bed rest significantly reduces the risk of complicated cases of the disease.
The most effective way of primary prevention of angina is to maintain the body's immunity in proper status. This is achieved through hardening, good nutrition and giving up bad habits, primarily smoking.
If a sore throat is detected in one family member, everyone else is advised to avoid close contact with him and use gauze masks at least in the first 2-3 days of illness. The rooms where the sick patient is located must be regularly ventilated; in hospitals, quartzing is also carried out - treating the rooms with ultraviolet rays.
Causes
The occurrence of follicular tonsillitis is associated with exposure to infection while simultaneously weakening the immune system. Before illness, a patient may suffer from hypothermia, hypovitaminosis, suffer from chronic fatigue, and poor nutrition.
The pathogen can enter the source of the disease in several ways:
- Endogenous. Once in the body, the infectious agent can circulate in the blood and enter the tonsil area, starting an inflammatory process there.
- By airborne droplets.
- Along with food and drinks.
- Contact-household way.
Tonsils are responsible for cellular and humoral immunity. But if they are weakened, and bacteria enter in large quantities, inflammation may begin to develop in them, which ultimately leads to follicular sore throat.
Diagnostic methods
If you experience the symptoms described above, do not self-medicate, but go to your local clinic to see a general practitioner or otolaryngologist.
The doctor will listen to complaints, visually examine the throat and make a preliminary diagnosis based on external data:
- Presence of red follicles behind the pharynx.
- Redness and puffiness of the mucous membrane.
- Enlargement of nearby lymph nodes.
- Certain areas will be covered with dense mucus mixed with purulent masses.
- If the disease is neglected by the patient, then nearby tissues atrophy (thinner).
- On the doctor's recommendation, additional examination with a pharyngoscope may be required.
- A bacterial culture (mucosal smear) is done to determine the type of causative agent of the disease.
- You may need to consult other specialists: dentist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
- Ascorbic acid activates the humoral immune system
- Reception course - only 4 days
- Proven clinical effect
- The unique formula of Cytovir-3® includes bendazole hydrochloride (dibazole)
Photo
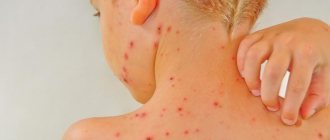
This is what follicular tonsillitis looks like in photographs: it is clearly visible that the palatine tonsils are significantly increased in size due to swelling. Against the background of severe hyperemia, white dots are visible - follicles filled with purulent contents.
Content may be difficult to view
Content may be difficult to view
Content may be difficult to view
This is what the main causative agent of sore throat looks like - streptococcus.
Main symptoms
In most cases, follicular tonsillitis has typical symptoms. Among the external signs of the disease are inflammation of the tonsils and follicles in the throat with the formation of ulcers. The main symptoms of angina are:
- increase in body temperature to 38-40 degrees;
- chills;
- redness and swelling of the tonsils;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- increased salivation;
- dry throat, cough;
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing and radiates to the ear;
- signs of intoxication of the body: headache, nausea accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, weakness;
- lack of appetite in children and constipation in adults;
- insomnia;
- heartache;
- aches in the joints and lumbar region;
- increased heart rate;
- change in voice timbre (nasality);
- inflammation of the lymph nodes, the occurrence of pain in them when turning the head.
The disease is characterized by a sudden onset and severe course, especially in the first days. The duration of the acute form of tonsillitis varies from 6 to 8 days, and symptoms persist for two weeks. It is very important to start treatment in a timely manner, which means detecting the disease in time.
Immunomodulatory drugs
Follicular tonsillitis negatively affects the body's condition, leading to a decrease in immunity. It is further undermined by the use of antibacterial drugs, so immunomodulators play an equally important role in getting rid of tonsillitis. By increasing the functioning of the immune system, the body will begin its recovery much earlier, and this also reduces the risk of recurrence of the disease.
The pharmaceutical market offers a large number of drugs to choose from to strengthen the immune system, which helps to cope with residual symptoms. These include:
- Ribomunil;
- IRS-19;
- Tonsipret;
- Imudon;
- Tonsilgon.
Imudon
Tonsipret
Tonsilgon
Ribomunil
IRS 19
If follicular tonsillitis occurs, it is also necessary to take systemic medications: Imudon, Immunal and others, which contain echinacea.
Local and antiseptic drugs
You can speed up the healing process for follicular sore throat by gargling. Taking antibacterial agents helps destroy pathogenic microbes, but they are not able to remove purulent plugs from the tonsils, reduce sore throat and remove plaque.
Gargling is carried out using folk remedies and medications. At home, you can prepare a decoction of chamomile or calendula, brew it and let it cool slightly. In the first days of the disease, you need to gargle every 30 minutes; only after improvement, the frequency of irrigation can be gradually reduced.
There are many methods and means for gargling for follicular tonsillitis:
- use of Furacilin solution;
- rinsing with lemon water;
- beet juice;
- a solution of salt and soda;
- infusions of propolis or eucalyptus;
- antiseptics: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
Furacilin
Chlorhexidine, Miramistin
Infusions of propolis or eucalyptus
Soda and salt
Beet juice
Water and lemon
For sore throat, you can use other local remedies:
- anesthetic sprays: Ingalipt, Cameton, Hexoral;
- for treating the throat: Lugol, Chlorophyllipt;
- absorbable lozenges or tablets: Lizobact, Strepsils, Septolete.
Hexoral
Chlorophyllipt
Ingalipt
Kameton
Lysobacter
Lugol
Septolete
Strepsils
Each method of rinsing helps remove pus from the tonsils, reduce inflammation and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Complications due to neglect of the disease
Many, when any signs of symptoms appear, are negligent in treatment, not following all the doctor’s instructions. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed, which are falsely believed to cause more harm than good. When the disease is advanced, pathogenic microbes attack the immune system, which leads to subsequent frequent occurrence of colds. Also, sore throat can lead to complications from the larynx and oropharynx: phlegmon, abscesses, otitis media, blood discharge from the tonsils.
In more severe conditions, if left untreated, complications may arise from the functioning of internal organs. Among the dangerous consequences: myocarditis, sepsis, pyelonephritis, rheumatism.
The development of the disease in pregnant women is considered especially dangerous. Due to the fact that tonsillitis causes general intoxication of the body, this has a detrimental effect on the development of the fetus, which can lead to miscarriage.
Antipyretics and antihistamines
You can cope with follicular sore throat only with complex therapy prescribed by your doctor. This form of the disease is always accompanied by elevated temperature, while the patient feels unwell and there is a feeling of body aches, which indicates a progressive inflammatory process. In this case, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs can help.
Most often, Ibuprofen or its analog Panadol, which contain analgin, aspirin and paracetamol, are prescribed for such purposes. The drugs can not only reduce the temperature, but also improve the general condition: headaches are eliminated, and due to anti-inflammatory components, discomfort in the throat is reduced.
With excessive and improper use of drugs, patients may complain of poor health, headaches and an increase in body temperature up to 37.3 degrees.
Since treatment involves taking antibiotics, which in some cases can cause an allergic reaction, antihistamines must be taken at the same time. Their action is aimed at preventing a reaction when antibiotics and pathogenic bacteria penetrate into the blood. The most popular antihistamines include:
- Zyrtec;
- Tavegil;
- Ebastine;
- Pipolfen;
- Telfast;
- Fenistil;
- Erius;
- Suprastin.
Ebastine
Fenistil
Erius
Pipolfen
Suprastin
Tavegil
Telfast
Zyrtec
Most modern drugs do not have a sedative effect on the body.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, this form is very dangerous. Often the disease even leads to the death of the fetus. The circulation of toxins in the blood, an increase in temperature to exorbitant levels, weakened immunity - all this provokes a miscarriage. If a pregnant woman has signs of a purulent form of sore throat, she should be hospitalized immediately and thoroughly examined.
The doctor must choose medications for treatment in order to select only those that will not harm the unborn child. Thus, most antibiotics are contraindicated for pregnant women, especially in the early stages.